Democratic Republic of the Congo
(République Democratique du Congo (Democratic Republic of the Congo))

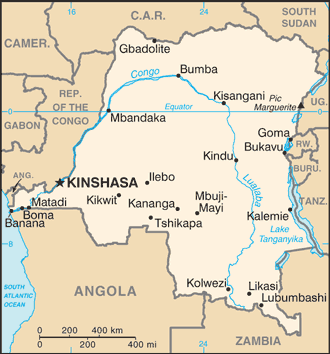




Capital: Kinshasa
Population (Estimated July 2012): 73,599,190
Area: 2,345,410 km2 or 905,568 mi2
Currency: Congolese franc (FC)
Official Language: French
Political Information: Semi-Presidential Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 50% of the population are Roman Catholic, 20% are Protestant, 10% are Kimbanguist, 10% are Muslim and 10% have other religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Mont Ngaliema (Mount Stanley) 5,110m or 16,765ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a country’s economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $15.3 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $25.19 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $300 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): Between +1:00 to +2:00
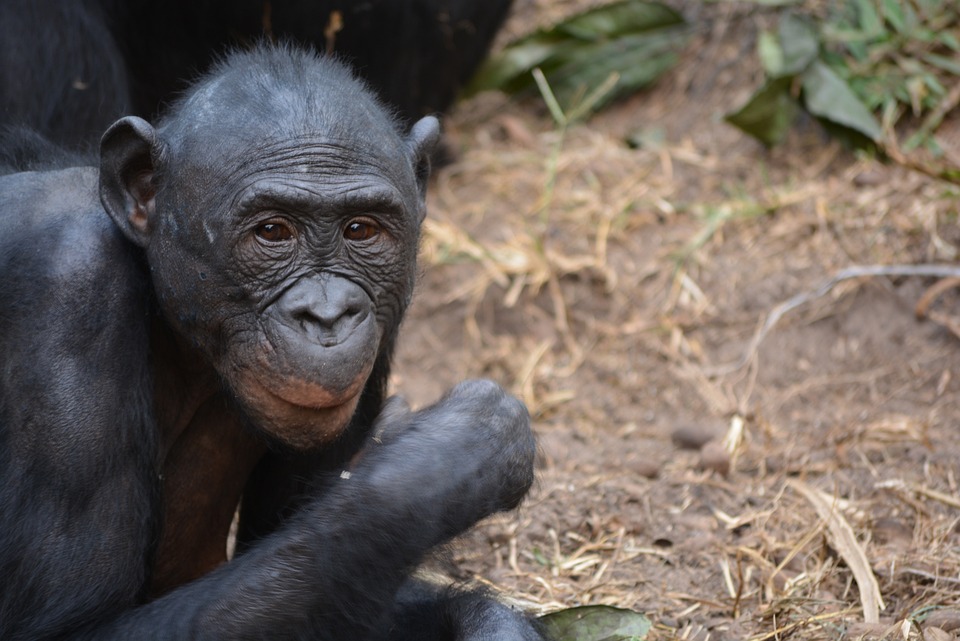
Wildlife:
Counties/Provinces/States: 10 provinces (provinces, singular – province) and 1 city* (ville); Bandundu, Bas-Congo (Lower Congo), Equateur, Kasai-Occidental (West Kasai), Kasai-Oriental (East Kasai), Katanga, Kinshasa*, Maniema, Nord-Kivu (North Kivu), Orientale, Sud-Kivu (South Kivu)
Leaders: President Joseph Kabila with Adolphe Muzito as Prime Minister.
Additional: Independence from Belgium on the 30th of June 1960
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo, commonly referred to as DRC or Congo-Kinshasa, is a country located in Central Africa. It is the second-largest country in Africa by land area and the fourth-most populous country on the continent. The DRC shares borders with nine other countries, including Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, and Angola. The capital city is Kinshasa, which is also the largest city in the country.
The population of the DRC is estimated to be over 85 million people, making it one of the most populous countries in Africa. The official language is French, which is widely spoken in government and business sectors. However, there are also over 200 ethnic groups in the country, each with its own language and culture. Some of the major languages spoken include Lingala, Swahili, and Kikongo.
History and Colonialism in the Congo
The history of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is complex and marked by colonization and political instability. The region was first explored by Europeans in the late 19th century, with Belgian explorer Henry Morton Stanley famously navigating the Congo River. In 1885, King Leopold II of Belgium established the Congo Free State as his personal colony, exploiting its natural resources and subjecting the Congolese people to forced labour and brutal treatment.
In 1908, due to international pressure and reports of human rights abuses, the Belgian government took over control of the colony and renamed it Belgian Congo. Under Belgian rule, there was some improvement in infrastructure and education, but political power remained concentrated in the hands of a small elite. The Congolese people were denied political rights and economic opportunities.
In 1960, following a wave of independence movements across Africa, the Democratic Republic of the Congo gained independence from Belgium. However, this transition was not smooth, and the country soon descended into political chaos and violence. The first Prime Minister, Patrice Lumumba, was overthrown and assassinated in 1961, and the country was subsequently ruled by a series of military leaders and dictators.
Political System and Government Structure
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a presidential republic, with a multi-party system. The President is both the head of state and the head of government and is elected by popular vote for a five-year term. The President appoints the Prime Minister, who is responsible for running the day-to-day affairs of the government.
The country also has a bicameral parliament, consisting of the National Assembly and the Senate. Members of the National Assembly are elected by popular vote, while Senators are elected by provincial assemblies. The parliament is responsible for making laws and overseeing the government’s activities.
In recent years, the DRC has faced significant political challenges. The 2018 presidential election was marred by allegations of fraud and irregularities, leading to widespread protests and violence. However, a peaceful transfer of power eventually took place, with Felix Tshisekedi becoming the country’s new President. Despite this progress, there are still concerns about political stability and the government’s ability to address the needs of its citizens.
Economic Overview and Challenges
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is rich in natural resources, including minerals such as copper, cobalt, and diamonds. These resources have the potential to drive economic growth and development in the country. However, the DRC’s economy has been plagued by corruption, mismanagement, and a lack of infrastructure.
Corruption is a major challenge in the DRC, with high levels of embezzlement and bribery. This has hindered economic development and discouraged foreign investment. The lack of infrastructure, including roads, railways, and electricity, also poses significant challenges to economic growth. Many parts of the country are inaccessible, making it difficult to transport goods and services.
Additionally, the DRC has a high poverty rate, with over 70% of the population living below the poverty line. This is due in part to the unequal distribution of wealth and resources. The majority of the population relies on subsistence agriculture for their livelihoods, which is vulnerable to climate change and natural disasters.
Natural Resources and Environmental Issues
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is known for its rich natural resources, which include minerals, forests, and wildlife. The country is one of the world’s largest producers of cobalt, a key component in batteries for electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies. It also has significant reserves of copper, gold, and diamonds.
However, the extraction and trade of these resources have been linked to human rights abuses and environmental degradation. Illegal mining and smuggling are widespread, with armed groups and criminal networks profiting from the trade. This has fueled conflict and instability in the eastern region of the country.
Deforestation is another major environmental issue in the DRC. The country’s forests are home to a diverse range of plant and animal species, including endangered gorillas and elephants. However, illegal logging and land conversion for agriculture have led to widespread deforestation, threatening biodiversity and contributing to climate change.
Culture and Society in the DRC
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a culturally diverse country, with over 200 ethnic groups. Each group has its own language, traditions, and customs. The Congolese people are known for their vibrant music and dance, with genres such as soukous and rumba gaining international recognition.
However, there are also social issues that need to be addressed in the DRC. Gender inequality is prevalent, with women facing discrimination in education, employment, and access to healthcare. Violence against women and children is also a serious problem, with high rates of sexual assault and domestic violence.
Access to education is another challenge in the DRC, particularly in rural areas. Many children are unable to attend school due to poverty, lack of infrastructure, and armed conflict. This limits their opportunities for social and economic advancement.
Human Rights and Conflict in the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo has a poor human rights record, with widespread violations including extrajudicial killings, torture, and arbitrary detention. Violence against women and children is particularly prevalent, with sexual violence being used as a weapon of war.
The eastern region of the country has been plagued by armed conflict for decades. Various armed groups, both domestic and foreign, have been involved in the conflict, which is fueled by competition over natural resources. The conflict has resulted in the displacement of millions of people and has had a devastating impact on the civilian population.
Efforts have been made to address these human rights abuses and bring perpetrators to justice. The International Criminal Court (ICC) has opened investigations into crimes committed in the DRC, and there have been some prosecutions at the national level. However, challenges remain in ensuring accountability and ending impunity.
International Relations and Foreign Policy
The Democratic Republic of the Congo has a complex relationship with its neighbouring countries and the international community. The country has faced accusations of supporting armed groups in neighbouring countries, particularly in the eastern region. This has strained relations with countries such as Rwanda and Uganda.
The DRC is also a member of several regional and international organizations, including the African Union (AU) and the United Nations (UN). It has participated in peacekeeping missions in other countries, including Sudan and Mali. These missions have helped to improve the country’s international standing and strengthen its relationships with other countries.
In recent years, there have been efforts to improve regional cooperation and resolve conflicts through diplomatic means. The DRC has engaged in dialogue with its neighbours to address security concerns and promote economic integration. However, challenges remain in achieving lasting peace and stability in the region.
Infrastructure and Development in the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo faces significant challenges in terms of infrastructure and development. The country has a limited road network, particularly in rural areas, which makes it difficult to transport goods and services. The lack of reliable electricity also hinders economic growth and limits access to basic services such as healthcare and education.
Access to clean water is another major challenge in the DRC. Many people rely on unsafe water sources, leading to high rates of waterborne diseases such as cholera. Improving access to clean water and sanitation is crucial for improving public health and reducing poverty.
Healthcare is also a major concern in the DRC, with limited access to quality medical services. The country has one of the highest maternal mortality rates in the world, and there are significant gaps in healthcare infrastructure and trained medical personnel.
Future Prospects and Challenges for the DRC
The Democratic Republic of the Congo has significant potential for economic growth and development, but there are also ongoing challenges that need to be addressed. Increased investment in infrastructure, including roads, railways, and electricity, could help to unlock the country’s economic potential and improve living standards for its citizens.
Renewable energy is another area of opportunity for the DRC. The country has vast hydropower potential, which could provide clean and affordable electricity to its population. Investing in renewable energy technologies could also help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
However, political instability and conflict remain major challenges for the DRC. The country needs to strengthen its institutions, promote good governance, and ensure respect for human rights. Addressing these challenges will require both domestic and international efforts, as well as sustained commitment from all stakeholders.
In conclusion, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is a country with a rich history, diverse culture, and significant potential for economic development. However, it also faces numerous challenges, including political instability, corruption, and conflict. Addressing these challenges will require a comprehensive approach that includes political reforms, investment in infrastructure, and efforts to promote human rights and social development. With the right policies and support from the international community, the DRC has the potential to overcome these challenges and build a brighter future for its citizens.
FAQs
What is the Democratic Republic of the Congo?
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is a country located in Central Africa. It is the second-largest country in Africa by area and the 11th-largest in the world.
What is the capital of the Democratic Republic of the Congo?
The capital of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is Kinshasa. It is the largest city in the country and one of the largest cities in Africa.
What is the population of the Democratic Republic of the Congo?
The population of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is estimated to be around 89 million people. It is the fourth most populous country in Africa.
What is the official language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo?
The official language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is French. However, there are over 200 other languages spoken in the country, including Lingala, Swahili, and Tshiluba.
What is the currency of the Democratic Republic of the Congo?
The currency of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the Congolese franc (CDF).
What is the economy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo like?
The economy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is largely dependent on its natural resources, including minerals such as copper, cobalt, and diamonds. However, the country has been plagued by political instability and conflict, which has hindered economic growth and development.
What is the political system of the Democratic Republic of the Congo?
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a presidential representative democratic republic. The President is both the head of state and the head of government and is elected by popular vote for a five-year term.
What are some of the major challenges facing the Democratic Republic of the Congo?
The Democratic Republic of the Congo faces a number of challenges, including political instability, conflict, poverty, and disease. The country has also been affected by the Ebola virus outbreak in recent years.
Terrain and Topography of Democratic Republic of the Congo: mountains, valleys, and plains.
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is a country located in Central Africa, known for its vast and diverse terrain. From towering mountains to expansive plains, the DRC’s landscape plays a crucial role in the country’s development. Understanding the topography of the DRC is essential for various sectors, including agriculture, mining, transportation, and disaster preparedness. By examining the different regions of the DRC and the challenges they present, we can gain a deeper understanding of the country’s potential and the need for sustainable development practices. Summary The Democratic Republic of Congo has a diverse terrain and topography, including mountains, valleys, plains, and the Congo River Basin. The mountainous regions of the DRC are home to active volcanoes and have a significant impact on the country’s landscape. The valleys of the DRC are important agricultural areas and are home to many of the country’s rivers. The plains of the DRC are vast and largely undeveloped, but have potential for future agricultural and industrial development. The Congo River Basin is a vital part of the DRC’s topography, providing water and resources for millions of people. The Mountainous Regions of the DRC: A Closer Look The DRC is home to several major mountain ranges, including the Rwenzori Mountains, Virunga Mountains, and Mitumba Mountains. These mountainous regions are not only breathtakingly beautiful but also hold significant importance for the country’s development. The fertile slopes of these mountains provide ideal conditions for agriculture, with crops such as coffee, tea, and potatoes thriving in these high-altitude areas. Additionally, these regions are rich in mineral resources, including gold, tin, and coltan, making them valuable for mining...
History of Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo, often referred to as Congo, is a country located in Central Africa. It is the second-largest country in Africa by land area and is rich in natural resources such as diamonds, gold, copper, and cobalt. However, the history of Congo is marred by colonization, exploitation, and conflict. In order to understand the present-day challenges and opportunities facing the country, it is crucial to delve into its complex history. Summary The Congo people have a rich pre-colonial history that dates back centuries. Belgian colonial rule was marked by the exploitation of Congo’s vast natural resources and the brutal treatment of its people. Patrice Lumumba led the fight for independence, but his government was overthrown in a coup and he was assassinated. The Mobutu era was characterized by dictatorship and corruption, which left the country in economic ruin. The First and Second Congo Wars were complex conflicts involving regional and international actors, resulting in millions of deaths and displacement. Joseph Kabila’s rise to power marked a transition to a democratic republic, but his rule was also marked by controversy and allegations of corruption. The 2006 elections were the first free and fair elections in 40 years, but the country still faced challenges in establishing a stable democracy. The UN peacekeeping mission played a crucial role in stabilizing the country’s fragile peace. The 2018 elections were controversial, with allegations of fraud and irregularities, raising questions about the future of Congo’s democracy. Congo’s history has left the country with many challenges, but also opportunities for growth and development. The Pre-Colonial Era: The Origins of the Congo People...
History of Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), located in Central Africa, has a rich and complex history that has shaped its present-day reality. Understanding the country’s past is crucial in order to comprehend the challenges it faces today. From pre-colonial societies and kingdoms to European exploration and colonization, from resistance against colonialism to the struggle for independence, and from the era of authoritarian rule to the ongoing political challenges, the DRC’s history is a tapestry of triumphs and tragedies. Summary The Congo region had early societies and kingdoms before European explorers arrived. Belgian colonial rule exploited the Congo’s resources, leading to resistance and rebellion. Patrice Lumumba played a significant role in the struggle for independence. The Cold War and foreign intervention worsened the Congo crisis. Mobutu Sese Seko’s authoritarian rule lasted for years before the transition to democracy in the 1990s. The pre-colonial era: early societies and kingdoms in the Congo region Before European arrival, the Congo region was home to various societies and kingdoms. The Kongo Kingdom, for example, was a powerful state that existed from the 14th to the 19th century. It was known for its sophisticated political structure, trade networks, and artistic achievements. The kingdom had a centralized government led by a king, and it engaged in trade with European powers such as Portugal. Trade and commerce played a significant role in the pre-colonial era. The Congo River served as a vital transportation route, connecting different regions and facilitating trade between communities. Ivory, copper, salt, and slaves were among the commodities exchanged. The region’s economic prosperity attracted the attention of European explorers who sought to exploit its...
Political Boundaries of Democratic Republic of the Congo: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is a vast country located in Central Africa. It is the second-largest country in Africa by land area and has a population of over 80 million people. The DRC is known for its rich natural resources, including minerals such as copper, cobalt, and diamonds. The political system of the DRC is a semi-presidential republic, with a President as the head of state and a Prime Minister as the head of government. The country is divided into 26 provinces, each with its own governor and provincial assembly. These provinces are further divided into districts and territories. Summary The Democratic Republic of the Congo is divided into 26 provinces with distinct names and locations. The country’s political boundaries have evolved from the Belgian Congo to present day, with historical and colonial influences. Districts play a crucial role in the DRC’s political system, contributing to the maintenance of political boundaries. Ethnic and linguistic diversity is an important factor in shaping the DRC’s political boundaries. Conflict and instability pose significant challenges to maintaining political boundaries in the DRC, with international actors playing a role in shaping the country’s future prospects for change and stability. The 26 Provinces of the DRC: Names and Locations The DRC is divided into 26 provinces, each with its own unique characteristics. Here is a list of the provinces and their locations on a map: 1. Bas-Uele – Located in the northeastern part of the country, bordering South Sudan and Uganda.2. Haut-Uele – Also located in the northeastern part of the country, bordering South Sudan.3. Ituri – Located in the northeastern part...
Climate Zones of Democratic Republic of the Congo: Different climate regions Of Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo, located in Central Africa, is a country known for its vast and diverse geography. From dense rainforests to expansive savannas, the country is home to a wide range of climate zones. Understanding these different climate zones is crucial for various reasons, including agriculture, conservation efforts, and tourism. Summary Democratic Republic of the Congo has a diverse range of climate zones. Equatorial climate zone is characterized by high temperatures and rainfall throughout the year. Tropical savanna climate zone experiences distinct wet and dry seasons. Humid subtropical climate zone has mild winters and hot summers with high humidity. Highland climate zone has cooler temperatures due to its higher elevation. Equatorial Climate Zone in Democratic Republic of the Congo The equatorial climate zone is characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall throughout the year. This climate zone covers a significant portion of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, particularly in the central and eastern regions. The equatorial rainforest, also known as the Congo Basin, is one of the largest tropical rainforests in the world and is found within this climate zone. The equatorial rainforest is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna. It is known for its towering trees, such as mahogany and ebony, as well as various species of orchids and ferns. The rainforest is also home to a wide variety of animal species, including gorillas, chimpanzees, elephants, and numerous bird species. Tropical Savanna Climate Zone in Democratic Republic of the Congo The tropical savanna climate zone in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons. This...
Population Density of Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), located in Central Africa, is the second-largest country on the continent and one of the most populous. It is bordered by nine countries and has a diverse geography that includes rainforests, savannas, and mountains. The DRC has a rich history, with indigenous tribes inhabiting the region for thousands of years before European colonization in the late 19th century. The country gained independence from Belgium in 1960 and has since faced numerous challenges, including political instability, armed conflict, and economic struggles. Despite these challenges, the DRC is home to a vibrant and resilient population. Summary The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a country located in Central Africa with a population of over 100 million people. Population density is the number of people living in a specific area and is important for understanding resource allocation and development planning. The DRC has a long history of population density, with indigenous groups and colonial powers impacting the population distribution. Currently, the DRC has a population density of 37 people per square kilometer, with higher densities in urban areas. Factors affecting population density in the DRC include natural resources, conflict, and migration patterns. Understanding Population Density and Its Importance Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured per square kilometer or square mile. It is an important indicator for understanding a country’s development as it provides insights into how resources are distributed, infrastructure needs, and social dynamics. High population density can put pressure on resources such as water, food, and housing, leading to increased competition and potential conflicts. On...
Natural Resources of Democratic Republic of the Congo: Where Natural Resources are located In Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), located in Central Africa, is a country rich in natural resources. It is the second-largest country in Africa by land area and is known for its vast reserves of minerals, forests, water, agriculture, wildlife, and human resources. These resources play a crucial role in the country’s economy and have significant implications for the global economy. The DRC’s natural resources are diverse and abundant. The country is known for its mineral wealth, including copper, cobalt, diamonds, gold, tin, and coltan. It is estimated that the DRC has over $24 trillion worth of untapped mineral resources, making it one of the richest countries in terms of mineral reserves. In addition to minerals, the DRC is home to the second-largest rainforest in the world, known as the Congo Basin. This vast greenery is a vital carbon sink and provides habitat for numerous species of plants and animals. The Congo River and its tributaries also offer significant water resources, while the fertile land supports agricultural activities. The natural resources of the DRC are of great importance to the global economy. The country’s mineral wealth contributes significantly to the global supply of minerals such as copper and cobalt. These minerals are essential for various industries, including electronics, automotive, construction, and renewable energy. The DRC is one of the world’s largest producers of cobalt, accounting for more than 60% of global production. Its copper reserves are also substantial, making it a key player in the global copper market. The Congo Basin’s rainforest plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. It...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Democratic Republic of the Congo: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of Congo, located in Central Africa, is a country known for its rich cultural heritage, diverse wildlife, and stunning natural landscapes. Despite facing numerous challenges, including political instability and economic struggles, the country has immense potential for tourism. Tourism plays a crucial role in the development of the country, providing employment opportunities and contributing to the overall economy. In this article, we will explore some of the most captivating attractions in the Democratic Republic of Congo that make it a must-visit destination for travelers. Summary Virunga National Park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site with diverse wildlife and stunning landscapes. Stanleyville is a city with a rich colonial heritage, including historic buildings and monuments. Ituri Forest’s rock paintings offer a glimpse into the past and the culture of the indigenous people. The Congo River is a lifeline for the nation, providing transportation, food, and hydroelectric power. The Kasai River is a cultural and historical icon, with traditional fishing practices and important archaeological sites. The Majestic Virunga National Park: A UNESCO World Heritage Site Virunga National Park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in the eastern part of the Democratic Republic of Congo. Spanning over 7,800 square kilometers, it is one of the most biologically diverse areas in Africa. The park is home to a wide range of wildlife, including endangered mountain gorillas, chimpanzees, elephants, and hippos. Visitors to Virunga National Park can embark on thrilling gorilla trekking expeditions, where they can observe these magnificent creatures in their natural habitat. In addition to its incredible wildlife, Virunga National Park also boasts stunning landscapes, including active volcanoes...