Guinea-Bissau
(Républica da Guiné-Bissau (Republic of Guinea-Bissau))

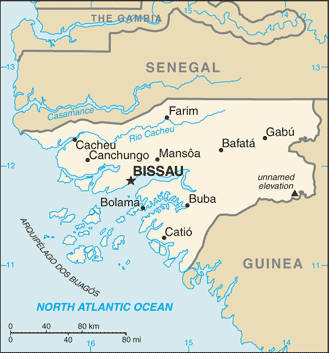




Capital: Bissau
Population (Estimated July 2012): 1,628,603
Area: 36,125 km2 or 13,948 mi2
Currency: CFA Franc (CFAF)
Official Language: Portuguese
Political Information: Semi Presidential Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion
(approximately 50% of the population are Muslim, 40% have indigenous beliefs and 10% are Christian)
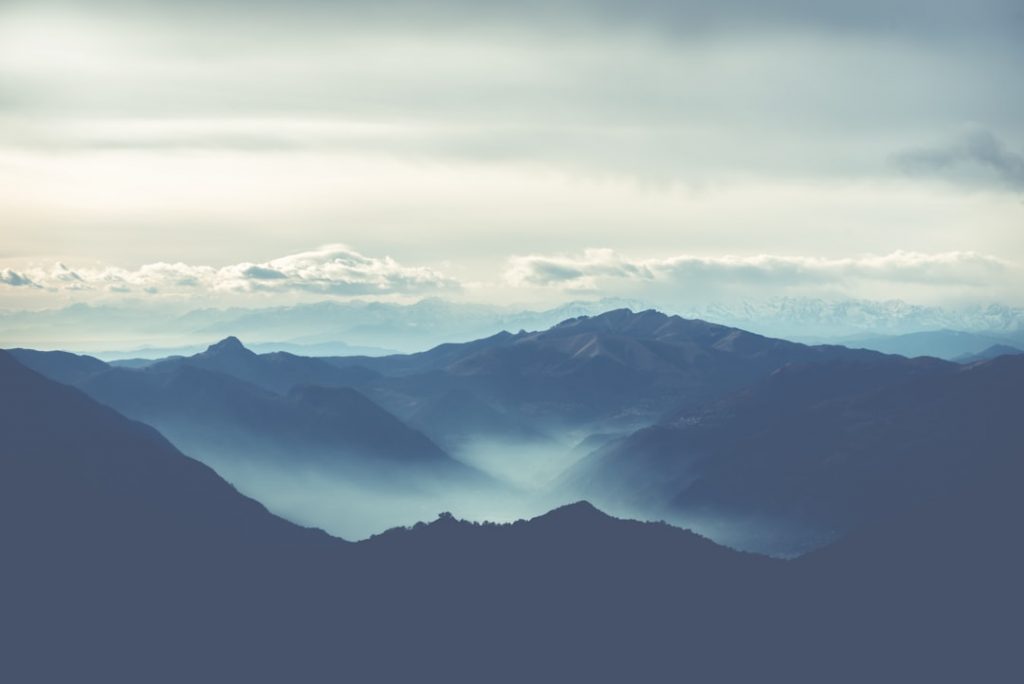
Highest Mountain: Unnamed Location at 300m or 984ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $1 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $1.938 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $1,100 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): GMT
Wildlife:
Counties/Provinces/States: 9 regions (regioes, singular – regiao); Bafata, Biombo, Bissau, Bolama, Cacheu, Gabu, Oio, Quinara, Tombali; note – Bolama may have been renamed Bolama/Bijagos
Leaders: Acting President Raimundo Pereira with acting Prime Minister Adiato Djaló Nandigna.
Additional: Gained Independence from Portugal on the 10th of September 1974.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau, officially known as the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, is a small West African country located on the Atlantic coast. It is bordered by Senegal to the north and Guinea to the south and east, with a coastline that stretches for 350 kilometres. The country gained independence from Portugal in 1973 and has since struggled with political instability and economic challenges. The capital city is Bissau, which is also the largest city in the country. The official language is Portuguese, and the majority of the population practices Islam and indigenous beliefs. Guinea-Bissau is known for its rich cultural heritage, diverse wildlife, and natural beauty, making it a unique and intriguing destination for travellers and researchers alike.
Guinea-Bissau has a complex history that has shaped its current identity and challenges. The country’s economy is largely dependent on agriculture, with cashew nuts being the primary export. However, political instability, corruption, and drug trafficking have hindered economic development and stability. Despite these challenges, Guinea-Bissau has a rich cultural heritage, with traditional music, dance, and art playing a significant role in the lives of its people. The country’s diverse wildlife and natural resources also offer potential opportunities for sustainable development and conservation efforts. As Guinea-Bissau continues to navigate its path towards stability and prosperity, it faces both challenges and opportunities that will shape its future.
Geography and Climate of Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau is a small country with a diverse geography that includes coastal plains, mangrove swamps, and low-lying plateaus. The country’s terrain is largely flat, with the highest point being just 300 meters above sea level. The Bijagos Archipelago, a group of islands off the coast of Guinea-Bissau, adds to the country’s natural beauty and biodiversity. The country’s rivers, including the Geba and Corubal rivers, are important for transportation and agriculture. The coastal region is characterized by mangrove forests, which provide important habitats for a variety of wildlife.
The climate of Guinea-Bissau is tropical, with distinct wet and dry seasons. The rainy season typically lasts from June to October, bringing heavy rainfall and high humidity. The dry season, from November to May, is characterized by hot temperatures and dry winds from the Sahara Desert. The country is also prone to tropical cyclones, which can cause significant damage to infrastructure and agriculture. The diverse geography and climate of Guinea-Bissau play a significant role in shaping the country’s ecosystems, agriculture, and livelihoods of its people.
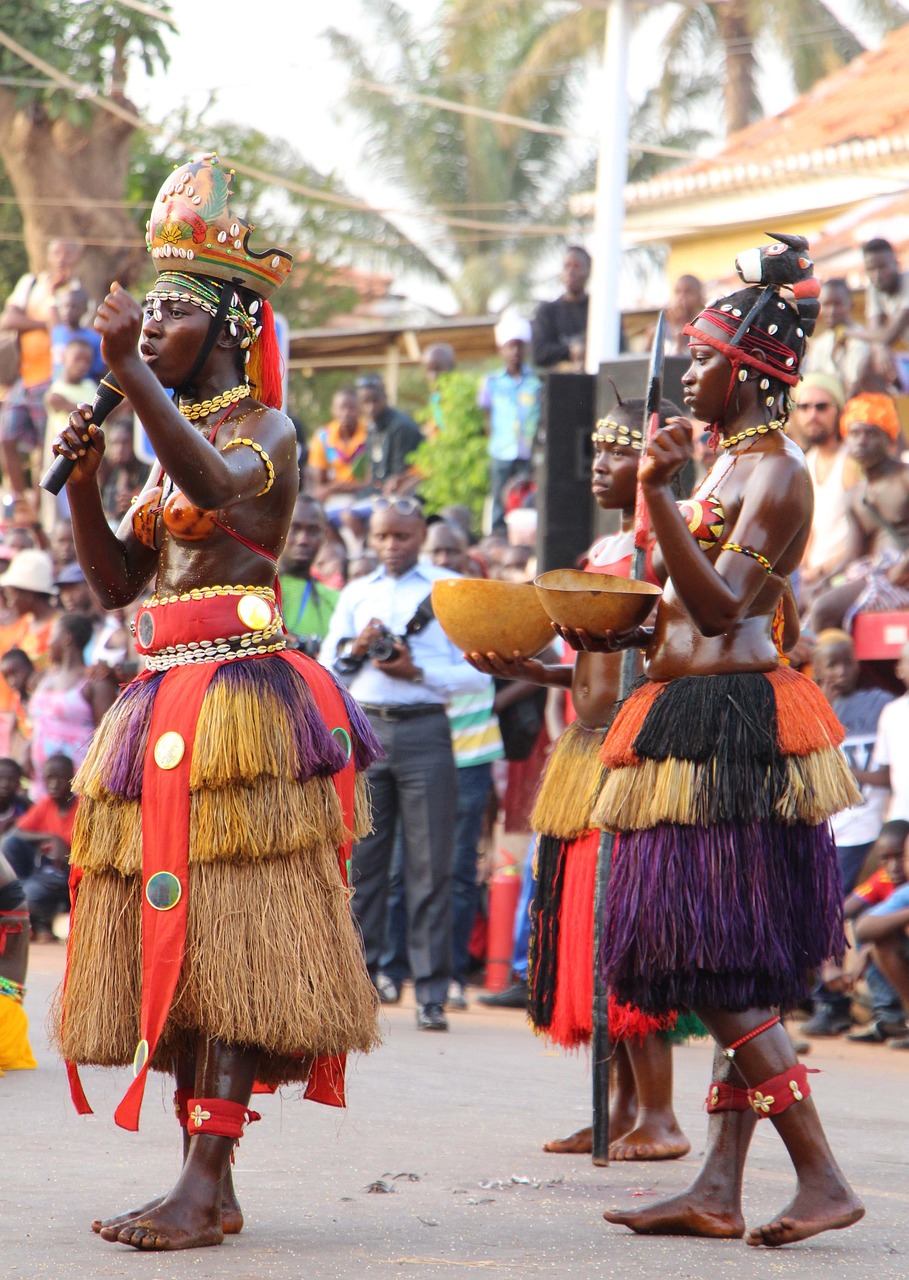
History and Culture of Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau has a rich history that dates back to ancient times, with evidence of human habitation dating back thousands of years. The region was once part of the powerful Mali Empire and later became a Portuguese colony in the 15th century. The legacy of Portuguese colonialism has had a lasting impact on the country’s culture, language, and social structures. Guinea-Bissau gained independence in 1973 after a long struggle against Portuguese rule, followed by years of political instability and civil war.
The culture of Guinea-Bissau is diverse and vibrant, with influences from indigenous traditions, Portuguese colonialism, and Islamic heritage. Traditional music and dance play a significant role in the lives of the people, with styles such as gumbe and kussunde being popular forms of expression. The country’s diverse ethnic groups each have their own unique traditions and customs, contributing to the rich tapestry of Guinea-Bissau’s cultural heritage. Despite the challenges of political instability and economic hardship, the people of Guinea-Bissau have maintained a strong sense of identity and resilience, which is reflected in their cultural traditions and community spirit.
Economy and Industry in Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau’s economy is largely dependent on agriculture, with cashew nuts being the primary export crop. Other important agricultural products include rice, peanuts, palm oil, and timber. Fishing is also a significant industry, with the country’s coastal waters teeming with a variety of fish species. However, the economy faces significant challenges due to political instability, corruption, and drug trafficking. These issues have hindered economic development and foreign investment, leading to high levels of poverty and unemployment.
The industrial sector in Guinea-Bissau is underdeveloped, with limited infrastructure and access to modern technology. The country has the potential for growth in industries such as tourism, renewable energy, and natural resource extraction. However, these opportunities are hindered by political instability and lack of investment in infrastructure and education. Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for sustainable development in Guinea-Bissau, particularly in the areas of agriculture, fisheries, and eco-tourism. With the right policies and investment, Guinea-Bissau has the potential to improve its economy and provide better livelihoods for its people.
Politics and Government in Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau has faced significant political instability since gaining independence from Portugal in 1973. The country has experienced multiple coups, civil wars, and periods of military rule, leading to a lack of effective governance and development. The political landscape is characterized by corruption, weak institutions, and a lack of accountability, which have hindered progress towards stability and prosperity.
The government of Guinea-Bissau is a semi-presidential republic with a multi-party system. The president is the head of state and government, while the prime minister is responsible for running the day-to-day affairs of the country. However, political infighting and lack of cooperation between different branches of government have led to frequent changes in leadership and policy direction. The international community has been involved in efforts to support democratic governance and stability in Guinea-Bissau through diplomatic initiatives and development assistance. Despite these efforts, the country continues to face challenges in building effective governance structures that can address the needs of its people.
Wildlife and Natural Resources in Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau is home to a diverse range of wildlife and natural resources that are important for both ecological conservation and economic development. The country’s coastal waters are rich in marine life, including fish, dolphins, sea turtles, and manatees. The Bijagos Archipelago is an important nesting site for sea turtles and a variety of bird species. The mangrove forests along the coast provide important habitats for numerous species of birds, fish, and other wildlife.
In addition to its wildlife, Guinea-Bissau has significant natural resources such as bauxite, phosphates, granite, clay, and limestone. These resources have the potential for sustainable extraction and exportation to support economic development. However, there are challenges related to illegal mining activities, deforestation, overfishing, and pollution that threaten the country’s natural resources. Conservation efforts are important for protecting Guinea-Bissau’s biodiversity and ensuring sustainable use of its natural resources for future generations.
Challenges and Opportunities for Guinea-Bissau’s Future
Guinea-Bissau faces numerous challenges as it seeks to build a stable and prosperous future for its people. Political instability, corruption, weak governance structures, poverty, unemployment, and lack of access to education are among the key challenges that hinder progress in the country. Additionally, environmental degradation, climate change impacts, illegal fishing activities, drug trafficking, and transnational crime pose significant threats to Guinea-Bissau’s stability and development.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for Guinea-Bissau to overcome its obstacles and build a brighter future. The country has potential for sustainable development in industries such as agriculture, fisheries, eco-tourism, renewable energy, and natural resource extraction. International cooperation and support for democratic governance can also help Guinea-Bissau address its political challenges and build effective institutions that serve the needs of its people.
In conclusion, Guinea-Bissau is a country with a rich cultural heritage, diverse wildlife, and natural beauty, but also significant challenges that hinder its development. With the right policies, investment in infrastructure and education, environmental conservation efforts, and international cooperation for democratic governance support; Guinea-Bissau can overcome its obstacles and build a brighter future for its people.
FAQs
What is the official name of Guinea-Bissau?
The official name of the country is the Republic of Guinea-Bissau.
What is the capital city of Guinea-Bissau?
The capital city of Guinea-Bissau is Bissau.
What is the population of Guinea-Bissau?
As of 2021, the estimated population of Guinea-Bissau is around 2 million people.
What is the official language of Guinea-Bissau?
The official language of Guinea-Bissau is Portuguese.
What is the currency used in Guinea-Bissau?
The currency used in Guinea-Bissau is the West African CFA franc.
What is the main religion in Guinea-Bissau?
The main religion in Guinea-Bissau is Islam, followed by Christianity and traditional indigenous beliefs.
What is the climate like in Guinea-Bissau?
Guinea-Bissau has a tropical climate with a wet season from June to November and a dry season from December to May.
What are the major industries in Guinea-Bissau?
The major industries in Guinea-Bissau include agriculture, fishing, and cashew nut production.
What is the political status of Guinea-Bissau?
Guinea-Bissau is a republic with a multi-party political system and a president as the head of state and government.
Natural Resources of Guinea-Bissau: Where Natural Resources are located In Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau, a small West African country, is rich in natural resources that play a significant role in its economy and livelihoods of its people. The country’s natural resources include mineral deposits, agricultural land, forests, water bodies, and energy sources. These resources are vital for the country’s development and sustainability. Guinea-Bissau’s natural resources have the potential to contribute to economic growth, poverty reduction, and sustainable development if managed effectively and sustainably. However, the country faces challenges in the management and conservation of its natural resources due to factors such as political instability, weak governance, and inadequate infrastructure. Despite these challenges, Guinea-Bissau has the opportunity to harness its natural resources for the benefit of its people and the environment. Guinea-Bissau’s natural resources are diverse and offer opportunities for economic development and environmental conservation. The country’s mineral resources, agricultural land, forests, water bodies, and energy sources are essential for its socio-economic development. However, the effective management and sustainable use of these resources are crucial for the country’s long-term prosperity. Guinea-Bissau has the potential to leverage its natural resources to improve the livelihoods of its people, promote economic growth, and protect its environment. The country needs to address governance issues, invest in infrastructure, and implement sound policies to harness the full potential of its natural resources. With proper management and conservation efforts, Guinea-Bissau can ensure the sustainable use of its natural resources for the benefit of current and future generations. Summary Guinea-Bissau is rich in natural resources including minerals, agriculture, forests, water, and energy. The country’s mineral resources include bauxite, phosphates, and granite, with potential for further exploration and development. Guinea-Bissau’s agricultural resources...
Political Boundaries of Guinea-Bissau: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Guinea-Bissau, a small West African country, is bordered by Senegal to the north and Guinea to the south and east, with the Atlantic Ocean to the west. The country covers an area of approximately 36,125 square kilometres and has a population of around 1.9 million people. The political boundaries of Guinea-Bissau are defined by its 8 administrative regions, which are further divided into 37 sectors. The capital city, Bissau, is located in the Bissau region, which is the most populous and economically important region in the country. Guinea-Bissau’s political boundaries have evolved over time, influenced by historical, cultural, and geopolitical factors. Summary Guinea-Bissau is a small country in West Africa with complex political boundaries. The country is divided into 8 provinces, each with its own unique characteristics and challenges. Within the provinces, there are 37 districts that play a crucial role in local governance and administration. Guinea-Bissau’s historical boundaries have been shaped by colonialism and post-independence struggles. The evolution of Guinea-Bissau’s political boundaries has been influenced by internal conflicts and external pressures. Provinces of Guinea-Bissau Guinea-Bissau is divided into 8 administrative regions, also known as provinces. These provinces are Biombo, Bissau, Bolama, Cacheu, Gabu, Oio, Quinara, and Tombali. Each province is further divided into sectors, which are the second-level administrative divisions in the country. The provinces are named after their respective capital cities, and each has its own unique cultural and historical significance. For example, the Bissau region, where the capital city is located, is the political and economic centre of the country. The provinces play a crucial role in the governance and administration of Guinea-Bissau, with each having...
Climate Zones of Guinea-Bissau: Different climate regions Of Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau, a small West African country, is characterized by a diverse range of climate zones. The country’s climate is influenced by its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean, as well as its position within the tropics. Guinea-Bissau experiences a tropical climate with distinct wet and dry seasons. The country can be divided into four main climate regions: the coastal region, the interior savannah region, the northern region, and the southern region. Each of these regions has its own unique climate characteristics, which have a significant impact on the country’s ecosystems, agriculture, and overall way of life. Understanding Guinea-Bissau’s climate zones is crucial for both residents and policymakers in order to effectively manage natural resources, plan for agricultural activities, and mitigate the impacts of climate change. Summary Guinea-Bissau has three main climate zones: coastal, interior savannah, and northern and southern regions. The coastal region experiences a hot and humid climate with heavy rainfall, making it suitable for rice cultivation. The interior savannah region has a more moderate climate with distinct wet and dry seasons, making it ideal for cashew nut production. The northern region has a tropical climate with high temperatures and heavy rainfall, while the southern region has a more arid climate with less rainfall. Understanding Guinea-Bissau’s climate zones is crucial for agricultural planning, resource management, and disaster preparedness. Coastal Climate Region The coastal region of Guinea-Bissau is characterized by its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean, which has a moderating effect on the climate. The region experiences high levels of humidity and relatively stable temperatures throughout the year. The average annual temperature in the coastal region ranges from 24°C to...
History of Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau, located on the west coast of Africa, has a rich and diverse history that dates back to the pre-colonial period. The early inhabitants of Guinea-Bissau were the indigenous ethnic groups such as the Balanta, Fula, Mandinka, and Papel. These groups had established their own distinct cultures, traditions, and social structures long before the arrival of European explorers. The Balanta people, for example, were known for their agricultural skills and their unique spiritual beliefs, while the Fula were predominantly nomadic herders. The Mandinka, on the other hand, were renowned for their trading networks and their strong warrior traditions. These diverse ethnic groups coexisted in the region for centuries, developing their own languages, customs, and ways of life. The early inhabitants of Guinea-Bissau lived in harmony with the natural environment, relying on agriculture, fishing, and hunting for their sustenance. They had a deep connection to the land and the sea, and their societies were often organised around kinship ties and communal decision-making. The region was also a hub for trade, with merchants from North Africa and the Middle East visiting the coast to exchange goods such as gold, ivory, and slaves. The pre-colonial period in Guinea-Bissau was characterised by a rich tapestry of cultures and traditions, with each ethnic group contributing to the vibrant mosaic of the region’s history. Summary Guinea-Bissau was inhabited by various ethnic groups before the arrival of European colonizers. Portuguese colonization had a significant impact on Guinea-Bissau, including the introduction of Christianity and the establishment of trade networks. Guinea-Bissau played a key role in the transatlantic slave trade, with many people being forcibly taken from the...
Terrain and Topography of Guinea-Bissau: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Guinea-Bissau, a small West African country, is known for its diverse and varied terrain and topography. The country is characterized by a combination of mountainous regions, valleys, lowlands, and coastal plains, making it a unique and fascinating landscape to explore. The terrain and topography of Guinea-Bissau play a crucial role in shaping the country’s climate, agriculture, and natural resources. Understanding the different geographical features of Guinea-Bissau is essential for appreciating the country’s natural beauty and understanding its environmental significance. The terrain and topography of Guinea-Bissau are a result of geological processes that have shaped the land over millions of years. The country is located on the Atlantic coast of West Africa, and its landscape is influenced by the presence of the Atlantic Ocean. Guinea-Bissau’s terrain is characterized by a mix of highlands and lowlands, with the Fouta Djallon Plateau in the east and the coastal plains in the west. The diverse topography of Guinea-Bissau provides a habitat for a wide range of flora and fauna, making it a biodiversity hotspot in the region. The country’s terrain and topography also play a significant role in determining its climate, which has a direct impact on the lives of its people and the economy. Summary Guinea-Bissau’s terrain is diverse, with mountainous regions, valleys, lowlands, and coastal plains. The mountainous regions of Guinea-Bissau are found in the eastern part of the country and are characterised by rugged terrain and dense vegetation. The valleys and lowlands of Guinea-Bissau are fertile areas that are suitable for agriculture and are home to a variety of wildlife. The coastal plains of Guinea-Bissau are low-lying areas that are...
Population Density of Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau is a small West African country located on the Atlantic coast. It is bordered by Senegal to the north and Guinea to the south and east. The country has a rich history, having been part of the Mali Empire and later the Portuguese Empire. It gained independence in 1973 and has since struggled with political instability and economic challenges. The population of Guinea-Bissau is estimated to be around 2 million people, with a diverse mix of ethnic groups and languages spoken. The country’s economy is largely dependent on agriculture, with cashew nuts being the main export. Guinea-Bissau faces numerous challenges, including high levels of poverty, political instability, and a lack of infrastructure. These factors have a significant impact on the population density of the country. Summary Guinea-Bissau is a small country located in West Africa, known for its diverse culture and rich history. The population density of Guinea-Bissau is relatively low compared to other countries, with the majority of the population living in rural areas. Factors affecting population density in Guinea-Bissau include limited access to healthcare, education, and economic opportunities, as well as environmental factors such as climate change and natural disasters. The impact of population density on Guinea-Bissau includes increased pressure on limited resources, infrastructure, and social services, leading to challenges in sustainable development. High population density in Guinea-Bissau presents challenges such as food security, healthcare access, and environmental degradation, but also opportunities for economic growth and cultural exchange. Strategies for managing population density in Guinea-Bissau include improving access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities, as well as implementing sustainable environmental practices and infrastructure development. In conclusion,...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Guinea-Bissau: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau, a small West African country, is known for its rich cultural heritage, stunning natural beauty, and vibrant history. The country is bordered by Senegal to the north and Guinea to the south and east, with the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Guinea-Bissau is a former Portuguese colony and gained independence in 1973. The country is home to diverse ethnic groups, including the Fula, Mandinka, Balanta, and Papel people, each with their own unique traditions and customs. The capital city, Bissau, is a bustling hub of activity, with colourful markets, lively music, and a welcoming atmosphere. The country’s economy is largely based on agriculture, with cashew nuts being the primary export. Guinea-Bissau is also known for its rich biodiversity, with lush forests, mangroves, and an abundance of wildlife. The country’s unique blend of African and Portuguese influences makes it a fascinating destination for travellers seeking an authentic and off-the-beaten-path experience. Guinea-Bissau’s history is marked by colonialism, struggle for independence, and political instability. Despite these challenges, the country has managed to preserve its cultural heritage and traditions. The people of Guinea-Bissau are known for their warmth and hospitality, and visitors are often welcomed with open arms. The country’s diverse landscapes, from pristine beaches to dense forests, offer a wealth of opportunities for outdoor activities such as birdwatching, hiking, and wildlife spotting. With its rich history, vibrant culture, and natural beauty, Guinea-Bissau is a hidden gem waiting to be discovered by intrepid travellers looking for an authentic African experience. Summary Guinea-Bissau is a small West African country known for its rich cultural heritage and stunning natural beauty. Fortaleza de São José...