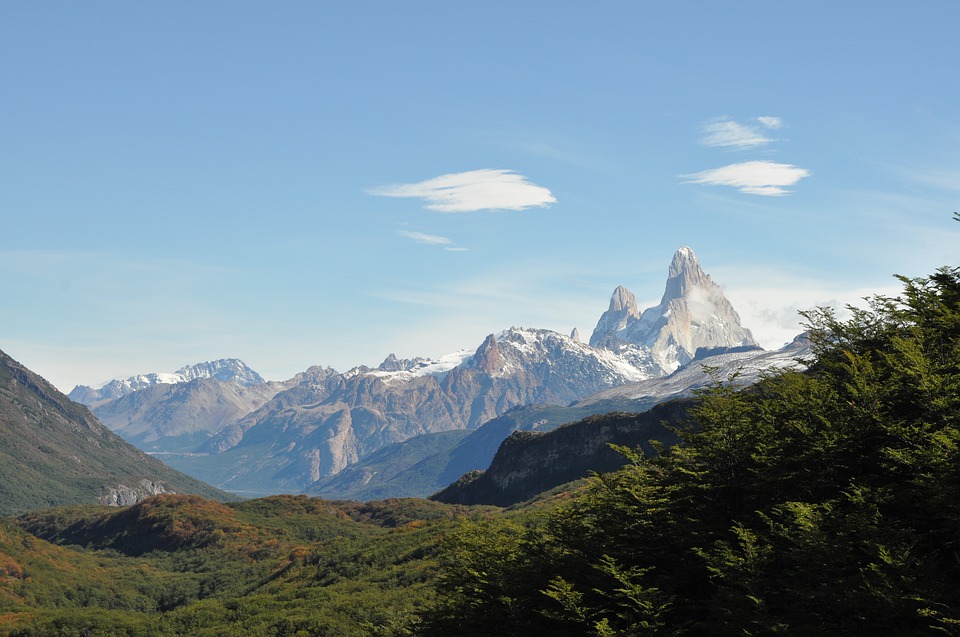
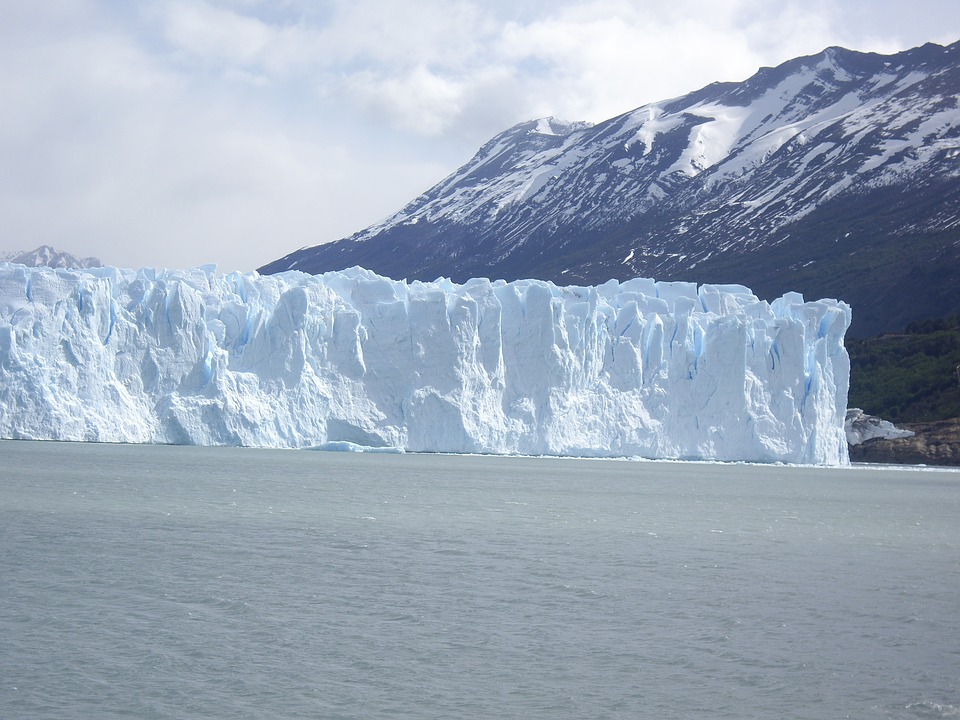
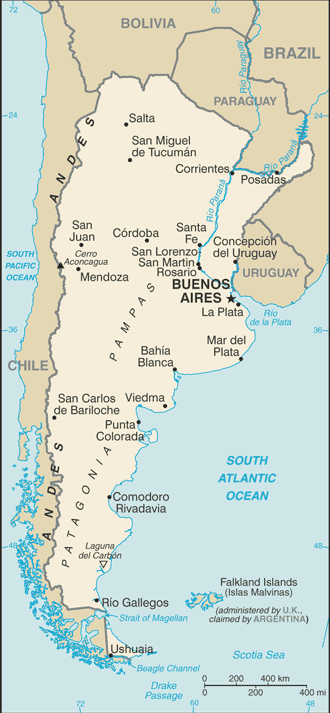
Argentina
(República Argentina (Argentine Republic))
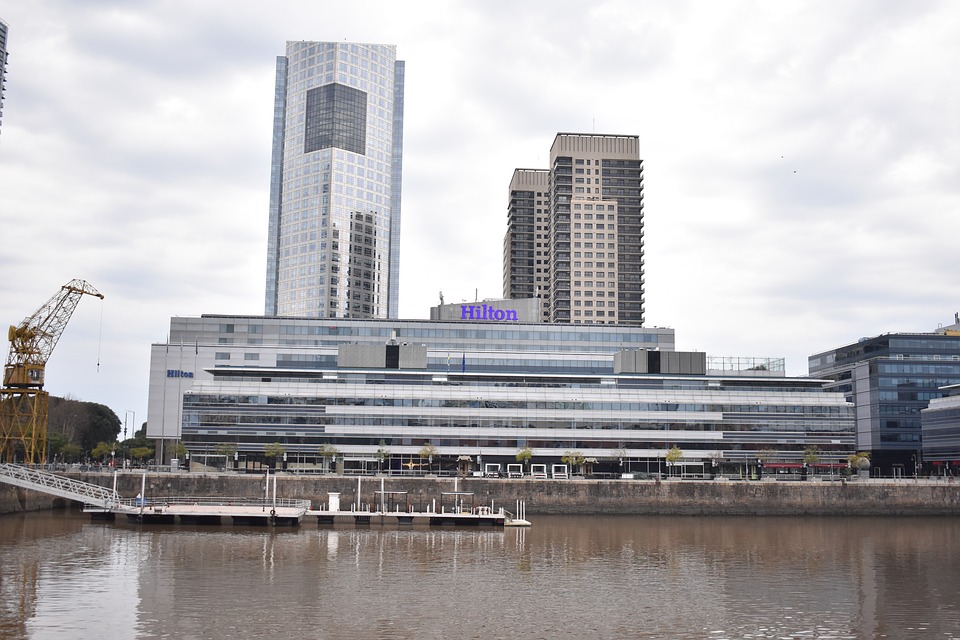







Capital: Buenos Aires
Population (Estimated July 2012): 42,192,494
Area: 2,780,403km2 or 1,073,520mi2
Currency: Peso (ARS)
Official Language: Spanish
Political Information: Federal Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 92% of the population are Roman Catholic, 2% are Protestant, 2% are Jewish and 4% have alternate other religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Cerro Aconcagua at 6,960m or 22834ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $435.2 billion (US$) or £261.12 billion(GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $709.7 billion (US$) or £425.82 billion(GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $17,400 (US$) or £10,440 (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): -3:00
Counties/Provinces/States: Provinces (provincias, singular – provincia) and 1 autonomous city*; Buenos Aires, Catamarca, Chaco, Chubut, Ciudad Autonoma de Buenos Aires*, Cordoba, Corrientes, Entre Rios, Formosa, Jujuy, La Pampa, La Rioja, Mendoza, Misiones, Neuquen, Rio Negro, Salta, San Juan, San Luis, Santa Cruz, Santa Fe, Santiago del Estero, Tierra del Fuego – Antartida e Islas del Atlantico Sur (Tierra del Fuego), Tucuman
Leaders: President Cristina Fernandez De Kirchner (since 10 December 2007); Vice President Amado Boudou
Additional: Argentina is the eighth largest country in the world and has the highest mountain in the Western Hemisphere
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica,
Argentina, located in the southern part of South America, is a country known for its vibrant culture, stunning landscapes, and passionate people. From the sultry rhythms of tango to the exhilarating sport of football, Argentina offers a unique blend of traditions and attractions that captivate visitors from around the world. With its rich history, diverse cuisine, and breathtaking natural wonders, Argentina truly has something for everyone.
Geography and Climate of Argentina: From the Andes to the Pampas
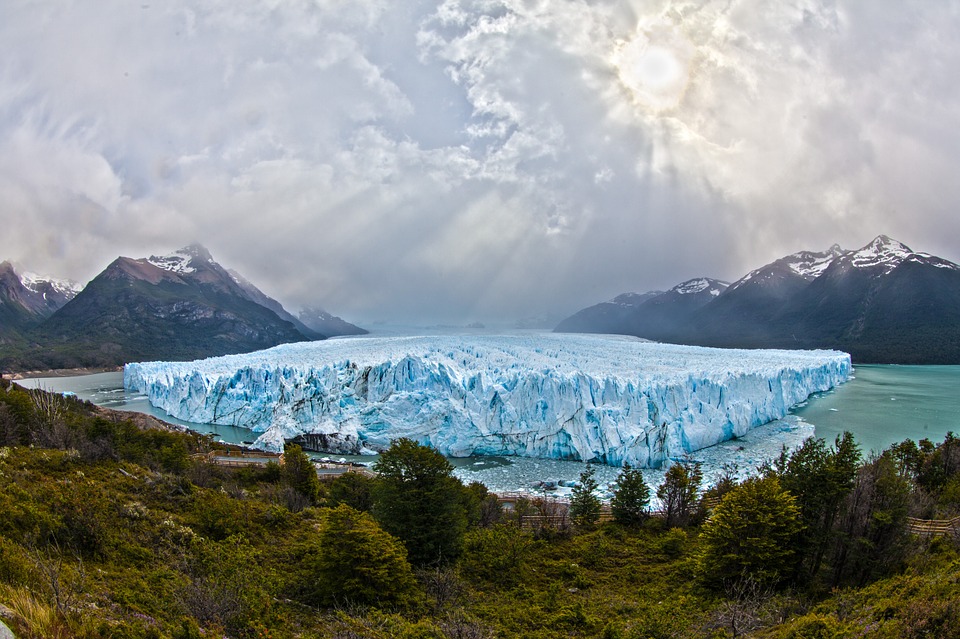
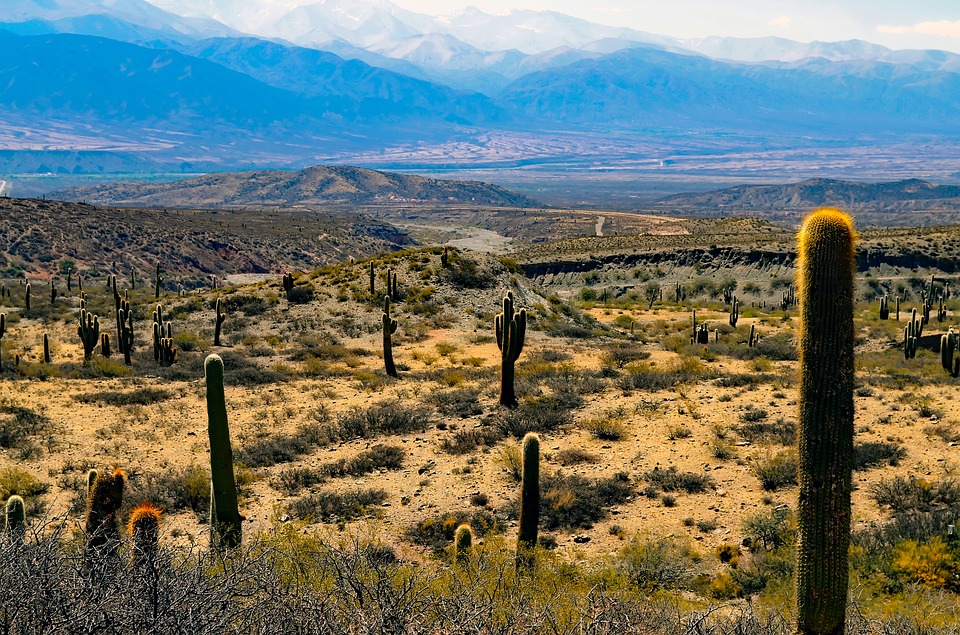
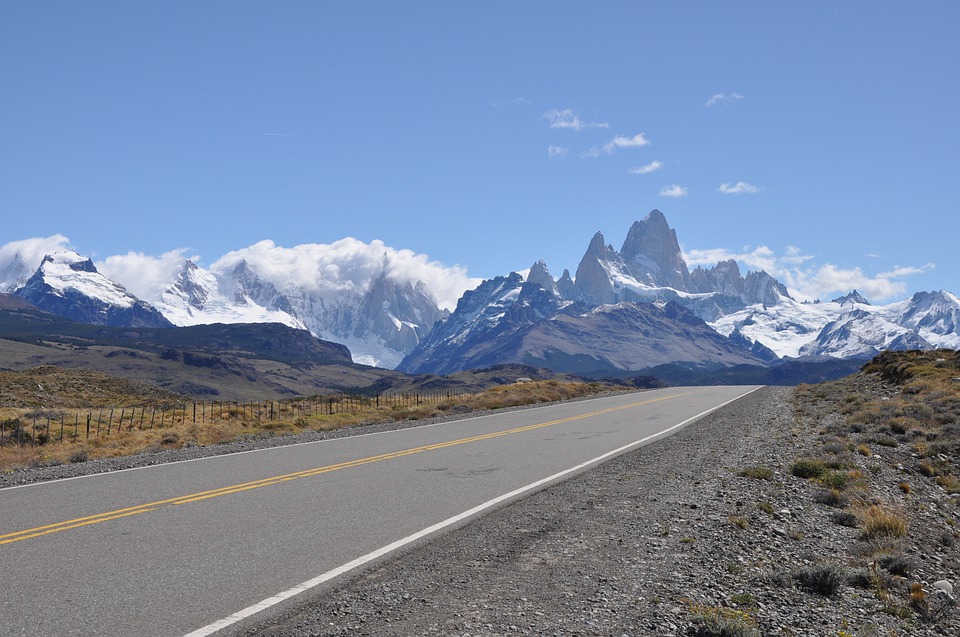
Argentina is a country of vast geographical diversity, with landscapes ranging from towering mountains to expansive grasslands. The Andes Mountains form the western border of Argentina, offering breathtaking views and opportunities for outdoor adventure. The Pampas grasslands, located in the central part of the country, are known for their fertile soil and agricultural productivity. Patagonia, in the southern part of Argentina, is a region of stunning beauty with its glaciers, lakes, and mountains.
The climate in Argentina varies greatly depending on the region. In the north, you will find a tropical climate with hot and humid summers. In the central region, including Buenos Aires, the climate is temperate with mild winters and hot summers. In Patagonia, the climate is cold and windy, with snowfall in the winter months. Overall, Argentina offers a diverse range of climates and landscapes that cater to all types of travellers.
History of Argentina: From Colonialism to Independence
Argentina has a rich history that dates back thousands of years. Before the arrival of European colonizers, indigenous peoples such as the Mapuche and Guarani inhabited the land. The Spanish arrived in the 16th century and established colonies throughout the region. Argentina gained independence from Spain in 1816 after a long struggle led by revolutionary figures such as General Jose de San Martin.
In the 20th century, Argentina experienced periods of political instability and economic turmoil. The rise of Peronism, a political movement led by Juan Peron and his wife Eva Peron, had a significant impact on Argentine society. Eva Peron, also known as Evita, became a symbol of social justice and fought for the rights of the working class. Today, Argentina continues to grapple with political and economic challenges while striving for social progress.
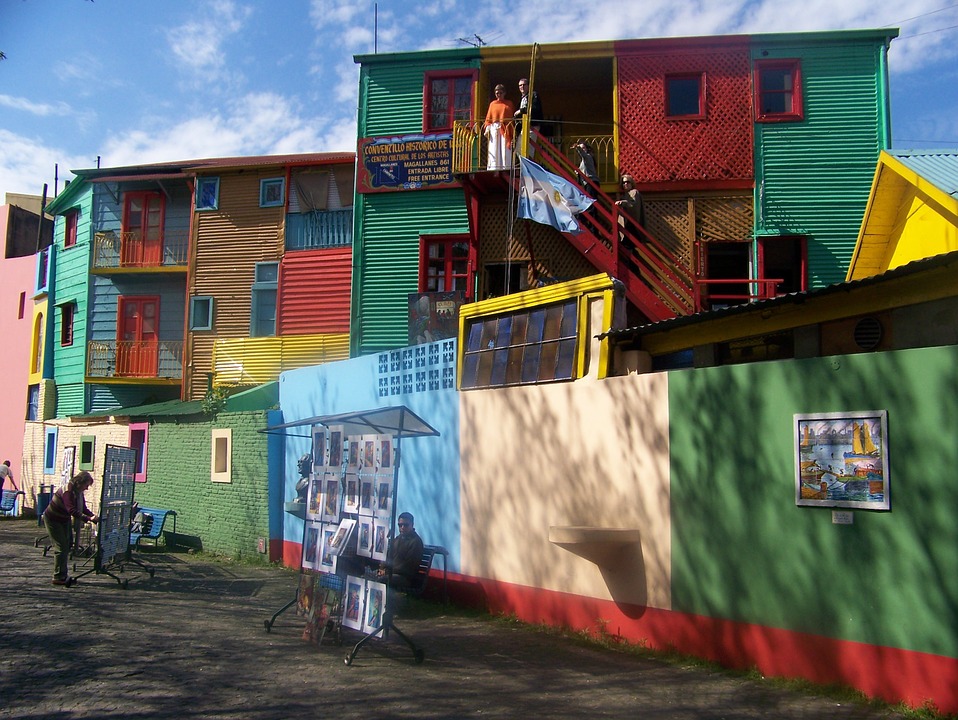
Cultural Diversity in Argentina: Indigenous Roots and European Influences
Argentina is a melting pot of cultures, with indigenous roots and strong European influences. The indigenous peoples of Argentina, such as the Mapuche and Guarani, have left a lasting impact on the country’s culture and traditions. Their influence can be seen in the music, dance, and art of Argentina.
European immigration in the late 19th and early 20th centuries brought a wave of cultural influences to Argentina. Large numbers of Italians, Spaniards, and Germans settled in the country, bringing with them their languages, customs, and cuisines. This European influence can be seen in the architecture of Buenos Aires, which is reminiscent of European cities such as Paris and Madrid.
Gastronomy in Argentina: Steak, Empanadas, and Mate Tea
Argentina is famous for its delicious cuisine, with steak, empanadas, and mate tea being some of its most iconic dishes. Asado, or Argentine barbecue, is a must-try when visiting the country. Argentines take great pride in their beef, which is known for its tenderness and flavor. The meat is cooked over an open flame and seasoned with salt to enhance its natural flavors.
Empanadas are another popular dish in Argentina. These savory pastries are filled with a variety of ingredients such as beef, chicken, cheese, or vegetables. They are typically baked or fried until golden brown and served as a snack or appetizer.
Mate tea is a traditional Argentine beverage that is enjoyed throughout the country. It is made by steeping dried leaves from the yerba mate plant in hot water. Mate is often shared among friends and family, with each person taking turns sipping from a shared gourd and passing it on to the next person.
Sports in Argentina: Passion for Football and Polo
Argentina is a nation obsessed with sports, with football (soccer) and polo being two of the most popular. Football is more than just a sport in Argentina; it is a way of life. The country has produced some of the world’s greatest football players, including Diego Maradona and Lionel Messi. The passion for football can be seen in the fervent support of local teams and the electric atmosphere at matches.
Polo is another sport that holds a special place in Argentine culture. Argentina is known as the birthplace of modern polo, and the country has a long history of success in the sport. The Argentine Polo Open Championship, held annually in Buenos Aires, is one of the most prestigious polo tournaments in the world.
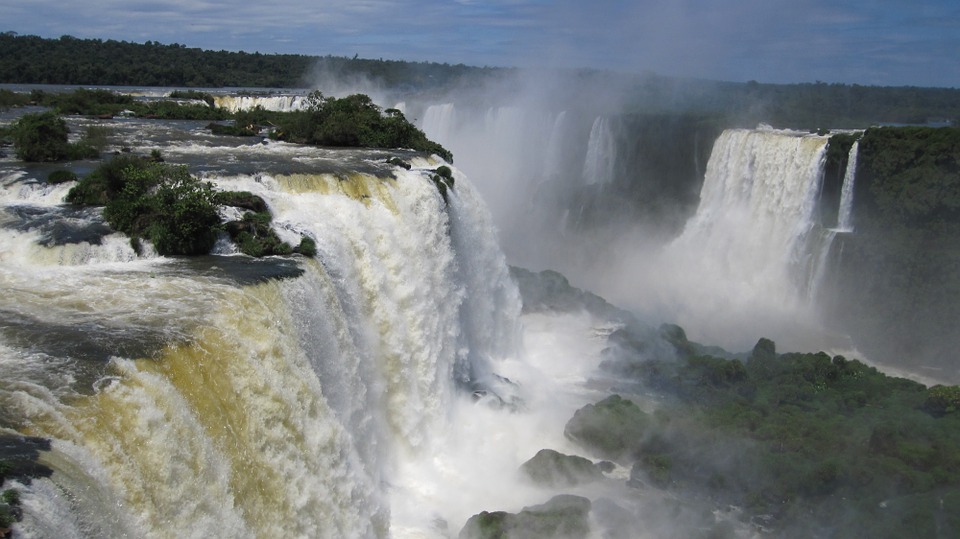
National Parks and Natural Wonders in Argentina: Iguazu Falls and Glaciers
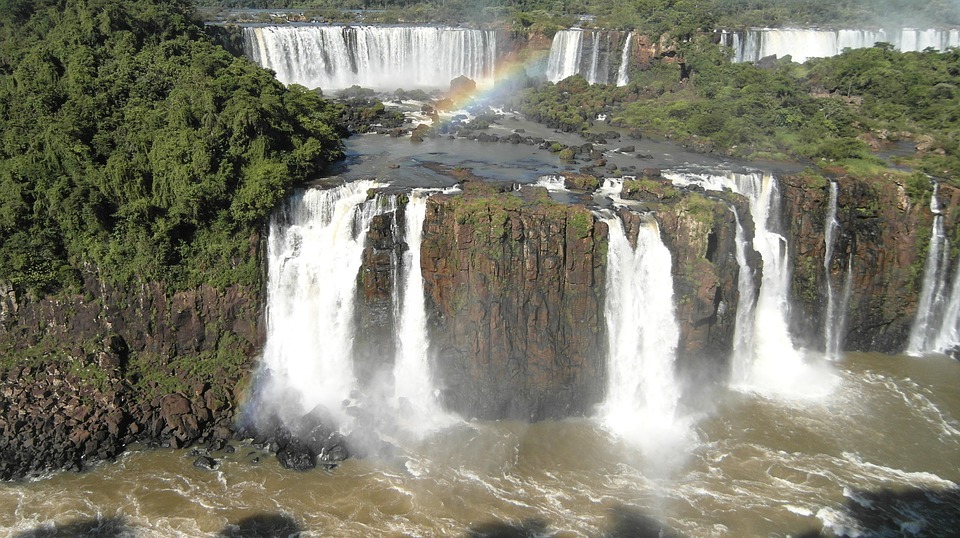
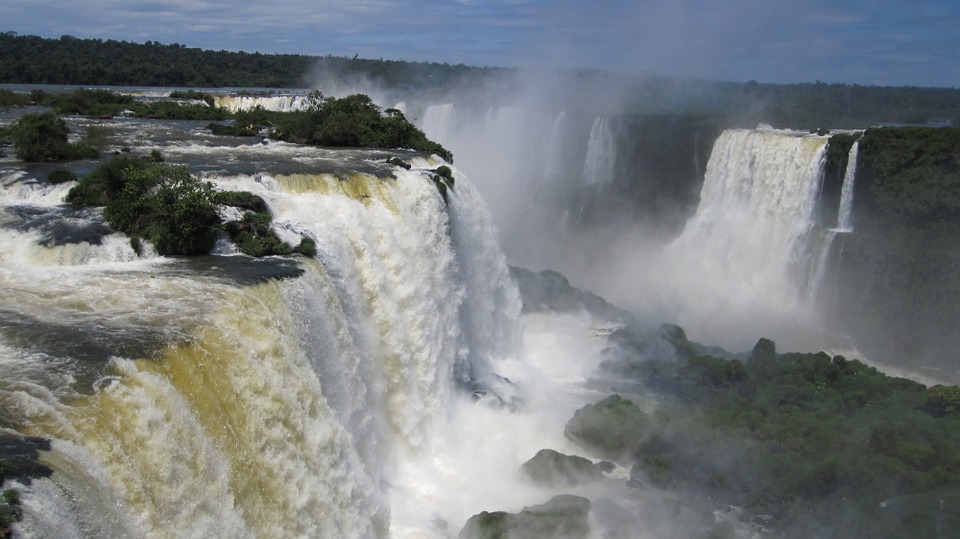
Argentina is home to some of the world’s most breathtaking natural wonders, including Iguazu Falls and the Perito Moreno Glacier. Iguazu Falls, located on the border between Argentina and Brazil, is one of the largest waterfall systems in the world. The falls are surrounded by lush rainforest, offering visitors a unique opportunity to explore both natural beauty and biodiversity.
The Perito Moreno Glacier, located in Los Glaciares National Park in Patagonia, is another must-see natural wonder in Argentina. This massive glacier stretches for miles and is constantly moving and changing shape. Visitors can witness the awe-inspiring sight of huge chunks of ice breaking off and crashing into the water below.
In addition to these famous attractions, Argentina is home to numerous national parks and protected areas that showcase the country’s diverse ecosystems. From the jagged peaks of the Fitz Roy mountain range to the pristine lakes of Nahuel Huapi National Park, there is no shortage of natural beauty to explore in Argentina.
Economy of Argentina: Agriculture, Mining, and Tourism
Argentina has a diverse economy that relies on several key industries, including agriculture, mining, and tourism. The country is one of the world’s largest producers of agricultural products, including soybeans, corn, and wheat. Argentina’s fertile soil and favorable climate make it an ideal location for farming.
Mining is another important industry in Argentina, with the country being rich in natural resources such as gold, silver, and lithium. The mining sector has seen significant growth in recent years, attracting foreign investment and creating jobs.
Tourism is also a major contributor to Argentina’s economy. The country’s natural beauty, vibrant culture, and rich history attract millions of visitors each year. Popular tourist destinations include Buenos Aires, with its European charm and vibrant nightlife, Mendoza, known for its world-class wineries, and Bariloche, a picturesque town nestled in the Andes mountains.
Politics and Society in Argentina: Peronism and Human Rights
Argentina has a complex political history that has shaped its society and continues to influence its present-day challenges. Peronism, a political movement founded by Juan Peron in the 1940s, has had a significant impact on Argentine politics. Peronism is characterized by its populist policies and focus on social justice. The movement has had both positive and negative effects on Argentine society, with some praising its efforts to improve the lives of the working class while others criticize its authoritarian tendencies.
Argentina has also faced significant human rights challenges throughout its history. The country experienced a period of military dictatorship from 1976 to 1983 during which thousands of people were forcibly disappeared and killed. The Mothers of the Plaza de Mayo, a group of women whose children were victims of the dictatorship, became a symbol of resistance and fought for justice and accountability.
Today, Argentina continues to grapple with issues of human rights and social inequality. The country has made significant progress in addressing past human rights abuses, but there is still work to be done to ensure justice and equality for all.
Travel Tips for Argentina: Visa Requirements, Safety, and Must-See Destinations
If you’re planning a trip to Argentina, there are a few things you should keep in mind. First, check the visa requirements for your country of residence. Some nationalities may require a visa to enter Argentina, while others may be eligible for visa-free entry or visa on arrival.
In terms of safety, Argentina is generally a safe country to visit. However, like any other destination, it’s important to take precautions and be aware of your surroundings. Avoid displaying valuable items and be cautious in crowded areas. It’s also a good idea to have travel insurance that covers medical expenses and trip cancellation.
When it comes to must-see destinations in Argentina, Buenos Aires is a must-visit. The capital city offers a mix of European charm and Latin American flair, with its beautiful architecture, vibrant street art, and lively tango scene. Mendoza is another popular destination, known for its world-class wineries and stunning mountain views. Bariloche, located in the heart of the Andes mountains, is a paradise for outdoor enthusiasts with its hiking trails, ski resorts, and crystal-clear lakes.
In conclusion, Argentina is a country that offers a unique blend of culture, natural beauty, and passion. From the vibrant streets of Buenos Aires to the breathtaking landscapes of Patagonia, Argentina has something for everyone. Whether you’re a food lover, sports enthusiast, or nature lover, you’re sure to find something to captivate your senses in this diverse and captivating country.
Political Boundaries of Argentina: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Political boundaries are the lines that separate different political entities, such as countries, states, or provinces. They define the jurisdictional authority of a particular government and determine the rights and responsibilities of its citizens. Understanding political boundaries is crucial for effective governance and administration, as well as for maintaining peace and order within a country. In Argentina, a vast and diverse country located in South America, political boundaries play a significant role in shaping its political, economic, and social landscape. With 23 provinces and one autonomous city, Argentina’s political boundaries define the distribution of power and resources across the country. It is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of these boundaries to grasp the complexities of Argentine politics and society. Summary Argentina is divided into 23 provinces and one autonomous city, Buenos Aires. Buenos Aires is the capital district and holds significant political power in the country. Argentina’s historical boundaries have evolved from the Viceroyalty to the Republic. The federal system of government in Argentina has its own powers and limitations. Municipalities play a crucial role in local governance and autonomy in Argentine politics. The 23 Provinces of Argentina: A Brief Overview Argentina is divided into 23 provinces, each with its own distinct characteristics and contributions to the country’s overall development. These provinces are: 1. Buenos Aires2. Catamarca3. Chaco4. Chubut5. Córdoba6. Corrientes7. Entre Ríos8. Formosa9. Jujuy10. La Pampa11. La Rioja12. Mendoza13. Misiones14. Neuquén15. Río Negro16. Salta17. San Juan18. San Luis19. Santa Cruz20. Santa Fe21. Santiago del Estero22. Tierra del Fuego, Antártida e Islas del Atlántico Sur23. Tucumán Each province has its own unique geography, culture, and economic activities that...
Climate Zones of Argentina: Different climate regions Of Argentina
Argentina is a country known for its vast and diverse landscapes, ranging from the towering Andes mountains to the expansive Pampas plains. This diversity is reflected in the country’s climate zones, which vary greatly from region to region. Argentina is located in the southern hemisphere, which means that its seasons are opposite to those in the northern hemisphere. The country’s geography and size contribute to its climate diversity, with influences from the Atlantic Ocean, the Andes mountains, and the surrounding landmasses. Summary Argentina has a diverse range of climate zones, each with unique characteristics and weather patterns. The Humid Pampas Region is known for its fertile soil and agricultural production, but also experiences frequent flooding. The Dry Andes Region is a high-altitude desert with extreme temperature fluctuations and limited vegetation. The Subtropical Region is hot and humid, with a rainy season and a dry season. The Temperate Forest Region has a mild climate and is home to diverse flora and fauna, including the iconic Argentinean national tree, the ombú. The Patagonian Desert Region is a cold and windy desert with sparse vegetation and unique geological formations. The Mediterranean Region has a mild, rainy winter and a hot, dry summer, making it ideal for wine production. Climate change is affecting Argentina’s climate zones, with increased temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns. Argentina’s climate zones offer a range of tourism opportunities, from skiing in the Andes to exploring the wildlife in the subtropical rainforest. Appreciating the diversity of Argentina’s climate zones is key to understanding the country’s natural beauty and cultural heritage. The Humid Pampas Region The Humid Pampas region is...
Terrain and Topography of Argentina: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Introduction Argentina is a country known for its diverse and stunning landscapes. From the majestic Andes Mountains to the vast plains of the Pampas, Argentina’s terrain offers a wide range of geographical features that contribute to its unique beauty and cultural heritage. Understanding the country’s geography is essential for appreciating its natural wonders and the importance they hold for Argentina’s economy, culture, and history. The Andes Mountains: A Majestic Range The Andes Mountains are a prominent feature of Argentina’s geography. Stretching along the western border of the country, this majestic range is one of the longest mountain ranges in the world. The highest peaks in Argentina, such as Aconcagua, reach heights of over 6,000 meters, making them some of the tallest mountains in the Americas. The Andes Mountains hold great significance for Argentina’s economy and culture. The region is rich in mineral resources, including copper, gold, and silver, which have played a crucial role in the country’s economic development. Additionally, the Andes are home to several indigenous communities that have preserved their traditional way of life and cultural practices for centuries. The Pampas: Vast Plains of Argentina The Pampas is a vast region of flat plains that covers a significant portion of central Argentina. This fertile land is known for its agricultural importance, as it provides ideal conditions for growing crops such as wheat, corn, and soybeans. The Pampas is often referred to as the “breadbasket” of Argentina due to its role in supplying food for the country and exporting agricultural products worldwide. Aside from its agricultural significance, the Pampas also boasts stunning natural beauty and diverse wildlife. The...
Population Density of Argentina
Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured per square kilometer. It is an important indicator of how crowded or sparsely populated an area is. Population density matters because it can have significant implications for various aspects of a country’s development, including infrastructure, resources, and social services. Argentina, the eighth-largest country in the world, has a population density of approximately 16 people per square kilometer. This makes it one of the least densely populated countries in the world. However, despite its low overall population density, Argentina has significant regional variations in population distribution. Understanding these variations and their underlying factors is crucial for understanding Argentina’s social and economic landscape. Summary Argentina has a population density of 16 people per square kilometer. Population density in Argentina has been increasing since the 19th century. Buenos Aires has the highest population density in Argentina, while Patagonia has the lowest. Urbanization and immigration are major factors contributing to high population density in urban areas. High population density areas in Argentina face challenges such as housing shortages and environmental degradation. Historical Overview of Population Density in Argentina Argentina’s population has experienced significant growth over time. In the early 19th century, the country had a relatively small population, with most people concentrated in urban areas such as Buenos Aires. However, with the expansion of agriculture and the influx of immigrants in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Argentina’s population began to grow rapidly. The period between 1869 and 1914 is known as the “Golden Age” of immigration in Argentina. During this time, millions of immigrants from Europe,...
Natural Resources of Argentina: Where Natural Resources are located In Argentina
Argentina’s Natural Resources and Mining Industry: A Hidden Powerhouse of South America Argentina, a nation better known for tango, wine, and football, is increasingly making headlines in the world of mineral resources and mining. Blessed with vast untapped natural resources, Argentina is positioning itself as a global leader in lithium, copper, petroleum, and more. This article offers an in-depth exploration of Argentina’s mining industry, the role of the World Bank, and the impact of foreign investment. Whether you’re a curious reader, investor, or policy watcher, this article is worth your time because it deciphers how Argentina’s mines could fuel the future of the green economy. Article Outline Why Are Argentina’s Natural Resources So Important? What Is the Current State of Mining in Argentina? How Has the World Bank Supported Argentina’s Mining Growth? What Role Does Lithium Play in Argentina’s Future? Is Argentina Rich in Other Mineral Resources? What Is the Impact of Foreign Investment in Mining? How Do Mines Influence Argentina’s GDP and Exports? What Challenges Face the Mining Industry in Argentina? How Are Sustainability and Transparency Addressed in Argentina’s Mining Sector? What Does the Future Hold for Argentina’s Natural Resources? Why Are Argentina’s Natural Resources So Important? Argentina is one of the most resource-rich countries in Latin America, boasting a wealth of mineral resources and energy reserves. From natural gas to petroleum and lithium, Argentina is uniquely positioned to support both regional and global industries, particularly those pivoting to renewable energy and sustainable technology. The World Bank has classified Argentina among the Latin American countries with great potential for economic transformation via natural resources. Notably,...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Argentina: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Argentina
Argentina is a country known for its rich cultural heritage and natural wonders. From the vibrant streets of Buenos Aires to the breathtaking landscapes of Patagonia, Argentina offers a diverse range of experiences for travellers. In this article, we will explore some of the most iconic and enchanting destinations in Argentina, from the historic quarter of Buenos Aires to the mystical ruins of Tiwanaku. Whether you are a history buff, a nature lover, or simply seeking adventure, Argentina has something to offer for everyone. Summary Buenos Aires’ historic quarter offers a glimpse into Argentina’s past Teatro Colón is a must-visit cultural gem in Buenos Aires Iguazu Falls is a magnificent natural wonder of Argentina Bariloche is an enchanting haven for culture and history buffs Tiwanaku’s ruins provide a mystical glimpse into Argentina’s pre-Columbian past The Historic Quarter of Buenos Aires: A Journey Through Argentina’s Past The historic quarter of Buenos Aires is a must-visit destination for anyone interested in Argentina’s history. This area is home to some of the country’s most important landmarks and monuments, including Plaza de Mayo and Casa Rosada. Plaza de Mayo is the main square in Buenos Aires and has been the site of many significant events in Argentina’s history, including the May Revolution in 1810. Casa Rosada, the presidential palace, is located on one side of Plaza de Mayo and is an iconic symbol of Argentina’s political history. The Iconic Teatro Colón: A Cultural Gem of Buenos Aires The Teatro Colón is one of the most prestigious opera houses in the world and a cultural gem of Buenos Aires. Built in 1908, the theater...
Exploring the Enchanting Wonders of Argentina: A Journey Through Its Vibrant Culture and Breathtaking Landscapes
Argentina, located in the southern part of South America, is a country known for its vast and diverse landscapes, rich culture, and passionate people. With an area of over 2.7 million square kilometers, Argentina is the eighth-largest country in the world. It is bordered by Chile to the west, Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, and Uruguay and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. The country’s geography ranges from the towering Andes Mountains in the west to the fertile plains of the Pampas in the center, and from the stunning glaciers of Patagonia in the south to the tropical rainforests of the northeast. Argentina is a melting pot of different cultures and influences. The majority of its population is of European descent, with a strong influence from Spain and Italy. However, there are also significant indigenous populations, as well as communities with African, Middle Eastern, and Asian roots. This diversity is reflected in Argentina’s cuisine, music, dance, art, and literature. Argentina plays a crucial role in South America both economically and politically. It is one of the largest economies in the region and has a strong agricultural sector, producing crops such as soybeans, corn, wheat, and beef. The country is also known for its natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals. In addition to its economic importance, Argentina has been a key player in regional politics and has had a significant influence on South American culture. Key Takeaways Argentina is a diverse and beautiful country with a rich culture and fascinating history. The music, dance, and art of Argentina are colorful and vibrant, reflecting the...