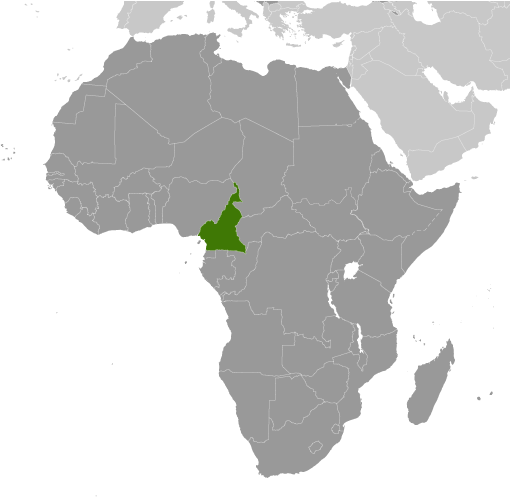
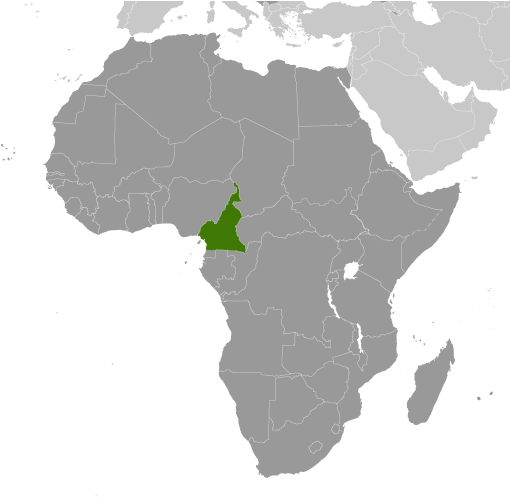
Cameroon
(République du Cameroun (French); Republic of Cameroon (English))

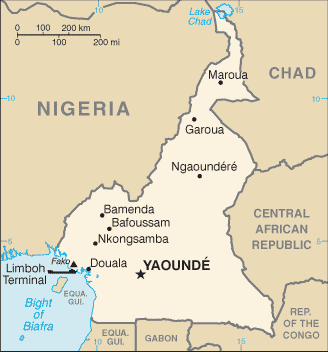




Capital: Yaoundé
Population (Estimated July 2012): 20,129,878
Area: 476,350 km2 or 183,920 mi2
Currency: CFA franc (CFAF)
Official Language: French and English
Political Information: Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 40% of the population have indigenous beliefs, 40% are Christian, and 20% are Muslim)
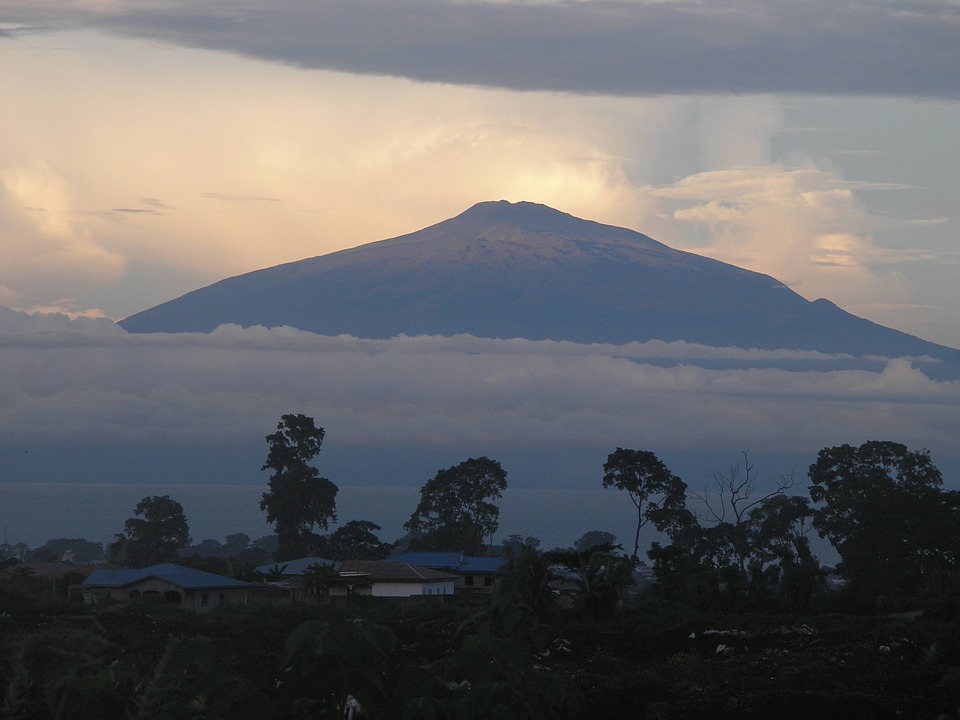
Highest Mountain: Cameroon Mountain at 4,040m or 13,255ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $25.8 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $47.12 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $2,300 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +1:00
Counties/Provinces/States: 10 regions (regions, singular – region); Adamaoua, Centre, Est, Extreme-Nord, Littoral, Nord, North-West (Nord-Ouest), Ouest, Sud, South-West (Sud-Ouest)
Leaders: President Paul BIYA (since 6 November 1982) with Philémon Yang as Prime Minister (since 30 June 2009); Deputy Prime Minister Amadou ALI (since 2014)and Jean NKUETE
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Cameroon
Cameroon, located in West Africa, is a country with a rich history and cultural heritage. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. The country gained independence from France and the United Kingdom in 1960 and has since become an important player in the region.
Cameroon holds great importance in West Africa due to its strategic location and natural resources. It is known as “Africa in miniature” because it showcases a diverse range of landscapes, cultures, and traditions within its borders. The country is home to dense rainforests, savannahs, mountains, and beautiful coastlines. Its cultural diversity is also remarkable, with over 250 ethnic groups speaking different languages and practising various customs.
Geography and Climate of Cameroon: From the Coast to the Mountains
Cameroon’s geography is incredibly diverse, ranging from coastal plains to mountainous regions. The country is divided into four major geographical regions: the coastal plain, the western highlands, the Adamawa Plateau, and the northern plains.
The coastal plain stretches along the Gulf of Guinea and is characterized by sandy beaches, mangroves, and estuaries. Moving inland, the landscape gradually rises into the western highlands, which include volcanic mountains such as Mount Cameroon, the highest peak in West Africa. The Adamawa Plateau lies in the central part of the country and is known for its grassy plains and rolling hills. Finally, the northern plains are semi-arid and consist of vast savannahs.
Cameroon’s climate varies depending on the region. The coastal areas experience a tropical climate with high humidity and heavy rainfall throughout the year. Inland regions have a more equatorial climate with distinct wet and dry seasons. The northern parts of the country have a Sahelian climate, characterized by hot and dry conditions.
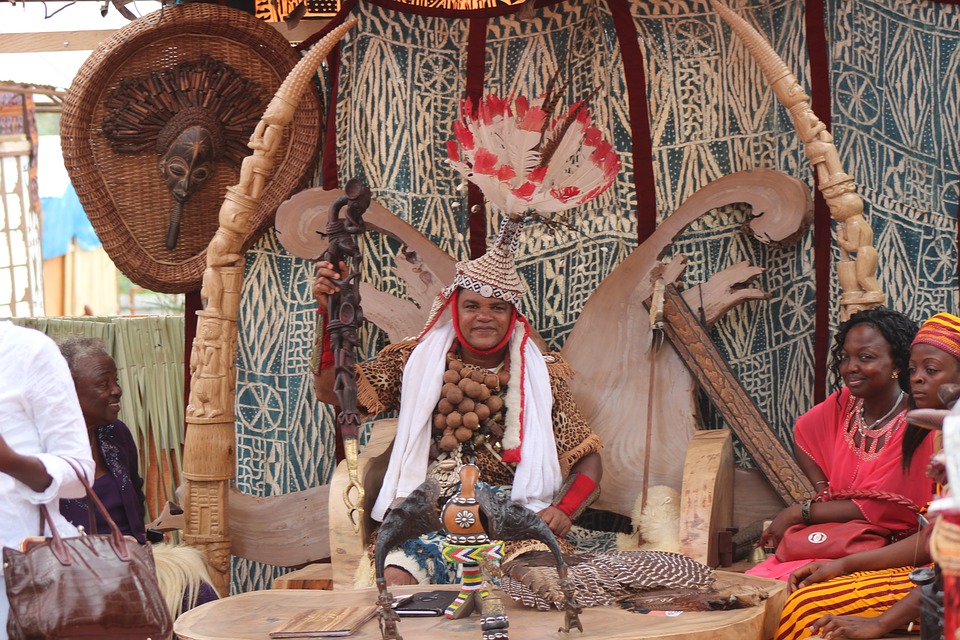
Culture and Traditions of Cameroon: Diversity and Unity
Cameroon is known for its cultural diversity, with over 250 ethnic groups living within its borders. Each group has its own unique customs, traditions, and languages. The major ethnic groups include the Bamileke, Bassa, Bamiléké, and Fulani.
Despite the diversity, there is a strong sense of unity among Cameroonians. The country’s motto, “Unity in Diversity,” reflects the harmonious coexistence of different cultures and ethnicities. Traditional customs and practices play a significant role in Cameroonian society, with ceremonies, dances, and rituals being an integral part of everyday life.
One of the most famous cultural events in Cameroon is the Ngondo Festival, celebrated by the Duala people. It is a week-long event that takes place in December and includes traditional dances, music performances, and canoe races. Another important cultural tradition is the Nso Palace Dance, which is held annually in the Nso Kingdom. It showcases the rich cultural heritage of the Nso people through music, dance, and elaborate costumes.
Languages Spoken in Cameroon: French, English and Local Dialects
Cameroon is a bilingual country with both French and English as its official languages. This linguistic diversity is a result of the country’s colonial history, with France colonizing the eastern part of Cameroon and Britain colonizing the western part.
In addition to French and English, there are also numerous local dialects spoken throughout Cameroon. These dialects vary from region to region and are often associated with specific ethnic groups. Some of the most widely spoken dialects include Ewondo, Duala, Bamileke, Fulfulde, and Bassa.
The linguistic diversity in Cameroon reflects the country’s multiculturalism and adds to its rich cultural tapestry. It also poses challenges in terms of communication and education, as not all Cameroonians are fluent in both official languages.
Economy of Cameroon: Agriculture, Oil and Mineral Resources
Cameroon’s economy is diverse, with agriculture, oil, and mineral resources being the major contributors. The country has a favourable climate for agriculture, and it is one of the largest producers of cocoa, coffee, and bananas in Africa. Other important agricultural products include palm oil, rubber, and timber.
In recent years, Cameroon has also emerged as a significant player in the oil and gas industry. It has offshore oil reserves in the Gulf of Guinea and onshore oil fields in the southwestern region. The country’s mineral resources include bauxite, iron ore, gold, and diamond.
Despite these abundant resources, Cameroon faces challenges in terms of economic development and poverty reduction. The economy is heavily reliant on primary commodities, making it vulnerable to fluctuations in global prices. There is a need for diversification and investment in sectors such as manufacturing and tourism to promote sustainable economic growth.
Political System of Cameroon: A Republic with a President
Cameroon is a republic with a presidential system of government. The President is both the head of state and the head of government. The current President of Cameroon is Paul Biya, who has been in power since 1982.
The country’s political system is characterized by a strong executive branch and limited checks and balances. The President has significant powers, including the ability to appoint and dismiss government officials, dissolve the National Assembly, and declare a state of emergency.
The National Assembly is the legislative body in Cameroon and consists of 180 members who are elected for a five-year term. However, the ruling party has maintained a strong grip on power for decades, leading to concerns about political pluralism and democratic governance.
Education in Cameroon: Challenges and Opportunities
Education in Cameroon faces numerous challenges, including limited access, low quality, and inadequate infrastructure. The country has made progress in increasing primary school enrollment rates, but there are still disparities between urban and rural areas.
The quality of education is also a concern, with overcrowded classrooms, a lack of qualified teachers, and outdated teaching materials. Many children drop out of school due to poverty, early marriage, or the need to work to support their families.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for improvement. The government has implemented policies to promote access to education and improve the quality of teaching. There is also a growing recognition of the importance of vocational training and technical education to address the skills gap and promote economic development.
Health and Healthcare in Cameroon: Progress and Challenges
Cameroon’s healthcare system has made significant progress in recent years, but challenges remain. The country has made strides in reducing child mortality rates and improving access to healthcare services. However, there are still disparities between urban and rural areas, with limited access to healthcare facilities in remote regions.
Infectious diseases such as malaria, HIV/AIDS, and tuberculosis are major health concerns in Cameroon. The government has implemented various programs to combat these diseases, including the distribution of mosquito nets, free HIV testing, and antiretroviral treatment.
There is also a need for investment in healthcare infrastructure and the training of healthcare professionals. Many rural areas lack basic healthcare facilities, and there is a shortage of doctors and nurses in the country.
Tourism in Cameroon: Natural Wonders and Cultural Heritage
Cameroon has great potential for tourism due to its natural wonders and cultural heritage. The country offers diverse landscapes, including national parks, mountains, waterfalls, and beautiful beaches.
One of the most popular tourist destinations in Cameroon is Mount Cameroon. It attracts climbers from around the world who want to conquer its challenging slopes. The Waza National Park is another must-visit destination, known for its diverse wildlife, including elephants, lions, and giraffes.
Cameroon is also rich in cultural heritage, with numerous cultural festivals and historical sites. The city of Foumban is famous for its traditional crafts, including pottery, weaving, and woodcarving. The Royal Palace in Foumban is a UNESCO World Heritage site and showcases the traditional architecture of the Bamoun people.
Sports in Cameroon: Football, Athletics and More
Sports play a significant role in Cameroonian society, with football being the most popular sport. The national football team, known as the Indomitable Lions, has achieved great success on the international stage, winning the African Cup of Nations multiple times.
In addition to football, athletics is also popular in Cameroon. The country has produced several world-class athletes, including Françoise Mbango Etone, who won two Olympic gold medals in the triple jump.
Other popular sports in Cameroon include basketball, handball, and boxing. The government has invested in sports infrastructure and programs to promote physical activity and talent development.
Conclusion: Recap of Cameroon’s rich history, diverse culture, and promising future.
Cameroon is a country with a rich history, diverse culture, and a promising future. Its strategic location in West Africa, coupled with its abundant natural resources, makes it an important player in the region. The country’s geography ranges from coastal plains to mountainous regions, offering a variety of landscapes for tourists to explore.
Cameroon’s cultural diversity is one of its greatest assets. With over 250 ethnic groups speaking different languages and practising various customs, the country showcases a harmonious coexistence of different cultures. Traditional customs and practices are an integral part of Cameroonian society and are celebrated through festivals and events.
Despite the challenges it faces in terms of education and healthcare, Cameroon has made progress in these areas. The government has implemented policies to promote access to education and improve the quality of teaching. In healthcare, efforts have been made to combat infectious diseases and improve access to healthcare services.
Cameroon’s tourism industry has great potential, with its natural wonders and cultural heritage attracting visitors from around the world. The country’s sports culture is also thriving, with football and athletics being the most popular sports.
In conclusion, Cameroon is a country with a rich history, diverse culture, and a promising future. Its geographical diversity, cultural heritage, and natural resources make it a unique destination for tourists. With continued investment in education, healthcare, and infrastructure, Cameroon has the potential to achieve sustainable economic growth and improve the quality of life for its citizens.
FAQs
What is Cameroon?
Cameroon is a country located in Central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south.
What is the capital city of Cameroon?
The capital city of Cameroon is Yaoundé. It is located in the southern part of the country and is the second-largest city in Cameroon after Douala.
What is the population of Cameroon?
As of 2021, the estimated population of Cameroon is around 27.2 million people.
What is the official language of Cameroon?
Cameroon has two official languages: English and French. English is spoken mainly in the western and southern regions of the country, while French is spoken mainly in the eastern and northern regions.
What is the currency of Cameroon?
The currency of Cameroon is the Central African CFA franc (XAF). It is also used by five other countries in Central Africa.
What is the climate like in Cameroon?
Cameroon has a tropical climate with two main seasons: a rainy season from March to October and a dry season from November to February. The coastal regions are generally hot and humid, while the northern regions are drier and hotter.
What are the main industries in Cameroon?
The main industries in Cameroon include agriculture, forestry, mining, and manufacturing. The country is known for its production of cocoa, coffee, and oil. It also has significant deposits of bauxite, iron ore, and gold.
Political Boundaries of Cameroon: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Cameroon, located in Central Africa, is a country with diverse political boundaries that have evolved over time. Understanding these boundaries is crucial for comprehending the country’s governance, resource allocation, and national development. This article...
Climate Zones of Cameroon: Different climate regions Of Cameroon
Introduction to Cameroon’s Climate Zones Cameroon, located in Central Africa, is known for its diverse geography and climate. The country is bordered by Nigeria to the west, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea,...
Terrain and Topography of Cameroon: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Cameroon, located in Central Africa, is a country known for its diverse and breathtaking terrain and topography. From towering mountain ranges to lush valleys and vast plains, Cameroon offers a wide range of landscapes that are both awe-inspiring and important for the...
History of Cameroon
Cameroon, located in Central Africa, is a country with a rich and complex history. Understanding Cameroon’s past is crucial for comprehending its present and shaping its future. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of Cameroon’s history, from...
Terrain and Topography of Cameroon: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Cameroon, located in Central Africa, is a country known for its diverse terrain and topography. From majestic mountains to vast plains and valleys, Cameroon offers a wide range of landscapes that contribute to its unique beauty and biodiversity. Understanding the...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Cameroon: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Cameroon
Cameroon, located in Central Africa, is a country known for its rich cultural heritage. With over 250 ethnic groups, each with its own unique traditions and customs, Cameroon is a melting pot of diverse cultures. From historical sites to ancient traditions, the...
Natural Resources of Cameroon: Where Natural Resources are located In Cameroon
Cameroon, located in Central Africa, is blessed with a wide range of natural resources that contribute significantly to its economy and the livelihoods of its people. These resources include minerals, forests and timber, agricultural land, water, petroleum and gas,...
Population Density of Cameroon
Cameroon, located in Central Africa, is a country with a diverse population and a wide range of geographical features. With an estimated population of over 25 million people, Cameroon has a population density of approximately 50 people per square kilometer....
Exploring the Vibrant Culture and Breathtaking Landscapes of Cameroon
Cameroon, located in Central Africa, is a country known for its rich cultural heritage, stunning landscapes, and warm hospitality. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and...