Kazakhstan
(Kyrgyz Respublikasy (Kyrgyz); Respublika Kirgizstan (Russian) (Kyrgyz Republic))



Capital: Bishkek
Population (Estimated July 2012): 5,496,737
Area: 199,945 km2 or 77,199 mi2
Currency: Kyrgyzstan Som (KGS)
Official Language: Kyrgyz; Russian
Political Information: Parliamentary Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 75% of the population are Muslim, 20% are Russian Orthodox and 5% have other religious beliefs).
Highest Mountain: Jengish Chokusu (Victory Peak) at 7,439m or 24,406ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $180.1 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $216.4 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $13,000 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +6:00
Wildlife:
Counties/Provinces/States: 7 provinces (oblastlar, singular – oblasty) and 1 city* (shaar); Batken Oblasty, Bishkek Shaary*, Chuy Oblasty (Bishkek), Jalal-Abad Oblasty, Naryn Oblasty, Osh Oblasty, Talas Oblasty, Ysyk-Kol Oblasty (Karakol)
Leaders: President Almazbek Atambayev, with Prime Minister Omurbek Babanov.
Additional: Gained independence from the Soviet Union on the 31st of August 1991.
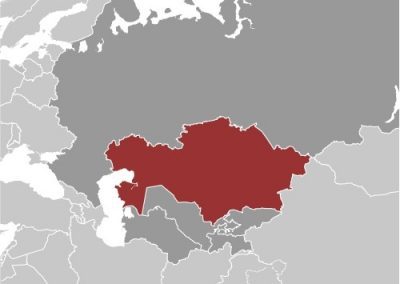
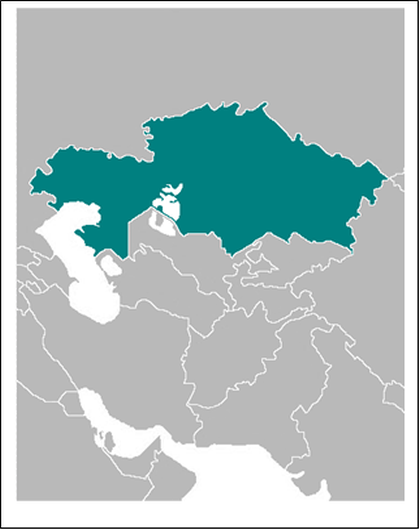
Kazakhstan
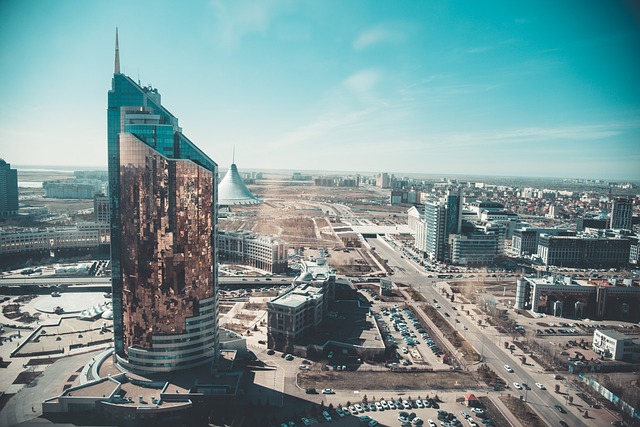
Kazakhstan, the world’s largest landlocked country, is located in Central Asia and Eastern Europe. It shares borders with Russia, China, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan, as well as the Caspian Sea to the west. The country is known for its diverse landscapes, ranging from the Caspian lowlands to the Altai Mountains and the vast steppes. With a population of over 18 million people, Kazakhstan is a multi-ethnic and multi-cultural society, with Kazakhs being the largest ethnic group, followed by Russians, Uzbeks, Ukrainians, and others. The capital city, Nur-Sultan, was formerly known as Astana, and is a modern metropolis with futuristic architecture and a thriving cultural scene.
Kazakhstan gained independence from the Soviet Union in 1991 and has since made significant strides in developing its economy and infrastructure. The country is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals, which have contributed to its economic growth. Kazakhstan is also a member of the Eurasian Economic Union and the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, which has strengthened its ties with neighbouring countries and enhanced its global influence. With its strategic location and abundant natural resources, Kazakhstan has become an important player in the region and on the world stage.
Summary
- Kazakhstan is the ninth largest country in the world and the largest landlocked country, located in Central Asia.
- The country has a diverse geography, including mountains, deserts, and steppe, and experiences an extreme continental climate with hot summers and cold winters.
- Kazakhstan has a rich history, with influences from nomadic tribes, the Mongol Empire, and the Soviet Union, and a unique culture with traditions like eagle hunting and yurt dwelling.
- The economy of Kazakhstan is driven by oil, gas, and mineral resources, and the country is working towards diversifying its industries and attracting foreign investment.
- Kazakh cuisine is influenced by the nomadic lifestyle and includes dishes like beshbarmak and kumis, and the country offers diverse tourism opportunities, from modern cities to natural wonders like the Charyn Canyon.
Geography and Climate of Kazakhstan
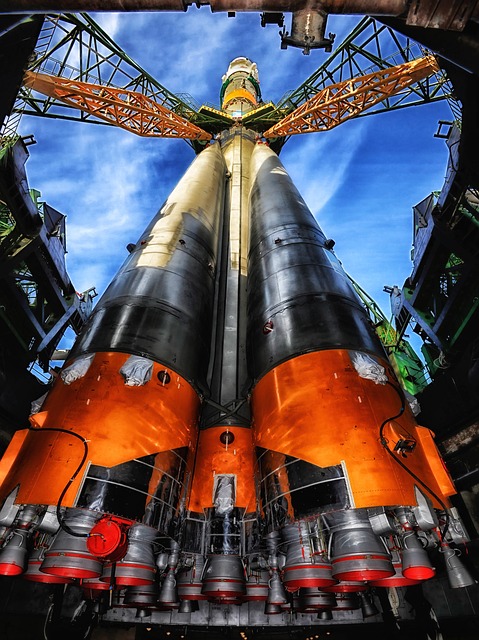
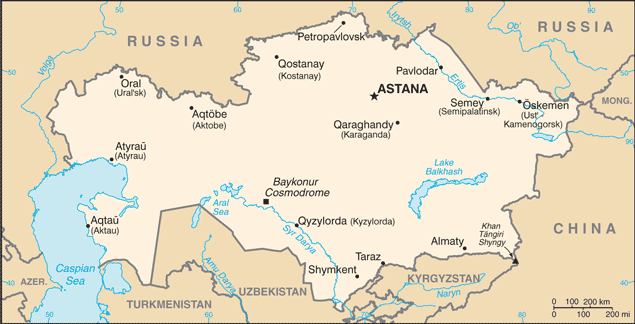
Kazakhstan’s vast territory covers over 2.7 million square kilometres, making it the ninth-largest country in the world. The landscape is incredibly diverse, with mountains, deserts, steppes, and lakes. The Altai Mountains in the east are a popular destination for outdoor enthusiasts, offering opportunities for hiking, skiing, and mountaineering. The Caspian lowlands in the west are home to rich oil and gas reserves, while the central steppes are known for their wide-open spaces and nomadic traditions. The country also boasts the Baikonur Cosmodrome, the world’s first and largest operational space launch facility.
The climate in Kazakhstan varies widely from region to region. In the south, the climate is arid and semi-arid, with hot summers and mild winters. In the north, the climate is continental, with cold winters and hot summers. The country experiences a wide range of temperatures throughout the year, from sub-zero temperatures in winter to scorching heat in summer. The diverse geography and climate of Kazakhstan make it a fascinating destination for nature lovers and adventure seekers.
History and Culture of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan has a rich history that dates back thousands of years. The region was inhabited by nomadic tribes and ancient civilizations, including the Scythians, Saka, and Huns. In the 13th century, Genghis Khan and his Mongol armies conquered the territory, leaving a lasting impact on the culture and traditions of the region. In the 15th century, Kazakhstan became part of the Kazakh Khanate, which was later incorporated into the Russian Empire in the 19th century. The Soviet era brought significant changes to Kazakhstan, including forced collectivisation and industrialisation, as well as the establishment of nuclear test sites.
Today, Kazakhstan is a melting pot of different cultures and traditions, with influences from Russia, China, Mongolia, and Central Asia. The country is known for its vibrant music and dance traditions, including the dombra, a traditional string instrument, and the lively Kazakh folk dances. The Kazakh people also have a rich tradition of storytelling and oral poetry, which has been passed down through generations. In recent years, Kazakhstan has made efforts to preserve and promote its cultural heritage through festivals, museums, and cultural events.
Economy and Industry in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan has experienced rapid economic growth since gaining independence in 1991. The country’s economy is driven by its abundant natural resources, including oil, gas, coal, and minerals. Kazakhstan is one of the world’s leading producers of uranium and has significant reserves of copper, iron ore, and gold. The energy sector plays a crucial role in the economy, with oil and gas accounting for a large portion of the country’s exports.
In recent years, Kazakhstan has made efforts to diversify its economy by investing in other industries such as agriculture, manufacturing, and technology. The government has also implemented economic reforms to attract foreign investment and promote entrepreneurship. The country’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia has made it an important hub for trade and transportation. With its growing economy and modern infrastructure, Kazakhstan offers numerous opportunities for business and investment.
Kazakh Cuisine and Traditions
Kazakh cuisine is a reflection of the country’s nomadic heritage and diverse cultural influences. Traditional Kazakh dishes often feature meat, dairy products, and grains, reflecting the nomadic lifestyle of the Kazakh people. Some popular dishes include beshbarmak, a hearty meat stew served with noodles; kazy, a type of horse sausage; and kumis, a fermented mare’s milk drink. Bread holds a special significance in Kazakh culture and is often served with every meal.
Kazakh traditions are deeply rooted in hospitality and respect for elders. Guests are welcomed with open arms and are often treated to an elaborate feast featuring an array of traditional dishes. The Kazakh people also have a strong tradition of horsemanship and equestrian sports, such as kokpar (a traditional horseback game) and horse racing. Traditional crafts such as carpet weaving and embroidery are also an important part of Kazakh culture, with intricate designs and patterns that reflect the country’s rich heritage.
Tourism in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan’s diverse landscapes and rich cultural heritage make it an attractive destination for tourists. The country offers a wide range of outdoor activities, including hiking in the Altai Mountains, exploring the Charyn Canyon, and visiting the beautiful Kolsai Lakes. The city of Almaty is known for its vibrant nightlife, modern architecture, and proximity to ski resorts in the nearby mountains. Nur-Sultan boasts futuristic skyscrapers, world-class museums, and a thriving arts scene.
In recent years, Kazakhstan has made significant investments in developing its tourism infrastructure, including new hotels, resorts, and transportation facilities. The government has also implemented visa-free entry for citizens of many countries to promote tourism. With its unique blend of natural beauty and cultural attractions, Kazakhstan has the potential to become a major player in the global tourism industry.
Future Prospects for Kazakhstan
Looking ahead, Kazakhstan faces both challenges and opportunities as it seeks to further develop its economy and society. The country’s reliance on natural resources makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in global commodity prices, highlighting the need for diversification and innovation. Kazakhstan has made efforts to promote sustainable development and green technologies to reduce its environmental impact.
The government has also prioritised education and human capital development to prepare the workforce for the challenges of the 21st century. Investments in healthcare, infrastructure, and technology are crucial for ensuring long-term prosperity for the people of Kazakhstan. With its strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, Kazakhstan has the potential to become a key player in regional cooperation and trade.
In conclusion, Kazakhstan is a country with a rich history, diverse culture, and vast potential for growth. Its unique blend of natural beauty and modern infrastructure makes it an attractive destination for tourists and investors alike. With continued investment in education, innovation, and sustainable development, Kazakhstan is well-positioned to thrive in the global economy while preserving its rich cultural heritage for future generations.
Terrain and Topography of Kazakhstan: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Kazakhstan, the ninth largest country in the world, is situated in Central Asia and is renowned for its diverse terrain and topography. The nation shares borders with Russia to the north, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan to the south, and the Caspian Sea to the west. Kazakhstan’s landscape is remarkably varied, comprising mountains, valleys, and expansive plains. The country’s topography is the result of millions of years of geological processes, including tectonic movements, erosion, and glaciation, which have shaped its distinctive features. The terrain of Kazakhstan offers a wide range of geographical elements, from the Tian Shan mountains in the southeast to the vast steppes that cover much of the country. The Kazakh Uplands, a region of low mountains and hilly plains, dominate the central and eastern parts of the country. In the west, the Caspian Depression, which includes areas below sea level, presents a unique topographical feature. Kazakhstan’s diverse landscapes support a rich variety of flora and fauna, contributing to the country’s biodiversity. The terrain provides opportunities for various outdoor activities, including hiking, mountaineering, and wildlife observation. The country’s natural features also play a significant role in its economy, influencing agriculture, mineral extraction, and energy production. The topography of Kazakhstan has had a profound impact on the nation’s history, culture, and development. It has shaped traditional nomadic lifestyles, influenced trade routes, and continues to affect modern infrastructure and urban planning. As Kazakhstan continues to develop, the preservation and sustainable use of its varied terrain remain important considerations for environmental and economic policies. Summary Kazakhstan’s terrain and topography are incredibly diverse, ranging from majestic mountains to...
Climate Zones of Kazakhstan: Different climate regions Of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, the ninth largest country in the world, is situated in Central Asia and is characterised by diverse climate zones. The nation’s expansive territory extends from the Caspian Sea in the west to the Altai Mountains in the east, and from the Siberian taiga in the north to the deserts of Central Asia in the south. This geographical diversity results in a wide range of climate zones, each with its own distinct characteristics and challenges. Understanding Kazakhstan’s climate zones is essential for both residents and visitors, as it influences various aspects of life, including agriculture, industry, daily activities and travel. Kazakhstan’s climate can be broadly categorised into six main zones: the continental climate of northern Kazakhstan, the arid climate of central Kazakhstan, the mountainous climate of eastern Kazakhstan, the semi-arid climate of southern Kazakhstan, and the steppe climate of western Kazakhstan. Each of these zones exhibits unique weather patterns, temperature ranges and precipitation levels, making them suitable for different types of flora, fauna and human activities. As global climate change continues, Kazakhstan’s climate zones are also experiencing shifts, which may have significant implications for the country’s environment, economy and society. This article will examine each of Kazakhstan’s climate zones in detail, exploring their unique characteristics and the potential impact of climate change on these regions. Summary Kazakhstan has diverse climate zones, including continental, arid, mountainous, semi-arid, and steppe climates. Northern Kazakhstan experiences a continental climate with cold winters and hot summers. Central Kazakhstan has an arid climate with low precipitation and extreme temperature variations. Eastern Kazakhstan is characterised by mountainous climate with cold winters and mild summers. Southern Kazakhstan...
Political Boundaries of Kazakhstan: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Kazakhstan, the largest landlocked country in the world, is situated in Central Asia. It shares borders with Russia to the north, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan to the south, and the Caspian Sea to the west. The country is administratively divided into 14 provinces (oblystar) and 3 cities (qalalar) with provincial status. The political boundaries in Kazakhstan have evolved over time, influenced by historical, cultural, and administrative factors. These boundaries play a crucial role in governance, administration, and the distribution of resources within the country. Understanding the political boundaries of Kazakhstan is essential for comprehending the country’s complex administrative structure and its impact on governance and development. Kazakhstan’s political boundaries have been shaped by a variety of factors, including historical conquests, cultural diversity, and administrative needs. The country’s vast territory has historically been inhabited by various ethnic groups, each with its own distinct cultural identity. As a result, the political boundaries in Kazakhstan have been influenced by the need to accommodate these diverse cultural regions whilst maintaining a unified administrative structure. The country’s transition from a Soviet republic to an independent nation in 1991 also had a significant impact on its political boundaries, as it led to the establishment of new administrative divisions and the reorganisation of existing ones. This complex history has contributed to the diverse and intricate political boundaries that exist in Kazakhstan today. Summary Kazakhstan is a vast country with diverse political boundaries, including provinces and administrative districts. Historical boundaries and cultural regions have played a significant role in shaping Kazakhstan’s political landscape. The impact of political boundaries on governance and administration has...
History of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan possesses a rich and diverse history spanning thousands of years. The region was inhabited by nomadic tribes as early as the 1st millennium BC, with evidence of early human settlement found in the form of ancient petroglyphs and archaeological sites. The Scythians, a nomadic people renowned for their horsemanship and martial prowess, were among the earliest known inhabitants of the region. They left behind a legacy of intricate gold jewellery and other artefacts that have been unearthed by archaeologists. The Silk Road, an ancient network of trade routes connecting the East and West, traversed Kazakhstan, fostering cultural exchange and economic prosperity. The region became a melting pot of diverse cultures and ethnicities, with influences from China, Persia, and the Middle East shaping Kazakhstan’s development. The ancient city of Otrar, situated in present-day southern Kazakhstan, served as a major trading hub along the Silk Road and a centre of commerce and cultural exchange. The city was renowned for its bustling markets and its role in facilitating trade between East and West. Summary Kazakhstan has a rich early history dating back to the Bronze Age, with evidence of ancient settlements and trade routes. The Mongol Empire and the Golden Horde had a significant impact on Kazakhstan, shaping its culture and society. The Kazakh Khanate emerged as a powerful state in the 15th century, eventually coming under the control of the Russian Empire in the 18th century. Soviet rule brought significant changes to Kazakhstan, including industrialization and the establishment of the Kazakh SSR. Kazakhstan gained independence from the Soviet Union in 1991 and has since focused on modernization and economic development....
Population Density of Kazakhstan
Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, typically measured in square kilometres or square miles. It is a crucial demographic indicator that offers insights into the distribution of people within a country or region. In Kazakhstan, population density varies significantly across the country, with some areas being densely populated whilst others are sparsely populated. Understanding population density is essential for policymakers, urban planners and researchers, as it aids in making informed decisions about resource allocation, infrastructure development and social services provision. Kazakhstan, the ninth largest country in the world by land area, has a relatively low population density compared to many other countries. The country’s population density stands at approximately 6 people per square kilometre, with the majority of the population concentrated in urban areas. However, there are significant regional variations in population density, with the southern regions being more densely populated compared to the northern and eastern parts of the country. This variation in population density is influenced by a range of factors, including geographical features, historical settlement patterns and economic opportunities. Understanding these factors is crucial for gaining insights into the dynamics of population distribution in Kazakhstan. Summary Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured in square kilometres. Factors affecting population density in Kazakhstan include natural resources, climate, economic opportunities, and government policies. Urban areas in Kazakhstan have higher population density compared to rural areas, where the population is more spread out. High population density can put a strain on infrastructure such as transportation, housing, and healthcare facilities. Challenges of high population density...
Natural Resources of Kazakhstan: Where Natural Resources are located In Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, the ninth largest country in the world, is abundant in natural resources. The nation’s diverse landscape encompasses vast steppes, deserts, mountains and forests, which harbour a wide variety of natural assets. Kazakhstan’s natural resources play a crucial role in the country’s economy and have the potential to contribute significantly to its future development. From oil and gas reserves to mineral resources, agricultural resources, water resources and renewable energy potential, Kazakhstan’s natural wealth is a key factor in shaping its economic and environmental future. Kazakhstan’s natural resources have been a driving force behind the country’s economic growth and development. The exploitation of these resources has led to significant foreign investment and has helped to establish Kazakhstan as a major player in the global energy market. However, the sustainable use and conservation of these resources are essential to ensure their availability for future generations. This article will explore the various natural resources found in Kazakhstan, their significance to the country’s economy and the importance of conservation and sustainable use for the future. Summary Kazakhstan is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, agriculture, water, and renewable energy potential. The country has significant oil and gas reserves, making it a major player in the global energy market. Kazakhstan also boasts abundant mineral resources, including coal, iron ore, copper, and gold. The country’s agricultural resources are diverse, with vast tracts of arable land and a variety of crops and livestock. Kazakhstan has ample water resources, with numerous rivers, lakes, and reservoirs providing water for irrigation and other uses. Oil and Gas Reserves in Kazakhstan Oil and Gas Reserves These fields are...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Kazakhstan: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, the ninth largest country in the world, boasts a rich cultural and historical heritage. The nation is home to a diverse array of cultural and historical sites that reflect its long and varied past. From ancient mausoleums to stunning natural landscapes, Kazakhstan offers a wealth of attractions for visitors to explore. The country’s cultural and historical sites stand as a testament to its rich history and the diverse influences that have shaped its identity over the centuries. Kazakhstan’s cultural and historical sites reflect the country’s unique blend of Eastern and Western influences. From the ancient Silk Road to the Soviet era, Kazakhstan has been moulded by a variety of cultural and historical forces. The country’s cultural and historical sites offer a glimpse into its past, from the ancient traditions of the Kazakh people to the legacy of the Soviet Union. Visitors to Kazakhstan can explore a wide range of cultural and historical sites, each offering a unique insight into the country’s rich heritage. Summary Kazakhstan is home to a rich array of cultural and historical sites that showcase its diverse heritage. The Mausoleum of Khoja Ahmed Yasawi is a UNESCO World Heritage site and an important pilgrimage destination for Muslims. The Aisha-Bibi Mausoleum is a stunning example of ancient architecture and a symbol of love and devotion. The Petroglyphs of Tamgaly offer a glimpse into the ancient rock art and spiritual practices of the region. The Kazakh traditional dwellings, known as yurts, are a fascinating insight into the nomadic lifestyle of the Kazakh people. The Mausoleum of Khoja Ahmed Yasawi Architectural Significance The mausoleum is a stunning example...
Discovering the Hidden Gems of Kazakhstan: A Journey Through Central Asia’s Best-Kept Secret
Kazakhstan, the ninth largest country in the world, is a hidden gem waiting to be explored. Located in Central Asia, this vast and diverse country offers a wealth of natural wonders, cultural treasures, and thrilling outdoor activities. From the majestic Altai Mountains to the stunning Kolsai Lakes and the breathtaking Charyn Canyon, Kazakhstan is a paradise for nature lovers. But it’s not just the landscapes that make Kazakhstan worth exploring; its rich heritage, delicious cuisine, modern cities, and warm hospitality also make it a fascinating travel destination. Summary Kazakhstan boasts natural wonders from mountains to deserts Cultural treasures await those who explore Kazakhstan’s rich heritage A gastronomic journey through Central Asia reveals the flavours of Kazakhstan Thrilling outdoor activities can be found in Kazakhstan’s wild landscapes Comfort and luxury can be found in the best places to stay in Kazakhstan The Natural Wonders of Kazakhstan: From Mountains to Deserts Kazakhstan is blessed with diverse landscapes that will leave any nature enthusiast in awe. The Altai Mountains, located in the northeastern part of the country, are a paradise for hikers and mountaineers. With their snow-capped peaks, alpine meadows, and crystal-clear lakes, the Altai Mountains offer breathtaking views and endless opportunities for adventure. Another natural wonder in Kazakhstan is the Kolsai Lakes. Located in the Tien Shan Mountains, these three stunning lakes are known for their turquoise waters and picturesque surroundings. Visitors can hike through lush forests, camp by the lakeside, or simply relax and enjoy the tranquility of nature. One of Kazakhstan’s most famous natural attractions is the Charyn Canyon. Often referred to as the “Grand Canyon’s little brother,” this...