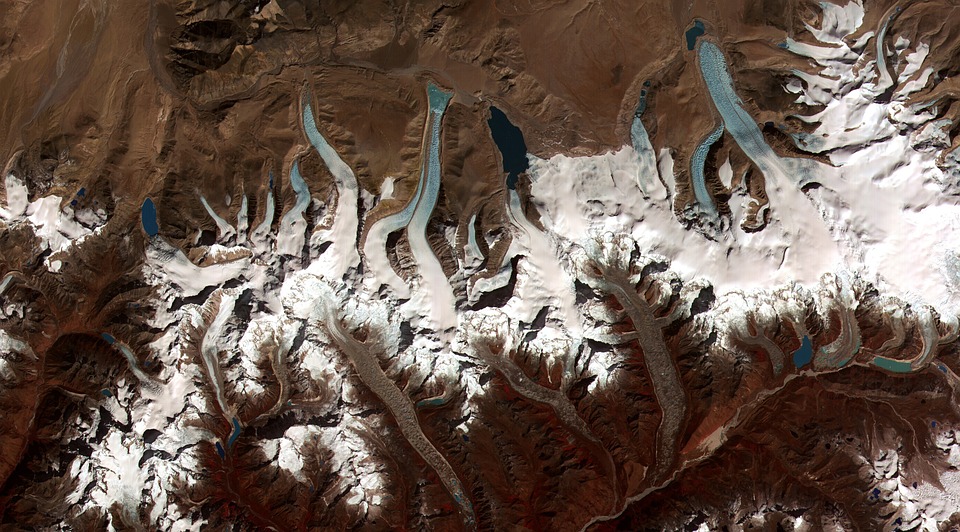
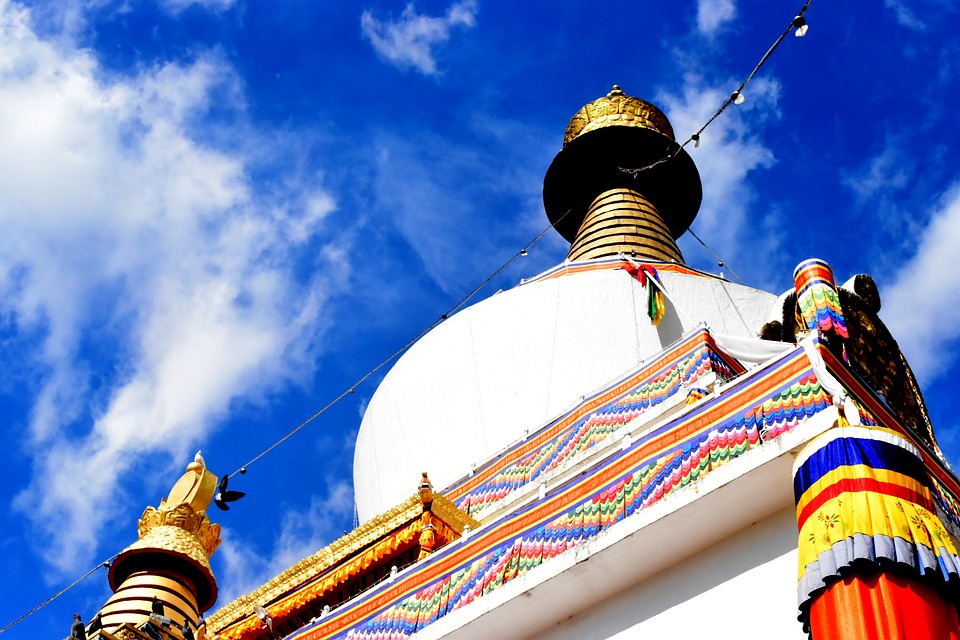
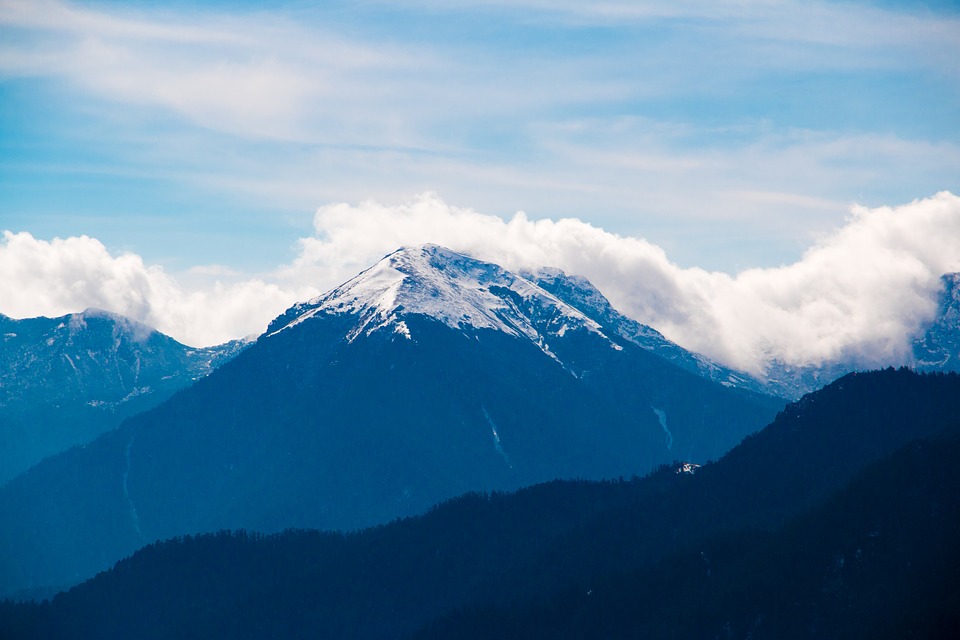
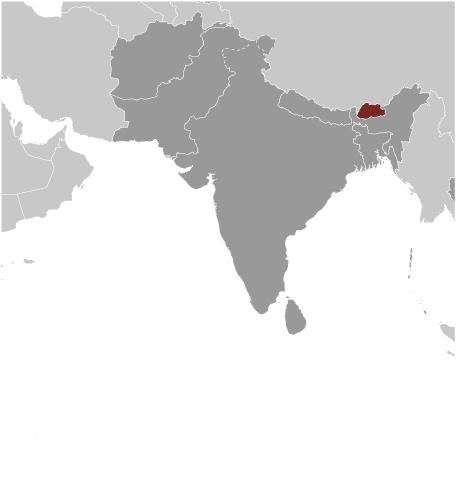
Bhutan
(Druk-Yul (Kingdom of Bhutan))
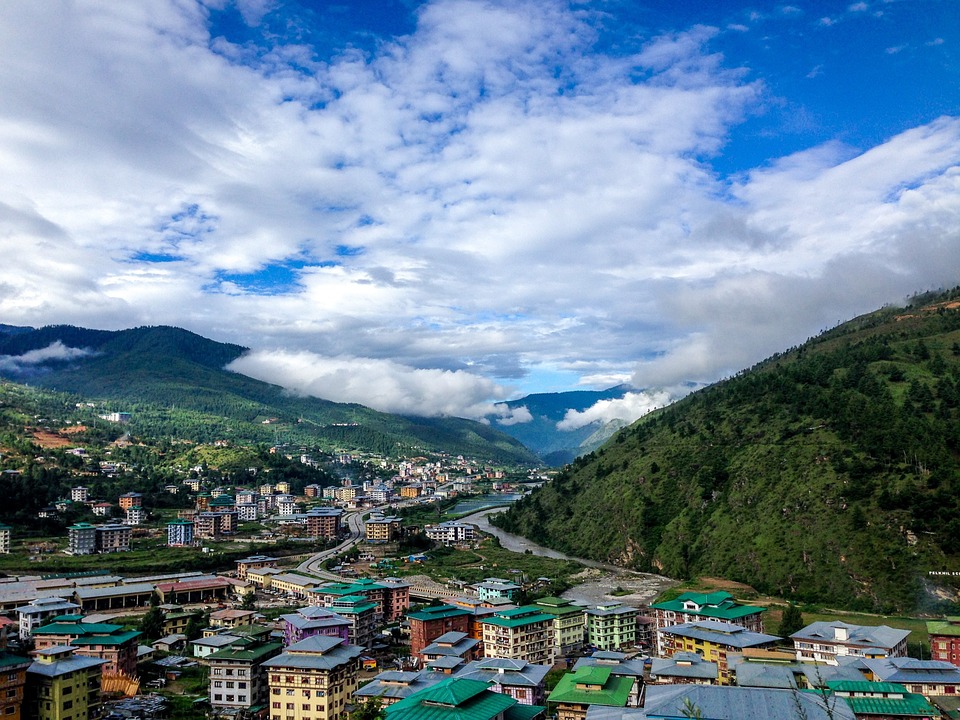
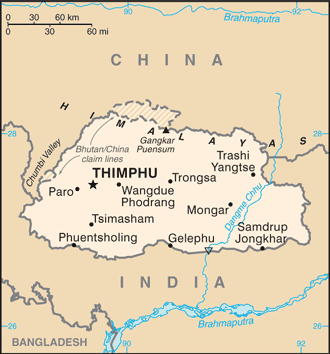
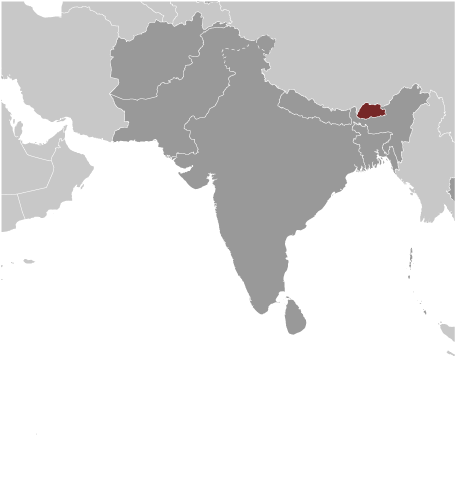




Capital of Bhutan : Thimphu
Population (Estimated July 2012): 716,896
Area: 38,394 km2 or 14,824 mi2
Currency: Ngultrum (BTN)
Official Language: Dzongkha (a Tibetan dialect)
Political Information: Constitutional Monarchy
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 75% of the population are Lamaistic Buddhist and 25% Hindu)
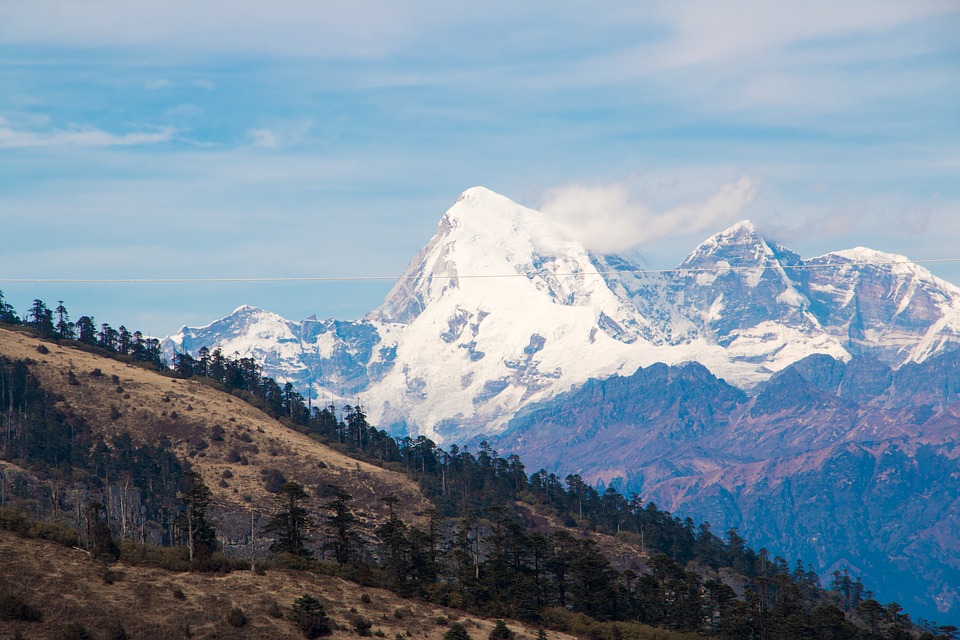
Highest Mountain: Gangkar Puensum at 7,570m or 24840ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $1.83 billion (US$) or £1.098 billion(GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $4.284 billion (US$) or £2.57 billion(GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $6,000 (US$) or £3,600 (GBP)
Time Zone: +6:00
Counties/Provinces/States: (districts or dzongkhag) Bumthang, Chhukha, Chirang, Daga, Gasa, Geylegphug, Ha, Lhuntshi, Mongar, Paro, Pemagatsel, Punakha, Samchi, Samdrup Jongkhar, Shemgang, Tashigang, Tashi Yangtse, Thimphu, Tongsa, Wangdi Phodrang
Leaders:King Jigme Khesar Namgyel WANGCHUCK (since 14 December 2006); Prime Minister Tshering TOBGAY (since 27 July 2013)
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Nestled in the eastern Himalayas, the small kingdom of Bhutan is a hidden gem waiting to be discovered. Known for its unique culture and approach to development, Bhutan has captivated the world with its commitment to Gross National Happiness (GNH) and sustainable practices. In this article, we will delve into the rich cultural heritage, breathtaking natural beauty, and unique governance system of Bhutan. We will also explore the significance of Buddhism in Bhutanese society and the country’s thriving economy. Join us on this journey to uncover the wonders of Bhutan.
Discovering Bhutan’s Rich Cultural Heritage and Traditions
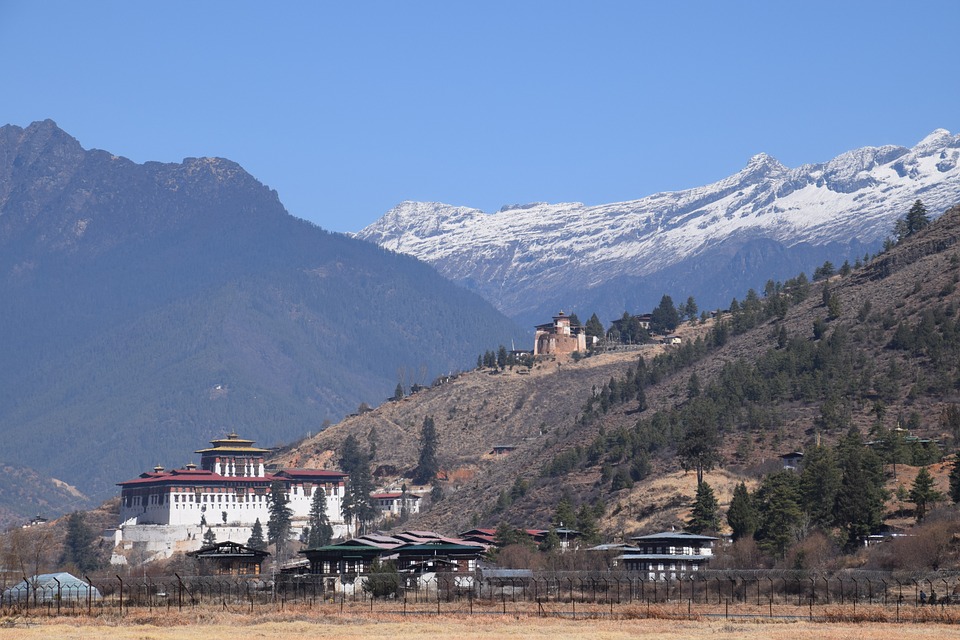
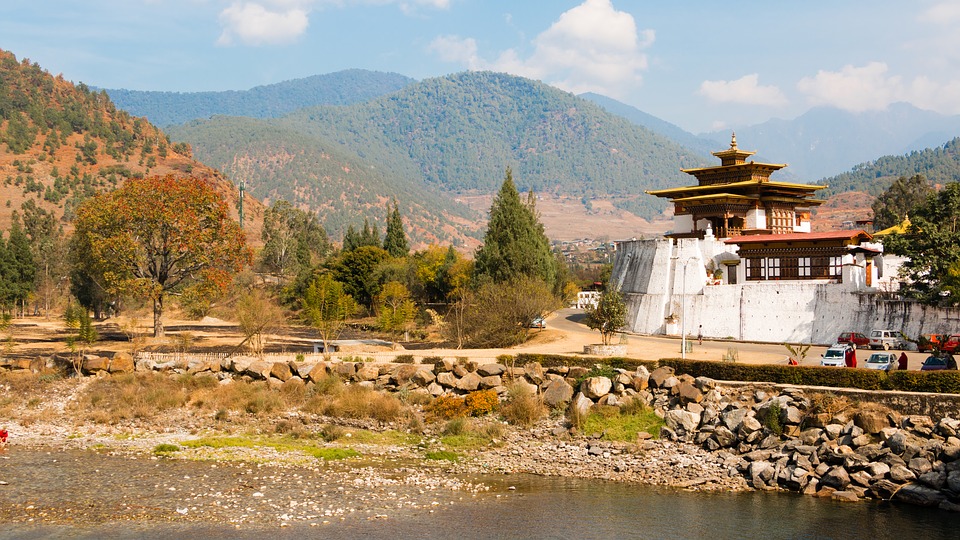
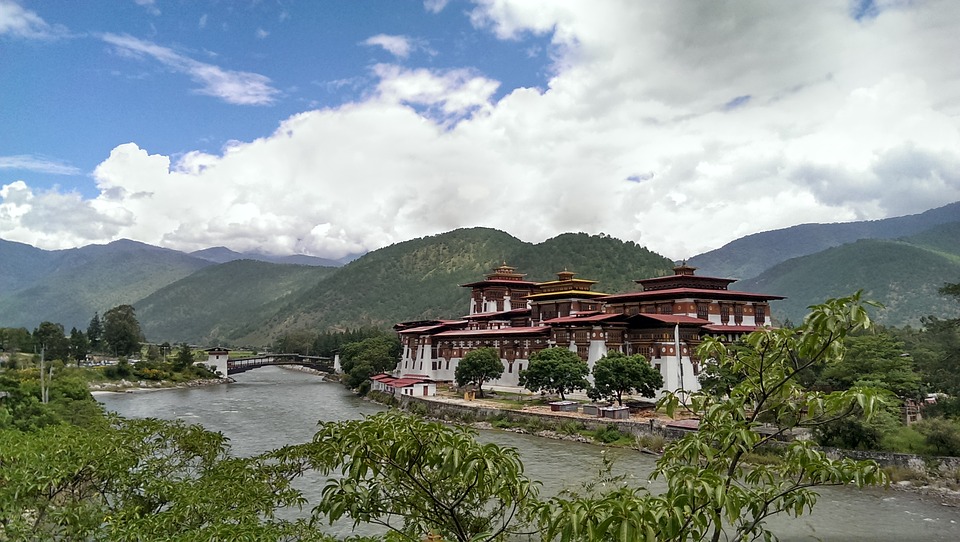
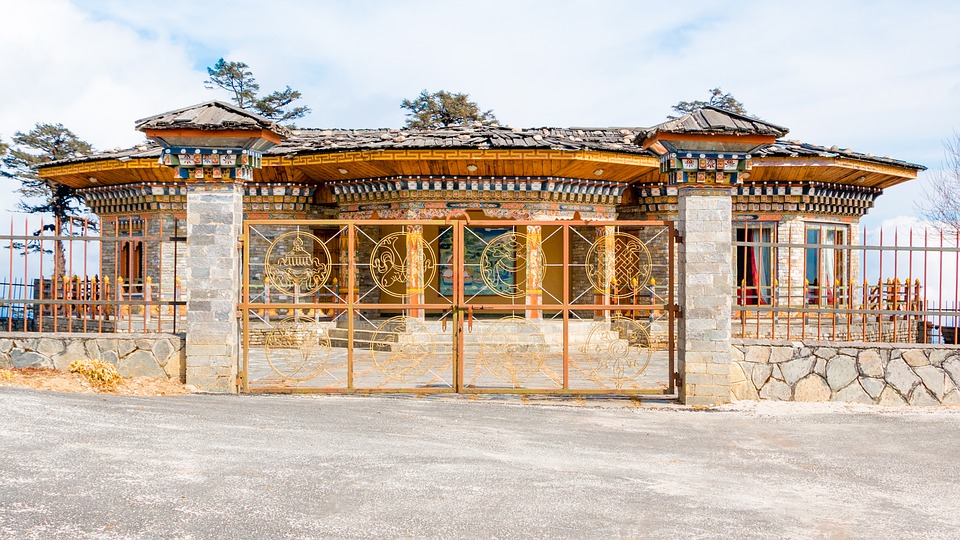
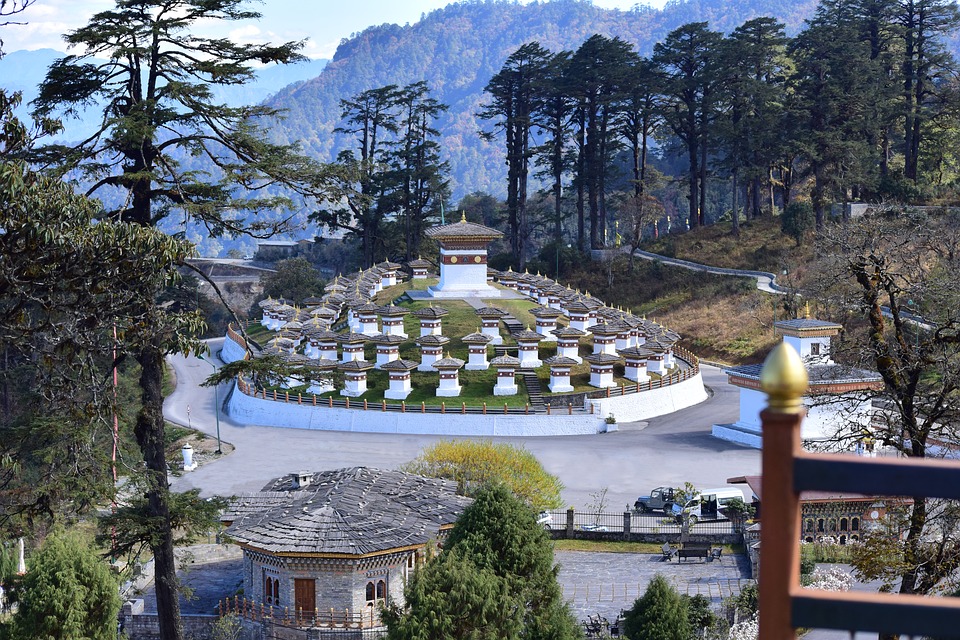
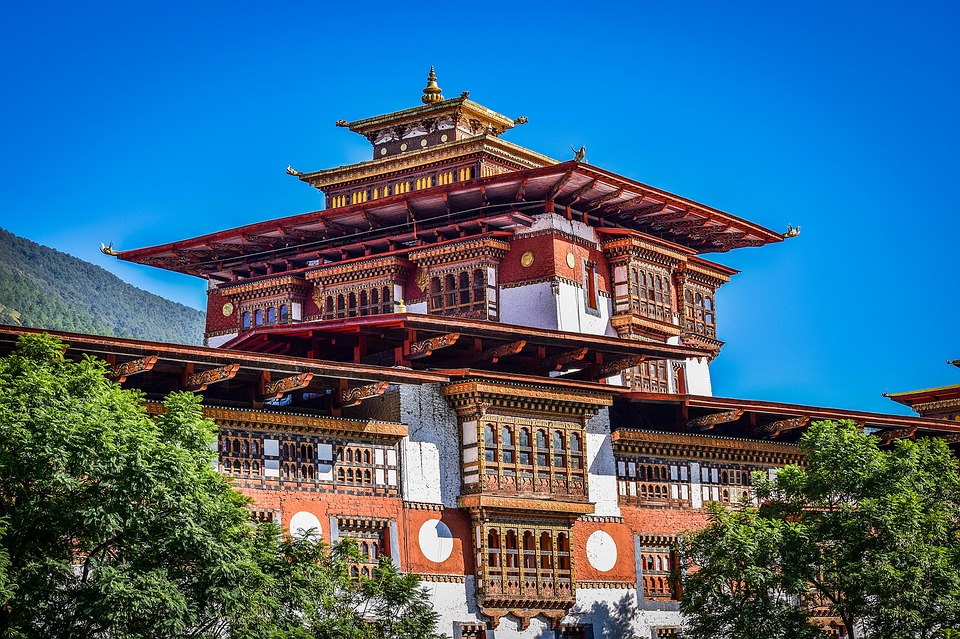
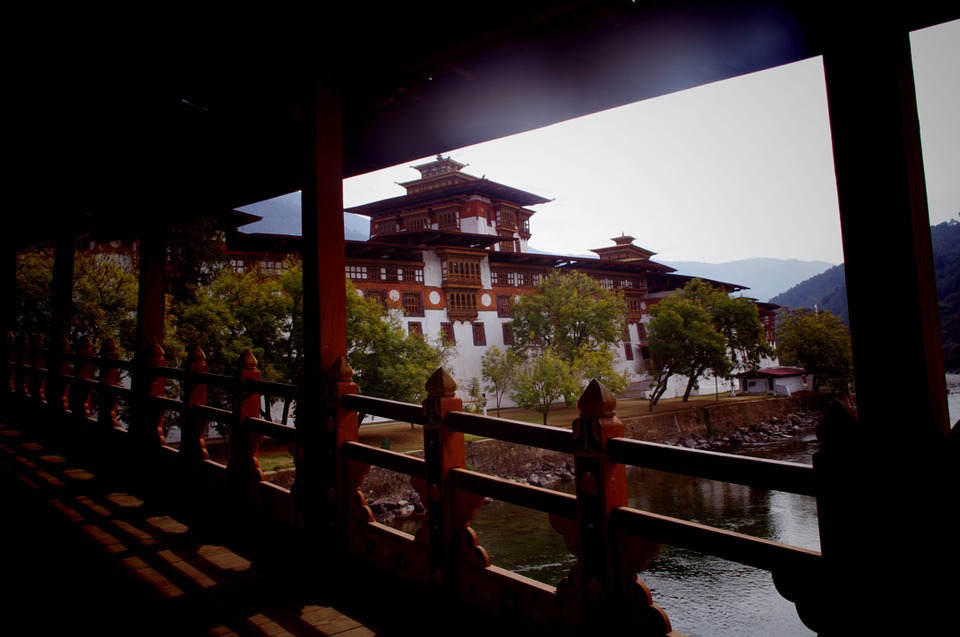
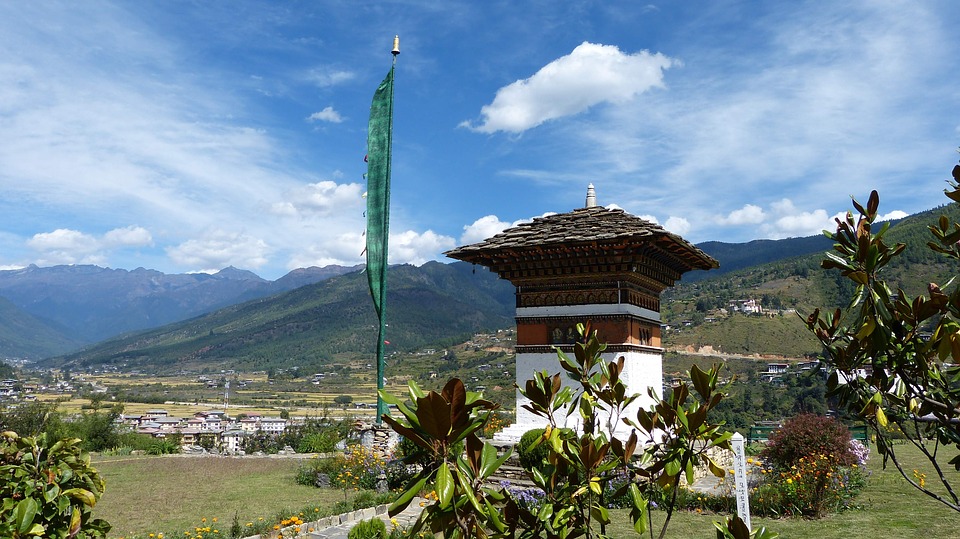
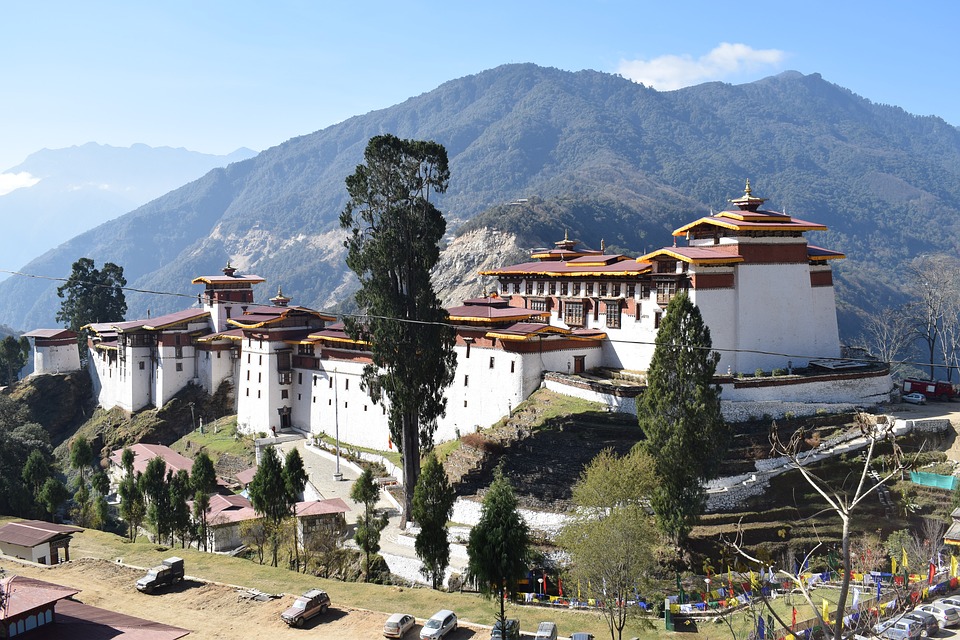
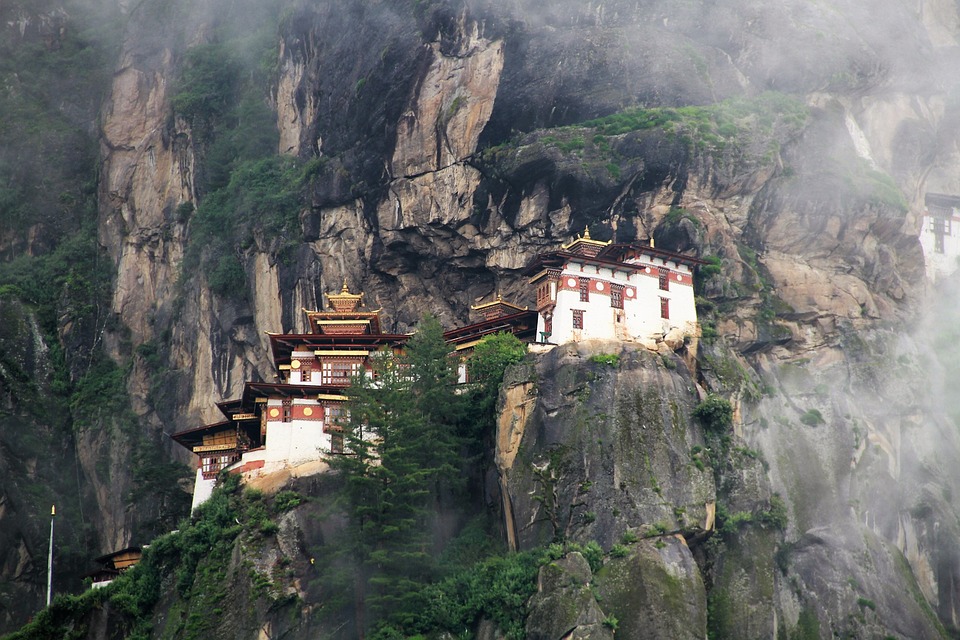
Bhutanese architecture and art are a testament to the country’s rich cultural heritage. Traditional Bhutanese architecture is characterized by intricate woodwork, vibrant colours, and unique designs. The dzongs, or fortress-monasteries, are prime examples of this architectural style. These majestic structures serve as administrative centres as well as religious institutions. The art of Bhutan is equally captivating, with intricate thangka paintings depicting Buddhist deities and mandalas.
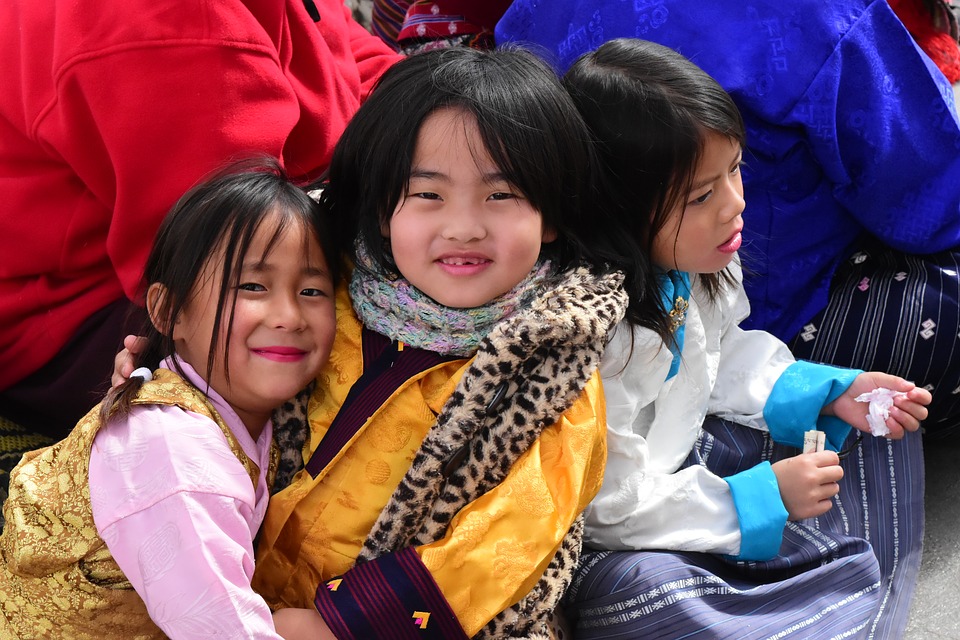
Traditional dress and customs play a significant role in Bhutanese society. The national dress for men is called the gho, a knee-length robe tied at the waist with a belt. Women wear the kira, a long-sleeved dress accompanied by a jacket called a tego. These traditional garments are not only worn on special occasions but also as everyday attire. Bhutanese customs are deeply rooted in Buddhist traditions and emphasize respect for elders, community harmony, and environmental stewardship.
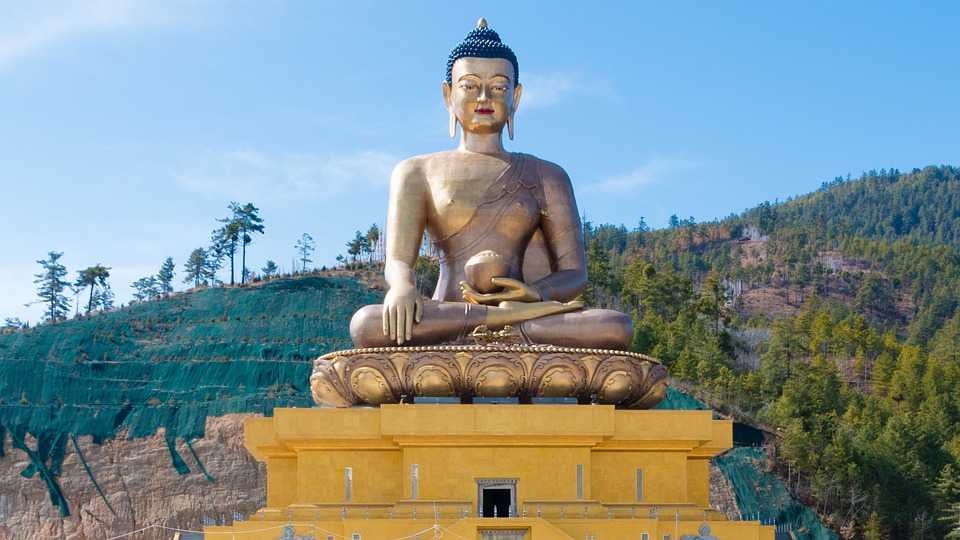
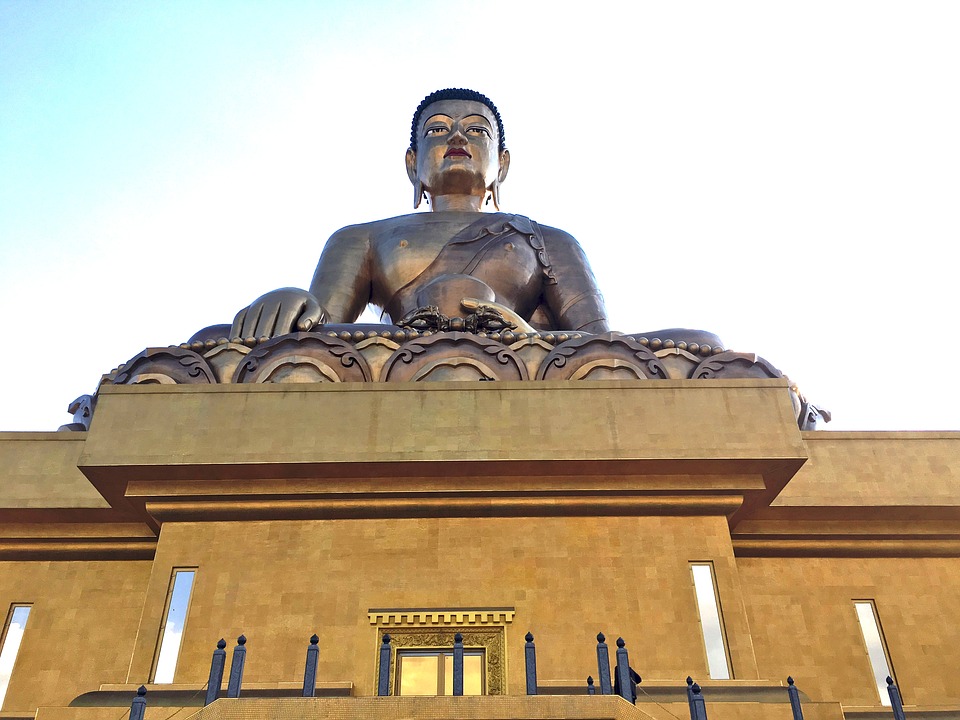
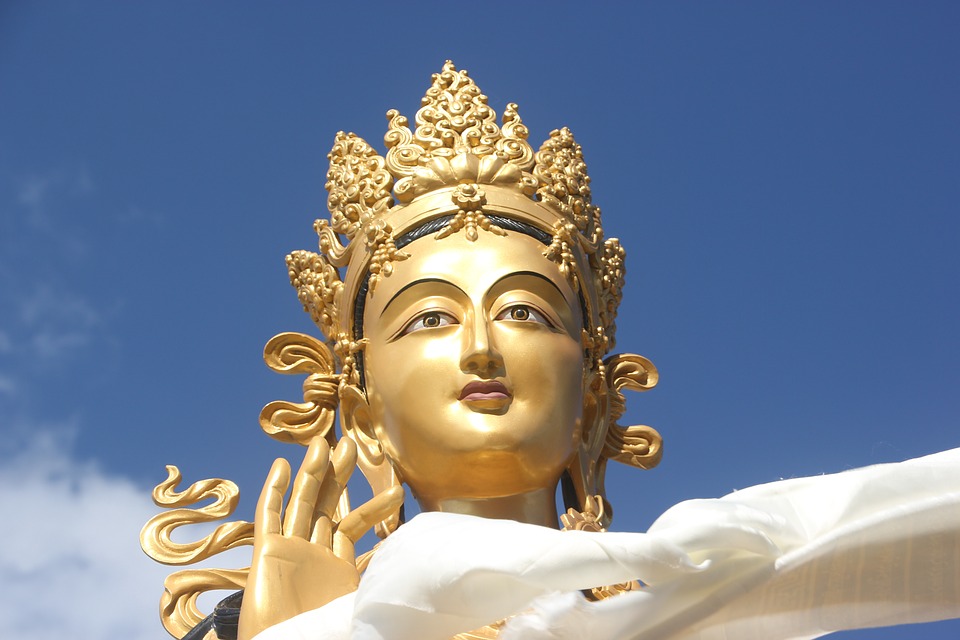
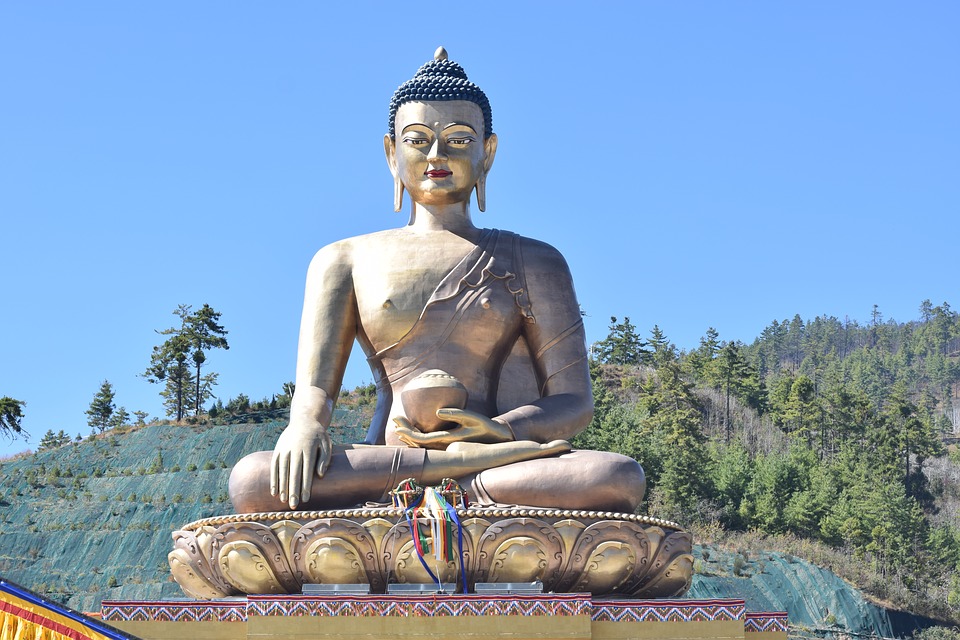
Buddhism holds a central place in Bhutanese society and is deeply intertwined with everyday life. The majority of Bhutanese people follow Vajrayana Buddhism, which emphasizes the importance of compassion and mindfulness. Monasteries and monks play a vital role in preserving and promoting Buddhist teachings. The monastic education system provides spiritual guidance and education to young Bhutanese, ensuring the continuation of Buddhist traditions for generations to come.
Exploring Bhutan’s Breathtaking Natural Beauty
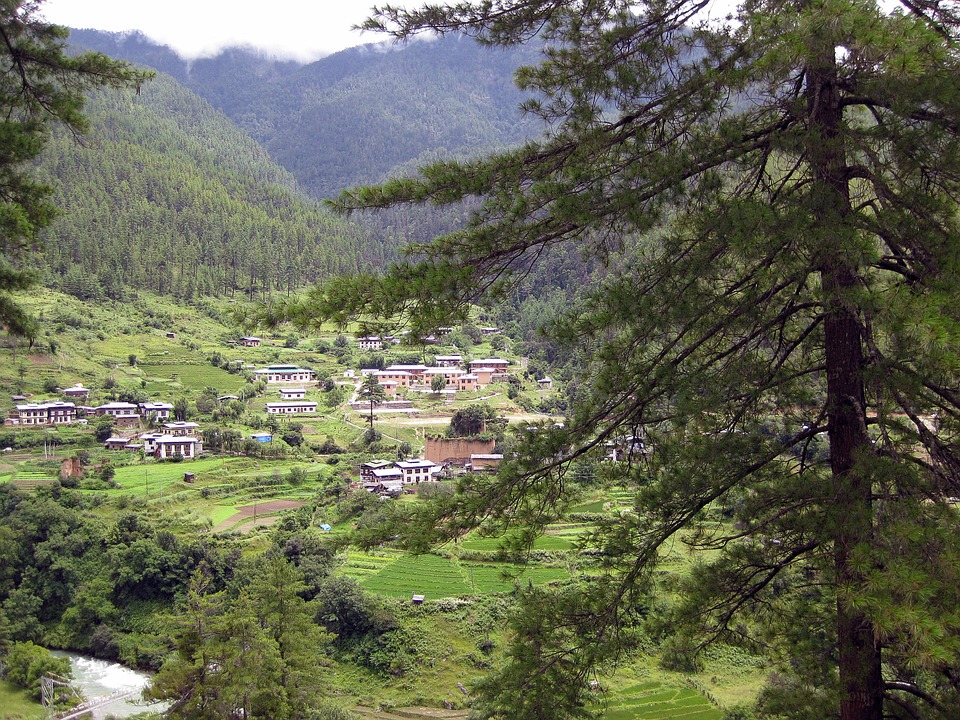
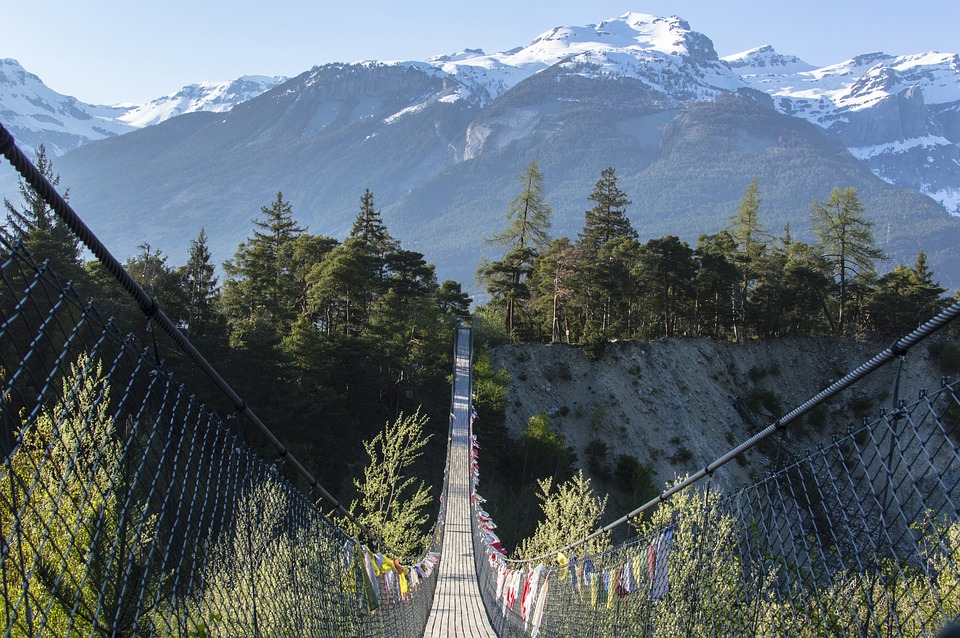
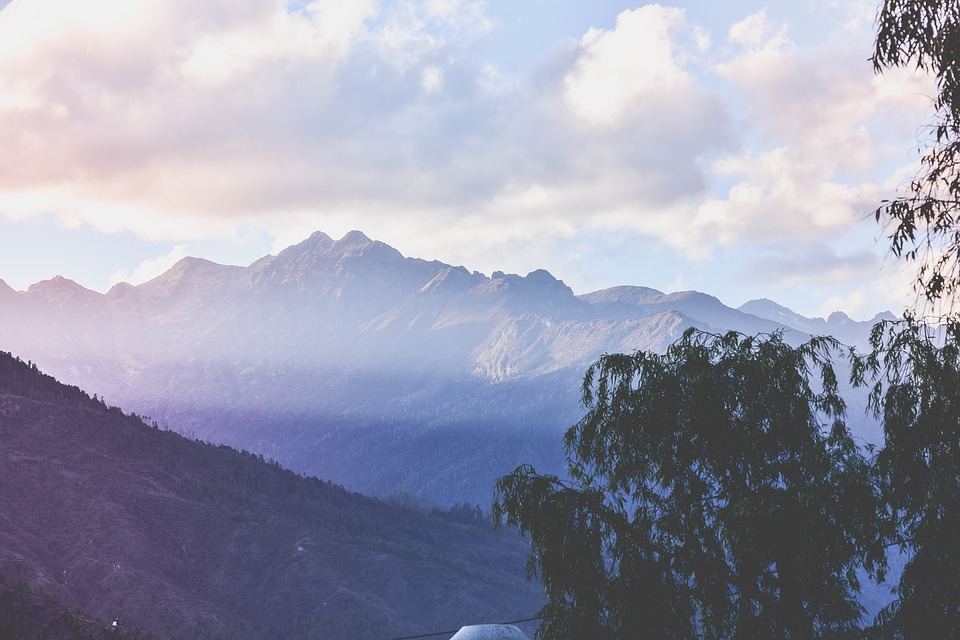
Bhutan’s natural beauty is unparalleled, thanks to its location in the Himalayan mountain range. The country is home to several peaks over 7,000 meters, including Gangkhar Puensum, the highest unclimbed mountain in the world. The snow-capped mountains provide a stunning backdrop to the lush valleys and forests that cover much of Bhutan’s landscape.
Bhutan is also known for its national parks and wildlife sanctuaries, which are havens for rare and endangered species. The Royal Manas National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage site, is home to Bengal tigers, Asian elephants, and the elusive golden langur. The Jigme Dorji National Park is another biodiversity hotspot, with over 300 species of birds and several species of mammals.
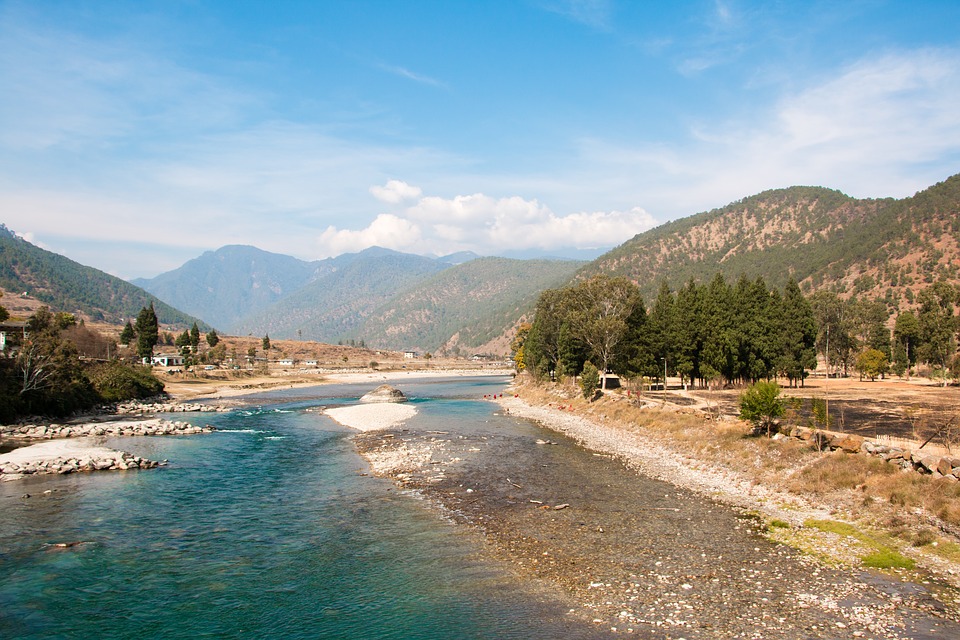
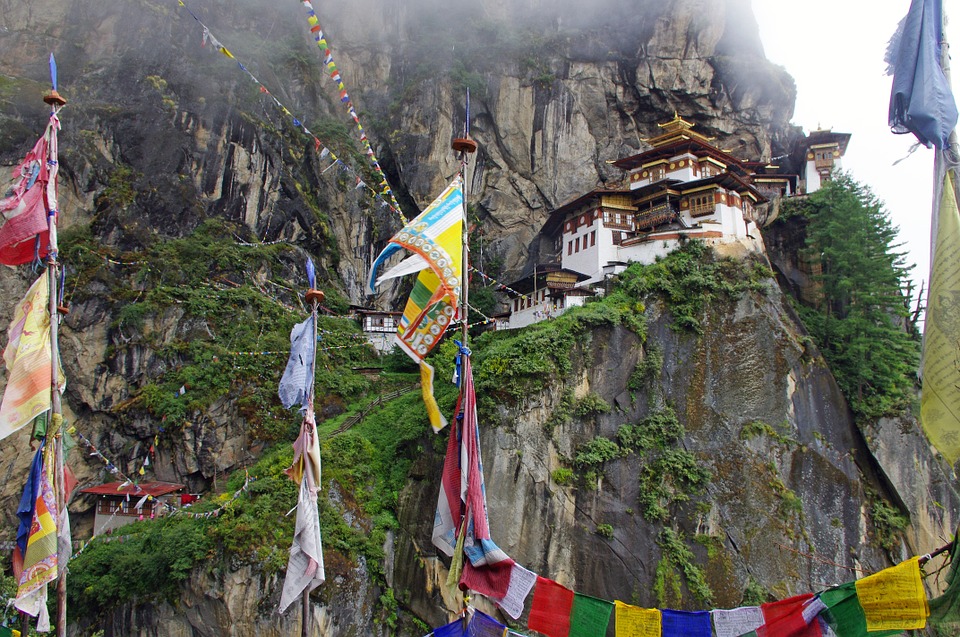
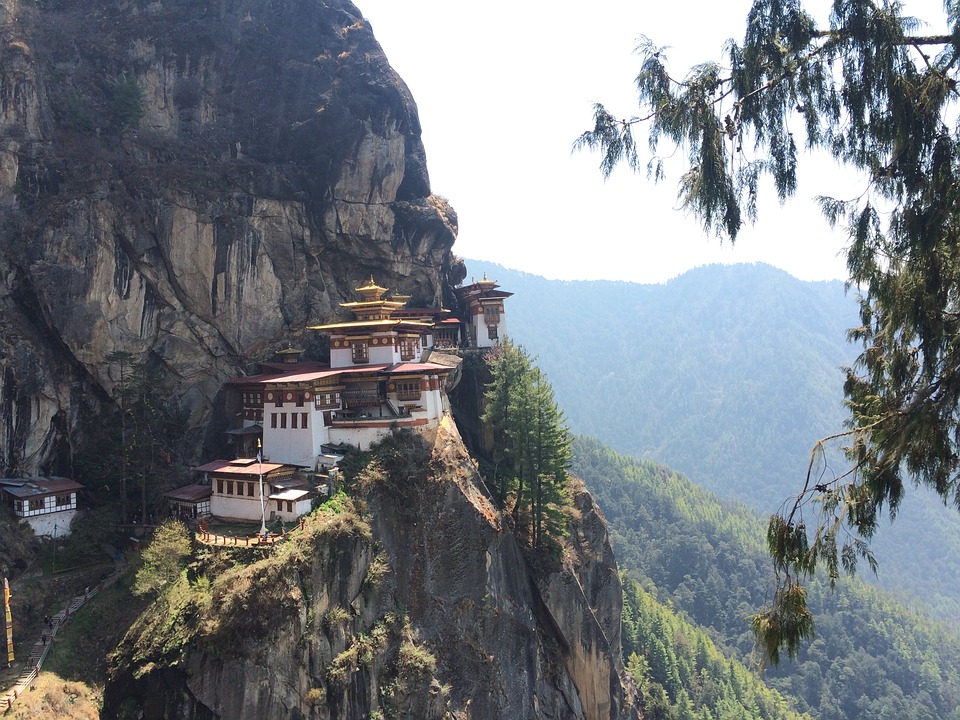
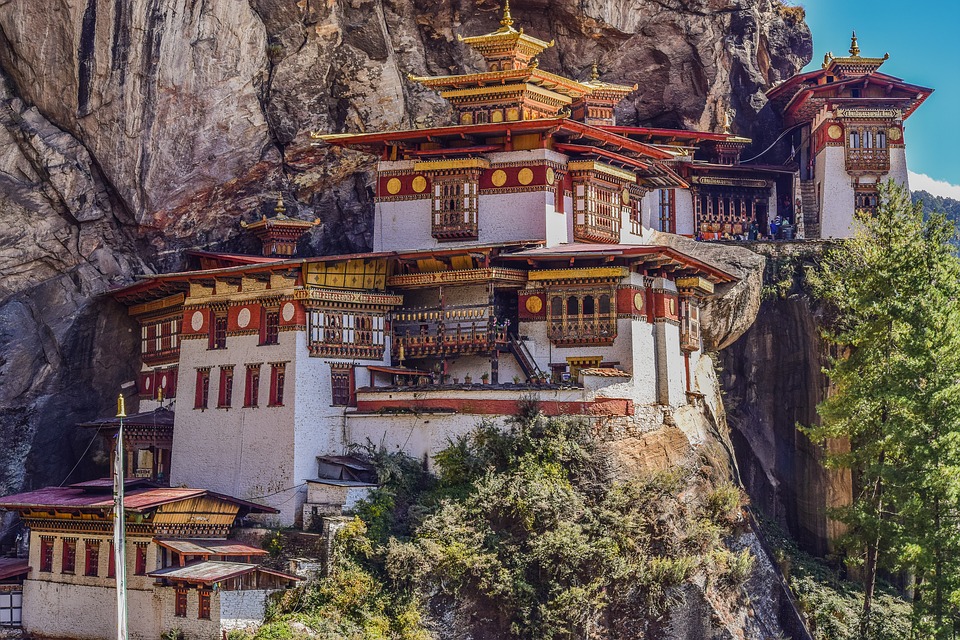
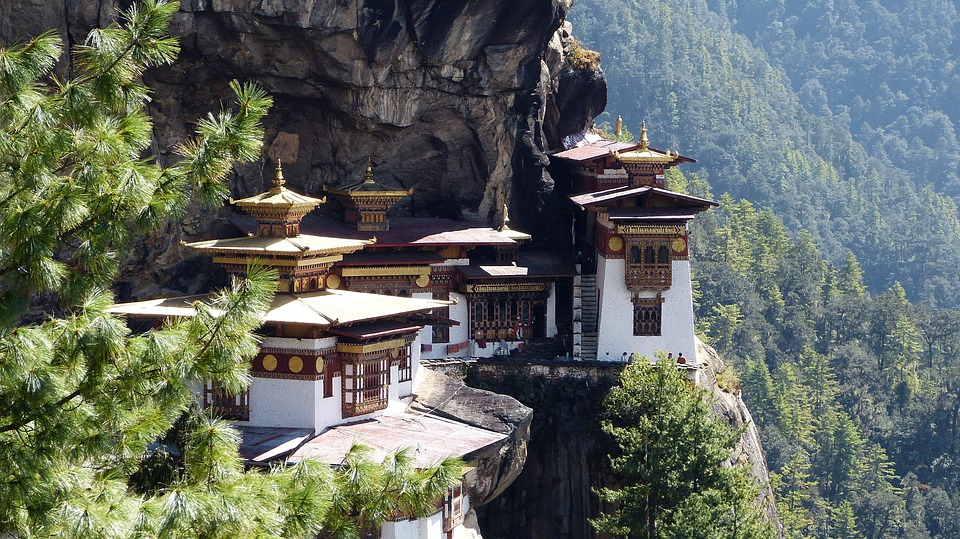
Glaciers, lakes, and rivers further enhance Bhutan’s natural beauty. Glacial lakes such as the famous Paro Taktsang (Tiger’s Nest) are not only visually stunning but also hold religious significance for Bhutanese people. The rivers that flow through Bhutan provide water for irrigation, hydropower generation, and recreational activities such as white-water rafting.
Bhutan’s Unique Approach to Gross National Happiness
Gross National Happiness (GNH) is a concept that was coined by the fourth king of Bhutan, Jigme Singye Wangchuck. It measures the progress of a nation based on the happiness and well-being of its citizens rather than solely on economic indicators. GNH recognizes that material wealth alone does not guarantee happiness and emphasizes the importance of spiritual, social, and environmental factors.
The four pillars of GNH are sustainable development, preservation and promotion of cultural values, conservation of the environment, and good governance. Bhutan has implemented various policies and programs to promote happiness and well-being. For example, the government has prioritized education and healthcare, ensuring that all Bhutanese have access to quality services. Additionally, Bhutan has embraced sustainable practices such as organic farming and renewable energy to protect the environment.
Understanding Bhutan’s Political System and Governance
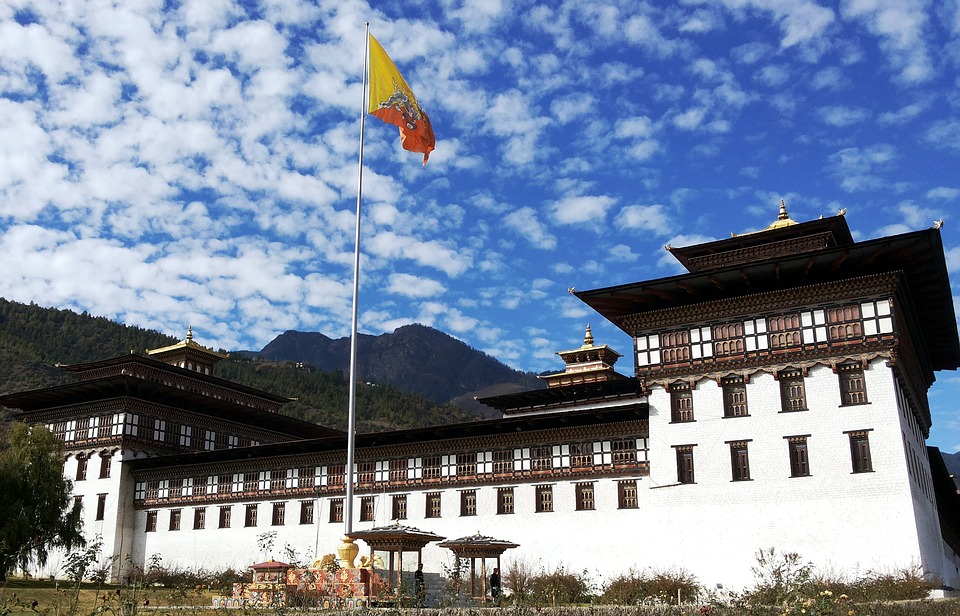
Bhutan is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary democracy. The king is the head of state, while the prime minister is the head of government. The king’s role is crucial in maintaining stability and unity in the country. The monarchs of Bhutan have played a significant role in shaping the nation’s development and preserving its unique culture.
The parliament consists of two houses: the National Council and the National Assembly. The National Council is made up of elected representatives from each district, while the National Assembly consists of members elected by the people. The government’s policies and decisions are guided by the principles of GNH, ensuring that the well-being of the citizens remains at the forefront.
Democracy and citizen participation are highly valued in Bhutan. The country transitioned to a democratic system in 2008, with the first parliamentary elections held that year. Since then, Bhutan has made significant progress in strengthening democratic institutions and promoting citizen engagement. The government encourages active participation through public consultations, town hall meetings, and other forms of engagement.
Bhutan’s Thriving Economy: A Model for Sustainable Development
Bhutan’s economy has experienced steady growth over the years, thanks to its emphasis on sustainable and equitable development. The government has implemented policies that prioritize social welfare, environmental conservation, and cultural preservation. This unique approach has garnered international recognition and admiration.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) play a crucial role in Bhutan’s economy. The government has implemented various initiatives to support SMEs, including providing access to finance, training, and market opportunities. These efforts have helped create employment opportunities and promote economic diversification.
Investment in education and healthcare is another key aspect of Bhutan’s economic development. The government has made significant investments in these sectors to ensure that all Bhutanese have access to quality education and healthcare services. This focus on human capital development has contributed to the overall well-being and happiness of the population.
The Significance of Buddhism in Bhutanese Society
Buddhism has a long and rich history in Bhutan, dating back to the 8th century. The arrival of Guru Rinpoche, also known as Padmasambhava, marked the beginning of Buddhism in Bhutan. Since then, Buddhism has played a central role in shaping Bhutanese culture, values, and way of life.
Monasteries and monks are an integral part of Bhutanese society. Monasteries serve as centres of learning, meditation, and religious practice. They also play a vital role in preserving Bhutan’s cultural heritage through the preservation of ancient texts, rituals, and traditions. Monks are highly respected and revered in Bhutanese society, and many young boys choose to enter monastic life to receive spiritual guidance and education.
Spiritual values such as compassion, mindfulness, and non-violence are deeply ingrained in Bhutanese society. These values guide the behaviour and interactions of individuals, fostering a sense of harmony and peace within communities. Buddhism also provides a framework for ethical decision-making and personal growth, contributing to the overall well-being of the population.
Festivals and Celebrations: An Insight into Bhutan’s Vibrant Culture
Bhutan is known for its vibrant festivals and celebrations, which provide a glimpse into the country’s rich cultural heritage. The major festivals, known as tshechus, are held annually in different districts across Bhutan. These festivals are a time for communities to come together, celebrate, and receive blessings from the Buddhist deities.
Traditional dances and music are an integral part of Bhutanese festivals. The mask dances, known as cham, are performed by monks and laypeople dressed in elaborate costumes. These dances depict stories from Buddhist mythology and serve as a form of spiritual practice. The music accompanying the dances is often played on traditional instruments such as the dramyin (a stringed instrument) and the gyaling (a wind instrument).
Festivals also provide an opportunity for social cohesion and community bonding. People from different villages and districts come together to participate in the festivities, exchange greetings, and strengthen social ties. The sense of community and belonging is palpable during these celebrations, creating a joyful and inclusive atmosphere.
Bhutan’s Education System: Prioritizing Quality and Access
Bhutan places a high priority on education and has made significant progress in ensuring universal access to education. The government has implemented policies to ensure that all Bhutanese children have access to quality education, regardless of their socio-economic background or geographical location.
The education system in Bhutan emphasizes holistic development and values-based education. In addition to academic subjects, students are taught life skills, ethical values, and environmental awareness. This holistic approach aims to nurture well-rounded individuals who are not only academically competent but also socially responsible.
Teacher training is a key focus of Bhutan’s education system. The government invests in the professional development of teachers to ensure that they have the necessary skills and knowledge to deliver quality education. Teacher training institutes provide pre-service and in-service training programs to equip teachers with the latest pedagogical techniques and subject knowledge.
Curriculum development is another area of focus in Bhutan’s education system. The government regularly reviews and updates the curriculum to ensure its relevance and alignment with national goals. The curriculum incorporates both traditional Bhutanese values and global perspectives, preparing students for the challenges and opportunities of the modern world.
Preserving Bhutan’s Environment: A Commitment to Conservation and Sustainability
Bhutan’s commitment to environmental conservation is deeply rooted in its culture and values. The country is often referred to as the “last Shangri-La” due to its pristine natural environment. Bhutan recognizes the importance of preserving its biodiversity, natural resources, and ecosystems for the well-being of its people and future generations.
Policies and programs aimed at preserving biodiversity and natural resources are a key focus of Bhutan’s environmental conservation efforts. The government has established a network of protected areas, including national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biological corridors. These protected areas serve as habitats for endangered species and contribute to the overall ecological balance.
Sustainable tourism is another area of focus in Bhutan’s environmental conservation efforts. The government has implemented a “high-value, low-impact” tourism policy, which aims to minimize the negative impacts of tourism on the environment and culture. Tourists are required to pay a daily fee, known as the Sustainable Development Fee, which goes towards funding conservation initiatives and community development projects.
Bhutan also promotes eco-friendly practices such as organic farming and renewable energy. The government encourages farmers to adopt organic farming methods to reduce the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Bhutan is also investing in renewable energy sources such as hydropower and solar energy to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels.
In conclusion, Bhutan is a country that offers a unique blend of rich cultural heritage, breathtaking natural beauty, and sustainable development practices. Its commitment to Gross National Happiness, preservation of cultural values, conservation of the environment, and good governance sets it apart from other nations. Bhutan’s emphasis on education, healthcare, and small and medium-sized enterprises contributes to its thriving economy. Buddhism plays a central role in Bhutanese society, shaping its values, traditions, and way of life. Festivals and celebrations provide a glimpse into Bhutan’s vibrant culture and sense of community. The education system prioritizes quality and access, ensuring that all Bhutanese have the opportunity to receive a holistic education. Bhutan’s commitment to environmental conservation and sustainability is evident in its policies and programs. As we conclude this journey through the wonders of Bhutan, let us reflect on the lessons we can learn from this small kingdom and support its efforts towards a happier and more sustainable future.
Political Boundaries of Bhutan: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Bhutan, also known as the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country located in the Eastern Himalayas. It is bordered by China to the north and India to the south, east, and west. With an area of approximately 38,394 square kilometers, Bhutan is a relatively small...
Terrain and Topography of Bhutan: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Bhutan, a small landlocked country nestled in the eastern Himalayas, is known for its stunning and diverse terrain. From towering mountains to deep valleys and lush plains, Bhutan’s landscape is a testament to the country’s natural beauty. Understanding...
History of Bhutan
Introduction to Bhutan’s Rich Cultural Heritage Bhutan, a small landlocked country nestled in the eastern Himalayas, is known for its rich cultural heritage. The country’s unique culture and traditions have been preserved for centuries, making it a...
Climate Zones of Bhutan: Different Climate Regions Of Bhutan
Bhutan, a small landlocked country nestled in the eastern Himalayas, is known for its stunning landscapes, rich biodiversity, and unique culture. The country’s geography is diverse, ranging from subtropical plains in the south to alpine valleys and snow-capped...
Population Density of Bhutan
Bhutan, a small landlocked country nestled in the eastern Himalayas, is known for its stunning landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and commitment to Gross National Happiness. With a population of approximately 750,000 people, Bhutan has a relatively low population...
Natural Resources of Bhutan: Where Natural Resources are Located in Bhutan
Bhutan, a small landlocked country nestled in the eastern Himalayas, is known for its rich natural resources and pristine environment. With an area of approximately 38,394 square kilometers, Bhutan is blessed with diverse geographical features, including towering...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Bhutan: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Bhutan
Introduction Bhutan, a small landlocked country nestled in the Eastern Himalayas, is known for its rich cultural heritage and historical significance. This article will explore some of the most iconic and important sites in Bhutan, highlighting their significance in...
Discovering the Hidden Gems of Bhutan: A Journey Through the Land of the Thunder Dragon
Nestled in the eastern Himalayas, Bhutan is a small landlocked country known for its breathtaking landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and unique approach to measuring progress. Bhutan is often referred to as the Land of the Thunder Dragon due to its dramatic...