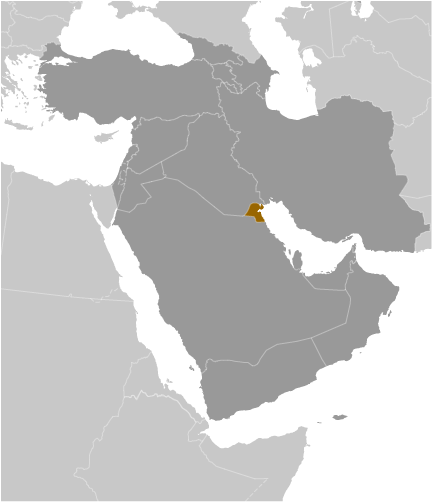
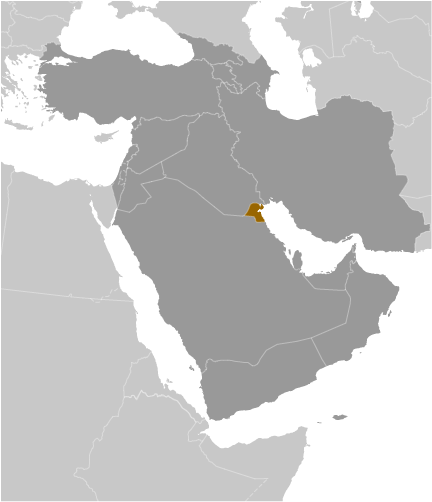
Kuwait
(Dawlat al-Kuwayt (State of Kuwait))
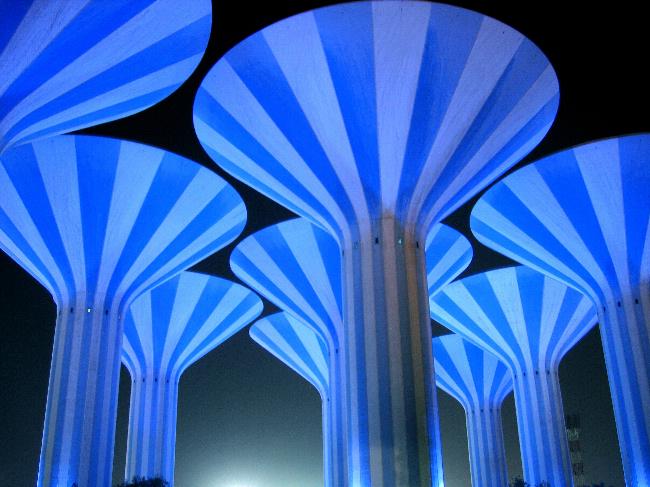

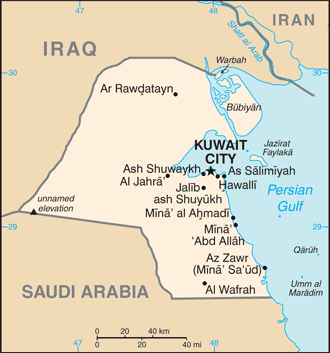




Capital: Kuwait (City)
Population (Estimated July 2012): 2,646,314
Area: 17,818 km2 or 6,880 mi2
Currency: Kuwaiti Dinar (KD)
Official Language: Arabic
Political Information: Hereditary Constitutional Monarchy
Official Religion: Islam (approximately 85% of the population are Muslim and 15% have other religious beliefs)
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $171.1 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $149.8 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $40,700 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +3:00
Counties/Provinces/States: 6 governorates (muhafazat, singular – muhafazah); Al Ahmadi, Al ‘Asimah, Al Farwaniyah, Al Jahra’, Hawalli, Mubarak al Kabir
Leaders: Amir SABAH al-Ahmad al-Jabir al-Sabah (since 29 January 2006); Crown Prince NAWAF al-Ahmad al-Jabir al-Sabah (born 25 June 1937), with Prime Minister JABIR AL-MUBARAK al-Hamad al-Sabah (since 30 November 2011); First Deputy Prime Minister NASIR al-Sabah al-Ahmad al-Sabah (since 12 December 2017); Deputy Prime Ministers SABAH al-KHALD al-Sabah (since 4 August 2013), KHALD al-Jarrah al-Sabah (since December 2016), Anas al-SALEH (since 2015)
Additional: Gained independence from the UK on the 19th of June 1961.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Kuwait
Kuwait, officially known as the State of Kuwait, is a small country situated in the Middle East, bordering Iraq and Saudi Arabia. With a population of approximately 4.5 million people, Kuwait is renowned for its rich history, vibrant culture, and prosperous economy. The capital city, Kuwait City, is a bustling metropolis that functions as the political, cultural, and economic centre of the country.
Kuwait is also notable for its picturesque coastline along the Arabian Gulf, which boasts beautiful beaches and clear blue waters. Kuwait experiences a desert climate with extremely hot summers and mild winters, making it a favoured destination for tourists seeking warm weather and sunshine. The country is home to a diverse population, comprising Kuwaiti nationals and expatriates from various parts of the world.
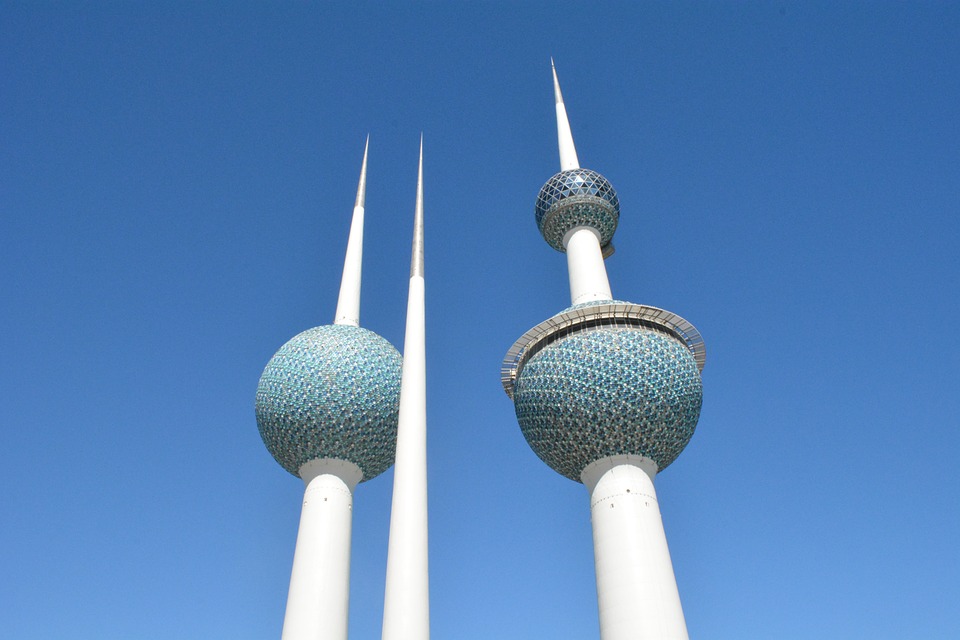
Arabic is the official language of Kuwait, and Islam is the predominant religion, with mosques being a common sight throughout the landscape. The country possesses a rich heritage and is known for its traditional architecture, including the iconic Kuwait Towers and the Grand Mosque. With its unique combination of modernity and tradition, Kuwait offers visitors an intriguing glimpse into Middle Eastern culture and history.
Summary
- Kuwait is a small but wealthy country located in the Middle East, known for its oil reserves and modern infrastructure.
- The history and culture of Kuwait is influenced by its Bedouin roots, Islamic traditions, and the impact of British colonialism.
- Kuwait’s economy is heavily reliant on oil exports, but the government is working to diversify into other sectors such as finance and tourism.
- The education and healthcare systems in Kuwait are well-developed, with free education and healthcare services provided to citizens.
- Tourist attractions in Kuwait include the Kuwait Towers, Grand Mosque, and the Souq Mubarakiya, offering a mix of modern and traditional experiences for visitors.
- Kuwaiti cuisine is a blend of Arabian, Persian, Indian, and Mediterranean influences, with dishes like machboos, harees, and various types of kebabs.
- Future developments in Kuwait include infrastructure projects and efforts to reduce reliance on oil, while challenges include environmental sustainability and political stability.
History and Culture of Kuwait
Founding and Early Development
In the 18th century, Kuwait City was established as a trading port, and the ruling Al-Sabah family came to power, laying the foundation for modern-day Kuwait.
Modernisation and Cultural Heritage
The discovery of oil in the 20th century transformed the country’s economy and led to rapid development and modernisation. Kuwaiti culture is deeply rooted in Islamic traditions and customs, with a strong emphasis on family, hospitality, and respect for elders. The traditional clothing for men is the dishdasha, a long white robe, while women wear the abaya, a long black cloak, and headscarf.
Festivals and Celebrations
The country celebrates several annual festivals and events, including National Day and Liberation Day, which commemorate important milestones in Kuwait’s history. Traditional music and dance are also an integral part of Kuwaiti culture, with performances often featuring the oud, a stringed instrument, and lively folk dances.
Economy and Business in Kuwait
Kuwait has one of the most prosperous economies in the Middle East, largely due to its vast oil reserves. The country is a leading exporter of oil and petroleum products, which account for the majority of its revenue. In recent years, Kuwait has made efforts to diversify its economy by investing in other sectors such as finance, real estate, and tourism.
The government has also implemented economic reforms to attract foreign investment and promote private sector growth. The business environment in Kuwait is characterised by a strong emphasis on personal relationships and trust. Business meetings often begin with small talk and social niceties before getting down to business.
It is important to show respect for seniority and authority in Kuwaiti business culture. The workweek in Kuwait typically runs from Sunday to Thursday, with Friday being the day of rest. English is widely spoken in business circles, but it is advisable to have any important documents translated into Arabic.
Overall, Kuwait offers numerous opportunities for business and investment, particularly in the energy, construction, and finance sectors.
Education and Healthcare in Kuwait
Kuwait places a high value on education and healthcare, with significant investment in both sectors. The country has a well-developed public education system that provides free education to all citizens from kindergarten through university. In recent years, there has been an increased focus on improving the quality of education and promoting innovation in schools.
Additionally, there are several private international schools that cater to expatriate families living in Kuwait. The healthcare system in Kuwait is also highly regarded, with modern hospitals and medical facilities offering a wide range of services. The government provides free or heavily subsidized healthcare to citizens, with expatriates having access to private healthcare options.
Kuwait has made significant investments in healthcare infrastructure and technology to ensure that its population has access to high-quality medical care. The country also has a strong focus on preventive care and public health initiatives to promote overall well-being.
Tourist Attractions in Kuwait
Kuwait offers visitors a wide range of attractions and activities to explore. The iconic Kuwait Towers are a must-see landmark, offering panoramic views of the city and the Arabian Gulf from their observation decks. The Grand Mosque is another popular tourist destination, known for its stunning architecture and intricate Islamic design.
For history enthusiasts, the National Museum of Kuwait provides an insight into the country’s rich heritage through its extensive collection of artefacts and exhibits. The coastline of Kuwait boasts beautiful beaches such as Al Kout Beach and Al Khiran Beach, where visitors can relax and enjoy water sports activities. The Souq Al Mubarakiya is a bustling traditional market where visitors can shop for local handicrafts, spices, and souvenirs.
For those interested in nature and wildlife, the Al Shaheed Park offers a peaceful retreat with landscaped gardens, walking trails, and outdoor art installations. With its blend of cultural landmarks, natural beauty, and modern attractions, Kuwait has something to offer every type of traveller.
Kuwaiti Cuisine and Food Culture
Staple Ingredients and Flavours
Rice, lamb, chicken, and fish are staple ingredients in Kuwaiti dishes, often flavoured with aromatic spices such as saffron, cardamom, and cinnamon.
Traditional Dishes and Desserts
One of the most popular traditional dishes is machboos, a fragrant rice dish served with meat or fish and accompanied by a tangy tomato sauce known as daqqus. Kuwaitis also have a sweet tooth and enjoy desserts such as baklava, kunafa, and halwa, which are often served with strong Arabic coffee or sweet mint tea.
Hospitality and Food Culture
The country’s food culture places a strong emphasis on hospitality and generosity, with large family meals being a common tradition. Visitors to Kuwait can experience authentic local cuisine at traditional restaurants or street food stalls throughout the country.
Future Developments and Challenges in Kuwait
Looking ahead, Kuwait faces several challenges as it seeks to diversify its economy and promote sustainable development. The country’s heavy reliance on oil exports makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in global oil prices, highlighting the need for economic diversification. Additionally, Kuwait is grappling with environmental issues such as water scarcity and air pollution due to rapid urbanisation and industrial growth.
To address these challenges, the government has outlined ambitious plans for future development, including investments in renewable energy sources such as solar power and wind energy. There are also ongoing efforts to promote entrepreneurship and innovation through initiatives such as startup incubators and business accelerators. By embracing these opportunities for growth while addressing its challenges head-on, Kuwait is poised to continue thriving as a dynamic and forward-thinking nation in the Middle East.
FAQs
What is the capital of Kuwait?
The capital of Kuwait is Kuwait City.
What is the population of Kuwait?
As of 2021, the population of Kuwait is estimated to be around 4.3 million people.
What is the official language of Kuwait?
The official language of Kuwait is Arabic.
What is the currency of Kuwait?
The currency of Kuwait is the Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD).
What is the climate like in Kuwait?
Kuwait has a desert climate, with hot and dry summers and mild winters. Temperatures can reach up to 50°C (122°F) in the summer months.
What are the major industries in Kuwait?
The major industries in Kuwait include petroleum, petrochemicals, desalination, and construction.
What are the popular tourist attractions in Kuwait?
Popular tourist attractions in Kuwait include the Kuwait Towers, the Grand Mosque, the Kuwait National Museum, and the Souq Al-Mubarakiya.
What is the government system in Kuwait?
Kuwait is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. The Emir of Kuwait is the head of state, and the Prime Minister is the head of government.
Political Boundaries of Kuwait: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Kuwait, a small yet significant country in the Middle East, is situated at the northern end of the Persian Gulf. It shares land borders with Iraq to the north and northwest, and with Saudi Arabia to the south and southwest. The nation boasts a coastline of approximately 499 kilometres along the Persian Gulf. Kuwait‘s political boundaries are defined by these international borders, as well as by its internal administrative divisions, governorates, and districts. These political boundaries play a crucial role in shaping the country’s governance, society, and international relations. A thorough understanding of Kuwait’s historical and current political boundaries is essential for comprehending the country’s geopolitical significance and its impact on the region. Kuwait’s political boundaries extend beyond its physical borders to include its territorial waters and exclusive economic zone in the Persian Gulf. The nation’s maritime boundaries are particularly significant due to its abundant oil reserves and strategic location. Kuwait’s political boundaries are also influenced by historical ties with neighbouring countries, as well as international treaties and agreements. The demarcation of Kuwait’s political boundaries has been a subject of historical disputes and controversies, which have shaped the country’s geopolitical landscape. As Kuwait continues to navigate its position in the region and on the global stage, its political boundaries remain a critical aspect of its identity and governance. Summary Kuwait’s political boundaries have evolved over time, shaping the country’s governance and society. The historical boundaries of Kuwait have been influenced by various factors, including colonial powers and regional conflicts. Kuwait is divided into six governorates, each further divided into districts, which play a significant role in local governance and...
Climate Zones Of Kuwait: Different Climate Regions Of Kuwait
Kuwait is a small nation situated in the Middle East, bordered by Iraq to the north and Saudi Arabia to the south. The country is characterised by its arid desert climate, with hot and dry weather predominating throughout the year. However, Kuwait‘s climate is not uniform across the entire nation, and it can be divided into several distinct climate zones. These climate zones include the arid desert climate, the coastal climate, the semi-arid climate, and the mountainous climate. Each of these climate zones possesses its own unique characteristics and influences the weather patterns and environmental conditions in different parts of the country. Understanding these climate zones is essential for comprehending the environmental challenges and opportunities that Kuwait faces. Summary Kuwait has four main climate zones: arid desert, coastal, semi-arid, and mountainous. The arid desert climate of Kuwait is characterized by extremely hot and dry conditions, with very little rainfall. The coastal climate of Kuwait experiences milder temperatures and higher humidity due to its proximity to the sea. The semi-arid climate of Kuwait has hot summers and mild winters, with slightly more rainfall than the desert region. The mountainous climate of Kuwait is cooler and receives more rainfall than the other regions, making it more suitable for agriculture. Kuwait City experiences the urban heat island effect, with higher temperatures and lower humidity due to urbanization and human activities. Climate change is expected to impact Kuwait’s climate zones, leading to increased temperatures, reduced rainfall, and more extreme weather events. The Arid Desert Climate of Kuwait Characteristics of the Arid Desert Climate This climate zone is typified by extremely hot and dry...
Terrain and Topography of Kuwait: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Kuwait, a small nation situated in the Middle East, is characterised by its distinctive terrain and topography. The country is predominantly flat, featuring extensive plains and a dearth of significant geographical features such as mountains and valleys. Kuwait‘s terrain has exerted a considerable influence on the nation’s climate, environment and the manner in which its inhabitants have adapted to their surroundings. This article shall examine the various aspects of Kuwait’s terrain and topography, as well as the implications they hold for the country and its populace. Summary Kuwait’s terrain is characterized by flat plains and the absence of mountains and valleys. The flat plains of Kuwait make up the majority of the country’s landscape, with sandy desert covering much of the terrain. Unlike many other countries, Kuwait does not have any significant mountain ranges within its borders. Valleys are scarce in Kuwait, with only a few wadis and dry riverbeds present in the desert landscape. The terrain of Kuwait has a significant impact on the country’s climate and environment, with hot and arid conditions dominating the region. The Flat Plains of Kuwait Challenges and Opportunities However, the lack of natural barriers in the form of hills or mountains means that the country is susceptible to sandstorms and other extreme weather events. Despite this, the flat plains of Kuwait have also provided opportunities for the development of renewable energy sources such as solar power, due to the abundance of sunlight that the country receives. Economic Impact The flat plains of Kuwait have also had an impact on the country’s economy, particularly in terms of oil production. The vast oil fields...
History of Kuwait
Kuwait possesses a rich history dating back to ancient times, with archaeological evidence indicating human settlement from the early Bronze Age. The region served as a significant hub for trade and commerce, owing to its strategic location along the ancient Silk Road, which connected the East and West. Early inhabitants were predominantly nomadic tribes who relied on trade and fishing for their livelihoods. The discovery of Mesopotamian artefacts in the area suggests that Kuwait was part of the ancient Sumerian civilisation, one of the world’s earliest urban societies. Kuwait’s early settlement was influenced by its proximity to the Arabian Peninsula and the Persian Gulf, establishing it as an important trading post for merchants. The region’s natural harbour and abundant marine resources made it an attractive destination for seafarers and traders from across the area. Over time, Kuwait became a key player in the pearl trade, a highly sought-after commodity in the ancient world. This early trade and commerce laid the foundation for Kuwait’s future economic prosperity and its role as a significant player in the global economy. Summary Early settlement in the region dates back to ancient times, with trade playing a key role in the development of the area. Ottoman rule and British influence shaped the political and economic landscape of the region in the 19th and 20th centuries. Independence and the discovery of oil in the region led to significant economic and social changes. The Gulf War and its aftermath had a lasting impact on the region, leading to political and social challenges. Modern development and economic growth have transformed the region into a global economic powerhouse,...
Population Density of Kuwait
Kuwait, a small nation situated in the Middle East, boasts one of the highest population densities globally. With a total land area of just over 17,800 square kilometres and a population of approximately 4.5 million people, Kuwait‘s population density stands at around 200 people per square kilometre. This high concentration of inhabitants is primarily attributed to the country’s limited size and rapid urbanisation. The majority of Kuwait’s population resides in urban areas, particularly in the capital city of Kuwait City. The elevated population density in Kuwait presents numerous challenges for the nation, including strain on infrastructure and resources, as well as social and environmental concerns. Comprehending the factors influencing population density in Kuwait, as well as its impact on the country, is crucial for developing effective strategies to manage and sustain the population in the future. Kuwait’s population density is the result of various factors, encompassing both natural and human-induced causes. The nation’s small land area and limited natural resources have led to a high concentration of people in urban areas, particularly along the coast. Moreover, Kuwait’s rapid economic development and urbanisation have attracted a substantial influx of migrants seeking employment opportunities, further contributing to the high population density. The government’s policies on immigration and citizenship also play a significant role in shaping the population density in Kuwait. Additionally, cultural and social factors, such as family size and migration patterns, influence population distribution within the country. Understanding these factors is essential for developing effective strategies to manage population density and ensure sustainable development in Kuwait. Summary Kuwait has a high population density, with a majority of its population residing...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Kuwait: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites in Kuwait
The Grand Mosque of Kuwait, also known as Al-Masjid Al-Kabir, stands as a prominent example of Islamic architecture and culture. This notable mosque is amongst the largest and most impressive in Kuwait, featuring a remarkable design with intricate details. The mosque’s architecture combines traditional Islamic elements with modern influences, resulting in a noteworthy feat of art and engineering. The Grand Mosque’s imposing structure is characterised by its tall minarets, elaborate domes, and expansive prayer halls, which can accommodate thousands of worshippers simultaneously. The interior is adorned with fine calligraphy, complex geometric patterns, and ornate chandeliers, creating a tranquil and spiritual environment for those in attendance. The Grand Mosque of Kuwait serves not only as a place of worship but also as a cultural landmark that embodies the rich heritage and traditions of Islam. The mosque’s design and architecture exemplify Islamic principles of aesthetics, harmony, and spirituality. Visitors to the mosque can observe its impressive architecture, learn about Islamic art and calligraphy, and gain insight into Islamic culture and traditions. The Grand Mosque is a significant destination for those interested in Islamic architecture and culture, offering a unique opportunity to experience one of Kuwait’s most important religious and cultural landmarks. Summary The Grand Mosque of Kuwait is a stunning example of Islamic architecture and a symbol of the country’s rich cultural heritage. The Kuwait National Museum offers a fascinating insight into the history and heritage of Kuwait, showcasing artefacts and exhibits from ancient times to the present day. Failaka Island provides a unique opportunity to explore ancient Greek and Mesopotamian settlements, offering a glimpse into Kuwait’s rich historical past. The...
Natural Resources of Kuwait: Where Natural Resources are Located in Kuwait
Kuwait, a small nation situated in the Middle East, is renowned for its abundant natural resources. The country possesses substantial oil and gas reserves, rendering it one of the most affluent nations globally. In addition to its hydrocarbon resources, Kuwait also boasts significant water, renewable energy, agricultural, and mineral resources. The effective management and conservation of these natural resources are vital for the country’s sustainable development. Through meticulous planning and investment, Kuwait can continue to reap the benefits of its natural resources whilst safeguarding the environment for future generations. Kuwait’s natural resources have played a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s economy and development. The profusion of oil and gas reserves has enabled Kuwait to become a significant player in the global energy market. The country’s water resources, albeit limited, have been carefully managed to meet the needs of its population and support agricultural activities. In recent years, there has been an increasing emphasis on renewable energy sources as Kuwait seeks to diversify its energy mix and reduce its dependence on fossil fuels. The nation’s mineral resources also hold potential for further economic development. With appropriate policies and practices in place, Kuwait can ensure the sustainable utilisation of its natural resources for the benefit of its citizens and the environment. Summary Kuwait is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, water, renewable energy potential, agricultural resources, and mineral resources. The country has significant oil and gas reserves, making it one of the leading producers in the world. Kuwait faces challenges in managing its water resources due to limited freshwater sources and high demand for water. There is potential for...