Exploring the Mysteries of Neptune: The Eighth Planet in Our Solar System
Welcome to the outer reaches of our celestial neighborhood, where icy giants and distant moons dance in the darkness. In this article, we’re diving deep into the enigmatic world of Neptune, the eighth planet in the solar system and farthest planet from the sun. From its discovery to the latest missions, we’ll uncover the wonders of this captivating planet.
Why Neptune? Unveiling the Secrets of the Distant Planet
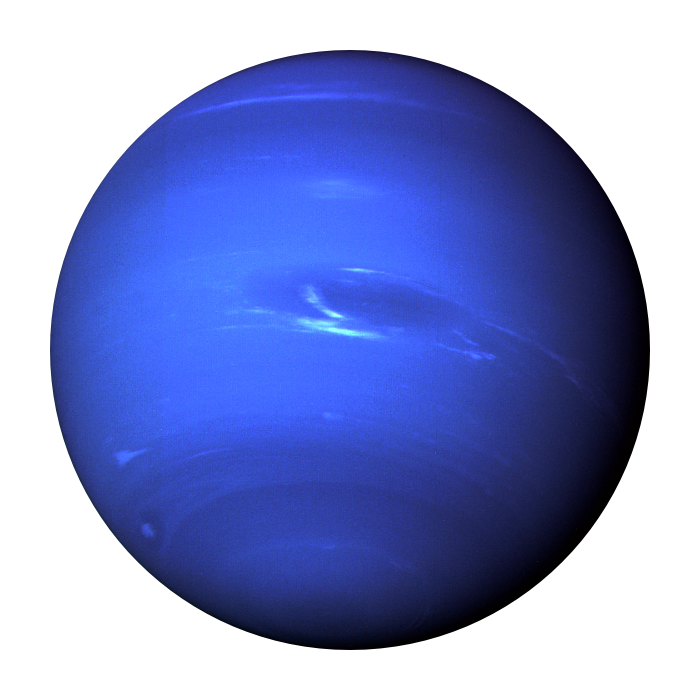
Neptune, named after the Roman god of the sea, holds a unique place in our solar system. This giant, icy world is 16 to 55 times the mass of Earth, making it one of the four gas giants along with Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus. Its striking blue hue, caused by the presence of methane in its atmosphere, sets it apart as one of the most visually stunning planets.
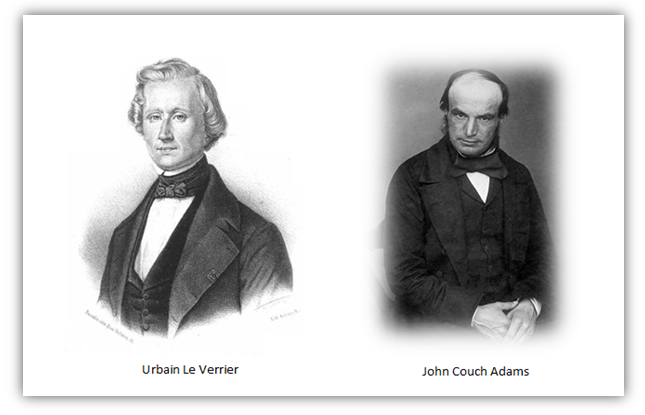
Intriguingly, Neptune was the first planet to be discovered through mathematical predictions rather than through direct observation. French astronomer Urbain Le Verrier predicted its existence based on irregularities in the orbit of Uranus. Then, in 1846, Johann Gottfried Galle and Heinrich Louis d’Arrest observed Neptune for the first time, confirming its existence.
But Neptune’s mysteries didn’t stop there. The planet boasts a turbulent atmosphere with winds that can reach up to 1,500 miles per hour (2,400 kilometers per hour), the fastest in the solar system. Its iconic feature, the Great Dark Spot, is a massive storm system comparable to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. However, unlike Jupiter’s storm, the Great Dark Spot on Neptune was short-lived and has since disappeared, leaving scientists eager to understand its transient nature.
So, what else lies beneath the surface of this distant giant? Let’s embark on a journey through Neptune’s orbit, moons, and the groundbreaking Voyager 2 mission.
Composition of Neptune
Neptune, the farthest planet in our solar system, is a fascinating celestial body with a unique composition, including an abundance of gases. The atmosphere is composed of methane, hydrogen and helium, giving it a mesmerizing blue hue. These gases play a crucial role in forming the distinct weather patterns observed on the planet, such as its raging storms and colossal winds. Despite being located over 2.7 billion miles away from Earth, exploring the gases in Neptune opens up a world of wonder and discovery, showcasing the beauty and complexity of our universe. It’s truly a mesmerizing dance of elements that reminds us of the incredible diversity present in our cosmic neighborhood.
An image of neptune showing the blue hue from it’s gasious atmosphere.
Neptune’s Orbit: A Dance in the Outer Reaches
Neptune’s orbit around the sun is a vast ellipse, taking approximately 165 Earth years to complete a single orbit. Due to its distance as the outermost planet, a year on Neptune lasts about 165 Earth years! This extreme distance means that Neptune receives much less sunlight and warmth than planets closer to the sun.
Interestingly, despite its great distance, Neptune has only been observed through a telescope since its discovery. The planet is not visible to the naked eye, making it a challenging target for ancient astronomers. Even today, observing Neptune requires powerful telescopes due to its faint appearance from Earth.
Neptune’s Moons: The Fascinating World of Neptune and Triton
Neptune is home to a diverse array of moons, the most famous of which is Triton. Triton is unique among the large moons in our solar system because it orbits in the opposite direction of Neptune’s rotation, suggesting it may have been captured by Neptune’s gravity rather than formed alongside the planet.
Triton’s surface is a frozen landscape, with geysers erupting from beneath its icy crust. These geysers spew nitrogen gas into space, creating a thin atmosphere around the moon. Voyager 2, the first and only spacecraft to visit Neptune, captured stunning images of Triton’s icy plains and active geology during its flyby in 1989.
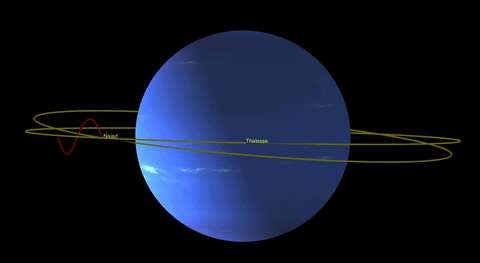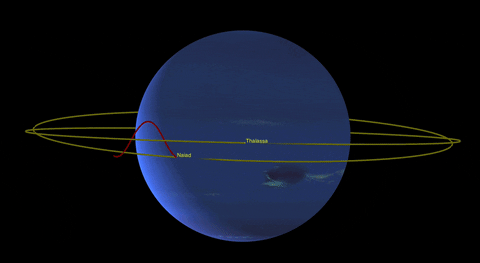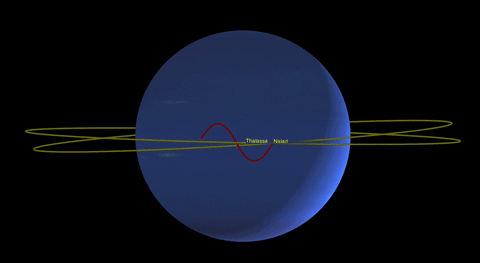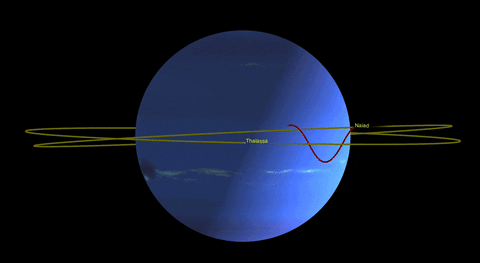
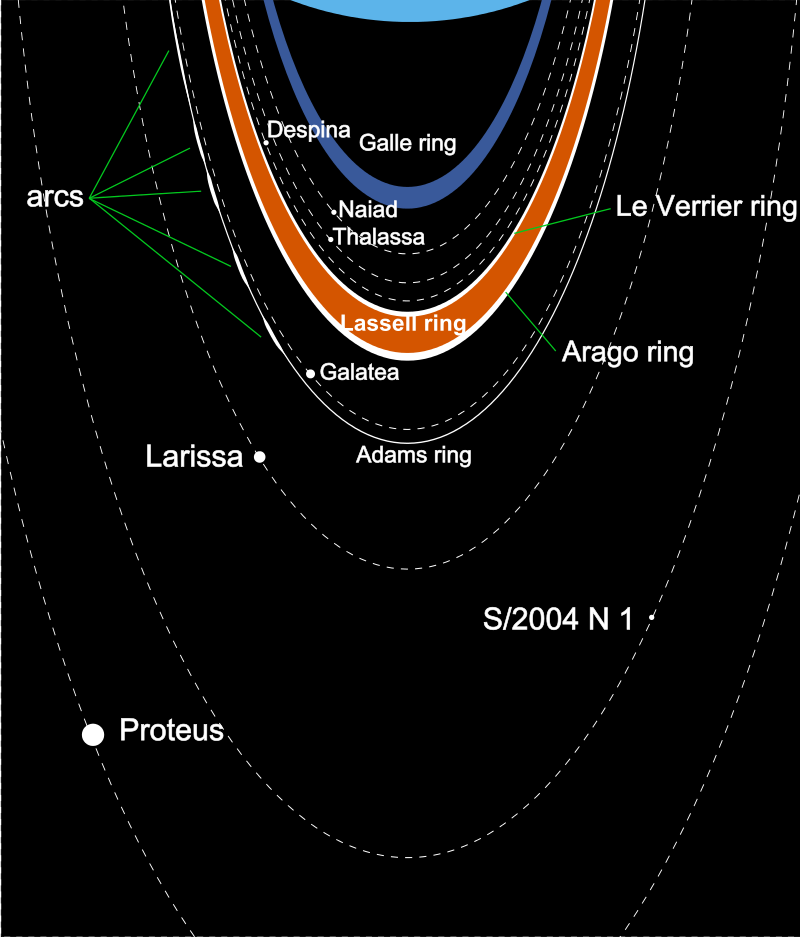
In addition to Triton, Neptune has 13 other known moons, each with its own unique characteristics. Nereid, the third-largest moon, has an unusually eccentric orbit, while Proteus is one of the largest irregularly shaped moons in the solar system.
Voyager 2: Unveiling Neptune’s Secrets Up Close
In 1989, NASA’s Voyager 2 spacecraft made its historic flyby of Neptune, providing humanity’s first close-up look at this distant world. Voyager 2’s mission revealed a wealth of information about Neptune’s atmosphere, moons, and rings, revolutionizing our understanding of the outer solar system.
One of the most surprising discoveries was Neptune’s dynamic atmosphere, with winds that far surpass those of any other planet in our solar system. Voyager 2 also captured images of the planet’s rings, which are faint and composed primarily of dust particles. These rings are thought to be relatively young compared to the rings of Saturn, indicating ongoing geological activity in the Neptunian system.
Discovery of The Planet Neptune: A Triumph of Mathematical Prediction
The story of Neptune’s discovery is a testament to the power of scientific prediction. Urbain Le Verrier’s calculations, based on observed deviations in Uranus’s orbit, led to the precise location of Neptune before it was ever seen through a telescope. Simultaneously, British mathematician John Couch Adams independently made similar calculations, providing further evidence for the existence of the mysterious eighth planet.
When Neptune was finally observed through a telescope, on the 23rd of Septmber 1846, it marked a historic moment in astronomy. The discovery is given to Johann Gottfried Galle who was aided by his student Heinrich Louis d’Arrest. The discovery of Neptune expanded our understanding of the solar system and demonstrated the incredible accuracy of mathematical modeling in predicting celestial phenomena.
The discovery of Neptune was crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it validated the theories of celestial mechanics proposed by Sir Isaac Newton, demonstrating the power of mathematical calculations in predicting the existence of celestial bodies. Secondly, it expanded our knowledge of the outer solar system and provided insights into the gravitational interactions between planets.
Neptune’s Rings: A Thin Halo of Dust
While not as prominent as Saturn’s majestic rings, Neptune also possesses a system of rings. These rings are incredibly faint and were first discovered in 1984 when they were backlit by the sun. The rings consist mainly of dust particles, with some possibly composed of ice grains or carbon-based compounds.
The exact origin of Neptune’s rings remains a subject of study. Some theories suggest that they are the remnants of shattered moons or captured asteroids, while others propose that they are continually replenished by material ejected from nearby moons.
The Methane Mystery: Creating Neptune’s Blue Hue
One of the most striking features of Neptune is its vibrant blue color, which is due to the presence of methane in its atmosphere. Methane absorbs red light, giving the planet its characteristic hue. The exact mechanisms behind the formation and distribution of methane on Neptune are still not fully understood.
Scientists believe that Neptune’s methane may be a remnant from the planet’s formation or continuously replenished by ongoing geological processes. Understanding the role of methane in Neptune’s atmosphere is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of its weather patterns and atmospheric dynamics.
Neptune and Uranus: Ice Giants of the Solar System
Uranus and Neptune are often referred to as “ice giants,” distinct from the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn. These ice giants have compositions rich in water, ammonia, and methane, which differentiate them from their larger counterparts. While both planets share similarities, such as their blue coloration due to methane, they also exhibit unique characteristics.
One notable difference is their magnetic fields. Neptune’s magnetic field is tilted at a considerable angle compared to its rotation axis, causing it to undergo unusual variations. This tilt is thought to be due to the planet’s extreme winds and its unusual magnetic field structure.
The Future of Neptune Exploration: New Horizons
As we continue to explore our solar system, Neptune remains a tantalizing target for future missions. While Voyager 2 provided invaluable data during its flyby, there is still much more to learn about this distant world. Concepts for future missions, such as a Neptune orbiter or even a dedicated mission to Triton, are actively being discussed by the scientific community.
The upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, set to launch in 2021, may also provide new insights into Neptune and its moons. With its powerful infrared capabilities, the telescope will peer through Neptune’s thick atmosphere and study its composition in unprecedented detail.
Neptune’s Place in the Solar System: Farthest and Most Mysterious
In our cosmic dance around the sun, Neptune occupies a distant and mysterious realm. Its position as the eighth planet from the sun, far beyond the gas giants, makes it a unique and captivating world. Despite its distance, Neptune continues to intrigue scientists and stargazers alike, offering glimpses into the outer reaches of our solar system.
Unveiling Neptune: What We’ve Learned
- Neptune is the eighth planet in our solar system, located far beyond the gas giants.
- Its striking blue color is due to the presence of methane in its atmosphere.
- The planet has a dynamic atmosphere with winds reaching up to 1,500 miles per hour.
- Voyager 2 provided our first close-up look at Neptune during its historic flyby in 1989.
- Neptune’s moons, including Triton, exhibit diverse and fascinating features.
- The discovery of Neptune was a triumph of mathematical prediction by Urbain Le Verrier and John Couch Adams.
- The planet’s rings, although faint, add to its mysterious allure.
- Neptune’s position as an ice giant, along with Uranus, sets it apart from the gas giants.
- Future missions, including a possible Neptune orbiter, hold promise for further exploration.
- Neptune’s distant orbit and enigmatic features continue to captivate astronomers and the public alike.
As we gaze into the depths of our solar system, Neptune remains a beacon of mystery and discovery. From its turbulent winds to its icy moons, this distant planet offers a glimpse into the wonders of our celestial neighborhood. As we continue to explore and unravel its secrets, Neptune will undoubtedly hold its place as one of the most intriguing destinations in our cosmic journey.
Neptune Overview – Quick planetary Stats
| Moons | 16 |
| Rings | At least 5 main |
| Orbit period | 60,195 Earth Days |
| Rotation Period | 16.1 Hours |
| Equatorial Circumference | 154,705 km (96,129 miles) |
| Overall Density | 1.638 g/cm3 |
| Mass (Earth = 1) | 17.1478134 |
| Gravity (Earth = 1) | 1.1 |
| Minimum Temperature | -218°C (-360°F or 55 °K) |
| Maximum Temperature (core) | 7000°C (12632°F or 7273 °K) |
Frequently Asked Questions about Neptune
1. What is Neptune?
Neptune is the eighth planet in our solar system, known as a giant planet and classified as an ice giant.
2. How far is Neptune from the sun?
Neptune is the eighth planet from the sun and is located at 4.4722 billion km distance from the sun.
3. How many moons does Neptune have?
Neptune has a total of 16 moons in its system, including Triton and other known moons.
4. Can Neptune be observed with a telescope?
Yes, Neptune can be observed using a telescope, as it is not visible to the naked eye.
5. When was Neptune discovered?
Neptune was discovered in 1846 by Le Verrier and Galle through observations and calculations.
6. What is the significance of Voyager 2 in relation to Neptune?
Voyager 2 was a spacecraft that performed a mission to Neptune in 1989, providing valuable data and images of the planet.
7. Are there rings around Neptune?
Yes, Neptune has rings of its own, similar to the structure seen around other giant planets.
8. What is the magnetic field of Neptune like?
Neptune possesses a significant magnetic field that influences its orbit and interactions with moons like Triton.