Benin
(République du Bénin (Republic of Benin))

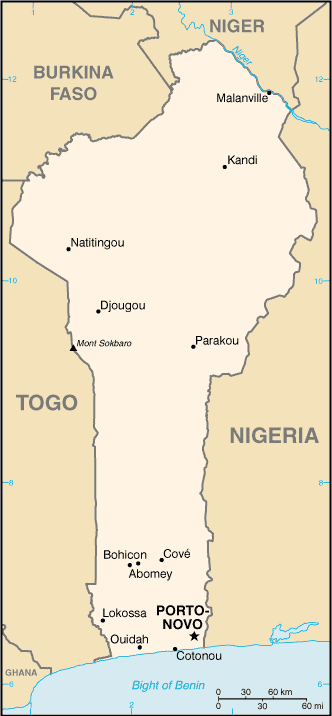



Capital of Benin : Porto-Novo
Population (Estimated July 2012): 9,598,787
Area: 112,622km2 or 43,484mi2
Currency: CFA Franc (CFAF)
Official Language: French
Political Information: Parliamentary Democracy
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 27.1% of the population are Roman Catholic, 24.4% are Muslim, 17.3% are Vodoun, 10.4% are Protestant and 20.8% have other religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Mont Sokbaro at 658m or 2,158ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $7.5 billion (US$) or £4.5 billion (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $14.79 billion (US$) or £8.874 billion (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $1,500 (US$) or £900 (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +1:00
Counties/Provinces/States: (departments) Alibori, Atakora, Atlantique, Borgou, Collines, Kouffo, Donga, Littoral, Mono, Oueme, Plateau, Zou
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Benin, officially known as the Republic of Benin, is a small country located in West Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the east, Togo to the west, Burkina Faso and Niger to the north, and the Atlantic Ocean to the south. Despite its small size, Benin is a country with a rich cultural heritage that dates back centuries. From its ancient kingdoms to its vibrant traditions and customs, Benin is a country that has much to offer in terms of history and culture.
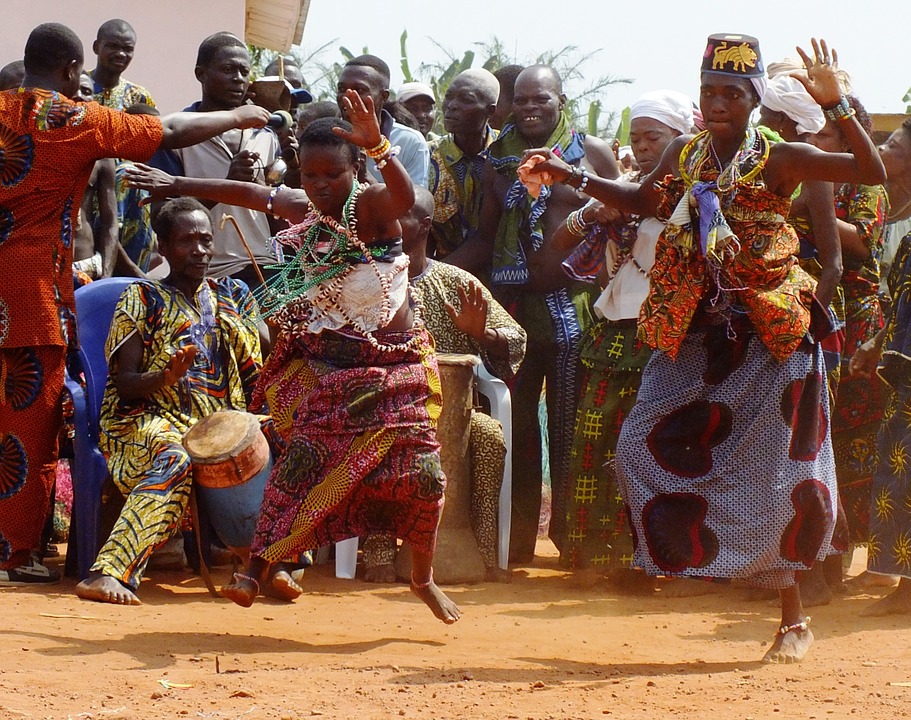
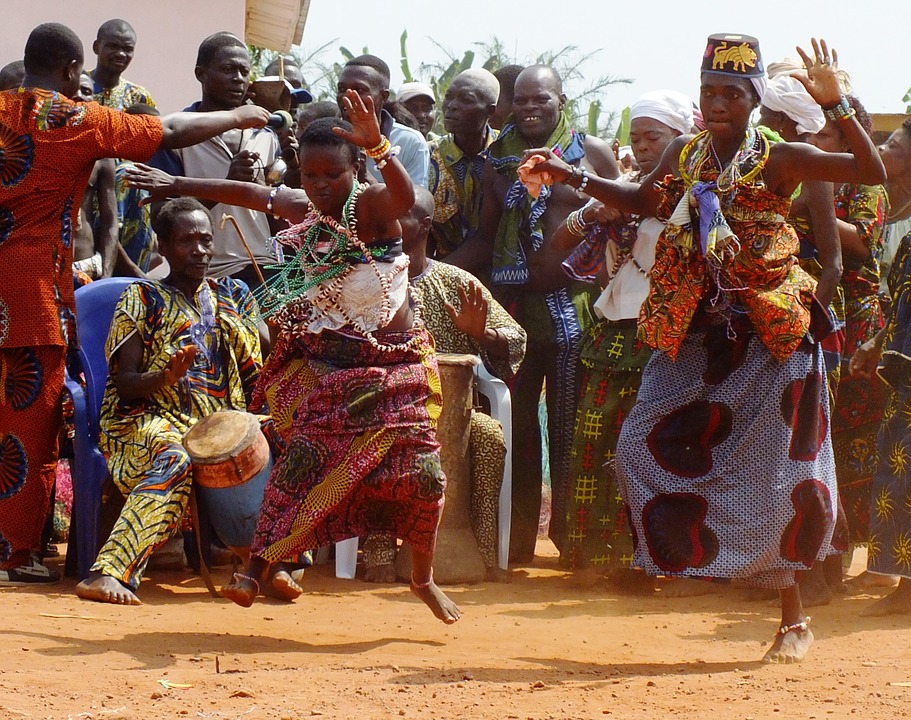
The cultural heritage of Benin is of great importance not only to its people but also to the world. The country is home to several UNESCO World Heritage Sites, including the Royal Palaces of Abomey, which were the seat of power for the Kingdom of Dahomey. These palaces are a testament to the rich history and architectural prowess of the Beninese people. Additionally, Benin is known for its vibrant music and dance traditions, as well as its unique voodoo religion. The cultural heritage of Benin is not only a source of pride for its people but also a valuable asset that attracts tourists from around the world.
Geography and Climate of Benin: A Land of Diversity and Natural Beauty
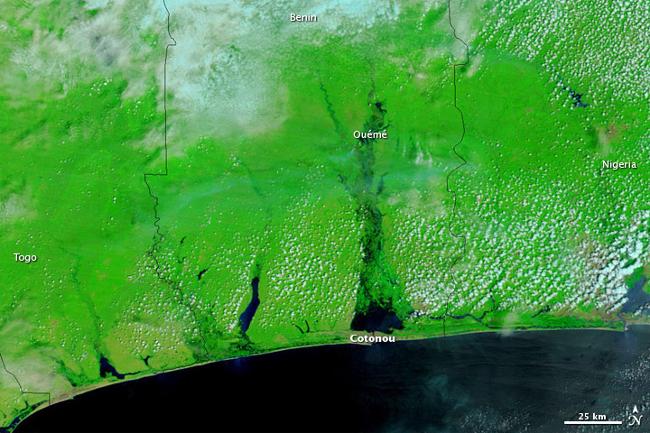
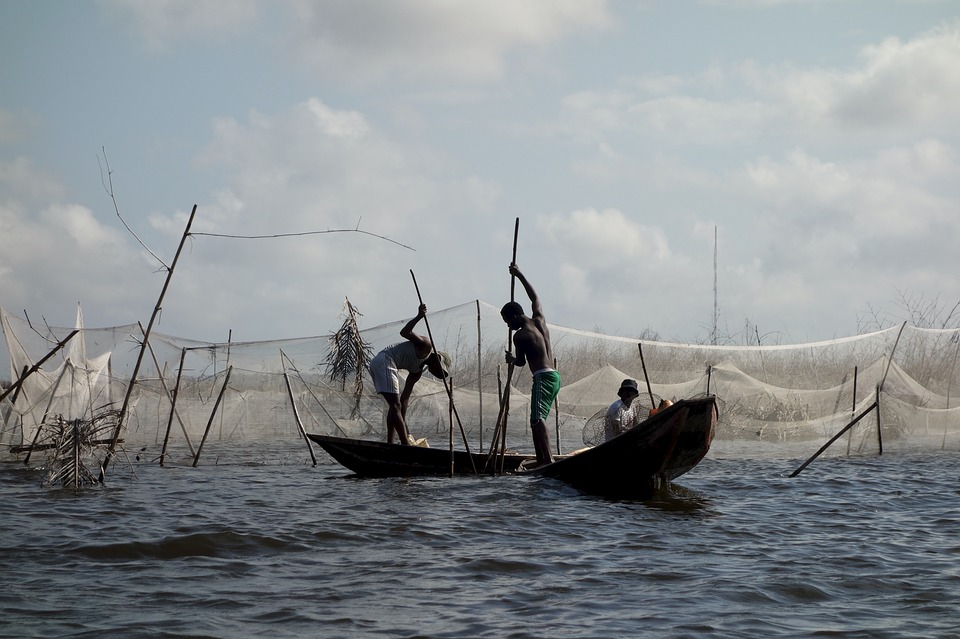
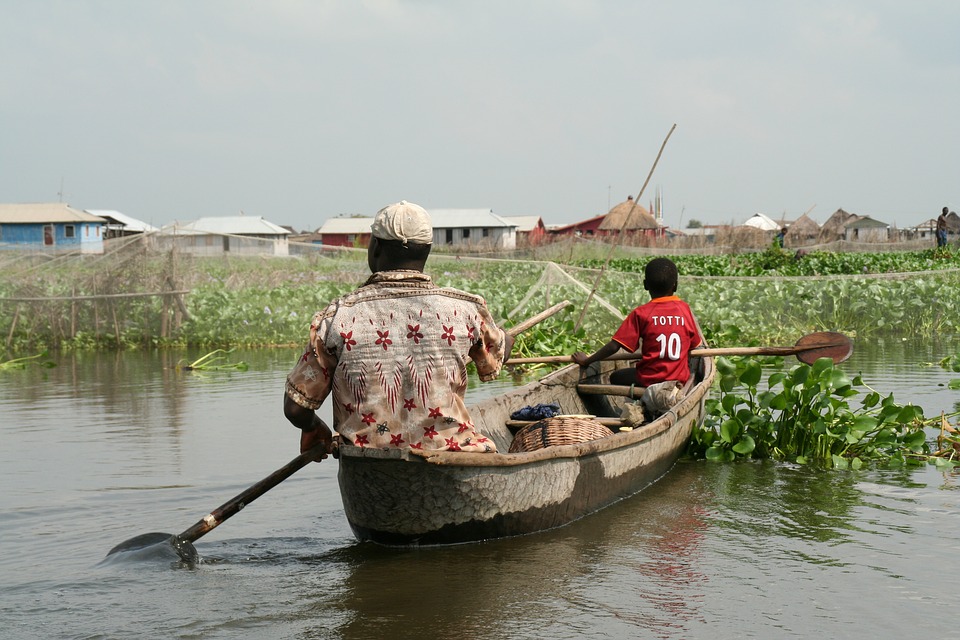
Benin is a country with diverse geography and topography. It is characterized by coastal plains in the south, plateaus in the centre, and savannahs in the north. The country is also home to several rivers, including the Niger River, which flows through the northern part of Benin. The diverse geography of Benin contributes to its natural beauty and provides a habitat for a wide range of plant and animal species.
In terms of climate, Benin experiences a tropical climate with two distinct seasons: a wet season and a dry season. The wet season typically lasts from April to October and is characterized by heavy rainfall. The dry season, on the other hand, lasts from November to March and is characterized by hot and dry weather. The climate of Benin is influenced by the country’s proximity to the equator and the Atlantic Ocean, which helps to moderate temperatures.
History of Benin: From Ancient Kingdoms to Modern Independence
The history of Benin is rich and complex, with a legacy that dates back centuries. The region that is now known as Benin was once home to several powerful kingdoms, including the Kingdom of Dahomey. The Kingdom of Dahomey was one of the most powerful and influential kingdoms in West Africa during the 17th to 19th centuries. It was known for its military prowess and its involvement in the transatlantic slave trade.
The legacy of the Kingdom of Dahomey can still be seen today in the form of the Royal Palaces of Abomey, which were the seat of power for the kingdom. These palaces are a UNESCO World Heritage Site and serve as a reminder of Benin’s rich history. In the late 19th century, Benin came under French colonial rule and was known as French Dahomey. It remained a French colony until it gained independence in 1960.
Politics and Government of Benin: A Democratic Republic in Africa
Benin is a democratic republic with a multi-party political system. The country’s political system is based on a constitution that was adopted in 1990, following a period of military rule. The president is the head of state and is elected by popular vote for a maximum of two five-year terms. The president appoints the prime minister, who is responsible for running the government.
Benin has a vibrant democracy with regular elections and a strong civil society. The country has a number of political parties that compete in elections, including the Union Progressiste, which is currently in power. Elections in Benin are generally considered to be free and fair, although there have been some concerns about the fairness of recent elections.
Economy of Benin: Agriculture, Trade, and Development
The economy of Benin is primarily based on agriculture, which accounts for a significant portion of the country’s GDP and employs a large percentage of the population. The main agricultural products in Benin include cotton, corn, yams, and palm oil. In recent years, there has been a push to diversify the economy and promote other sectors such as tourism and manufacturing.
Benin is also involved in international trade, with its main trading partners being Nigeria, China, and India. The country has made efforts to improve its trade infrastructure and attract foreign investment. Additionally, Benin has implemented several development initiatives aimed at reducing poverty and improving the standard of living for its citizens.
People and Society of Benin: A Multicultural Nation with Unique Traditions
Benin is a multicultural nation with a diverse population. The country is home to over 60 different ethnic groups, each with its own unique traditions and customs. The largest ethnic group in Benin is the Fon people, who are concentrated in the southern part of the country. Other major ethnic groups include the Yoruba, Bariba, and Dendi.
The people of Benin are known for their hospitality and warmth. They take great pride in their cultural heritage and are eager to share it with visitors. Traditional music and dance play an important role in Beninese culture, with various festivals and ceremonies held throughout the year to celebrate these traditions.
Languages and Education in Benin: A Linguistically Diverse and Educated Population
Benin is a linguistically diverse country with over 50 different languages spoken. The official language of Benin is French, which is widely spoken in urban areas and used in government and education. However, many Beninese people also speak their native languages, such as Fon, Yoruba, and Bariba.
Education is highly valued in Benin, and the country has made significant progress in improving its education system. Primary education is compulsory and free, and the government has implemented initiatives to increase access to education for all children. However, there are still challenges in terms of quality and access to education, particularly in rural areas.
Religion and Beliefs in Benin: A Blend of Traditional and Modern Faiths
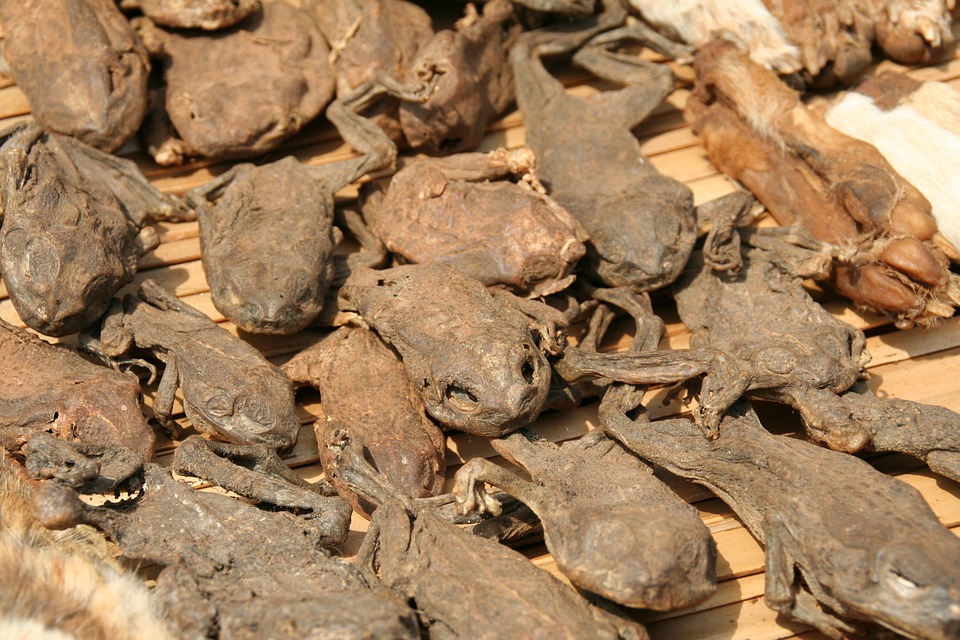
Religion plays a significant role in the lives of the people of Benin. The country is known for its blend of traditional and modern faiths. Traditional beliefs and practices, such as voodoo, are still widely followed in Benin. Voodoo is an indigenous religion that originated in West Africa and is practised by a significant portion of the population.
In addition to traditional beliefs, Benin is also home to various modern religions, including Christianity and Islam. Christianity is the largest religion in Benin, with Catholicism being the dominant denomination. Islam is also practised by a significant minority of the population, particularly in the northern part of the country.
Tourism in Benin: Exploring the Land of Voodoo, Music, and Festivals
Benin has a growing tourism industry that attracts visitors from around the world. The country offers a unique cultural experience with its vibrant music and dance traditions, as well as its rich history and heritage. One of the main attractions for tourists is voodoo, which is deeply rooted in Beninese culture. Visitors can learn about voodoo practices and rituals through guided tours and visits to voodoo temples.
Benin is also known for its music festivals, which showcase traditional music and dance from different ethnic groups. These festivals provide an opportunity for visitors to immerse themselves in the vibrant culture of Benin and experience the country’s rich musical heritage.
Challenges and Opportunities in Benin: Moving Forward as a Developing Nation
Benin faces several challenges as it strives for economic and social development. One of the main challenges is poverty, with a significant portion of the population living below the poverty line. The government has implemented various initiatives to reduce poverty and improve the standard of living for its citizens, but there is still much work to be done.
Another challenge is the lack of infrastructure, particularly in rural areas. Access to basic services such as healthcare and education is limited in many parts of the country. The government is working to improve infrastructure and provide better access to these services, but progress has been slow.
Despite these challenges, Benin has many opportunities for growth and progress. The country has a young and dynamic population that can contribute to economic development. Additionally, Benin’s rich cultural heritage and natural beauty make it an attractive destination for tourism. By harnessing these opportunities and addressing its challenges, Benin can move forward as a developing nation and improve the lives of its people.
Population Density of Benin
Benin, officially known as the Republic of Benin, is a country located in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso and Niger to the north, and the Atlantic Ocean to the south. With a population of approximately 12 million...
History of Benin
The Kingdom of Benin, located in present-day Nigeria, was one of the most powerful and influential states in African history. It existed from the 13th century until the late 19th century and played a significant role in shaping the political, economic, and cultural...
Terrain and Topography of Benin: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Benin, located in West Africa, is a country with a diverse and varied terrain. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north, and the Atlantic Ocean to the south. The country’s geography is characterized by mountains,...
Climate Zones of Benin: Different Climate Regions Of Benin
Benin, located in West Africa, is a country known for its diverse geography and climate. From the coastal areas to the north, Benin experiences a range of climate zones that have a significant impact on its agriculture and economy. Understanding these climate zones is...
Political Boundaries of Benin: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Benin, officially known as the Republic of Benin, is a country located in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso and Niger to the north, and the Atlantic Ocean to the south. Understanding the political boundaries of Benin is...
Natural Resources of Benin: Where Natural Resources are Located in Benin
Benin, located in West Africa, is a country known for its rich and diverse natural resources. With a total land area of approximately 112,622 square kilometers, Benin is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso and Niger to the north, and the...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Benin: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Benin
Benin, located in West Africa, is a country with a rich cultural and historical heritage. From its ancient kingdoms to its vibrant traditions, Benin offers a wealth of experiences for those interested in exploring and learning about its past. By visiting the...
Discovering the Hidden Gems of Benin: A Journey Through West Africa’s Best-Kept Secret
Benin, located in West Africa, is a country that often goes unnoticed by travelers. However, those who do venture to this hidden gem are rewarded with a rich cultural heritage, stunning natural wonders, beautiful beaches, a thriving art scene, delicious cuisine, and...