Portugal
(República Portuguesa (Portuguese Republic))




Capital: Lisbon
Population (Estimated July 2012): 10,781,459
Area: 92,094km2 or 35,558mi2
Currency: Euro (€)
Official Language: Portuguese
Political Information: Parliamentary Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion
(approximately 84.5% of the population are Roman Catholic, 2.2% have other Christian beliefs, 9.3% have other or unknown religious beliefs and 3.9% have no religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Ponta do Pico at 2,351m or 7,713ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a country’s economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $241.9 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $23,200 (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and the use of resources but is not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $246.9 (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $23,200 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): GMT
Wildlife:
Counties/Provinces/States: 18 districts (distritos, singular – distrito) and 2 autonomous regions* (regioes autonomas, singular – regiao autonoma); Aveiro, Acores (Azores)*, Beja, Braga, Braganca, Castelo Branco, Coimbra, Evora, Faro, Guarda, Leiria, Lisboa (Lisbon), Madeira*, Portalegre, Porto, Santarem, Setubal, Viana do Castelo, Vila Real, Viseu
Leaders: President Aníbal Cavaco Silva with Prime Minister Pedro Passos Coelho.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Portugal
Portugal, officially known as the Portuguese Republic, is a country situated in Southern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. It shares land borders with Spain to the east and north, whilst the Atlantic Ocean lies to the west and south. Lisbon, the capital and largest city, serves as the country’s political and economic centre.
Portugal boasts a rich historical heritage and is renowned for its diverse culture, picturesque landscapes, and acclaimed cuisine. The nation has a population exceeding 10 million inhabitants and is a member state of the European Union, utilising the Euro as its official currency. Portugal’s maritime legacy is significant, as it was once a formidable global empire with colonies across Africa, Asia, and South America.
In contemporary times, Portugal is celebrated for its pristine beaches, historic urban centres, and warm hospitality, rendering it a favoured destination for international tourists. Portugal’s history spans millennia, with archaeological evidence of human habitation dating to the Palaeolithic era. The region was subsequently inhabited by various Celtic tribes before Roman conquest in 45 BC.
Following the decline of the Roman Empire, Portugal experienced invasions by Germanic tribes and later became part of the Moorish Empire. The 12th century saw Portugal gain independence from Moorish rule and establish itself as a sovereign kingdom. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal emerged as a global maritime power, exploring and colonising territories across Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
This period of exploration brought considerable wealth and cultural exchange to Portugal, but also facilitated the transatlantic slave trade. The 20th century saw Portugal endure a period of dictatorship under António de Oliveira Salazar, which persisted until the Carnation Revolution in 1974. Since then, Portugal has transitioned to a democratic republic and joined the European Union, experiencing substantial economic growth and development.
Summary
- Portugal is a country located in Southern Europe, known for its rich history, stunning landscapes, and delicious cuisine.
- The history and culture of Portugal is influenced by its maritime past, with a mix of Roman, Moorish, and Christian heritage.
- Portugal’s geography varies from lush mountains and forests to beautiful beaches, and its climate is generally mild and Mediterranean.
- Portuguese cuisine is famous for its seafood, pastries, and wine, with the country being a major producer of port wine.
- Tourism in Portugal is booming, with attractions like Lisbon, Porto, the Algarve region, and the Azores drawing in millions of visitors each year.
- Portugal’s economy is diverse, with industries like tourism, agriculture, and technology playing a significant role in its growth and development.
- The future of Portugal looks promising, with continued growth in tourism, investment in renewable energy, and a focus on sustainable development.
History and Culture of Portugal
Music and Dance
Fado music is a traditional genre of Portuguese music that is known for its melancholic and soulful melodies, often accompanied by guitar.
Cuisine and Wine
Portuguese cuisine is also an important aspect of the country’s culture, with dishes such as bacalhau (salted cod), caldo verde (kale soup), and pastéis de nata (custard tarts) being popular favourites. The country is also famous for its wine production, particularly port wine from the Douro Valley and vinho verde from the Minho region.
Architecture and Literature
The architecture of Portugal reflects its diverse cultural influences, with Romanesque, Gothic, Manueline, Baroque, and Moorish styles all being present in the country’s historic buildings. The city of Porto is known for its stunning Baroque churches and colourful tiled facades, while Lisbon is famous for its Moorish-inspired Alfama district and elegant Belem Tower. Portugal also has a strong tradition of literature and poetry, with writers such as Luís de Camões, Fernando Pessoa, and José Saramago being celebrated both at home and abroad.
Festivals and Celebrations
The country’s rich cultural heritage is also evident in its numerous festivals and celebrations, such as the Festa de São João in Porto, the Festa dos Tabuleiros in Tomar, and the Carnaval in Loulé. These events showcase traditional music, dance, costumes, and cuisine, providing visitors with a unique insight into Portuguese culture.
Geography and Climate of Portugal
Portugal is known for its diverse geography and climate, with a varied landscape that includes mountains, plains, forests, and coastline. The country is divided into two main regions: the mainland and the autonomous regions of Madeira and the Azores. The mainland is characterised by the Tagus River Valley in the north, the Alentejo plains in the south, and the mountain ranges of Serra da Estrela and Serra de São Mamede.
The coastline of Portugal stretches for over 800 kilometres and is home to beautiful beaches, rugged cliffs, and picturesque fishing villages. The autonomous regions of Madeira and the Azores are located in the Atlantic Ocean and are known for their volcanic landscapes, lush vegetation, and subtropical climate. Portugal has a Mediterranean climate with hot dry summers and mild wet winters.
The southern region of Algarve is known for its long sandy beaches and warm temperatures, making it a popular destination for sun-seekers. The northern region of Minho experiences more rainfall and has a lush green landscape that is ideal for agriculture. The mountainous regions of Portugal experience cooler temperatures and are popular destinations for hiking, skiing, and wildlife watching.
The islands of Madeira and the Azores have a more temperate climate with mild temperatures year-round, making them ideal for outdoor activities such as hiking, diving, and whale watching. Overall, Portugal’s diverse geography and climate make it an attractive destination for nature lovers and outdoor enthusiasts.
Cuisine and Wine of Portugal
Portuguese cuisine is known for its delicious flavours, fresh ingredients, and diverse influences from around the world. The country’s cuisine is heavily based on seafood due to its long coastline, with dishes such as grilled sardines, seafood rice, and cataplana being popular choices. Bacalhau (salted cod) is also a staple ingredient in Portuguese cuisine and is used in a variety of dishes such as bacalhau à brás (shredded cod with potatoes) and bacalhau com natas (cod with cream).
Portuguese cuisine also includes a wide variety of soups such as caldo verde (kale soup), sopa de peixe (fish soup), and canja de galinha (chicken soup), which are often enjoyed as a starter or light meal. In addition to its delicious cuisine, Portugal is also famous for its wine production. The country has a long history of winemaking dating back to Roman times and produces a wide variety of wines including reds, whites, rosés, and sparkling wines.
Port wine is one of Portugal’s most famous exports and is produced in the Douro Valley region in northern Portugal. This sweet fortified wine is often enjoyed as a dessert wine or paired with cheese or chocolate. Vinho verde is another popular Portuguese wine that comes from the Minho region in the north of the country.
This light and refreshing wine is perfect for sipping on a hot summer day and pairs well with seafood dishes. Overall, Portuguese cuisine and wine are an integral part of the country’s culture and are enjoyed by locals and visitors alike.
Tourism in Portugal
Portugal is a popular tourist destination known for its stunning landscapes, historic cities, vibrant culture, and warm hospitality. The country offers a wide range of attractions for visitors to explore including UNESCO World Heritage sites such as the historic centre of Porto, the Tower of Belém in Lisbon, and the cultural landscape of Sintra. The Algarve region in southern Portugal is famous for its beautiful beaches, crystal-clear waters, and picturesque coastal towns such as Lagos, Albufeira, and Faro.
The city of Lisbon is known for its charming neighbourhoods, historic monuments, vibrant nightlife, and delicious cuisine. Visitors can explore iconic landmarks such as São Jorge Castle, Jerónimos Monastery, and Belém Tower while enjoying panoramic views from the city’s many miradouros (viewpoints). In addition to its cultural attractions, Portugal also offers a wide range of outdoor activities such as hiking in the Serra da Estrela mountains, surfing along the Atlantic coast, or exploring the volcanic landscapes of Madeira and the Azores.
The country’s mild climate makes it an ideal destination for outdoor enthusiasts year-round. Portugal also has a rich maritime heritage that can be explored through visits to historic port cities such as Porto or through boat tours along the Douro River or Ria Formosa Natural Park. With its diverse attractions and warm climate, Portugal offers something for every type of traveller whether they are seeking relaxation on the beach or adventure in nature.
Economy and Industry in Portugal
Portugal has a mixed economy that relies on various industries including tourism, agriculture, manufacturing, technology, and renewable energy. The country has a strong agricultural sector that produces a wide variety of crops including wine grapes, olives, cork, citrus fruits, and vegetables. Portugal is also known for its production of cork products such as wine stoppers, flooring, and fashion accessories.
The manufacturing industry in Portugal includes textiles, clothing, footwear, ceramics, glassware, and furniture which are exported around the world. The technology sector in Portugal has been growing rapidly in recent years with a focus on software development, telecommunications, biotechnology, aerospace engineering, and renewable energy. Tourism is an important part of Portugal’s economy with millions of visitors coming to explore the country’s cultural attractions each year.
The tourism industry provides jobs for many people in areas such as hospitality, transportation, entertainment, and retail. In addition to tourism, Portugal has been investing in renewable energy sources such as wind power, solar power, hydroelectricity, and biomass to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels. The country has made significant progress in developing sustainable energy solutions which has led to job creation in the renewable energy sector.
Overall, Portugal’s economy continues to grow through diversification into various industries while maintaining its traditional strengths in agriculture and tourism.
The Future of Portugal
As Portugal continues to develop economically and culturally it faces both opportunities and challenges in shaping its future. The country has made significant progress in recent years through investments in infrastructure development such as transportation networks including highways and high-speed rail connections between major cities. This has improved accessibility for both domestic travellers as well as international visitors which has contributed to economic growth through increased tourism.
Portugal also faces challenges such as an ageing population which requires investment in healthcare services as well as education to ensure future generations are equipped with necessary skills to contribute to the economy. Additionally there are ongoing efforts to address environmental concerns through sustainable practices particularly within agriculture industry which will be crucial to maintain natural resources for future generations. Overall Portugal’s future looks promising with continued investment in diverse industries including technology innovation which will contribute to economic growth while preserving its rich cultural heritage making it an attractive destination for tourists from around the world.
FAQs
What is the capital of Portugal?
The capital of Portugal is Lisbon.
What is the official language of Portugal?
The official language of Portugal is Portuguese.
What is the currency used in Portugal?
The currency used in Portugal is the Euro (EUR).
What is the population of Portugal?
As of 2021, the population of Portugal is estimated to be around 10.3 million people.
What are some popular tourist attractions in Portugal?
Some popular tourist attractions in Portugal include the historic city of Porto, the Algarve region with its beautiful beaches, the historic Belém Tower in Lisbon, and the Douro Valley wine region.
What is the climate like in Portugal?
Portugal has a Mediterranean climate, with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
What are some traditional dishes in Portuguese cuisine?
Some traditional dishes in Portuguese cuisine include bacalhau (salted cod), caldo verde (green soup), and pastéis de nata (custard tarts).
What are some famous Portuguese festivals and events?
Some famous Portuguese festivals and events include the Festa de São João in Porto, the Carnaval in Lisbon, and the Festa dos Tabuleiros in Tomar.
Population Density of Portugal
Portugal, situated in southwestern Europe, is a nation renowned for its rich history, striking landscapes and vibrant culture. With a population of approximately 10.3 million inhabitants, Portugal ranks amongst the smaller European countries in terms of population. Despite its relatively modest size, Portugal exhibits a diverse population density that varies considerably across different regions of the country. The population density of Portugal stands at roughly 111 people per square kilometre, with the majority of inhabitants concentrated in urban areas such as Lisbon, Porto and the Algarve region. This uneven distribution of population density has significant implications for the country’s infrastructure, resources and overall development. This article shall examine the factors influencing population density in Portugal, the impact of this density on infrastructure and resources, and future projections for Portugal’s population density. Summary Portugal has a population density of around 111 people per square kilometre, making it one of the lowest in Europe. Factors influencing population density in Portugal include historical settlement patterns, economic opportunities, and natural geography. The majority of Portugal’s population is concentrated in urban areas, with rural areas experiencing depopulation. Population density in Portugal has implications for infrastructure, housing, and natural resource management. Compared to other European countries, Portugal’s population density is relatively low, with potential for future growth. Future projections for Portugal’s population density suggest a continued shift towards urban areas and potential challenges for rural communities. Strategies for managing population density in Portugal include urban planning, investment in rural development, and sustainable resource management. Factors influencing Population Density in Portugal Several factors influence the population density in Portugal, including historical, geographical, and economic factors. Historically,...
History of Portugal
Portugal possesses a rich and diverse history dating back to prehistoric times. The Iberian Peninsula, where Portugal is situated, was inhabited by various Celtic and Iberian tribes prior to the Roman arrival in the 3rd century BC. The Romans established their rule over the region and named it Lusitania, which encompassed present-day Portugal and parts of Spain. Under Roman rule, Lusitania flourished as a prosperous province with thriving cities, infrastructure, and a robust economy. The Romans also introduced Christianity to the region, which would later become a defining aspect of Portuguese culture and identity. The Roman influence on Portugal’s language, culture, and architecture remains evident today. Numerous Portuguese words have Latin roots, and Roman ruins can be found throughout the country. The Roman legacy also includes the development of agriculture, trade, and governance systems that laid the foundation for Portugal’s future growth and prosperity. The Roman era concluded in the 5th century AD with the fall of the Western Roman Empire, leading to a period of instability and invasions by various Germanic tribes. This marked the beginning of a new chapter in Portugal’s history as it transitioned from Roman rule to the Moorish conquest. The early settlement and Roman rule in Portugal established the groundwork for the country’s future development and cultural identity. The legacy of the Romans can be observed in the language, architecture, and governance systems that continue to shape Portugal to this day. The Roman era also marked the introduction of Christianity to the region, which would play a significant role in shaping Portuguese culture and society. As Portugal transitioned from Roman rule to the Moorish...
Terrain and Topography of Portugal: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Portugal, situated in the south-western region of Europe, is renowned for its diverse and striking terrain and topography. The nation is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west and south, which has significantly influenced its landscape. Portugal‘s terrain is characterised by a combination of mountains, valleys, lowlands, plains and plateaus, rendering it a geographically rich and varied country. The topography of Portugal has played a crucial role in shaping the nation’s climate, natural resources and human settlement patterns. From the craggy mountains of the north to the undulating plains of the south, Portugal’s terrain and topography have contributed to the country’s unique and diverse natural beauty. Portugal’s terrain and topography have also been instrumental in moulding the nation’s history and culture. The varied landscape has influenced the way people have lived and interacted with the land for centuries. From agriculture in the fertile valleys to mining in the mountainous regions, Portugal’s terrain has presented both challenges and opportunities for its inhabitants. The country’s topography has also influenced the development of its infrastructure, with roads and settlements often following the natural contours of the land. In sum, Portugal’s terrain and topography have had a profound impact on the country’s physical and cultural landscape. Summary Portugal’s terrain is diverse, with mountain ranges, valleys, lowlands, plains, and plateaus. The mountain ranges of Portugal, such as the Serra da Estrela and the Serra de Montejunto, offer stunning landscapes and outdoor recreational opportunities. The valleys and lowlands of Portugal, including the Tagus and Douro valleys, are fertile areas for agriculture and vineyards. The plains and plateaus of Portugal, like the Alentejo and the...
Climate Zones of Portugal: Different Climate Regions Of Portugal
Portugal, situated on the Iberian Peninsula in Southern Europe, is renowned for its varied climate, which is influenced by its geographical position and topography. The country is divided into three primary climate regions: northern, central and southern. Each region exhibits distinct climatic characteristics, affected by factors such as latitude, elevation and proximity to the Atlantic Ocean. The northern region experiences a temperate maritime climate, whilst the central region has a transitional Mediterranean climate, and the southern region possesses a Mediterranean climate with hot, arid summers and mild, wet winters. Moreover, Portugal encompasses the islands of Madeira and the Azores, each with its own unique climate. Comprehending the different climate zones of Portugal is crucial for prospective visitors or residents, as it can significantly impact activities and lifestyle choices. The climate zones of Portugal are not only significant for inhabitants and tourists but also for the nation’s agriculture, tourism and economy. The diverse climate zones enable the cultivation of a wide array of agricultural products, from grapes for wine production in the north to citrus fruits in the south. The climate also plays a pivotal role in the tourism sector, attracting visitors seeking both coastal holidays in the south and outdoor pursuits in the north. Furthermore, the climate influences energy consumption and production, as well as water management and conservation efforts. Understanding the unique characteristics of each climate zone is vital for sustainable development and future planning. Given the growing concerns surrounding climate change, it is essential to study and comprehend how Portugal’s climate zones may be affected in the coming years. Summary Portugal has three main climate zones: Northern,...
Political Boundaries of Portugal: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Political boundaries in Portugal have played a significant role in shaping the country’s identity and history. From the ancient provinces to the modern administrative districts, these boundaries have defined the territorial organisation of Portugal and influenced its cultural, social and economic development. The evolution of these boundaries reflects the country’s rich history and the impact of various political, social and economic forces. Understanding the significance of these boundaries is crucial to comprehending Portugal’s complex and diverse regional dynamics. The political boundaries in Portugal are not only geographical divisions but also represent historical, cultural and administrative entities. These boundaries have evolved over centuries, reflecting the country’s changing political landscape and societal dynamics. From the ancient Roman provinces to the modern administrative districts, Portugal’s political boundaries have undergone numerous transformations, each leaving a lasting imprint on the country’s identity. This article will explore the historical significance of Portugal’s provinces and districts, their evolution over time and their impact on the country’s cultural and administrative landscape. Summary Portugal is divided into provinces and districts, each with its own historical significance and administrative functions. The provinces of Portugal have evolved over time and have played a crucial role in shaping the country’s identity. Districts in Portugal serve as important administrative divisions, each with its own local government and responsibilities. The historical boundaries of Portugal have undergone significant changes, impacting the country’s political and cultural landscape. The debate over the current political boundaries in Portugal continues, with future prospects for potential changes and reforms. Provinces of Portugal: History and Significance The Evolution of Provinces The provinces played a crucial role in shaping Portugal’s identity,...
Natural Resources of Portugal: Where Natural Resources are Located in Portugal
Portugal, situated on the Iberian Peninsula in Southern Europe, possesses a diverse array of natural resources that have significantly influenced the nation’s economy and culture. The country’s wealth of mineral, agricultural, forestry, water and energy resources has been instrumental in driving its development and prosperity. Portugal‘s strategic position along the Atlantic Ocean has also contributed to its abundant marine resources, establishing it as a centre for fishing and maritime activities. Through a commitment to sustainable management practices, Portugal has effectively utilised its natural resources to support various industries whilst preserving its environment for future generations. Summary Portugal is rich in natural resources, including minerals, agriculture, forests, water, and energy sources. The country has significant mineral resources such as copper, tin, and uranium, which contribute to its economy. Portugal’s agricultural resources are diverse, with a focus on wine production, olive oil, and cork. The country’s forest resources are valuable for timber production, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration. Portugal’s water resources are abundant, with a focus on sustainable management and conservation efforts. Mineral Resources in Portugal Portugal boasts a rich array of mineral resources, with significant deposits of copper, tin, tungsten, and uranium. The country has a long history of mining, dating back to Roman times, and has continued to be a major player in the global mining industry. The Iberian Pyrite Belt, located in the south of Portugal, is one of the most important mineral provinces in the world, known for its massive sulphide deposits containing valuable minerals such as copper, zinc, and lead. In addition to metallic minerals, Portugal also has substantial reserves of industrial minerals such as marble, granite,...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Portugal: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Portugal
Portugal boasts a wealth of cultural and historical heritage, with numerous sites showcasing its diverse past. The country’s historical landmarks range from ancient Roman ruins to mediaeval castles and Renaissance palaces, offering visitors insight into Portugal‘s vibrant history. The cultural landscape of Portugal reflects the various influences that have shaped the nation over the centuries, including the Moorish occupation and the Age of Discovery. Each site presents a unique narrative, illustrating the country’s rich and complex history. This article shall examine some of Portugal’s most significant cultural and historical sites, exploring their importance and the tales they recount about Portugal’s past. Summary Portugal is home to a rich tapestry of cultural and historical sites, each with its own unique story to tell. The Moorish Castle of Sintra stands as a powerful symbol of Portugal’s Islamic heritage, offering a glimpse into the country’s diverse history. The University of Coimbra is not only a centre of learning but also a place steeped in tradition, making it a must-visit for those interested in Portugal’s academic and cultural legacy. The Tower of Belém serves as a testament to Portugal’s Age of Exploration, showcasing the country’s maritime history and global influence. The Monastery of Batalha is a masterpiece of Gothic architecture, offering visitors a chance to marvel at the intricate design and historical significance of the building. The Moorish Castle of Sintra: A Symbol of Portugal’s Islamic Heritage The Moorish Castle of Sintra, located in the picturesque town of Sintra, is a striking reminder of Portugal’s Islamic heritage. Built during the 8th and 9th centuries during the Moorish occupation of the Iberian Peninsula, the...
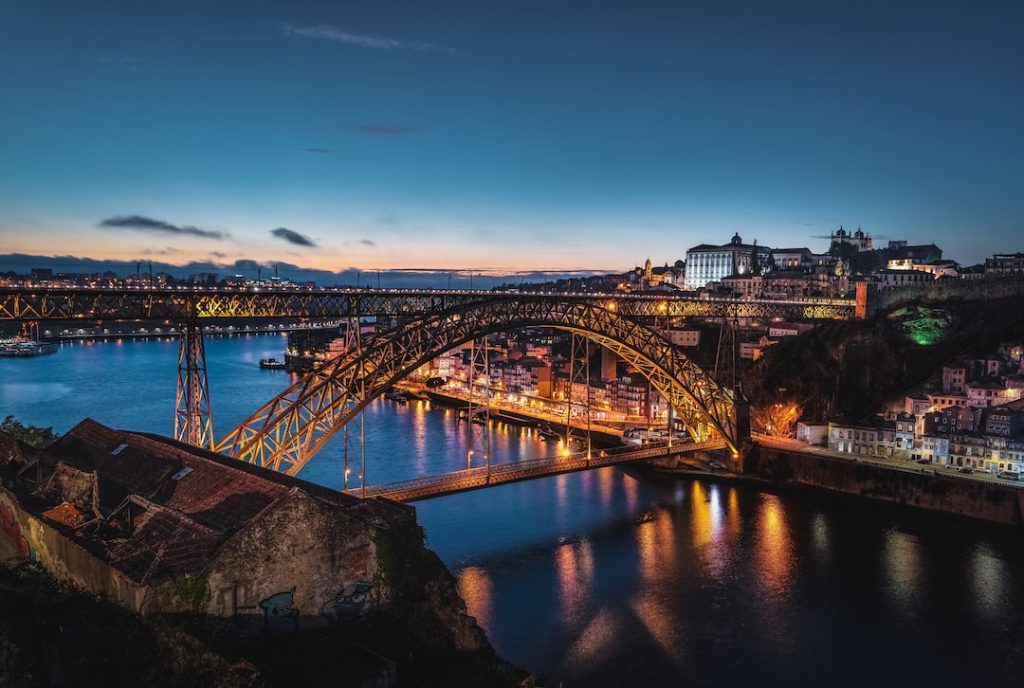
Discovering the Charm of Portugal: A Journey through its Colourful Cities and Breathtaking Landscapes
Nestled on the western edge of the Iberian Peninsula, Portugal is a country that is often overlooked by travellers in favour of its more popular neighbours, Spain and France. However, those who do venture to this enchanting land are rewarded with a rich history, vibrant culture, and stunning landscapes. From the bustling streets of Lisbon to the picturesque vineyards of the Douro Valley, Portugal offers a diverse range of experiences that are sure to captivate any visitor. Portugal has a long and storied history, with influences from various civilizations including the Romans, Moors, and Celts. This rich tapestry of cultures is evident in the country’s architecture, cuisine, and traditions. The Portuguese people are known for their warm hospitality and love for life, which is reflected in their colourful festivals and lively music. Whether you’re exploring the narrow streets of Porto or relaxing on the sun-kissed beaches of the Algarve, you’ll find that Portugal is a land of colour and charm. Summary Portugal is a land of colour and charm, with a rich cultural and historical heritage. Lisbon is a vibrant city that offers a wealth of cultural and historical attractions. Porto is a coastal haven that is famous for its wine and stunning natural beauty. Coimbra is a cultural and academic gem that is home to some of Portugal’s most beautiful architecture. Sintra is a fairy tale destination that is famous for its magnificent castles and palaces. Exploring the Vibrant City of Lisbon: A Cultural and Historical Hub Lisbon, the capital city of Portugal, is a vibrant hub of culture and history. With its winding streets, colourful buildings, and...


























