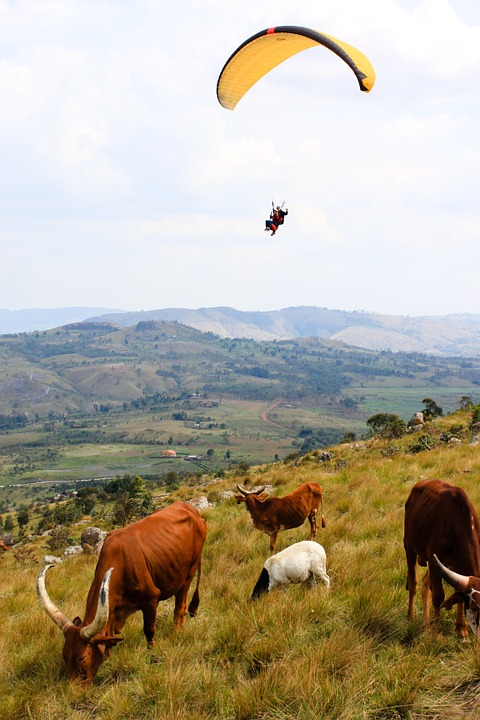
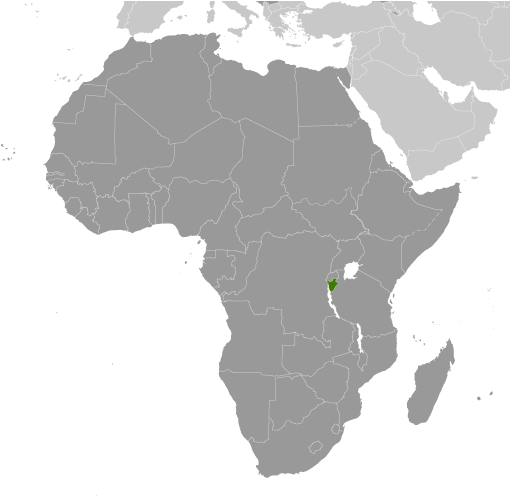
Burundi
(Republika y’u Burundi (Rundi); République du Burundi (French) (Republic of Burundi))

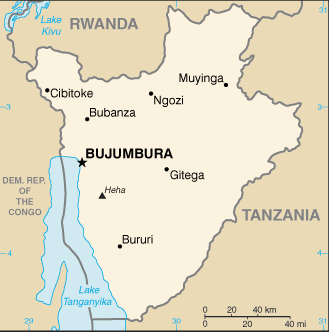
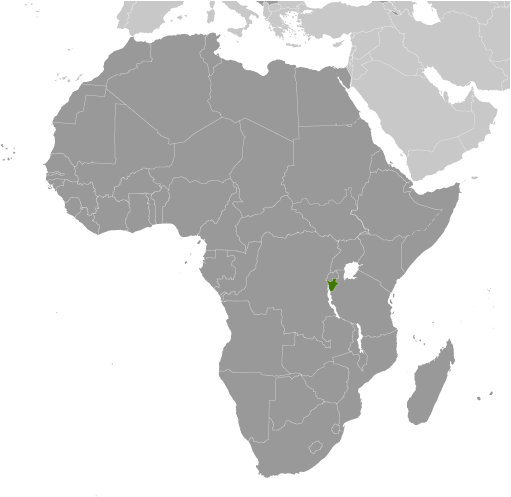




Capital of Burundi : Bujumbura
Population (Estimated July 2012): 10,557,259
Area: 27,816 km2 or 10,740 mi2
Currency: Burundi Franc (FBu)
Official Language: Rundi; French
Political Information: Presidential Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 67% of the population are Christian, 23% have indigenous beliefs and 10% are Muslim)
Highest Mountain: Mount Heha at 2,670m 8,760ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $1.7 billion (US$) or £1,020 million(GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $3.672 billion (US$) or £2,203.2 million (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $400 (US$) or £240(GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +2:00
Counties/Provinces/States: 17 provinces; Bubanza, Bujumbura Mairie, Bujumbura Rural, Bururi, Cankuzo, Cibitoke, Gitega, Karuzi, Kayanza, Kirundo, Makamba, Muramvya, Muyinga, Mwaro, Ngozi, Rutana, Ruyigi
Leaders: President Pierre Nkurunziza with Terence Sinunguruza as 1st Vice President and Gervais Rufyikiri as 2nd Vice President.
Additional: Gained Independence from Belgium on the 1st of July 1962.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Burundi
Burundi is a small landlocked country located in East Africa. It is bordered by Rwanda to the north, Tanzania to the east and south, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. With a population of approximately 11 million people, Burundi is one of the most densely populated countries in Africa. Understanding the history and culture of Burundi is crucial for gaining insight into the challenges and opportunities facing this nation.
History of Burundi: From Pre-colonial Times to Independence
Burundi has a rich history that dates back to pre-colonial times. The region was once home to several powerful kingdoms, including the Kingdom of Burundi and the Kingdom of Rwanda. These kingdoms were known for their strong central authority and complex social structures. European colonization had a significant impact on Burundi, as it did on many African nations. The Germans were the first to colonize Burundi in the late 19th century, followed by the Belgians after World War
The colonial period brought about significant changes in Burundi’s political and social landscape.
The struggle for independence in Burundi was marked by political unrest and violence. In 1962, Burundi gained independence from Belgium, but it was followed by years of ethnic tensions between the Hutu and Tutsi populations. This culminated in a series of ethnic conflicts and civil wars that plagued the country for decades. The post-independence period was marked by political instability, military coups, and human rights abuses. It was not until the early 2000s that Burundi began to experience relative stability and a move towards democracy.
Burundi’s Geography: A Diverse Landscape with Natural Wonders
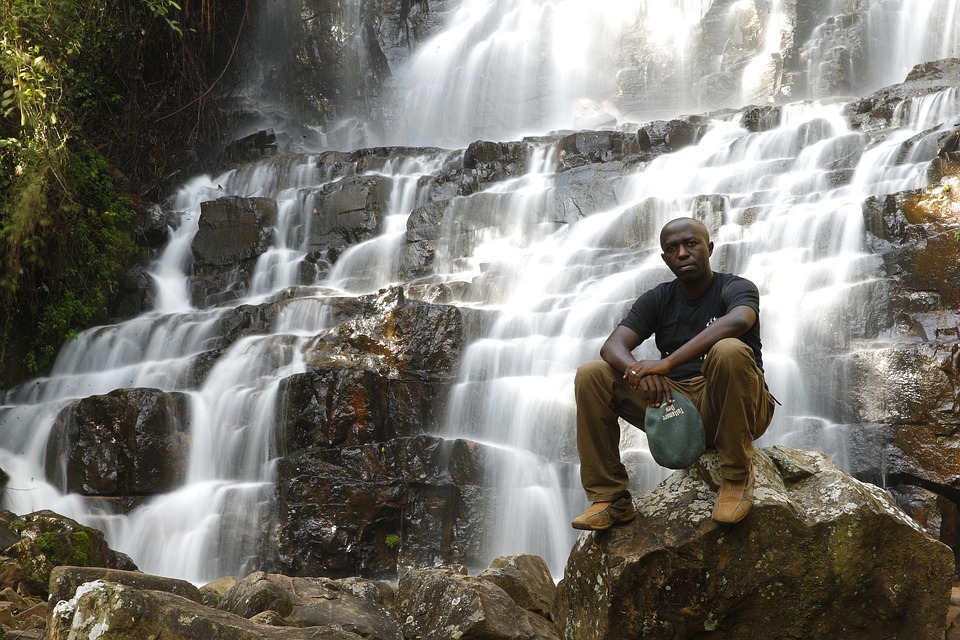
Burundi is known for its diverse geography, which includes mountains, lakes, and forests. The country is situated in the Great Rift Valley, which has resulted in a varied terrain. The highest peak in Burundi is Mount Heha, which stands at an elevation of 2,670 meters. The country is also home to several lakes, including Lake Tanganyika, which is one of the largest freshwater lakes in the world.
Burundi’s national parks and wildlife reserves are home to a wide range of flora and fauna. Kibira National Park is one of the most important protected areas in Burundi, known for its dense rainforests and diverse wildlife. Rusizi National Park, located along the Rusizi River, is another popular destination for nature lovers. These natural wonders are not only important for tourism but also for the preservation of Burundi’s biodiversity.
Preserving Burundi’s natural resources is crucial for the country’s sustainable development. Deforestation, soil erosion, and pollution are some of the major environmental challenges facing Burundi. Efforts are being made to promote sustainable agriculture and protect the country’s forests and water sources. It is essential to strike a balance between economic development and environmental conservation to ensure a better future for Burundi.
Burundi’s Culture: Rich Traditions and Festivals
Burundi has a rich cultural heritage that is deeply rooted in its history and traditions. Music and dance play a significant role in Burundian culture, with traditional drumming being an integral part of celebrations and ceremonies. The royal drummers of Burundi are renowned worldwide for their rhythmic performances.
Traditional Burundian clothing reflects the country’s cultural diversity. The women wear colourful wrap-around skirts called “imishanana” or “kitenge,” while men often wear loose-fitting trousers called “ishabure.” Traditional hairstyles and body art are also important aspects of Burundian culture.
Burundian cuisine is diverse and influenced by its neighbouring countries. Staple foods include maize, beans, sweet potatoes, and cassava. Meat dishes such as goat, beef, and fish are also popular. Traditional beverages include banana beer and urwarwa, a fermented drink made from sorghum.
Burundi is known for its vibrant festivals and celebrations. One of the most important festivals is the Umuganura Festival, which celebrates the country’s agricultural heritage. It is a time for farmers to give thanks for the harvest and for the community to come together in celebration. Other festivals include the Drum Festival, which showcases traditional drumming, and the Independence Day celebrations on July 1st.
Burundi’s Economy: Agriculture and Mining as Major Industries
Agriculture is the backbone of Burundi’s economy, employing the majority of the population. The country is known for its coffee production, with coffee being one of its major exports. Other important agricultural products include tea, cotton, and tobacco. However, Burundi faces challenges in terms of low productivity, limited access to markets, and vulnerability to climate change.
Mining is another important industry in Burundi, with deposits of nickel, gold, tin, and tungsten. The mining sector has the potential to contribute significantly to the country’s economy. However, there are challenges in terms of inadequate infrastructure, lack of investment, and issues related to transparency and governance.
Poverty and corruption are major challenges facing Burundi’s economy. The country ranks among the poorest in the world, with high levels of unemployment and inequality. Corruption is also a significant issue, hindering economic development and undermining public trust in government institutions.
Sustainable economic development is crucial for Burundi’s future. Efforts are being made to promote private sector growth, improve infrastructure, and attract foreign investment. It is essential to address the root causes of poverty and corruption to create a more inclusive and prosperous society.
Politics in Burundi: A Troubled Past and Present
Burundi has a troubled political history marked by periods of conflict and instability. The post-independence period was characterized by ethnic tensions between the Hutu and Tutsi populations, leading to a series of ethnic conflicts and civil wars. The Arusha Accords, signed in 2000, aimed to bring an end to the violence and establish a power-sharing government. However, political tensions persisted, leading to the 2015 crisis.
The 2015 crisis was triggered by President Pierre Nkurunziza’s decision to run for a controversial third term. This led to widespread protests, violence, and a failed coup attempt. The crisis resulted in a significant loss of life and a mass exodus of refugees. The political situation remains fragile, with concerns about human rights abuses and restrictions on freedom of expression.
Promoting democracy and human rights is crucial for Burundi’s stability and development. Efforts are being made to promote dialogue, reconciliation, and inclusive governance. International support and engagement are essential in helping Burundi navigate its political challenges and build a more democratic society.
Burundi’s Education System: Challenges and Progress
Burundi’s education system faces numerous challenges, including limited access to quality education, inadequate infrastructure, and a lack of qualified teachers. The country has one of the lowest literacy rates in the world, with significant disparities between urban and rural areas.
Efforts are being made to improve education in Burundi. The government has implemented policies to increase access to education and improve the quality of teaching. Non-governmental organizations and international partners are also working to support education initiatives in Burundi.
Education is crucial for Burundi’s future development. It plays a vital role in reducing poverty, promoting social inclusion, and empowering individuals to contribute to society. Investing in education is essential for building a skilled workforce and creating opportunities for economic growth.
Health in Burundi: Issues and Initiatives
Burundi faces significant health challenges, including high rates of disease, malnutrition, and limited access to healthcare services. Malaria, HIV/AIDS, and respiratory infections are among the leading causes of death in the country. Malnutrition is also a major concern, particularly among children.
Efforts are being made to improve healthcare in Burundi. The government has implemented policies to increase access to healthcare services and improve the quality of care. International organizations and non-governmental organizations are also working to support health initiatives in Burundi.
Investing in healthcare is crucial for Burundi’s future. Access to quality healthcare is a basic human right and essential for promoting well-being and reducing poverty. It is important to address the underlying causes of poor health, such as poverty, inadequate sanitation, and limited access to clean water.
Tourism in Burundi: Exploring the Country’s Hidden Gems
Burundi has great potential for tourism, with its diverse landscapes and natural wonders. Lake Tanganyika offers opportunities for swimming, fishing, and boating. Kibira National Park is a haven for nature lovers, with its dense rainforests and abundant wildlife. The Rusizi Delta is a popular destination for birdwatching and boat safaris.
However, the tourism industry in Burundi faces challenges. Limited infrastructure, political instability, and negative perceptions about safety have hindered the growth of tourism. Efforts are being made to promote Burundi as a tourist destination and attract international visitors.
Sustainable tourism is crucial for Burundi’s economic development. It can create jobs, generate revenue, and promote cultural exchange. It is important to develop tourism in a way that preserves the country’s natural and cultural heritage while benefiting local communities.
Future Prospects for Burundi: Opportunities and Challenges Ahead
Burundi faces both opportunities and challenges in the coming years. The country has made progress in terms of stability and economic development, but there are still significant obstacles to overcome. Key opportunities include harnessing the potential of agriculture and mining, promoting tourism, and investing in human capital.
However, there are also challenges that need to be addressed. These include poverty, corruption, political instability, and limited access to education and healthcare. International support and engagement are crucial in helping Burundi overcome these challenges and achieve sustainable development.
In conclusion, understanding the history, culture, geography, economy, politics, education, health, and tourism of Burundi is essential for gaining insight into the challenges and opportunities facing this landlocked country in East Africa. Burundi has a rich cultural heritage and diverse natural landscapes that offer great potential for economic development. However, it also faces significant challenges in terms of poverty, corruption, political instability, and limited access to education and healthcare. International support and engagement are crucial in helping Burundi overcome these challenges and build a more prosperous and inclusive society.
If you’re interested in learning more about Burundi, a small landlocked country in East Africa, you might want to check out this informative article on Array. It provides a comprehensive overview of Burundi’s history, culture, and current affairs. From its colonial past to its struggles with political instability and poverty, this article delves into the challenges and unique aspects of this lesser-known African nation. So, if you’re curious to explore the rich tapestry of Burundi’s story, click here to read the article on Array.
FAQs
What is Burundi?
Burundi is a landlocked country located in East Africa. It is bordered by Rwanda to the north, Tanzania to the east and south, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west.
What is the capital of Burundi?
The capital of Burundi is Bujumbura, which is also the largest city in the country.
What is the population of Burundi?
As of 2021, the estimated population of Burundi is around 12.3 million people.
What is the official language of Burundi?
The official languages of Burundi are Kirundi and French.
What is the currency of Burundi?
The currency of Burundi is the Burundian franc (BIF).
What is the economy of Burundi like?
Burundi is one of the poorest countries in the world, with a largely agricultural economy. Coffee and tea are the main cash crops, and the country also has deposits of nickel, uranium, and other minerals.
What is the political situation in Burundi?
Burundi has a presidential representative democratic republic system of government. The country has experienced political instability and violence in recent years, including a civil war that lasted from 1993 to 2005.
What are some popular tourist attractions in Burundi?
Some popular tourist attractions in Burundi include Lake Tanganyika, Rusizi National Park, and the Gishora Drum Sanctuary. The country is also known for its traditional drumming and dancing.
Population Density of Burundi
Burundi, a small landlocked country in East Africa, is known for its high population density. With a population of over 11 million people, Burundi has one of the highest population densities in Africa, with an average of 463 people per square kilometer. Understanding population density is crucial for policymakers and researchers as it provides insights into the social, economic, and environmental challenges faced by the country. Population density refers to the number of individuals living in a specific area, usually measured in terms of people per square kilometer. It is an important indicator of how crowded an area is and can provide valuable information about resource allocation, infrastructure development, and social services provision. In the case of Burundi, its high population density poses unique challenges in terms of land scarcity, access to basic services, and environmental sustainability. Summary Burundi has a high population density, with over 11 million people living in an area roughly the size of Maryland. The country’s geography and demographics play a significant role in its population density, with most people living in rural areas. Population growth in Burundi has been influenced by historical events such as colonization and conflict, as well as cultural and religious factors. Factors such as access to healthcare, education, and economic opportunities can impact population density in Burundi. The government’s policies on urbanization, land use, and family planning will play a crucial role in shaping future population density in Burundi. Understanding the Geography and Demographics of Burundi Burundi is located in the Great Lakes region of East Africa and is bordered by Rwanda to the north, Tanzania to the east and...
History of Burundi
Burundi, a small landlocked country in East Africa, has a rich and complex history that spans thousands of years. From its early inhabitants to the arrival of the Tutsi and Hutu peoples, the rise of the Burundian monarchy, and the impact of European colonization, Burundi’s past has shaped its present. Understanding this history is crucial for comprehending the challenges and opportunities that Burundi faces today. By delving into the country’s past, we can gain insights into its cultural heritage, political landscape, and social dynamics. Summary Burundi was inhabited by hunter-gatherer communities for thousands of years before the arrival of the Tutsi and Hutu peoples. The Tutsi and Hutu peoples arrived in Burundi in the 15th century and established a complex social hierarchy based on cattle ownership and agriculture. The Kingdom of Burundi emerged in the 17th century and was ruled by a monarchy until the arrival of European explorers and traders in the late 19th century. Burundi was colonized by Germany in 1899 and later by Belgium, which imposed a system of forced labor and racial segregation that had a lasting impact on the country’s society and economy. Burundi gained independence in 1962, but political instability and ethnic tensions led to a series of coups and a genocide in 1972 under the rule of President Micombero. Burundi has since transitioned to a democratic system of government, but faces ongoing challenges related to poverty, corruption, and human rights abuses. Burundi has a rich cultural heritage that includes traditional music, dance, and storytelling, as well as unique customs related to marriage, birth, and death. The Early Inhabitants of Burundi Before the...
Terrain and Topography of Burundi: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Burundi, a small landlocked country in East Africa, is known for its diverse and stunning terrain. Nestled between Rwanda, Tanzania, and the Democratic Republic of Congo, Burundi is home to majestic mountains, lush valleys, fertile plains, the Great Rift Valley, scenic hills, unique plateaus, mesmerizing waterfalls, abundant lakes, and mysterious volcanoes. Understanding the geography of Burundi is crucial in appreciating the country’s natural beauty and the importance of preserving its resources. Summary Burundi’s terrain and topography is diverse and varied, with mountains, valleys, plains, plateaus, and more. The majestic mountains of Burundi are awe-inspiring landmarks that offer stunning views and challenging hikes. The valleys of Burundi are a natural haven for wildlife, with lush vegetation and abundant water sources. The plains of Burundi are fertile grounds for agriculture, providing a vital source of food and income for the country. The Great Rift Valley is a geological marvel of Burundi, offering a glimpse into the earth’s history and natural wonders. The Majestic Mountains of Burundi: Awe-Inspiring Landmarks Burundi is blessed with several mountain ranges that add to its picturesque landscape. The most prominent mountain range is the Mitumba Mountains, which stretch across the western part of the country. These mountains are part of the Albertine Rift, a branch of the East African Rift System. The Mitumba Mountains are characterized by their steep slopes and dense vegetation, making them a haven for hikers and nature enthusiasts. Notable peaks in Burundi include Mount Heha, the highest peak in the country at 2,670 meters (8,760 feet) above sea level. Mount Heha offers breathtaking views of the surrounding landscape and is a popular destination...
Political Boundaries of Burundi: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Burundi, a landlocked country located in East Africa, is known for its rich history and diverse culture. It shares borders with Rwanda to the north, Tanzania to the east and south, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. Understanding the political boundaries of Burundi is crucial for comprehending its history, culture, and political system. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Burundi’s political boundaries, including its provinces, districts, historical boundaries, and the challenges it faces in maintaining these boundaries. Summary Burundi is divided into 18 provinces and 129 districts. The historical boundaries of Burundi have been shaped by various factors, including colonialism and ethnic tensions. Ethnicity plays a significant role in Burundi’s political boundaries, with the Hutu and Tutsi groups being the most prominent. Maintaining political boundaries in Burundi is challenging due to ongoing conflicts and political instability. Burundi’s political boundaries have implications for regional and international relations, and their future prospects and challenges remain uncertain. Burundi’s Provinces: Names and Characteristics Burundi is divided into 18 provinces, each with its own unique characteristics. These provinces are Bubanza, Bujumbura Mairie, Bujumbura Rural, Bururi, Cankuzo, Cibitoke, Gitega, Karuzi, Kayanza, Kirundo, Makamba, Muramvya, Muyinga, Mwaro, Ngozi, Rumonge, Rutana, and Ruyigi. Bubanza is located in the northwest region of Burundi and is known for its agricultural production. Bujumbura Mairie is the capital city of Burundi and is an important economic and political center. Bujumbura Rural surrounds the capital city and is known for its scenic landscapes. Bururi is located in the southwest region and is known for its coffee production. Cankuzo is situated in the eastern part of...
Climate Zones of Burundi: Different climate regions Of Burundi
Burundi, a landlocked country located in East Africa, is known for its diverse geography and climate. The country is situated on the eastern edge of the Albertine Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley. This geographical location gives rise to a variety of climate zones within Burundi. Understanding these climate zones is crucial for the country’s agriculture sector, as it helps farmers determine the most suitable crops to grow and the best farming practices to adopt. Summary Burundi has a diverse range of climate zones, each with unique characteristics and impacts on agriculture and the economy. The Equatorial Climate Zone is characterized by high temperatures and rainfall, making it ideal for growing crops such as coffee and bananas. The Highland Climate Zone has cooler temperatures and is suitable for growing crops such as maize and beans. The Semi-Arid Climate Zone experiences low rainfall and is prone to drought, making it difficult for farmers to grow crops and sustain their livelihoods. The Tropical Savanna Climate Zone has a distinct wet and dry season, making it suitable for growing crops such as sorghum and millet. The Equatorial Climate Zone of Burundi The equatorial climate zone in Burundi is characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall throughout the year. This climate zone is found in the low-lying areas of the country, particularly in the western and central regions. The equatorial climate zone is ideal for growing crops such as bananas, coffee, tea, and maize. In the equatorial climate zone, farmers rely heavily on rainwater for irrigation, as there are no distinct dry seasons. The abundant rainfall supports the growth of...
Natural Resources of Burundi: Where Are The Natural Resources In Burundi and Its Emerging Mining Industry
Natural Resources of Burundi: Where Are The Natural Resources In Burundi and Its Emerging Mining Industry Burundi, a landlocked country nestled in Africa’s Great Lakes region, is often overlooked when discussing natural wealth. However, the natural resources of Burundi hold untapped potential that could transform its economic landscape. From valuable mineral deposits like nickel, tantalum, and tungsten, to promising peat reserves, Burundi is quietly rich in natural assets. This article explores natural resources in Burundi in detail, addressing what makes the mining industry significant, how these resources are currently used, and what challenges and opportunities lie ahead. For policymakers, investors, environmentalists, and anyone interested in Africa’s future, this article offers deep insights into the reserves in Burundi and the steps needed for sustainable development. Outline: A Deep Dive into Burundi’s Natural Resources Where Is Burundi and Why Are Its Natural Resources Important? What Are the Main Natural Resources in Burundi? How Significant Are Nickel Deposits in Burundi? What Role Does Tantalum Play in Burundi’s Resource Sector? Tungsten in Burundi: A Hidden Asset? Understanding Burundi’s Peat Reserves and Energy Potential How Is Artisanal Mining Shaping Burundi’s Mining Industry? Is There a Strategy for the Sustainable Use of Natural Resources? What Are the Environmental Impacts of Resource Extraction in Burundi? What Does the Future Hold for Burundi’s Mining Sector and Economic Growth? 1. Where Is Burundi and Why Are Its Natural Resources Important? Burundi is a landlocked country in East Africa, bordered by Rwanda to the north, Tanzania to the east and south, and the Democratic Republic of Congo to the west. It lies within Africa’s Great Lakes region, near...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Burundi: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Burundi
Burundi, a small landlocked country in East Africa, may not be on the top of everyone’s travel list, but it is a destination rich in cultural and historical significance. From its traditional drummers to its sacred forests and national parks, Burundi offers a unique blend of natural beauty and cultural heritage. Preserving these cultural sites is crucial not only for the people of Burundi but also for future generations to appreciate and learn from. Summary Burundi has a rich cultural and historical heritage worth exploring. The Royal Drummers of Burundi are a cultural icon and a must-see attraction. The National Museum of Gitega is a treasure trove of Burundian history and culture. The Sacred Forests of Burundi are a testament to traditional beliefs and practices. The Karera Waterfalls are a natural wonder with a rich cultural history. The Royal Drummers of Burundi: A Cultural Icon The Royal Drummers of Burundi are renowned worldwide for their mesmerizing performances and rhythmic beats. This group of drummers has a long history dating back centuries and holds a significant role in Burundian culture. The drums are not just instruments; they are considered sacred objects that connect the living with the spirits of their ancestors. The drummers can be seen performing at various events and festivals throughout the country, but one of the best places to witness their captivating performances is at the Gishora Drum Sanctuary. Located near the capital city of Bujumbura, this sanctuary is a place of worship and cultural preservation. Visitors can experience the power and energy of the drummers as they perform traditional rhythms passed down through generations. The National...
Exploring the Hidden Gems of Burundi: A Journey Through the Heart of Africa
Nestled in the heart of East Africa, Burundi is a small landlocked country that often goes unnoticed by travelers. However, this hidden gem is a treasure trove of natural wonders, rich culture, and warm hospitality. Located between Rwanda, Tanzania, and the Democratic Republic of Congo, Burundi has a tumultuous history but is now emerging as an up-and-coming travel destination. Burundi’s history dates back centuries, with influences from various African kingdoms and colonial powers. The country gained independence from Belgium in 1962 and has since faced political instability and conflict. Despite these challenges, Burundi has managed to preserve its unique cultural heritage and natural beauty. Key Takeaways Burundi is a hidden gem in Africa with rich culture, natural wonders, historical sites, and vibrant markets. The country boasts of mountains, lakes, and wildlife, making it a perfect destination for nature lovers. Burundi’s friendly and hospitable people make it a great place to experience local cuisine and participate in traditional festivals. Despite facing development challenges, Burundi has triumphed in preserving its heritage and promoting adventure activities like trekking and rafting. Planning a trip to Burundi requires careful consideration, but the journey promises to be a memorable one with tips and recommendations. Discovering the Rich Culture and Heritage of Burundi Burundi is a country with a vibrant cultural scene. Traditional dance and music play a significant role in the daily lives of its people. The Intore dance, performed by men and women dressed in colorful costumes, is a captivating display of agility and rhythm. Traditional drumming is also an integral part of Burundian culture, with the Gishora Drum Sanctuary being a must-visit for...