Algeria
(Al-Jumhūriyyah al-Jazāʾiriyyah al-Dīmuqrāṭiyyah al-Shaʿbiyyah (People’s Democratic Republic of Algeria))

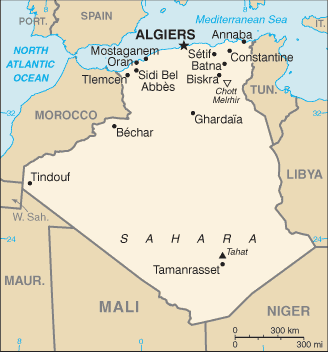
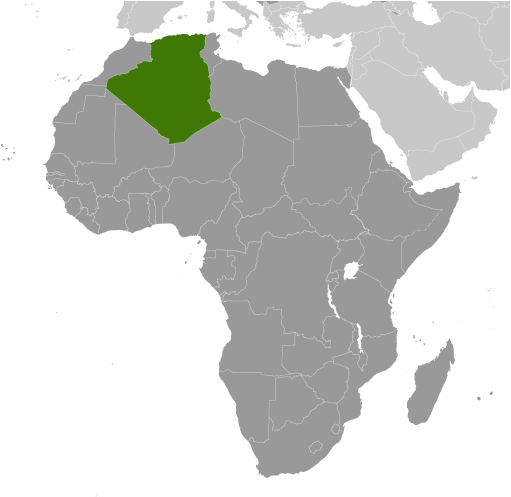




Capital: Algiers
Population (Estimated July 2012): 35,406,303
Area: 2,381,741km2 or 919,595mi2
Currency: Algerian Dinar (DA)
Official Language: Arabic
Political Information: Presidential Republic
Official Religion: Islam
(with approximately 99% of the population are Sunni Muslim and 1% are Christian or Jewish)
Highest Mountain: Tahat at 3,003m or 9852ft
Largest River: Chelif River at 700km long
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $183.4 billion (US$) or £110,040 million (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $264.1 billion (US$) or £158,460 million(GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $7,200 (US$) or £4,320(GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +1:00
Counties/Provinces/States: Provinces (wilayat, singular – wilaya); Adrar, Ain Defla, Ain Temouchent, Alger, Annaba, Batna, Bechar, Bejaia, Biskra, Blida, Bordj Bou Arreridj, Bouira, Boumerdes, Chlef, Constantine, Djelfa, El Bayadh, El Oued, El Tarf, Ghardaia, Guelma, Illizi, Jijel, Khenchela, Laghouat, Mascara, Medea, Mila, Mostaganem, M’Sila, Naama, Oran, Ouargla, Oum el Bouaghi, Relizane, Saida, Setif, Sidi Bel Abbes, Skikda, Souk Ahras, Tamanghasset, Tebessa, Tiaret, Tindouf, Tipaza, Tissemsilt, Tizi Ouzou, Tlemcen
Leaders: President Abdelaziz Bouteflika
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica,
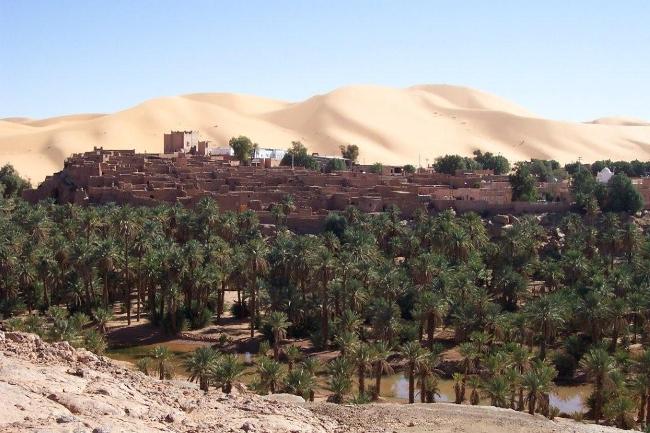
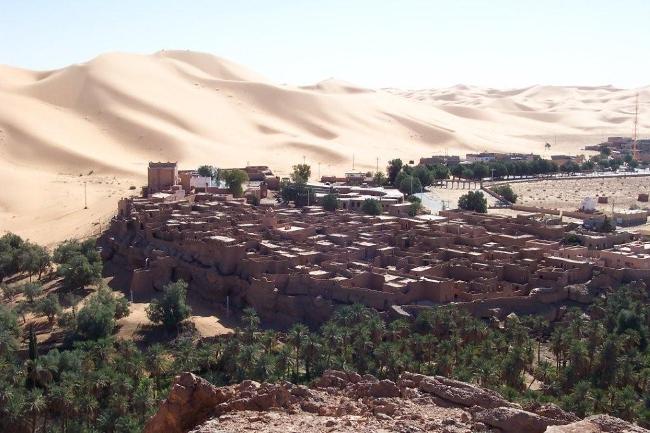
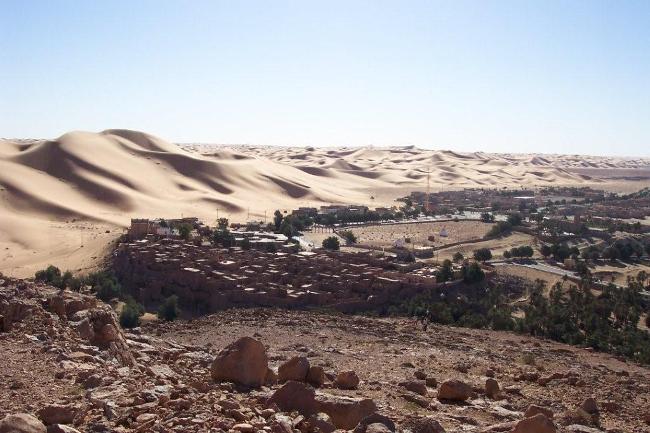
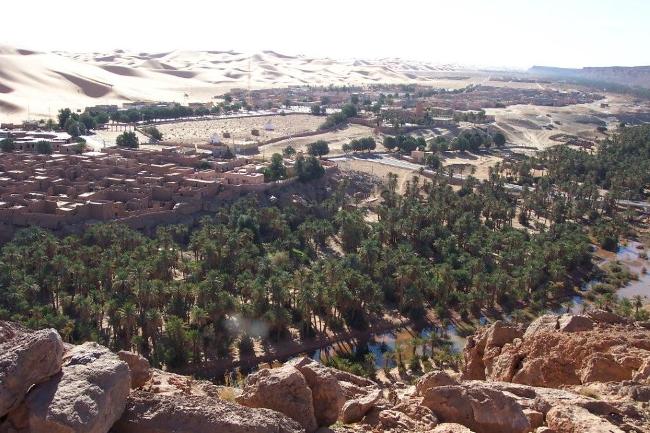
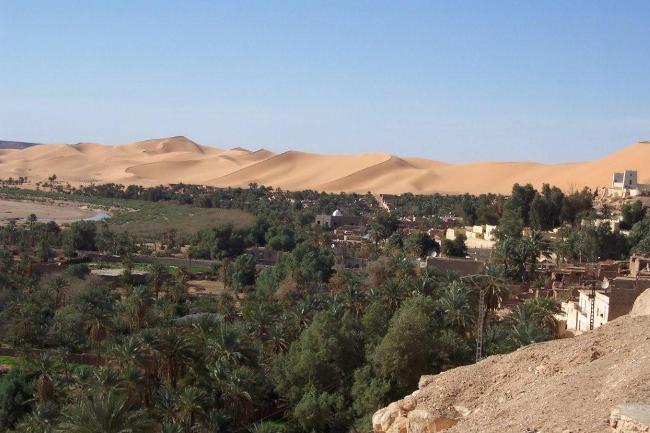
Algeria, located in North Africa, is the largest country on the continent and the 10th largest in the world. It is bordered by Tunisia and Libya to the east, Niger and Mali to the south, Mauritania, Western Sahara, and Morocco to the west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north. With its strategic location, Algeria has played a significant role in North African history and politics.
A Brief History of Algeria: From French Colonization to Independence
Algeria’s history is marked by its colonization by France and its struggle for independence. The French arrived in Algeria in 1830 and gradually established control over the country. The Algerian people resisted French rule, leading to a long and bloody war for independence that lasted from 1954 to 1962.
Key events and figures in Algeria’s history include the Battle of Algiers in 1957, which was a turning point in the war for independence. The National Liberation Front (FLN), led by figures such as Ahmed Ben Bella and Houari Boumediene, played a crucial role in the fight against French colonialism. Finally, on July 5, 1962, Algeria gained its independence from France.
Geography and Climate of Algeria: A Diverse Landscape
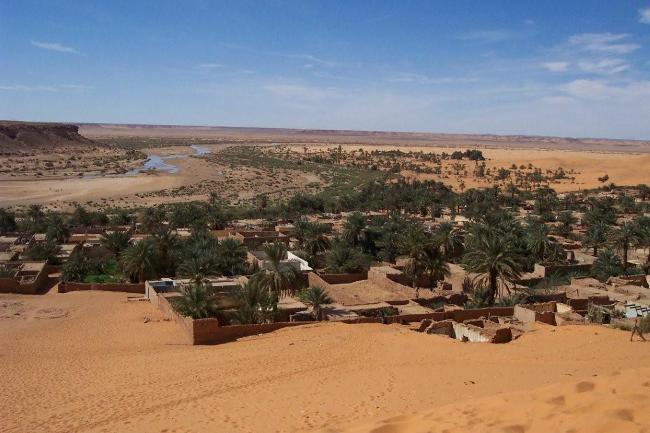
Algeria’s geography is incredibly diverse, with a wide range of landscapes including mountains, deserts, and coastline. The Atlas Mountains run through the northern part of the country, providing stunning views and opportunities for hiking and exploration.
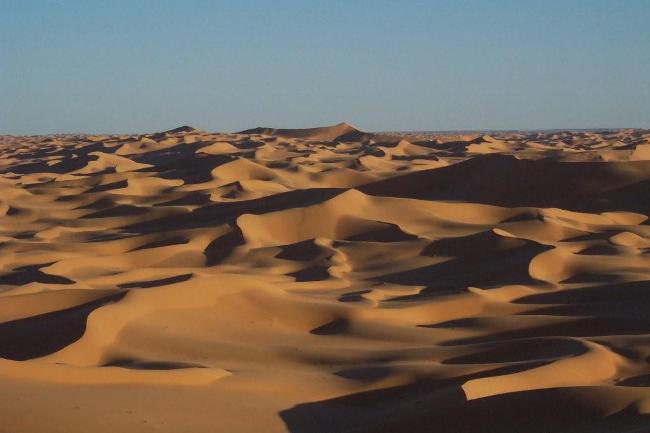
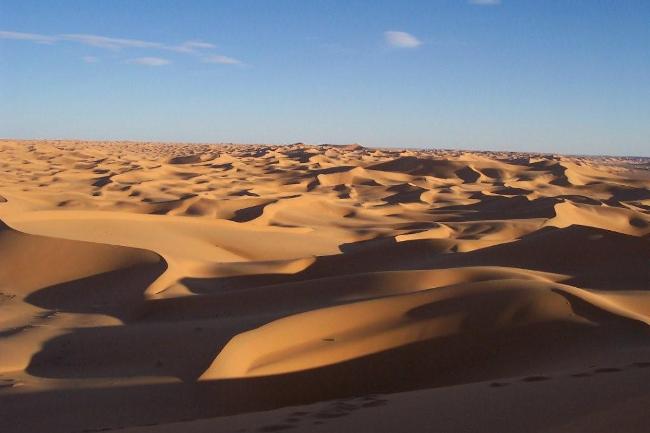
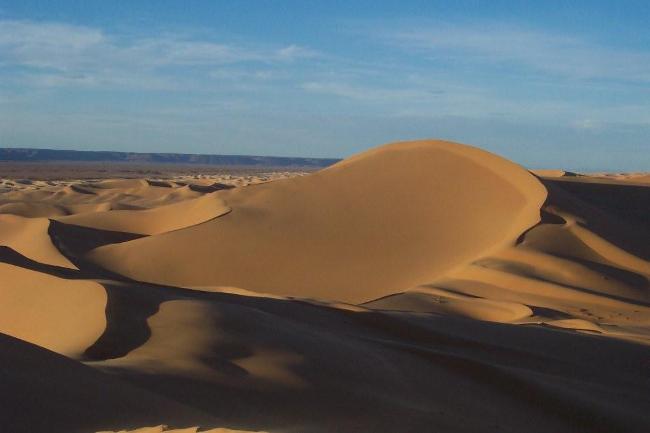
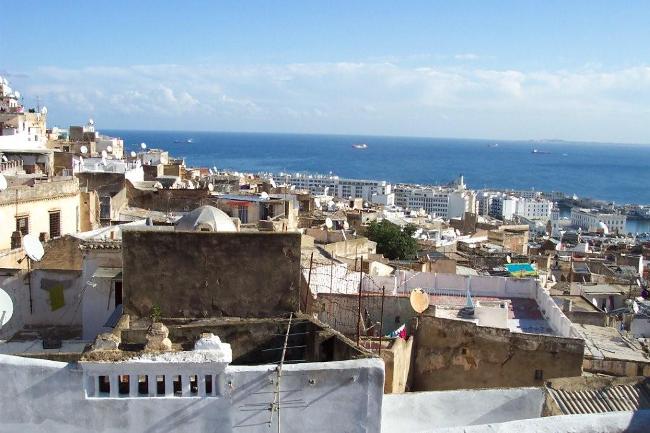
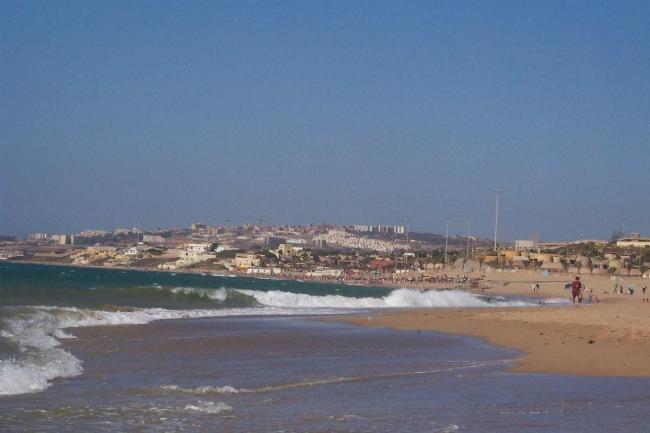
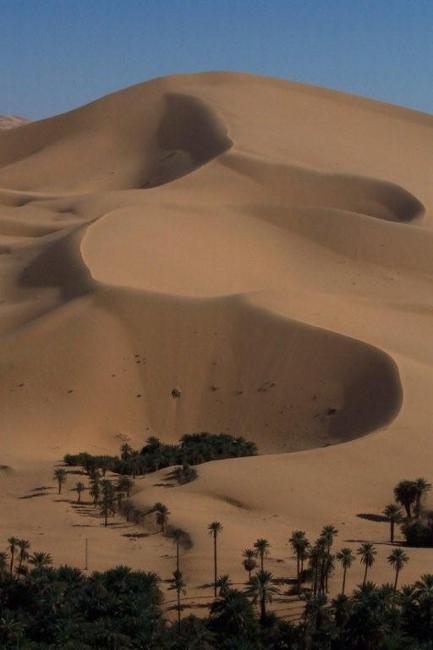
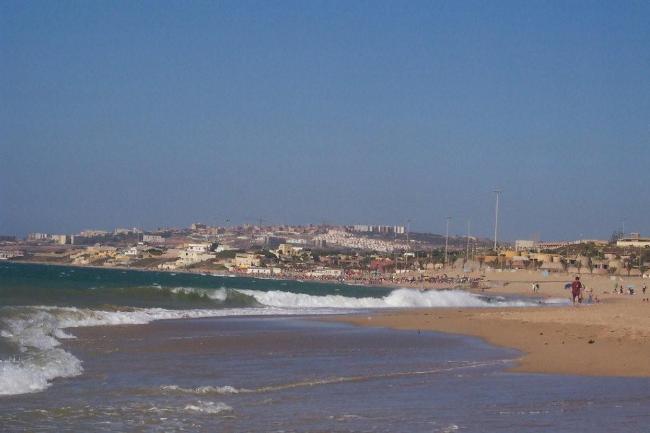
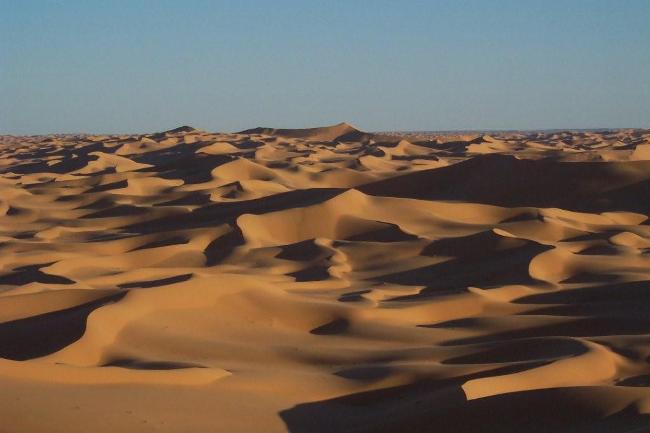
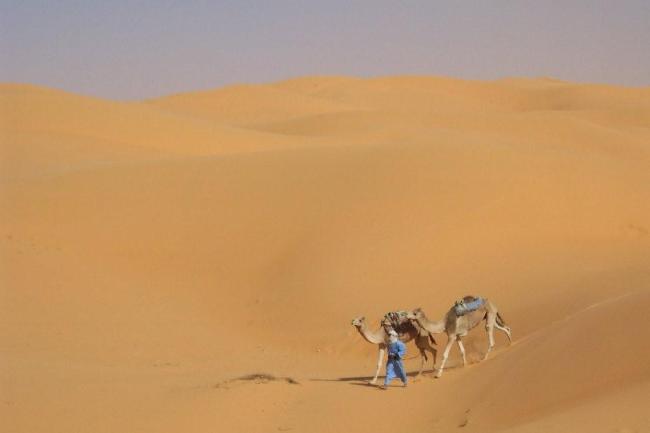
The Sahara Desert covers much of southern Algeria, offering a unique experience for adventurous travellers. The coastline along the Mediterranean Sea is dotted with beautiful beaches and vibrant cities such as Algiers and Oran.
In terms of climate, Algeria experiences a Mediterranean climate along the coast, with hot summers and mild winters. Inland areas have a desert climate, with extremely hot summers and cooler winters. The mountainous regions have a more temperate climate, with colder temperatures and more rainfall.
Culture and Society in Algeria: A Blend of Arab and Berber Traditions
Algeria’s culture is a rich blend of Arab and Berber traditions. The majority of the population is Arab, with Arabic being the official language. However, the Berber population, who are indigenous to North Africa, also play a significant role in Algerian culture.
The traditional dress in Algeria varies depending on the region, with many women wearing the hijab or traditional Berber clothing. Algerian cuisine is also influenced by both Arab and Berber traditions, with dishes such as couscous, tagines, and mint tea being popular.
Algeria’s society is predominantly Muslim, with Islam being the state religion. However, there is also a significant Christian minority in the country. Family is highly valued in Algerian society, with strong bonds between relatives and an emphasis on hospitality.
The Algerian Economy: Oil and Gas Dominance
Algeria’s economy is heavily reliant on oil and gas exports, which account for the majority of its revenue. The country has significant reserves of oil and natural gas, making it one of the largest producers in Africa.
However, Algeria faces challenges in diversifying its economy and reducing its dependence on oil and gas. The government has made efforts to promote other sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism, but progress has been slow.
Politics and Government in Algeria: A Presidential Republic
Algeria is a presidential republic, with a president serving as both the head of state and the head of government. The president is elected by popular vote for a five-year term.
The political system in Algeria has been dominated by the National Liberation Front (FLN) since independence. However, there have been calls for political reform and greater democracy in recent years, particularly from the younger generation.
Education and Healthcare in Algeria: Progress and Challenges
Algeria has made significant progress in the areas of education and healthcare since independence. The government has invested heavily in these sectors, resulting in increased access to education and improved healthcare outcomes.
However, there are still challenges to be addressed. The quality of education and healthcare services varies across the country, with rural areas often lacking adequate facilities and resources. There is also a need for greater investment in research and development to drive innovation in these sectors.
Tourism in Algeria: A Hidden Gem in North Africa
Algeria has a wealth of historical and cultural attractions that make it a hidden gem in North Africa. The country is home to several UNESCO World Heritage sites, including the ancient Roman ruins of Djemila and Timgad, the medieval city of Algiers, and the prehistoric rock art of Tassili n’Ajjer.
In addition to its historical sites, Algeria also offers stunning natural landscapes such as the Sahara Desert, the Atlas Mountains, and the Mediterranean coastline. However, the tourism industry in Algeria is still relatively underdeveloped compared to its North African neighbours.
Cuisine of Algeria: A Fusion of Mediterranean and African Flavours
Algerian cuisine is a fusion of Mediterranean and African flavours, reflecting the country’s diverse cultural heritage. Staple foods include couscous, bread, lamb, chicken, and a variety of vegetables such as tomatoes, peppers, and olives.
Popular dishes include couscous with meat or vegetables, tagines (slow-cooked stews), merguez sausages, and pastries such as baklava and makroudh. Mint tea is a common beverage in Algeria and is often served with meals or as a gesture of hospitality.
Sports in Algeria: Football and More
Football is the most popular sport in Algeria, with the national team, known as the Desert Foxes, enjoying success on the international stage. The team has qualified for several FIFA World Cups and won the Africa Cup of Nations in 1990.
In addition to football, other popular sports in Algeria include athletics, handball, and basketball. The country has produced several successful athletes in these sports, including Olympic medalists and world champions.
Conclusion: Recap of Algeria’s unique history, culture, and opportunities for growth and development.
Algeria is a fascinating country with a rich history, diverse culture, and stunning natural landscapes. From its struggle for independence to its unique blend of Arab and Berber traditions, Algeria offers a unique experience for travellers.
While the country faces challenges in diversifying its economy and improving education and healthcare services, there are also opportunities for growth and development. With its historical and cultural attractions, Algeria has the potential to become a popular tourist destination in North Africa.
Overall, Algeria is a hidden gem that is waiting to be discovered by the world. Its unique history, culture, and natural beauty make it a truly special place that should not be overlooked.
Natural Resources of Algeria: Unlocking the Natural Wealth of Algeria: Oil, Gas, and Beyond
Natural Resources of Algeria: Unlocking the Natural Wealth of Algeria: Oil, Gas, and Beyond Algeria, a nation rich in energy reserves and minerals, stands as a powerhouse in North Africa thanks to its abundant natural resources. From its vast oil and gas fields to significant mineral deposits and renewable energy potential, Algeria is pivotal in the global resource economy. This article delves deep into the natural resources of Algeria, how they shape its economy, and what the future may hold as the country aims to diversify and strengthen its industries. Whether you’re an investor, policy maker, or just curious about resource-rich nations, this article provides critical insights into Algeria’s economic backbone. Outline What Makes Algeria Rich in Natural Resources? How Important Are Oil and Gas to the Algerian Economy? What Are Algeria’s Major Natural Gas Reserves? Where Are the Key Oil Fields Located in Algeria? What Other Mineral Resources Are Found in Algeria? Is Helium a Game-Changer for Algeria’s Resource Portfolio? How Is Algeria Approaching Renewable Energy Development? What Is the Role of the Mining Sector in Algeria? Can Algeria Diversify Its Economy Beyond Hydrocarbons? How Do Algeria’s Water and Fishing Resources Fit into the Picture? 1. What Makes Algeria Rich in Natural Resources? Algeria is one of the largest countries in Africa by land area, and much of this vast territory is rich in natural resources. From the heart of the Sahara to the coastline along the Mediterranean Sea, Algeria is home to substantial deposits of petroleum, natural gas, and valuable minerals like phosphate, zinc, and iron ore. These resources make Algeria a significant energy supplier...
Political Boundaries of Algeria: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Political boundaries are the lines that separate one political entity from another, such as countries, provinces, or districts. These boundaries play a crucial role in a country’s governance and development, as they define the jurisdiction and authority of the government. In the case of Algeria, a country located in North Africa, its political boundaries have evolved over time due to various historical, colonial, and ethnic factors. Algeria is a country with a rich history and diverse population. It is bordered by several countries including Tunisia, Libya, Niger, Mali, Mauritania, Western Sahara, Morocco, and the Mediterranean Sea. These political boundaries have shaped Algeria’s governance and development, as they determine the country’s territorial integrity and influence its relationships with neighboring countries. Summary Algeria is a country in North Africa with distinct political boundaries. The country is divided into 48 provinces, each with its own unique boundaries. Within each province, there are multiple districts that also have their own boundaries. Algeria’s historical boundaries have been shaped by various factors, including colonialism and ethnic diversity. Maintaining political boundaries in Algeria remains a challenge, but they are crucial for the country’s development. Overview of Algeria’s Provincial Boundaries Provincial boundaries in Algeria refer to the divisions within the country that are responsible for local governance and administration. There are currently 48 provinces in Algeria, each with its own capital city. These provinces are further divided into municipalities and districts. The role of provinces in Algeria’s governance and administration is significant. They are responsible for implementing national policies at the local level, providing public services such as education and healthcare, and promoting economic development in their...
Climate Zones of Algeria: Different climate regions Of Algeria
Algeria, located in North Africa, is the largest country on the continent and is known for its diverse geography and climate. The country stretches from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the Sahara Desert in the south, and its climate zones vary greatly across its vast expanse. Understanding these climate zones is crucial for various sectors, including agriculture, tourism, and conservation. Summary Algeria has five main climate zones: Saharan, Mediterranean, Highland, Steppe, and Coastal. The Saharan climate zone covers about 80% of Algeria and is characterized by extreme heat and aridity. The Mediterranean climate zone is found along the northern coast and experiences mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. The Highland climate zone is located in the Atlas Mountains and has cooler temperatures and more precipitation than other regions. The Steppe climate zone is semi-arid and covers the central plateau, while the Coastal climate zone is characterized by mild temperatures and high humidity. Climate variations in Algeria’s mountainous regions can lead to significant differences in temperature and precipitation. The impact of climate zones on Algeria’s agriculture is significant, with certain crops only able to grow in specific regions. Climate change is expected to have a significant impact on Algeria’s climate zones in the future. Despite the challenges posed by climate variability, Algeria’s diverse climate zones offer unique opportunities for tourism and economic development. Overall, Algeria’s climate zones demonstrate the country’s rich natural diversity and highlight the importance of sustainable management practices. The Saharan Climate Zone of Algeria The Saharan climate zone covers a significant portion of Algeria, particularly in the southern regions. This zone is characterized by...
Terrain and Topography of Algeria: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Algeria, the largest country in Africa, is a land of diverse and breathtaking landscapes. From the majestic Atlas Mountains to the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert, Algeria’s terrain is as varied as it is beautiful. Understanding the geography and topography of Algeria is crucial to understanding its culture, economy, and ecology. In this article, we will explore the different regions of Algeria’s terrain and delve into the unique features and significance of each. Summary Algeria’s terrain is diverse, ranging from mountains to deserts to coastal plains. The Atlas Mountains are a majestic range that runs through the country. The Saharan Plateau is a vast expanse of desert terrain that covers much of Algeria. The Tell Atlas is a chain of mountains that runs along the northern coast. The High Plateaus of Algeria offer a diverse landscape with unique flora and fauna. Overview of Algeria’s Terrain and Topography Algeria is located in North Africa, bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Tunisia and Libya to the east, Niger and Mali to the south, and Morocco and Western Sahara to the west. With an area of approximately 2.38 million square kilometers, it is the tenth-largest country in the world. The diverse terrain of Algeria can be divided into several distinct regions. The Majestic Atlas Mountains of Algeria The Atlas Mountains are a prominent feature of Algeria’s geography. Stretching across several countries in North Africa, including Morocco, Tunisia, and Algeria, they are one of the longest mountain ranges in the world. In Algeria, the Atlas Mountains cover a vast area, running from the northeastern corner of the country to its...
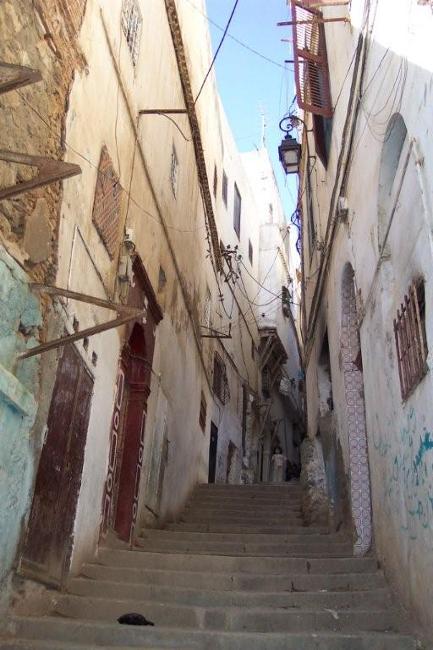
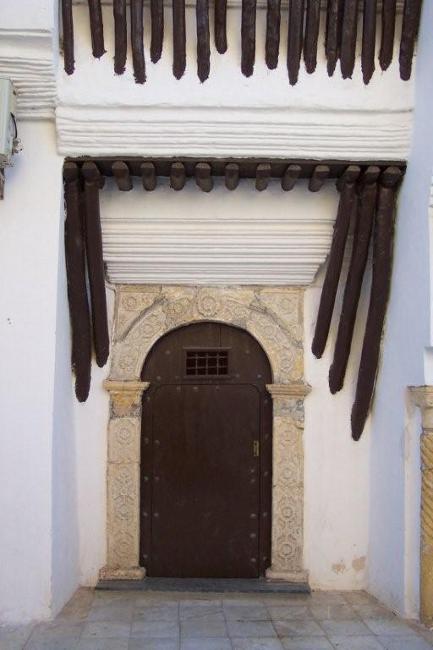
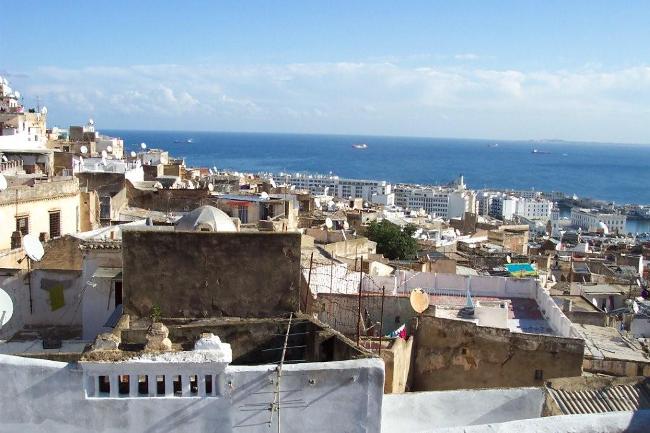
Cultural or Historical Sites of Algeria: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Algeria
Introduction Algeria, located in North Africa, is a country with a rich cultural and historical heritage. From ancient Roman ruins to iconic mosques and historic cities, Algeria offers a wealth of attractions that showcase its diverse history and cultural influences. It is important to preserve and promote Algeria’s heritage to ensure that future generations can appreciate and learn from the country’s past. The Iconic Casbah of Algiers: A UNESCO World Heritage Site One of the most iconic sites in Algeria is the Casbah of Algiers, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Casbah has a long history dating back to the 17th century and is a symbol of the city’s rich cultural heritage. It is a maze-like complex of narrow streets, traditional houses, and historic buildings. The architecture of the Casbah is a blend of different styles, including Ottoman, Moorish, and French influences. The houses are built with traditional materials such as clay and wood, and many have beautiful courtyards and intricate tile work. The layout of the Casbah reflects its defensive nature, with narrow streets and high walls that were designed to protect the inhabitants from invaders. Within the Casbah, there are several must-see attractions. One of them is the Ketchaoua Mosque, which was originally built as a mosque in the 17th century but was later converted into a cathedral during the French colonial period. Another highlight is the Dar Hassan Pacha, a beautifully restored mansion that now serves as a museum showcasing Algerian art and culture. Visitors can also explore traditional craft shops, where they can buy handmade carpets, pottery, and other local products. Discovering the...
Population Density of Algeria
Algeria, the largest country in Africa, is home to a diverse population. Understanding the population density of Algeria is crucial for sustainable development. Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured in terms of persons per square kilometer. By analyzing population density, policymakers and researchers can gain insights into various aspects of development, such as resource allocation, infrastructure planning, and environmental management. Summary Algeria has a population density of 17 people per square kilometer. Population density in Algeria has fluctuated throughout history due to factors such as migration and political instability. Factors affecting population density in Algeria include climate, natural resources, and economic opportunities. Population density varies greatly across regions in Algeria, with the highest densities in the north and coastal areas. Urban areas in Algeria have much higher population densities than rural areas. High population density in Algeria has both positive and negative impacts on the economy. Managing high population density in Algeria is a challenge due to limited resources and infrastructure. Future projections suggest that population density in Algeria will continue to increase, particularly in urban areas. Algeria’s population density is lower than many other African countries, but still presents challenges for sustainable development. Sustainable development in Algeria will require careful management of population density and its impacts on the economy and environment. Historical Overview of Population Density in Algeria Algeria’s population has experienced significant changes over time. In the early 20th century, the country had a relatively low population density due to its vast size and harsh desert climate. However, with the advent of modern medicine and improvements in...
Discovering the Hidden Gems of Algeria: A Journey Through its Rich Culture and History
Algeria, located in North Africa, is a country that is often overlooked when it comes to tourism. However, this beautiful and diverse nation is home to a wealth of hidden treasures that are waiting to be discovered. From its rich cultural heritage to its stunning natural landscapes, Algeria has something to offer every traveler. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of Algeria’s hidden gems and explore why it is important to promote and embrace these treasures. Algeria’s tourism industry has long been overshadowed by its neighboring countries such as Morocco and Tunisia. However, in recent years, there has been a growing interest in exploring the hidden gems of Algeria. This is due in part to the country’s efforts to promote its tourism industry and showcase its unique attractions. By uncovering Algeria’s hidden treasures, we not only contribute to the growth of its tourism sector but also gain a deeper understanding and appreciation for the country’s rich history, culture, and natural beauty. Key Takeaways Algeria has a rich cultural heritage that includes indigenous peoples, Islamic art and architecture, Berber kingdoms, Roman ruins, traditional crafts, vibrant music and dance, delicious cuisine, and stunning desert landscapes. Algeria’s indigenous peoples have a unique culture and history that is worth exploring and preserving. Islamic art and architecture have left a lasting impact on Algeria’s cities and landmarks, showcasing the country’s rich history and heritage. The Berber kingdoms of Algeria have a fascinating history that is still being uncovered and studied today. Algeria’s ancient cities and Roman ruins offer a glimpse into the country’s past and are a must-see for history...
Albania
Albania (Republika e Shqipërisë (republic of Albania)) Capital: Tirana (Tiranë) Population (Estimated July 2012): 3,002,859 Area: 28,748km2 or 11,100mi2 Currency: Lek Official Language: Albanian Political Information: Parliamentary Republic Official Religion: No Official Religion (but approximately 70% of the population is Muslim, 20% are Albanian Orthodox and 10% are Roman Catholic) Highest Mountain: Mount Korab (Maja e Korabit (Golem Korab)) at 2,764m or 9,068ft Largest River: River Drin GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power) (Estimated 2011): $13.3 billion (US$) or £7,980,000 million(GBP) GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP) GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States) (Estimated 2011): $24.99 billion (US$) or £14,994 million(GBP) GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $7,800 (US$) or £4,680 (GBP) Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +1:00 Counties/Provinces/States: 37 municipalities (komunat/opstine, singular – komuna/opstina); Decan/Decani, Dragash/Dragas, Ferizaj/Urosevac, Fushe Kosove/Kosovo Polje, Gjakove/Dakovica, Gjilan/Gnjilane, Gllogovc/Glogovac, Gracanice/Gracanica, Hani i Elezit/Deneral Jankovic, Istog/Istok, Junik, Kacanik/Kacanik, Kamenice/Kamenica, Kline/Klina, Kllokot/Klokot, Leposaviq/Leposavic, Lipjan/Lipljan, Malisheve/Malisevo, Mamushe/Mamusa, Mitrovice/Mitrovica, Novoberde/Novo Brdo, Obiliq/Obilic, Partesh/Partes, Peje/Pec, Podujeve/Podujevo, Prishtine/Pristina, Prizren, Rahovec/Orahovac, Ranillug/Ranilug, Shterpce/Strpce, Shtime/Stimlje, Skenderaj/Srbica, Suhareke/Suva Reka, Viti/Vitina, Vushtrri/Vucitrn, Zubin Potok, Zvecan/Zvecan Leaders: President Bujar Nishani; Prime Minister Edi Rama Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica, Albania, located in Southeastern Europe, is a country with a rich history and vibrant culture. It is bordered by Montenegro to...





























