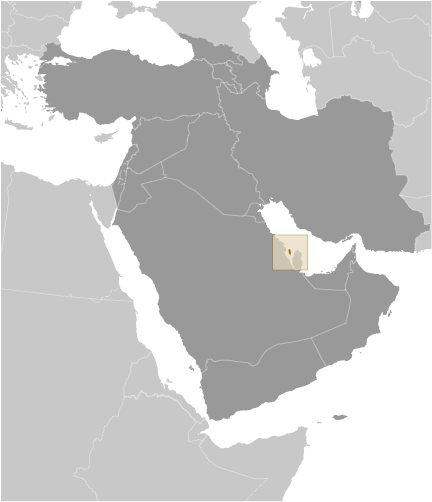
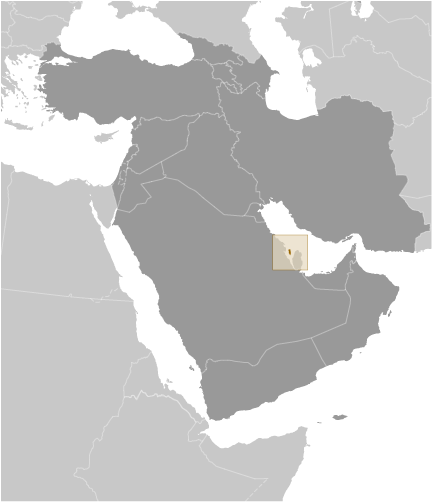
Bahrain
(Mamlakat al-Bahrain (Kingdom of Bahrain))

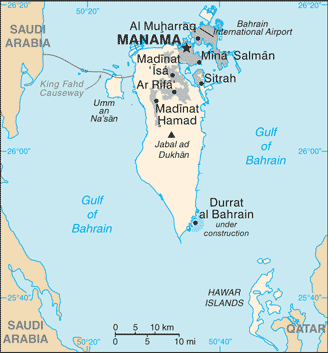




Capital of Bahrain : Manama
Population (Estimated July 2012): 1,248,348
Area: 757km2 or 292mi2
Currency: Bahraini Dinar (BD)
Official Language: Arabic
Political Information: Constitutional Monarchy
Official Religion: Islam
(approximately 81.2% of the population are Muslim (Shia and Sunni), 9% are Christian and 9.8% have other religious beliefs)
Highest Point: Jabal ad Dukhan at 122m or 400ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $26.4 billion (US$) or £15.84 billion (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $30.8 billion (US$) or £18.48 billion (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $27,300 (US$) or £16,380 (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +3:00
Governorates: Asamah, Janubiyah, Muharraq, Shamaliyah, Wasat
Leaders: King Hamad bin Isa Al-Khalifa; Crown Prince Salman bin Hamad Al-Khalifa; Prime Minister Khalifa bin Salman Al-Khalifa
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica,
Introduction to Bahrain: A small island nation in the Persian Gulf
Bahrain, a small island nation located in the Persian Gulf, is often referred to as the “Pearl of the Gulf” due to its rich history, vibrant culture, and stunning natural beauty. It is an archipelago consisting of 33 islands, with Bahrain Island being the largest and most populous. The country is strategically located between Saudi Arabia and Qatar, making it an important hub for trade and commerce.
With a land area of just 765 square kilometres, Bahrain may be small in size, but it is big in charm and character. The capital city, Manama, is a bustling metropolis that blends modern skyscrapers with traditional Arabian architecture. The country’s landscape is diverse, ranging from sandy beaches and palm groves to desert plains and rocky hills.
Bahrain has a population of approximately 1.7 million people, with a diverse mix of nationalities and cultures. The majority of the population is made up of Bahraini nationals, but there are also significant expatriate communities from countries such as India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and the Philippines. This multicultural environment adds to the richness and diversity of Bahrain’s society.
History of Bahrain: From ancient Dilmun to modern-day monarchy
Bahrain has a long and storied history that dates back thousands of years. It was once home to the ancient civilization of Dilmun, which flourished around 2000 BCE. Dilmun was known for its thriving trade routes and was a major centre for the trade of pearls, copper, and other goods.
Over the centuries, Bahrain came under the rule of various empires and civilizations, including the Assyrians, Babylonians, Persians, and Greeks. In the 16th century, the Portuguese arrived in Bahrain and established a stronghold on the island. However, their rule was short-lived as they were expelled by the Persians in the 17th century.
In the 19th century, Bahrain came under British influence and became a protectorate of the British Empire. The British played a significant role in modernizing Bahrain’s infrastructure and economy, particularly in the areas of trade and commerce. Bahrain gained independence from Britain in 1971 and became a constitutional monarchy.
Economy of Bahrain: Oil, finance, and tourism industries
Bahrain’s economy is diverse and relies on several key industries, including oil and gas, finance, and tourism. The country has significant reserves of oil and natural gas, which have been a major source of revenue for the government. However, in recent years, Bahrain has been working towards diversifying its economy to reduce its dependence on oil.
The financial services sector is a major contributor to Bahrain’s economy, accounting for a significant portion of its GDP. The country is home to numerous international banks and financial institutions, making it a regional hub for finance and investment. Bahrain’s financial sector is known for its regulatory framework, transparency, and stability.
Tourism is also an important industry in Bahrain, with the country attracting visitors from around the world. The country offers a range of attractions, including historical landmarks, cultural festivals, and luxury resorts. Bahrain’s warm climate, beautiful beaches, and rich cultural heritage make it an ideal destination for tourists seeking a unique and authentic Arabian experience.
Culture and traditions of Bahrain: Islamic heritage and modern influences
Bahrain has a rich Islamic heritage that is deeply ingrained in its culture and traditions. Islam is the official religion of the country, and the majority of Bahrainis are Muslims. Islamic customs and practices are followed by the people, including daily prayers, fasting during Ramadan, and celebrating religious festivals such as Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha.
Traditional clothing in Bahrain reflects the Islamic culture of the country. Men typically wear a thobe (a long white robe) and a ghutra (a white headdress), while women wear an abaya (a black cloak) and a hijab (a headscarf). However, in recent years, there has been a growing trend towards more modern and Western-style clothing among the younger generation.
Bahrain’s cultural scene is vibrant and diverse, with a mix of traditional and modern influences. Traditional arts and crafts, such as pottery, weaving, and calligraphy, are still practised and celebrated. The country is also home to several art galleries and museums that showcase the works of local and international artists.
The cuisine of Bahrain: Spices, seafood, and traditional dishes
Bahraini cuisine is a reflection of the country’s rich history and cultural influences. The cuisine is known for its bold flavours, aromatic spices, and use of fresh ingredients. Seafood is a staple in Bahraini cuisine, thanks to the country’s proximity to the sea.
Spices play a crucial role in Bahraini cooking, adding depth and complexity to dishes. Common spices used in Bahraini cuisine include cardamom, saffron, turmeric, cinnamon, and cloves. These spices are used to flavour rice dishes, stews, and grilled meats.
Rice is a staple in Bahraini cuisine and is often served with fish or meat. One popular rice dish is machbous, which is made with spiced rice, meat (usually chicken or lamb), and vegetables. Another traditional dish is muhammar, which is made with sweetened rice flavoured with dates or molasses.
Bahrainis also have a sweet tooth and enjoy indulging in traditional desserts. One popular dessert is halwa showaiter, which is a dense and sticky sweet made with semolina, sugar, rosewater, and saffron. Another favourite is luqaimat, which are small deep-fried dough balls drizzled with date syrup or honey.
Education in Bahrain: A focus on quality and innovation
Bahrain places a strong emphasis on education and has made significant investments in its education system. The country has a well-developed education infrastructure, with a range of public and private schools, colleges, and universities.
The education system in Bahrain follows a similar structure to that of other countries, with primary, secondary, and tertiary levels of education. Education is compulsory for children between the ages of 6 and 14. The Ministry of Education oversees the education system and is responsible for setting curriculum standards and ensuring quality.
Bahrain has also made significant investments in research and development (R&D) to promote innovation and technological advancements. The government has established research centres and institutes to support scientific research in various fields, including medicine, engineering, and information technology.
Furthermore, Bahrain has formed partnerships and collaborations with international educational institutions to enhance the quality of education in the country. These partnerships provide opportunities for students and faculty to engage in exchange programs, joint research projects, and academic collaborations.
Healthcare in Bahrain: Public and private healthcare systems
Bahrain has a well-developed healthcare system that provides both public and private healthcare services to its residents. The country has invested heavily in healthcare infrastructure and facilities to ensure that its citizens have access to high-quality medical care.
Public healthcare in Bahrain is provided through a network of government-run hospitals, clinics, and health centres. These facilities offer a wide range of medical services, including primary care, specialist consultations, diagnostic tests, surgeries, and emergency care. The government also provides free or subsidized healthcare services to Bahraini nationals.
In addition to public healthcare, Bahrain also has a thriving private healthcare sector. Private hospitals and clinics offer a range of specialized medical services and treatments. Many expatriates living in Bahrain prefer to seek medical care from private healthcare providers due to the convenience and quality of services offered.
Bahrain’s healthcare policies and initiatives are focused on promoting preventive care, improving healthcare outcomes, and ensuring patient safety. The government has implemented various health programs and initiatives to address public health issues, such as chronic diseases, infectious diseases, and mental health.
Sports and recreation in Bahrain: Formula One racing and water sports
Bahrain is a haven for sports enthusiasts, offering a wide range of sporting activities and facilities. One of the most popular sports in Bahrain is Formula One racing. The Bahrain International Circuit, located in Sakhir, hosts the annual Bahrain Grand Prix, which attracts racing fans from around the world.
In addition to Formula One racing, Bahrain is also known for its water sports and activities. The country’s warm climate and crystal-clear waters make it an ideal destination for diving, snorkelling, sailing, and fishing. The coastline is dotted with marinas and beach clubs that offer a range of water-based activities.
Bahrain is also home to several sports clubs and facilities that cater to different sports and fitness activities. These clubs offer state-of-the-art facilities, including gyms, swimming pools, tennis courts, football fields, and basketball courts. They also organize regular sporting events and tournaments for both amateurs and professionals.
Tourism in Bahrain: Attractions, festivals, and events
Bahrain offers a wealth of attractions for tourists to explore and enjoy. The country’s rich history is evident in its numerous historical landmarks and archaeological sites. One of the most famous historical sites in Bahrain is the Bahrain Fort, also known as Qal’at al-Bahrain. This ancient fort is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and offers visitors a glimpse into Bahrain’s past.
Bahrain is also known for its vibrant cultural festivals and events. The country celebrates several religious festivals throughout the year, including Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha. These festivals are marked by feasting, family gatherings, traditional music and dance performances, and fireworks displays.
Shopping is another popular activity in Bahrain, with the country offering a range of shopping malls, traditional markets, and boutique stores. The Bahrain City Centre, Seef Mall, and Moda Mall are some of the popular shopping destinations in the country. Visitors can find a wide range of products, including luxury brands, traditional handicrafts, and local souvenirs.
Future of Bahrain: Vision 2030 and plans for sustainable development
Bahrain has set ambitious goals for its future development through its Vision 2030 plan. The plan aims to transform Bahrain into a sustainable and diversified economy, with a focus on sectors such as finance, tourism, manufacturing, and technology.
One of the key objectives of Vision 2030 is to reduce Bahrain’s dependence on oil by diversifying its economy. The government is actively promoting sectors such as finance, tourism, and manufacturing to attract foreign investment and create new job opportunities.
Sustainable development is also a priority for Bahrain, with the government implementing various initiatives to protect the environment and promote renewable energy. The country has set targets for reducing carbon emissions and increasing the use of renewable energy sources.
Furthermore, Bahrain is investing in technology and innovation to drive economic growth and enhance its competitiveness on the global stage. The government has established technology parks and innovation centres to support research and development in areas such as artificial intelligence, blockchain technology, and cybersecurity.
Bahrain is a unique and dynamic country that offers a blend of ancient traditions and modern amenities. Its rich history, diverse culture, and promising future make it an attractive destination for tourists, investors, and expatriates alike. Whether you are interested in exploring its ancient past, enjoying its vibrant cultural scene, or taking advantage of its business opportunities, Bahrain has something to offer everyone. With its strategic location in the Persian Gulf and its commitment to sustainable development, Bahrain is poised to become a leading player in the region’s economy and a hub for innovation and technology.
Population Density of Bahrain
Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured per square kilometer. It is an important indicator that helps us understand how crowded or sparsely populated an area is. In the case of Bahrain, a small island country in...
Terrain and Topography of Bahrain: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Bahrain, a small island country located in the Persian Gulf, is known for its rich history, vibrant culture, and stunning landscapes. Understanding Bahrain’s topography is crucial in order to appreciate the country’s unique characteristics and the impact...
Climate Zones of Bahrain: Different climate regions Of Bahrain
Bahrain, a small island country located in the Persian Gulf, has a diverse range of climate zones due to its unique geography. Understanding these climate zones is crucial for various reasons, including planning and decision-making in sectors such as agriculture,...
Political Boundaries of Bahrain: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Political boundaries are the lines that define the territorial limits of a country or region. They are crucial for maintaining order, establishing governance, and ensuring the efficient allocation of resources. In Bahrain, a small island nation located in the Persian...
Natural Resources of Bahrain: Where Natural Resources are located In Bahrain
Bahrain, a small island nation located in the Arabian Gulf, is known for its rich natural resources. Despite its small size, Bahrain has a diverse range of natural resources that have played a significant role in shaping its economy. These resources include oil and...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Bahrain: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Bahrain
Bahrain, a small island nation in the Arabian Gulf, is known for its rich cultural heritage that dates back thousands of years. The country has been influenced by various civilizations throughout history, resulting in a unique blend of traditions, customs, and...
Discovering the Hidden Gems of Bahrain: A Guide to the Kingdom’s Best-Kept Secrets
Bahrain, a small island nation in the Arabian Gulf, may not be the first destination that comes to mind when planning a trip. However, this hidden gem is filled with rich history, stunning natural landscapes, vibrant neighborhoods, delicious cuisine, a thriving art...