Natural Resources of Algeria: Unlocking the Natural Wealth of Algeria: Oil, Gas, and Beyond
Algeria, a nation rich in energy reserves and minerals, stands as a powerhouse in North Africa thanks to its abundant natural resources. From its vast oil and gas fields to significant mineral deposits and renewable energy potential, Algeria is pivotal in the global resource economy. This article delves deep into the natural resources of Algeria, how they shape its economy, and what the future may hold as the country aims to diversify and strengthen its industries. Whether you’re an investor, policy maker, or just curious about resource-rich nations, this article provides critical insights into Algeria’s economic backbone.
Outline
-
What Makes Algeria Rich in Natural Resources?
-
How Important Are Oil and Gas to the Algerian Economy?
-
What Are Algeria’s Major Natural Gas Reserves?
-
Where Are the Key Oil Fields Located in Algeria?
-
What Other Mineral Resources Are Found in Algeria?
-
Is Helium a Game-Changer for Algeria’s Resource Portfolio?
-
How Is Algeria Approaching Renewable Energy Development?
-
What Is the Role of the Mining Sector in Algeria?
-
Can Algeria Diversify Its Economy Beyond Hydrocarbons?
-
How Do Algeria’s Water and Fishing Resources Fit into the Picture?
1. What Makes Algeria Rich in Natural Resources?
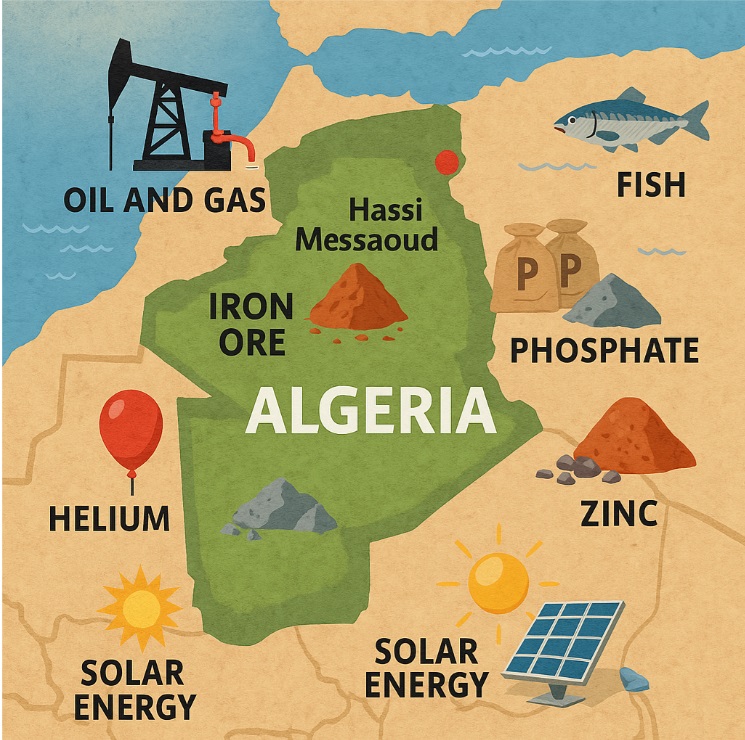
Algeria is one of the largest countries in Africa by land area, and much of this vast territory is rich in natural resources. From the heart of the Sahara to the coastline along the Mediterranean Sea, Algeria is home to substantial deposits of petroleum, natural gas, and valuable minerals like phosphate, zinc, and iron ore. These resources make Algeria a significant energy supplier and mineral exporter on the global stage.
According to the World Factbook, Algeria has abundant natural resources that underpin its gross domestic product (GDP) and provide a substantial portion of national income. Algeria’s natural resources are not just limited to hydrocarbons but also include a range of underexplored mining assets that have the potential to transform its economy in the coming decades.
2. How Important Are Oil and Gas to the Algerian Economy?
The oil and gas sector dominates the Algerian economy, accounting for over 95% of the country’s export revenues and nearly 60% of its GDP. Algeria is a key OPEC member and ranks among the world’s top ten natural gas producers. The state-owned company Sonatrach oversees the bulk of oil and natural gas production in Algeria.
Algeria’s economy is highly dependent on hydrocarbon exports, which include crude oil, natural gas, and petroleum products. The country’s oil and gas reserves are among the largest in Africa, with approximately 12.2 billion barrels of proven oil reserves and vast gas fields that supply Europe and beyond. This dependency, however, also exposes Algeria to fluctuations in oil prices, making economic diversification a national priority.
3. What Are Algeria’s Major Natural Gas Reserves?
Natural gas is Algeria’s crown jewel when it comes to natural resources. The country boasts some of the largest natural gas reserves on the continent, and it is a critical gas exporter to Europe through multiple pipeline routes, including the Trans-Mediterranean Pipeline and the Medgaz Pipeline.
Much of the gas resources are located in the Sahara Desert region, including the Hassi R’Mel gas field, one of the largest in the world. With billions of cubic meters of natural gas, Algeria plays a pivotal role in the gas industry, especially during global energy crises. The country has also invested in liquefied natural gas (LNG) facilities to enhance its global reach in energy exports.
4. Where Are the Key Oil Fields Located in Algeria?
The Hassi Messaoud oil field, located in the southeastern part of the country, is Algeria’s most significant oil field. This area alone contributes a large share of the country’s oil production. Other prominent petroleum sites include Ourhoud and Rhourd El Baguel, which are managed through joint ventures with international oil companies.
The Algerian petroleum industry is heavily centralized under Sonatrach, though foreign companies are increasingly involved through exploration and mining projects. The Algerian government has taken steps to attract foreign investors by improving terms for exploration and development, hoping to increase oil output and modernize the industry in Algeria.
5. What Other Mineral Resources Are Found in Algeria?
In addition to hydrocarbons, Algeria is endowed with a range of mineral resources. These include vast phosphate deposits, significant iron ore deposits, and valuable quantities of zinc and other industrial minerals. The mining sector remains underdeveloped, but recent reforms are aimed at boosting output and attracting foreign investment.
One of Algeria’s most promising mining industry sites is the Gara Djebilet iron ore deposit, estimated to hold billions of tons of iron ore. The development of this site could fuel the iron and steel and construction industry and contribute significantly to national GDP and employment.
6. Is Helium a Game-Changer for Algeria’s Resource Portfolio?
Surprisingly, Algeria is one of the few countries with large-scale helium production capabilities. Helium is extracted as a byproduct from natural gas fields and is used globally in scientific, medical, and industrial applications.
With the global shortage of helium affecting prices and availability, Algeria’s reserves could play a critical role in the international market. The country’s Sahara gas fields, particularly around Hassi R’Mel, produce helium in significant volumes. As demand for helium grows, Algeria may find a new niche in the global natural resources economy.
7. How Is Algeria Approaching Renewable Energy Development?
Despite being rich in hydrocarbon resources, Algeria is increasingly focused on renewable energy. The Algerian government recognizes the need to diversify its economy and reduce dependency on fossil fuels. With abundant sunlight, Algeria has significant potential for solar power—a cornerstone of its renewable energy sources.
Projects like the “Desertec” initiative and national power generation programs aim to transform Algeria into a solar energy exporter. While progress is slow, the country’s commitment to renewable energy development aligns with global climate goals and offers new growth opportunities for the economy.
8. What Is the Role of the Mining Sector in Algeria?
The mining sector in Algeria is often overshadowed by the oil and gas industry, but it holds significant untapped potential. Rich phosphate, iron ore, and zinc deposits, as well as other minerals, remain largely underdeveloped. The government aims to revitalize the sector to support diversification and industrial growth.
The Ministry of Energy and Mines has introduced new frameworks to promote mining projects and encourage foreign companies to invest. As industry is underdeveloped, infrastructure challenges remain, but efforts to improve rail networks and logistics are underway.
9. Can Algeria Diversify Its Economy Beyond Hydrocarbons?
Algeria’s overreliance on hydrocarbon exports makes it vulnerable to market shocks. As such, the need to diversify has become a major economic objective. Sectors like renewable energy, mining, construction, fishing, and manufacturing are being promoted as part of the national development plan.
The Algerian government is investing in renewable energy infrastructure and liberalizing policies to attract foreign investors in sectors beyond oil and gas. The success of such efforts is vital for the sustainability of Algeria’s economy and to provide employment for its growing population.
10. How Do Algeria’s Water and Fishing Resources Fit into the Picture?
Beyond minerals and hydrocarbons, Algeria also has water resources and a growing fishing industry. With a long coastline along the Mediterranean Sea, the country is well-positioned to expand its fish exports and improve food security.
Algeria’s coastline supports diverse species of marine life, and the government is working to improve the sustainability of fishing practices. In addition, water resources are crucial for agriculture and urban development, especially in arid inland regions near the Sahara Desert.
Summary
- Algeria’s natural resources include oil and gas reserves, abundant minerals, fertile land and water resources, rich biodiversity, renewable energy potential, scarce water resources, coastal fisheries, and natural building materials.
- Oil and gas reserves are a major economic driver in Algeria, accounting for a significant portion of the country’s GDP and exports.
- Algeria’s mining sector is rich in minerals such as iron, zinc, lead, and phosphate, with potential for further exploration and development.
- The country’s fertile land and water resources support a diverse range of agricultural activities, including crops, livestock, and fisheries.
- Algeria’s forests and wildlife are home to a rich biodiversity, including endangered species such as the Barbary macaque and Mediterranean monk seal.
- Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power have significant potential for development in Algeria, which has abundant sunshine and wind resources.
- Managing scarce water resources is a key challenge for Algeria, which faces increasing demand and climate change impacts.
- Algeria’s coastal fisheries provide an important source of food and income for local communities, but face challenges from overfishing and illegal fishing practices.
- Natural building materials such as stone and clay deposits are abundant in Algeria, providing opportunities for sustainable construction and economic development.
- Sustainable development of Algeria’s natural resources requires addressing challenges such as environmental degradation, climate change, and social and economic inequality, while also leveraging opportunities for innovation and investment.
Algeria’s Oil and Gas Reserves: A Major Economic Driver
Algeria is one of the largest producers of oil and gas in Africa. The country’s oil and gas industry has been a major driver of its economy for decades. Oil and gas exports account for a significant portion of Algeria’s revenue and foreign exchange earnings. The industry has attracted foreign investment and created job opportunities for the Algerian population.
However, the oil and gas sector in Algeria faces several challenges. The decline in global oil prices has affected the country’s revenue from exports. There is also a need to diversify the economy to reduce dependence on oil and gas. Algeria has recognized the importance of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power to meet its domestic energy needs and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Mining in Algeria: Abundant Mineral Wealth
Algeria is blessed with abundant mineral resources, including gold, phosphate, iron ore, zinc, lead, mercury, and uranium. The mining industry plays a vital role in Algeria’s economy by contributing to its GDP and providing employment opportunities. The country has attracted foreign investment in mining projects.
However, the mining sector faces challenges such as outdated infrastructure, limited access to financing, and environmental concerns. There is a need for investment in modernizing mining operations and improving infrastructure to maximize the potential of Algeria’s mineral wealth. Additionally, sustainable mining practices and environmental regulations are crucial to minimize the negative impact on the environment and local communities.
Agricultural Resources in Algeria: Fertile Land and Water Resources
Algeria has fertile land and abundant water resources, making it suitable for agriculture. The country produces a variety of crops, including cereals, vegetables, fruits, and olives. Agriculture contributes to Algeria’s food security and provides employment opportunities for rural communities.
However, the agricultural sector faces challenges such as limited access to modern farming techniques, inadequate irrigation systems, and climate change. There is a need for investment in agricultural infrastructure, research and development, and training programs to improve productivity and sustainability. Additionally, sustainable water management practices are essential to ensure the long-term availability of water resources for agriculture.
Algeria’s Forests and Wildlife: Rich Biodiversity
Algeria is home to diverse forests and wildlife. The country has various ecosystems, including Mediterranean forests, coastal wetlands, and desert habitats. Algeria’s forests provide timber, fuelwood, and non-timber forest products. The country’s wildlife includes species such as the Barbary macaque, gazelles, wild boars, and various bird species.
The conservation of forests and wildlife is crucial for Algeria’s economy and environment. Forests play a vital role in carbon sequestration, soil conservation, and water regulation. Wildlife tourism has the potential to generate revenue and create employment opportunities. However, deforestation, habitat loss, illegal hunting, and climate change pose significant threats to Algeria’s forests and wildlife. There is a need for conservation efforts, sustainable use of forest resources, and the implementation of wildlife protection measures.
Renewable Energy in Algeria: Potential for Solar and Wind Power
Algeria has significant potential for renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. The country receives abundant sunlight throughout the year and has vast areas suitable for wind farms. Renewable energy can help Algeria reduce its dependence on fossil fuels, mitigate climate change, and provide electricity to remote areas.
The development of renewable energy in Algeria faces challenges such as limited infrastructure, high upfront costs, and the need for technology transfer. However, the government has taken steps to promote renewable energy projects through incentives and partnerships with international organizations. There is a need for further investment in renewable energy infrastructure, research and development, and capacity building to harness Algeria’s renewable energy potential.
Water Resources in Algeria: Managing Scarce Resources
Algeria faces water scarcity due to its arid climate and limited water resources. The country relies on groundwater, rivers, and reservoirs for its water supply. Water is essential for agriculture, industry, and domestic use.
The management of water resources in Algeria is crucial for sustainable development. The country needs to invest in water infrastructure, improve water efficiency in agriculture and industry, and promote water conservation practices. Additionally, there is a need for integrated water resource management and cooperation with neighboring countries to address transboundary water issues.
Fisheries in Algeria: A Coastal Nation’s Bounty
Algeria’s coastline stretches over 1,600 kilometers, providing abundant fishery resources. The country’s fisheries industry plays a vital role in providing food security, employment opportunities, and revenue from fish exports.
However, overfishing, illegal fishing practices, and pollution pose significant threats to Algeria’s fisheries. There is a need for sustainable fishing practices, the implementation of fishing regulations, and the protection of marine ecosystems. Additionally, investment in fisheries infrastructure, research and development, and capacity building can help maximize the potential of Algeria’s fisheries resources.
Building Materials in Algeria: Natural Stone and Clay Deposits
Algeria has abundant natural resources used for construction, including limestone, marble, granite, clay, and sand. These resources are essential for infrastructure development and the construction industry.
The sustainable use of building materials is crucial to minimize the environmental impact and ensure the long-term availability of resources. There is a need for responsible mining practices, recycling of construction waste, and the use of sustainable building materials. Additionally, investment in research and development can help improve the efficiency and sustainability of the construction industry in Algeria.
Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Development of Algeria’s Natural Resources
Algeria’s natural resources offer significant opportunities for economic growth, job creation, and sustainable development. However, there are several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the responsible use and management of these resources.
The challenges include outdated infrastructure, limited access to financing, environmental concerns, climate change, water scarcity, overfishing, illegal mining practices, and pollution. To overcome these challenges, Algeria needs to invest in modernizing infrastructure, promoting sustainable practices, implementing environmental regulations, and fostering international partnerships.
Sustainable development is crucial for Algeria’s future. It requires a balance between economic growth, social development, and environmental protection. The responsible use and management of natural resources are essential to ensure their availability for future generations.
In conclusion, Algeria’s natural resources play a vital role in its economy and development. From oil and gas reserves to abundant mineral wealth, fertile land for agriculture, diverse forests and wildlife, renewable energy potential, water resources, fisheries, and building materials, Algeria has a wide range of resources that contribute to its growth. However, the sustainable management and responsible use of these resources are crucial for Algeria’s future. It requires investment in infrastructure, research and development, capacity building, and the implementation of sustainable practices. By harnessing its natural resources responsibly, Algeria can achieve sustainable development and ensure a better future for its people.
FAQs
What are the natural resources of Algeria?
Algeria is rich in natural resources such as petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, phosphates, lead, zinc, uranium, and mercury.
Where are the oil and gas reserves located in Algeria?
The oil and gas reserves in Algeria are mainly located in the Sahara desert, particularly in the Hassi Messaoud and Hassi R’Mel fields.
What is the status of Algeria’s iron ore reserves?
Algeria has significant iron ore reserves, with the majority located in the Tindouf province in the western part of the country. However, the country’s iron and steel industry is underdeveloped.
Where are the phosphates reserves located in Algeria?
Algeria’s phosphates reserves are mainly located in the Djebel Onk and Tebessa regions in the northeast of the country.
What other minerals are found in Algeria?
Apart from the aforementioned minerals, Algeria also has significant reserves of lead, zinc, mercury, and uranium. These minerals are mainly located in the northern and central parts of the country.
How important are natural resources to Algeria’s economy?
Natural resources are a crucial part of Algeria’s economy, accounting for over 95% of the country’s exports. The oil and gas sector is particularly important, contributing around 60% of the country’s GDP.