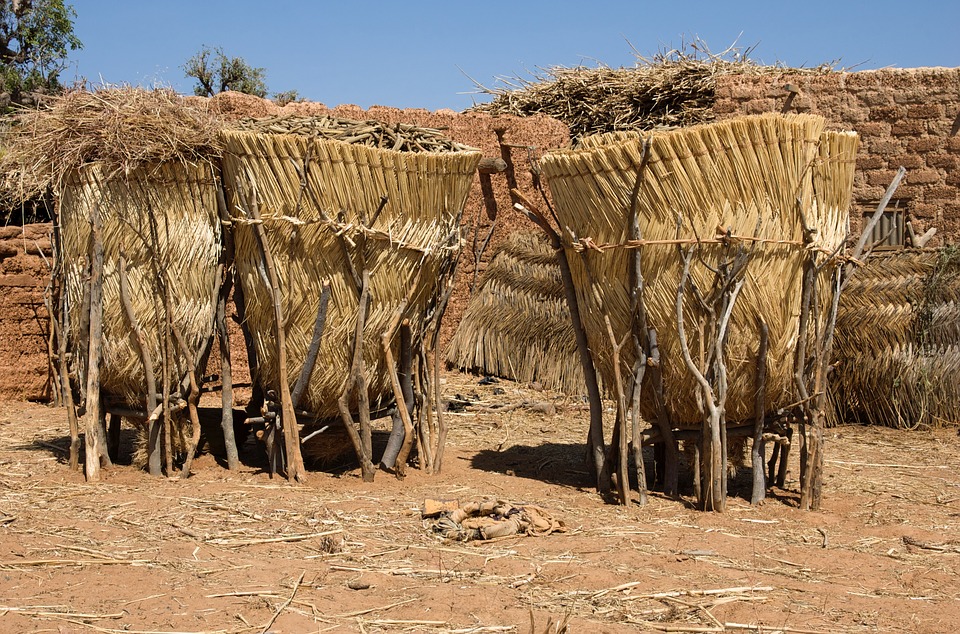
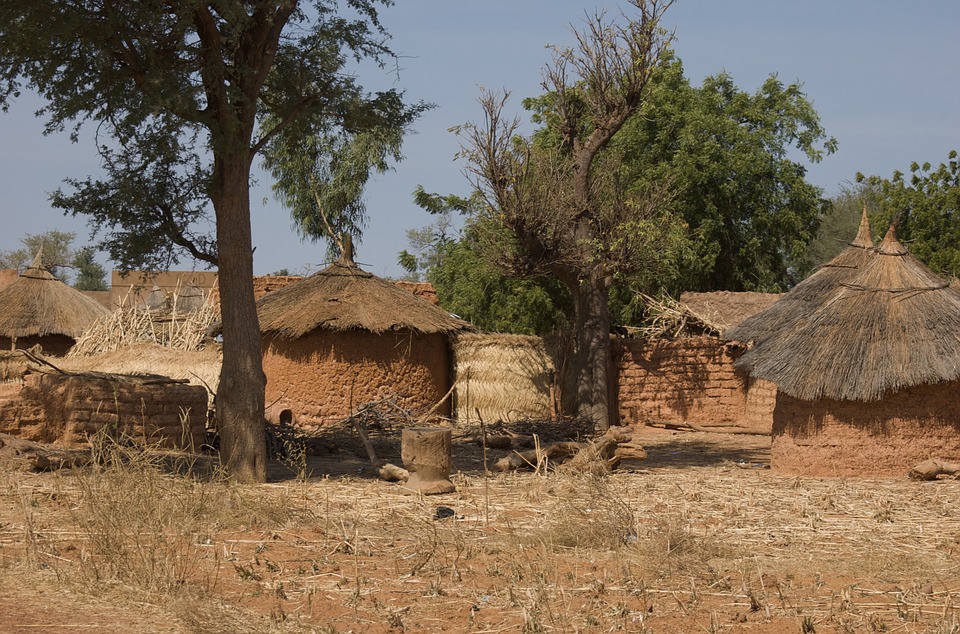
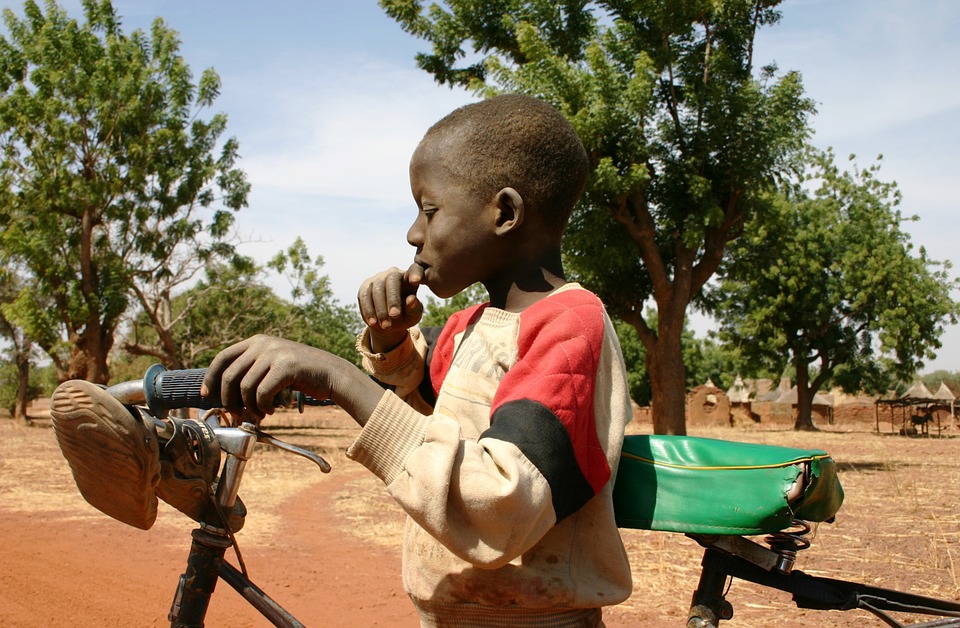
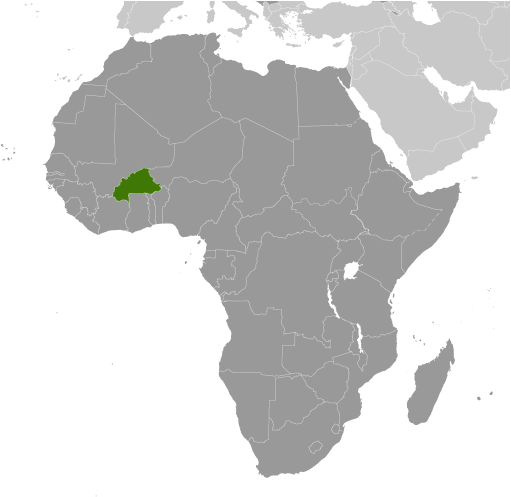
Burkina Faso

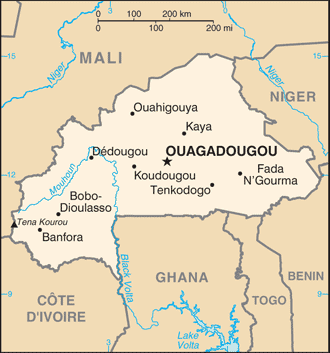




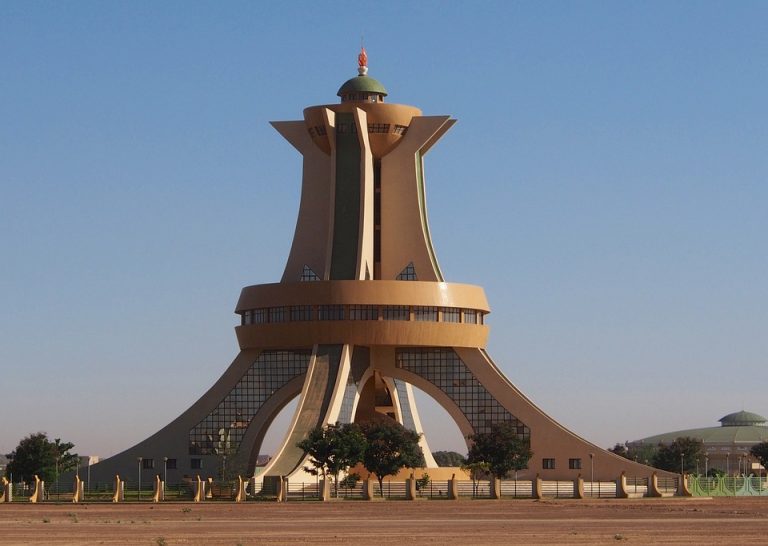
bb.Capital of Burkina Faso : Ouagadougou
Population (Estimated July 2012): 17,275,115
Area: 270,764 km2 or 104,543 mi2
Currency: CFA franc (CFAF)
Official Language: French
Political Information: Semi-Presidential Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 60.5% of the population are Muslim, 19% are Catholic, 15.3% are Animist, 4.2% are Protestant, and 1% have other or no religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Tena Kourou at 749m or 2,457ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $10.1 billion (US$) or £6.06 billion (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $21.83 billion (US$) or £13,098 billion(GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $1,500 (US$) or £900 (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): GMT
Counties/Provinces/States: 13 regions; Boucle du Mouhoun, Cascades, Centre, Centre-Est, Centre-Nord, Centre-Ouest, Centre-Sud, Est, Hauts-Bassins, Nord, Plateau-Central, Sahel, Sud-Ouest
Leaders: President Roch Marc Christian KABORE (since 29 December 2015) with Prime Minister Paul Kaba THIEBA (since 6 January 2016)
Additional: Gained independence from France on the 5th of August 1960.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Burkina Faso, officially known as the Republic of Burkina Faso, is a landlocked country located in West Africa. It is bordered by six countries: Mali to the north, Niger to the east, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest. With an area of approximately 274,200 square kilometres, Burkina Faso is one of the largest countries in West Africa.
The population of Burkina Faso is estimated to be around 20 million people. The country is home to more than 60 different ethnic groups, each with its own language and cultural traditions. The official language is French, which was inherited from its colonial past. However, many Burkinabé also speak their native languages such as Mossi, Fulfulde, and Dioula.
History of Burkina Faso: From Pre-Colonial Times to Independence
Burkina Faso has a rich history that dates back to pre-colonial times. The region was once home to several powerful kingdoms and empires, including the Mossi Kingdoms and the Gurma Kingdoms. These kingdoms were known for their advanced agricultural practices and trade networks.
In the late 19th century, Burkina Faso came under French colonial rule. The French established control over the region through military conquest and imposed their own administrative systems and economic policies. However, the Burkinabé people resisted French colonization through various means, including armed uprisings and political movements.
Burkina Faso gained independence from France on August 5, 1960. The country was initially led by President Maurice Yaméogo, who ruled for over a decade before being overthrown in a military coup in 1966. Since then, Burkina Faso has experienced several periods of political instability, including multiple coups and changes in leadership. However, in recent years, the country has made significant progress towards democratic governance.
Geography and Climate of Burkina Faso: A Country of Diverse Landscapes
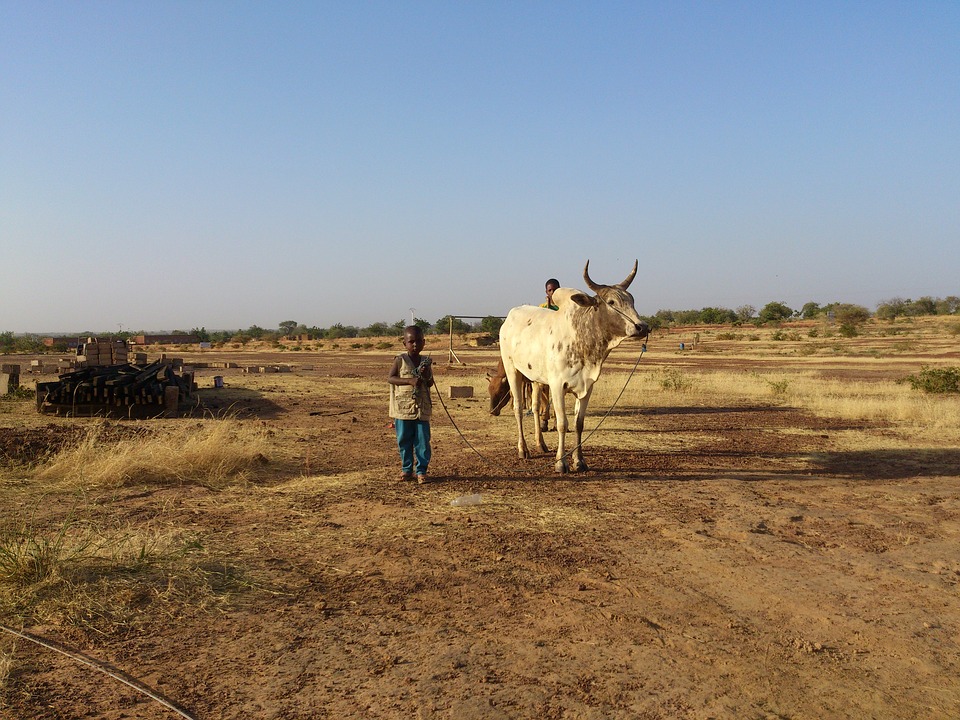
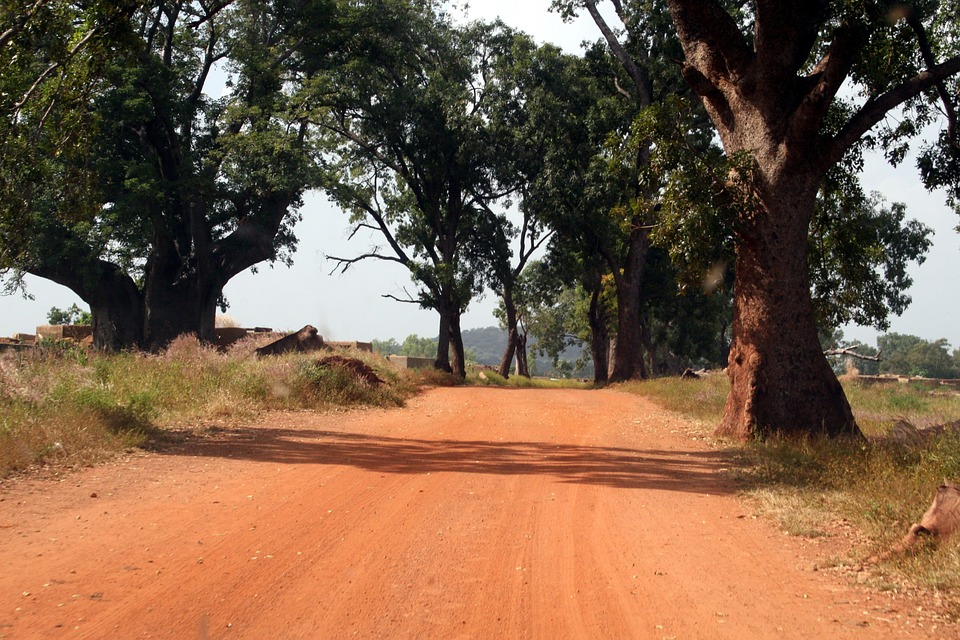
Burkina Faso is a landlocked country with a diverse range of landscapes. The country is characterized by vast savannahs, rolling hills, and the Sahel region in the north. The Sahel is a semi-arid region that stretches across several countries in West Africa and is known for its dry climate and sparse vegetation.
Burkina Faso can be divided into several distinct regions, each with its own unique geography. The northern part of the country is dominated by the Sahel region, while the central and southern regions are characterized by savannahs and agricultural land. The southwest region is home to the Comoé National Park, which is known for its diverse wildlife and natural beauty.
The climate in Burkina Faso is generally hot and dry, with distinct wet and dry seasons. The country experiences a rainy season from May to October, during which most of the annual rainfall occurs. The dry season, from November to April, is characterized by high temperatures and little to no rainfall.
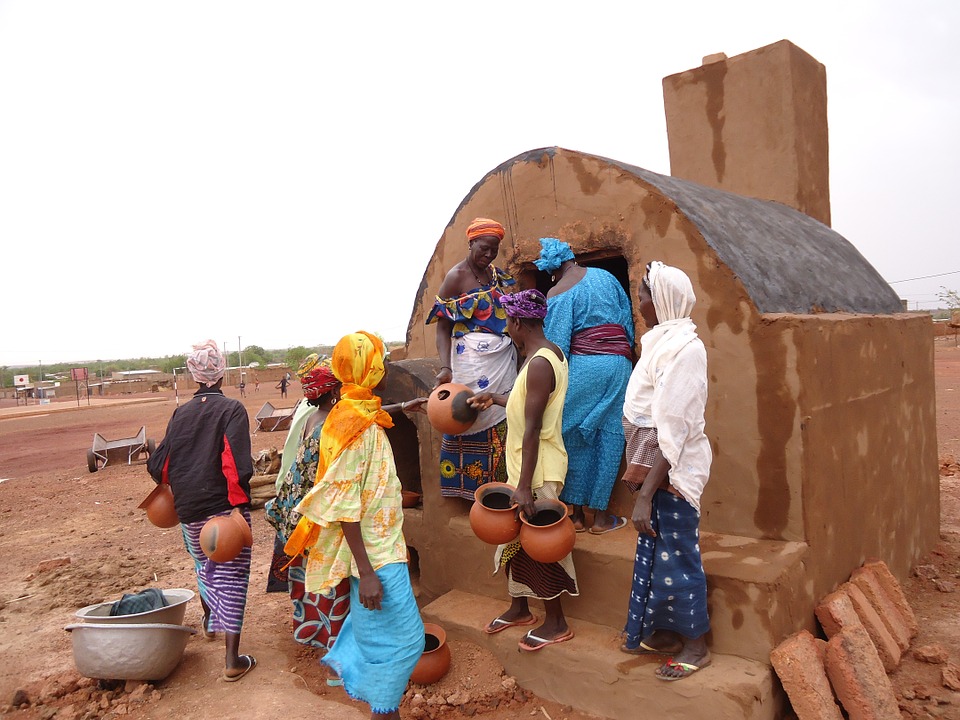
Culture and Traditions of Burkina Faso: Rich and Vibrant Heritage
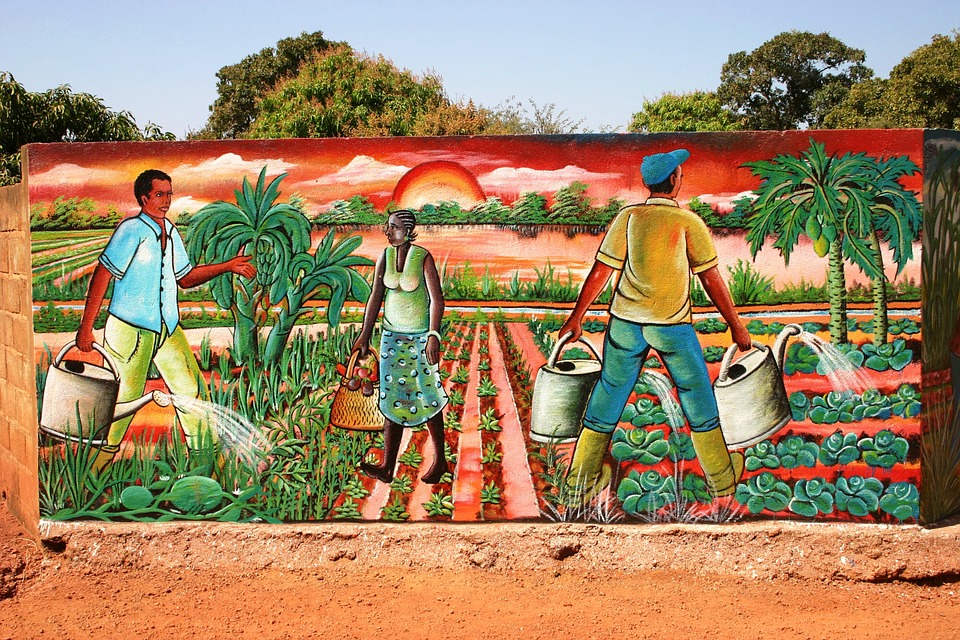
Burkina Faso has a rich cultural heritage that is reflected in its music, dance, art, and traditional practices. The country is known for its vibrant music scene, with traditional instruments such as the balafon (a type of xylophone) and the kora (a string instrument) being widely used. Traditional dance forms such as the bwa and the gourounsi are also an important part of Burkinabé culture.
Artistic expression is highly valued in Burkina Faso, with many talented artists creating beautiful sculptures, paintings, and textiles. The country is also known for its vibrant festivals and celebrations, which showcase the diversity and richness of Burkinabé culture. The FESPACO (Pan-African Film and Television Festival of Ouagadougou) is one of the largest film festivals in Africa and attracts filmmakers from all over the continent.
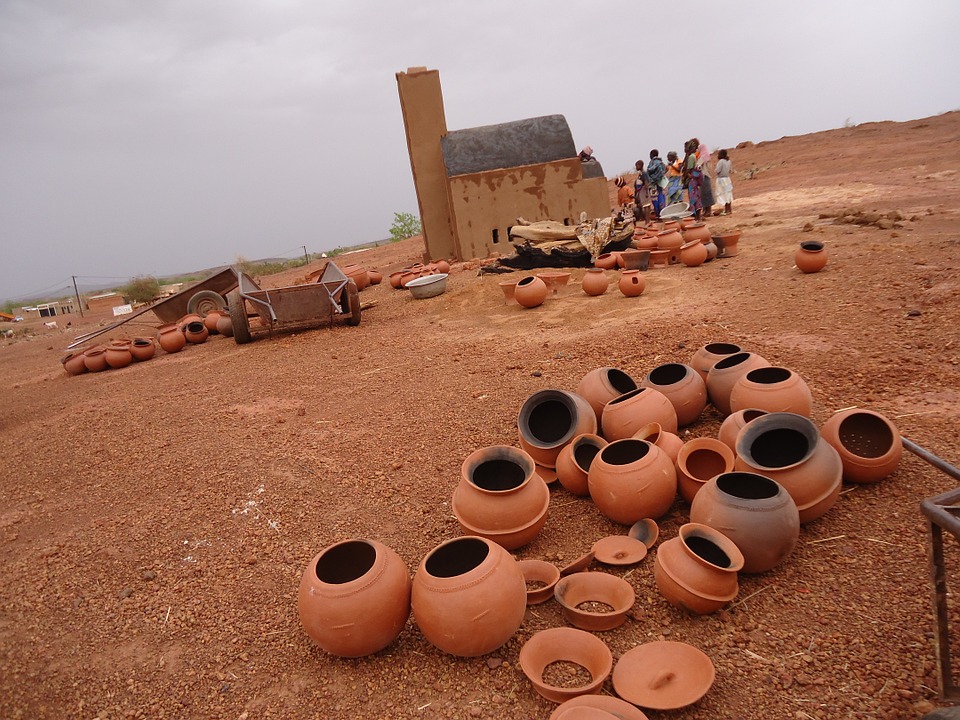
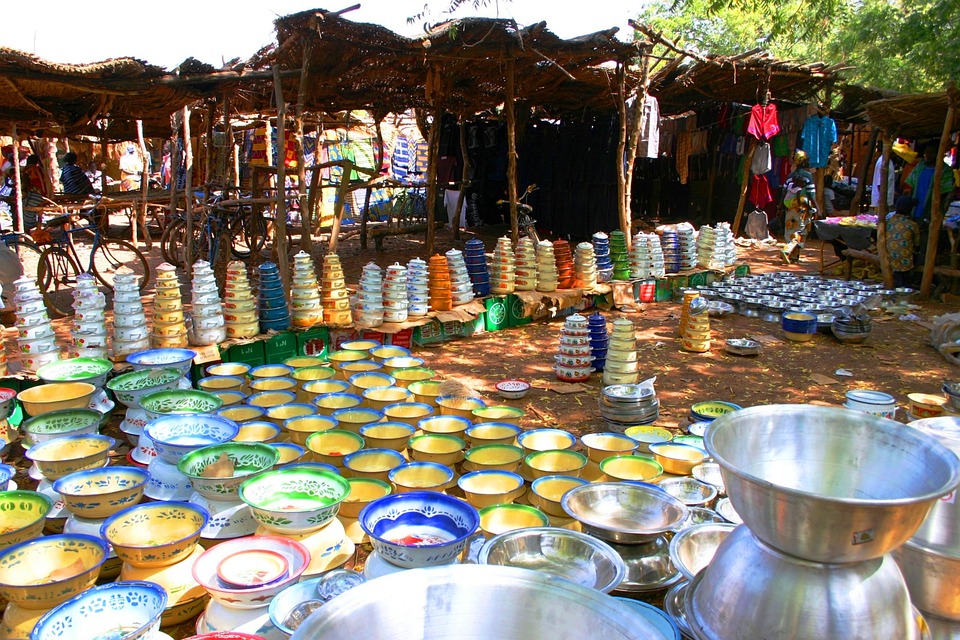
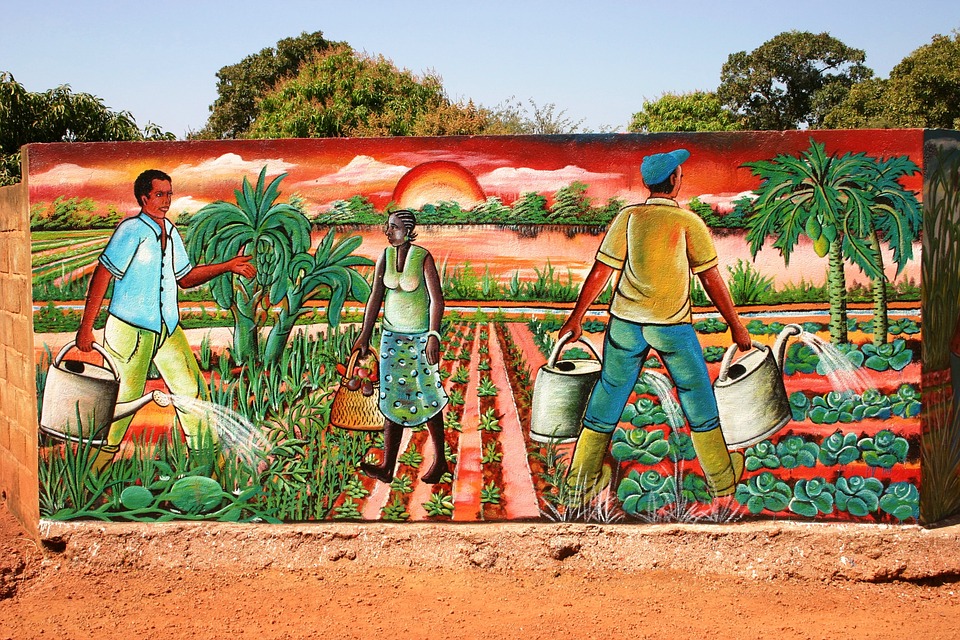
Economy of Burkina Faso: Agriculture, Mining and Tourism
The economy of Burkina Faso is primarily based on agriculture, which employs the majority of the population. The country is known for its production of cotton, which is one of its main cash crops. Other important agricultural products include sorghum, millet, maize, and peanuts.
In recent years, Burkina Faso has also seen growth in its mining sector. The country is rich in mineral resources, including gold, manganese, zinc, and limestone. Gold mining in particular has become a major industry, attracting foreign investment and contributing to the country’s economic growth.
Tourism is another potential source of income for Burkina Faso. The country has a wealth of cultural and historical attractions, including ancient ruins, traditional villages, and vibrant markets. In addition, Burkina Faso is home to several national parks and nature reserves, which offer opportunities for ecotourism and wildlife viewing.
Politics and Governance in Burkina Faso: A Democratic Republic
Burkina Faso is a democratic republic with a multi-party political system. The country’s government is headed by a president who is elected by popular vote for a five-year term. The president serves as both the head of state and the head of government.
In recent years, Burkina Faso has made significant progress towards democratic governance. However, the country has also faced challenges such as political instability, corruption, and human rights abuses. In 2014, mass protests erupted against then-President Blaise Compaoré, who had been in power for 27 years. The protests eventually led to his resignation and the establishment of a transitional government.
Since then, Burkina Faso has held several successful elections and witnessed peaceful transfers of power. However, the country continues to face challenges in terms of ensuring political stability, promoting good governance, and protecting human rights and civil liberties.
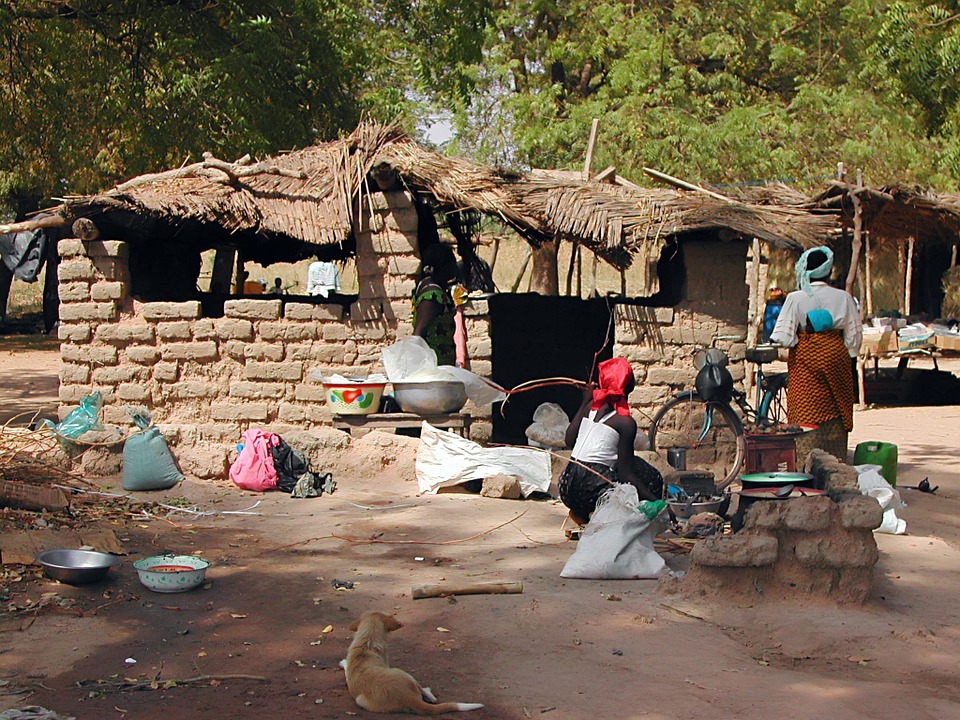
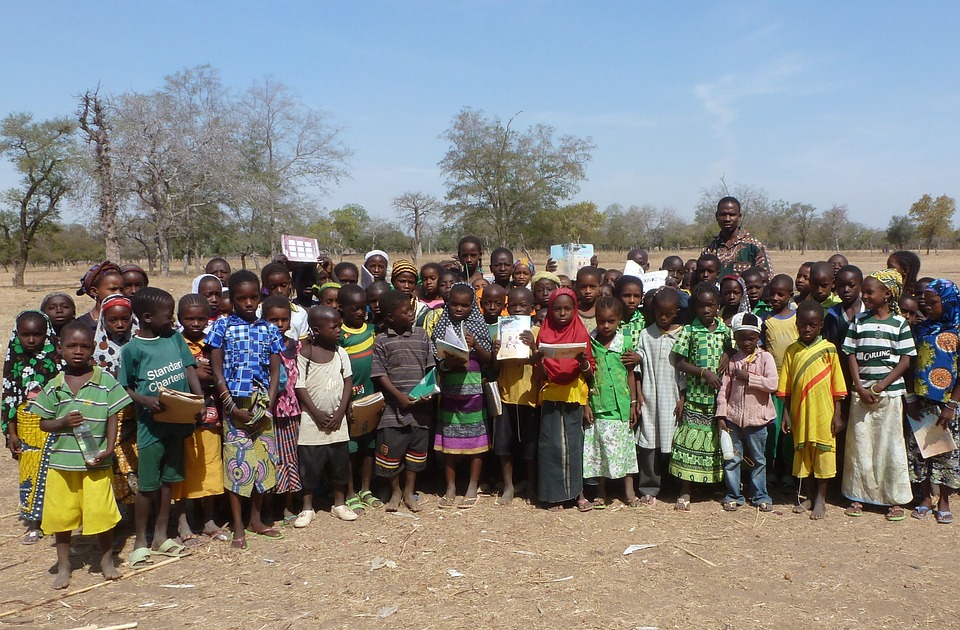
Education and Health in Burkina Faso: Challenges and Progress
Burkina Faso faces significant challenges in the areas of education and health. The country has one of the lowest literacy rates in the world, with only about 36% of adults being able to read and write. Access to education is also limited, particularly in rural areas where schools are often poorly equipped and understaffed.
In terms of healthcare, Burkina Faso has made progress in recent years but still faces significant challenges. The country has a high infant mortality rate and a low life expectancy. Access to healthcare is limited, particularly in rural areas where there is a shortage of medical facilities and trained healthcare professionals.
The government of Burkina Faso has implemented various initiatives to improve education and healthcare in the country. These include increasing funding for education and healthcare, improving infrastructure, and training more teachers and healthcare workers. However, more needs to be done to ensure that all Burkinabé have access to quality education and healthcare services.
Religion in Burkina Faso: A Diverse Mix of Beliefs and Practices
Burkina Faso is known for its religious diversity, with Islam and Christianity being the two main religions practised in the country. Islam is the largest religion, with about 60% of the population being Muslim. Christianity is practised by about 25% of the population, with Roman Catholicism being the largest Christian denomination.
In addition to Islam and Christianity, Burkina Faso is also home to various traditional beliefs and practices. Many Burkinabé people incorporate elements of traditional African religions into their daily lives, including the worship of ancestral spirits and the belief in supernatural forces.
Religious tolerance is generally high in Burkina Faso, with Muslims and Christians living side by side and participating in each other’s religious celebrations. Interfaith dialogue and cooperation are encouraged, and religious leaders play an important role in promoting peace and unity in the country.
Wildlife and Conservation in Burkina Faso: Protecting the Country’s Natural Resources
Burkina Faso is home to a diverse range of wildlife and natural resources. The country has several national parks and nature reserves that are dedicated to the conservation of its unique ecosystems and wildlife. These protected areas are home to a variety of species, including elephants, lions, hippos, and crocodiles.
However, Burkina Faso faces significant challenges when it comes to wildlife conservation. Illegal hunting, deforestation, and habitat destruction are major threats to the country’s biodiversity. In addition, climate change and desertification pose further challenges to the sustainability of Burkina Faso’s natural resources.
Efforts are being made to address these challenges and protect Burkina Faso’s natural resources. The government has implemented various conservation programs and initiatives, including the establishment of new protected areas and the enforcement of anti-poaching laws. In addition, local communities are being involved in conservation efforts through community-based natural resource management projects.
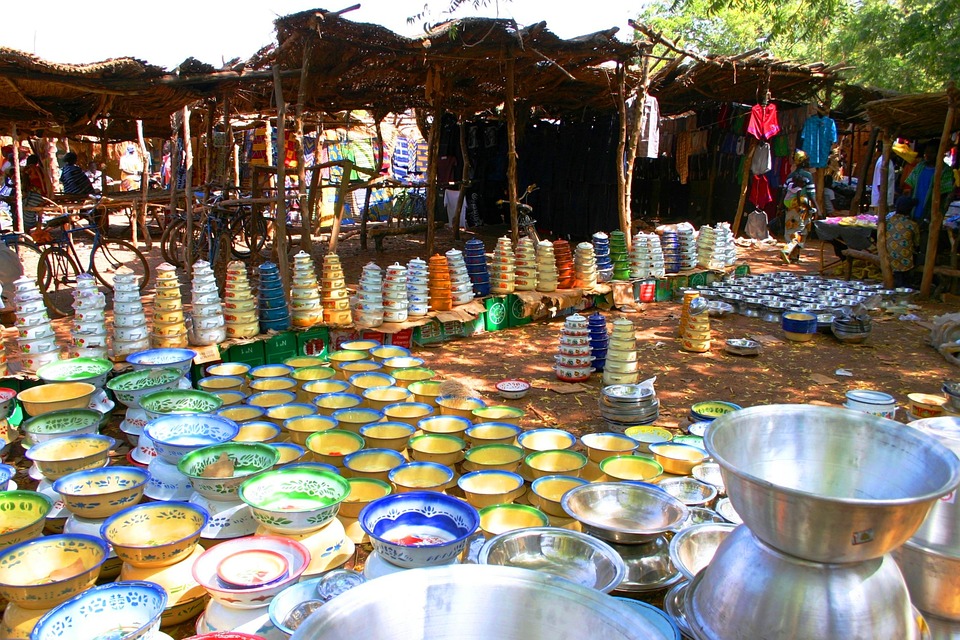
Tourism in Burkina Faso: Discovering the Hidden Gems of West Africa
Burkina Faso has a wealth of cultural, historical, and natural attractions that make it an ideal destination for tourists. The country offers a unique blend of traditional African culture, vibrant festivals, ancient ruins, and stunning landscapes.
One of the highlights of visiting Burkina Faso is experiencing its vibrant festivals and celebrations. The country is known for its lively music and dance festivals, such as the Nuits Atypiques de Koudougou and the Festival International de Théâtre et de Marionnettes de Ouagadougou. These festivals showcase the diversity and richness of Burkinabé culture and provide visitors with a unique cultural experience.
Burkina Faso is also home to several historical and cultural attractions. The Ruins of Loropéni, a UNESCO World Heritage site, are an ancient fortress that dates back to the 11th century. The city of Bobo-Dioulasso is known for its colonial architecture and vibrant marketplaces. The village of Tiébélé is famous for its traditional painted houses, which are decorated with intricate designs and symbols.
In terms of natural attractions, Burkina Faso offers opportunities for ecotourism and wildlife viewing. The Comoé National Park is home to a variety of wildlife, including elephants, lions, and antelopes. The Sindou Peaks, located in the southwest region of the country, are a series of stunning rock formations that offer breathtaking views.
Despite its potential as a tourist destination, Burkina Faso faces several challenges in developing its tourism industry. These include limited infrastructure, political instability, and security concerns. However, with the right investments and support, Burkina Faso has the potential to become a popular destination for travellers seeking an authentic African experience.
Conclusion: Burkina Faso is a fascinating and diverse country with a rich cultural heritage, unique natural resources, and a growing economy. Despite its challenges, the country has made significant progress in recent years and offers many opportunities for visitors and investors alike. From its vibrant festivals and historical attractions to its stunning landscapes and wildlife, Burkina Faso has much to offer those who are willing to explore its hidden gems. With continued investment in infrastructure, education, healthcare, and conservation efforts, Burkina Faso has the potential to become a thriving nation in West Africa.
Population Density of Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso, located in West Africa, is a landlocked country with a diverse geography that includes savannahs, mountains, and desert regions. It is bordered by six countries and has a population of approximately 20 million people. Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured in terms of persons per square kilometer. Understanding population density is crucial for policymakers and stakeholders as it helps in planning and resource allocation. Summary Burkina Faso has a population density of 76 people per square kilometer. Population growth in Burkina Faso has been steadily increasing since the 1950s. The Sahel region has the lowest population density in Burkina Faso, while the Centre-Est region has the highest. Urbanization has led to a significant increase in population density in Burkina Faso’s cities. High fertility rates and low levels of education are key demographic factors contributing to population density in Burkina Faso. Historical trends in population growth and migration Over the years, Burkina Faso has experienced significant population growth and migration patterns. In the 1960s, the population was around 4 million, and by 2020, it had quadrupled to approximately 20 million. This rapid growth can be attributed to several factors, including high fertility rates, improved healthcare leading to lower mortality rates, and increased life expectancy. Migration has also played a significant role in shaping Burkina Faso’s population density. Many people from rural areas have migrated to urban centers in search of better economic opportunities. This internal migration has led to increased population density in cities such as Ouagadougou and Bobo-Dioulasso. Regional variations in population density across Burkina Faso Burkina Faso...
History of Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso, a landlocked country in West Africa, has a rich and complex history that has shaped its present and will continue to shape its future. Understanding the country’s past is crucial in order to comprehend its current political and economic challenges, as well as its potential for growth and development. From the pre-colonial era of the Mossi Kingdoms to French colonial rule, the struggle for independence, and the subsequent political turmoil, Burkina Faso has experienced a series of significant events that have shaped its identity and trajectory. Summary The Mossi Kingdoms were powerful pre-colonial states in Burkina Faso French colonial rule led to the establishment of Upper Volta Burkina Faso gained independence after a struggle for freedom Thomas Sankara’s presidency brought about a revolution in Burkina Faso Sankara’s assassination led to political turmoil and controversial rule under Blaise Compaoré Compaoré was overthrown in a popular uprising in 2014 Burkina Faso transitioned to democracy and elected President Roch Marc Christian Kaboré Burkina Faso faces challenges such as terrorism and economic instability Burkina Faso plays a role in regional and international affairs. Pre-colonial era: the Mossi Kingdoms Before European contact, Burkina Faso was home to several powerful kingdoms, most notably the Mossi Kingdoms. The Mossi people established a series of kingdoms in the region, with Ouagadougou as their capital. These kingdoms were known for their political organization and military strength, as well as their cultural achievements. The Mossi Kingdoms had a hierarchical social structure, with a king at the top and various chiefs and nobles below him. They also had a complex system of governance and justice. European contact with...
Terrain and Topography of Burkina Faso: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Burkina Faso, located in West Africa, is a landlocked country known for its rich cultural heritage and diverse landscapes. Understanding the country’s terrain and topography is crucial for various reasons, including tourism, agriculture, and infrastructure development. With its unique geographical features, Burkina Faso offers a range of opportunities and challenges that shape the lives of its people. Summary Burkina Faso’s terrain is diverse, with regions of rolling hills, plains, rocky outcrops, and gorges. The Sahel region has a significant impact on Burkina Faso’s landscape, with desertification and droughts affecting the country. The Volta River Basin influences the topography of Burkina Faso, with the Black Volta River Valley being a major agricultural hub. The Atakora Mountains are the highest peaks in Burkina Faso, while the Gambaga Escarpment acts as a natural barrier in the north. The Comoé River Basin is a vital ecosystem for wildlife, while the Plateau Central is a region of rolling hills and plains. Overview of Burkina Faso’s Terrain and Topography Burkina Faso is situated in the heart of West Africa and covers an area of approximately 274,200 square kilometers. It is bordered by six countries: Mali to the north, Niger to the east, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Côte d’Ivoire to the southwest. The country’s diverse landscapes include savannahs, grasslands, mountains, plateaus, and river valleys. The Sahel Region and its Impact on Burkina Faso’s Landscape The Sahel region is a transitional zone between the Sahara Desert to the north and the Sudanian Savanna to the south. It stretches across several countries in West Africa, including Burkina Faso. The Sahel is...
Climate Zones of Burkina Faso: Different climate regions Of Burkina Faso
Introduction to Burkina Faso’s Climate Zones Burkina Faso, located in West Africa, is a landlocked country known for its diverse geography and climate. Understanding the different climate zones in Burkina Faso is crucial for various reasons, including agriculture, human settlements, and wildlife conservation. The country experiences a range of climates, from the arid Sahel region in the north to the humid South Sudanian region in the south. Each climate zone presents unique challenges and opportunities for the communities living there. The Sahel Region: Burkina Faso’s Hottest Climate Zone The Sahel region is located in the northern part of Burkina Faso and is characterized by its hot and dry climate. This region experiences high temperatures throughout the year, with average temperatures often exceeding 40 degrees Celsius (104 degrees Fahrenheit) during the hottest months. Rainfall is scarce and irregular, making it difficult for communities to rely on agriculture as a source of livelihood. Communities in the Sahel region face numerous challenges due to the harsh climate. Water scarcity is a major issue, as there are limited water sources available for both human consumption and agricultural activities. The lack of rainfall also leads to desertification and soil degradation, making it even more challenging for farmers to cultivate crops. Additionally, the extreme heat poses health risks for residents, especially vulnerable populations such as children and the elderly. The Sudan Savanna Region: A Transitional Climate Zone The Sudan Savanna region lies between the Sahel and Guinea Savanna regions and experiences a transitional climate. This region has a longer rainy season compared to the Sahel, with more reliable rainfall patterns. The temperature is generally lower...
Political Boundaries of Burkina Faso: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Burkina Faso, a landlocked country in West Africa, is known for its rich cultural heritage and diverse ethnic groups. Understanding the political boundaries of Burkina Faso is crucial for comprehending the country’s governance and development. Political boundaries define the territorial limits within which a government exercises its authority and provide a framework for administrative divisions and governance structures. Summary Burkina Faso is a country with defined political boundaries that have evolved over time. The country is divided into 13 provinces, each with its own unique characteristics and challenges. Understanding the districts within each province is crucial for effective governance and development. Burkina Faso’s historical boundaries have been shaped by colonialism and post-independence political changes. Political boundaries play a significant role in shaping Burkina Faso’s society, economy, and ethnic diversity. Provinces of Burkina Faso: An Overview Burkina Faso is divided into 13 provinces, each with its own distinct characteristics and administrative structures. These provinces include Balé, Bam, Banwa, Bazèga, Bougouriba, Boulgou, Boulkiemdé, Comoé, Ganzourgou, Gnagna, Gourma, Houet, and Ioba. Each province has its own capital city and is further divided into districts. The provinces play a crucial role in Burkina Faso’s governance as they serve as administrative units responsible for implementing government policies and programs at the local level. They also have their own elected officials who represent the interests of their respective provinces in the national government. Mapping Burkina Faso’s Districts: A Comprehensive Guide Burkina Faso’s districts are the second level of administrative divisions within the country. Each province is further divided into districts, which are responsible for implementing government policies and programs at the local level. There are...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Burkina Faso: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso, a landlocked country in West Africa, may not be the first destination that comes to mind when thinking about tourism. However, this vibrant nation is home to a rich cultural heritage and stunning natural landscapes that are waiting to be explored. From ancient ruins to contemporary art events, Burkina Faso offers a diverse range of attractions that showcase its unique history and traditions. In this article, we will delve into some of the must-visit sites in Burkina Faso, highlighting their significance and providing visitor information and tips. Summary Loropéni is a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Burkina Faso with ancient ruins. The Grand Mosque of Bobo-Dioulasso is a symbol of Islamic architecture in West Africa. The Royal Palace of Ouagadougou is a historical monument of Burkina Faso’s traditional kingship. The National Museum of Music showcases Burkina Faso’s rich musical heritage. The Nazinga Game Ranch is a wildlife sanctuary and tourist attraction. The Ruins of Loropéni: A UNESCO World Heritage Site in Burkina Faso The Ruins of Loropéni, located in the southern part of Burkina Faso, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site that dates back to the 11th century. These ruins are the remains of an ancient fortress that was once part of the trans-Saharan trade route. The site is of great historical and archaeological significance, as it provides insights into the region’s past and its connections with other civilizations. The Ruins of Loropéni feature stone walls and towers that were built without mortar, showcasing the architectural skills of the people who inhabited the area centuries ago. The site also includes a burial ground and other structures that...
Natural Resources of Burkina Faso: And Their Powerful Mineral Mining Industry
Natural Resources of Burkina Faso: And Their Powerful Mineral Mining Industry Burkina Faso, a landlocked country in the heart of the Sahel region, is fast becoming a focal point in Africa’s mining industry. Despite facing political and economic hurdles, including recent military coups, the country is rich in mineral wealth—particularly gold, which has placed it among the top gold producers on the African continent. This article explores the natural resources of Burkina Faso, their economic significance, and how the mining industry is reshaping the nation’s destiny. This is a must-read for anyone interested in Africa’s development, resource economics, or the geopolitics of natural wealth. Learn how Burkina Faso’s buried treasures are driving its GDP, changing local communities, and catching the eye of the World Bank, the African Development Bank, and the International Monetary Fund. Article Outline 1. Why Is Burkina Faso Emerging as a Mining Powerhouse in West Africa? 2. What Are the Key Minerals Found in Burkina Faso? 3. How Central Is Gold to the Economy of Burkina Faso? 4. What Role Does the Mining Industry Play in Burkina Faso’s GDP? 5. Who Are the Major Players in Burkina Faso’s Mining Sector? 6. What Is the Legal Framework for Mining in Burkina Faso? 7. How Do Mining Activities Affect Local Communities? 8. How Is Water and Sanitation Linked to Mining Operations? 9. What Are the Security Challenges in Mining Regions? 10. What Does the Future Hold for Burkina Faso’s Mining Industry? 1. Why Is Burkina Faso Emerging as a Mining Powerhouse in West Africa? Burkina Faso has rapidly evolved from a relatively unknown mining destination into a...
Discovering the Hidden Gems of Burkina Faso: Exploring the Rich Culture and Natural Beauty of West Africa
Burkina Faso, a landlocked country in West Africa, is often overlooked by travelers in favor of its more well-known neighbors. However, this hidden gem has much to offer for those willing to explore its rich cultural heritage, natural beauty, vibrant music and dance scene, delicious cuisine, and friendly people. From ancient Mossi Kingdoms to stunning waterfalls and wildlife-filled national parks, Burkina Faso is a destination that will surprise and delight visitors. Key Takeaways Burkina Faso is a hidden gem in West Africa with rich cultural heritage and natural beauty. The country boasts stunning waterfalls, wildlife, vibrant music and dance scene, and delicious cuisine. Visitors can expect a warm welcome from the friendly people of Burkina Faso. Exploring the ancient Mossi Kingdoms and trekking through the Sahel offer a journey through history and desert landscapes. The lively markets and colorful festivals make Burkina Faso a shopper’s paradise and a joyful experience. Exploring the Rich Cultural Heritage of Burkina Faso Burkina Faso is home to a diverse range of ethnic groups, each with their own unique customs and rituals. Traditional practices are deeply ingrained in the fabric of Burkinabe society and play a significant role in daily life. From birth ceremonies to initiation rites and funeral rituals, these customs are passed down through generations and serve as a way to connect with ancestors and maintain cultural identity. One of the most iconic symbols of Burkina Faso’s culture is the mask. Masks hold great significance in traditional ceremonies and performances, representing spirits or ancestors and serving as a means of communication between the human and spiritual realms. The craftsmanship and artistry that...