Romania
(România)





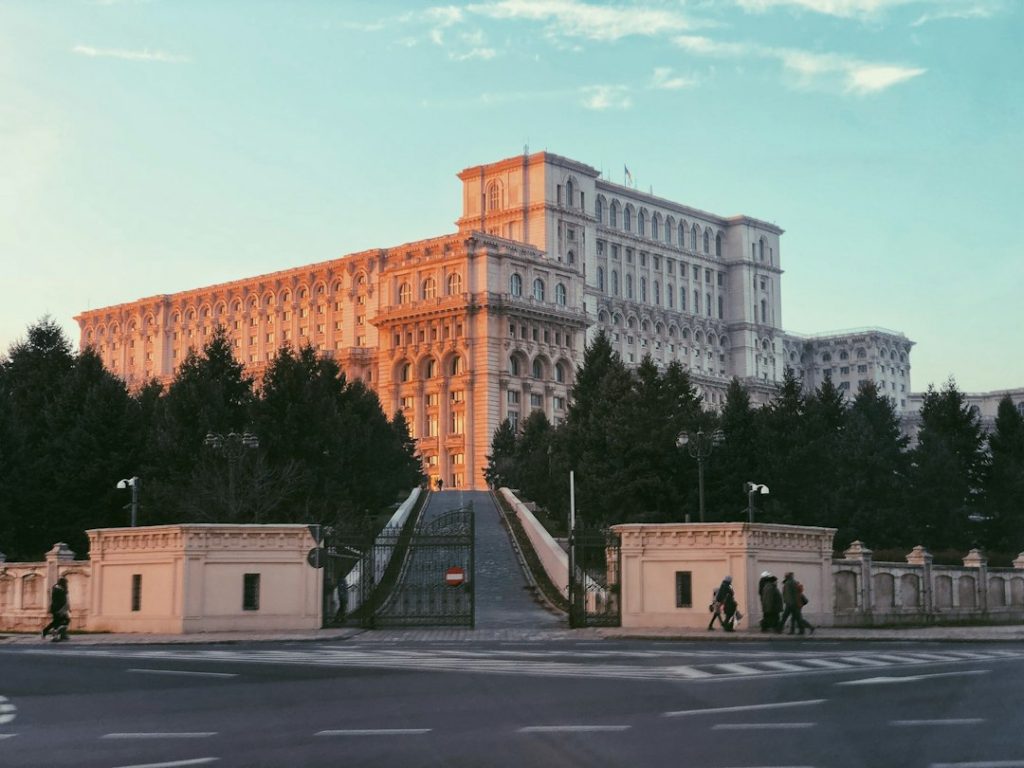
Capital: Bucharest
Population (Estimated July 2012): 21,848,504
Area: 238,391km2 or 92,043mi2
Currency: Leu (Plural Lei)
Official Language: Romanian
Political Information: Presidential Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion
(approximately 86.8% of the population are Eastern Orthodox, 7.5% are Protestant, 4.7% are Roman Catholic, 0.9% have other or unspecified beliefs and 0.1% have no religious beliefs).
Highest Mountain: Moldoveanu at 2,544 m or 8,346ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a country’s economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $185.3 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and the use of resources but is not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $263.9 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $12,300 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +2:00
Wildlife:
Counties/Provinces/States: 41 counties (judete, singular – judet) and 1 municipality* (municipiu); Alba, Arad, Arges, Bacau, Bihor, Bistrita-Nasaud, Botosani, Braila, Brasov, Bucuresti (Bucharest)*, Buzau, Calarasi, Caras-Severin, Cluj, Constanta, Covasna, Dimbovita, Dolj, Galati, Gorj, Giurgiu, Harghita, Hunedoara, Ialomita, Iasi, Ilfov, Maramures, Mehedinti, Mures, Neamt, Olt, Prahova, Salaj, Satu Mare, Sibiu, Suceava, Teleorman, Timis, Tulcea, Vaslui, Vilcea, Vrancea
Leaders: President Traian Băsescu with Prime Minister: Mihai Răzvan Ungureanu.
Additional: Proclaimed independence from the Ottoman Empire on the 9th of May 1877 which was recognised by the Treaty of Berlin on the 13th of July 1878.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Romania
Romania, situated in South-eastern Europe, boasts a rich tapestry of history, diverse cultural heritage and striking natural landscapes. With a population exceeding 19 million, it ranks as the seventh most populous member state of the European Union. Bucharest, the capital, is a dynamic metropolis featuring an eclectic mix of modern and historic architecture, lively thoroughfares and a flourishing cultural milieu.
The country encompasses the renowned Transylvania region, celebrated for its mediaeval castles, fortified churches and awe-inspiring mountainous terrain. Romania’s cultural identity is shaped by a fascinating amalgamation of influences from neighbouring countries, coupled with its distinctive traditions and customs that have evolved over centuries of historical development.
Summary
- Romania is a beautiful country located in Eastern Europe, known for its rich history, diverse culture, and stunning natural landscapes.
- The history and culture of Romania are influenced by a mix of Roman, Dacian, and other European traditions, resulting in a unique and vibrant heritage.
- Romania boasts a diverse geography, including the Carpathian Mountains, the Danube River, and the Black Sea coast, offering a wide range of natural landscapes for visitors to explore.
- Romanian cuisine is a delicious blend of influences from Turkish, Hungarian, and German cuisines, with traditional dishes like sarmale and mămăligă being popular among locals and tourists alike.
- From the medieval castles of Transylvania to the stunning Danube Delta, Romania is home to a wealth of famous landmarks and tourist attractions that draw visitors from around the world.
History and Culture of Romania
Romania has a rich and complex history that dates back thousands of years. The region was once part of the Roman Empire, which is where the country gets its name. Over the centuries, Romania has been influenced by various cultures, including the Dacians, Romans, Byzantines, Ottomans, and Austro-Hungarians.
This diverse heritage has contributed to Romania’s unique cultural identity, which is reflected in its art, music, literature, and traditions. One of the most famous aspects of Romanian culture is its folklore, which includes mythical creatures, traditional dances, and colourful costumes. The country is also known for its vibrant music scene, with a strong tradition of folk music and dance, as well as a growing contemporary music industry.
Romanian cuisine is another important part of the country’s culture, with dishes such as sarmale (cabbage rolls), mămăligă (polenta), and cozonac (sweet bread) being popular staples.
Geography and Natural Landscapes of Romania
Romania is a land of diverse and stunning natural landscapes, ranging from the Carpathian Mountains to the Black Sea coast. The country is home to a wealth of biodiversity, with dense forests, rolling hills, and fertile plains. The Carpathian Mountains dominate the central and northern regions of Romania, offering breathtaking scenery and opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, skiing, and wildlife spotting.
The Danube River flows through the southern part of the country, providing fertile land for agriculture and a vital transportation route. The Danube Delta, where the river meets the Black Sea, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the most biodiverse areas in Europe. Romania also has a number of beautiful lakes, including the glacial Lake Balea in the Fagaras Mountains and the volcanic Lake Saint Ana in Harghita County.
The country’s natural beauty has made it a popular destination for ecotourism and outdoor enthusiasts.
Romanian Cuisine and Traditions
Romanian cuisine is a delicious blend of flavours and influences from various cultures, including Turkish, Hungarian, German, and Slavic. Traditional Romanian dishes are often hearty and filling, making use of local ingredients such as pork, beef, poultry, dairy products, and vegetables. One of the most iconic Romanian dishes is sarmale, which consists of cabbage leaves stuffed with a mixture of rice and minced meat, cooked in a savoury tomato sauce.
Mămăligă is another staple of Romanian cuisine, made from boiled cornmeal that is similar to polenta. It is often served as a side dish with stews or topped with cheese and sour cream. Desserts are also an important part of Romanian culinary traditions, with sweet treats such as cozonac (a sweet bread filled with nuts and raisins), papanasi (fried doughnuts topped with sour cream and jam), and clatite (thin pancakes filled with fruit or cheese) being popular choices.
Romanian cuisine is often enjoyed as part of traditional celebrations and festivals, where families come together to share meals and enjoy music and dancing.
Famous Landmarks and Tourist Attractions in Romania
Romania is home to a wealth of famous landmarks and tourist attractions that showcase its rich history and natural beauty. One of the most iconic sites in Romania is Bran Castle, often associated with the legend of Dracula due to its eerie appearance and connections to Bram Stoker’s novel. The castle is located in Transylvania and attracts thousands of visitors each year who are drawn to its mysterious atmosphere and stunning mountain backdrop.
Another must-see destination in Romania is the medieval town of Sighisoara, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site known for its well-preserved historic centre and colourful buildings. The Painted Monasteries of Bucovina are also a popular attraction, featuring intricate frescoes that depict religious scenes and folklore. For nature lovers, the Transfagarasan Highway offers a spectacular drive through the Carpathian Mountains, passing by waterfalls, glacial lakes, and dramatic cliffs.
The coastal town of Constanta on the Black Sea coast is home to ancient ruins, sandy beaches, and vibrant nightlife, making it a popular destination for sun-seekers and history enthusiasts alike.
Economy and Politics of Romania
Romania has undergone significant economic and political changes since the fall of communism in 1989. The country has transitioned to a market economy and has become one of the fastest-growing economies in the European Union. Romania’s main industries include manufacturing, agriculture, energy production, and tourism.
The country has a diverse range of natural resources, including oil, natural gas, coal, timber, and fertile land for agriculture. In recent years, Romania has also seen growth in sectors such as information technology, automotive manufacturing, and renewable energy. Politically, Romania is a semi-presidential republic with a multi-party system.
The President is the head of state, while the Prime Minister is the head of government. The country has made significant progress in strengthening its democratic institutions and rule of law since joining the European Union in 2007.
Romania’s Future and Global Impact
Looking ahead, Romania faces both opportunities and challenges as it continues to develop its economy and strengthen its position on the global stage. The country has made strides in improving infrastructure, education, healthcare, and environmental protection in recent years. However, there are still issues such as corruption, poverty, regional disparities, and emigration that need to be addressed.
Romania’s membership in the European Union has brought increased investment, trade opportunities, and access to EU funds for development projects. The country also plays an important role in regional security as a member of NATO. In terms of global impact, Romania has contributed to peacekeeping missions, humanitarian aid efforts, and cultural exchange programmes around the world.
The country’s rich cultural heritage and natural beauty continue to attract tourists from all over the globe, contributing to its international reputation. In conclusion, Romania is a fascinating country with a rich history, diverse culture, stunning landscapes, delicious cuisine, and promising future. From its ancient folklore to its modern economy, Romania offers a unique blend of tradition and innovation that continues to captivate visitors and inspire admiration around the world.
As the country continues to evolve and make its mark on the global stage, it will undoubtedly remain an intriguing destination for travellers seeking adventure, culture, and natural beauty.
FAQs
What is the capital of Romania?
The capital of Romania is Bucharest.
What is the population of Romania?
As of 2021, the population of Romania is estimated to be around 19 million people.
What is the official language of Romania?
The official language of Romania is Romanian.
What is the currency used in Romania?
The currency used in Romania is the Romanian leu (RON).
What are some popular tourist attractions in Romania?
Some popular tourist attractions in Romania include the Bran Castle, Peleș Castle, the Transfăgărășan Highway, the Danube Delta, and the medieval town of Sighișoara.
What is the climate like in Romania?
Romania has a temperate-continental climate, with hot summers and cold winters. The climate can vary depending on the region, with mountainous areas experiencing colder temperatures and more snowfall.
What are some traditional Romanian dishes?
Some traditional Romanian dishes include sarmale (cabbage rolls), mămăligă (polenta), ciorbă (sour soup), and mici (grilled minced meat rolls).
What are some famous Romanian people?
Some famous Romanian people include gymnast Nadia Comăneci, sculptor Constantin Brâncuși, and tennis player Simona Halep.
Political Boundaries of Romania: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Romania, a nation steeped in history and cultural diversity, is situated in Southeast Europe, bordered by the Black Sea to the east and sharing land borders with Ukraine to the north, Moldova to the east, Hungary to the west, and Serbia to the southwest. The political boundaries of Romania have been shaped by a multitude of historical events, territorial disputes, and socio-political changes over the centuries. These boundaries not only delineate the geographical extent of the country but also reflect the complex interplay of ethnicities, languages, and cultures that characterise this vibrant nation. Understanding Romania’s political boundaries is essential for grasping the broader context of its governance, regional relationships, and national identity. The delineation of Romania’s political boundaries has evolved significantly since its formation as a modern state in the 19th century. The unification of the principalities of Wallachia and Moldavia in 1859 marked a pivotal moment in Romanian history, laying the groundwork for the establishment of a cohesive national identity. Subsequent territorial adjustments, particularly following the World Wars and the shifting political landscape of Eastern Europe during the Cold War, have further influenced Romania’s borders. Today, Romania is divided into several administrative units that reflect both historical legacies and contemporary governance structures, making it a fascinating case study in the dynamics of political geography. Summary Romania’s political boundaries have evolved over time, influenced by historical, geographical, and cultural factors. The country is divided into 41 provinces, each with its own unique characteristics and significance. Romania is further divided into 320 districts, each playing a crucial role in the governance and administration of the country. The historical boundaries of...
History of Romania
The history of Romania is inextricably linked with the ancient Dacians, a group of Thracian tribes that inhabited the region now known as Romania. The Dacians were renowned for their formidable warrior culture and rich traditions, which encompassed advanced agricultural practices and a complex social structure. They established numerous fortified settlements, with Sarmizegetusa Regia being the most notable, serving as their capital and religious centre. The Dacians exhibited exceptional skill in metalwork, particularly with gold and silver, and their craftsmanship was highly esteemed throughout the ancient world. Their society was characterised by a strong sense of identity and resistance to external influences, especially from the expanding Roman Empire. The Roman conquest of Dacia, which reached its culmination in 106 AD under Emperor Trajan, marked a significant turning point in the region’s history. The Romans sought to exploit Dacia’s abundant mineral resources, particularly gold, and to expand their empire’s borders. The conquest presented considerable challenges; the Dacians, led by their king Decebalus, mounted fierce resistance against the Roman legions. However, after a series of intense battles, the Romans emerged victorious, leading to the establishment of Dacia as a Roman province. This conquest facilitated a profound transformation of the region, as Roman culture, language, and governance began to permeate Dacian society. The integration of Dacia into the Roman Empire laid the foundation for the development of Romanian identity, as the Latin language and Roman customs merged with local traditions. Summary The Dacians were an ancient people who inhabited the territory of modern-day Romania and were conquered by the Romans in 106 AD. Wallachia and Moldavia emerged as powerful medieval Romanian principalities...
Climate Zones of Romania: Different Climate Regions Of Romania
Romania, a country steeped in history and natural beauty, boasts a remarkable diversity of climate zones that reflect its varied topography and geographical position in southeastern Europe. This rich tapestry of climates is shaped by the interplay of the Carpathian Mountains, the Danube River, and the Black Sea, each contributing to the unique weather patterns experienced across the nation. From the temperate continental climate that dominates much of the country to the subtropical influences found in certain regions, Romania‘s climate is as multifaceted as its cultural heritage. Understanding these climate zones is essential not only for appreciating the natural environment but also for grasping how they influence agriculture, tourism, and daily life in Romania. The climate of Romania is characterised by significant regional variations, which can be attributed to its geographical features and location. The country is bordered by Ukraine to the north, Moldova to the east, and Bulgaria to the south, whilst the west is flanked by Hungary. This positioning creates a complex climatic landscape that ranges from cold winters to hot summers, with distinct seasonal changes. The interplay between continental and maritime influences results in a variety of microclimates, each with its own unique characteristics. As we delve deeper into the specific climate zones of Romania, we will uncover how these diverse environments shape not only the physical landscape but also the cultural and economic activities of its inhabitants. Summary Romania has a diverse range of climate zones, from continental to subtropical, due to its varied topography and geographical location. The continental climate in Romania is characterized by hot summers and cold winters, with significant temperature variations...
Natural Resources of Romania: Where Natural Resources are Located in Romania
Romania, a nation rich in history and natural splendour, possesses a diverse array of natural resources that are crucial to its economy and cultural identity. Situated in Eastern Europe, Romania‘s geographical location has bestowed upon it a varied landscape, ranging from the Carpathian Mountains to the fertile Danube River plains. This topographical diversity not only contributes to the country’s picturesque scenery but also supports a wealth of natural resources essential for its development. The country is endowed with abundant minerals, forests, agricultural land, and water bodies, all of which are vital for sustaining its population and promoting economic growth. The importance of these resources extends beyond their economic value; they are deeply interwoven with Romania’s cultural heritage and environmental sustainability. The forests, for example, serve not only as a source of timber and biodiversity but also hold cultural significance for many communities. Similarly, the agricultural lands are not merely crop fields but are imbued with traditions and practices that have been handed down through generations. As Romania grapples with the complexities of modernisation and globalisation, the challenge lies in striking a balance between resource exploitation and the imperative of conservation and sustainable management. This delicate equilibrium is crucial to ensure that future generations can continue to benefit from Romania’s natural wealth. Summary Romania is rich in natural resources, including minerals, forests, agriculture, water, and energy sources. The country has significant mineral resources, including coal, oil, natural gas, and various metals. Romania’s forest resources are extensive, covering over a quarter of the country’s land area and providing valuable timber and biodiversity. The agricultural sector in Romania is diverse, with fertile...
Terrain and Topography of Romania: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Romania, a country rich in history and culture, boasts a remarkably diverse terrain that captivates both locals and visitors alike. Situated in Eastern Europe, it is bordered by the Carpathian Mountains to the west and the Black Sea to the east, creating a striking contrast between rugged highlands and serene coastal landscapes. The country’s topography comprises various geographical features, including mountains, plateaus, rivers and plains, each contributing to Romania‘s unique ecological and cultural identity. This rich variety not only shapes the natural environment but also influences the lifestyle, traditions and economic activities of its inhabitants. The interplay of these geographical elements has resulted in a landscape that is both varied and beautiful. From the snow-capped peaks of the Carpathians to the verdant valleys of Transylvania, Romania’s terrain offers numerous opportunities for exploration and adventure. The Danube River, one of Europe’s most significant waterways, meanders through the country, providing vital resources and serving as a natural boundary with neighbouring nations. As one delves deeper into the distinct regions of Romania, one uncovers the intricate relationship between its topography and the cultural heritage that has flourished in this captivating land. Summary Romania’s terrain and topography are diverse, ranging from mountains to plains and plateaus. The Carpathian Mountains are the backbone of Romania, running from the north to the southwest. The Transylvanian Plateau is characterized by rolling hills and valleys, making it a picturesque region. The Danube River Basin is known for its fertile plains and wetlands, making it an important agricultural area. The Moldavian and Wallachian Plains are the agricultural heartlands of Romania, known for their rich soil and productive farms....
Cultural or Historical Sites of Romania: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Romania
Romania, a country steeped in rich history and vibrant culture, offers numerous cultural and historical sites that reflect its diverse heritage. Situated in Eastern Europe, Romania is a land where ancient traditions intertwine with modern influences, creating a unique tapestry that attracts visitors from around the world. From the Carpathian Mountains to the Danube Delta, the landscape is dotted with architectural marvels, ancient ruins and picturesque villages that illustrate the story of a nation shaped by centuries of tumultuous events and cultural exchanges. The country’s historical sites are not merely relics of the past; they are living testaments to the resilience and creativity of the Romanian people. As one traverses this captivating land, one cannot help but be drawn to its myriad cultural treasures. Each site offers insight into Romania’s complex history, showcasing influences from the Roman Empire, the Ottoman Empire and various European powers that have left their mark on the nation. The rich folklore and traditions that permeate Romanian culture further enhance the appeal of its historical sites, inviting exploration and discovery. Whether one is wandering through medieval towns, admiring intricate frescoes in monasteries or observing grand palaces, Romania’s cultural and historical sites provide a remarkable journey through time, revealing the essence of a nation that has endured and thrived through adversity. Summary Romania is home to a wealth of cultural and historical sites, each with its own unique story and significance. Bran Castle, often associated with the legend of Dracula, is a must-visit for those interested in the mysterious and mythical side of Romania’s history. The Painted Monasteries of Bucovina showcase stunning frescoes that depict religious...
Population Density of Romania
Romania, a country steeped in history and cultural diversity, presents a fascinating case study when it comes to population density. As of the latest estimates, Romania‘s population stands at approximately 19 million, spread across a land area of about 238,397 square kilometres. This results in a population density of around 80 people per square kilometre, which is relatively moderate compared to other European nations. However, this figure belies the complexities of demographic distribution within the country. The population density is not uniform; it varies significantly from one region to another, influenced by a myriad of factors including geography, economic opportunities, and historical migration patterns. Understanding these nuances is essential for grasping the broader socio-economic landscape of Romania. The implications of population density extend beyond mere numbers; they shape the very fabric of Romanian society. High-density areas often experience a concentration of resources, services, and infrastructure, whilst sparsely populated regions may struggle with access to basic amenities. This uneven distribution can lead to significant disparities in quality of life, economic development, and social cohesion. As Romania continues to evolve in the wake of globalisation and European integration, examining its population density becomes crucial for policymakers and citizens alike. It serves as a lens through which one can assess the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for this vibrant nation. Summary Romania has a population density of 84 people per square kilometre, making it one of the least densely populated countries in Europe. Factors affecting population density in Romania include historical migration patterns, economic opportunities, and natural geographical barriers. The urban population in Romania is increasing, leading to a higher population...
Discovering the Hidden Gems of Romania: A Journey Through its Rich History and Culture
Romania, located in Eastern Europe, is a country that often goes unnoticed by travelers. However, this hidden gem is a treasure trove of natural beauty, rich history, and vibrant culture. From picturesque landscapes to ancient castles, Romania offers a unique and authentic travel experience that is sure to leave a lasting impression. While many tourists flock to popular destinations like Bucharest and Transylvania, there are countless lesser-known attractions and experiences waiting to be discovered. Whether it’s exploring the charming villages of Maramures or hiking through the breathtaking Carpathian Mountains, Romania has something for every type of traveler. Summary Romania is a land of hidden gems waiting to be discovered. The rich history of Romania is worth exploring, from ancient times to modern day. Romania’s cultural diversity is fascinating, with influences from various ethnic groups. The natural wonders of Romania, from the Carpathian Mountains to the Danube Delta, are breathtaking. Romania’s traditional cuisine is a delight for foodies, with unique flavours and dishes to try. Uncovering the Rich History of Romania Romania has a fascinating history that dates back thousands of years. From the Dacians and Romans to the Ottoman Empire and communist era, the country has seen its fair share of conquests and influences. Today, visitors can explore historical landmarks and sites that offer a glimpse into Romania’s past. One such landmark is the Bran Castle, often associated with the legend of Dracula. This medieval fortress is perched on a hilltop in Transylvania and is said to have inspired Bram Stoker’s famous novel. Another must-visit site is the Palace of Parliament in Bucharest, which is the second-largest administrative building...































