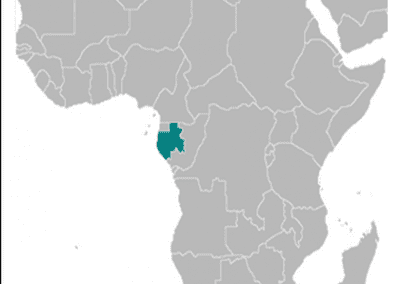
Gabon
(République Gabonaise (Gabonese Republic))

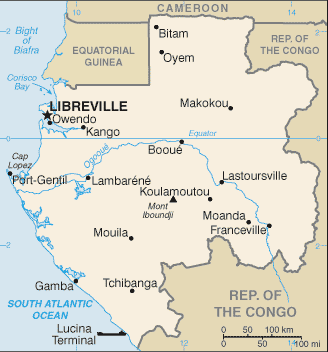




Capital: Libreville
Population (Estimated July 2012): 1,608,321
Area: 267,667 km2 or 103,347 mi2
Currency: CFA Franc (CFAF)
Official Language: French
Political Information: Presidential Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion
(approximately 55% – 75% of the population are Christian, with the remainder animist and Muslim less than 1%)
Highest Mountain: Mont Bengoué at 1,070m or 3,510 ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $16.7 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $24.28 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $16,000 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (UTC): +1:00
Wildlife:
Counties/Provinces/States: Provinces; Estuaire, Haut-Ogooue, Moyen-Ogooue, Ngounie, Nyanga, Ogooue-Ivindo, Ogooue-Lolo, Ogooue-Maritime, Woleu-Ntem
Leaders: President Ali Bongo Ondimba with Prime Minister Raymond Ndong Sima.
Additional: Gained Independence from France on the 17th of August 1960.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Gabon
Gabon, officially known as the Gabonese Republic, is a country located on the west coast of Central Africa. It is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo on the east and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. The capital city of Gabon is Libreville, which is also the largest city in the country. The official language is French, and the currency used is the Central African CFA franc. Gabon gained independence from France in 1960 and has since been a republic with a strong presidential system.
Gabon is known for its rich biodiversity, with over 80% of its land covered in tropical rainforests. The country is also home to a diverse range of wildlife, including forest elephants, gorillas, and chimpanzees. The economy of Gabon is heavily reliant on oil, which has led to significant economic growth in recent years. Despite this, Gabon faces challenges such as income inequality and high levels of poverty. The country has made efforts to promote sustainable development and conservation, with a focus on preserving its natural resources and wildlife. Gabon is also a popular destination for ecotourism, attracting visitors from around the world to explore its pristine landscapes and diverse ecosystems. With its unique blend of natural beauty and cultural heritage, Gabon offers a fascinating experience for travellers seeking adventure and exploration in Africa.
Geography and Climate of Gabon
Gabon is located on the equator, giving it a tropical climate with high levels of humidity and rainfall throughout the year. The country is characterized by its dense rainforests, which are part of the Congo Basin, one of the largest tropical rainforest areas in the world. The landscape of Gabon also includes coastal plains along the Atlantic Ocean, as well as savannahs and plateaus further inland. The Ogooué River is the largest river in Gabon and plays a crucial role in the country’s transportation and economy.
The climate in Gabon is generally hot and humid, with temperatures ranging from 24°C to 31°C (75°F to 88°F) throughout the year. The rainy season typically occurs from October to May, with heavy rainfall and occasional thunderstorms. The dry season, from June to September, brings slightly cooler temperatures and less precipitation. The diverse geography and climate of Gabon contribute to its rich biodiversity, with a wide variety of plant and animal species thriving in its forests, rivers, and coastal areas.
History and Culture of Gabon
Gabon has a rich history dating back thousands of years, with evidence of human habitation found in archaeological sites across the country. The earliest inhabitants of Gabon were hunter-gatherers, followed by Bantu-speaking tribes who migrated to the region around 2,000 years ago. European exploration and colonization began in the 15th century when Portuguese explorers arrived on the coast of Gabon. The country later became a part of French Equatorial Africa in the late 19th century before gaining independence in 1960.
The culture of Gabon is diverse and influenced by its many ethnic groups, each with its own traditions, languages, and customs. The Fang people are one of the largest ethnic groups in Gabon and are known for their vibrant music and dance traditions. Traditional Gabonese music often features drums, harps, and other percussion instruments, accompanied by energetic dancing and singing. The country also has a rich tradition of storytelling and oral literature, with myths and legends passed down through generations.
Gabonese cuisine reflects the country’s natural resources, with an emphasis on fresh seafood, tropical fruits, and locally grown vegetables. Popular dishes include grilled fish, plantains, cassava, and peanut-based stews. Traditional ceremonies and rituals are an important part of Gabonese culture, often involving music, dance, and elaborate costumes. These cultural practices are celebrated during festivals and special occasions throughout the year.
Economy and Natural Resources of Gabon
Gabon has a relatively small population compared to its land area, with a population of around 2 million people. The economy of Gabon is heavily reliant on oil production, which accounts for a significant portion of the country’s GDP and exports. Other natural resources in Gabon include manganese, uranium, timber, and iron ore. The government has made efforts to diversify the economy by investing in sectors such as agriculture, tourism, and renewable energy.
Despite its natural wealth, Gabon faces challenges such as income inequality and high levels of poverty. The government has implemented social welfare programs to address these issues and promote economic development. Efforts have also been made to improve infrastructure and access to education and healthcare services for all citizens.
Gabon is a member of the Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS) and the Central African Economic and Monetary Community (CEMAC), which promote economic cooperation and integration among member countries. The government has also prioritized sustainable development and environmental conservation to protect its natural resources for future generations.
Wildlife and Conservation in Gabon
Gabon is renowned for its rich biodiversity and diverse ecosystems, making it a haven for wildlife enthusiasts and conservationists. The country is home to a wide variety of animal species, including forest elephants, western lowland gorillas, chimpanzees, leopards, and numerous bird species. The dense rainforests of Gabon provide vital habitats for these animals, as well as a wide range of plant species.
The government of Gabon has made significant efforts to protect its natural resources through the establishment of national parks and protected areas. In 2002, President Omar Bongo Ondimba created a network of 13 national parks covering over 11% of the country’s land area. These parks are managed by the National Agency for National Parks (ANPN) and play a crucial role in preserving Gabon’s unique ecosystems.
Conservation organisations such as the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) have also been involved in research and conservation efforts in Gabon. They work closely with local communities to promote sustainable resource management and wildlife protection. Ecotourism has become an important source of revenue for conservation efforts in Gabon, as visitors from around the world come to experience its pristine landscapes and observe its iconic wildlife.
Tourism in Gabon
Gabon offers a wealth of natural attractions for tourists seeking adventure and exploration in Africa. The country’s diverse landscapes include pristine beaches along the Atlantic coast, dense rainforests teeming with wildlife, and picturesque rivers and waterfalls. Visitors can explore national parks such as Loango National Park, known for its diverse wildlife including elephants, hippos, and marine life; Ivindo National Park with its stunning waterfalls; and Lopé National Park which is a UNESCO World Heritage site.
In addition to its natural beauty, Gabon also has a rich cultural heritage waiting to be discovered by travellers. The capital city of Libreville is home to historical landmarks such as the Presidential Palace and the National Museum of Arts and Traditions. Visitors can also experience traditional music and dance performances at cultural events throughout the year.
Ecotourism is a growing industry in Gabon, offering opportunities for visitors to engage in activities such as birdwatching, hiking, fishing, and wildlife safaris. The country has made efforts to promote sustainable tourism practices that support local communities and protect its natural resources. With its unspoiled landscapes and unique wildlife experiences, Gabon provides an unforgettable adventure for travellers seeking an authentic African experience.
Political Landscape of Gabon
Gabon is a republic with a strong presidential system, where the President holds significant executive power. The current President of Gabon is Ali Bongo Ondimba, who has been in office since 2009 following the death of his father, President Omar Bongo Ondimba. The political landscape in Gabon has been marked by a single-party system for much of its history since gaining independence from France.
In recent years, there have been calls for political reform and greater transparency in government institutions. Civil society organisations have advocated for democratic principles and human rights protections in Gabon. The government has made efforts to address these concerns by implementing reforms aimed at promoting good governance and accountability.
Gabon is a member of several international organisations such as the United Nations (UN), African Union (AU), and Organisation Internationale de la Francophonie (OIF). The country has also played a role in regional diplomacy within Central Africa through its participation in organisations such as ECCAS and CEMAC.
Overall, Gabon continues to navigate political challenges while striving to promote stability, democracy, and economic development for its citizens. The government has expressed commitment to addressing social issues such as poverty reduction and improving access to education and healthcare services for all citizens.
FAQs
What is the capital of Gabon?
The capital of Gabon is Libreville.
What is the official language of Gabon?
The official language of Gabon is French.
What is the currency used in Gabon?
The currency used in Gabon is the Central African CFA franc.
What is the population of Gabon?
As of 2021, the population of Gabon is estimated to be around 2.2 million people.
What is the climate like in Gabon?
Gabon has a tropical climate with high humidity and heavy rainfall throughout the year. The country experiences a wet season from October to May and a dry season from June to September.
What are the major natural resources of Gabon?
Gabon is rich in natural resources, including oil, manganese, and timber.
What are the popular tourist attractions in Gabon?
Some popular tourist attractions in Gabon include Loango National Park, Lopé National Park, Pongara National Park, and the coastal beaches. Gabon is also known for its diverse wildlife and ecotourism opportunities.
Population Density of Gabon
Gabon, a country located on the west coast of Central Africa, is known for its rich biodiversity and natural resources. With a population of approximately 2.2 million people, Gabon has a relatively low population density compared to other countries in the region. The population density of Gabon is around 8.6 people per square kilometer, making it one of the least densely populated countries in Africa. The majority of the population is concentrated in urban areas, particularly in the capital city of Libreville and the surrounding areas. The rest of the country is sparsely populated, with large areas of dense rainforest and limited infrastructure. Despite its low population density, Gabon faces unique challenges and opportunities related to population distribution and density. Gabon’s population density is influenced by a variety of factors, including geography, climate, and historical settlement patterns. The country’s dense rainforests and rugged terrain have historically made it difficult for people to settle in certain areas, leading to uneven population distribution. Additionally, the coastal areas, where the capital city is located, have historically been more accessible and attractive for settlement due to their proximity to the sea and natural resources. The equatorial climate of Gabon also plays a role in population distribution, as it can be challenging for people to live and work in certain parts of the country due to the hot and humid conditions. Furthermore, historical factors such as colonialism and migration have also influenced the distribution of Gabon’s population. These factors have contributed to the uneven population density in Gabon, with the majority of people living in urban areas along the coast, while large parts of...
History of Gabon
Gabon, located on the west coast of Central Africa, has a rich history dating back thousands of years. The earliest inhabitants of Gabon were the Pygmy people, who are believed to have lived in the region for over 10,000 years. These hunter-gatherer communities were the first to settle in the dense rainforests of Gabon, living in harmony with the natural environment and developing a deep understanding of the flora and fauna of the region. In addition to the Pygmy people, several Bantu-speaking groups migrated into Gabon around 2,000 years ago, bringing with them advanced agricultural techniques and ironworking skills. These Bantu groups established several powerful kingdoms in the region, including the Kingdom of Loango, the Kingdom of Kongo, and the Kingdom of Orungu. These kingdoms were known for their sophisticated political systems, vibrant cultural traditions, and extensive trade networks that connected them to other parts of Africa and beyond. The Kingdom of Loango, in particular, was renowned for its wealth and influence, attracting traders from Europe and the Arab world. The pre-colonial history of Gabon is a testament to the resilience and ingenuity of its early inhabitants, who developed thriving societies in the midst of the dense rainforests and along the Atlantic coast. The legacy of these early kingdoms continues to shape Gabonese culture and identity to this day, as evidenced by the rich tapestry of traditions, languages, and customs that are celebrated throughout the country. Summary Pre-Colonial Gabon was inhabited by various ethnic groups and kingdoms, including the Fang, Punu, and Kwele, each with their own unique cultural traditions and social structures. The arrival of the Portuguese and...
Terrain and Topography of Gabon: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Gabon, located on the west coast of Central Africa, is a country known for its diverse and varied terrain. The landscape of Gabon is characterized by a combination of mountain ranges, valleys, lowlands, and coastal plains, making it a unique and fascinating destination for nature enthusiasts and researchers alike. The topography of Gabon is largely influenced by the Congo Basin, which covers a significant portion of the country and is home to some of the world’s most diverse and pristine rainforests. The terrain of Gabon plays a crucial role in shaping the country’s ecosystems, wildlife, and human settlements, making it an important aspect of the country’s identity and natural heritage. The diverse terrain of Gabon is a result of geological processes that have shaped the land over millions of years. The country is home to a wide range of geological formations, including ancient rock formations, volcanic mountains, and sedimentary basins. The terrain of Gabon is also influenced by its location within the Congo Basin, which is one of the largest tropical rainforest regions in the world. This unique combination of geological features has resulted in a landscape that is rich in biodiversity and natural beauty, making Gabon a truly remarkable destination for those interested in exploring the wonders of the natural world. Summary Gabon’s terrain is diverse, with mountain ranges, valleys, lowlands, and coastal plains. The mountain ranges in Gabon include the Crystal Mountains and the Chaillu Massif, which are important for biodiversity. The valleys and lowlands of Gabon are home to rivers, swamps, and forests, supporting a variety of wildlife. The coastal plains of Gabon are characterized by...
Climate Zones Of Gabon: Different climate regions Of Gabon
Gabon, located on the west coast of Central Africa, is a country known for its rich biodiversity and diverse climate zones. The country is divided into several distinct climate zones, each with its own unique characteristics and weather patterns. Understanding these climate zones is crucial for anyone planning to visit or do business in Gabon, as it can greatly impact travel plans, agricultural practices, and overall quality of life. From the equatorial climate zone in the north to the coastal climate zone in the west and the highland climate zone in the east, Gabon offers a wide range of climates that contribute to its natural beauty and ecological diversity. Summary Gabon has a diverse range of climate zones, each with its own unique characteristics and weather patterns. The Equatorial Climate Zone in Gabon is characterized by high temperatures, heavy rainfall, and high humidity throughout the year. The Tropical Climate Zone experiences distinct wet and dry seasons, with high temperatures and moderate to high rainfall. The Transition Zone in Gabon has a mix of characteristics from both the equatorial and tropical zones, with varying levels of rainfall and temperature. The Coastal Climate Zone in Gabon experiences milder temperatures and lower rainfall compared to other zones, with a more moderate climate influenced by the ocean. Equatorial Climate Zone The equatorial climate zone covers the northern part of Gabon and is characterized by high temperatures, heavy rainfall, and high humidity throughout the year. This region experiences very little variation in temperature, with average highs of around 30°C and lows of around 23°The equatorial zone is also known for its dense rainforests, which...
Political Boundaries of Gabon: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Gabon, a country located on the west coast of Central Africa, is known for its rich biodiversity and diverse culture. The political boundaries of Gabon are defined by its borders with Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. The country covers an area of 267,667 square kilometers and is divided into nine provinces and further subdivided into 50 districts. The political boundaries of Gabon have evolved over time, influenced by historical, geographical, and cultural factors. These boundaries play a crucial role in shaping the governance, administration, and development of the country. Summary Gabon’s political boundaries are defined by its borders with Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, and the Atlantic Ocean. Gabon is divided into 9 provinces, each with its own administrative capital and governor. The provinces are further divided into 50 districts, each with its own district chief and administrative structure. Gabon’s historical boundaries have been shaped by colonialism and the scramble for Africa by European powers. The political boundaries of Gabon have a significant impact on governance, resource allocation, and infrastructure development. Challenges and controversies surrounding Gabon’s political boundaries include disputes with neighbouring countries and issues of resource exploitation. The future of Gabon’s political boundaries will likely be influenced by regional integration efforts and the need for sustainable development. Provinces of Gabon Gabon is divided into nine provinces, each with its own unique characteristics and cultural heritage. The provinces are Estuaire, Haut-Ogooué, Moyen-Ogooué, Ngounié, Nyanga, Ogooué-Ivindo, Ogooué-Lolo, Ogooué-Maritime, and Woleu-Ntem. Each province is further divided into districts, which are the primary...
Natural Resources of Gabon: Where Natural Resources are located In Gabon
Gabon, located on the west coast of Central Africa, is blessed with a rich abundance of natural resources. The country’s natural resources include forests, minerals, oil and gas, water, wildlife, and biodiversity. These resources play a crucial role in the country’s economy and are vital for the livelihoods of the Gabonese people. The sustainable management of these resources is essential for the long-term development and prosperity of the nation. Gabon’s natural resources have attracted significant attention from both domestic and international investors. The government has implemented policies to promote sustainable development and conservation of these resources, while also seeking to leverage them for economic growth. The country’s natural beauty and diverse ecosystems make it a unique and valuable resource for the world. As such, Gabon has made efforts to balance the exploitation of its resources with conservation efforts to ensure their preservation for future generations. Summary Gabon is rich in natural resources, including forests, minerals, oil and gas, water, and wildlife. The forests in Gabon cover about 85% of the country and are home to a diverse range of plant and animal species. Gabon has significant mineral resources, including manganese, iron, gold, and uranium. The oil and gas industry is a major contributor to Gabon’s economy, with the country being one of the largest oil producers in sub-Saharan Africa. Gabon’s water resources are abundant, with numerous rivers and lakes providing important sources of freshwater for the country. Forest Resources in Gabon Gabon is home to one of the largest intact tropical rainforests in the world, covering approximately 85% of the country’s land area. These forests are a vital natural...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Gabon: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites in Gabon
Gabon, a country located on the west coast of Central Africa, is home to a rich tapestry of cultural and historical sites that offer a glimpse into the country’s fascinating past. From the lush rainforests to the vibrant cities, Gabon’s cultural and historical sites are a testament to the country’s diverse heritage and the resilience of its people. The country’s history is deeply intertwined with the slave trade, colonialism, and the struggle for independence, and these themes are reflected in the various cultural and historical sites that can be found throughout Gabon. One of the most striking aspects of Gabon’s cultural and historical sites is the way in which they are integrated into the natural landscape. From the dense rainforests to the winding rivers, these sites are not only a testament to the country’s history but also a celebration of its natural beauty. Whether it’s the sacred Ivindo River and the Kongou Falls or the Lopé-Okanda World Heritage Site, Gabon’s cultural and historical sites offer visitors a unique opportunity to explore the country’s history while immersing themselves in its stunning natural surroundings. Summary Gabon is home to a rich cultural and historical heritage, with a variety of sites that showcase the country’s unique history and traditions. The Sacred Ivindo River and the Kongou Falls offer visitors a chance to experience the natural beauty and spiritual significance of these iconic landmarks. The Historical Slave Route in Loango National Park provides a sobering look at Gabon’s role in the transatlantic slave trade and its impact on the country’s history. The Lopé-Okanda World Heritage Site is a must-visit for those interested in...