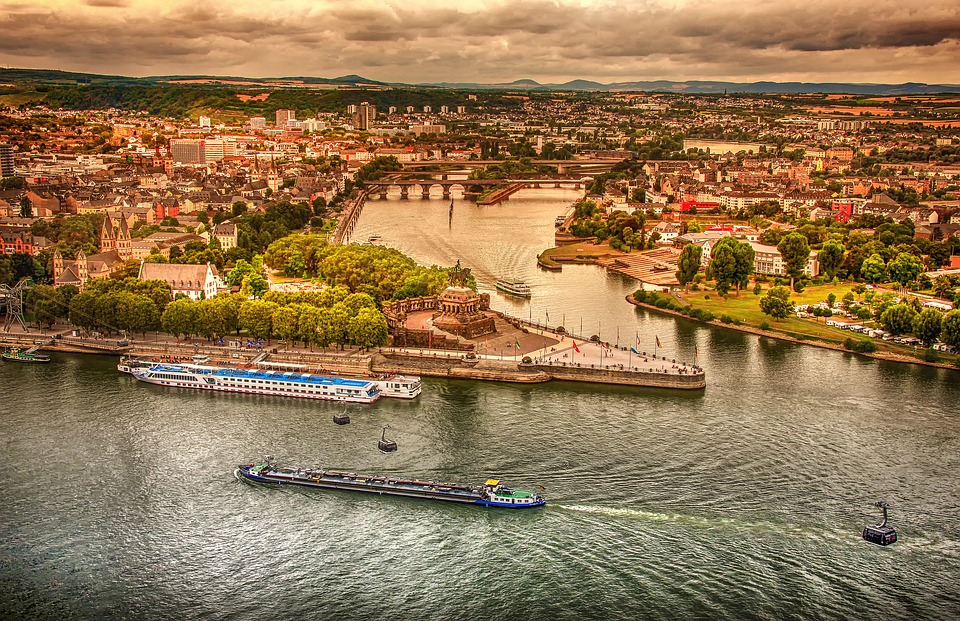
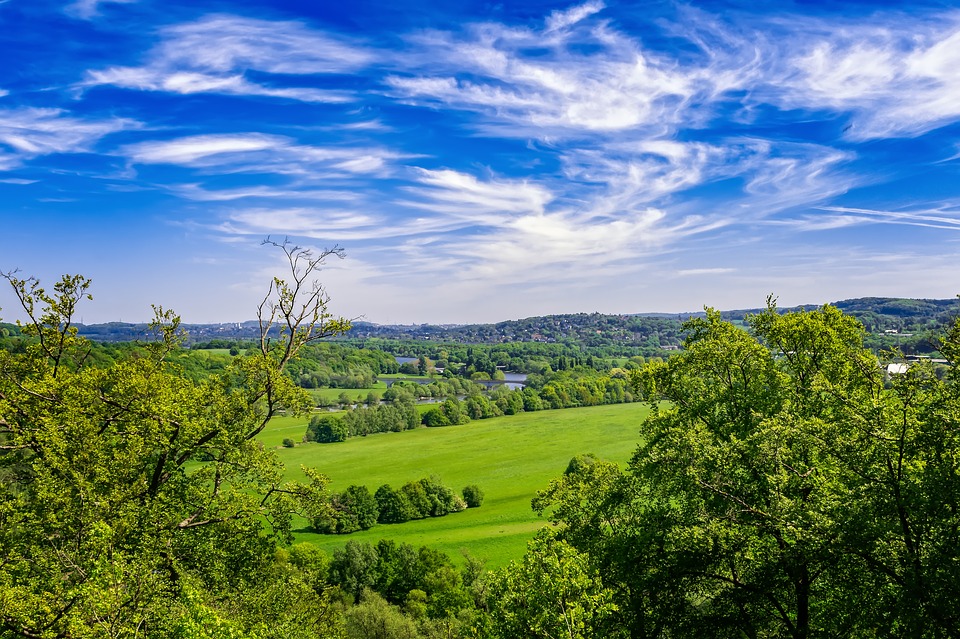
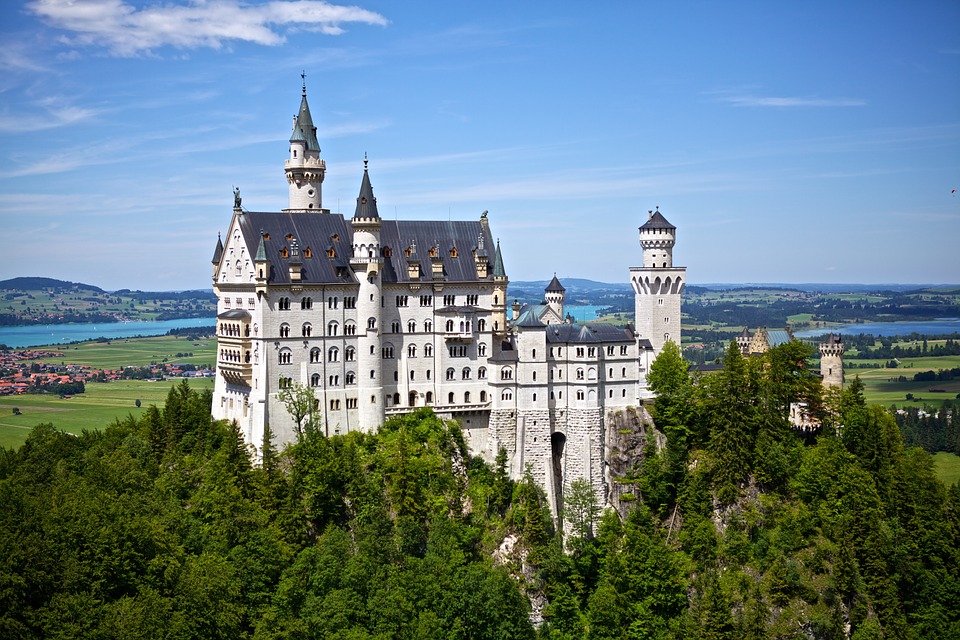
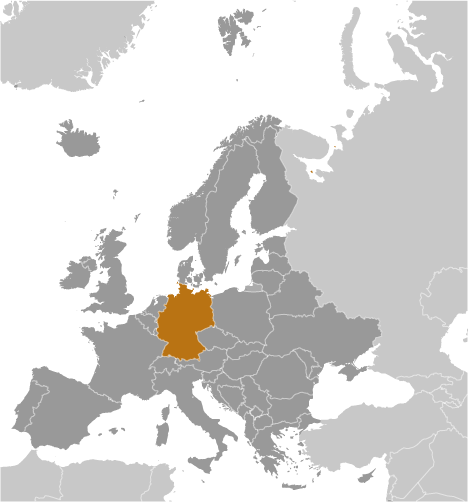
Germany
(Bundesrepublik Deutschland (Federal Republic of Germany))
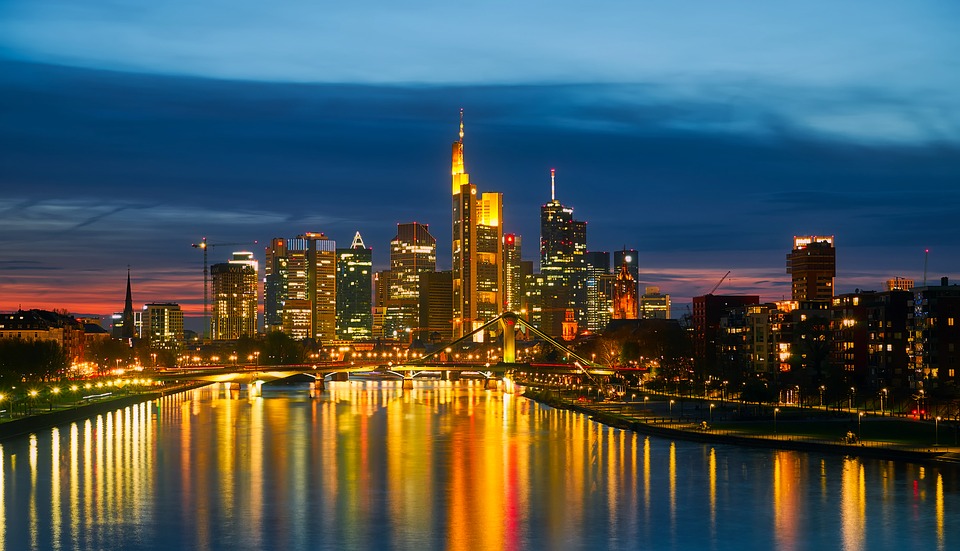
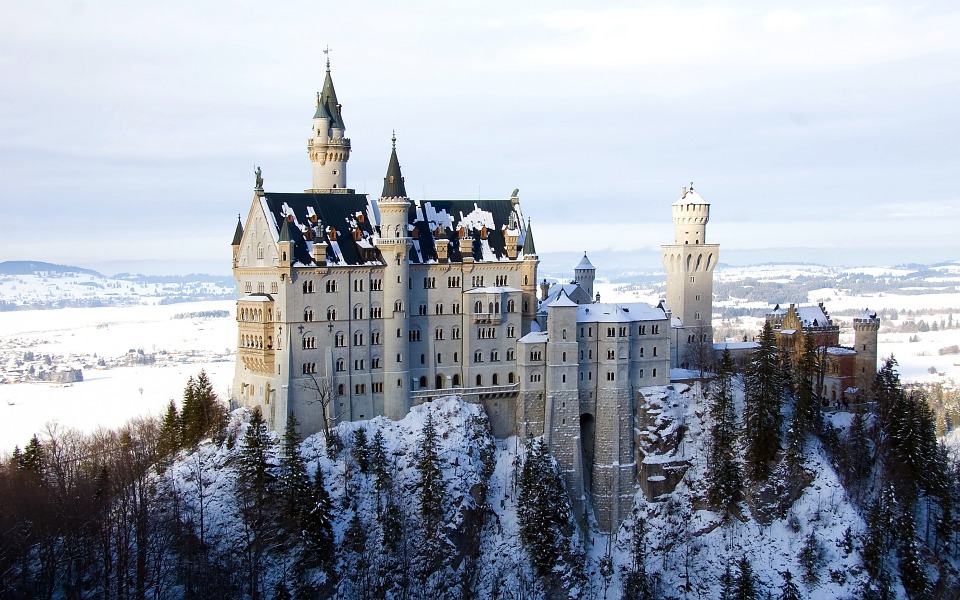
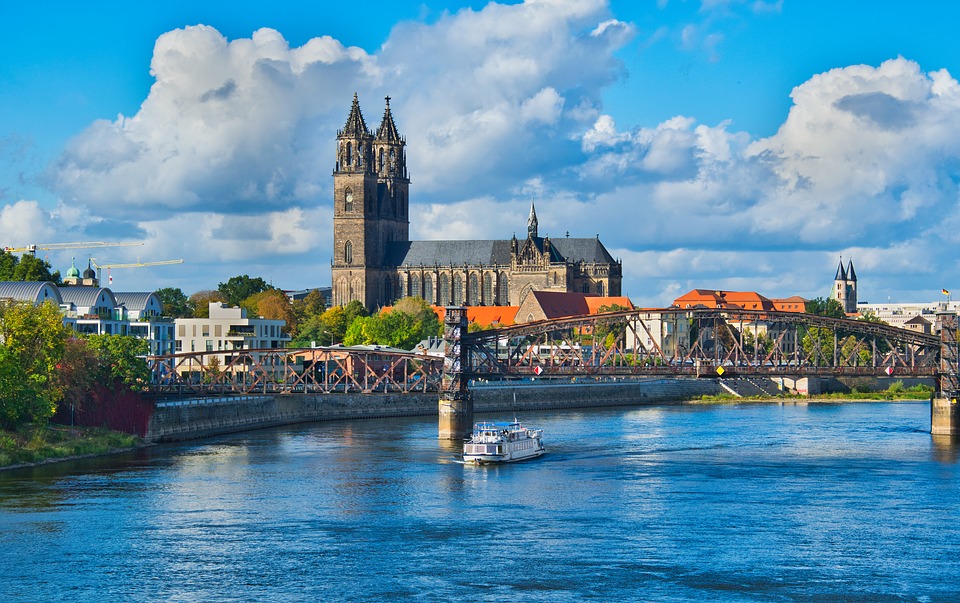
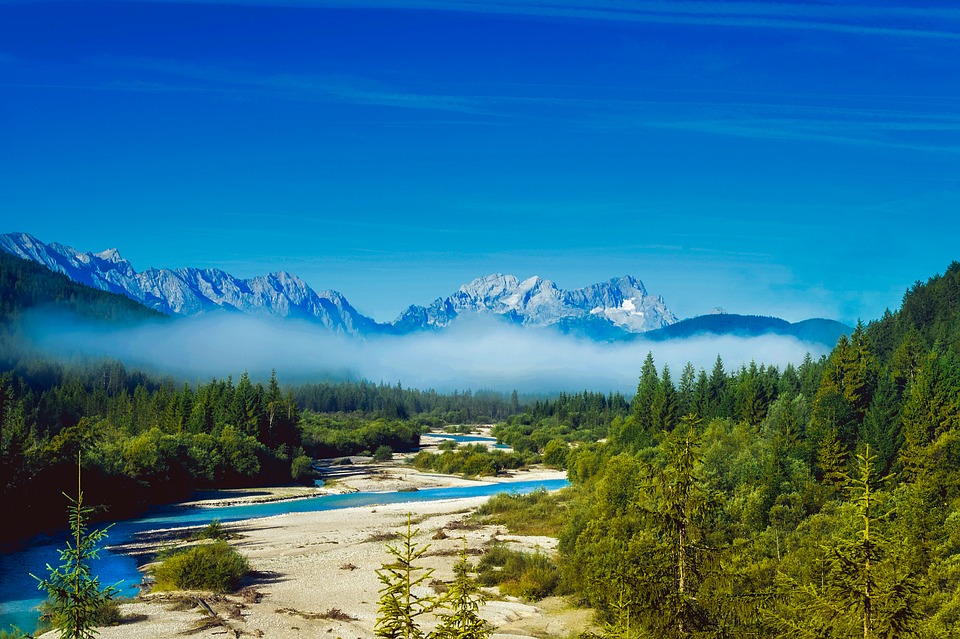

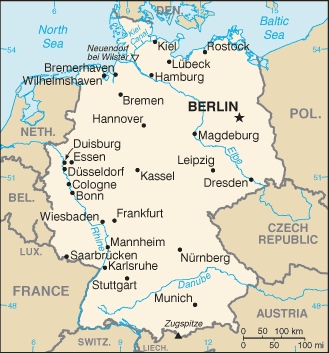
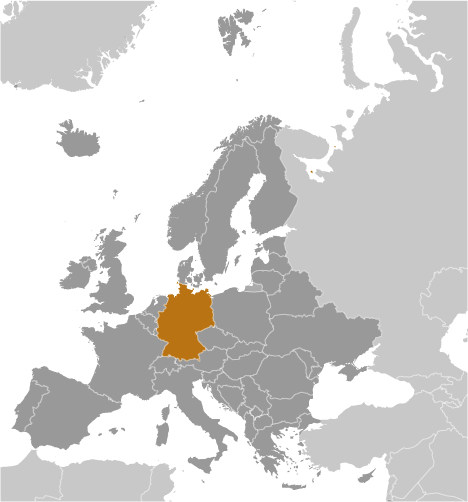





Capital: Berlin
Population (Estimated July 2012): 81,305,856
Area: 357,104 km2 or 137,879 mi2
Currency: Euro (€)
Official Language: German
Political Information: Federal Parliamentary Constitutional Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 34% of the population are Protestant, 34% are Roman Catholic, 3.7% are Muslim and 28.3% have other religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Zugspitze at 2,963m or 9,721ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $3.629 trillion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $3.085 trillion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $37,900 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +1:00
Counties/Provinces/States: 16 states (Laender, singular – Land); Baden-Wurttemberg, Bayern (Bavaria), Berlin, Brandenburg, Bremen, Hamburg, Hessen (Hesse), Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania), Niedersachsen (Lower Saxony), Nordrhein-Westfalen (North Rhine-Westphalia), Rheinland-Pfalz (Rhineland-Palatinate), Saarland, Sachsen (Saxony), Sachsen-Anhalt (Saxony-Anhalt), Schleswig-Holstein, Thuringen (Thuringia); note – Bayern, Sachsen, and Thuringen refer to themselves as free states (Freistaaten, singular – Freistaat)
Leaders: Acting President Horst Seehofer with Chancellor Angela Merkel.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Germany
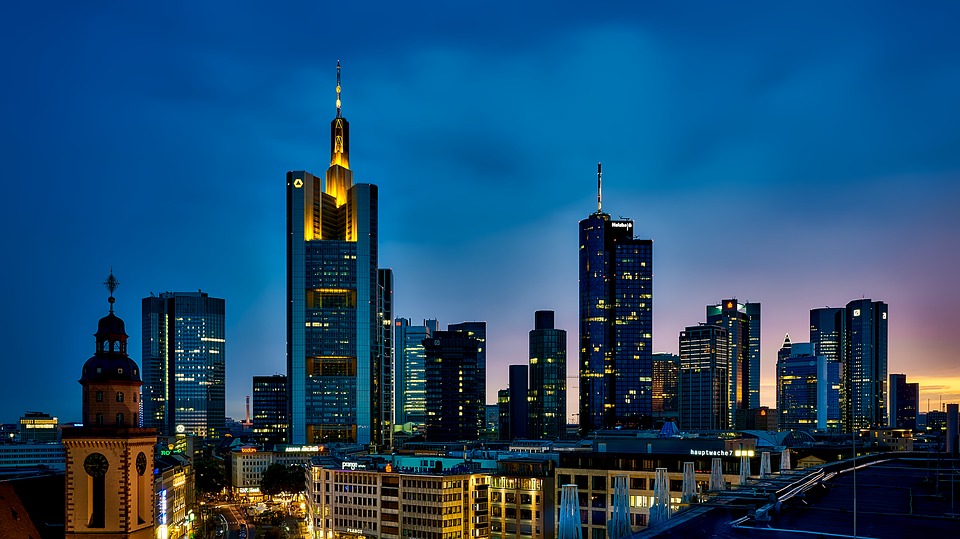
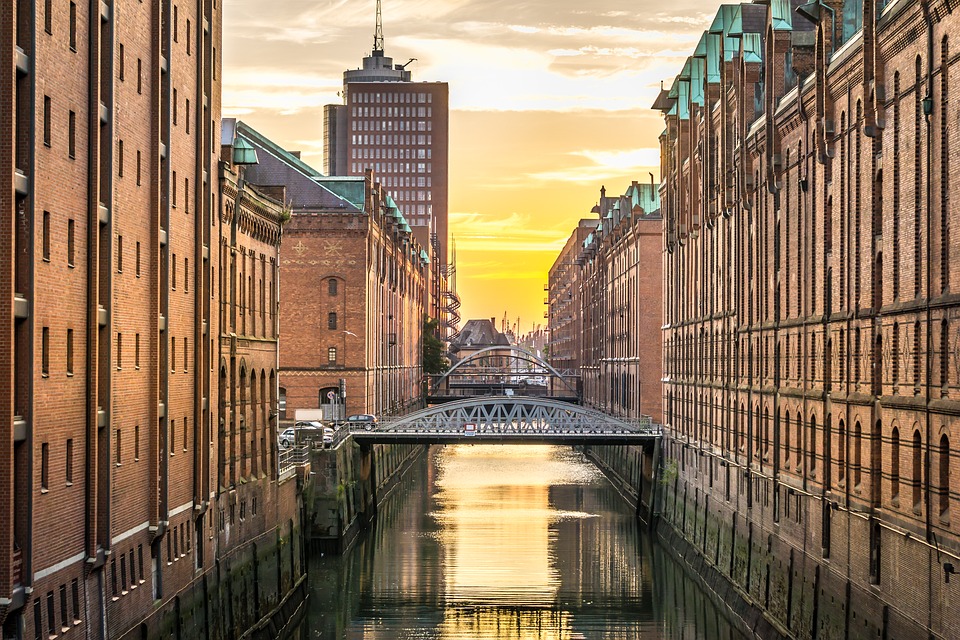
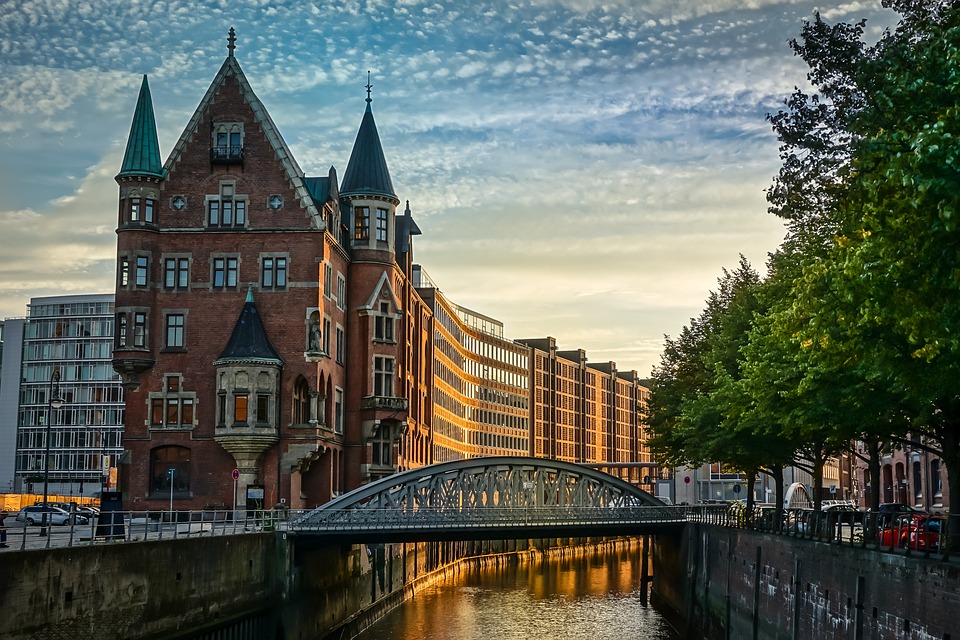
Germany, officially known as the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country located in the heart of Europe. It is bordered by nine other countries, making it a central hub for trade and cultural exchange. With a population of over 83 million people, Germany is the most populous country in the European Union and the fourth-largest economy in the world. The capital city, Berlin, is known for its rich history, vibrant arts scene, and diverse population. Germany is also home to other major cities such as Munich, Hamburg, and Frankfurt, each with its own unique charm and character.
The country is known for its strong economy, efficient infrastructure, and high standard of living. Germany has a rich cultural heritage, with a long history of contributions to art, music, literature, and philosophy. The country is also famous for its engineering and technological innovations, with companies like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Siemens leading the way in their respective industries. Germany is a popular tourist destination, attracting millions of visitors each year with its picturesque landscapes, historic castles, and world-class museums. From the bustling streets of Berlin to the serene beauty of the Bavarian Alps, Germany offers something for everyone.
German Culture and Traditions
German culture is rich and diverse, with a long history of traditions and customs that have been passed down through generations. One of the most famous German traditions is Oktoberfest, a 16-day festival held in Munich that celebrates Bavarian culture with beer, food, and traditional music. Germans are also known for their love of sausages, pretzels, and hearty dishes like schnitzel and sauerkraut. The country is also famous for its Christmas markets, where visitors can shop for handmade crafts, enjoy festive treats, and soak up the holiday spirit.
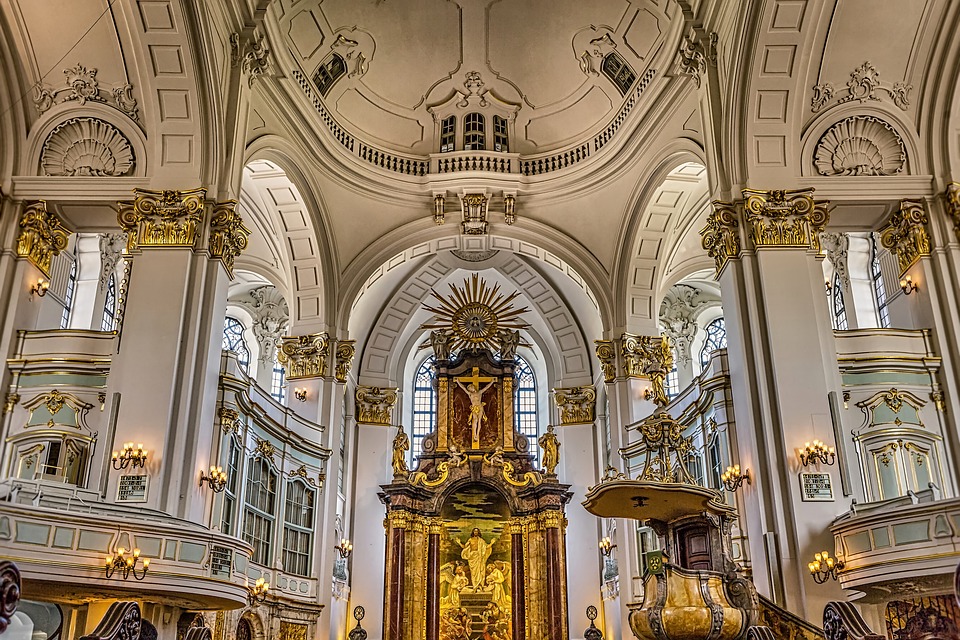
Music is an integral part of German culture, with classical composers like Beethoven, Bach, and Mozart hailing from the region. Germany is also known for its contributions to the world of electronic music, with influential artists like Kraftwerk and Tangerine Dream shaping the genre. The country has a strong tradition of theatre and opera, with world-renowned venues like the Berlin State Opera and the Bayreuth Festival Theatre attracting audiences from around the globe. German literature has also made a significant impact on the world, with authors like Goethe, Kafka, and Hesse producing timeless works that continue to be studied and celebrated today.
The History of Germany
The history of Germany is a complex tapestry of triumphs and tragedies that have shaped the country into what it is today. From the time of the Holy Roman Empire to the devastation of World War II, Germany has experienced a wide range of political and social upheavals. The country has been home to influential figures such as Martin Luther, whose Protestant Reformation had a profound impact on European history, and Otto von Bismarck, who played a key role in the unification of Germany in 1871.
The 20th century saw Germany embroiled in two devastating world wars, leading to widespread destruction and loss of life. The aftermath of World War II saw the country divided into East and West Germany, with the Berlin Wall symbolising the divide between the capitalist West and the communist East. The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 marked a turning point in German history, leading to the reunification of the country and the eventual dissolution of the Soviet Union. Today, Germany is a thriving democracy with a strong commitment to human rights and social justice.
German Cuisine and Beer
German cuisine is hearty and satisfying, with a focus on meat, potatoes, and bread. Sausages are a staple of German cuisine, with varieties like bratwurst, currywurst, and weisswurst enjoyed throughout the country. Pork is also a popular choice for meat dishes, with classics like schnitzel and roast pork served with rich gravies and tangy sauerkraut. Potatoes are a versatile ingredient in German cooking, used to make dishes like potato salad, dumplings, and mashed potatoes.
Beer is an integral part of German culture, with a long history of brewing dating back to the Middle Ages. The country is famous for its beer purity law, known as the Reinheitsgebot, which dictates that beer can only be made from water, hops, malt, and yeast. This commitment to quality has led to Germany producing some of the finest beers in the world, with styles like pilsner, hefeweizen, and bock enjoyed by beer enthusiasts around the globe. The annual Oktoberfest celebration in Munich is a testament to Germany’s love of beer, with millions of litres consumed during the two-week festival.
Famous Landmarks in Germany
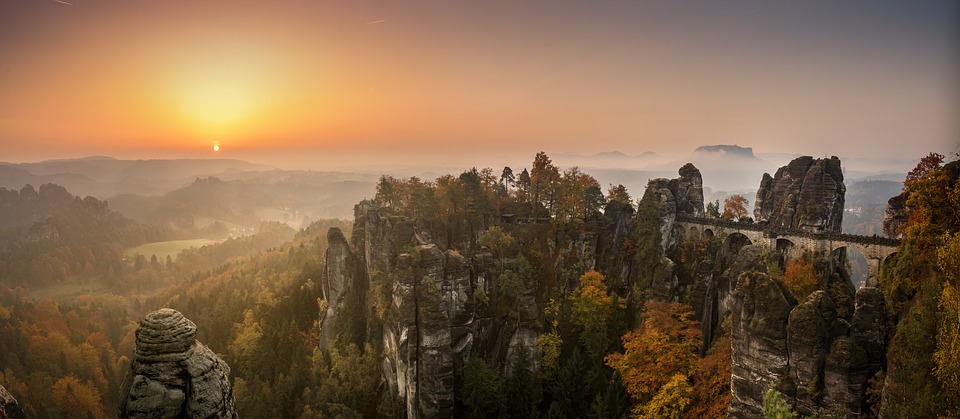
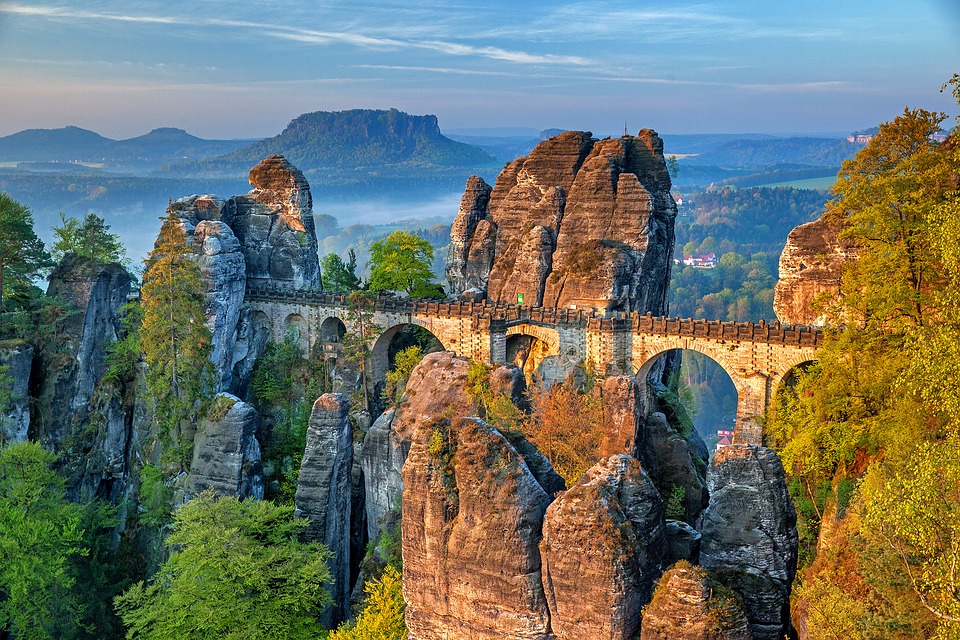
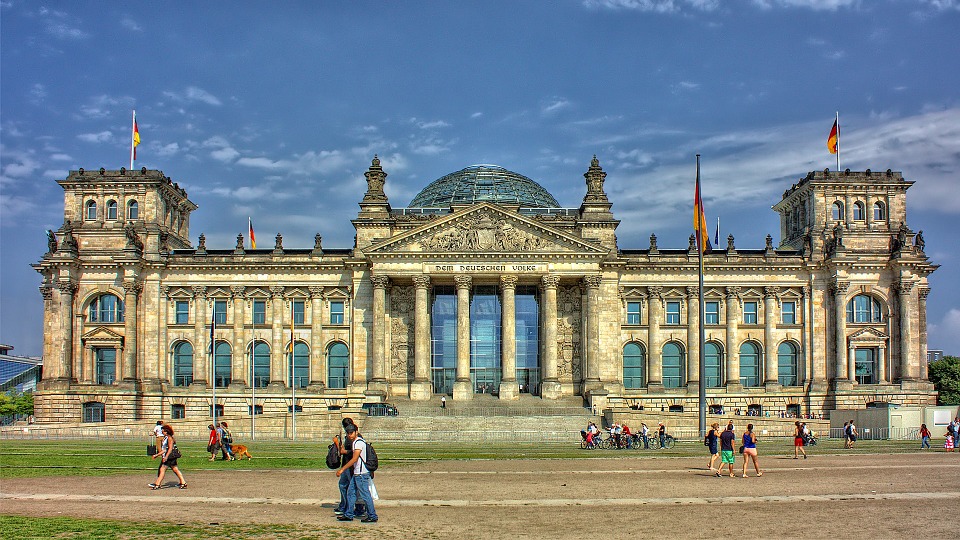
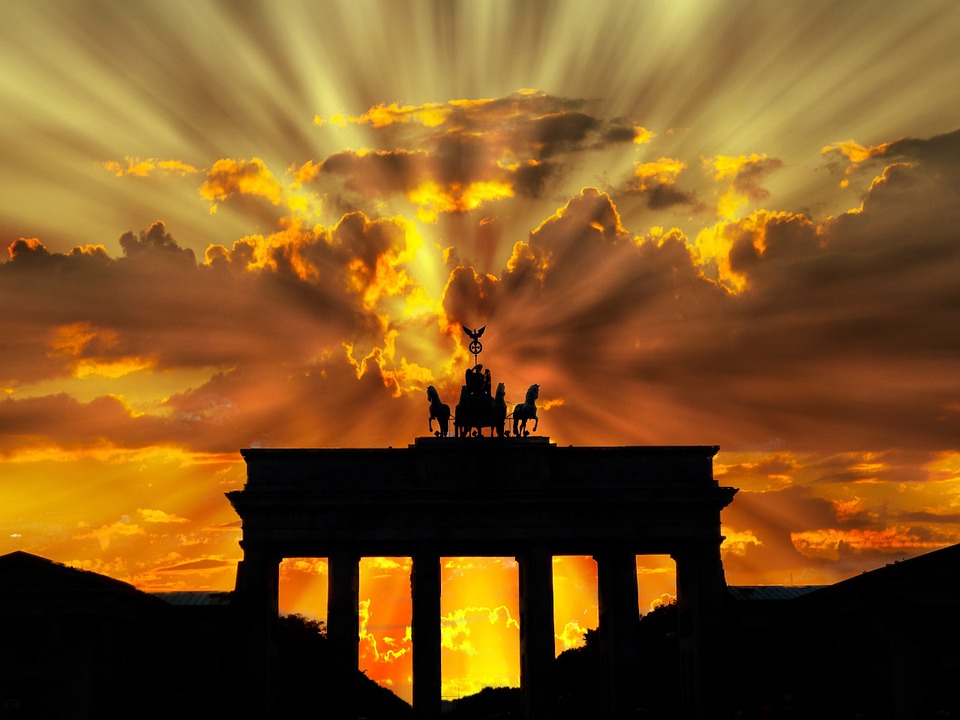
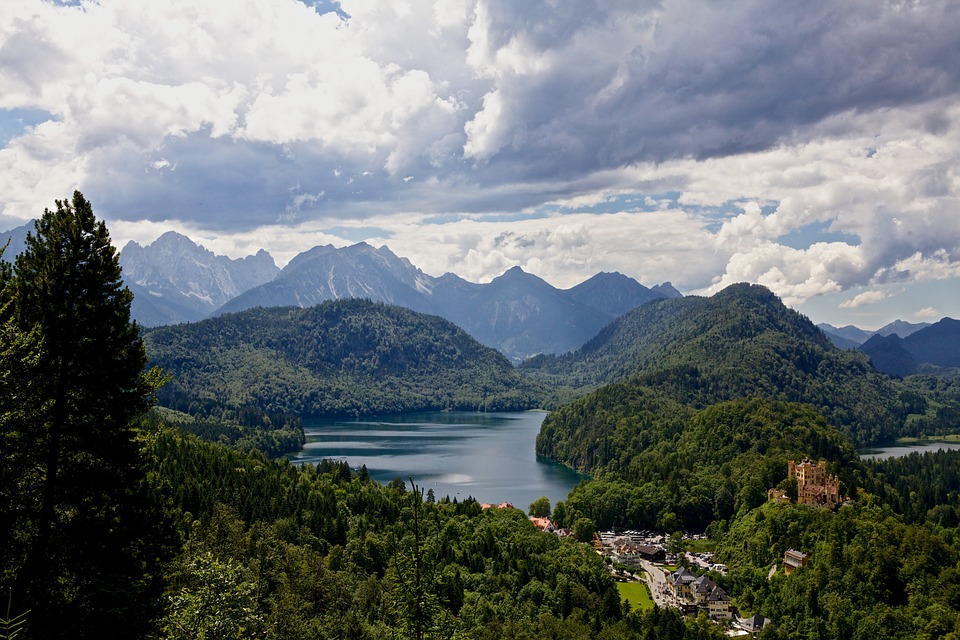
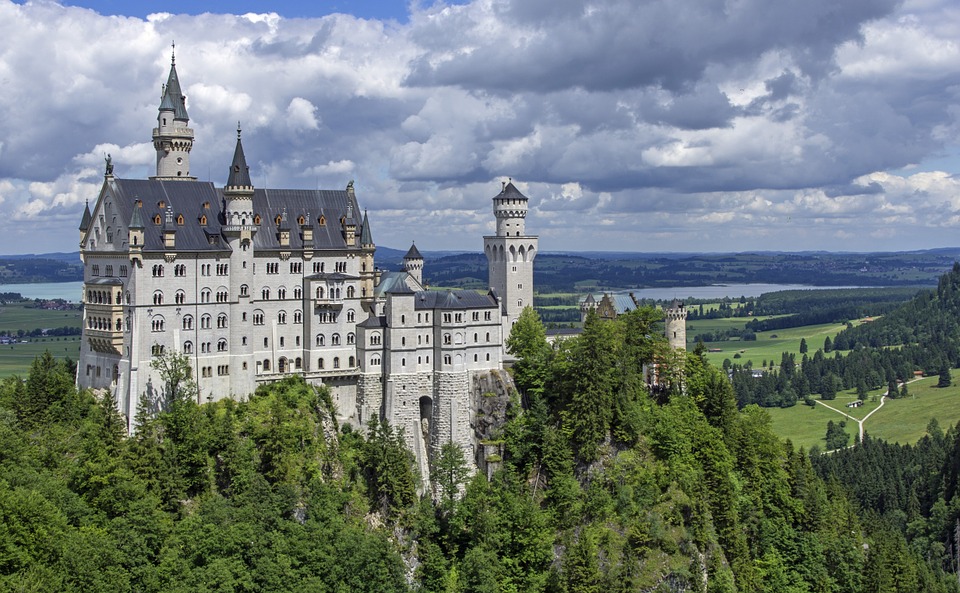
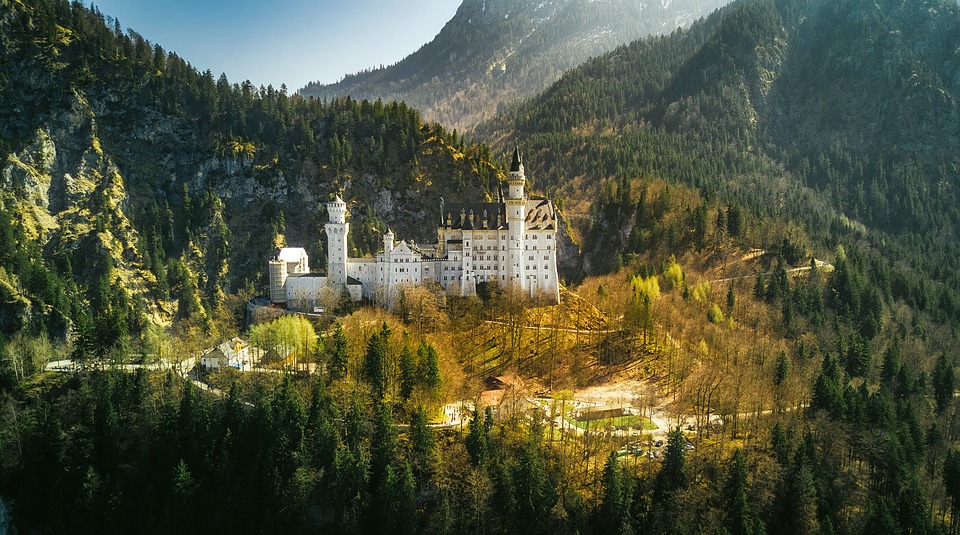
Germany is home to a wealth of famous landmarks that attract visitors from all over the world. The Brandenburg Gate in Berlin is one of the most iconic symbols of German unity and freedom, standing as a testament to the country’s tumultuous history. The Neuschwanstein Castle in Bavaria is a fairytale-like fortress that inspired Walt Disney’s Sleeping Beauty Castle and continues to captivate tourists with its stunning architecture and picturesque surroundings.
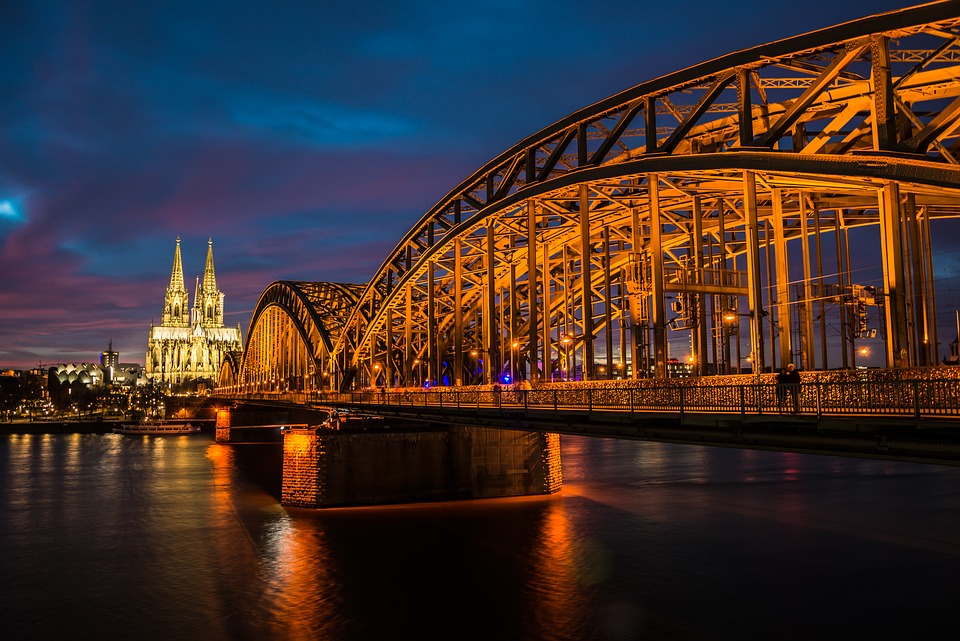
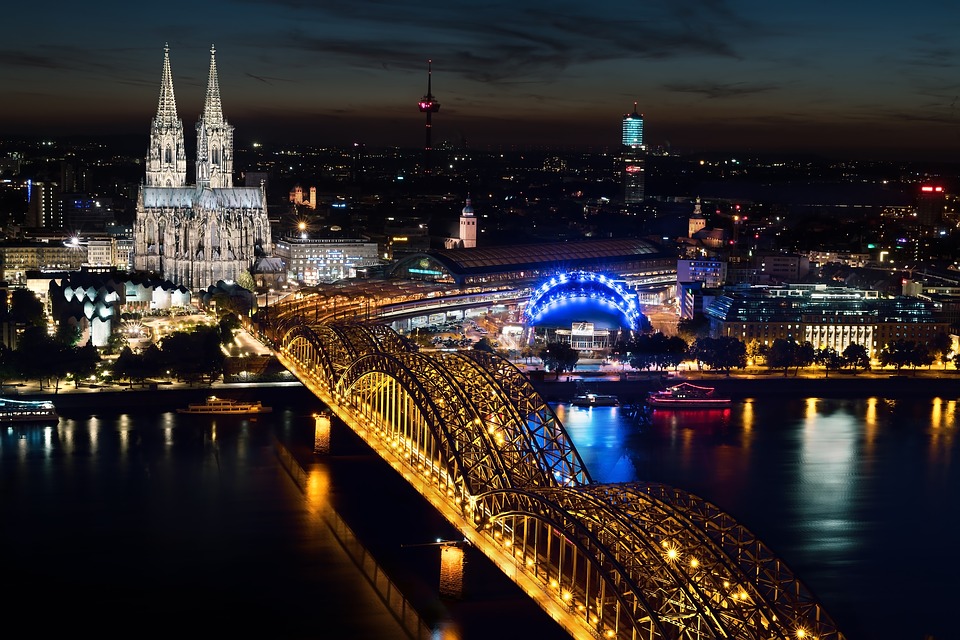
The Cologne Cathedral is a masterpiece of Gothic architecture that took over 600 years to complete and remains one of the most visited sites in Germany. The Black Forest is a sprawling woodland region known for its dense forests, charming villages, and scenic hiking trails. The Romantic Road is a popular tourist route that winds through picturesque towns and medieval castles, offering visitors a glimpse into Germany’s rich history and culture.
German Economy and Industry
Germany has one of the largest economies in the world, known for its strong manufacturing sector, innovative technology companies, and robust export market. The country is a global leader in automotive production, with companies like Volkswagen, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz setting the standard for quality and performance. Germany is also renowned for its engineering prowess, with firms like Siemens and Bosch leading the way in industrial automation and renewable energy solutions.
The country has a highly skilled workforce and a strong emphasis on vocational training, ensuring that its industries remain competitive on the global stage. Germany’s commitment to research and development has led to breakthroughs in fields such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and aerospace. The country’s central location in Europe makes it an ideal hub for trade and commerce, with efficient transportation networks connecting it to markets across the continent.
German Language and Education
The German language is widely spoken around the world, with over 100 million people speaking it as their first language. It is known for its complex grammar rules and compound words that can be challenging for non-native speakers to master. German universities are renowned for their high-quality education system, offering a wide range of courses in fields such as engineering, medicine, and business.
Germany has produced numerous Nobel Prize winners in various disciplines and continues to be a leader in scientific research and innovation. The country’s commitment to education is evident in its free tuition policy for domestic and international students at public universities. This has made Germany an attractive destination for students seeking affordable yet high-quality education. The country also boasts a strong network of research institutions and academic partnerships that contribute to its reputation as a global centre for learning and knowledge creation.
In conclusion, Germany is a country with a rich cultural heritage, a complex history, a thriving economy, and a commitment to education and innovation. Its contributions to art, music, literature, science, and technology have had a lasting impact on the world. From its delicious cuisine to its stunning landmarks, Germany offers visitors a diverse range of experiences that showcase its unique blend of tradition and modernity. Whether you’re exploring its historic cities or hiking through its scenic countryside, Germany has something for everyone to enjoy.
FAQs
What is the capital of Germany?
The capital of Germany is Berlin.
What is the population of Germany?
As of 2021, the population of Germany is approximately 83 million people.
What is the currency used in Germany?
The currency used in Germany is the Euro (€).
What are some famous landmarks in Germany?
Some famous landmarks in Germany include the Brandenburg Gate, Neuschwanstein Castle, Cologne Cathedral, and the Berlin Wall.
What are some popular dishes in German cuisine?
Popular dishes in German cuisine include bratwurst, sauerkraut, schnitzel, pretzels, and Black Forest cake.
What is the climate like in Germany?
Germany has a temperate seasonal climate with moderate rainfall throughout the year. Winters can be cold and summers are generally mild.
What are some famous festivals in Germany?
Some famous festivals in Germany include Oktoberfest in Munich, the Berlin International Film Festival, and the Christmas markets held throughout the country.
What is the official language of Germany?
The official language of Germany is German.
Political Boundaries of Germany: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Germany, located in the heart of Europe, is a country known for its rich history, diverse culture, and strong economy. The political boundaries of Germany play a crucial role in the governance and administration of the country. These boundaries are essential for the organization and management of the various administrative units within the country. From provinces to districts, each political boundary serves a specific purpose in the functioning of the German state. Understanding the intricacies of these boundaries is essential for comprehending the political landscape of Germany and its impact on the lives of its citizens. The political boundaries in Germany are not only a product of modern administrative needs but also have deep historical roots that reflect the country’s complex past. The provinces, districts, and historical boundaries of Germany all contribute to the unique identity and governance structure of the country. This article will delve into the various aspects of political boundaries in Germany, exploring their administrative, cultural, and geographical significance, as well as the challenges and controversies surrounding them. Additionally, we will discuss the potential changes and developments that may shape the future of political boundaries in Germany. Summary Germany is divided into 16 federal states, each with its own government and administrative structure. Provinces in Germany are known as “Länder” and have significant autonomy in areas such as education and law enforcement. Districts in Germany are smaller administrative units within the provinces, responsible for local governance and public services. Historical boundaries in Germany, such as the former East and West Germany divide, continue to influence cultural and political dynamics. The debate over the restructuring of political...
Natural Resources of Germany: Where Natural Resources are located In Germany
Germany is a country rich in natural resources, which have played a significant role in its economic development and industrial growth. The diverse range of natural resources in Germany includes mineral resources, agricultural resources, forest resources, water resources, and energy resources. These resources have been crucial in shaping the country’s economy and have contributed to its status as one of the leading industrial nations in the world. However, the sustainable management of these natural resources is essential to ensure their availability for future generations and to minimize the environmental impact of their exploitation. Germany’s natural resources have been a driving force behind its economic success, and the country has a long history of utilizing these resources for industrial and agricultural purposes. The sustainable management of these resources is crucial for the country’s future development and environmental protection. This article will explore the various natural resources in Germany and the importance of their sustainable management for the country’s continued prosperity. Summary Germany is rich in natural resources, including minerals, agriculture, forests, water, and energy sources. The country has a diverse range of mineral resources, including coal, lignite, potash, and salt, which are crucial for its industrial and economic development. Germany’s agricultural resources are vital for food production, with the country being a leading producer of wheat, barley, and sugar beets. The forest resources in Germany are well-managed, providing timber for various industries and contributing to the country’s biodiversity and ecosystem. Germany’s water resources are abundant, with the country’s rivers and lakes providing essential water supply for various purposes, including agriculture, industry, and domestic use. Mineral Resources in Germany Germany is...
Climate Zones Of Germany: Different climate regions Of Germany
Germany is a country known for its diverse climate zones, ranging from maritime in the north to alpine in the south. These climate zones are influenced by various factors such as latitude, proximity to the sea, and topography. Understanding the different climate zones in Germany is essential for understanding the country’s weather patterns, agricultural practices, and overall environmental diversity. In this article, we will explore the various climate zones in Germany, from the maritime climate of the north to the alpine climate of the south, and discuss the effects of climate change on these regions. Summary Germany has a diverse range of climate zones, influenced by its geographical location and topography. Northern Germany experiences a maritime climate, characterized by mild winters and cool summers with high levels of precipitation. Central Germany has a continental climate, with hot summers, cold winters, and lower levels of precipitation compared to the north. Southern Germany is home to the Alpine climate, with colder temperatures, heavy snowfall in winter, and milder summers. Transitional climate zones exist between the main climate regions, creating a variety of microclimates across the country. The Maritime Climate of Northern Germany The northern region of Germany, including cities like Hamburg and Bremen, experiences a maritime climate due to its proximity to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. This climate is characterized by mild temperatures, relatively high humidity, and a significant amount of precipitation throughout the year. Winters are mild, with temperatures rarely dropping below freezing, while summers are cool and pleasant. The maritime climate also brings frequent cloud cover and fog, particularly in the coastal areas. The maritime climate...
History of Germany
The history of Germany can be traced back to the early Germanic tribes that inhabited the region. These tribes, including the Saxons, Franks, and Goths, were known for their fierce warrior culture and their contributions to the development of the German language. The Germanic tribes were also known for their complex social structures and their pagan religious beliefs. They were often in conflict with the Roman Empire, and their interactions with the Romans had a significant impact on their culture and society. The Germanic tribes were skilled in agriculture, metalworking, and trade, and they established a network of trade routes that connected them with other parts of Europe. They also had a strong tradition of storytelling and oral poetry, which played a crucial role in preserving their history and cultural identity. The Germanic tribes eventually came into contact with Christianity through the efforts of missionaries, and this led to the gradual conversion of the Germanic people to Christianity. This conversion had a profound impact on the development of German culture and society, as it brought them into closer contact with the wider Christian world and influenced their political and social structures. Summary Early Germanic tribes were diverse and often in conflict with each other, but they shared common cultural and linguistic roots. Charlemagne’s Holy Roman Empire was a significant political and cultural force in Europe, promoting Christianity and education. The Protestant Reformation and the Thirty Years’ War had a profound impact on the religious and political landscape of Germany. The unification of Germany under Prussian leadership in 1871 marked a significant turning point in European history. World War I...
Terrain and Topography of Germany: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Germany is a country located in central Europe, known for its diverse and varied terrain. The topography of Germany is characterized by a mix of mountainous regions, valleys, lowlands, plains, and plateaus. The country’s terrain has played a significant role in shaping its climate, environment, history, and culture. From the towering peaks of the Bavarian Alps to the fertile plains of the North German Plain, Germany’s landscape offers a rich tapestry of natural beauty and geographical diversity. The terrain of Germany is a result of geological processes that have shaped the land over millions of years. The country is situated at the crossroads of several tectonic plates, which has led to the formation of diverse landforms. The Rhine River, one of the most important waterways in Europe, has carved its way through the western part of the country, creating deep valleys and dramatic landscapes. The North German Plain, on the other hand, is a vast expanse of flat and fertile land that stretches across the northern part of the country. With such a varied topography, Germany offers a wide range of natural environments, each with its own unique characteristics and significance. Summary Germany’s terrain is diverse and varied, consisting of mountainous regions, valleys, lowlands, plains, and plateaus. The mountainous regions of Germany, such as the Bavarian Alps and the Black Forest, offer stunning natural landscapes and opportunities for outdoor activities. The valleys and lowlands of Germany, including the Rhine Valley and the Elbe Valley, are home to fertile farmland and picturesque river landscapes. The plains and plateaus of Germany, such as the North German Plain and the Central Uplands,...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Germany: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites in Germany
Germany is a country rich in cultural and historical sites that attract millions of visitors from around the world each year. From ancient castles to modern memorials, Germany offers a diverse range of attractions that showcase its rich heritage and history. The country’s cultural and historical sites are not only a testament to its past, but also a reflection of its present and future. Visitors to Germany can explore the iconic Brandenburg Gate in Berlin, the majestic Neuschwanstein Castle in Bavaria, the historic city of Nuremberg, the intriguing Berlin Wall Memorial, the enchanting Cologne Cathedral, and the fascinating Museum Island in Berlin. Each of these sites offers a unique glimpse into Germany’s cultural and historical significance, making it a must-visit destination for history enthusiasts and cultural aficionados alike. Summary Germany is home to a wealth of cultural and historical sites that attract visitors from around the world. Nuremberg is a historic city with well-preserved medieval architecture and significant sites such as the Nuremberg Castle and the Nazi Party Rally Grounds. The Brandenburg Gate in Berlin is an iconic symbol of Germany’s reunification and a must-see landmark for visitors to the capital city. Neuschwanstein Castle in Bavaria is a majestic fairytale-like castle that inspired the design of Disney’s Sleeping Beauty Castle. The Berlin Wall Memorial is an intriguing site that offers a glimpse into the history of the Cold War and the division of Germany. The Historic City of Nuremberg Nuremberg is a historic city in the state of Bavaria, known for its well-preserved medieval architecture and rich history. The city’s old town is a testament to its medieval past,...
Population Density of Germany
Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured per square kilometre or square mile. It is an important demographic indicator that provides insights into the distribution of people within a country or region. Understanding population density is crucial for urban planning, resource allocation, and policy-making. In the case of Germany, population density plays a significant role in shaping the country’s social, economic, and environmental landscape. Germany is known for its diverse population distribution, with densely populated urban areas and sparsely populated rural regions. The country’s population density stands at around 240 people per square kilometre, making it one of the most densely populated countries in Europe. However, this density is not evenly distributed across the country, with some regions experiencing high concentrations of people while others remain relatively uninhabited. Understanding the factors that influence population density in Germany is essential for comprehending the country’s demographic patterns and their implications for various aspects of society. Summary Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured in square kilometres. Factors affecting population density in Germany include economic opportunities, infrastructure, and government policies. Urban areas in Germany have higher population density compared to rural areas due to better job opportunities and amenities. Regional variations in population density in Germany are influenced by historical, economic, and geographical factors. High population density in urban areas can strain infrastructure and resources, leading to challenges in providing services and maintaining quality of life. Factors Affecting Population Density in Germany Several factors contribute to the population density in Germany, including historical, economic, and geographical...
Discovering the Hidden Gems of Germany: A British Perspective
Germany is often overlooked as a travel destination for British travellers. Many people opt for more popular destinations like France, Spain, or Italy. However, Germany has a lot to offer, from stunning natural landscapes to rich history and culture. This blog post will explore the best German cities to visit, natural landscapes to explore, historical sites to uncover, festivals to attend, culinary delights to try, unique attractions to discover, and accommodation options to suit all budgets. Summary Germany is a hidden gem for British travellers Berlin and Munich are two of the best German cities to visit The Black Forest and other natural landscapes are stunning to explore Germany’s rich history can be uncovered through castles, museums and more Oktoberfest and other festivals offer a unique cultural experience The Best German Cities to Visit: From Berlin to Munich Germany is home to many vibrant and diverse cities that are worth exploring. Berlin, the capital city, is a must-visit for its rich history and culture. From the iconic Brandenburg Gate to the remnants of the Berlin Wall, there are plenty of historical sites to discover. Munich is another popular city known for its beer gardens and Oktoberfest. It’s a great place to experience Bavarian culture and indulge in traditional German cuisine. Hamburg is a port city with a lively music and arts scene. It’s also home to the famous Reeperbahn, a street known for its nightlife and entertainment. Cologne is famous for its cathedral and Christmas markets, which are a must-visit during the holiday season. Frankfurt, on the other hand, is a financial hub with a mix of modern and...