Iran
(Jomhūrī-ye Eslāmī-ye Īrān (Islamic Republic of Iran))

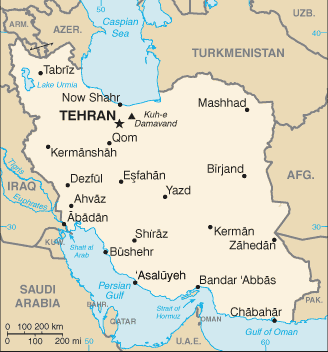



Capital: Tehrān
Population (Estimated July 2012): 78,868,711
Area: 1,648,200 km2 or 636,374 mi2
Currency: Rial (Rls)
Official Language: Farsī (Persian
Political Information: Unitary Islamic Republic
Official Religion: Islam
(approximately 98% of the population are Muslim and 2% have other religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Mount Damāvand at 5,610m or 18,406ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a country’s economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $480.3 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and the use of resources but is not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $928.9 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $12,200 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +3:30
Wildlife:
Counties/Provinces/States: 31 provinces (ostanha, singular – ostan); Alborz, Ardabil, Azarbayjan-e Gharbi (West Azerbaijan), Azarbayjan-e Sharqi (East Azerbaijan), Bushehr, Chahar Mahal va Bakhtiari, Esfahan, Fars, Gilan, Golestan, Hamadan, Hormozgan, Ilam, Kerman, Kermanshah, Khorasan-e Jonubi (South Khorasan), Khorasan-e Razavi (Razavi Khorasan), Khorasan-e Shomali (North Khorasan), Khuzestan, Kohgiluyeh va Bowyer Ahmad, Kordestan, Lorestan, Markazi, Mazandaran, Qazvin, Qom, Semnan, Sistan va Baluchestan, Tehran, Yazd, Zanjan
Leaders: Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei with President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad and First Vice President Mohammad-Reza Rahimi.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Iran
Iran, also known as Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Turkmenistan to the north, Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and Turkey and Iraq to the west. To the south, Iran is bordered by the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. With a population of over 83 million people, Iran is the 18th most populous country in the world. The capital city of Iran is Tehran, which is also the largest city in the country. Iran has a rich history dating back thousands of years, and its culture is deeply rooted in ancient traditions and customs. The official language of Iran is Persian, and the majority of the population practices Islam, with Shia Islam being the dominant sect.
Iran is known for its diverse landscapes, from deserts and mountains to forests and coastlines. The country has a complex political and social landscape, and its role in the Middle East has been a subject of international interest and concern. Despite its challenges, Iran has a rich cultural heritage and a resilient population that continues to shape its future. In recent years, Iran has become an increasingly popular destination for tourists seeking to explore its historical sites, natural beauty, and vibrant cities. With its unique blend of ancient history and modernity, Iran offers a fascinating and enriching experience for visitors from around the world.
History and Culture of Iran
Iran has a long and storied history that dates back to ancient times. It was once the centre of the Persian Empire, one of the largest empires in history, which ruled over a vast territory that stretched from Egypt to India. The Persian Empire made significant contributions to art, architecture, and literature, and its influence can still be seen in modern-day Iran. Over the centuries, Iran has been ruled by various dynasties and empires, including the Achaemenid Empire, the Parthian Empire, and the Sassanian Empire. In the 7th century, Islam was introduced to Iran, and it became the dominant religion in the region.
Iranian culture is deeply rooted in tradition and history. The country has a rich artistic heritage, with contributions to literature, poetry, music, and visual arts. Persian literature is renowned for its epic poems such as the Shahnameh, written by Ferdowsi in the 10th century. Iranian music is characterized by its melodic and rhythmic patterns, often accompanied by traditional instruments such as the tar, setar, and santur. Iranian cuisine is also a significant aspect of its culture, with dishes such as kebabs, stews, and rice-based dishes being popular staples. The people of Iran are known for their hospitality and warmth, and social gatherings and celebrations play an important role in their daily lives.
Geography and Climate of Iran
Iran is a vast country with diverse geographical features. It is home to several mountain ranges, including the Alborz and Zagros mountains, as well as vast deserts such as the Dasht-e Kavir and Dasht-e Lut. The Caspian Sea borders the northern part of Iran, while the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman are located to the south. The country’s varied landscapes provide habitats for a wide range of flora and fauna, making it a haven for nature enthusiasts.
The climate in Iran varies from region to region. In general, the northern parts of the country have a subtropical climate with hot summers and mild winters, while the southern regions experience a hot desert climate with extremely high temperatures during the summer months. The central plateau of Iran has a more arid climate with hot summers and cold winters. The country experiences four distinct seasons, with spring and autumn being particularly pleasant times to visit due to milder temperatures and blooming landscapes.
Economy and Industry in Iran
Iran has a mixed economy that is heavily reliant on its oil and gas reserves. It is one of the largest oil producers in the world and has significant natural gas reserves as well. The oil industry plays a crucial role in Iran’s economy, accounting for a large portion of its export earnings. In recent years, Iran has sought to diversify its economy by investing in other industries such as agriculture, manufacturing, and technology. The country also has a growing tourism sector that has become an important source of revenue.
Agriculture is an important sector in Iran, with crops such as wheat, rice, fruits, and nuts being major contributors to the country’s economy. Iran also has a strong tradition of handicrafts such as carpet weaving, pottery, and metalwork, which are highly valued both domestically and internationally. The manufacturing industry in Iran includes sectors such as automotive production, textiles, and petrochemicals. The government has made efforts to promote entrepreneurship and innovation in recent years, leading to a burgeoning startup scene in cities like Tehran.
Politics and Government in Iran
Iran is an Islamic republic with a complex political system that combines elements of democracy with religious governance. The Supreme Leader holds ultimate authority in the country and is responsible for overseeing all major decisions related to foreign policy, defence, and national security. The President is elected by popular vote and serves as the head of government, responsible for domestic affairs and economic policies. The Iranian parliament, known as the Majlis, is responsible for passing laws and overseeing government actions.
The political landscape in Iran is characterized by a complex interplay between religious leaders, elected officials, and various factions within society. The country has experienced periods of political unrest and social movements seeking greater freedoms and reforms. Despite these challenges, Iran has a relatively stable political system compared to some of its neighbours in the region. The government has made efforts to improve relations with other countries and engage in diplomatic efforts to address international concerns about its nuclear program and human rights record.
Iran’s Role in the Middle East
Iran plays a significant role in shaping political dynamics in the Middle East region. It has been involved in various conflicts and alliances that have had far-reaching implications for regional stability. Iran’s support for groups such as Hezbollah in Lebanon and Hamas in Palestine has been a source of tension with other countries in the region and with Western powers. Its involvement in conflicts such as the Syrian civil war has further complicated its relations with other countries.
At the same time, Iran has sought to position itself as a regional power with influence beyond its borders. It has pursued alliances with countries such as Russia and China to counterbalance Western influence in the region. Iran’s strategic location at the crossroads of Asia, Europe, and Africa gives it significant geopolitical importance. Its oil reserves also make it an important player in global energy markets. As a result, Iran’s actions and policies have implications that extend far beyond its borders.
Tourism and Attractions in Iran
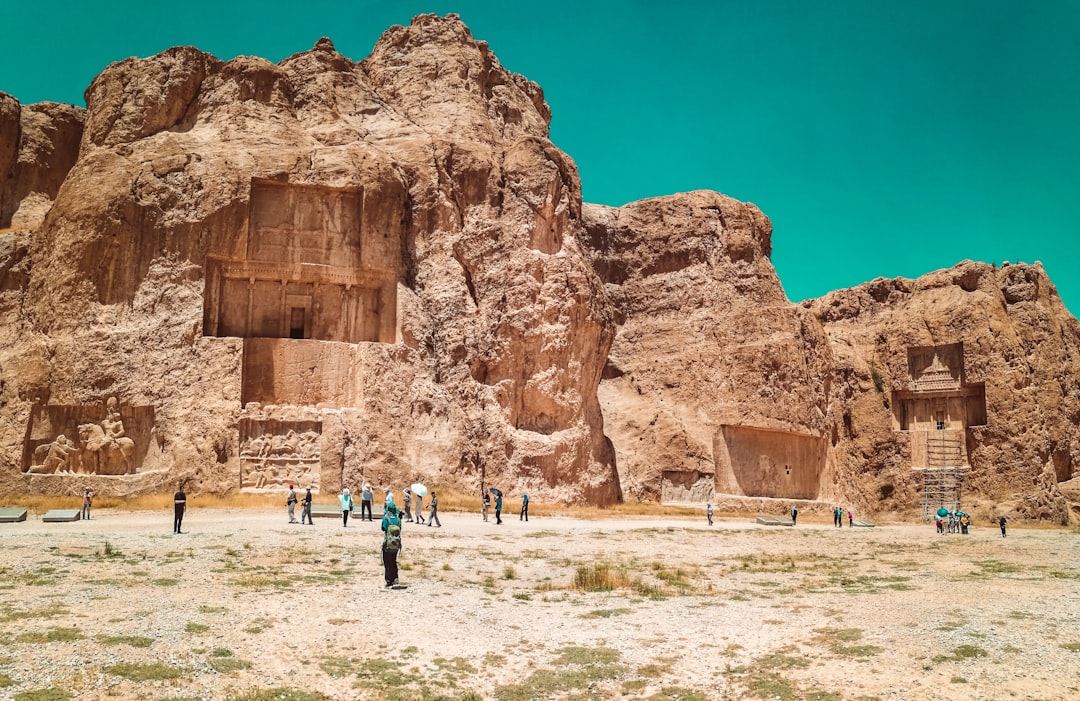
Iran is home to a wealth of historical sites, natural wonders, and vibrant cities that make it an attractive destination for tourists. The ancient city of Persepolis, once the capital of the Achaemenid Empire, is a UNESCO World Heritage site that showcases impressive ruins dating back over 2,500 years. The city of Isfahan is known for its stunning Islamic architecture, including the Imam Mosque and Sheikh Lotfollah Mosque. The city’s historic bazaar is also a popular destination for visitors seeking traditional crafts and local cuisine.
Nature enthusiasts will find plenty to explore in Iran’s diverse landscapes. The Caspian Sea region offers lush forests and scenic coastlines that are popular for beach holidays and outdoor activities. The deserts of central Iran provide opportunities for desert trekking, sandboarding, and stargazing under clear night skies. The Alborz mountains offer hiking opportunities with breathtaking views of snow-capped peaks.
In addition to its historical sites and natural beauty, Iran’s cities offer a vibrant cultural scene with art galleries, museums, theatres, and music venues. Tehran is a bustling metropolis with modern amenities alongside historical landmarks such as Golestan Palace and Azadi Tower. Shiraz is known for its beautiful gardens and poetry traditions, while Yazd boasts well-preserved traditional architecture and Zoroastrian heritage sites.
In recent years, Iran has seen an increase in tourism as more visitors discover its unique attractions and warm hospitality. The government has made efforts to improve infrastructure and promote tourism initiatives to attract more international visitors while preserving its cultural heritage. With its rich history, diverse landscapes, and welcoming people, Iran offers a truly enriching travel experience for those seeking to explore this fascinating country.
FAQs
What is the capital of Iran?
The capital of Iran is Tehran.
What is the population of Iran?
As of 2021, the population of Iran is estimated to be around 83 million people.
What is the official language of Iran?
The official language of Iran is Persian, also known as Farsi.
What is the currency of Iran?
The currency of Iran is the Iranian rial.
What type of government does Iran have?
Iran is an Islamic Republic with a system of government based on the principles of Islamic law.
What are the major industries in Iran?
Iran’s major industries include oil and gas production, petrochemicals, agriculture, and manufacturing.
What are some popular tourist attractions in Iran?
Popular tourist attractions in Iran include the ancient city of Persepolis, the Nasir al-Mulk Mosque, the Golestan Palace, and the city of Isfahan with its stunning architecture.
What are some traditional dishes in Iranian cuisine?
Traditional Iranian dishes include kebabs, rice dishes such as chelo kebab and tahchin, and stews such as ghormeh sabzi and fesenjan.
What are the major religions in Iran?
The major religion in Iran is Islam, with the majority of the population being Shia Muslims. There are also small communities of Sunni Muslims, Christians, Jews, and Zoroastrians.
Political Boundaries of Iran: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Iran, officially known as the Islamic Republic of Iran, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Turkmenistan to the north, Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and Turkey and Iraq to the west. To the south, Iran is bordered by the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. The country has a rich history dating back thousands of years, and its political boundaries have evolved significantly over time. Iran is currently divided into 31 provinces, each with its own administrative divisions, including districts and sub-districts. These political boundaries play a crucial role in the governance and administration of the country, shaping its cultural, ethnic, and historical landscape. The political boundaries of Iran have been shaped by a complex interplay of historical, cultural, and geopolitical factors. The country’s diverse ethnic and cultural makeup has also influenced the evolution of its provinces and districts. This article will explore the evolution of Iran’s political boundaries, the influence of historical boundaries on modern Iran, the role of ethnic and cultural diversity in shaping these boundaries, as well as the challenges and controversies surrounding them. Additionally, we will examine the impact of political boundaries on Iran’s governance and administration, and consider future prospects for Iran’s political boundaries. Summary Iran’s political boundaries have evolved over time, influenced by historical, ethnic, and cultural factors. The provinces and districts in Iran have undergone changes, reflecting shifts in governance and administration. Historical boundaries continue to shape modern Iran, impacting its political landscape and governance. Ethnic and cultural diversity play a significant role in shaping Iran’s political boundaries and governance. Challenges and...
Climate Zones of Iran: Different climate regions Of Iran
Iran is a country of diverse landscapes and climates, with a wide range of climate zones that vary from arid and semi-arid to Mediterranean and subtropical, cold and mountainous, desert, and continental and steppe. This diversity is due to Iran‘s vast size and its location between the Caspian Sea to the north and the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the south. The country’s topography, which includes mountains, plateaus, and deserts, also contributes to the variety of climates found in Iran. Understanding the different climate zones in Iran is essential for appreciating the country’s natural beauty and for planning travel or outdoor activities. The climate zones in Iran are influenced by several factors, including latitude, altitude, and proximity to bodies of water. The country’s location near the Tropic of Cancer means that it experiences hot summers and mild winters in most regions. However, the presence of mountain ranges, such as the Alborz and Zagros Mountains, creates significant variations in temperature and precipitation across different parts of the country. Additionally, the Caspian Sea and the Persian Gulf have a moderating effect on the climate in their respective regions, leading to milder temperatures and higher levels of humidity. Overall, Iran’s climate zones offer a rich tapestry of natural environments, each with its own unique characteristics and attractions. Summary Iran has a diverse range of climate zones, including arid, semi-arid, Mediterranean, sub-tropical, cold and mountainous, desert, and continental and steppe. The arid and semi-arid climate zones cover a large portion of Iran, with very little rainfall and high temperatures, making agriculture and water resources a challenge. The Mediterranean and sub-tropical...
Natural Resources of Iran: Where Natural Resources are Located in Iran
Iran is a country rich in natural resources, with a diverse range of assets that contribute to its economic development and global significance. From oil and gas reserves to mineral deposits, agricultural land, water resources, and renewable energy potential, Iran‘s natural wealth is a key factor in its national prosperity. The country’s strategic location and geological features have made it a hub for natural resource extraction and production, attracting international attention and investment. Understanding the scope and potential of Iran’s natural resources is essential for appreciating the country’s economic significance and its role in global markets. Iran’s natural resources have played a crucial role in shaping its economy and geopolitical influence. The country’s vast reserves of oil and gas have made it a major player in the global energy market, while its mineral wealth has contributed to its industrial development and export potential. In addition, Iran’s agricultural resources and water reserves have sustained its population and supported its food security, while its renewable energy potential has positioned it as a key player in the transition towards sustainable energy sources. As Iran continues to develop and modernize its economy, its natural resources will remain a central pillar of its growth and prosperity. Summary Iran is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, agriculture, water, and renewable energy sources. Iran holds the world’s fourth-largest proven oil reserves and the second-largest natural gas reserves. The country is abundant in mineral resources such as copper, iron ore, zinc, and uranium. Iran’s agricultural resources include wheat, rice, fruits, and vegetables, supported by its diverse climate and fertile soil. Iran faces challenges in managing...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Iran: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Iran
Iran is a country steeped in history and culture, with a rich tapestry of ancient civilisations, stunning architecture, and breathtaking landscapes. The country is home to a myriad of cultural and historical sites that offer a glimpse into its illustrious past, from the ancient ruins of Persepolis to the grandeur of the Golestan Palace in Tehran. These sites are not only a testament to Iran‘s rich heritage but also a source of pride for its people, who have worked tirelessly to preserve and showcase these treasures to the world. Visitors to Iran are often left in awe of the country’s cultural and historical sites, which offer a unique insight into the country’s past. From the towering columns of Persepolis to the intricate tile work of Naqsh-e Jahan Square, each site tells a story of Iran’s ancient civilisations and their enduring legacy. As such, these sites are not only important for their historical significance but also for their cultural and artistic value, making them a must-see for anyone with an interest in history, architecture, or art. Summary Iran is home to a wealth of cultural and historical sites that showcase its rich heritage and ancient civilisations. Persepolis, the ancient capital of the Achaemenid Empire, is a remarkable archaeological site that offers a glimpse into the grandeur of the Persian Empire. Naqsh-e Jahan Square in Isfahan is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a stunning example of Persian-Islamic architecture and urban planning. The ancient city of Yazd is a living museum of Persian architecture, with its well-preserved traditional buildings and windcatchers. Golestan Palace in Tehran is a symbol of the grandeur...
Terrain and Topography of Iran: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Iran is home to a diverse range of mountain ranges that span across the country, offering a variety of landscapes and natural beauty. The Alborz mountain range, located in the north of Iran, is one of the most prominent mountain ranges in the country. It stretches from the border with Azerbaijan and Armenia in the northwest to the end of the Khorasan province in the northeast. The Alborz range is home to Mount Damavand, the highest peak in Iran and the highest volcano in Asia. The Zagros mountain range, on the other hand, runs from the northwest to the southeast of Iran, covering a vast area and offering stunning views and diverse ecosystems. These mountain ranges are not only important for their natural beauty but also for their cultural and historical significance. They have been home to ancient civilizations and have played a crucial role in shaping the history and culture of Iran. The mountain ranges of Iran are not only a sight to behold but also play a crucial role in the country’s ecosystem. They act as natural barriers, influencing weather patterns and providing habitats for a wide variety of flora and fauna. The diverse climate and topography of these mountain ranges have led to the evolution of unique species of plants and animals, making them important areas for conservation and biodiversity. Additionally, these mountain ranges are a valuable source of natural resources such as minerals, water, and timber, which are essential for the country’s economy. The mountainous terrain also provides opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, rock climbing, and skiing, making them popular destinations for adventure...
History of Iran
Ancient Persia, also known as Iran, has a rich and storied history that dates back thousands of years. The birth of Iranian civilization can be traced back to the ancient Persian Empire, which was one of the most powerful and influential empires in the ancient world. The Persian Empire was known for its advanced and sophisticated culture, as well as its impressive military and administrative capabilities. The ancient Persians were also known for their contributions to art, literature, and science, and their influence can still be seen in modern Iranian culture. The ancient Persians were skilled in the art of warfare and were able to conquer vast territories, including parts of modern-day Iran, Iraq, Turkey, and Egypt. They were also known for their impressive architectural achievements, such as the construction of the famous city of Persepolis. The ancient Persians were also known for their religious beliefs, which included the worship of a variety of gods and goddesses. Their religious practices and beliefs played a significant role in shaping their culture and society. Overall, the ancient Persian Empire was a powerful and influential force in the ancient world, and its legacy continues to be felt in modern-day Iran. Summary Ancient Persia laid the foundation for Iranian civilization, with a rich history dating back thousands of years. The Achaemenid Empire marked the golden age of Persia, with significant advancements in art, architecture, and governance. The Islamic conquest and the rise of the Safavid Dynasty shaped Iran’s religious and cultural identity. The Qajar Dynasty saw the influence of European powers, leading to modernization and reforms in Iran. The Pahlavi Era brought about...
Population Density of Iran
Iran, a country located in the Middle East, has a population of over 83 million people, making it the 18th most populous country in the world. With a land area of 1,648,195 square kilometers, Iran has a population density of around 50 people per square kilometer. However, this figure does not accurately represent the distribution of the population across the country, as there are significant variations in population density between different regions. The population density in Iran is influenced by a variety of factors, including geographical features, economic opportunities, and government policies. Understanding the population density in Iran is crucial for policymakers and urban planners to address the challenges and opportunities associated with high population density. Summary Iran has a population density of around 52 people per square kilometre, making it one of the most densely populated countries in the Middle East. Factors affecting population density in Iran include geographical features, climate, economic opportunities, and government policies. Iran’s population is predominantly urban, with over 70% of people living in cities, leading to challenges in infrastructure and resource management. High population density in Iran puts pressure on infrastructure, water resources, and healthcare, but also presents opportunities for economic growth and innovation. Iran’s population density is higher than the global average, but lower than some other countries in the region, such as Bangladesh and Japan. Future trends suggest continued urbanisation and potential strain on resources. Factors Affecting Population Density in Iran Several factors contribute to the population density in Iran. Geographical features such as mountains, deserts, and fertile plains play a significant role in determining where people settle. The majority of...