Afghanistan
(Islamic Republic of Afghanistan (Jomhūrī-ye Eslāmī-ye Afghānestān [Dari]); Da Afghanestan Eslami Jamhuriyat (Pashto))

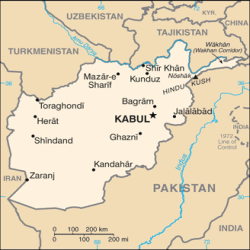




Capital
of Afghanistan: Kabul
Population (Estimated July 2012): 30,419,928
Area of Afghanistan: 652,864km2 or 252,072mi2
Currency: Afghani (AFN)
Official Language: Dari and Pashto
Political Information: Islamic Republic
Official Religion: Islam
(approximately 99% of the population is Muslim and 1% have other religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: The Hindu Kush at 7,492 m or 24,580ft
Longest River: Amu Darya 1,415km
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): + 4:30
Wildlife: Alta Weasel, Asiatic Black Bear, Asiatic Brown Bear, Caracal, Eurasian Otter, Geoffroy’s Bat, Gray Wolf, Hare, Ibex, Kashmir Cave Bat, Leopard, Lesser Horseshoe Bat, Long-Tailed Marmat, Lynx, Marco Polo Sheep, Markhor, Mehely’s Horseshoe Bat, Mouflon, Pallas’ Cat, Pikas, Red Fox, Sind Bat, Snow Leopard, Stoat, Stone Marten, Wild Goat and Zarudny’s Jird.
Counties/Provinces/States:
Badakhshan, Badghis, Baghlan, Balkh, Bamyan, Daykundi, Farah, Faryab, Ghazni, Ghor, Helmand, Herat, Jowzjan, Kabul, Kandahar, Kapisa, Khost, Kunar, Kunduz, Laghman, Logar, Nangarhar, Nimruz, Nuristan, Oruzgan, Paktia, Paktika, Panjshir, Parwan, Samangan, Sar-e Pol, Takhar, Wardak and Zabul.
Leaders: President Hamid Karzai
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica,
Afghanistan, located in Central Asia, is a country that has been at the center of global attention for many years. It is a landlocked country bordered by Iran to the west, Pakistan to the east and south, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan to the north, and China to the northeast. Afghanistan has a rich history and a diverse culture, but it has also faced numerous challenges and conflicts throughout its existence.
The purpose of this blog post is to provide a comprehensive overview of Afghanistan, covering its geography, history, politics, culture, economy, education, human rights, foreign relations, and tourism. By exploring these different aspects of Afghanistan, we can gain a better understanding of the country and its significance in the global context.
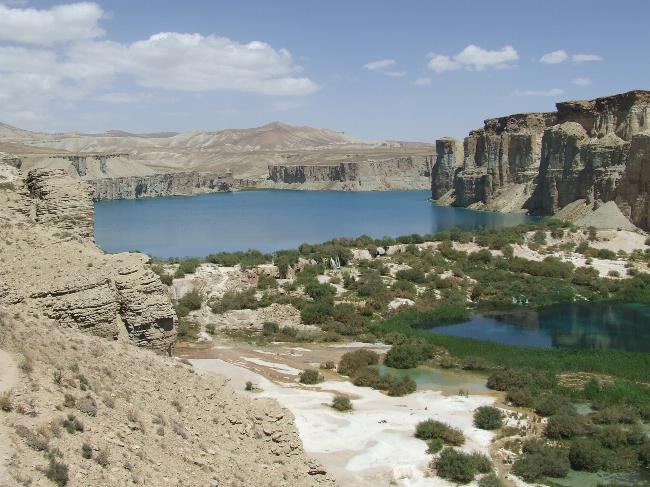
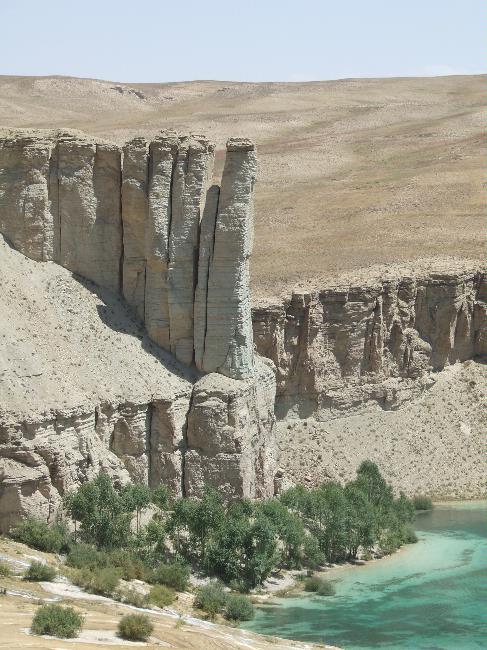
Afghanistan’s Geography and Climate
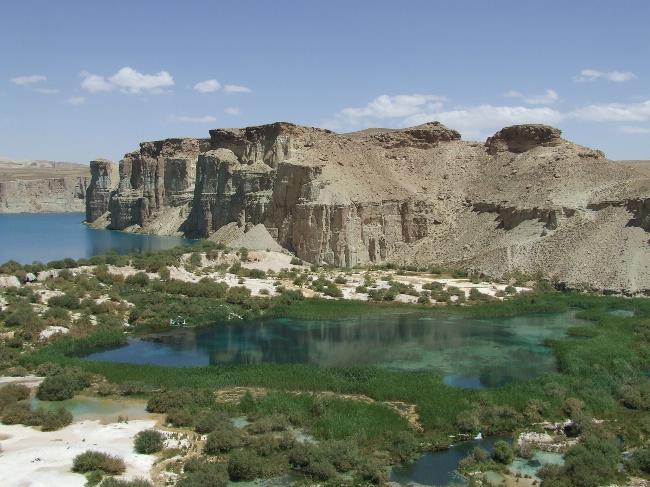
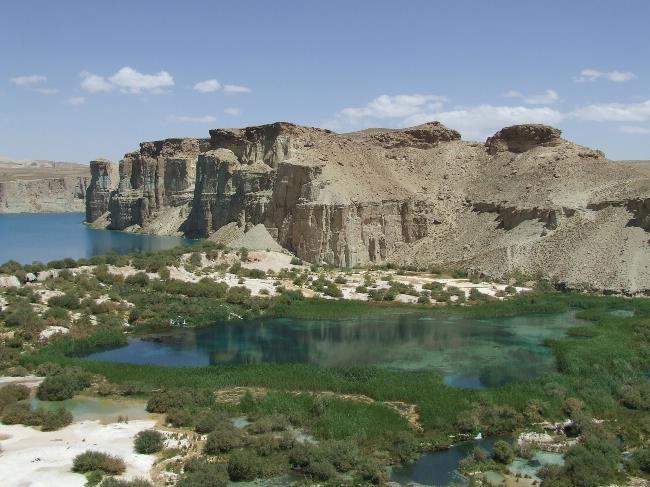
Afghanistan is located in a strategic position at the crossroads of Central Asia, South Asia, and the Middle East. Its geography is characterized by rugged mountains, vast deserts, and fertile valleys. The Hindu Kush mountain range runs through the country from east to west, with peaks reaching over 7,000 meters. The Amu Darya and Hari River are the major rivers in Afghanistan.
The climate in Afghanistan varies depending on the region. The northern part of the country experiences cold winters and hot summers, while the southern part has a desert climate with extremely hot summers and mild winters. The central highlands have a more moderate climate with cold winters and cool summers. The country also experiences periodic droughts and is prone to earthquakes.
The History of Afghanistan: From Ancient Times to Modern Day
Afghanistan has a long and complex history that dates back thousands of years. It has been inhabited since prehistoric times and has been influenced by various civilizations including the Persians, Greeks, Mauryans, Kushans, Arabs, Mongols, Timurids, Mughals, and British. The region has also been a major trade route between the East and the West.
Key events and periods in Afghanistan’s history include the Achaemenid Empire, the conquests of Alexander the Great, the Mauryan Empire, the Islamic conquest, the Mongol invasions, the Timurid Empire, the Mughal Empire, and British colonial rule. In more recent history, Afghanistan experienced a communist coup in 1978, followed by a Soviet invasion in 1979. The country then descended into a civil war and was later ruled by the Taliban from 1996 to 2001. The US-led invasion in 2001 toppled the Taliban regime and led to the establishment of a new government.
The Taliban and the War in Afghanistan
The Taliban is an extremist Islamist group that emerged in Afghanistan in the early 1990s. They gained control of most of the country in 1996 and imposed a strict interpretation of Islamic law. Under their rule, women were denied basic rights and education, cultural activities were banned, and public executions were common.
The US-led war in Afghanistan began in 2001 in response to the September 11 attacks. The goal was to remove the Taliban from power and dismantle Al-Qaeda, the terrorist group responsible for the attacks. The war has been ongoing for nearly two decades and has had a significant impact on Afghanistan. While progress has been made in terms of security and governance, the country still faces many challenges including ongoing violence, corruption, and political instability.
The Afghan Government and Politics
Afghanistan is an Islamic republic with a presidential system of government. The President is both the head of state and the head of government. The National Assembly consists of two houses: the Wolesi Jirga (House of People) and the Meshrano Jirga (House of Elders). The judiciary is independent of the executive and legislative branches.
Key political figures in Afghanistan include President Ashraf Ghani, Chief Executive Abdullah Abdullah, and former President Hamid Karzai. There are also various political parties and factions in the country, including the National Unity Government, the Taliban, and other opposition groups.
Afghan Culture and Society: Customs and Traditions
Afghanistan has a rich and diverse culture that is influenced by its history, geography, and religion. The majority of Afghans are Muslims, with Sunni Islam being the dominant sect. Islam plays a central role in Afghan society and influences many aspects of daily life.
Afghanistan is known for its hospitality and strong sense of community. Family is considered the most important social unit, and extended families often live together in the same household. Traditional gender roles are still prevalent, with men being the primary breadwinners and women taking care of the household and children.
Key customs and traditions in Afghanistan include the celebration of religious holidays such as Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha, traditional music and dance, traditional clothing such as the Afghan national dress (the shalwar kameez), and traditional cuisine which includes dishes such as kabuli pulao (rice with meat) and mantu (dumplings).
The Afghan Economy: Challenges and Opportunities
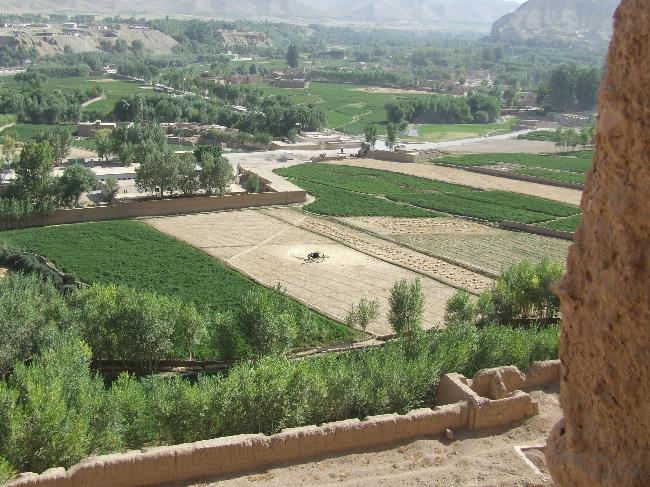
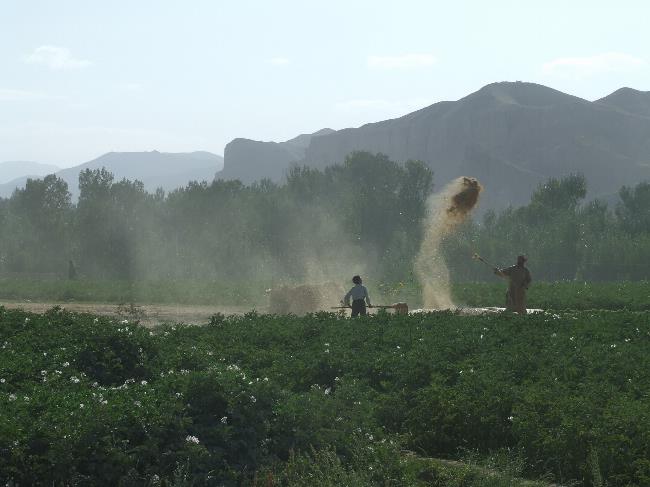
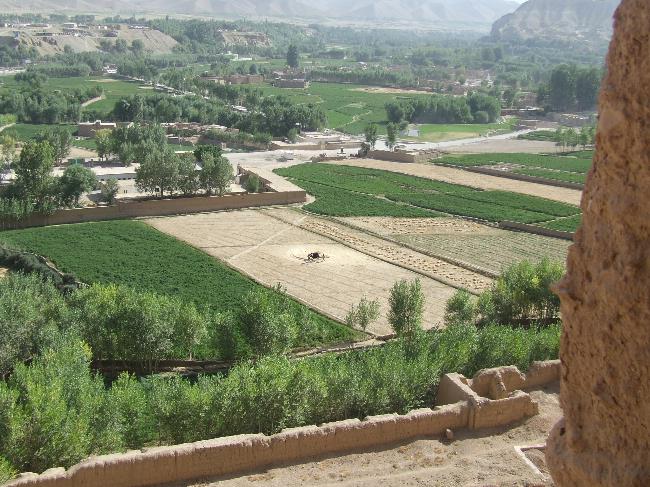
Afghanistan has one of the least developed economies in the world, with a heavy reliance on agriculture. The country is rich in natural resources including natural gas, oil, coal, copper, gold, and gemstones. However, due to ongoing conflict and political instability, these resources have not been fully exploited.
The Afghan economy faces numerous challenges including high levels of poverty, unemployment, corruption, lack of infrastructure, and limited access to markets. However, there are also opportunities for economic growth in sectors such as mining, agriculture, manufacturing, construction, and services. The government has implemented various reforms to attract foreign investment and promote economic development.
Education in Afghanistan: Progress and Challenges
Education in Afghanistan has made significant progress since the fall of the Taliban regime. Under the Taliban, education for girls was banned, and schools were destroyed. However, since 2001, millions of children, including girls, have enrolled in schools and universities.
Despite these achievements, Afghanistan still faces many challenges in the education sector. Access to education remains limited, especially in rural areas. The quality of education is also a concern, with a shortage of qualified teachers and inadequate infrastructure. The government and international organizations are working to address these challenges and improve the education system.
Human Rights in Afghanistan: Issues and Concerns
Afghanistan has made some progress in promoting human rights since the fall of the Taliban regime. However, the country still faces many challenges in this area. Women’s rights are a particular concern, with high levels of gender-based violence, limited access to education and healthcare, and restrictions on their participation in public life.
Other human rights issues in Afghanistan include freedom of expression, freedom of the press, freedom of religion, and the rights of ethnic and religious minorities. The government and civil society organizations are working to address these issues and promote human rights in the country.
Afghanistan’s Relations with its Neighbours and the International Community
Afghanistan’s relations with its neighbours and the international community have been complex and influenced by various factors including geopolitics, security concerns, economic interests, and historical ties. Afghanistan shares borders with Iran, Pakistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and China.
Afghanistan has historically had a difficult relationship with Pakistan due to border disputes and allegations of support for militant groups. Relations with Iran have also been strained at times due to political differences and concerns over drug trafficking. However, there have been efforts to improve relations with both countries in recent years.
Afghanistan has also been a recipient of international aid and support, particularly from the United States and its allies. The international community has played a key role in supporting Afghanistan’s reconstruction and development efforts, as well as in promoting peace and stability in the country.
Terrain and Topography Of Afghanistan: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Afghanistan, located in Central Asia, is a country known for its diverse and rugged terrain. The country is landlocked and surrounded by six countries, including Iran, Pakistan, and Tajikistan. Understanding Afghanistan’s geography is crucial for various...
Political Boundaries Of Afghanistan: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Afghanistan, located in Central Asia, is a landlocked country with a complex history of political boundaries. Understanding these boundaries is crucial for comprehending the country’s political, social, and economic dynamics. Afghanistan shares borders with six...
Natural Resources Of Afghanistan: Where Natural Resources are located In Afghanistan
Afghanistan, located in South Asia, is a landlocked country with a diverse range of natural resources. Its geography is characterized by rugged mountains, vast deserts, and fertile valleys. These natural features have endowed Afghanistan with a wealth of mineral...
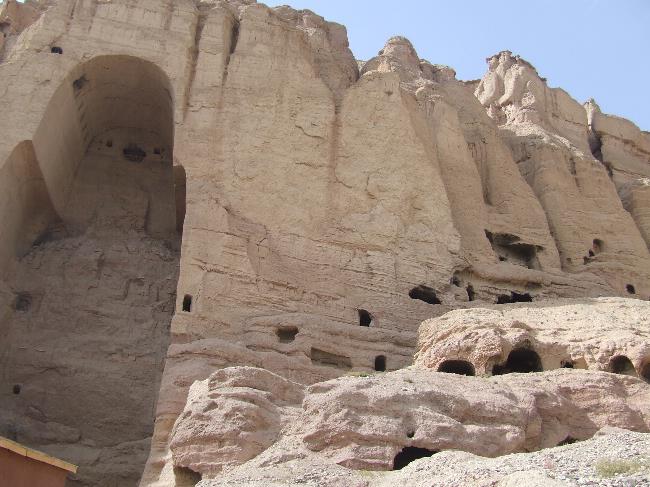
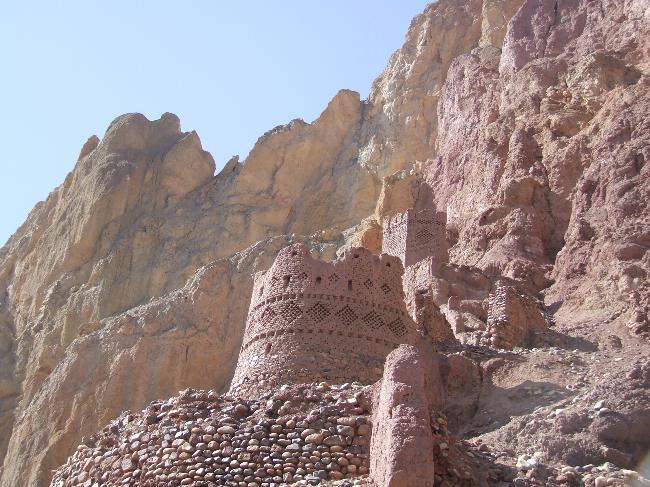
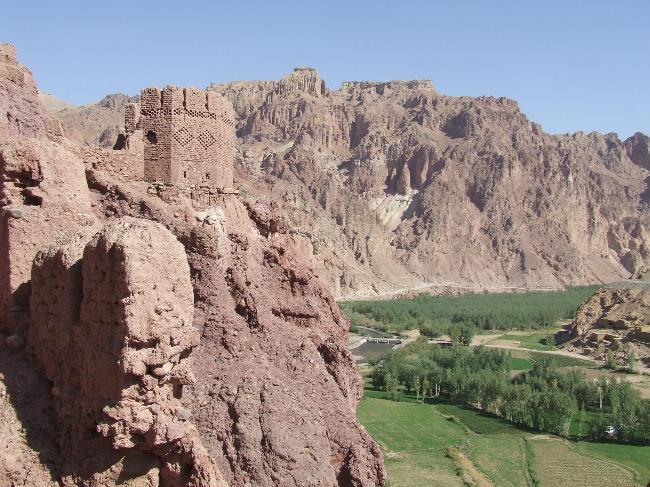
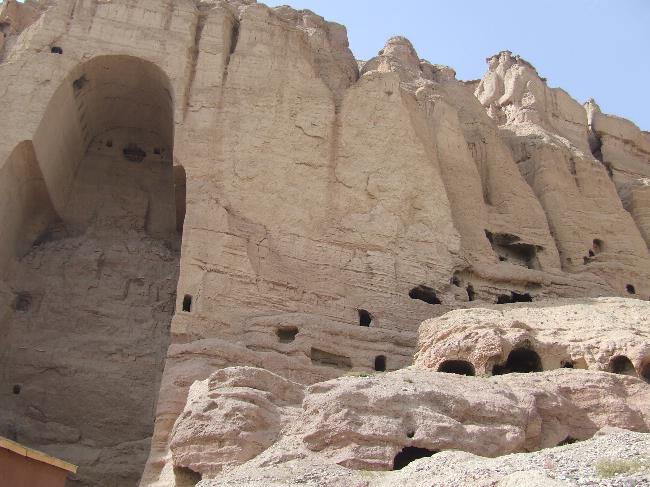
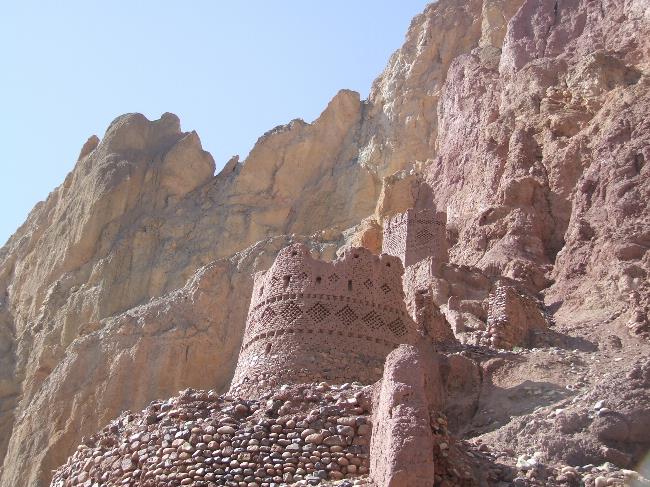
Cultural or Historical Sites Of Afghanistan: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Afghanistan
Afghanistan is a country with a rich cultural heritage that spans thousands of years. From ancient archaeological sites to stunning architectural wonders, Afghanistan’s cultural sites are a testament to its diverse history and vibrant traditions. However, these...
Climate Zones Of Afghanistan: Different climate regions Of Afghanistan
Afghanistan, located in Central Asia, is a landlocked country with a diverse geography and climate. It is surrounded by mountains, including the Hindu Kush and the Pamir, which greatly influence its climate. The country experiences a wide range of temperatures and...
Population Density Of Afghanistan
Afghanistan, a landlocked country in South Asia, is known for its rugged terrain and diverse cultural heritage. With a population of over 38 million people, Afghanistan is the 40th most populous country in the world. Understanding the population density of Afghanistan...
Uncovering the Beauty and Complexity of Afghanistan: Exploring the Rich Culture and History of the Land of the Afghans
Afghanistan, a landlocked country in Central Asia, has a rich and diverse cultural heritage that spans thousands of years. From its ancient history to its modern struggles, Afghanistan has a story to tell that is both fascinating and complex. Learning about...





















