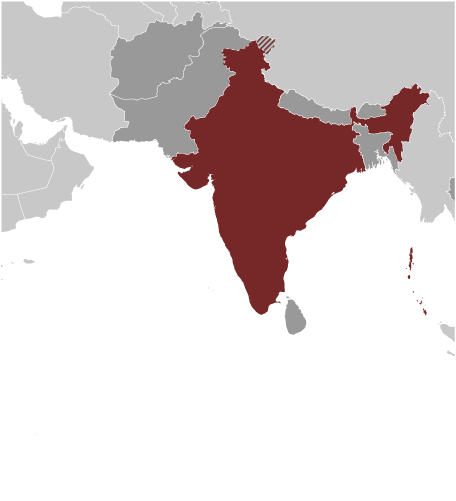
India
(Bharat (Hindi); Republic of India (English))

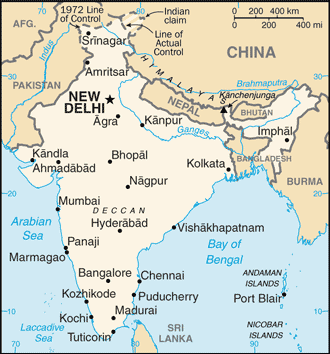





Capital of India: New Delhi
Population (Estimated July 2012): 1,205,073,612
Area: 3,166,414 km2 or 1,222,559 mi2
Currency: Indian Rupee (Re, Plural Rs)
Official Language: Hindi and English
Political Information: Federal Parliamentary Constitutional Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 80.5% of the population are Hindu, 13.4% are Muslim, 2.3% are Christian, 1.9% are Sikh 1.9% have other or unspecified religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Anamudi 2,695m or 8,842ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $1.843 trillion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $4.463 trillion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $3,700 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +5:30
Counties/Provinces/States: 28 states and 7 union territories*; Andaman and Nicobar Islands*, Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chandigarh*, Chhattisgarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli*, Daman and Diu*, Delhi*, Goa, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep*, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Odisha, Puducherry*, Punjab, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, West Bengal
Leaders: President Ram Nath KOVIND (since 25 July 2017); Vice President M. Venkaiah NAIDU (since 11 August 2017) and Prime Minister Narendra MODI (since 26 May 2014).
Additional: Gained independence from the UK on the 15th of August 1947.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
India
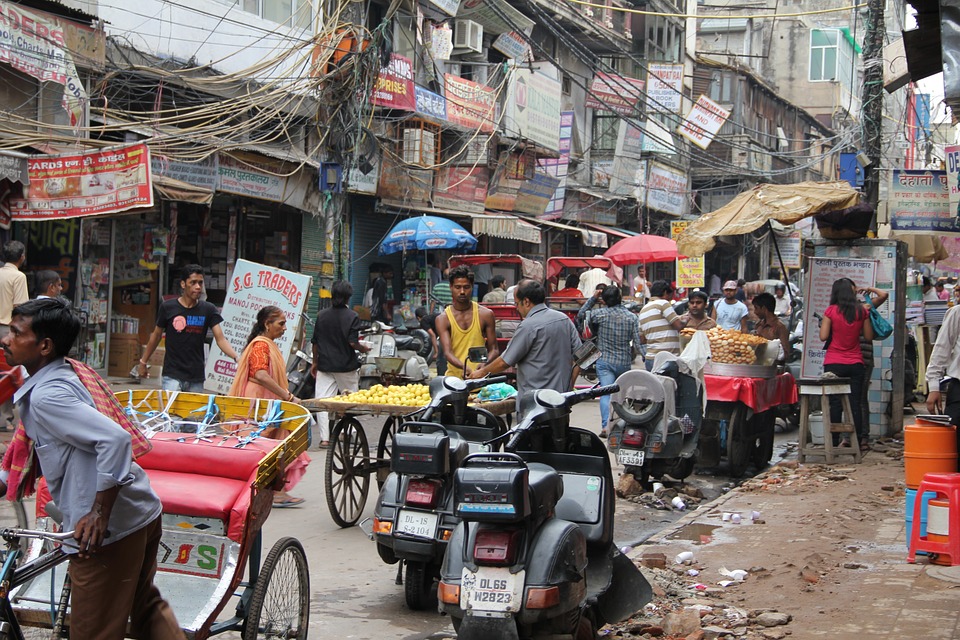
India, officially known as the Republic of India, is a country located in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by land area and the second-most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion people. India is known for its rich history, diverse culture, and vibrant traditions. The country is a melting pot of different religions, languages, and ethnicities, making it a truly unique and fascinating place to explore. From the snow-capped peaks of the Himalayas to the sun-kissed beaches of Goa, India offers a wide range of landscapes and experiences for travellers to enjoy. With its ancient temples, bustling cities, and stunning natural beauty, India has something to offer for everyone.
Culture and Traditions of India
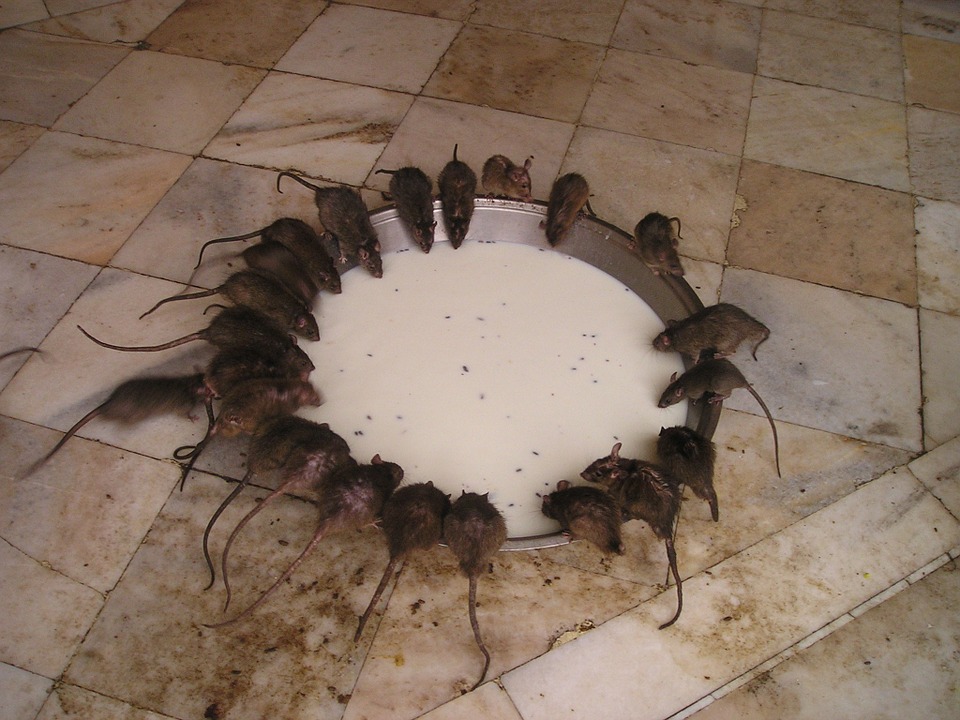
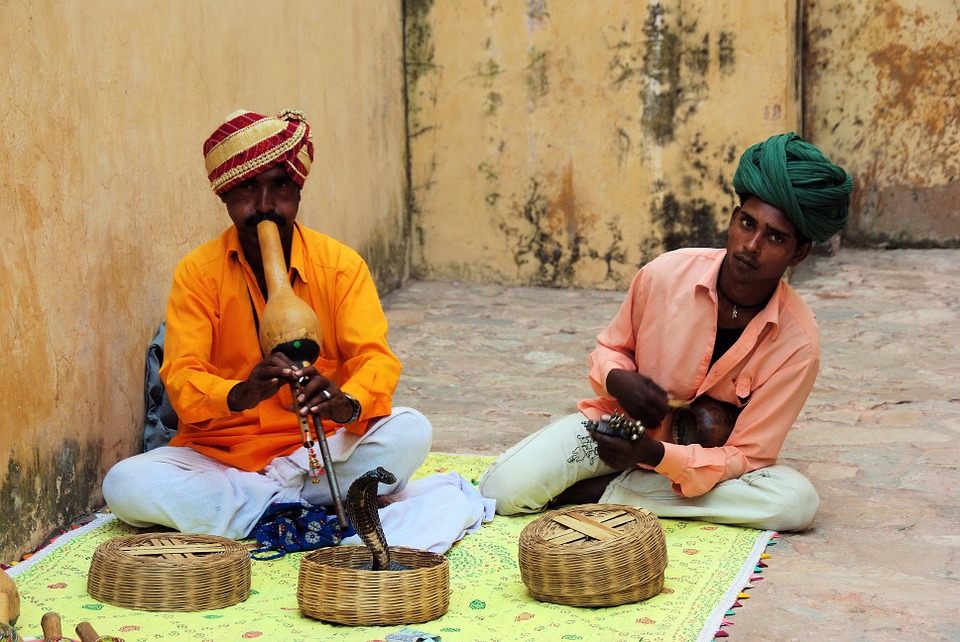
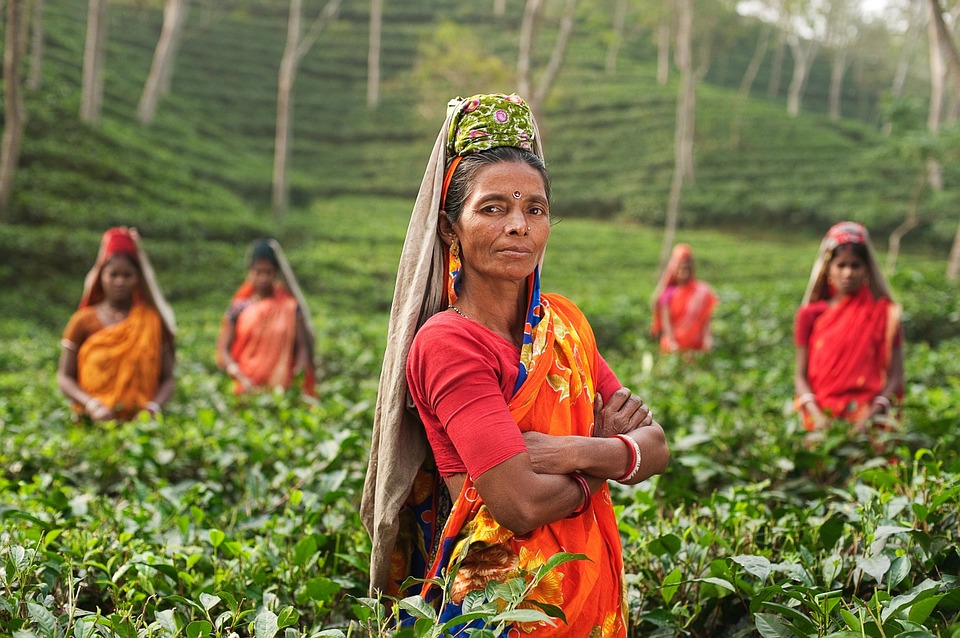
India is a land of diverse cultures and traditions, with each region having its own unique customs and practices. The country is known for its colourful festivals, intricate art forms, and traditional dances. One of the most famous cultural exports from India is Bollywood, the Hindi-language film industry that produces a large number of films each year. Indian cuisine is also a significant part of the country’s culture, with each region having its own distinct flavours and cooking styles. The traditional clothing of India, such as the saree for women and the dhoti for men, reflects the rich cultural heritage of the country. The people of India are known for their hospitality and warmth, making it a popular destination for tourists looking to experience the vibrant culture and traditions of the country.
Cuisine and Food of India
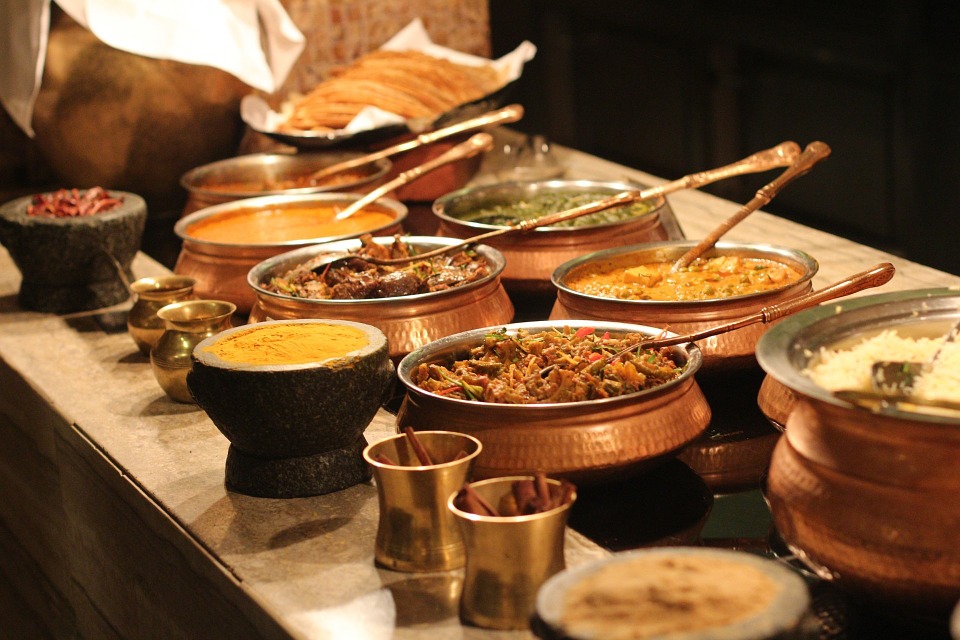
Indian cuisine is renowned for its bold flavours, aromatic spices, and diverse range of dishes. Each region of India has its own unique culinary traditions, influenced by factors such as climate, geography, and cultural practices. Some of the most popular dishes in Indian cuisine include biryani, a fragrant rice dish cooked with meat or vegetables; butter chicken, a creamy and rich chicken curry; and dosa, a crispy pancake made from fermented rice batter. Vegetarianism is also widely practiced in India, leading to a wide variety of delicious vegetarian dishes such as paneer tikka, a marinated and grilled cheese dish, and chana masala, a spicy chickpea curry. Indian street food is also a major part of the country’s culinary scene, with popular snacks such as samosas, pakoras, and chaat being enjoyed by locals and tourists alike.
Famous Landmarks and Tourist Attractions in India
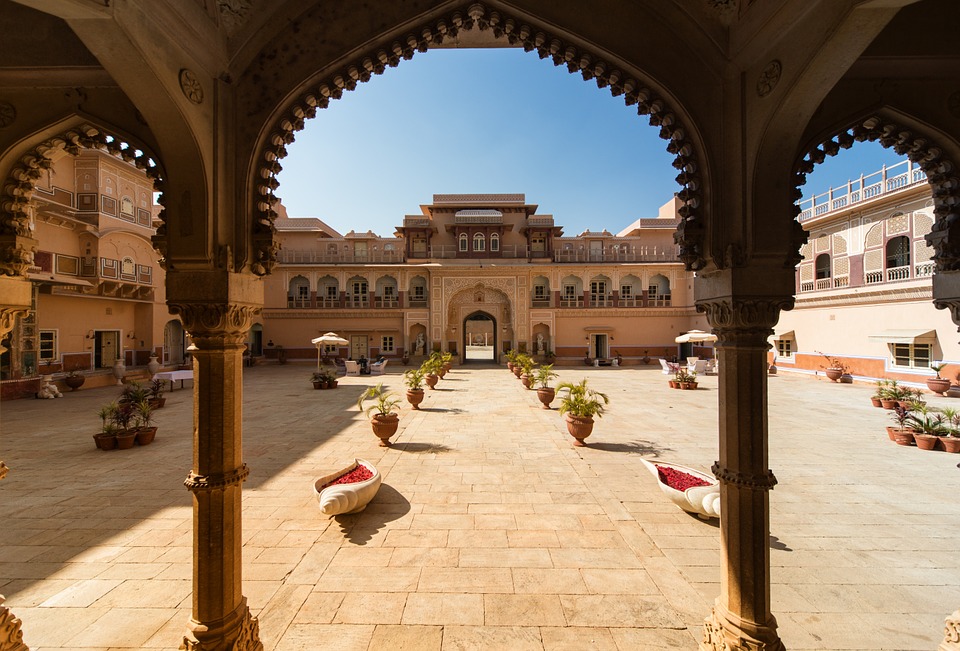
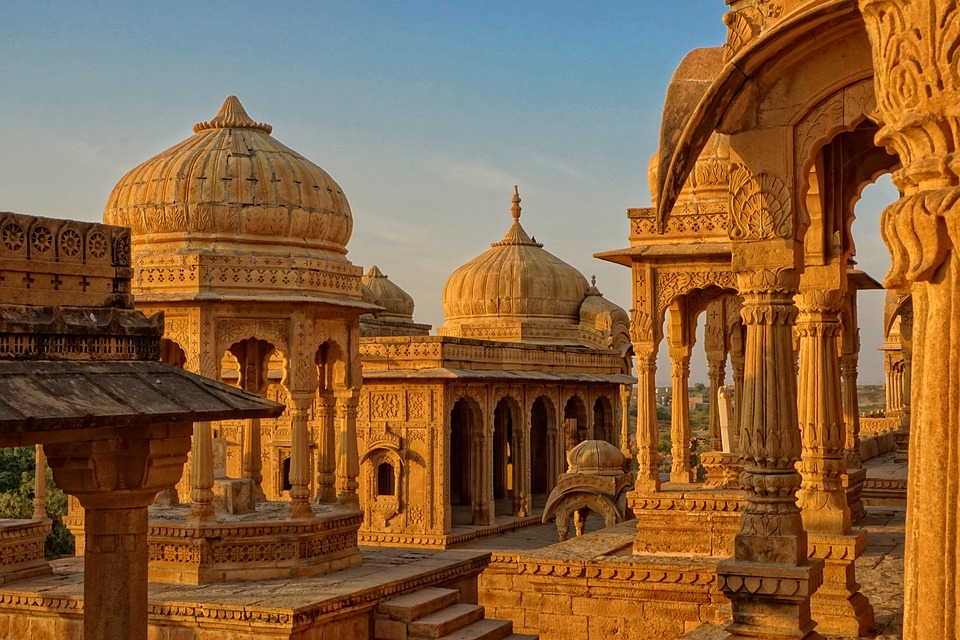
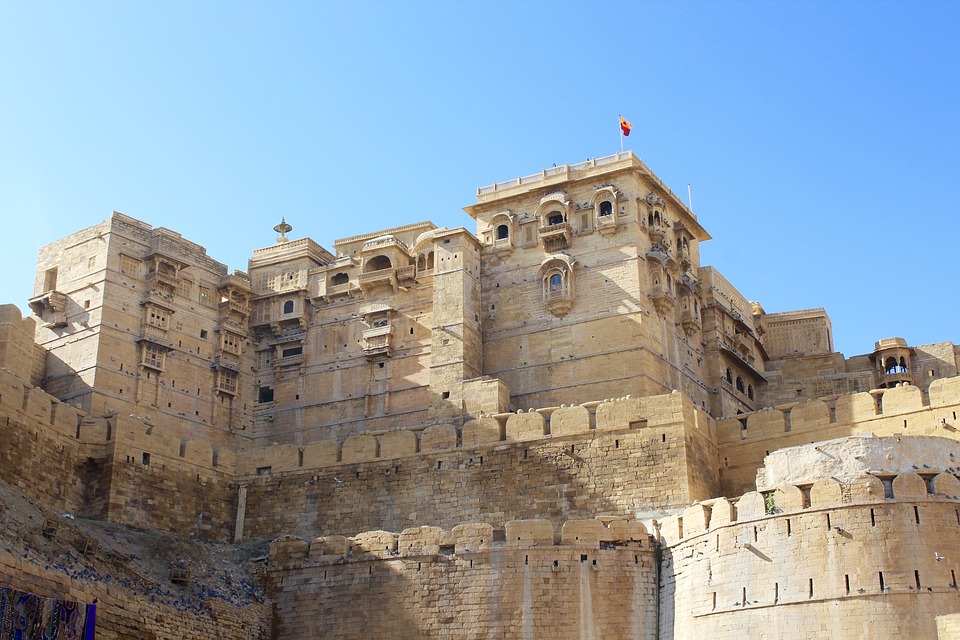
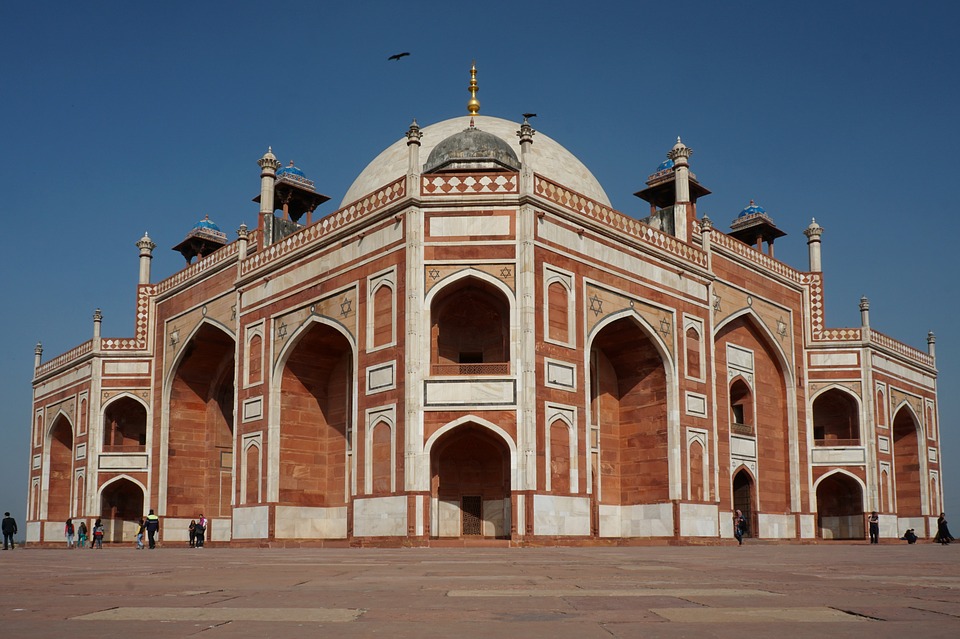
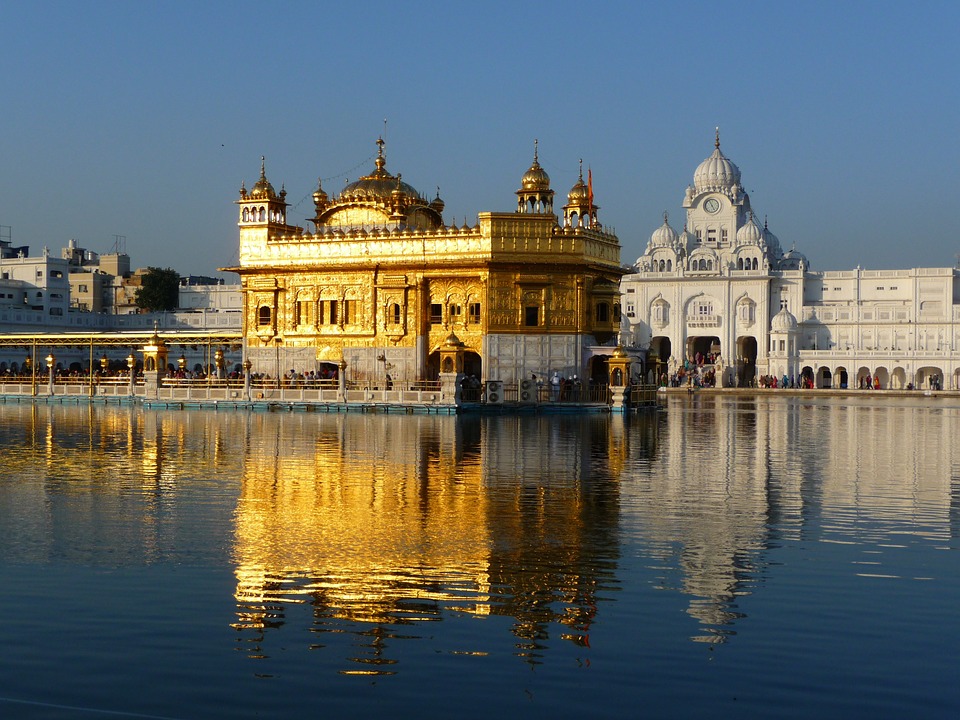
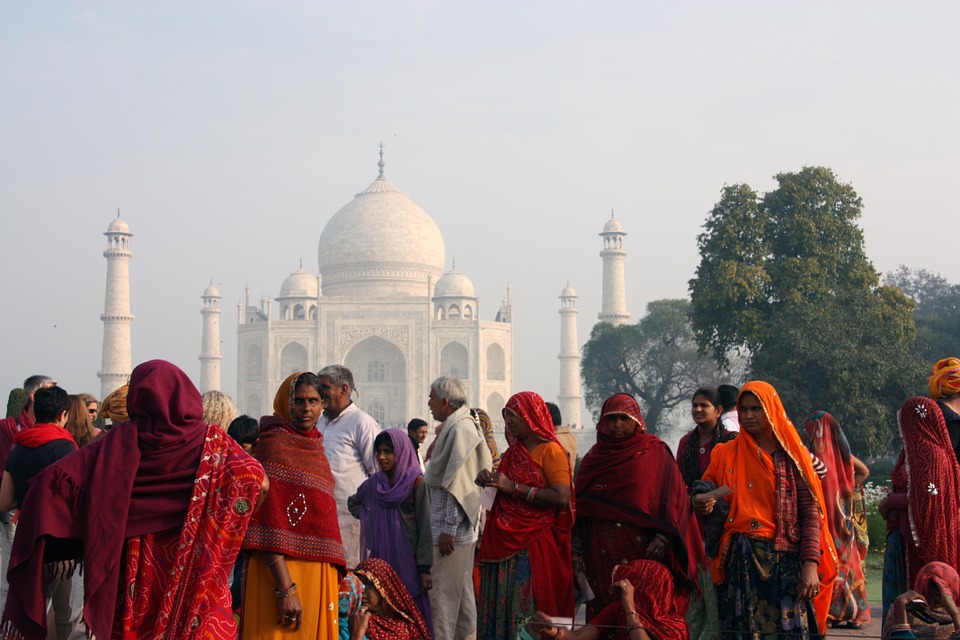
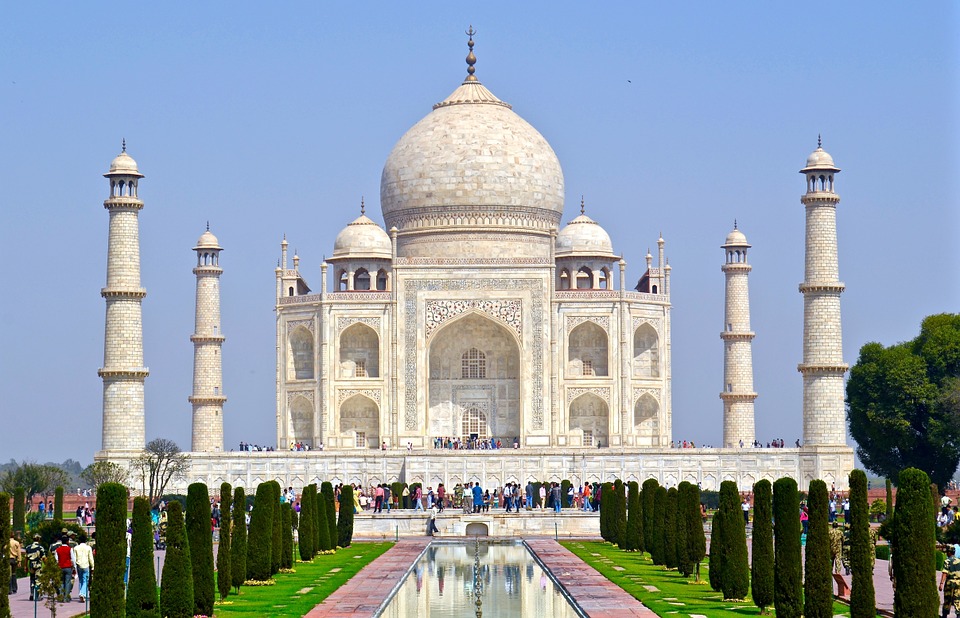
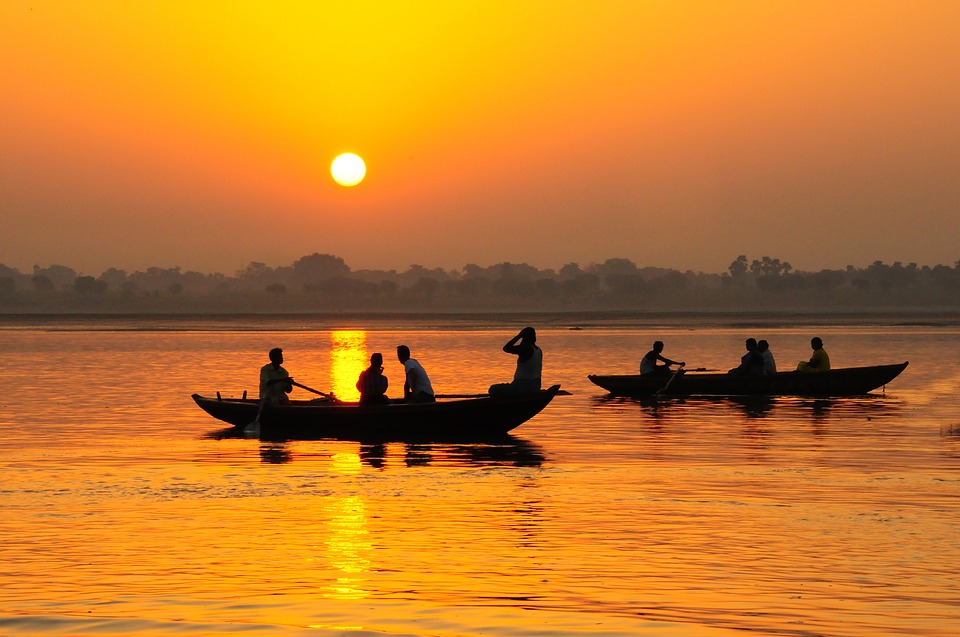
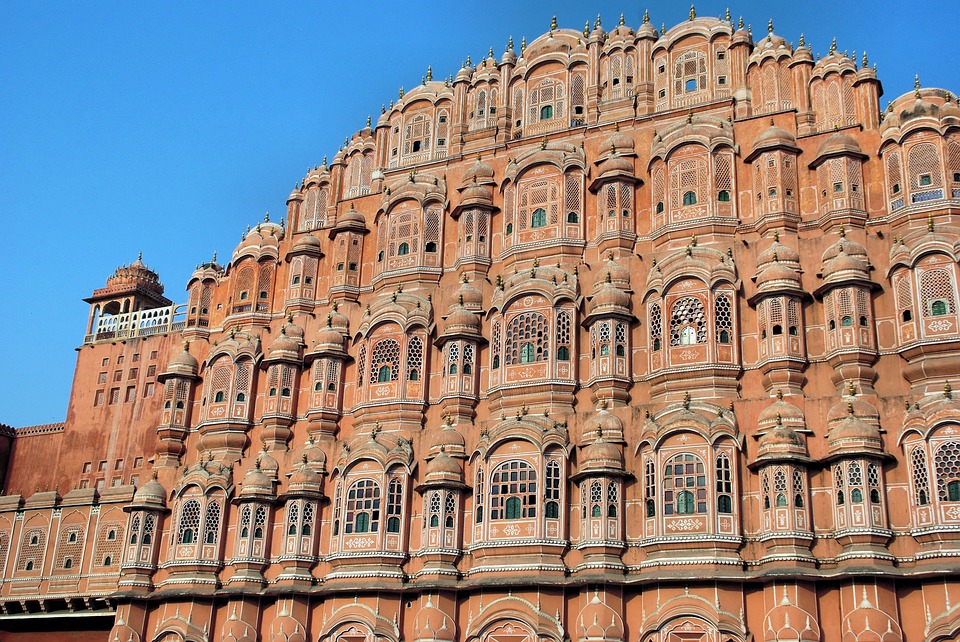
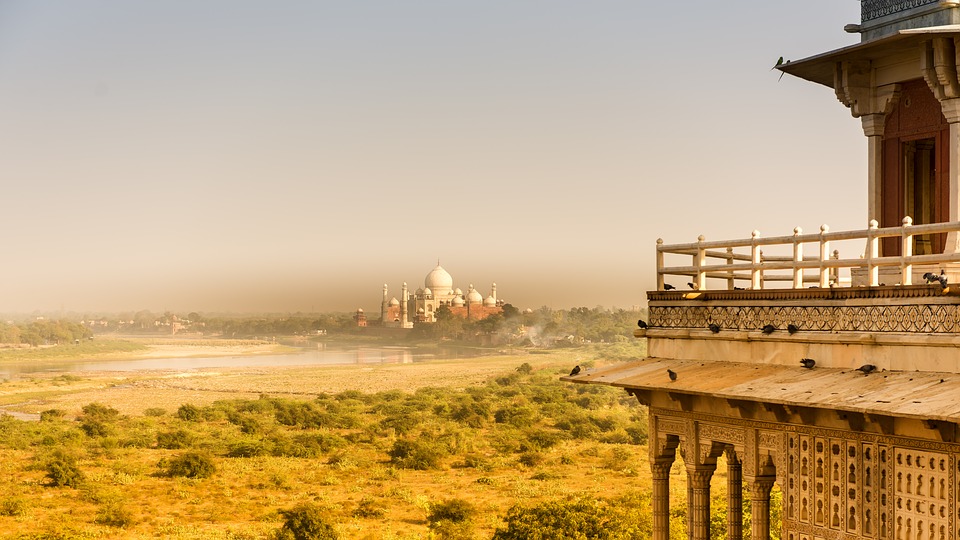
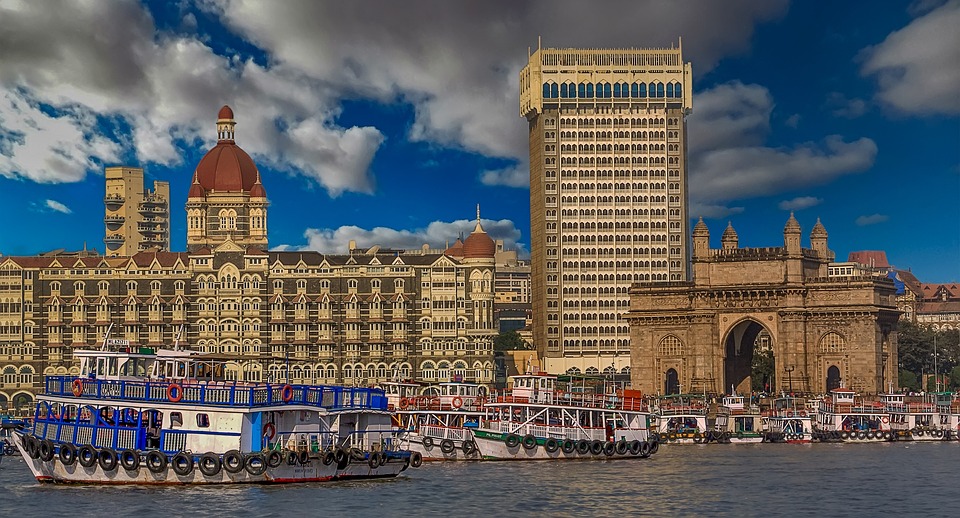
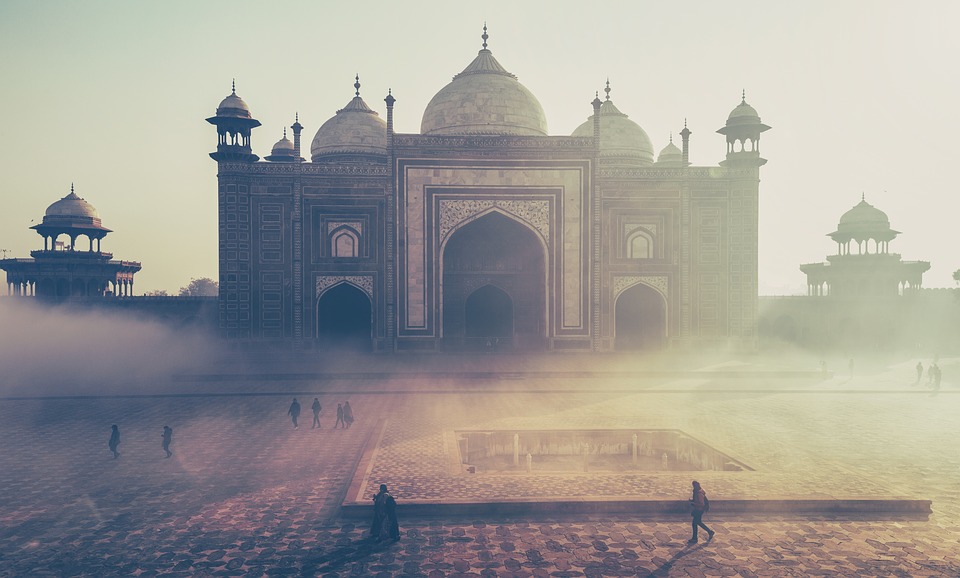
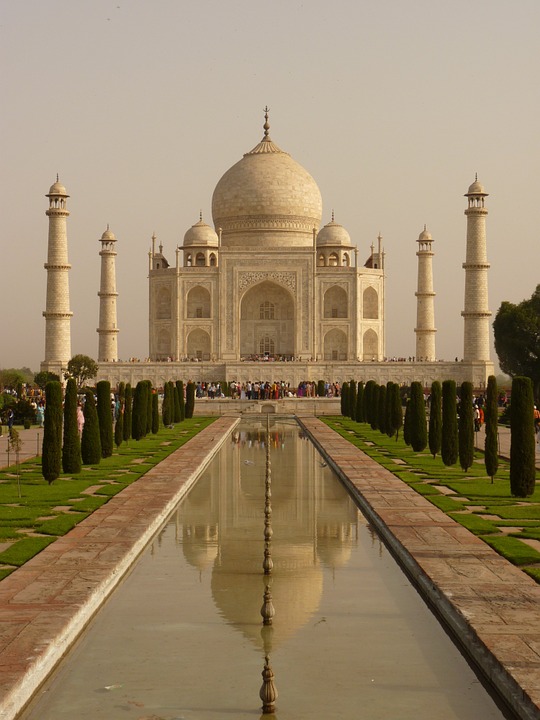
India is home to a wealth of famous landmarks and tourist attractions that draw visitors from all over the world. The Taj Mahal, located in Agra, is one of the most iconic symbols of India and is considered one of the New Seven Wonders of the World. This stunning white marble mausoleum was built by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his wife Mumtaz Mahal and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Another must-visit destination in India is the ancient city of Varanasi, situated on the banks of the Ganges River. Varanasi is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world and is considered the spiritual capital of India. The city is famous for its ghats, where pilgrims come to bathe in the sacred waters of the Ganges and perform religious rituals. Other popular tourist attractions in India include the Red Fort in Delhi, the Amber Fort in Jaipur, and the backwaters of Kerala.
Economy and Business in India
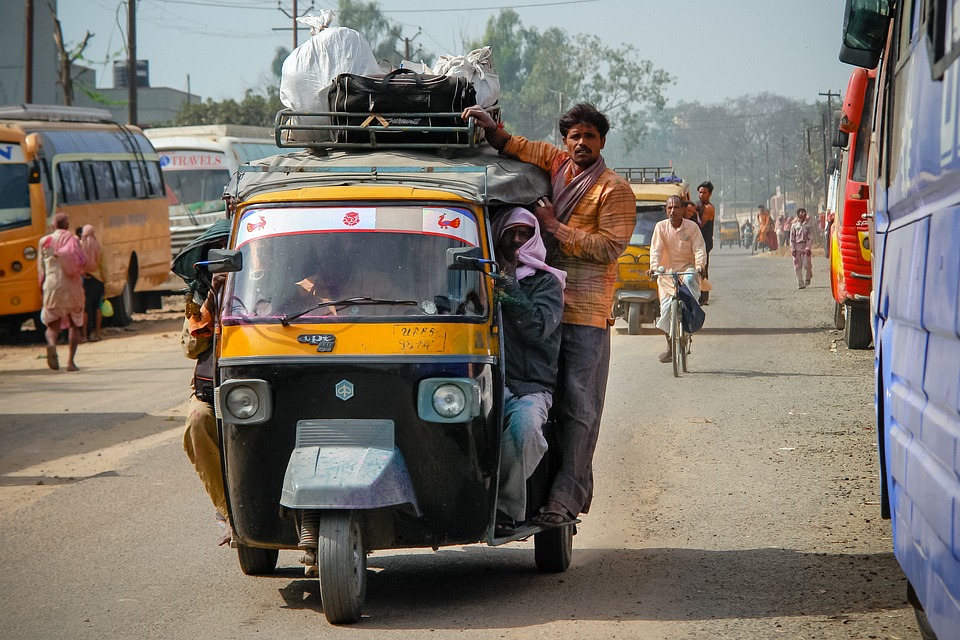
India has one of the fastest-growing major economies in the world and is considered a newly industrialised country. The country has a diverse economy that encompasses agriculture, manufacturing, services, and technology sectors. India is known for its information technology industry, with cities such as Bangalore and Hyderabad being major hubs for IT companies and startups. The country also has a thriving film industry, with Bollywood being one of the largest centres of film production in the world. In recent years, India has seen significant growth in sectors such as e-commerce, renewable energy, and pharmaceuticals. The government has also implemented various economic reforms to attract foreign investment and promote business growth in the country.
Wildlife and Natural Beauty of India
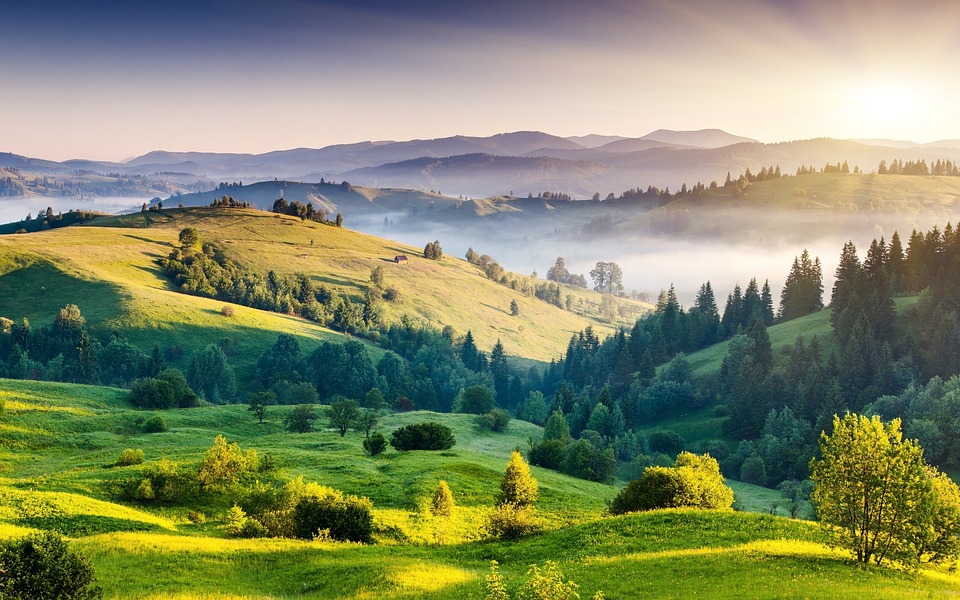
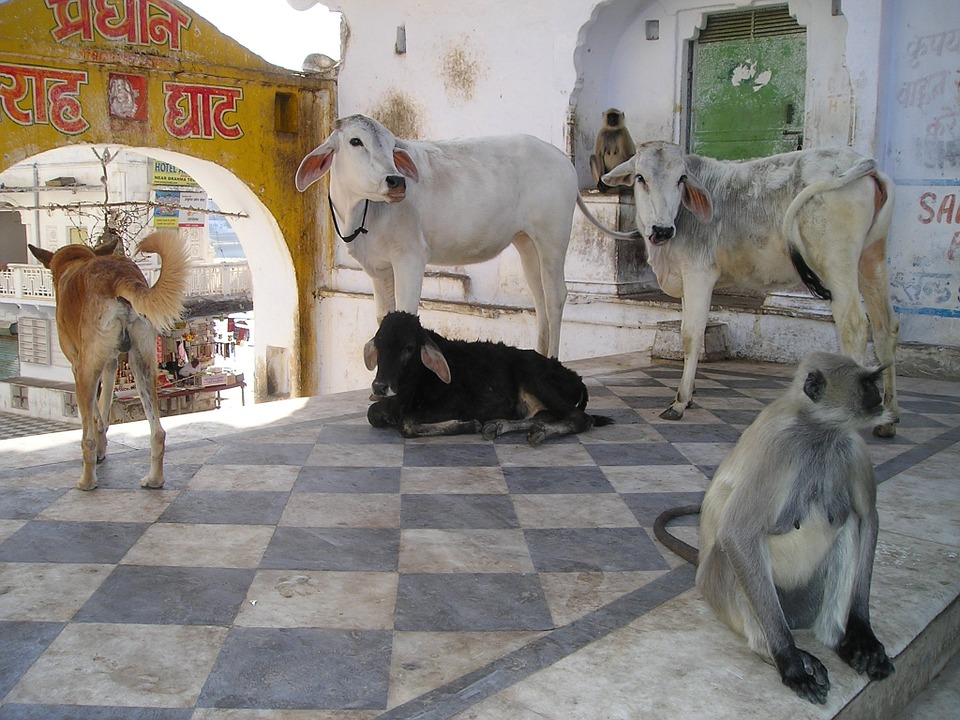
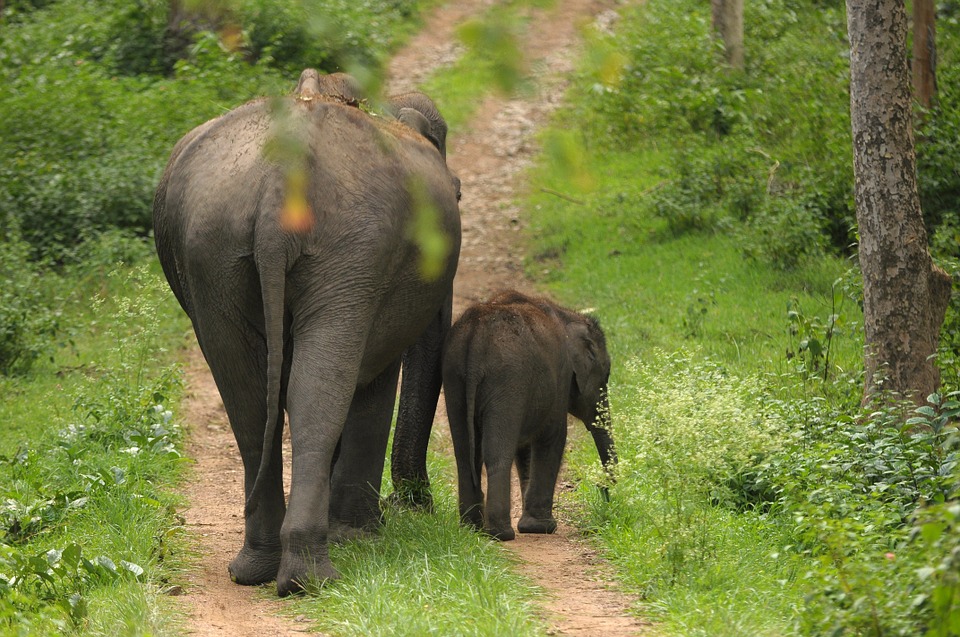
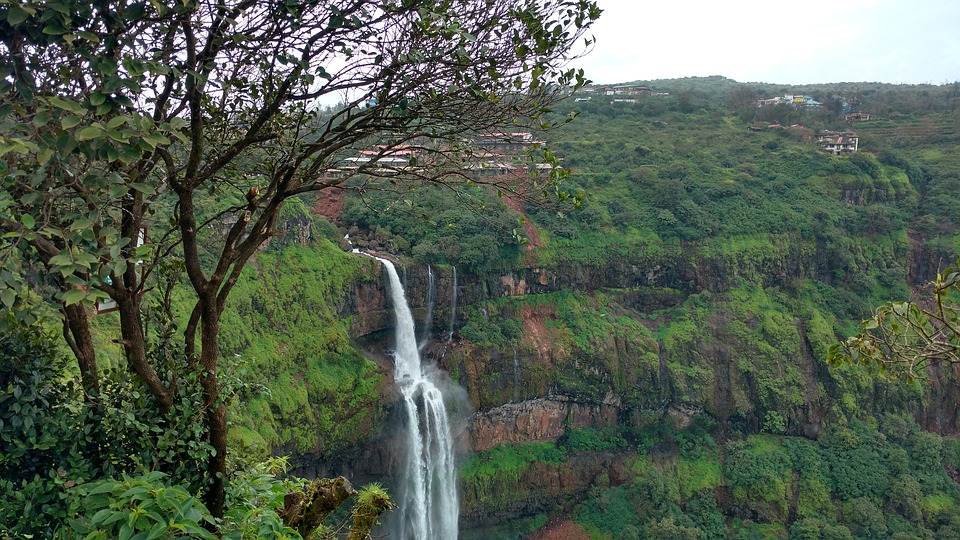
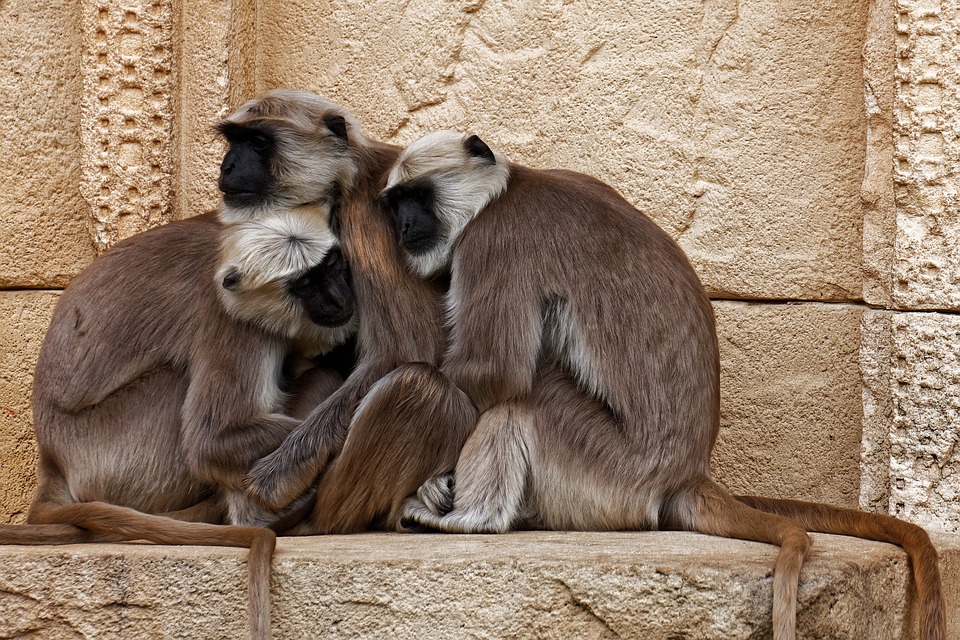
India is home to a rich variety of wildlife and natural beauty, with diverse ecosystems ranging from lush forests to arid deserts. The country has several national parks and wildlife sanctuaries that are home to endangered species such as tigers, elephants, rhinoceroses, and lions. One of the most famous national parks in India is Ranthambore National Park, located in Rajasthan, which is known for its population of Bengal tigers. The Western Ghats mountain range in southern India is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is home to an incredible array of flora and fauna. The backwaters of Kerala offer a tranquil and picturesque landscape that attracts visitors looking to experience the natural beauty of India. From the snow leopards of the Himalayas to the tropical beaches of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India’s natural beauty is truly awe-inspiring.
Challenges and Opportunities in Modern India
While India has made significant progress in various areas such as technology, economy, and infrastructure, the country still faces several challenges. One of the major issues facing India is poverty, with a large percentage of the population living below the poverty line. Access to clean water, sanitation, healthcare, and education remains a challenge for many people in India. The country also grapples with environmental issues such as air pollution, deforestation, and water scarcity. However, India also presents numerous opportunities for growth and development. The government has been investing in infrastructure projects such as highways, railways, and smart cities to improve connectivity and urban development. The rise of technology startups and innovation hubs has positioned India as a global leader in the digital economy. With its young and dynamic workforce, India has the potential to become a major player in the global economy in the coming years.
In conclusion, India is a country that offers a rich tapestry of culture, traditions, cuisine, natural beauty, and economic opportunities. With its vibrant festivals, ancient landmarks, diverse wildlife, and booming industries, India continues to captivate visitors from around the world. While facing challenges such as poverty and environmental issues, India also presents numerous opportunities for growth and development. As a land of contrasts and diversity, India remains an enigmatic destination that leaves a lasting impression on all who visit.
FAQs
What is the population of India?
India is the second most populous country in the world, with a population of over 1.3 billion people.
What is the capital of India?
The capital of India is New Delhi.
What are the major languages spoken in India?
Hindi is the most widely spoken language in India, followed by Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, Tamil, and Urdu.
What are the major religions in India?
The major religions in India are Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, and Jainism.
What is the currency of India?
The currency of India is the Indian Rupee (INR).
What are the major industries in India?
India’s major industries include textiles, telecommunications, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and agriculture.
What are the popular tourist attractions in India?
Popular tourist attractions in India include the Taj Mahal, Jaipur’s Amber Fort, Kerala’s backwaters, the beaches of Goa, and the temples of Varanasi.
Cultural or Historical Sites of India: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In India
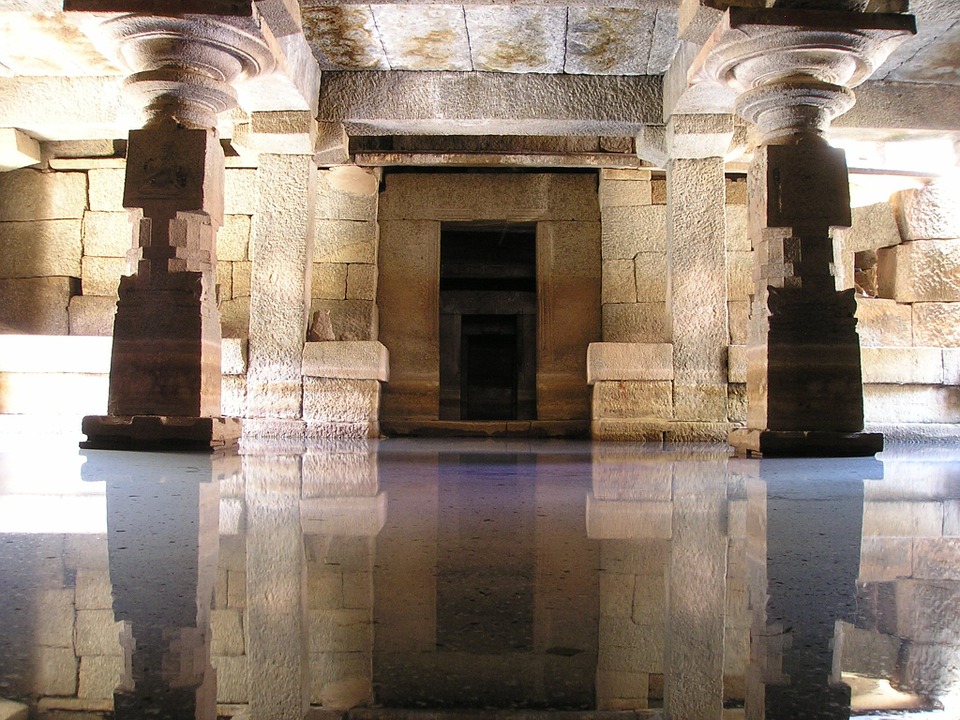
Cultural or Historical Sites of India: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In India The Taj Mahal, located in Agra, India, is one of the most iconic and recognisable landmarks in the world. Built by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his beloved wife Mumtaz Mahal, the Taj Mahal is a symbol of eternal love and beauty. The stunning white marble mausoleum is renowned for its intricate architectural design, including its symmetrical layout, intricate carvings, and beautiful gardens. The Taj Mahal is a masterpiece of Mughal architecture and is considered one of the most beautiful buildings in the world.Visitors to the Taj Mahal are often struck by its sheer grandeur and beauty. The main mausoleum is flanked by four minarets, each standing at over 40 meters tall, and the entire complex is set amidst lush gardens and reflecting pools. The interior of the Taj Mahal is equally impressive, with intricate marble inlay work and delicate carvings adorning the walls and ceilings. The central dome, which reaches a height of over 70 meters, is a marvel of engineering and design. As the sun sets, the white marble of the Taj Mahal takes on a warm, golden hue, adding to its ethereal beauty. The Taj Mahal is not only a testament to the enduring power of love but also a stunning example of architectural excellence. Summary The Taj Mahal is a symbol of undying love and exquisite beauty, built by Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his beloved wife Mumtaz Mahal. The Red Fort in Delhi is a stunning example of Mughal architecture, with its intricate design and...
Natural Resources of India: Where Natural Resources are Located in India
Natural Resources of India: Where Natural Resources are Located in India India is a country rich in natural resources, which play a crucial role in its economic development and sustenance of its vast population. These resources include minerals, forests, water, energy, and agricultural land. The diverse geographical features of India have endowed it with a wide variety of natural resources, making it one of the most resource-rich countries in the world. The sustainable management of these resources is essential for the country’s future growth and development.The natural resources in India are distributed unevenly across the country, with some regions being more abundant in certain resources than others. The exploitation and management of these resources have a significant impact on the environment and the livelihoods of the people. Therefore, it is crucial to strike a balance between economic development and environmental conservation to ensure the sustainable use of these resources for future generations. Summary India is rich in natural resources, including minerals, agriculture, forests, water, and energy. The mineral resources in India include coal, iron ore, and bauxite, making it one of the leading producers of these minerals globally. Agriculture is a significant part of India’s economy, with a wide variety of crops grown across the country, including rice, wheat, and sugarcane. India’s forest resources are diverse and provide habitat for a wide range of flora and fauna, as well as valuable timber and non-timber products. Water resources in India are crucial for agriculture, industry, and domestic use, but they are under increasing pressure due to population growth and climate change. Mineral Resources in India India is rich in mineral...
Political Boundaries of India: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Political Boundaries of India: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries. India, the seventh-largest country in the world, is known for its diverse culture, rich history, and complex political landscape. The political boundaries of India are a result of centuries of historical, cultural, and administrative developments. The country is bordered by Pakistan to the northwest, China and Nepal to the north, Bhutan to the northeast, and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. To the south, it is bounded by the Indian Ocean. India’s political boundaries are not only defined by its international borders but also by its administrative divisions, provinces, and districts. These boundaries play a crucial role in shaping the governance, economy, and society of the country.The political boundaries of India are a reflection of its diverse cultural and linguistic landscape. With over 1.3 billion people belonging to various ethnic groups and speaking different languages, India’s political boundaries have been shaped to accommodate this diversity. The country is divided into 28 states and 8 Union territories, each with its own unique identity and administrative structure. The federal structure of India’s political boundaries allows for a degree of autonomy and self-governance at the state and local levels, while also maintaining a strong central government. This complex web of political boundaries has been instrumental in managing the diverse needs and aspirations of India’s population. Summary India’s political boundaries are complex and diverse, reflecting the country’s rich history and cultural diversity. Provinces in India serve as administrative divisions, each with its own government and legislative assembly. Districts play a crucial role in local governance and jurisdiction, overseeing various aspects of public administration and...
Climate Zones of India: Different climate regions Of India
Climate Zones of India: Different climate regions Of India India is a vast and diverse country with a wide range of climate zones. The country’s climate is influenced by a variety of factors, including its geographical location, topography, and the monsoon winds. As a result, India is home to several distinct climate zones, each with its own unique characteristics and weather patterns. From the tropical climate of the southern coast to the alpine climate of the Himalayas, India’s diverse climate zones make it a fascinating and varied country to explore.The different climate zones in India have a significant impact on the country’s flora, fauna, and agricultural practices. Understanding these climate zones is essential for anyone looking to visit or do business in India, as they can greatly affect travel plans, crop cultivation, and even construction practices. In this article, we will explore the various climate zones in India, from the tropical regions in the south to the alpine regions in the north, and examine the unique features and characteristics of each zone. Summary India has a diverse range of climate zones, influenced by its geography and topography. The tropical climate zones in India are characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall, with distinct wet and dry seasons. Subtropical climate zones in India experience hot summers and cool winters, with moderate to high rainfall throughout the year. The temperate climate zones in India have mild summers and cold winters, with moderate to high rainfall and snowfall in some areas. Alpine climate zones in India are found in the mountainous regions and have cold temperatures, heavy snowfall, and short summers. Tropical...
Terrain and Topography of India: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Terrain and Topography of India: mountains, valleys, and plains. India is a land of diverse and varied terrain, with its topography ranging from majestic mountain ranges to vast plains, coastal regions, and plateaus. The country’s terrain has played a significant role in shaping its history, culture, and economy. From the towering peaks of the Himalayas in the north to the fertile plains of the Indo-Gangetic region, India’s landscape is as diverse as its people. The country’s topography has also influenced its climate, biodiversity, and agricultural practices, making it a fascinating subject for study and exploration.The diverse terrain of India has also contributed to the country’s rich biodiversity, with a wide range of flora and fauna thriving in different ecosystems. The varied topography has also led to the development of unique cultures and traditions in different regions of the country. From the snow-capped peaks of the Himalayas to the lush green valleys of the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers, India’s terrain is a source of inspiration and wonder. In this article, we will explore the different aspects of India’s topography, from its majestic mountain ranges to its fertile plains and coastal regions, and delve into the significance of each in shaping the country’s landscape and culture. Summary India’s terrain and topography are incredibly diverse, ranging from majestic mountain ranges to vast plains and lush valleys. The Great Himalayas, India’s highest and most majestic mountain range, are home to some of the world’s highest peaks, including Mount Everest. The Indo-Gangetic Plain is India’s most fertile region, known for its rich agricultural output and as the heartland of Indian civilization. The Western and...
History of India
History of India The Indus Valley Civilization, also known as the Harappan Civilization, was one of the world’s earliest urban societies. It flourished in the Indus River basin in what is now Pakistan and northwest India from about 2500 to 1700 BCE. The civilization was characterized by its advanced urban planning, sophisticated drainage systems, and impressive brick-built cities. The people of the Indus Valley were skilled in trade, with evidence of their goods reaching as far as Mesopotamia. They also had a system of writing, although it has not yet been fully deciphered.The cities of the Indus Valley Civilization were well-planned, with streets laid out in a grid pattern and buildings constructed from standardized bricks. The largest of these cities, Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa, were both home to tens of thousands of people. The people of the Indus Valley engaged in agriculture, with evidence of wheat, barley, and domesticated animals such as cattle and sheep. They also had a sophisticated system of weights and measures, indicating a high level of economic organization. Despite these advancements, the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization remains a mystery, with theories ranging from environmental factors such as climate change to invasion by outside forces. Nonetheless, the legacy of the Indus Valley Civilization lives on in India’s rich cultural heritage and its contributions to early human civilization. Summary The Indus Valley Civilization was one of the world’s earliest urban societies, with advanced infrastructure and trade networks. The Maurya Empire, under the rule of Ashoka, saw the spread of Buddhism and the development of art, architecture, and literature. The Mughal Empire brought about a flourishing of...
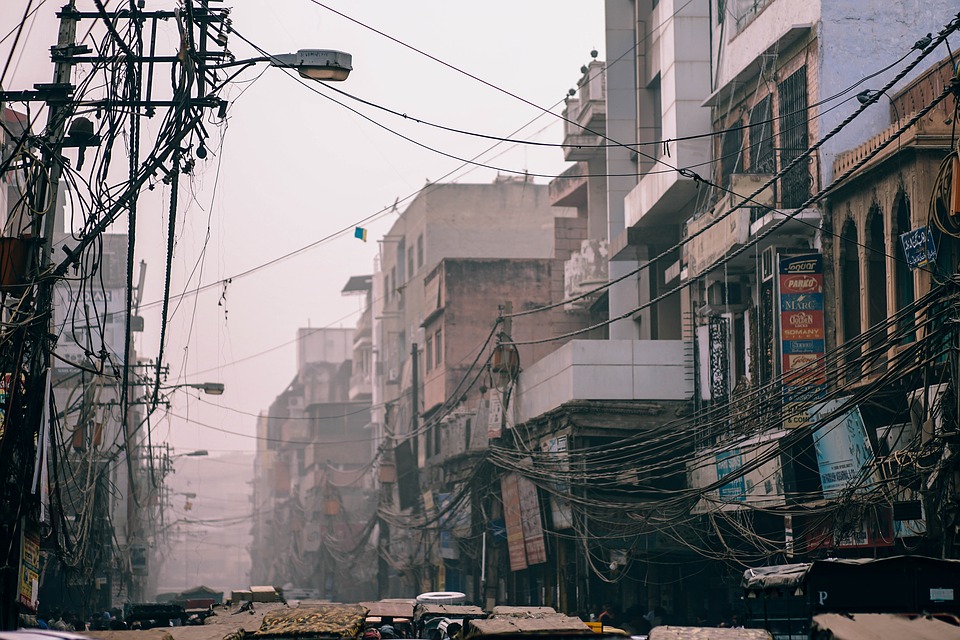
Population Density of India
Population Density of India India is the second most populous country in the world, with a population of over 1.3 billion people. The population density of India is the highest among the major countries of the world, with an average of 450 people per square kilometre. The population density varies greatly across different regions of the country, with some areas being densely populated while others are sparsely populated. The high population density in India has significant implications for the country’s infrastructure, resources, and environment. Understanding the factors affecting population density, the differences between urban and rural population density, regional variations, and the impact on infrastructure and resources is crucial for policymakers and planners to manage and sustain the growing population in India effectively. Summary India is the second most populous country in the world, with a high population density of over 450 people per square kilometre. Factors affecting population density in India include fertility rates, migration, urbanisation, and government policies. Urban population density in India is much higher than rural population density, leading to overcrowding and strain on resources in cities. Regional variations in population density exist, with the northern and western regions being more densely populated than the central and eastern regions. High population density in India puts pressure on infrastructure, water resources, and healthcare, leading to challenges for sustainable development. Factors Affecting Population Density in India Several factors contribute to the high population density in India. Firstly, the fertility rate in India has been historically high, although it has been declining in recent years. The cultural and social norms, lack of access to family planning services, and...
Exploring the Vibrant Culture and Rich Heritage of Incredible India
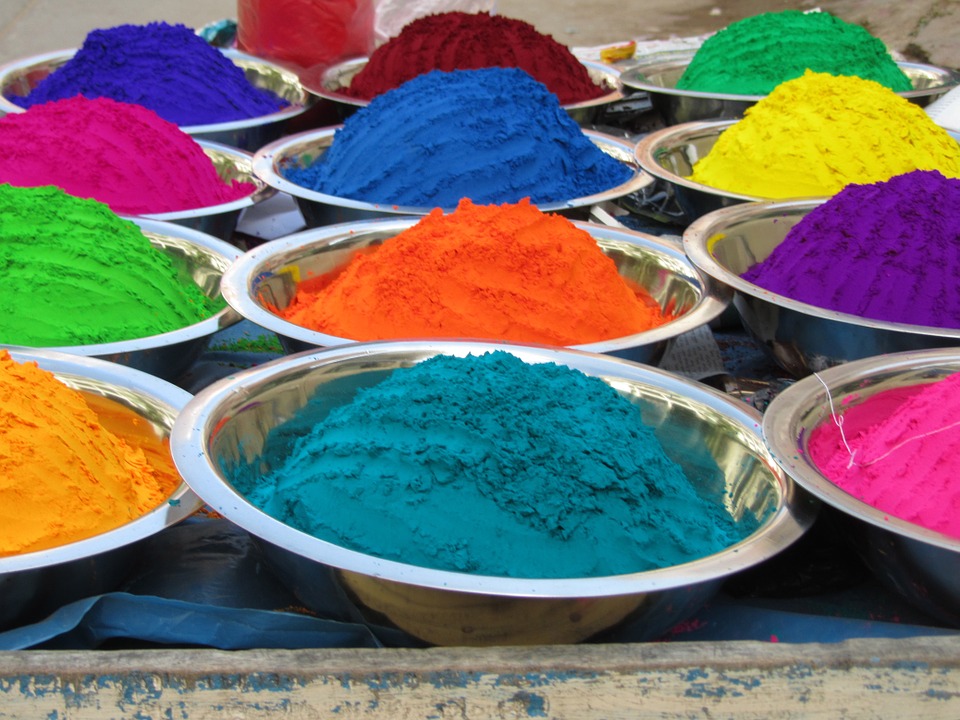
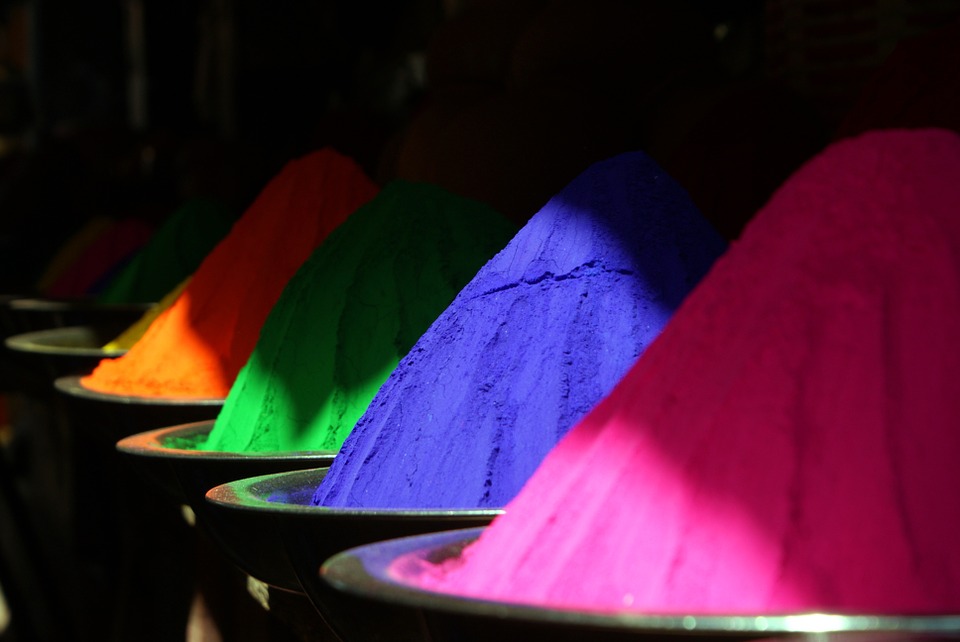
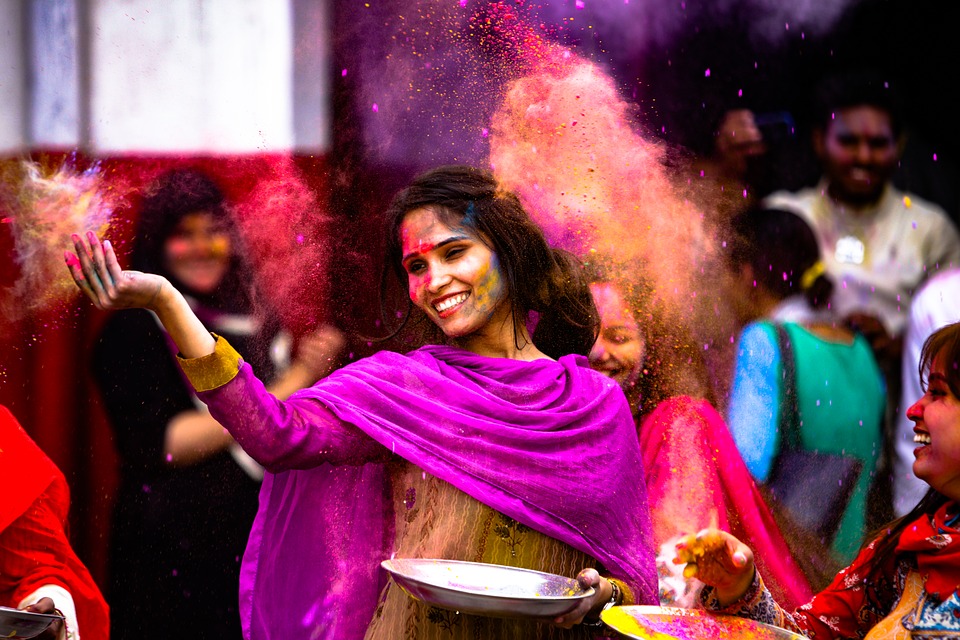
India is a land of diversity and heritage, with a rich tapestry of culture and traditions that have been passed down through generations. From its vibrant festivals to its ancient temples, from its culinary delights to its spiritual practices, India offers a treasure trove of experiences for those who seek to explore its cultural heritage. In this article, we will delve into the colourful festivals, artistic treasures, culinary delights, spiritual legacy, architectural marvels, musical heritage, traditional crafts, natural wonders, and modern innovations that make India truly incredible. Summary India is a land of diversity and heritage, with a rich cultural history. The colourful festivals of India celebrate life and spirituality and are a sight to behold. India’s artistic treasures range from ancient temples to modern museums, showcasing the country’s creativity and innovation. The culinary delights of India offer a journey through spices and flavours, with something to suit every palate. India’s spiritual legacy is evident in practices such as yoga and meditation, which have gained popularity worldwide. The Colourful Festivals of India India is known for its vibrant and lively festivals that are celebrated with great enthusiasm and fervour. One of the most famous festivals is Holi, also known as the Festival of Colors. During Holi, people come together to throw coloured powders and water at each other, symbolizing the victory of good over evil and the arrival of spring. Diwali, or the Festival of Lights, is another significant festival in India. It celebrates the victory of light over darkness and good over evil. During Diwali, people light oil lamps and candles, decorate their homes with colourful rangoli...