United States of America
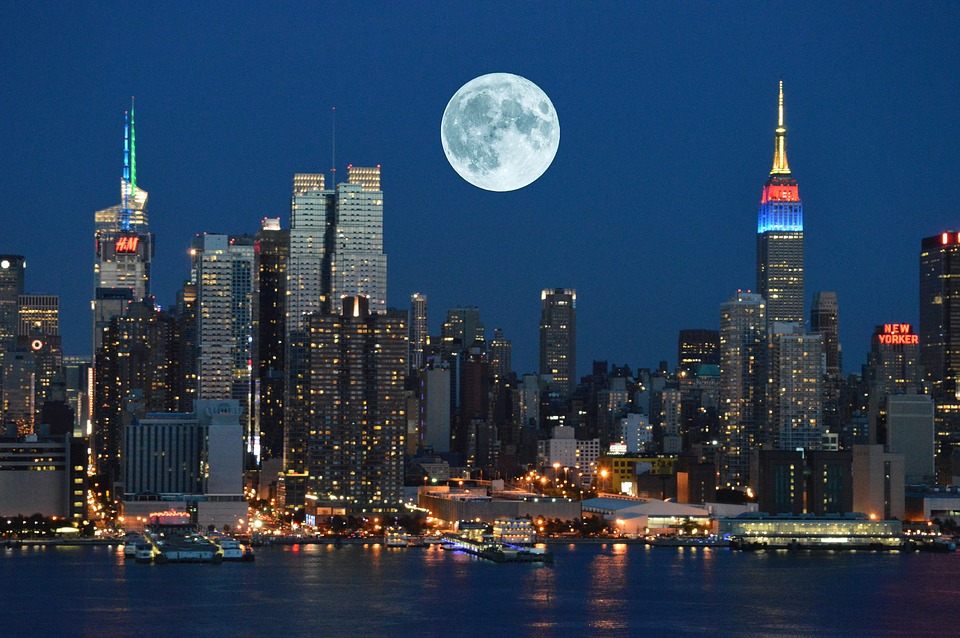
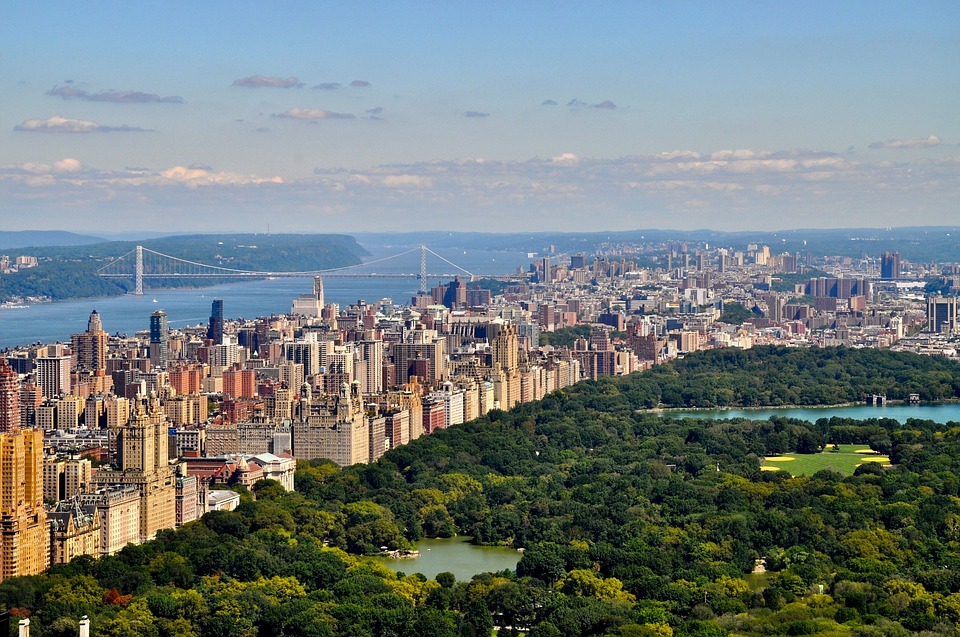






Capital: Washington, D.C.
Population (Estimated July 2012): 313,847,465
Area: 9,526,468km2 or 3,678,190mi2
Currency: United States Dollar (U.S.$)
Official Language: No official
(English Predominantly spoken)
Political Information: Federal Presidential Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 51.3% of the population is Protestant, 23.9% are Roman Catholic, 1.6% are other Christian, 1.7% are Mormon, 1.7% are Jewish, 0.7% are Buddhist, 0.7% are Muslim, 14.6% have other or unspecified religious beliefs and 4% have no religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Mount McKinley, Churchill Peaks and South Peak at 6,105m or 20,029.5ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $15.06 trillion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $15.04 trillion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $48,100 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): Between -5:00 and -10:00
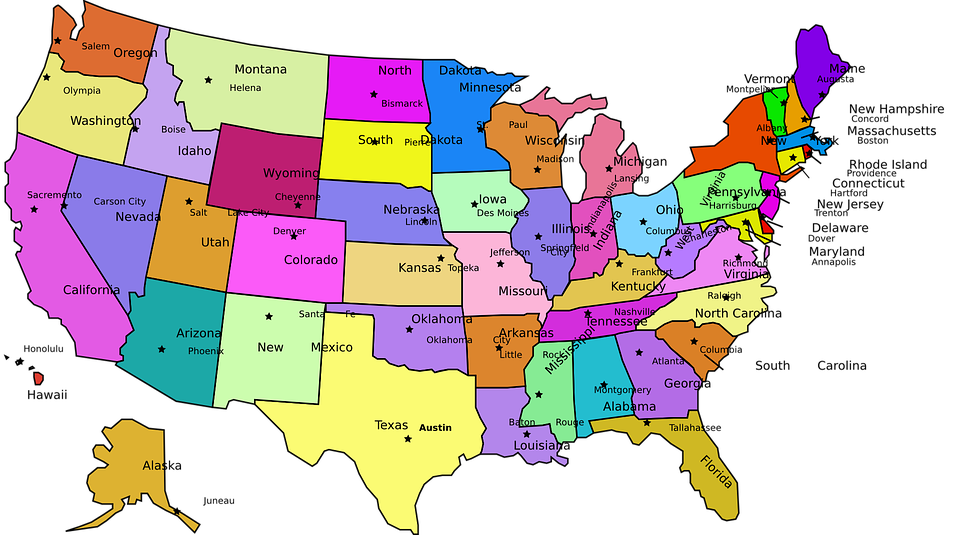
Counties/Provinces/States: 50 states and 1 district*;~
Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, District of Columbia*, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin, Wyoming
Leaders: President Donald J. TRUMP (since 20 January 2017); Vice President Michael R. PENCE (since 20 January 2017); note – the president is both chief of state and head of government
Additional: The United States of America declared its independence from Great Britain on the 4th of July 1776 which was recognised by Britain on the 3rd September 1783.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
United States of America
The history of the United States is a complex tapestry woven from the threads of indigenous cultures, European colonisation, and the quest for independence. The land that would become the United States was originally inhabited by diverse Native American tribes, each with its own distinct culture and social structure. The arrival of European explorers in the late 15th century marked the beginning of significant changes.
Christopher Columbus’s voyage in 1492, although not the first European contact, opened the floodgates for further exploration and colonisation. The Spanish, French, and British established settlements, leading to a clash of cultures and the eventual displacement of many indigenous peoples. The 18th century was pivotal in shaping the nation’s identity.
The Thirteen Colonies, primarily established by the British, began to develop their own sense of identity separate from their mother country. Tensions escalated over issues such as taxation without representation, culminating in the American Revolution (1775-1783). The Declaration of Independence in 1776, authored by Thomas Jefferson, articulated the colonies’ desire for self-governance and individual rights.
Following a hard-fought war, the United States emerged as an independent nation in 1783, with the ratification of the Constitution in 1788 establishing a framework for governance that has endured for over two centuries.
Summary
- The United States has a rich history, from the arrival of the first settlers to the American Revolution and the Civil Rights Movement.
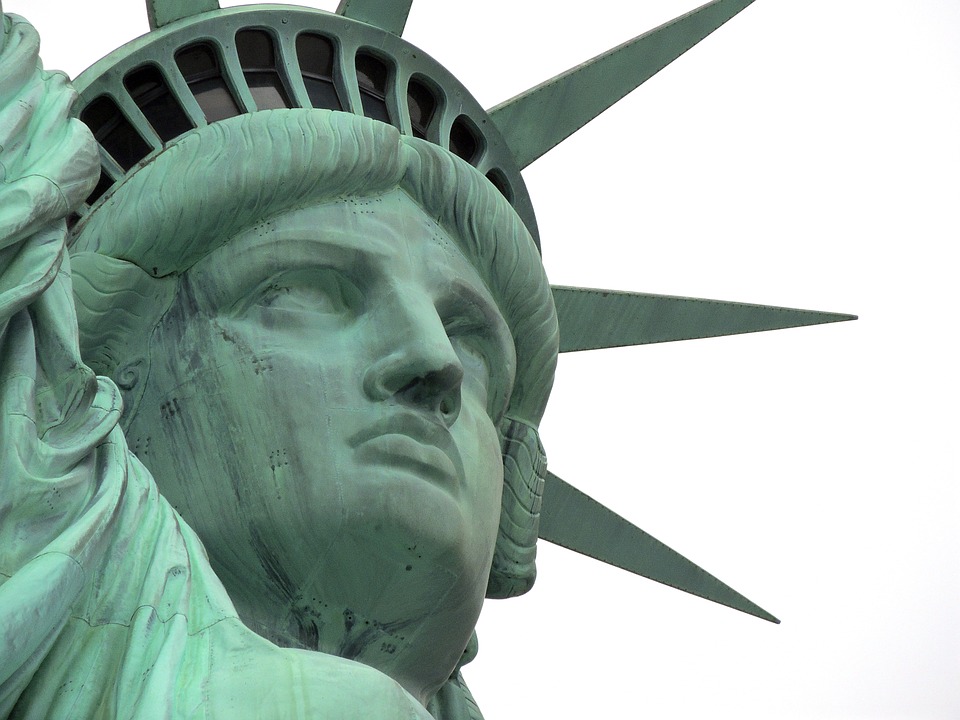
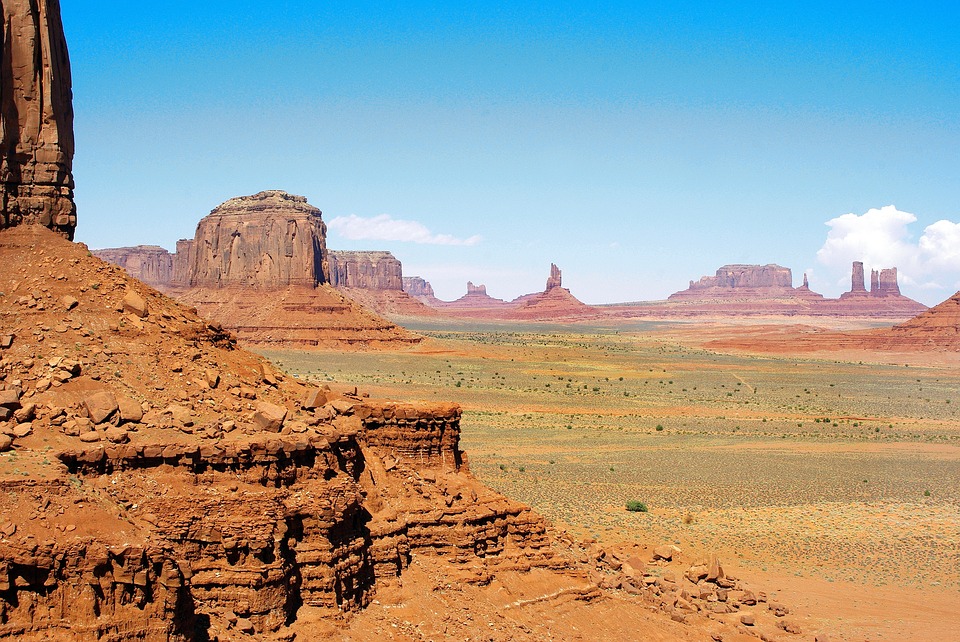
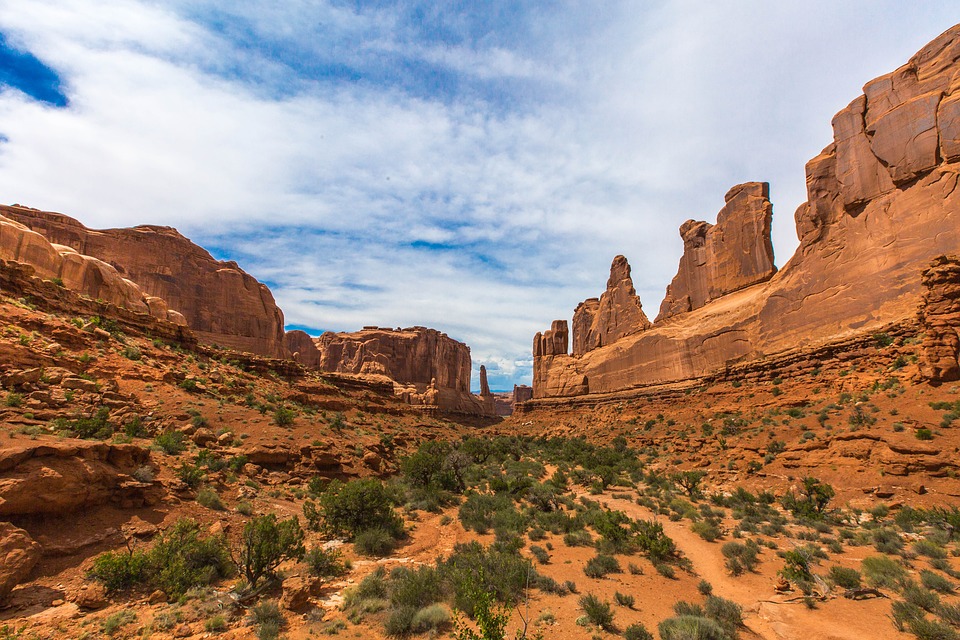
- The geography of the US varies greatly, from the Rocky Mountains to the Great Plains, and it is home to iconic landmarks such as the Statue of Liberty and the Grand Canyon.
- The US government operates as a federal republic, with a president as the head of state and a two-party political system dominating the landscape.
- The US has the world’s largest economy, driven by industries such as technology, finance, and manufacturing, and is a major player in global trade.
- American culture is diverse and influenced by a variety of factors, including music, art, literature, and sports, and society is known for its emphasis on individualism and freedom.
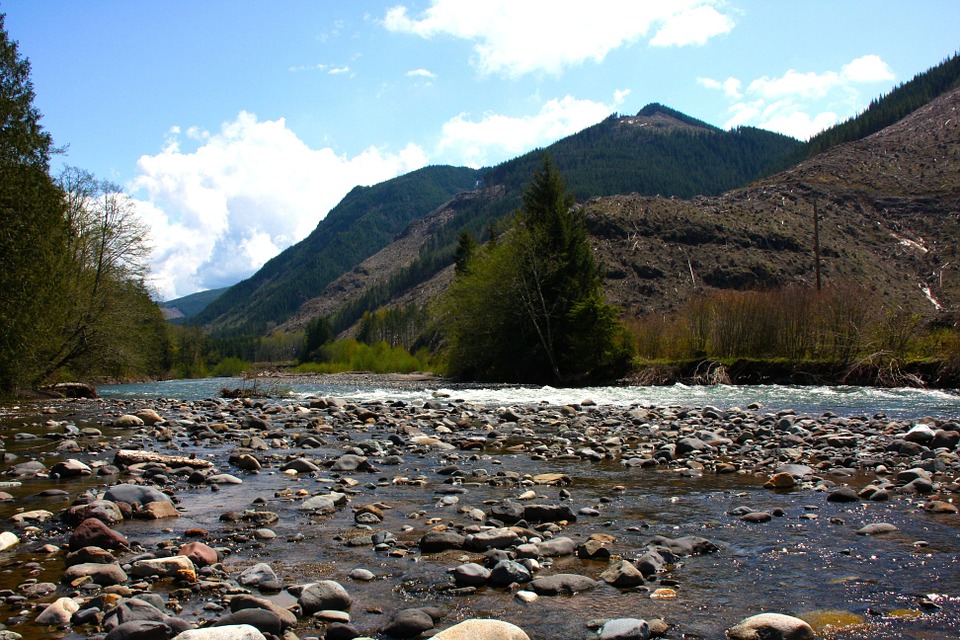
Geography and Landmarks
The Mountainous Landscape
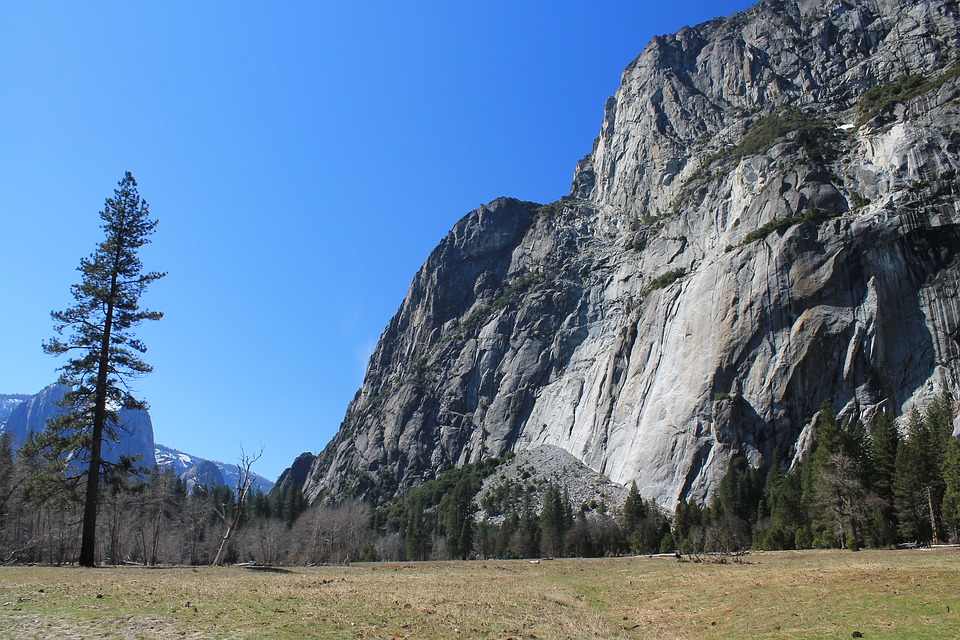
The Rocky Mountains dominate the western landscape, while the Appalachian Mountains stretch along the eastern seaboard.
The Great Plains and Iconic Landmarks
Between these two mountain ranges lies the Great Plains, a region characterised by its flat terrain and fertile soil, which has been crucial for agriculture. In addition to its varied topography, the United States is home to numerous iconic landmarks that reflect its cultural heritage and natural beauty. The Statue of Liberty, a gift from France, stands as a symbol of freedom and democracy at the entrance to New York Harbour.
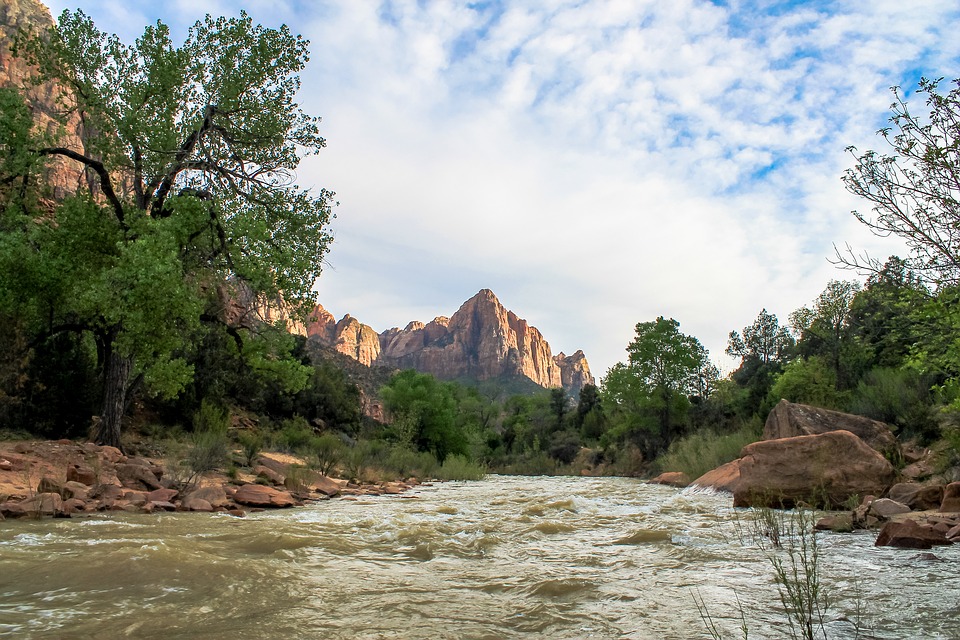
National Parks and Natural Wonders
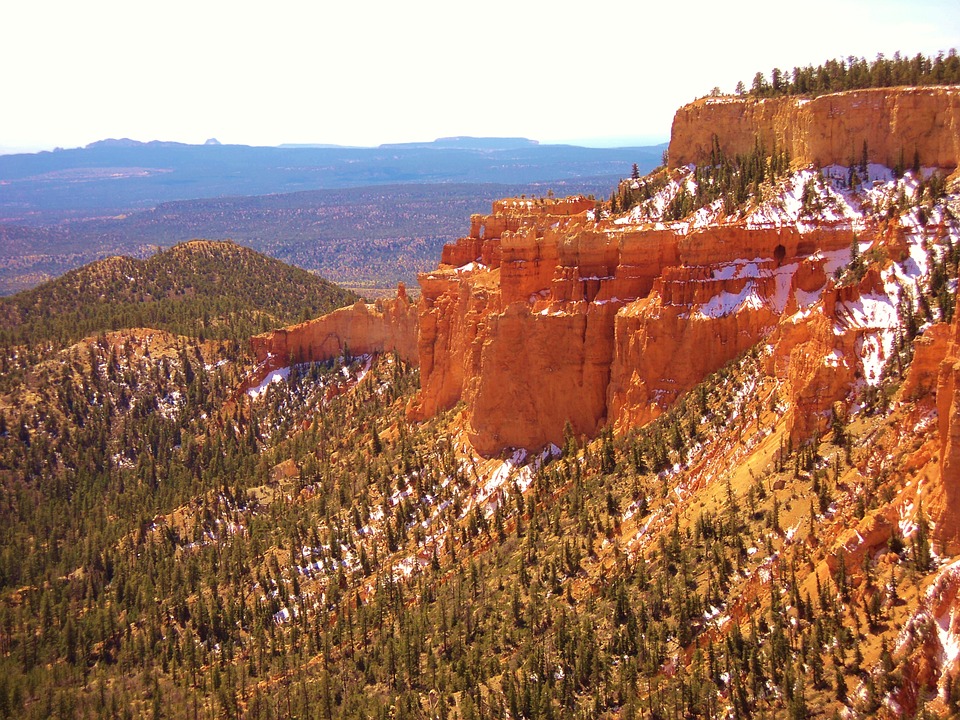
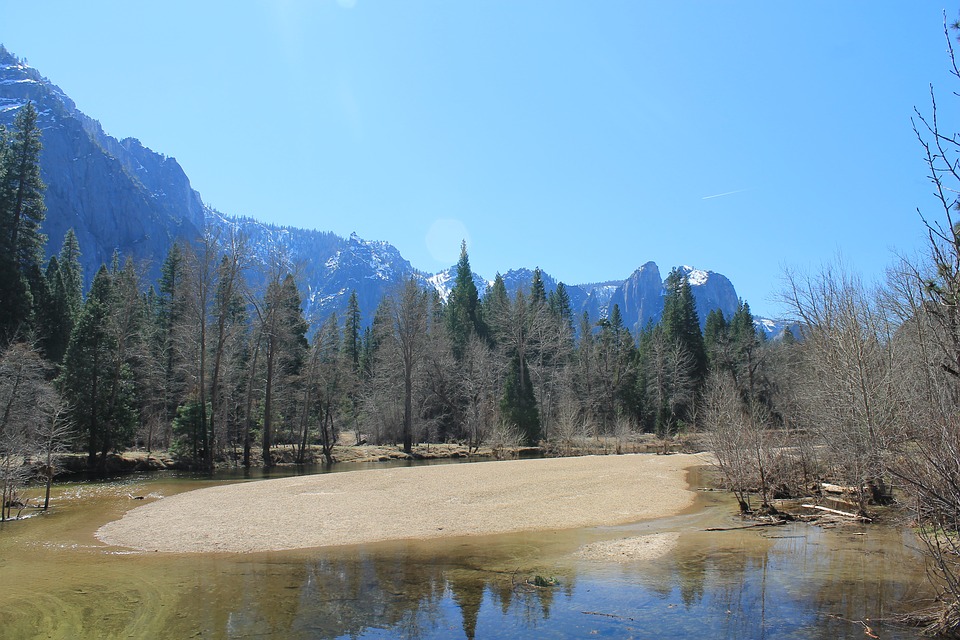
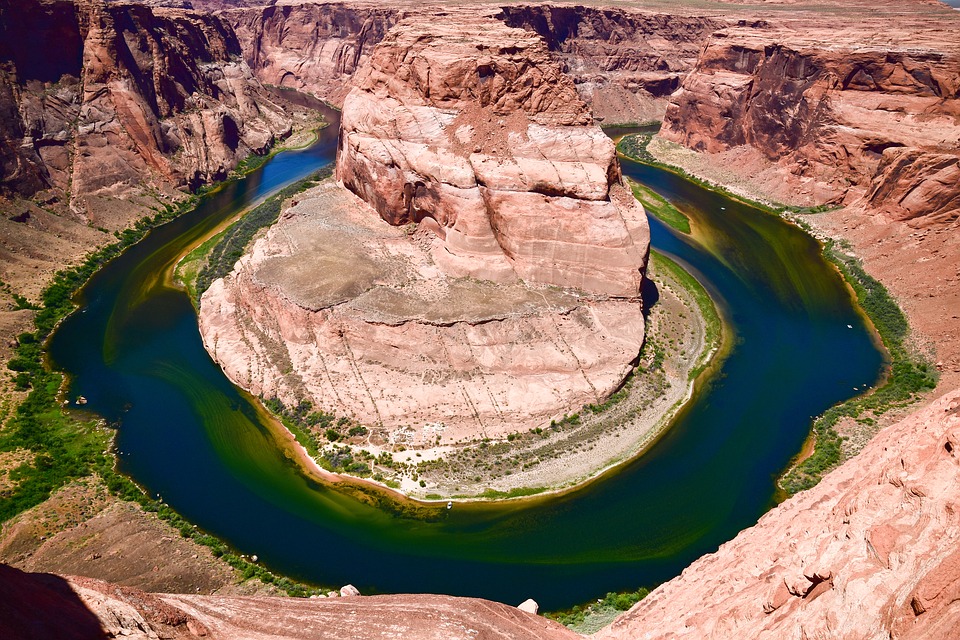
National parks such as Yellowstone and Yosemite showcase the country’s stunning natural landscapes, preserving unique ecosystems and geological features. The Grand Canyon, carved by the Colorado River, is one of the most visited natural wonders in the world, attracting millions of tourists each year who come to marvel at its breathtaking vistas.
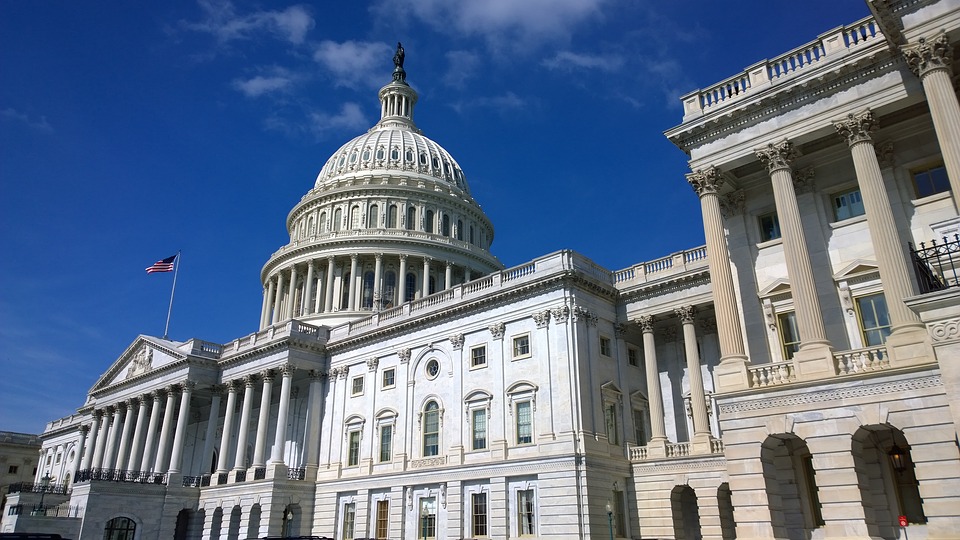
Government and Politics
The United States operates under a federal system of government defined by a Constitution that delineates powers between national and state authorities. The government is divided into three branches: the executive, legislative, and judicial. The President serves as the head of state and government, while Congress, composed of the Senate and House of Representatives, is responsible for making laws.
The judiciary interprets these laws and ensures they align with the Constitution. Political dynamics in the United States are characterised by a two-party system dominated by the Democratic and Republican parties. This system has shaped electoral politics and policy-making for over a century.
Elections are held at various levels—federal, state, and local—allowing citizens to participate in governance. The electoral process is often contentious, with debates over issues such as healthcare, immigration, and climate change reflecting broader societal divisions. Political campaigns are heavily influenced by media coverage and funding from various interest groups, which can significantly impact election outcomes.
Economy and Trade
The United States boasts one of the largest economies in the world, characterised by a mixed economy that incorporates elements of both capitalism and government intervention. As of 2023, it remains a global leader in technology, finance, healthcare, and agriculture. The country’s economic strength is underpinned by its vast natural resources, including oil, natural gas, coal, and fertile land for agriculture.
The agricultural sector is particularly significant; the U.S. is one of the world’s largest producers of corn, soybeans, and wheat. Trade plays a crucial role in the U.S.
economy, with international partnerships facilitating access to markets around the globe. The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), now replaced by the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), exemplifies how trade agreements can shape economic relationships between countries. Additionally, China has emerged as a key trading partner, although tensions over trade policies have led to tariffs and negotiations that reflect broader geopolitical dynamics.
The U.S. economy is also increasingly influenced by technology companies that drive innovation and create new markets.
Culture and Society
American culture is a rich amalgamation of influences from around the world, shaped by its history of immigration and diversity. This cultural melting pot manifests in various forms—music, art, literature, cuisine—each reflecting different ethnic backgrounds and traditions. Jazz and blues originated from African American communities in the early 20th century and have since influenced countless genres worldwide.
Hollywood remains a global powerhouse in film production, exporting American culture through cinema that often explores themes of freedom, individualism, and social justice. Socially, the United States grapples with issues related to race, gender equality, and class disparities. Movements such as Black Lives Matter have emerged in response to systemic racism and police brutality, highlighting ongoing struggles for civil rights.
Similarly, advocacy for LGBTQ+ rights has gained momentum over recent decades, culminating in landmark legal victories such as the Supreme Court’s decision to legalise same-sex marriage in 2015. These movements reflect a society that is continually evolving and striving towards greater inclusivity while facing resistance from various quarters.
Education and Healthcare
The education system in the United States is decentralised, with significant variations across states and localities. Public education is primarily funded through local property taxes, leading to disparities in resources between affluent and less wealthy areas. The U.S. boasts some of the world’s most prestigious universities—such as Harvard, Stanford, and MIT—attracting students globally due to their research opportunities and academic excellence. However, access to quality education remains a contentious issue, with ongoing debates about standardised testing, curriculum content, and educational equity. Healthcare in the United States is another area marked by complexity and controversy. Unlike many developed nations that offer universal healthcare systems, the U.S. relies on a mix of private insurance providers and government programmes like Medicare and Medicaid. This system has led to significant disparities in access to care; millions remain uninsured or underinsured despite reforms such as the Affordable Care Act (ACA) aimed at expanding coverage. The high cost of healthcare services continues to be a pressing concern for many Americans, prompting discussions about potential reforms to create a more equitable system.
The American Dream: A Promise of Success and Prosperity
At the heart of the Land of Opportunity lies the American Dream, a powerful narrative that suggests anyone, regardless of their background, can achieve success through hard work and perseverance. This dream is often symbolised by the idea of upward mobility, where individuals can improve their socio-economic status over time. The American Dream has evolved over the years, adapting to changing societal norms and economic conditions, yet it remains a central tenet of American identity.
Historically, the American Dream has been associated with home ownership, education, and financial stability. The post-World War II era saw a significant expansion of this dream, as returning soldiers were able to access education and housing through initiatives like the GI Bill. This period marked a time when many families could attain a middle-class lifestyle, reinforcing the belief that America was a land where dreams could be realised.
However, contemporary discussions around the American Dream also highlight challenges such as income inequality and systemic barriers that can hinder access to these opportunities. Despite these challenges, the dream persists as a motivating force for many who continue to strive for a better life.
Economic Opportunities in the United States
The United States boasts one of the largest and most dynamic economies in the world, providing a plethora of economic opportunities for individuals seeking to improve their financial standing. The country is home to a diverse range of industries, from technology and finance to agriculture and manufacturing. This economic diversity creates numerous pathways for employment and entrepreneurship, allowing individuals to find niches that align with their skills and interests.
In recent years, sectors such as technology have experienced exponential growth, driven by innovation and an ever-increasing demand for digital solutions. Cities like Silicon Valley have become synonymous with start-up culture, attracting talent from around the globe. The availability of venture capital and supportive ecosystems for entrepreneurs has led to the emergence of countless successful companies, further solidifying the United States’ reputation as a hub for economic opportunity.
Additionally, traditional industries continue to thrive, offering stable employment options for those seeking more conventional career paths.
Immigration and Diversity
Immigration has been a defining feature of American society since its inception. Waves of immigrants from Europe, Asia, Latin America, and beyond have contributed to the nation’s demographic diversity. This influx has enriched American culture but has also sparked debates about immigration policy and national identity.
The Immigration Act of 1965 marked a significant shift in U.S. immigration policy by abolishing quotas based on national origin and opening doors for immigrants from non-European countries. Today’s immigration landscape is characterised by complex challenges such as border security, undocumented immigration, and refugee resettlement programmes.
The Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) programme exemplifies efforts to address the status of young immigrants who arrived in the U.S. as children but lack legal documentation. As America continues to grapple with its identity as a nation of immigrants, discussions surrounding diversity often intersect with issues of race, religion, and socio-economic status.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
Looking ahead, the United States faces numerous challenges that will shape its trajectory in the coming decades. Climate change poses an existential threat that requires urgent action; rising sea levels and extreme weather events are already impacting communities across the country. Transitioning to renewable energy sources presents both an opportunity for innovation and economic growth while addressing environmental concerns.
Additionally, political polarization remains a significant hurdle to effective governance. The increasing divide between political ideologies complicates consensus-building on critical issues such as healthcare reform and immigration policy. However, this polarization also presents an opportunity for grassroots movements to emerge as citizens seek to influence change at local levels.
Technological advancements will continue to transform various sectors of society—from artificial intelligence reshaping industries to biotechnology revolutionising healthcare. Embracing these changes while ensuring ethical considerations are addressed will be crucial for fostering an inclusive future that benefits all Americans. In summary, while challenges abound for the United States as it navigates an increasingly complex global landscape, opportunities for growth and innovation also exist within its diverse society.
The interplay between history, geography, politics, economy, culture, education, immigration, and future prospects will undoubtedly shape what lies ahead for this dynamic nation.
One interesting article related to the United States of America is about the history of Thanksgiving. This traditional American holiday has its roots in the harvest festivals celebrated by the Pilgrims and Native Americans in the early 17th century. To learn more about the origins and evolution of Thanksgiving, you can read the article here.
Travel to and around the United States of America
When planning a trip to the United States, understanding the entry requirements is paramount. The first step for most international travellers is to determine whether they need a visa or if they qualify for the Visa Waiver Program (VWP). Citizens of 40 countries, including the United Kingdom, Australia, and many European nations, can enter the US for tourism or business purposes for up to 90 days without a visa, provided they have an approved Electronic System for Travel Authorization (ESTA).
It is advisable to apply for ESTA at least 72 hours before departure to avoid any last-minute complications. For those who do require a visa, the process can be more intricate.
The most common visa types for tourists are the B-1 (business) and B-2 (tourism) visas. Applicants must fill out the DS-160 form online, pay a visa application fee, and schedule an interview at a US embassy or consulate. During the interview, applicants should be prepared to provide documentation that demonstrates their intent to return to their home country, such as proof of employment, financial stability, and ties to family or property.
It is essential to start this process well in advance of travel plans, as wait times for interviews can vary significantly depending on the location and time of year.
Summary
- British citizens must have a valid passport and a visa or an approved ESTA to enter the USA
- Transportation options within the USA include domestic flights, trains, buses, and rental cars
- Top destinations to visit in the USA include New York City, Los Angeles, Las Vegas, and the Grand Canyon
- American cuisine offers a variety of options, including fast food, diners, and fine dining restaurants
- When in the USA, it’s important to be mindful of cultural etiquette, such as tipping in restaurants and addressing people with respect
Transportation Options within the USA
Flights: A Swift and Convenient Option
For those who prefer speed and convenience, domestic flights are a popular choice. Major airlines such as American Airlines, Delta, and Southwest operate extensive networks connecting major cities and regional hubs. Booking in advance can often yield significant savings, especially during peak travel seasons.
Exploring at a Leisurely Pace: Road Trips and Public Transport
For travellers looking to explore at a more leisurely pace, road trips are an iconic American experience. The US boasts an extensive motorway system, with interstates that crisscross the nation. Renting a car provides the freedom to stop at various attractions along the way, from national parks to quirky roadside diners. Additionally, cities like New York and San Francisco offer robust public transport systems, including undergrounds and buses, making it easy to navigate urban areas without the need for a car.
Rideshare Services: A Convenient Alternative
Rideshare services like Uber and Lyft have also gained popularity in many cities, providing a convenient alternative for short distances.
Top Destinations to Visit in the USA
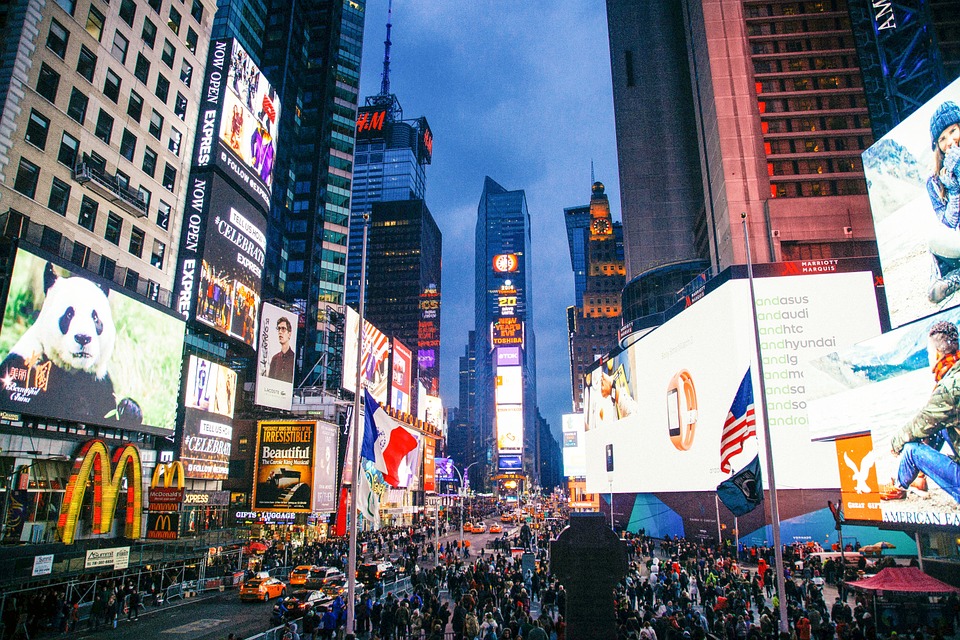
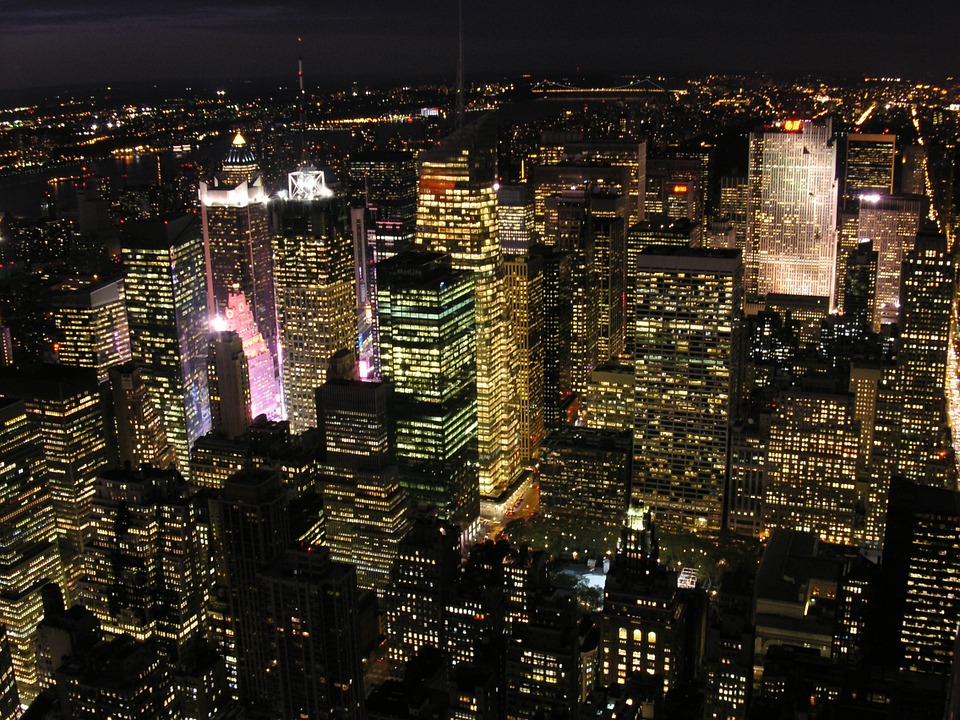
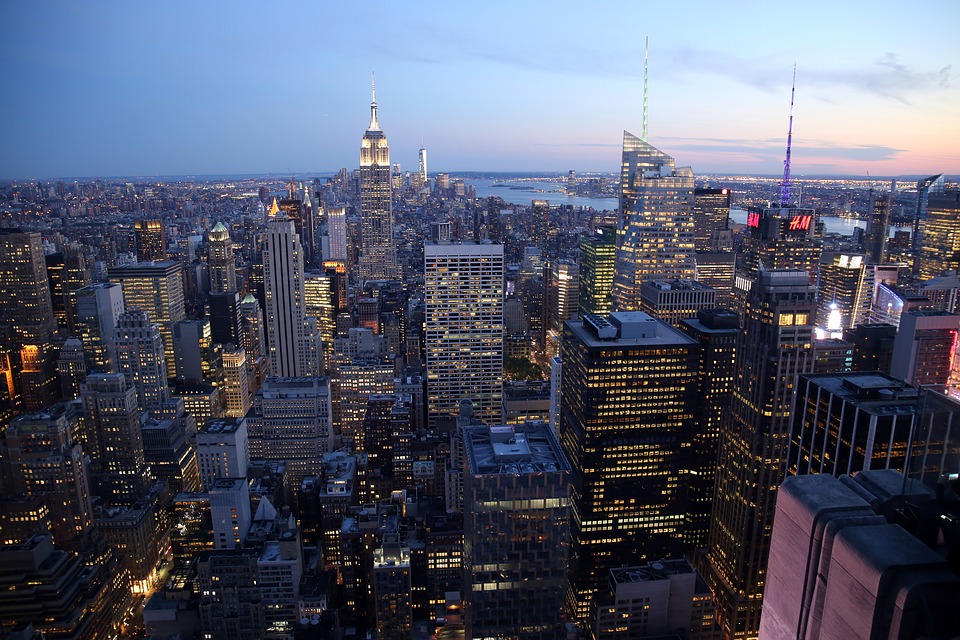
The United States is home to an array of destinations that cater to every type of traveller. New York City stands out as a cultural epicentre, offering iconic landmarks such as Times Square, Central Park, and the Statue of Liberty. The city’s vibrant arts scene is complemented by world-class museums like The Metropolitan Museum of Art and The Museum of Modern Art.
Visitors can immerse themselves in Broadway shows or explore diverse neighbourhoods that reflect the melting pot of cultures that define New York. On the opposite coast lies Los Angeles, a city synonymous with glamour and entertainment. Hollywood’s allure draws millions each year, with attractions like the Walk of Fame and Universal Studios providing glimpses into the film industry.
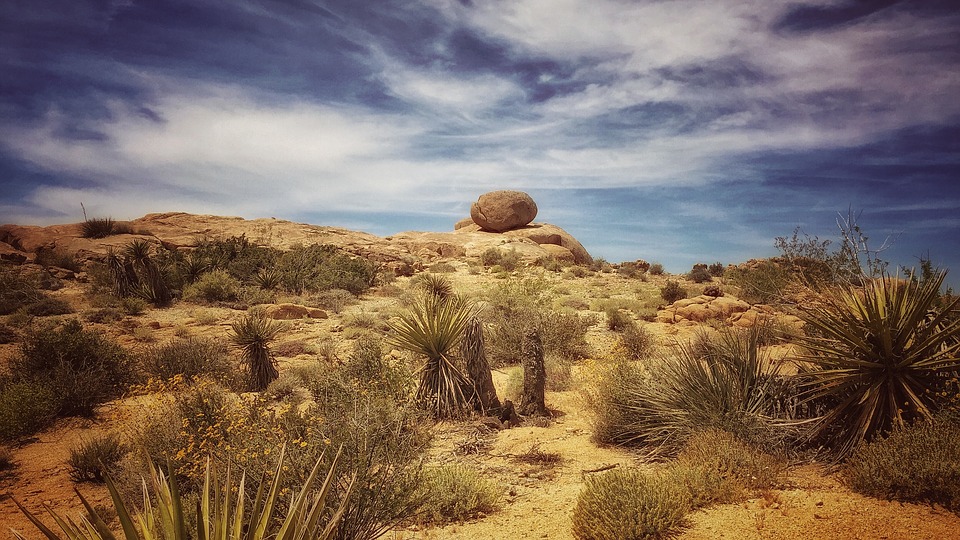
Beyond Hollywood, visitors can relax on the sun-soaked beaches of Santa Monica or Venice Beach, where a laid-back atmosphere contrasts with the bustling city life. For those seeking natural beauty, a short drive from LA leads to the stunning landscapes of Joshua Tree National Park or the scenic coastline of Big Sur.
American Cuisine and Dining Options
American cuisine is as diverse as its population, reflecting a rich tapestry of cultural influences from around the world. Each region boasts its own culinary specialities that are worth exploring. In the South, for instance, traditional dishes such as fried chicken, gumbo, and barbecue are staples that showcase bold flavours and hearty portions.
Cities like New Orleans are renowned for their unique Creole and Cajun cuisines, where dishes like jambalaya and beignets tantalise the taste buds. In contrast, the Pacific Northwest is celebrated for its emphasis on fresh, local ingredients. Seattle’s seafood scene is particularly noteworthy; visitors can indulge in dishes featuring salmon or Dungeness crab while enjoying views of Puget Sound.
Furthermore, food trucks have become increasingly popular across major cities, offering everything from gourmet tacos to artisanal ice cream. Dining options range from casual eateries to Michelin-starred restaurants, ensuring that every palate is catered for.
Cultural Etiquette and Customs in the USA
Understanding cultural etiquette in the United States can enhance interactions with locals and contribute to a more enjoyable travel experience. Americans are generally known for their friendliness and openness; however, there are certain customs that visitors should be aware of. For instance, personal space is highly valued; standing too close during conversations may make some individuals uncomfortable.
A firm handshake is a common greeting in professional settings, while casual greetings among friends may include hugs or friendly waves. Tipping is also an important aspect of American culture. In restaurants, it is customary to leave a gratuity of 15-20% of the total bill before tax.
This practice extends to other service industries as well; taxi drivers, bartenders, and hotel staff typically expect tips as a sign of appreciation for good service. While tipping is not mandatory, it is considered polite and contributes significantly to workers’ incomes in service-oriented jobs.
Tips for Navigating US Currency and Tipping
The currency used in the United States is the US dollar (USD), which is divided into 100 cents. Familiarising oneself with the denominations—ranging from one-cent coins (pennies) to hundred-dollar bills—can help avoid confusion when making purchases. ATMs are widely available throughout urban areas and even in some rural locations; however, it is advisable to notify your bank before travelling to prevent any issues with card usage abroad.
When it comes to tipping practices, understanding local customs can prevent awkward situations. In addition to restaurants, tipping is expected in various scenarios such as hair salons or when receiving taxi services. For hotel staff, it is customary to tip bellhops $1-2 per bag and housekeepers $1-5 per night depending on service quality.
In bars, leaving $1-2 per drink is standard practice. While tipping may seem excessive compared to other countries where service charges are included in bills, it plays a crucial role in supporting service workers’ livelihoods.
Outdoor Activities and National Parks in the USA
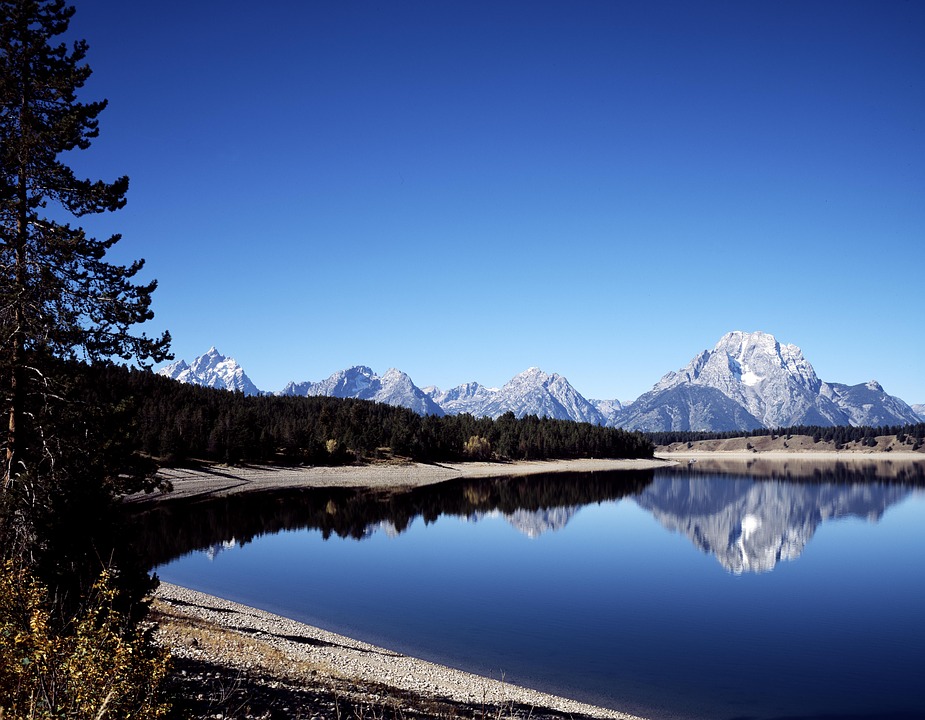
The United States offers an abundance of outdoor activities that cater to nature enthusiasts and adventure seekers alike. With over 63 national parks spread across the country, each park showcases unique landscapes ranging from towering mountains to expansive deserts. Yellowstone National Park, established in 1872 as the first national park in the world, features geothermal wonders such as Old Faithful geyser and vibrant hot springs.
Hiking trails abound here, allowing visitors to explore diverse ecosystems teeming with wildlife. Another remarkable destination is Yosemite National Park in California, known for its stunning granite cliffs and cascading waterfalls. The park offers numerous opportunities for rock climbing, hiking, and photography amidst breathtaking scenery.
For those seeking coastal adventures, Acadia National Park in Maine provides picturesque views of rugged shorelines and lush forests. Kayaking along its coastline or cycling on scenic carriage roads allows visitors to immerse themselves in nature while enjoying fresh ocean air.
Safety and Health Considerations for Travel in the USA
While travelling in the United States can be an exhilarating experience, it is essential to remain vigilant regarding safety and health considerations. The US has a relatively low crime rate compared to many other countries; however, like any destination, certain areas may pose risks. It is advisable for travellers to stay informed about their surroundings and avoid poorly lit or isolated areas at night.
Health-wise, travellers should ensure they have adequate health insurance coverage during their stay in the US as medical costs can be exorbitant without insurance. It is also wise to carry any necessary medications along with prescriptions when travelling internationally.
Additionally, staying updated on vaccinations recommended by health authorities can help prevent illness during travel. In light of recent global health concerns, maintaining good hygiene practices such as frequent handwashing and wearing masks in crowded places may also be prudent measures while exploring this vast country.
FAQs
What is the United States of America?
The United States of America (USA) is a country located in North America, consisting of 50 states, a federal district, five major self-governing territories, and various possessions.
What is the capital of the United States of America?
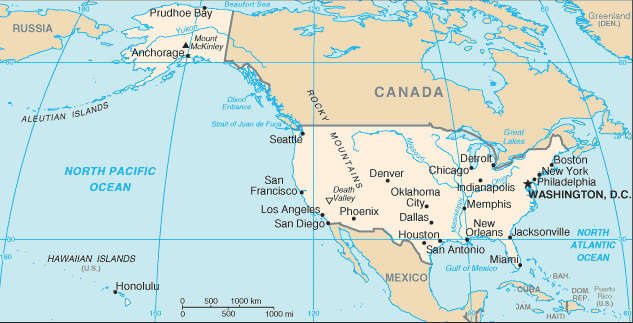
The capital of the United States of America is Washington, D.C.
What is the population of the United States of America?
As of 2021, the estimated population of the United States of America is over 331 million people, making it the third most populous country in the world.
What is the official language of the United States of America?
The United States of America does not have an official language at the federal level, but English is the most widely spoken language.
What is the government system of the United States of America?
The United States of America operates under a federal presidential constitutional republic, with a separation of powers between the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of government.
What are some major cities in the United States of America?
Some major cities in the United States of America include New York City, Los Angeles, Chicago, Houston, and Philadelphia.
What are some popular tourist attractions in the United States of America?
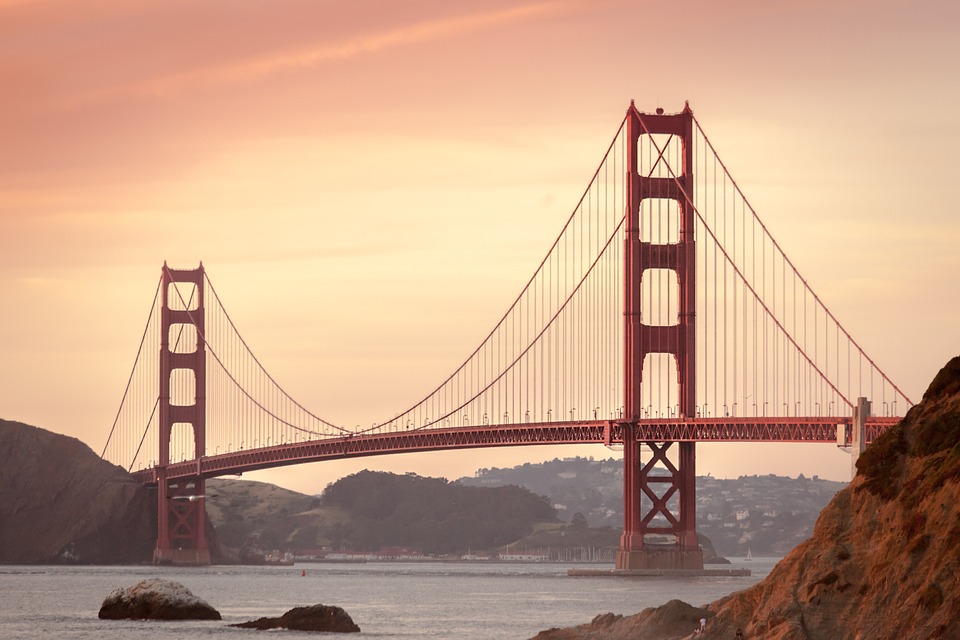
Popular tourist attractions in the United States of America include the Grand Canyon, Statue of Liberty, Yellowstone National Park, Walt Disney World Resort, and the Golden Gate Bridge.
Climate Zones of The United States of America: Different climate regions Of The United States of America
The United States is a vast country characterised by a remarkable diversity of climate zones, each contributing to the unique environmental tapestry of the nation. Spanning from the frigid Arctic conditions of Alaska to the tropical warmth of Hawaii, the climatic variations are influenced by a multitude of factors, including latitude, elevation, and proximity to bodies of water. This diversity not only shapes the natural landscapes but also affects the lifestyles, economies, and cultures of the regions within the country. Understanding these climate zones is essential for grasping how weather patterns influence agriculture, urban development, and even social dynamics across the United States. The classification of climate zones in the U.S. can be broadly categorised into several distinct regions, each with its own characteristics and seasonal variations. The Köppen climate classification system is often employed to delineate these zones, which include temperate, arid, tropical, and polar climates. Each region experiences its own unique weather patterns, temperature ranges, and precipitation levels, which in turn dictate the types of flora and fauna that thrive there. As we delve into the specifics of each climate region, it becomes evident how these environmental factors intertwine with human activity and ecological systems. Summary The United States has a diverse range of climate zones, each with its own unique characteristics and weather patterns. The Northeastern Climate Region experiences four distinct seasons, with cold winters and hot summers. The Southeastern Climate Region is known for its high humidity and frequent thunderstorms, with mild winters and hot summers. The Midwestern Climate Region has a continental climate with cold winters and hot summers, and experiences a wide range...
Terrain and Topography of The United States of America: mountains, valleys, and plains.
The United States boasts an incredibly diverse terrain and topography, shaped by a multitude of geological processes over millions of years. Spanning approximately 3. 8 million square miles, the country features a wide array of landscapes, from towering mountain ranges to expansive plains, rolling hills, and intricate coastlines. This geographical diversity not only contributes to the stunning natural beauty of the nation but also plays a significant role in its climate, ecosystems, and human activities. The interplay of these various landforms has influenced settlement patterns, agriculture, and even cultural development throughout American history. The topography of the United States can be broadly categorised into several distinct regions, each with its own unique characteristics. The Rocky Mountains dominate the western landscape, while the Great Plains stretch across the central part of the country. The Appalachian Mountains provide a contrasting backdrop in the east, and the coastal plains along both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans offer a different perspective on the relationship between land and water. Each of these regions contributes to the overall tapestry of the United States, creating a rich mosaic of environments that support a wide range of flora and fauna, as well as diverse human experiences. Summary The United States boasts a diverse and spectacular terrain, ranging from majestic mountain ranges to vast and flat landscapes. The Rocky Mountains stand as a majestic range, offering breathtaking views and challenging terrain for outdoor enthusiasts. The Great Plains feature vast and flat landscapes, providing a unique and expansive backdrop to the central region of the United States. The Appalachian Mountains are a historic and diverse range, offering a rich...
Political Boundaries of The United States of America: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Political boundaries in the United States serve as the invisible lines that delineate the various jurisdictions within the country, shaping the landscape of governance, identity, and social interaction. These boundaries are not merely geographical markers; they represent a complex interplay of historical events, cultural identities, and political decisions that have evolved over centuries. From the original thirteen colonies to the fifty states and numerous local jurisdictions, the political boundaries of the United States reflect a rich tapestry of American history and the ongoing struggle for representation and autonomy. The significance of these boundaries extends beyond mere administrative convenience. They influence everything from electoral processes to resource allocation, impacting the lives of millions of citizens. Understanding the origins and implications of these boundaries is crucial for comprehending the broader political landscape of the United States. As we delve into the evolution of provinces and districts, we will uncover how historical events have shaped these lines and how they continue to affect governance and societal dynamics today. Summary The United States is divided into political boundaries such as states, provinces, and districts, each with its own governance and administration. Provinces and districts in the United States have evolved over time, often reflecting changes in population, economy, and political power. Historical boundaries in the United States hold significant cultural and political importance, shaping the identity and governance of different regions. Political boundaries play a crucial role in governance and administration, influencing policies, resource allocation, and representation. Challenges and controversies surrounding political boundaries in the United States can impact society, culture, and political dynamics, requiring careful navigation and resolution. The Evolution of Provinces...
Cultural or Historical Sites of The United States of America: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In The United States of America
The Statue of Liberty, an iconic figure standing majestically on Liberty Island in New York Harbour, is a powerful emblem of freedom and hope for millions around the world. Gifted to the United States by France in 1886, this colossal statue was designed by French sculptor Frédéric Auguste Bartholdi and built by Gustave Eiffel, the same engineer behind the Eiffel Tower. The statue represents Libertas, the Roman goddess of freedom, and is adorned with a torch that signifies enlightenment and a broken chain at her feet, symbolising liberation from oppression. Standing at 151 feet tall, with the pedestal adding another 154 feet, the Statue of Liberty is not only a remarkable feat of engineering but also a profound statement about the values that underpin American society. For many immigrants arriving in America during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the sight of the Statue of Liberty was a momentous occasion. It marked their arrival in a land that promised opportunity and freedom from the hardships they faced in their homelands. The statue became a beacon of hope, welcoming those seeking a better life. The inscription on the pedestal, featuring Emma Lazarus’s poem “The New Colossus,” encapsulates this sentiment beautifully: “Give me your tired, your poor, your huddled masses yearning to breathe free.” This message resonates deeply with the immigrant experience, as it reflects the aspirations of countless individuals who sought refuge and a chance to thrive in a new world. Summary The Statue of Liberty represents freedom and immigration to the United States. The White House is the official residence of the President of the United States. The...
History of The United States of America
The founding of the United States is a complex narrative that intertwines the aspirations for liberty, governance, and identity. The early 17th century saw the establishment of several colonies along the eastern seaboard, primarily by English settlers seeking economic opportunities and religious freedom. The Jamestown settlement in Virginia, founded in 1607, marked the first permanent English colony in North America. Over the next century, more colonies were established, each with its unique character and governance structures. The New England colonies, for instance, were heavily influenced by Puritan ideals, while the Southern colonies developed a plantation economy reliant on enslaved labour. As these colonies flourished, tensions began to mount between the colonists and the British Crown. The imposition of taxes without representation, such as the Stamp Act of 1765 and the Townshend Acts of 1767, ignited widespread dissent. The slogan “No taxation without representation” became a rallying cry for those who felt their rights as Englishmen were being violated. This growing discontent culminated in the First Continental Congress in 1774, where delegates from twelve colonies convened to address their grievances. The seeds of independence were sown during this period, leading to a collective identity that transcended regional differences. Summary The United States was founded in 1776 after declaring independence from Britain, with the signing of the Declaration of Independence. The American Revolution was a war fought between the American colonies and Britain from 1775 to 1783, resulting in the independence of the United States. The Civil War, fought from 1861 to 1865, was a conflict between the Northern states (Union) and the Southern states (Confederacy) over issues of slavery and...
Natural Resources of The United States of America: Where Natural Resources are Located in The United States of America
Natural resources are the foundation upon which the economy of the United States is built. These resources, which include everything from minerals and forests to water and agricultural land, play a crucial role in supporting various industries and sustaining the livelihoods of millions of Americans. The United States is endowed with a vast array of natural resources, making it one of the most resource-rich countries in the world. This abundance has not only facilitated economic growth but has also shaped the nation’s history, culture, and development. The management and utilisation of these resources have evolved over time, reflecting changes in technology, societal needs, and environmental awareness. As the nation grapples with challenges such as climate change, resource depletion, and sustainability, understanding the significance of natural resources becomes increasingly important. This article delves into the rich diversity of natural resources in the United States, exploring their various types, geographic distribution, and their critical role in the economy. Summary The United States is rich in natural resources, including forests, minerals, energy, agriculture, and water. The diversity of natural resources in the US contributes to its economic strength and global influence. Forests and timber resources are abundant in the US, supporting industries such as lumber, paper, and furniture. The US has vast mineral and energy resources, including coal, oil, natural gas, and renewable energy sources. Agricultural resources play a crucial role in the US economy, with the country being a leading producer of crops and livestock. The Rich Diversity of Natural Resources in the United States The United States boasts an impressive variety of natural resources that can be categorised into several...
Climate Zones Of Georgia: Different climate regions Of Georgia
Georgia is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is known for its diverse climate, which is influenced by its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Mexico, and the Appalachian Mountains. The state is divided into six distinct climate regions, each with its own unique characteristics and weather patterns. These climate regions include the Coastal Plain, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Ridge and Valley, and the Appalachian Plateau. Understanding the climate zones of Georgia is essential for residents and visitors alike, as it can help in planning outdoor activities, agriculture, and overall preparedness for the weather. Summary Georgia has a diverse climate with six distinct climate regions: Coastal Plain, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Ridge and Valley, Appalachian Plateau. The Coastal Plain region has a humid subtropical climate with hot summers and mild winters, and is prone to hurricanes and tropical storms. The Piedmont region has a moderate climate with hot summers and cold winters, and experiences occasional snow and ice storms. The Blue Ridge region has a mountainous climate with cool temperatures and high precipitation, making it ideal for outdoor activities and tourism. The Ridge and Valley region has a transitional climate with mild temperatures and moderate precipitation, and is known for its scenic landscapes and agricultural activities. The Appalachian Plateau region has a cooler climate with higher elevations and significant rainfall, and is characterised by its rugged terrain and natural resources. The Coastal Plain Climate Region The Coastal Plain climate region covers the southern and eastern parts of Georgia and is characterized by its flat terrain and proximity to the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf...
Political Boundaries of Georgia: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Political boundaries in Georgia refer to the demarcation lines that separate different administrative regions within the country. These boundaries are crucial for the governance and administration of the country, as they determine the allocation of resources, representation, and the implementation of policies. Georgia, a country located at the crossroads of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, has a complex system of political boundaries that have evolved over centuries. The country is divided into provinces and districts, each with its own unique characteristics and administrative functions. Understanding the historical and current political boundaries in Georgia is essential for comprehending the country’s governance structure and the challenges it faces in maintaining these boundaries. Summary Georgia’s political boundaries have evolved over time, shaping the country’s administrative divisions and governance structure. The historical boundaries of Georgia have been influenced by various empires and kingdoms, leading to a diverse and complex territorial history. Georgia is divided into provinces, each with its own distinct cultural and historical significance, contributing to the country’s rich heritage. Districts in Georgia serve as smaller administrative units within provinces, playing a crucial role in local governance and public service delivery. The comparison of provinces and districts in Georgia highlights the varying levels of autonomy and responsibilities within the country’s political boundaries. Historical Boundaries of Georgia The historical boundaries of Georgia have been shaped by centuries of geopolitical changes and conquests. Throughout its history, Georgia has been influenced by various empires, including the Persian, Ottoman, and Russian empires, which have all left their mark on the country’s territorial boundaries. The modern boundaries of Georgia were largely established during the Soviet era, when...
Terrain and Topography of Georgia: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Georgia, a country located at the crossroads of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, boasts a diverse and stunning terrain that is a paradise for nature lovers and adventure seekers. The topography of Georgia is characterized by its majestic mountains, lush valleys, and vast plains, offering a wide range of landscapes to explore and enjoy. From the snow-capped peaks of the Caucasus Mountains to the fertile valleys of the Alazani and Kura rivers, Georgia’s terrain is as varied as it is breathtaking. The country’s diverse topography has also played a significant role in shaping its unique culture and history, making it a fascinating destination for travellers seeking to immerse themselves in the natural beauty and rich heritage of the region. Summary Georgia’s terrain is diverse and varied, with majestic mountains, lush valleys, and vast plains. The mountains of Georgia offer stunning views and are a popular destination for hikers and nature enthusiasts. The lush valleys of Georgia are home to rich biodiversity and provide fertile land for agriculture. The vast plains of Georgia offer expansive landscapes and are ideal for outdoor activities such as camping and wildlife watching. The diverse landscapes of Georgia provide a range of outdoor activities and adventures for visitors to explore and enjoy. The Majestic Mountains of Georgia One of the most striking features of Georgia’s terrain is its majestic mountains, which dominate much of the country’s landscape. The Caucasus Mountains, which stretch across the northern border of Georgia, are home to some of the highest peaks in Europe, including Mount Shkhara and Mount Kazbek. These towering mountains are a haven for outdoor enthusiasts, offering a...
History of Georgia
Georgia has a rich history of early settlement and Native American influence. Before the arrival of European settlers, the area that is now Georgia was home to several Native American tribes, including the Cherokee, Creek, and Seminole. These tribes had established complex societies with advanced agricultural practices, trade networks, and political structures. The Native Americans had a profound influence on the culture, economy, and landscape of the region. The Native American tribes in Georgia had developed sophisticated agricultural techniques, including the cultivation of corn, beans, and squash. They also engaged in trade with other tribes, exchanging goods such as pottery, shells, and copper. The Native Americans had a deep connection to the land and the natural environment, and their influence can still be seen in the names of many towns and rivers in Georgia. The arrival of European settlers in the 16th century brought significant changes to the region, as the newcomers sought to establish their own settlements and trade networks. However, the legacy of the Native American tribes continues to be an important part of Georgia’s history and culture. The early settlement of Georgia was also shaped by the arrival of Spanish explorers in the 16th century. The Spanish established several missions in the region, seeking to convert the Native American tribes to Christianity and to expand their influence in the New World. These missions had a lasting impact on the culture and religion of the Native American tribes in Georgia. The Spanish also introduced new crops and livestock to the region, including horses, cattle, and citrus fruits. The arrival of European settlers from England and other European...
Population Density of Georgia
Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured per square kilometre or square mile. It is an important demographic indicator that provides insights into the distribution of people within a region. In the context of Georgia, population density plays a crucial role in shaping the social, economic, and environmental landscape of the state. Understanding population density is essential for urban planning, resource allocation, and the provision of public services. As such, it is important to explore the factors affecting population density in Georgia, the differences between urban and rural population density, historical trends, impacts on infrastructure and services, and future projections for managing population density. Summary Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured in square kilometres or square miles. Factors affecting population density in Georgia include natural resources, climate, economic opportunities, and government policies. Urban areas in Georgia tend to have higher population density compared to rural areas due to better job opportunities and access to services. Historical trends show an increase in population density in urban areas and a decrease in rural areas due to migration and urbanisation. High population density in Georgia puts pressure on infrastructure and services, leading to challenges in transportation, housing, and healthcare. Factors Affecting Population Density in Georgia Several factors influence population density in Georgia. One of the primary factors is economic opportunities. Urban areas in Georgia, such as Atlanta, Savannah, and Augusta, tend to have higher population densities due to the concentration of job opportunities, higher wages, and better access to amenities and services. On the other...
Natural Resources of Georgia: Where Natural Resources are located In Georgia
Georgia is a state rich in natural resources, boasting a diverse landscape that includes coastal plains, rolling hills, and mountainous regions. These natural resources have played a significant role in shaping the state’s economy and culture. From the fertile soil of the coastal plains to the mineral deposits in the Appalachian Plateau, Georgia’s natural resources have been a source of wealth and opportunity for its residents. The state’s natural beauty and abundance of resources have also made it a popular destination for outdoor enthusiasts and nature lovers. In this article, we will explore the various natural resources found in Georgia and their importance to the state’s economy and environment. Summary Georgia is rich in natural resources, including a diverse range of geographical features and ecosystems. The Coastal Plains region is characterized by its flat landscape, marshes, and barrier islands, and is home to a variety of wildlife. The Piedmont region is known for its red clay soil and rolling hills, and is an important agricultural area in Georgia. The Blue Ridge region is dominated by the Appalachian Mountains and is a popular destination for outdoor activities such as hiking and camping. The Valley and Ridge region is known for its fertile valleys and ridges, and is an important area for mining and agriculture in Georgia. The Appalachian Plateau region is the smallest region in Georgia and is known for its rugged terrain and rich coal deposits. Georgia’s natural resources are vital for the state’s economy, environment, and overall well-being, and it is important to protect and preserve them for future generations. The Coastal Plains Region The Coastal Plains region...