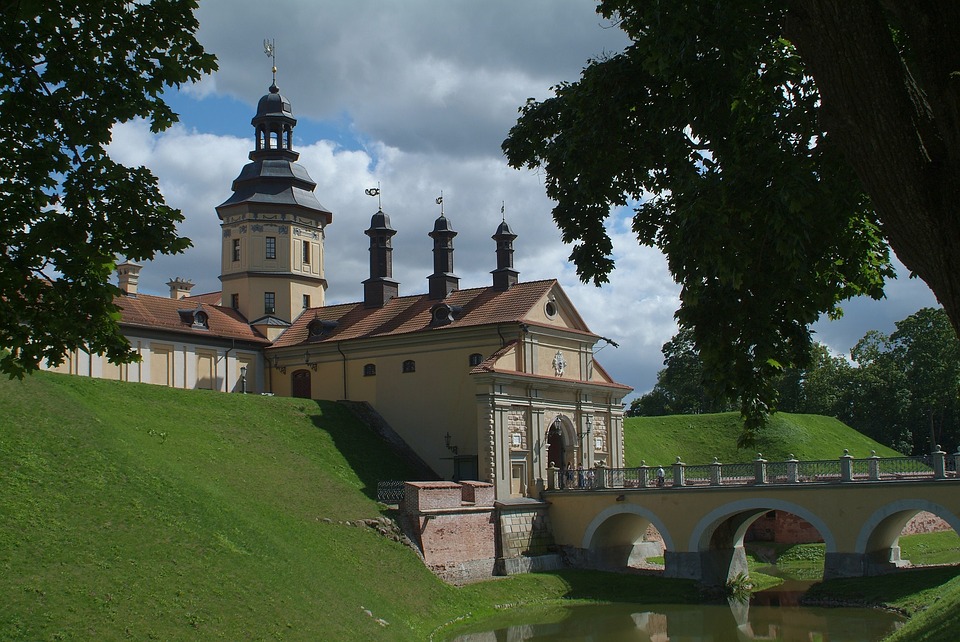
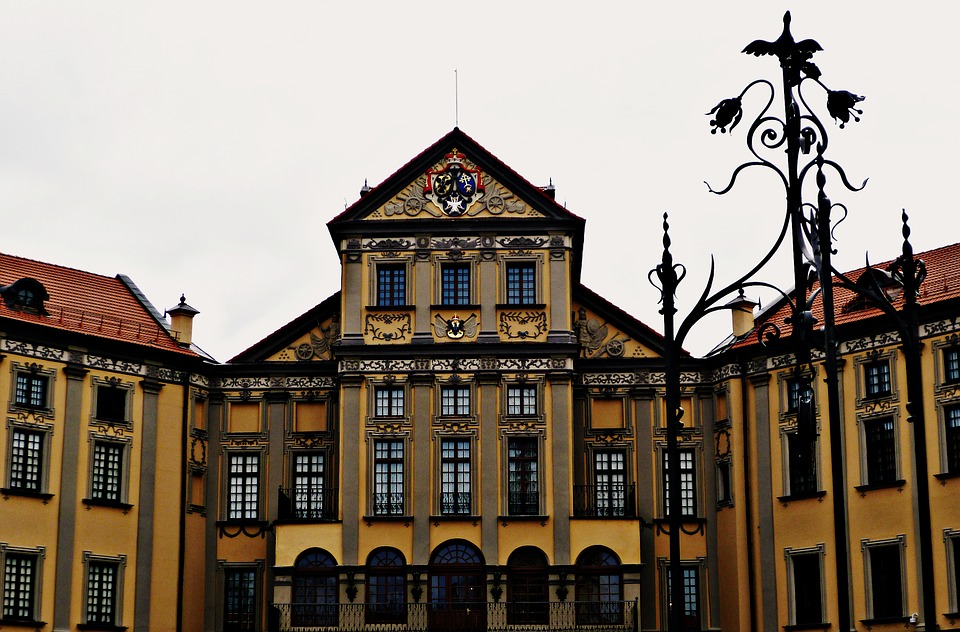
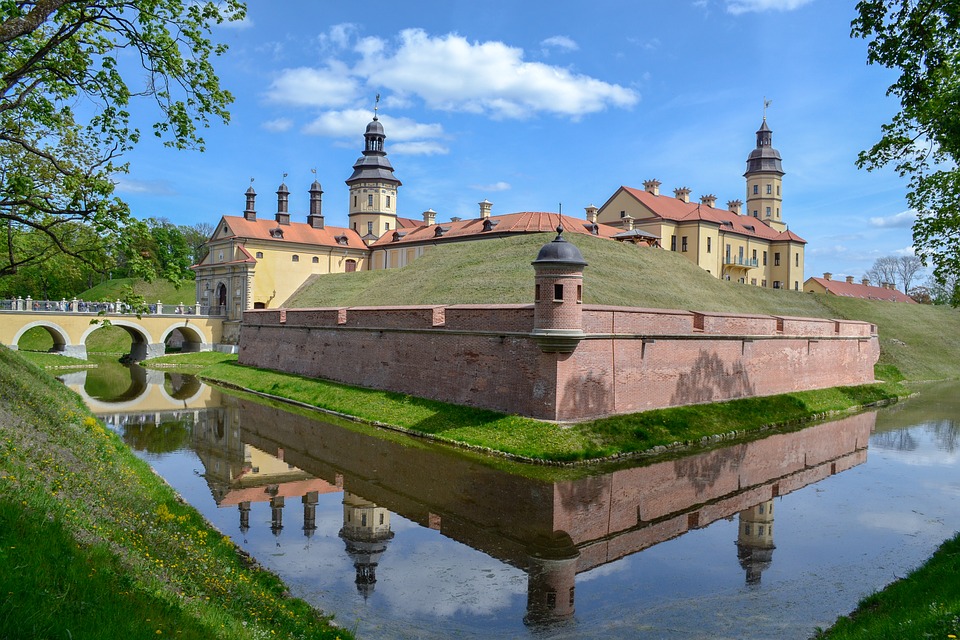
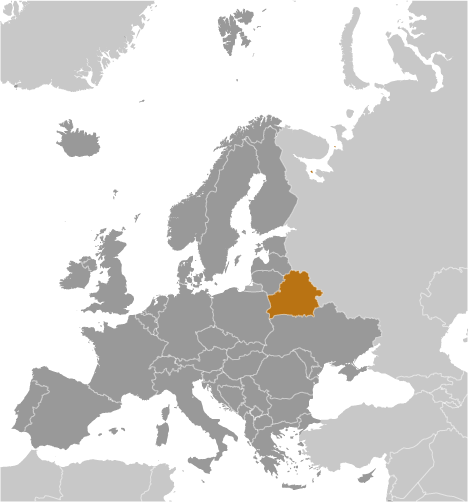
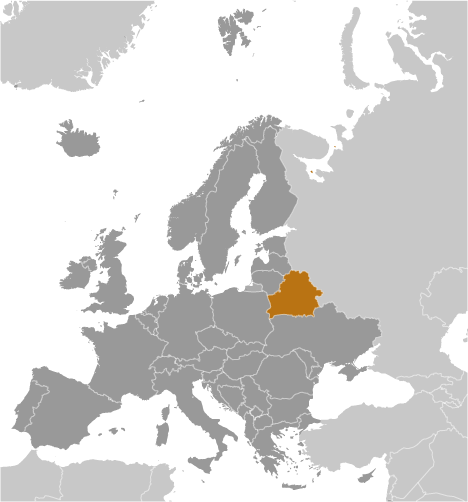
Belarus
(Respublika Belarus (Republic of Belarus))
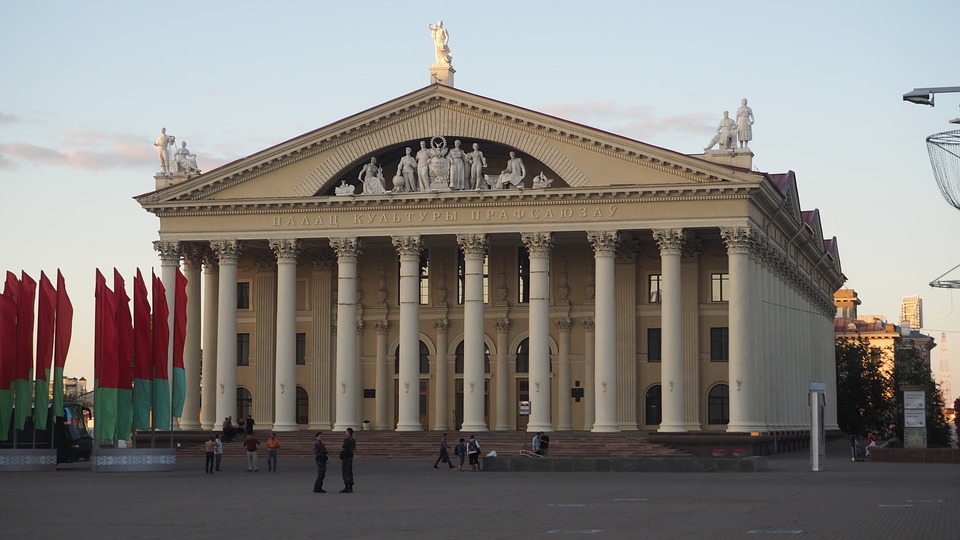
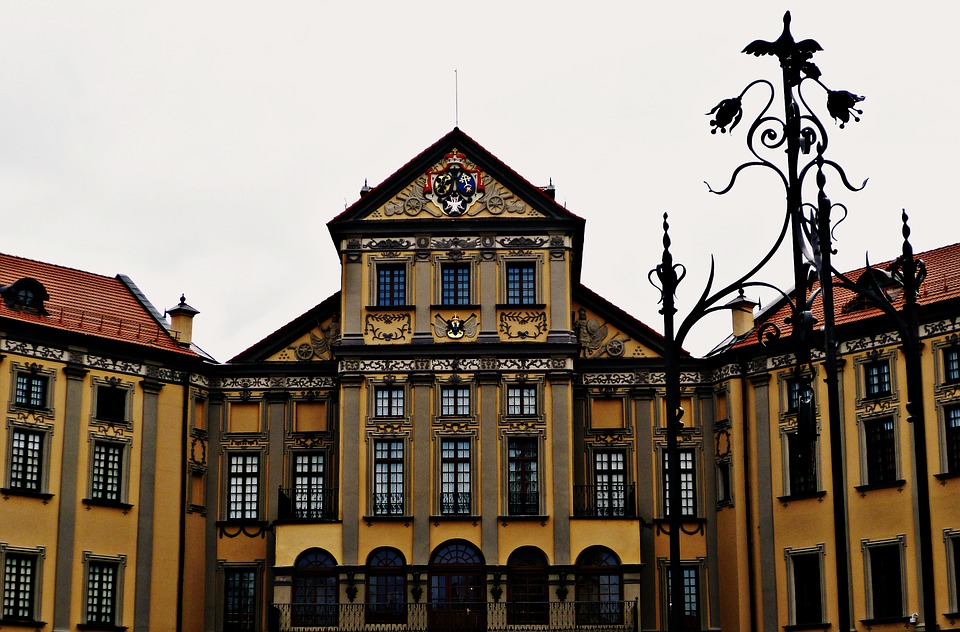
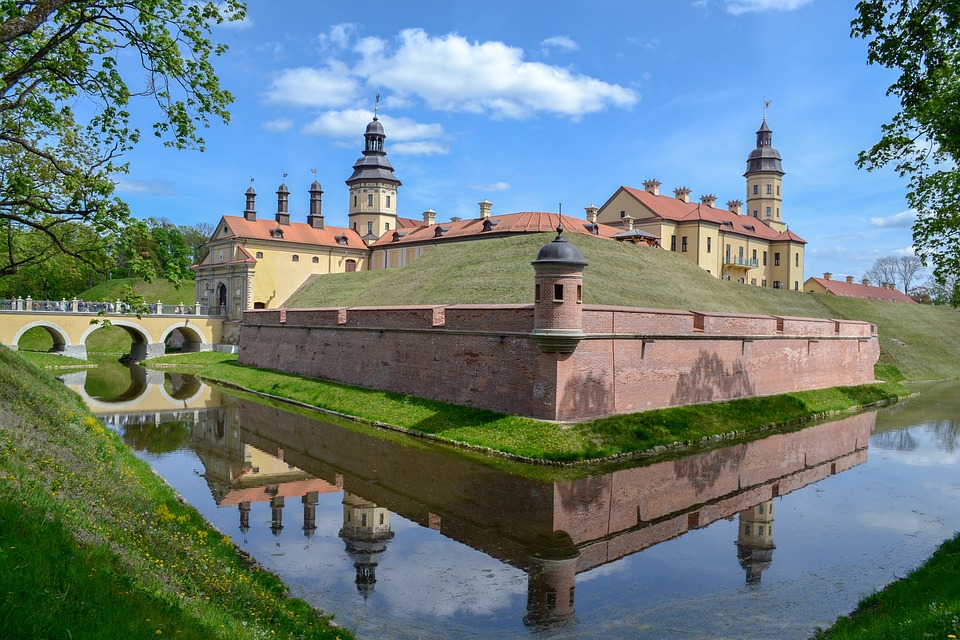

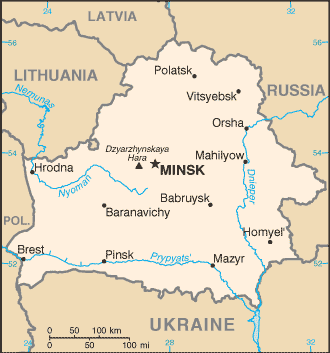




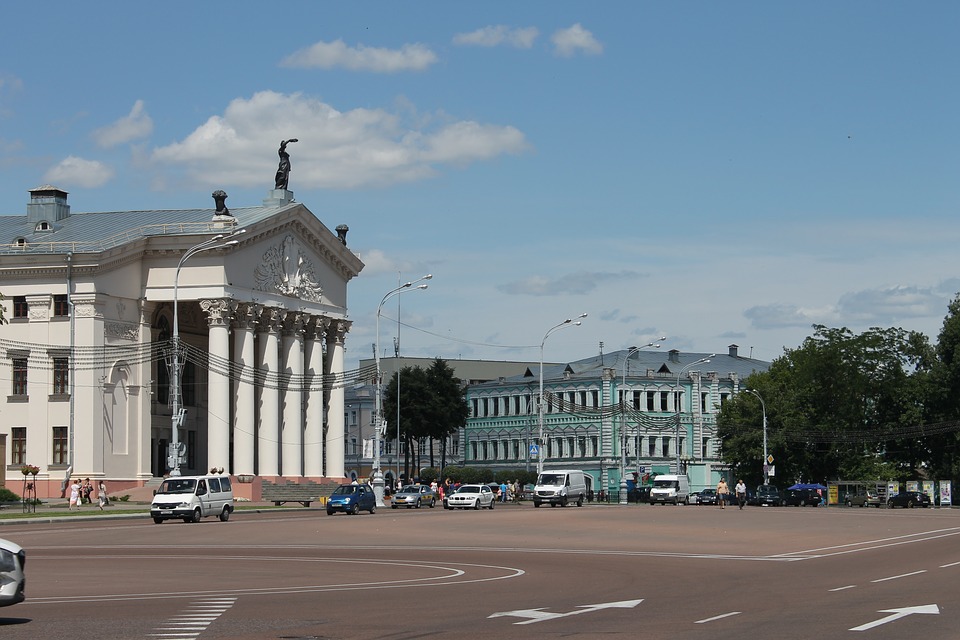
Capital of Belarus : Minsk
Population (Estimated July 2012): 9,542,883
Area: 207,595km2 or 80,153mi2
Currency: Belarusian rubel (or ruble) (Br)
Official Language: Belarusian; Russian
Political Information: Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 80% of the population are Eastern Orthodox and 20% have other religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Dzyarzhynskaya Hara at 346m or 1,135ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $57.7 billion (US$) or £34.62 billion (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $141.2 billion (US$) or £84.72 billion (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $14,900 (US$) or £8,940 (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +3:00
Provinces (Voblastsi): Brest, Homyel’ (Gomel), Hrodna (Grodno), Mahilyow (Mogilev), Minsk, Vitsyebsk (Vitebsk)
Municipality (Horad): Horad Minsk (Minsk City)
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica,
Belarus, officially known as the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country located in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. The capital and largest city of Belarus is Minsk.
Belarus has a rich history that dates back to ancient times. It was once part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and later became part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. In the 18th century, it was annexed by the Russian Empire and remained under Russian rule until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991.
The culture of Belarus is a unique blend of Eastern Slavic traditions and influences from neighbouring countries. The country is known for its rich folklore, traditional music and dance, and vibrant arts scene. Belarusian cuisine is also a significant part of the culture, with dishes such as draniki (potato pancakes) and machanka (pork stew) being popular.
Political System of Belarus: President, Parliament and Judiciary
Belarus has a presidential system of government, with the President serving as both the head of state and head of government. The President is elected by popular vote for a term of five years and has significant powers, including the ability to appoint and dismiss government officials, veto legislation, and dissolve parliament.
The Parliament of Belarus, known as the National Assembly, consists of two chambers – the House of Representatives and the Council of the Republic. The House of Representatives has 110 members who are elected by popular vote for a term of four years. The Council of the Republic has 64 members who are elected by local councils for a term of four years.
The judiciary in Belarus is independent but has been criticized for lacking impartiality. The Supreme Court is the highest judicial authority in the country and is responsible for ensuring the uniform application of the law. The Constitutional Court is responsible for reviewing the constitutionality of laws and other legal acts.
Economy of Belarus: Agriculture, Industry and Services
The economy of Belarus is a mixed economy with a strong emphasis on state ownership. The main sectors of the Belarusian economy are agriculture, industry, and services.
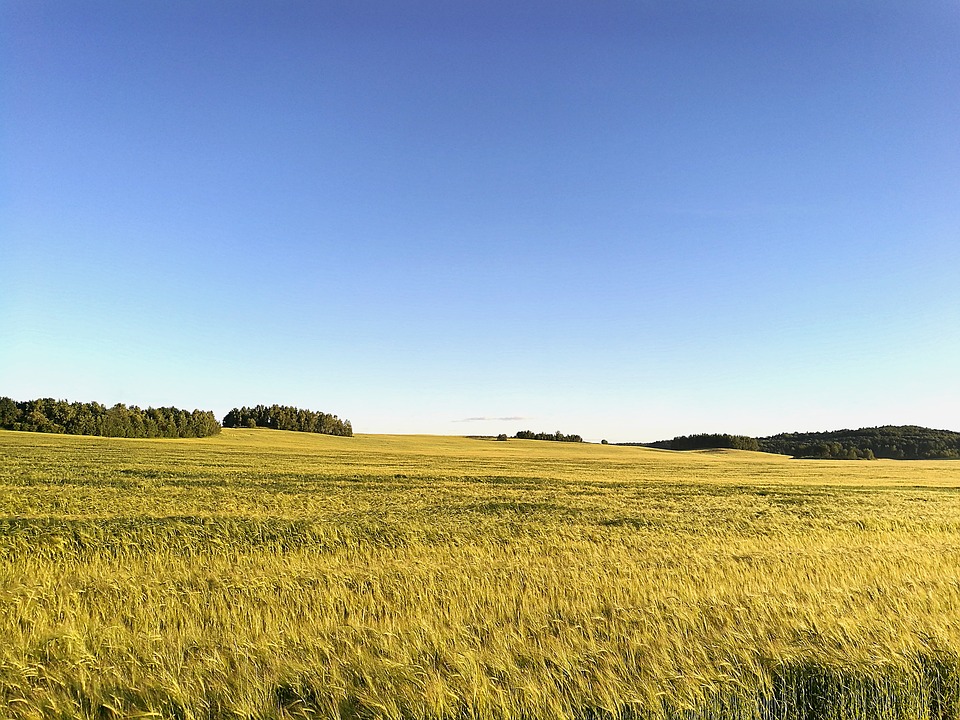
Agriculture plays a significant role in the Belarusian economy, with the country being known as the “breadbasket of Europe.” The main agricultural products include potatoes, wheat, barley, and flax. Belarus also has a strong dairy industry and is one of the largest exporters of dairy products in the world.
Industry is another important sector of the Belarusian economy, with manufacturing being a key driver of economic growth. The country has a strong industrial base, with sectors such as machinery and equipment manufacturing, chemical production, and food processing being prominent. Belarus is also known for its production of tractors and trucks.
The services sector in Belarus is relatively small compared to agriculture and industry but is growing rapidly. The country has seen an increase in tourism in recent years, which has led to the development of hotels, restaurants, and other tourism-related services. The IT sector is also growing rapidly, with many international companies outsourcing their IT services to Belarus.
Despite its economic potential, Belarus faces several challenges in terms of economic development. The country has a high level of state control over the economy, which has led to inefficiencies and a lack of competition. Additionally, Belarus has struggled with inflation and a lack of foreign investment. However, there are also opportunities for economic growth, such as increased trade with neighboring countries and further development of the IT sector.
Education in Belarus: Schools, Universities and Vocational Training
Education in Belarus is compulsory from the age of six to 17. The education system is divided into several levels, including preschool education, primary education, secondary education, and higher education.
Preschool education is available for children aged three to six and is not compulsory. It is provided in kindergartens and focuses on the social, emotional, and cognitive development of children.
Primary education in Belarus lasts for four years and is compulsory. It provides a basic education in subjects such as mathematics, science, language, and physical education.
Secondary education in Belarus is divided into two stages – basic secondary education and complete secondary education. Basic secondary education lasts for five years and is followed by an examination. Complete secondary education lasts for two years and prepares students for higher education or vocational training.
Higher education in Belarus is provided by universities, institutes, and academies. There are several universities in the country that offer a wide range of courses in various fields of study. The most prestigious university in Belarus is the Belarusian State University, which is located in Minsk.
Vocational training is also available in Belarus and provides practical skills and knowledge for specific occupations. Vocational training can be obtained through vocational schools or through apprenticeships.
Healthcare System in Belarus: Hospitals, Clinics and Medical Services
The healthcare system in Belarus is a mix of public and private healthcare providers. The government provides free healthcare to all citizens, with the majority of healthcare services being provided by state-owned hospitals and clinics.
There are several types of hospitals in Belarus, including general hospitals, specialized hospitals, and regional hospitals. General hospitals provide a wide range of medical services, including emergency care, surgery, and maternity care. Specialized hospitals focus on specific areas of medicine, such as cardiology or oncology. Regional hospitals provide healthcare services to specific regions of the country.
In addition to hospitals, there are also clinics and medical centers that provide outpatient care. These clinics offer a range of services, including primary care, specialist consultations, and diagnostic tests.
The quality of healthcare in Belarus is generally good, with well-trained medical professionals and modern facilities. However, there are some challenges facing the healthcare system, including a lack of funding and outdated infrastructure. The government is working to improve the healthcare system by investing in new medical equipment and facilities.
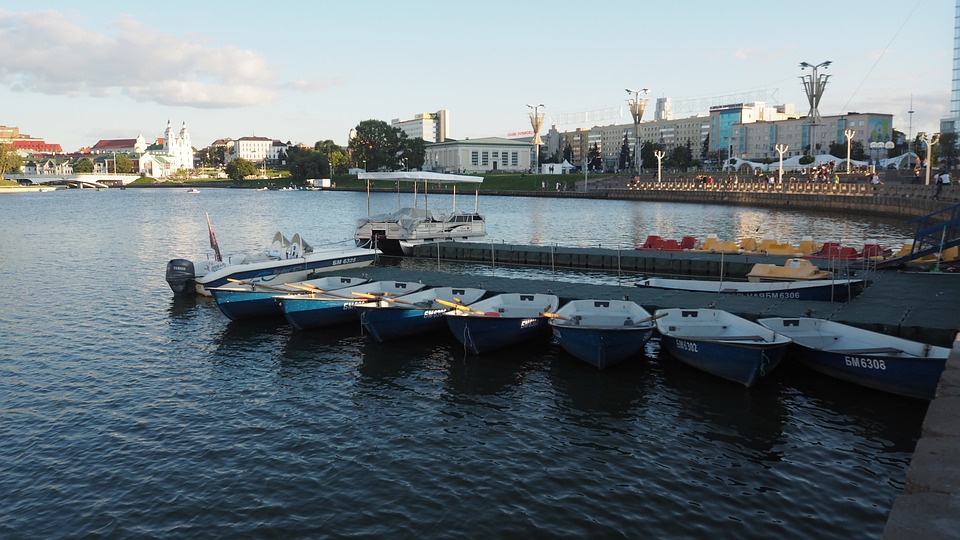
Tourism in Belarus: Places to Visit, Things to Do and Accommodation
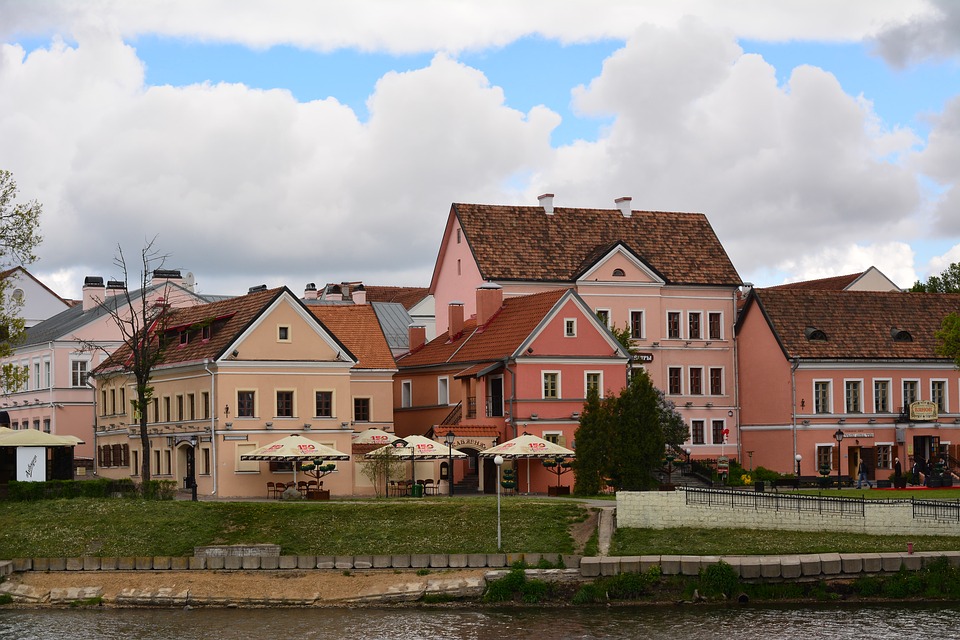
Belarus is a country with a rich cultural heritage and natural beauty, making it an attractive destination for tourists. There are several places to visit in Belarus, including historical sites, national parks, and cultural attractions.
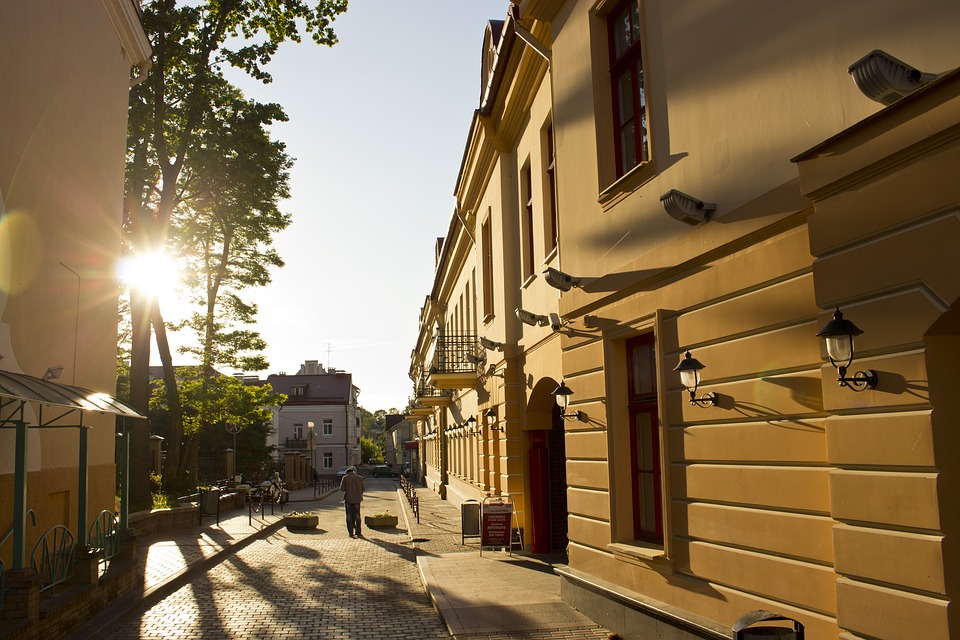
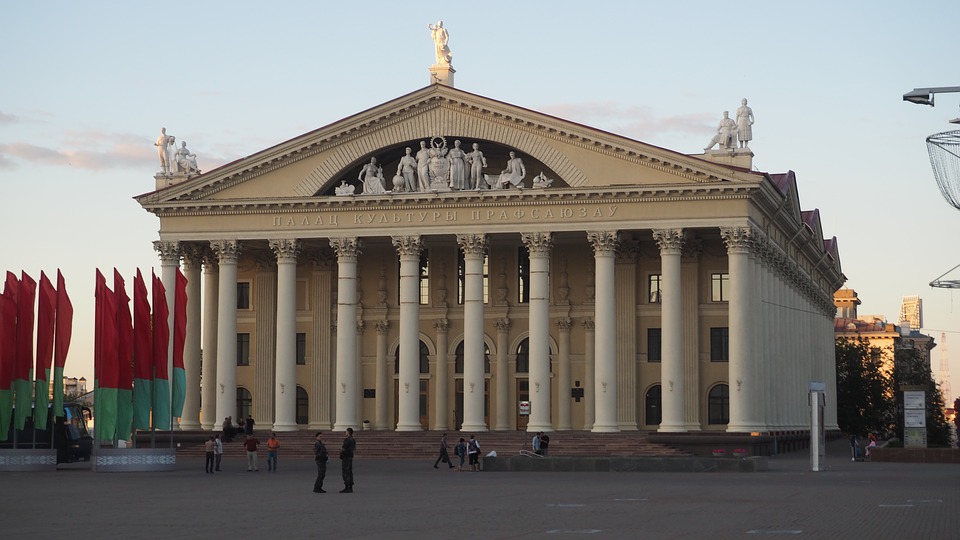
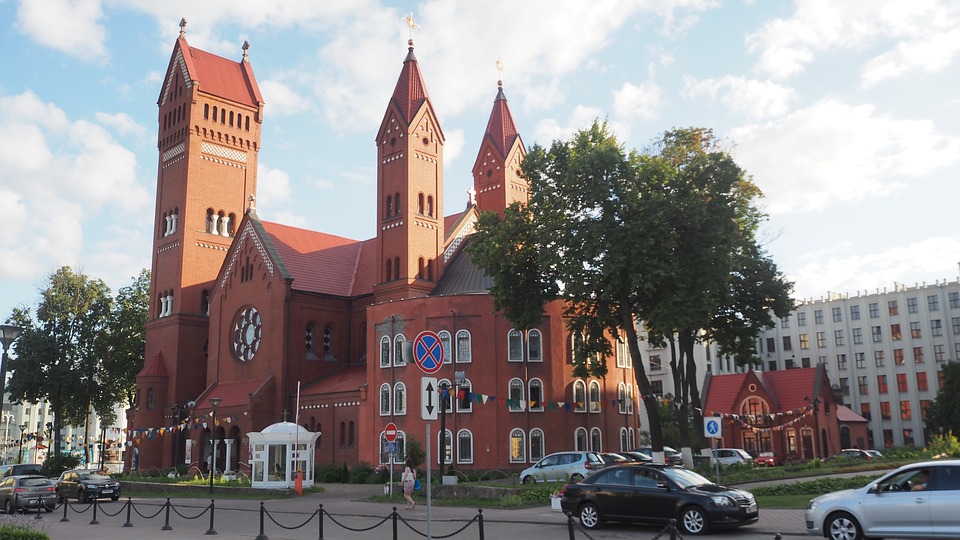
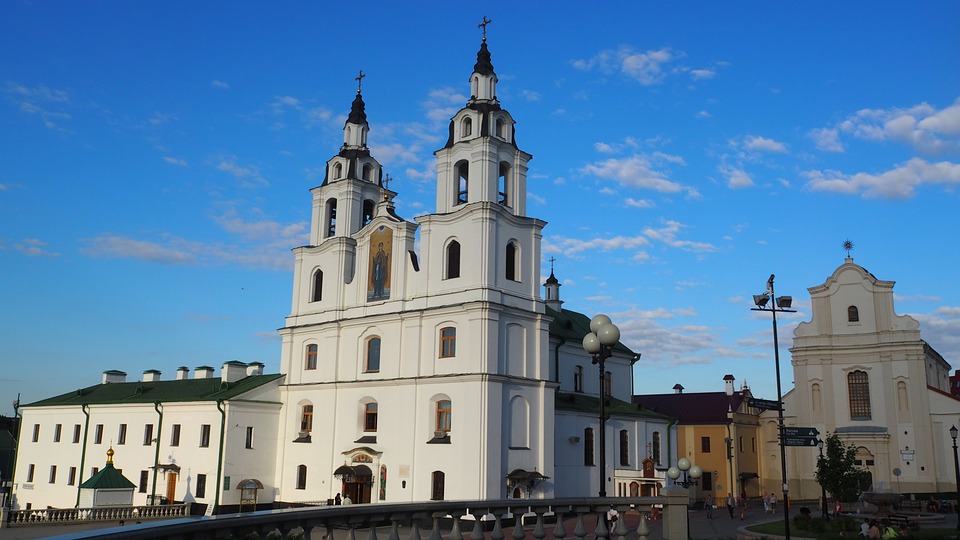
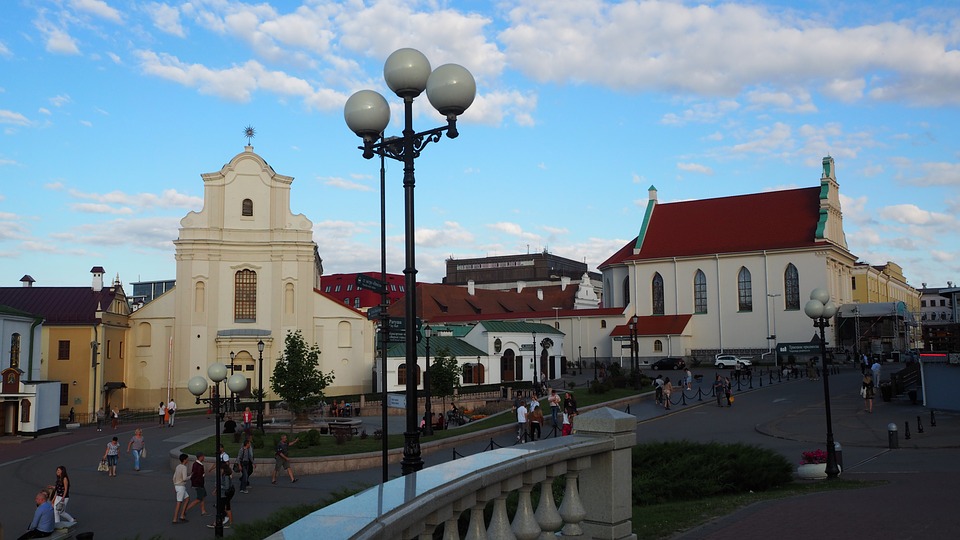
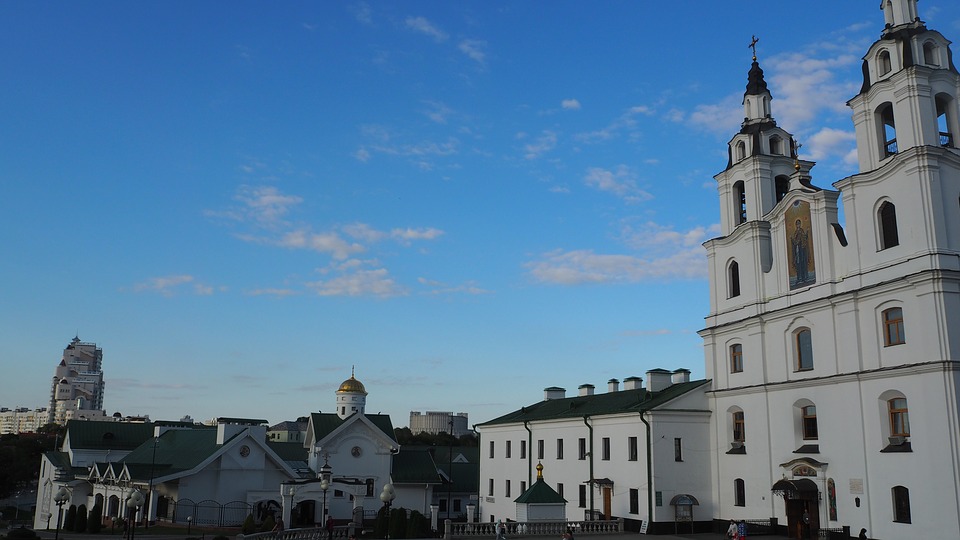
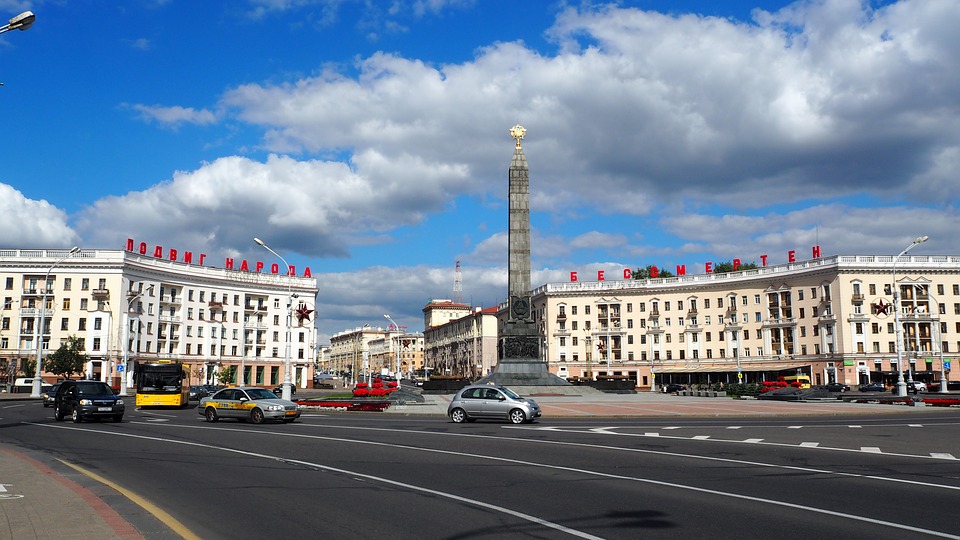
One of the most popular tourist destinations in Belarus is the capital city of Minsk. Minsk is known for its beautiful architecture, including Independence Square and the Church of Saints Simon and Helena. The city also has several museums, including the National Art Museum and the Museum of the Great Patriotic War.
Another popular tourist destination in Belarus is the Belovezhskaya Pushcha National Park. This national park is one of the last and largest remaining parts of the primaeval forest that once covered much of Europe. It is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including European bison.
Accommodation options in Belarus range from luxury hotels to budget guesthouses. In Minsk, there are several international hotel chains that offer comfortable accommodations for tourists. In rural areas, there are also guesthouses and farm stays that provide a more authentic experience.
Transport in Belarus: Roads, Railways and Airports
Belarus has a well-developed transport system that includes roads, railways, and airports. The country has an extensive network of roads that connect major cities and towns. The quality of roads in Belarus is generally good, with well-maintained highways and modern infrastructure.
The railway system in Belarus is also well-developed and provides an efficient mode of transportation. The country has an extensive network of railways that connects major cities and towns. The railway system is operated by the state-owned company Belarusian Railways.
Belarus has several international airports, including Minsk National Airport, which is the main gateway to the country. The airport offers flights to several destinations in Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. There are also several regional airports in Belarus that offer domestic and international flights.
Society in Belarus: Demographics, Languages and Religion
Belarus has a population of approximately 9.5 million people. The majority of the population is ethnic Belarusian, with minorities including Russians, Poles, and Ukrainians. The official language of Belarus is Belarusian, but Russian is also widely spoken.
The majority of the population in Belarus is Christian, with the majority belonging to the Eastern Orthodox Church. There are also significant Catholic and Protestant communities in the country. Religious freedom is guaranteed by the constitution of Belarus.
Sports in Belarus: Football, Hockey and Other Popular Games
Sports play an important role in Belarusian culture, with football and ice hockey being the most popular sports in the country. The national football team has had some success in international competitions, including qualifying for the UEFA European Championship in 2016.
Ice hockey is also a popular sport in Belarus, with the national ice hockey team competing in international tournaments such as the IIHF World Championship. The country has produced several talented ice hockey players who have gone on to play in the National Hockey League (NHL) in North America.
In addition to football and ice hockey, other popular sports in Belarus include basketball, volleyball, and athletics. The country has produced several successful athletes who have won medals at international competitions such as the Olympic Games and World Championships.
Future of Belarus: Challenges, Opportunities and Prospects
Belarus faces several challenges in the future, including economic development, political reform, and social issues. The country’s economy relies heavily on state-owned enterprises and lacks diversification. There is a need for economic reforms to attract foreign investment and promote private sector growth.
Politically, Belarus has been criticized for its lack of democracy and human rights abuses. There is a need for political reform to ensure greater transparency, accountability, and respect for human rights.
Despite these challenges, Belarus also has several opportunities for growth and development. The country has a well-educated workforce and a strong industrial base. There are opportunities for increased trade with neighbouring countries and further development of the IT sector.
In conclusion, Belarus is a country with a rich history, vibrant culture, and diverse economy. It faces several challenges in terms of economic development, political reform, and social issues. However, there are also opportunities for growth and development in the future. With the right policies and investments, Belarus has the potential to become a prosperous and modern country.
Population Density of Belarus
Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured as the number of individuals per square kilometer. It is an important indicator of the distribution of population within a country and provides insights into the social, economic, and environmental aspects of a region. Studying population density in Belarus is crucial for understanding the country’s demographic patterns, urbanization trends, and their impact on economic development and environmental sustainability. Belarus, officially known as the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country located in Eastern Europe. It shares borders with Russia to the east, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. With a total land area of approximately 207,600 square kilometers, Belarus is home to a diverse population that has experienced significant changes in population density over the years. Summary Belarus has a population density of 46 people per square kilometre. Population density in Belarus has fluctuated throughout history due to factors such as war and migration. The highest population densities in Belarus are found in the central and eastern regions. Factors influencing population density in Belarus include economic opportunities and access to resources. Urbanization has led to increased population density in Belarus, while rural-urban migration has had a mixed impact. Historical Trends in Belarusian Population Density In the early 20th century, Belarus had a relatively low population density compared to other European countries. This was primarily due to its rural nature and agricultural economy. The population density increased during Soviet rule as industrialization efforts led to urbanization and migration from rural areas to cities. The population density...
Terrain and Topography of Belarus: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Belarus, located in Eastern Europe, is a landlocked country known for its rich history, vibrant culture, and diverse natural landscapes. Understanding the terrain and topography of Belarus is crucial in comprehending the country’s unique characteristics and its impact on various aspects of life, including climate, agriculture, and development. From the flatlands of the Great European Plain to the hilly regions of the Grodno Upland and the marshy Polesian Lowland, Belarus offers a wide range of landscapes that contribute to its beauty and diversity. Summary Belarus is a country with diverse terrain and topography. The Great European Plain dominates the landscape of Belarus. The Belarusian Ridge is the highest point in the country. The Polesian Lowland is a marshy region in southern Belarus. The Belarusian Lake District is a region of glacial lakes in the north. The Flatlands of Belarus: The Great European Plain The Great European Plain is a vast lowland that stretches across several countries in Eastern Europe, including Belarus. This flatland covers a significant portion of Belarus’ territory and has a profound influence on the country’s climate and agriculture. The plain is characterized by fertile soil, making it ideal for agricultural activities such as farming and livestock rearing. The flatlands are home to several cities and landmarks that showcase Belarus’ rich history and culture. Minsk, the capital city, is situated in the central part of the country and serves as a hub for economic, political, and cultural activities. Other notable cities in the flatlands include Brest, Gomel, and Mogilev. These cities are known for their architectural beauty, historical sites, and vibrant cultural scenes. The Belarusian Ridge: The...
Political Boundaries of Belarus: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Belarus, officially known as the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country located in Eastern Europe. It shares its borders with five countries: Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, Lithuania to the northwest, and Latvia to the north. Understanding the political boundaries of Belarus is crucial for effective governance and administration of the country. Political boundaries define the territorial limits of a country and play a significant role in determining its governance structure. They establish the jurisdiction of different levels of government and help in the allocation of resources and provision of services. By understanding the political boundaries of Belarus, policymakers can make informed decisions about resource allocation, infrastructure development, and service delivery. Summary Belarus is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe with political boundaries that have evolved over time. The country is divided into six administrative regions called provinces, each with its own capital city. Belarus has 118 districts, which are important for local governance and economic development. The historical boundaries of Belarus have been shaped by wars, treaties, and political agreements. The future of Belarus political boundaries is uncertain, with challenges related to economic development, ethnic diversity, and international relations. Administrative Divisions of Belarus Belarus is divided into six administrative divisions: provinces, districts, cities with special status, urban districts, townships, and rural councils. The administrative divisions are hierarchical in nature, with each level having its own set of responsibilities and powers. The provinces, also known as oblasts, are the highest level of administrative division in Belarus. There are six provinces in total: Brest, Gomel, Grodno, Minsk, Mogilev, and Vitebsk....
Climate Zones of Belarus: Different climate regions Of Belarus
Belarus, located in Eastern Europe, is a landlocked country with a diverse geography and climate. It is bordered by Russia to the east, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. The country’s climate is influenced by its continental location and proximity to the Baltic Sea. Understanding Belarus’ climate zones is important for various reasons, including agriculture, tourism, and infrastructure planning. Summary Belarus has a diverse range of climate zones, including continental, oceanic, transitional, mountainous, boreal forest, steppe, and arid regions. The continental climate region is characterized by cold winters and warm summers, with significant temperature fluctuations throughout the year. The oceanic climate region experiences mild temperatures and high levels of precipitation throughout the year. The transitional climate region has a mix of continental and oceanic influences, resulting in moderate temperatures and moderate precipitation levels. Climate change is having a significant impact on Belarus’ climate zones, including changes in temperature, precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events. The continental climate region of Belarus The continental climate region covers a large part of Belarus and is characterized by cold winters and warm summers. The temperature range in this zone can be quite extreme, with temperatures dropping below freezing in winter and reaching highs of 30°C (86°F) or more in summer. Precipitation in this zone is relatively evenly distributed throughout the year, with slightly higher rainfall in summer. Cities or regions in this climate zone include Minsk, the capital city of Belarus, as well as Brest, Gomel, and Mogilev. These cities experience cold winters with average temperatures ranging from -4°C (24°F) to -8°C (18°F) and...
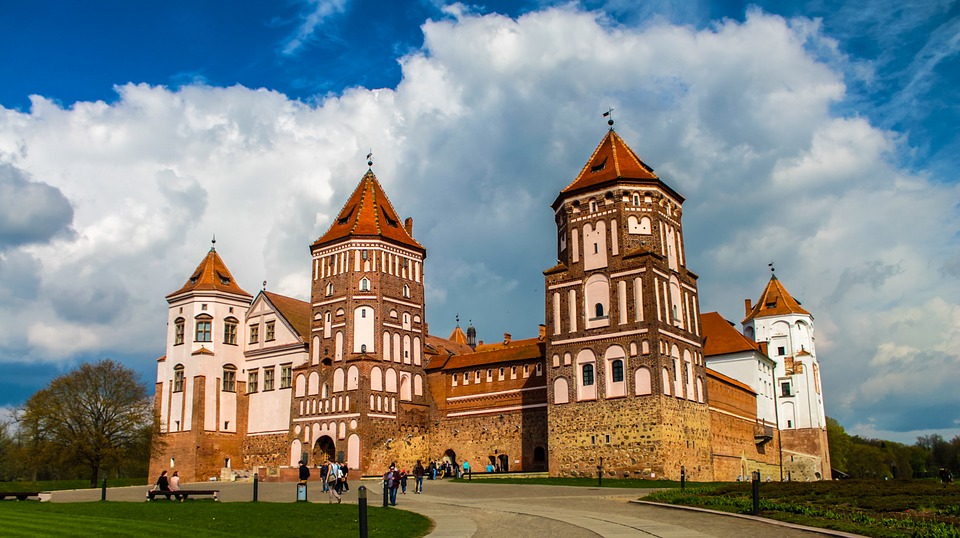
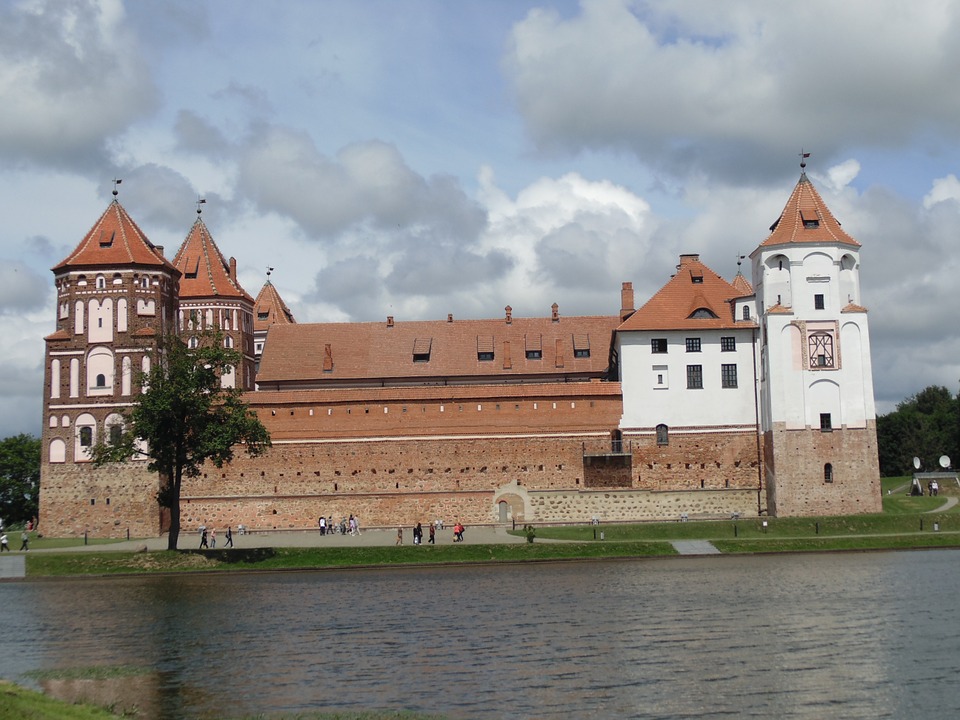
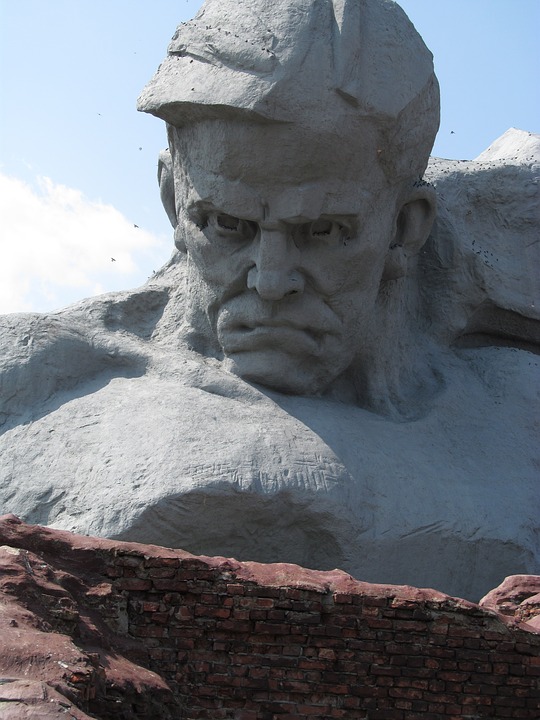
Cultural or Historical Sites of Belarus: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Belarus
Belarus, located in Eastern Europe, is a country rich in culture and history. Over the centuries, it has been influenced by various civilizations and empires, resulting in a unique blend of traditions and customs. From its medieval castles to its vibrant art scene, Belarusian culture is a testament to the resilience and creativity of its people. Preserving this cultural heritage is of utmost importance, as it allows future generations to connect with their roots and understand the country’s rich history. Summary Belarusian National Arts Museum showcases the country’s rich artistic heritage. Brest Fortress stands as a symbol of Belarusian resistance against Nazi invasion. Mir Castle Complex is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a stunning example of medieval architecture. Nesvizh Castle was once the residence of the powerful Radziwill family and is now a popular tourist attraction. The Great Synagogue of Slonim is a testament to Belarusian Jewish heritage and a reminder of the country’s diverse cultural history. Belarusian National Arts Museum: A Hub of Art and Culture The Belarusian National Arts Museum, located in Minsk, is a hub of art and culture in the country. Established in 1939, the museum houses an extensive collection of Belarusian and international art, spanning from the 12th century to the present day. Its collections include paintings, sculptures, graphic art, decorative art, and folk art. One of the highlights of the museum is its collection of Belarusian icons, which provides a glimpse into the country’s religious and artistic traditions. These icons are not only beautiful works of art but also important religious artifacts that have played a significant role in Belarusian culture. Another...
Discover the Natural Resources of Belarus: From Water to Mineral Resources In Belarus
Discover the Natural Resources of Belarus: From Water to Mineral Resources In Belarus Belarus, a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, holds a surprisingly diverse array of natural resources, from rich peat deposits and limestone to essential water resources and mineral resources. This article delves into the natural resources of Belarus, explaining what they are, where they’re found, how they’re used, and why they matter for both the Belarusian economy and its geopolitical significance. Whether you’re interested in the energy sector, environmental topics, or economic development, this is an essential read for understanding how Belarus leverages its natural wealth and what challenges lie ahead. Article Outline 1. What Natural Resources Are Found in Belarus? 2. Where Are the Major Peat Deposits in Belarus Located? 3. How Do Belarus’ Water Resources Influence Its Economy? 4. What Role Do Mineral Deposits Play in Belarus’ Industry? 5. How Important Is Natural Gas to Belarus’ Energy Sector? 6. What Are the Key Environmental Concerns Tied to Resource Extraction? 7. What is the Role of Timber and the Forestry Sector in Belarus? 8. How Does Belarus Balance Resource Use and Environmental Protection? 9. What Is the Import-Export Balance of Belarus in Natural Resources? 10. How Do Belarus’ Natural Resources Affect Its Relations with Neighbours? 1. What Natural Resources Are Found in Belarus? The Republic of Belarus may not be the first country that comes to mind when discussing resource-rich nations, but it possesses a variety of natural resources that support key economic sectors. These include peat, potash, limestone, timber, and significant water resources such as rivers and wetlands. Despite being landlocked, Belarus has leveraged...
Discovering the Hidden Gems of Belarus: A Journey Through Eastern Europe’s Best-Kept Secret
Belarus, a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, often remains a mystery to many travelers. Tucked away between Russia, Ukraine, Poland, Lithuania, and Latvia, Belarus offers a unique blend of cultures, history, and natural beauty that is waiting to be discovered. From its vibrant music and dance scene to its stunning landscapes and delicious cuisine, Belarus has something to offer every type of traveler. Despite its relatively small size, Belarus boasts a rich and diverse culture that is influenced by its neighboring countries. The country’s unique blend of Eastern and Western influences can be seen in its architecture, customs, and traditions. Whether you’re exploring the bustling streets of Minsk or venturing into the countryside, you’ll be captivated by the warmth and hospitality of the Belarusian people. Key Takeaways Belarusian culture is a fascinating blend of Eastern and Western influences. Belarus boasts stunning natural landscapes, including national parks and pristine lakes. Belarusian cuisine offers a delicious journey through local flavors, including traditional dishes like draniki and machanka. Belarus has a rich and complex history, with influences from neighboring countries and empires. Minsk, the capital of Belarus, is a vibrant city with a unique blend of Soviet-era architecture and modern culture. Belarusian Culture: A Fascinating Blend of East and West Belarusian culture is a fascinating blend of Eastern and Western influences. Throughout its history, the country has been influenced by neighboring countries such as Russia, Poland, Lithuania, and Ukraine. This cultural fusion can be seen in everything from the architecture to the cuisine. One of the most distinctive aspects of Belarusian culture is its traditional customs and celebrations. From Kupalle, a midsummer...