Bangladesh
(Gana Prajatantri Bangladesh (People’s Republic of Bangladesh))





Capital: Pago Pago
Population (Estimated July 2012): 68,061
Area: 200km2 or 77mi2
Currency: United States Dollar (U.S.$)
Official Language: English; Samoan
Political Information: Unincorporated and unorganized territory of the US
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 50% of the population is Christian Congregationalist, 20% are Roman Catholic and 30% are either protestant or have other religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Lata Mountain at 964m or 3162 feet
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2005): $462.2 million (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2007): $575.3 million (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2007): $8,000 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): -11:00
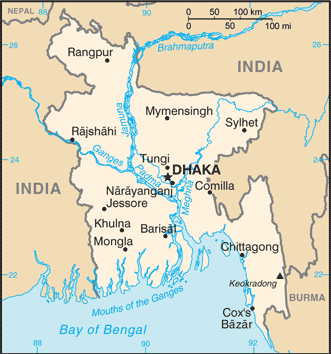
Counties/Provinces/States: three districts and two islands at the second order; Eastern, Manu’a, Rose Island, Swains Island, Western
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
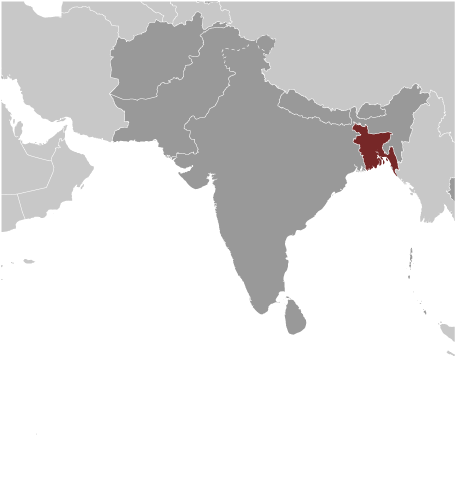
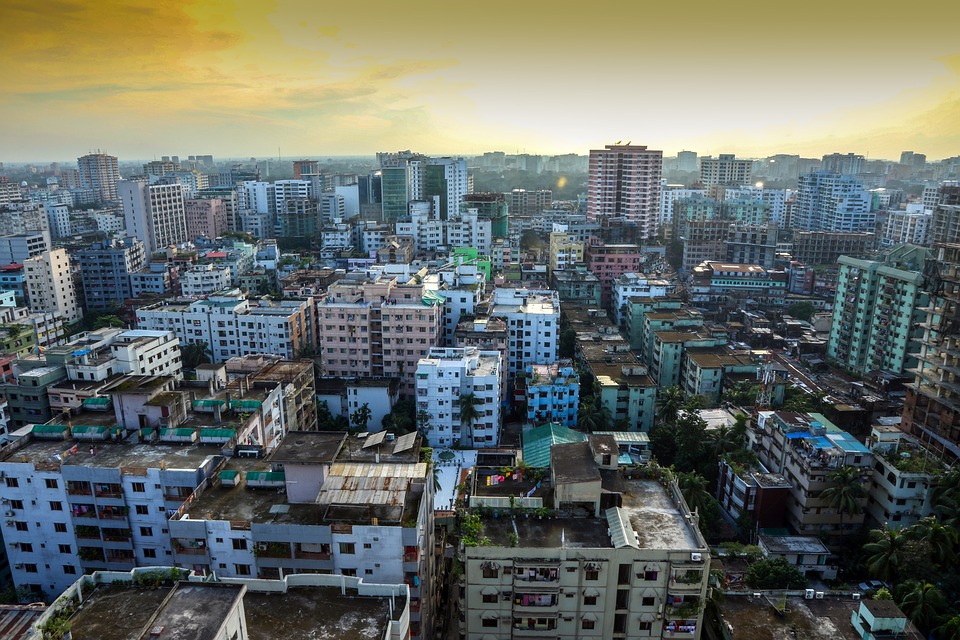
Bangladesh, officially known as the People’s Republic of Bangladesh, is a country located in South Asia. It is bordered by India to the west, north, and east, and by Myanmar to the southeast. With a population of over 160 million people, Bangladesh is the eighth-most populous country in the world. Despite its relatively small size, Bangladesh is known for its rich cultural heritage and diverse population.
Bangladesh holds great importance in South Asia due to its strategic location and economic potential. It serves as a gateway between South Asia and Southeast Asia, connecting the landlocked countries of Nepal and Bhutan to the Bay of Bengal. Additionally, Bangladesh has emerged as an important player in the global textile industry, making it a key player in the global economy.
Geography and Climate of Bangladesh: From the Himalayas to the Bay of Bengal
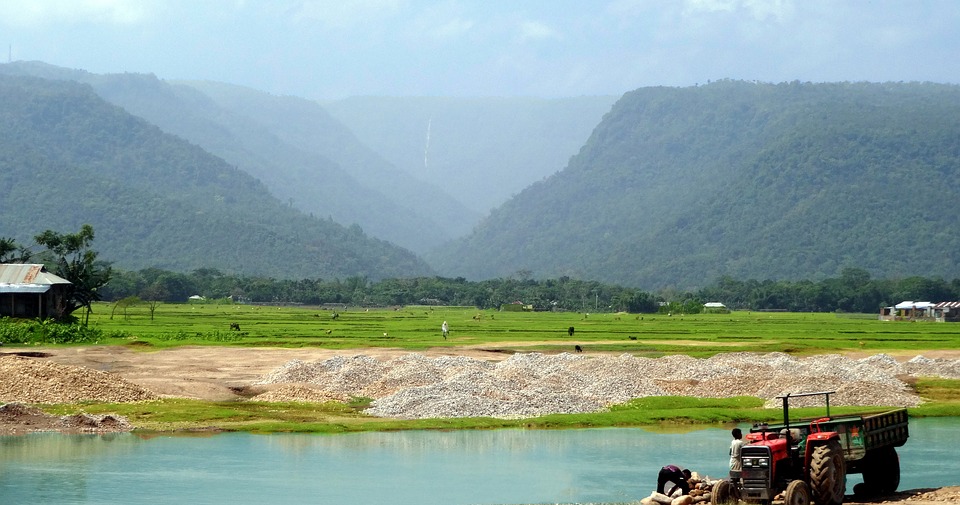
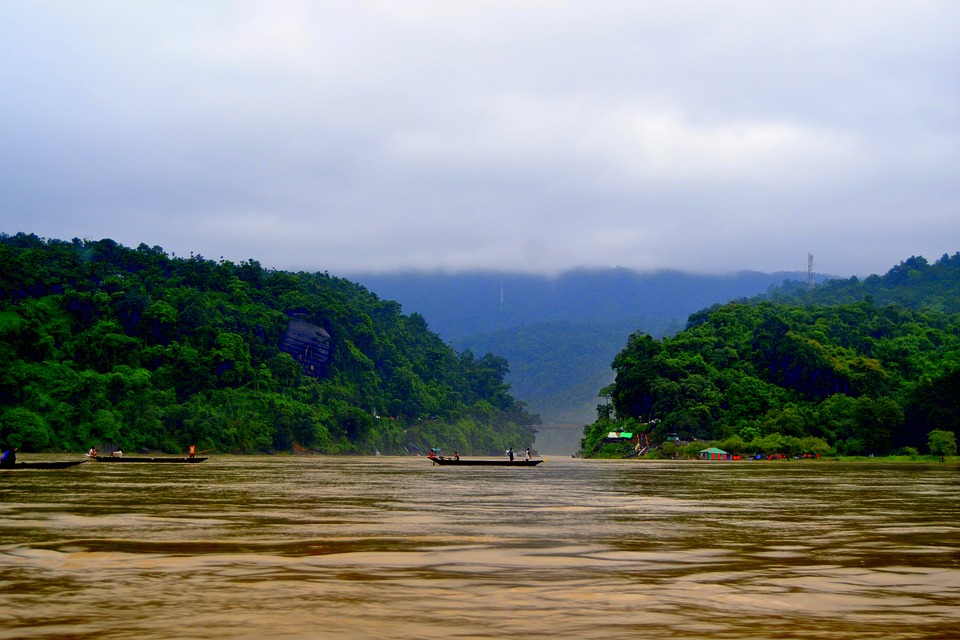
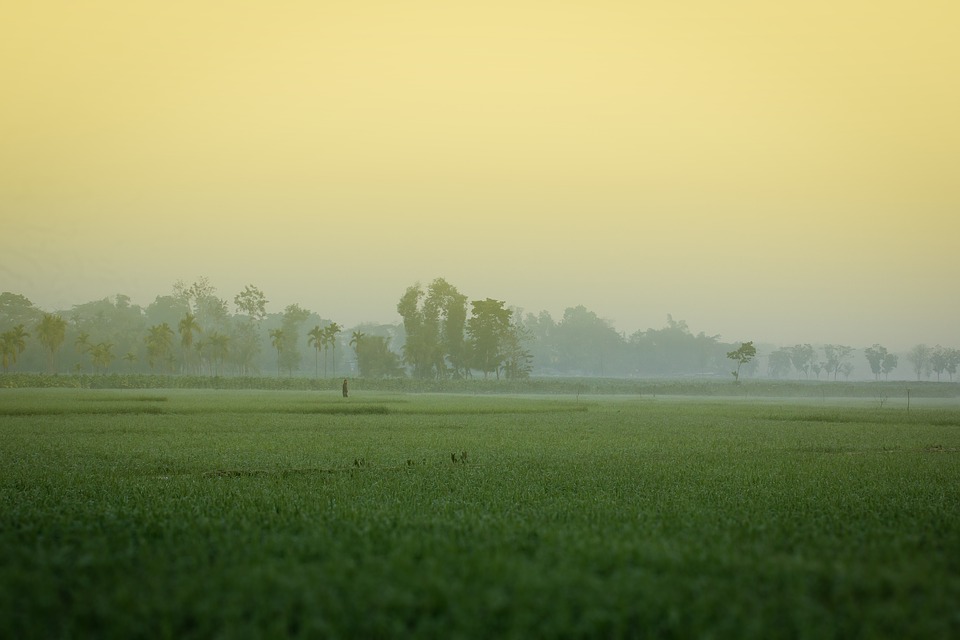
Bangladesh is located in the northeastern part of South Asia, between latitudes 20°34′ and 26°38′ north, and longitudes 88°01′ and 92°41′ east. It is a low-lying country with a diverse topography that ranges from the fertile plains of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna Delta to the hilly regions of Chittagong Hill Tracts in the southeast.
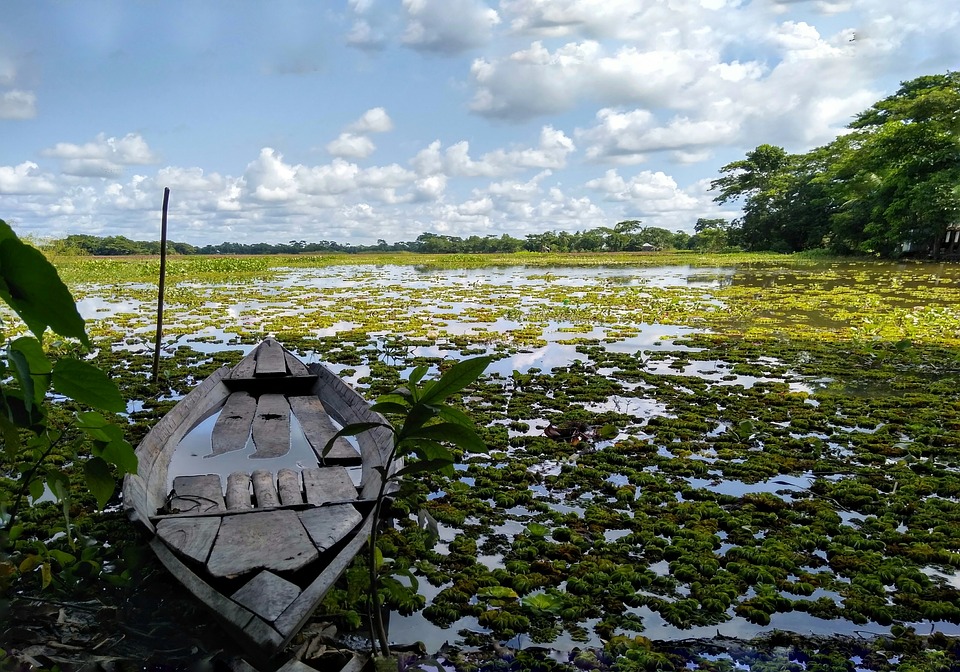
The country is blessed with abundant natural resources, including fertile soil, natural gas reserves, coal deposits, and water resources. The Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna Delta is one of the largest river deltas in the world and provides fertile land for agriculture. The Sundarbans, a mangrove forest located in southwestern Bangladesh, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and home to the Royal Bengal Tiger.
Bangladesh has a tropical monsoon climate characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall. The country experiences three distinct seasons: a hot summer from March to June, a monsoon season from June to October, and a cool winter from November to February. The monsoon season brings heavy rainfall, which can lead to flooding in some parts of the country. The coastal areas of Bangladesh are also prone to cyclones and storm surges.
History of Bangladesh: From Ancient Civilizations to Independence
Bangladesh has a rich history that dates back thousands of years. The region has been inhabited since prehistoric times, with evidence of human settlements dating back to the Neolithic period. The area was ruled by various empires and dynasties, including the Maurya Empire, Gupta Empire, Pala Empire, and Sena Dynasty.
In the 16th century, the region came under the control of the Mughal Empire, which ruled over much of South Asia. During this time, Bengal (which included present-day Bangladesh) was a prosperous province known for its textile industry and agricultural production.
In the 18th century, British colonial rule began in Bengal, as part of the larger British East India Company’s expansion in South Asia. The British introduced modern infrastructure and institutions but also exploited the region’s resources and imposed heavy taxes on the local population.
After years of struggle for independence, Bangladesh finally gained its freedom from Pakistan on December 16, 1971. The Bangladesh Liberation War, also known as the War of Independence, was a bloody conflict that resulted in the deaths of millions of people. The country’s founding father, Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, became the first President of Bangladesh.
Economy of Bangladesh: Emerging Market and Development Challenges
Bangladesh has made significant progress in recent decades in terms of economic growth and development. The country has transitioned from being one of the poorest nations in the world to a lower-middle-income country. Its economy is primarily driven by agriculture, industry, and services.
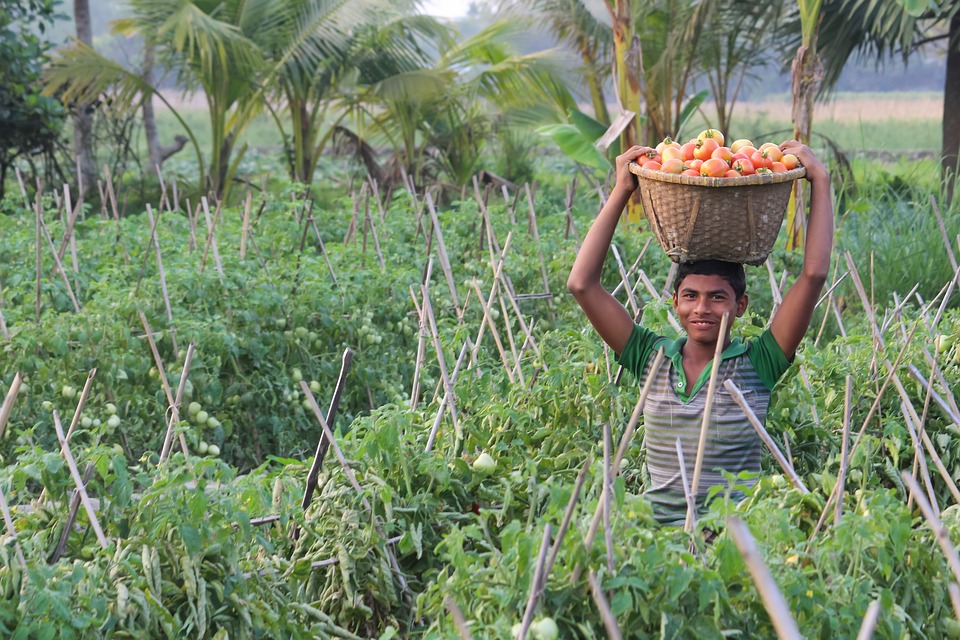
Agriculture plays a vital role in Bangladesh’s economy, employing a large portion of the population and contributing to food security. The country is known for its production of rice, jute, tea, and fish. In recent years, there has been a shift towards industrialization, with the garment industry becoming a major source of export earnings.
Bangladesh is the second-largest exporter of ready-made garments in the world, with its textile industry accounting for a significant portion of its GDP. The country also has a growing pharmaceutical industry and is becoming a hub for information technology and outsourcing services.
Despite its economic progress, Bangladesh faces several challenges in sustaining its growth and development. These challenges include poverty, income inequality, corruption, inadequate infrastructure, and limited access to quality education and healthcare. The government has implemented various policies and initiatives to address these issues and promote inclusive growth.
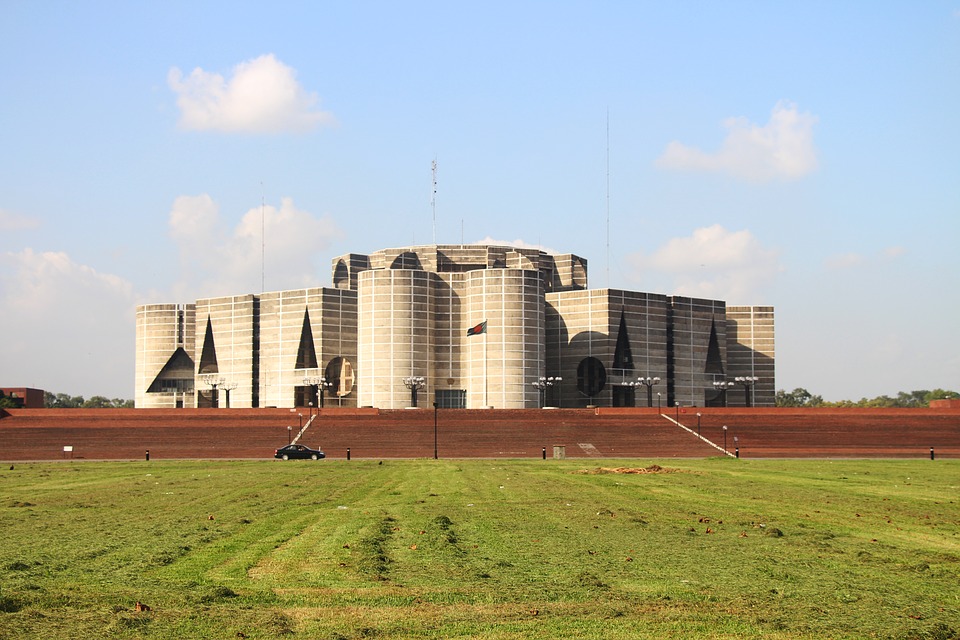
Politics and Government of Bangladesh: A Parliamentary Democracy
Bangladesh is a parliamentary democracy with a multi-party system. The President of Bangladesh is the head of state, while the Prime Minister is the head of government. The President is elected by members of Parliament, while the Prime Minister is elected by popular vote.
The political system in Bangladesh is characterized by a competitive and vibrant party system. The two major political parties in the country are the Awami League and the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP). These parties have dominated the political landscape since independence, with their leaders playing significant roles in shaping the country’s history.
In recent years, Bangladesh has witnessed some political turmoil and polarization. There have been allegations of human rights abuses, restrictions on freedom of speech and expression, and violence during elections. However, efforts are being made to strengthen democratic institutions and ensure free and fair elections.
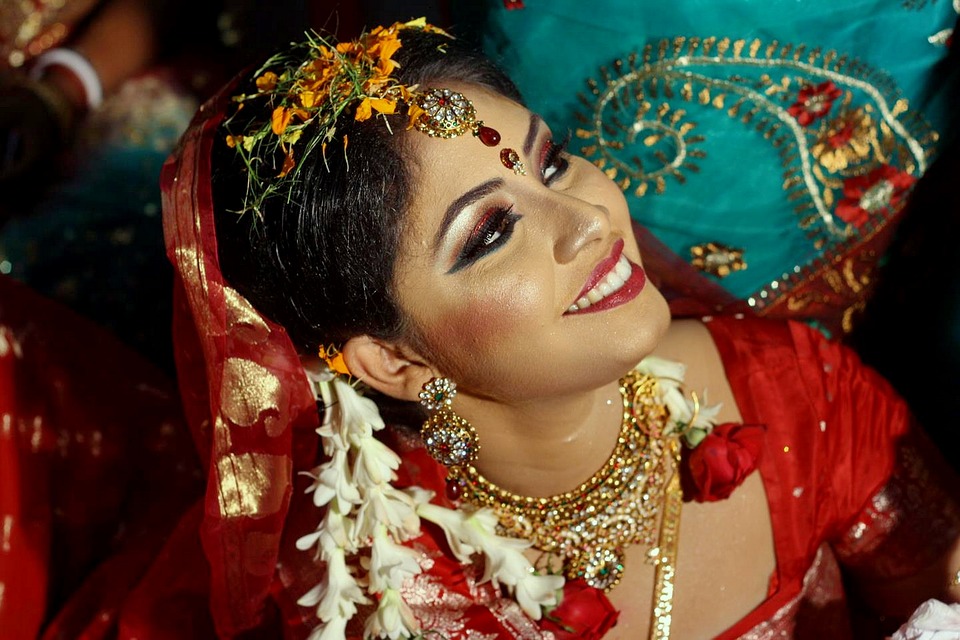
Society and Culture of Bangladesh: Religion, Language, and Festivals
Bangladesh is known for its religious diversity and tolerance. Islam is the predominant religion in the country, with over 90% of the population being Muslims. However, there are also significant Hindu, Buddhist, and Christian communities in Bangladesh.
Bengali is the official language of Bangladesh and is spoken by the majority of the population. English is also widely spoken and used in business and education. The country has a rich literary tradition, with Bengali literature being recognized globally for its contributions to poetry, novels, and plays.
Bangladesh celebrates a number of festivals throughout the year, reflecting its cultural diversity. The two major religious festivals in the country are Eid-ul-Fitr and Eid-ul-Adha, which mark the end of Ramadan and the pilgrimage to Mecca, respectively. Other important festivals include Durga Puja (celebrated by Hindus), Buddha Purnima (celebrated by Buddhists), and Christmas (celebrated by Christians).
Education and Healthcare in Bangladesh: Achievements and Challenges
Bangladesh has made significant progress in improving access to education and healthcare in recent years. The government has implemented various policies and programs to promote universal primary education and increase enrollment rates. As a result, the literacy rate in Bangladesh has increased significantly.
The country has also made strides in improving healthcare services, with a focus on maternal and child health. The government has implemented various initiatives to reduce maternal and child mortality rates, including the provision of free healthcare services for pregnant women and children under five.
However, Bangladesh still faces several challenges in the education and healthcare sectors. Access to quality education remains a challenge, particularly in rural areas where infrastructure is lacking. There is also a need for more investment in research and development to address health issues such as malnutrition, infectious diseases, and non-communicable diseases.
Tourism in Bangladesh: Natural Beauty and Cultural Heritage
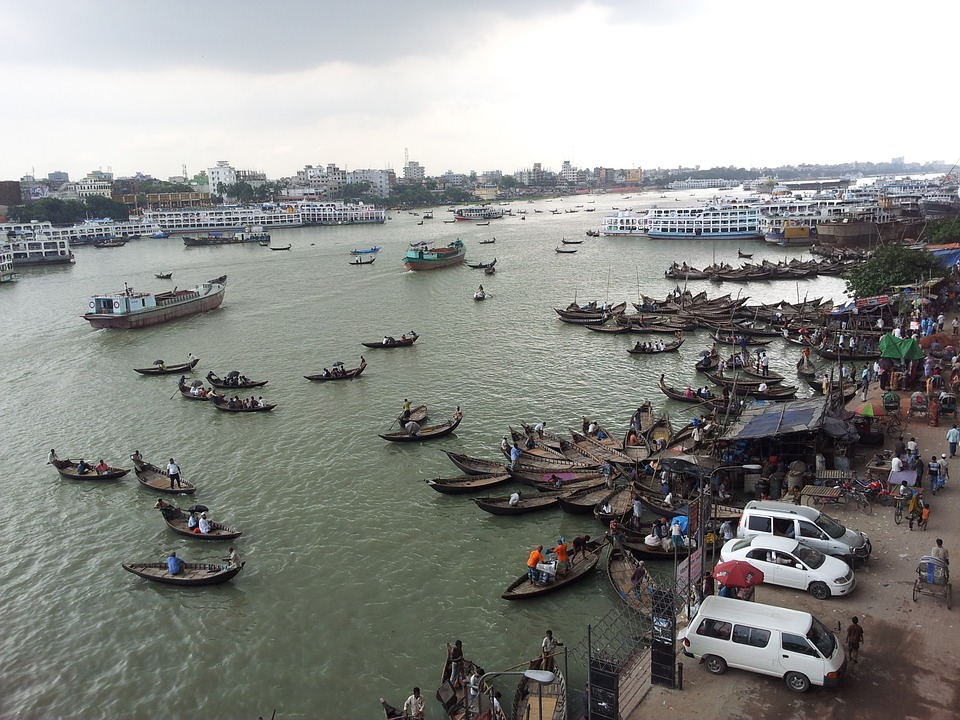
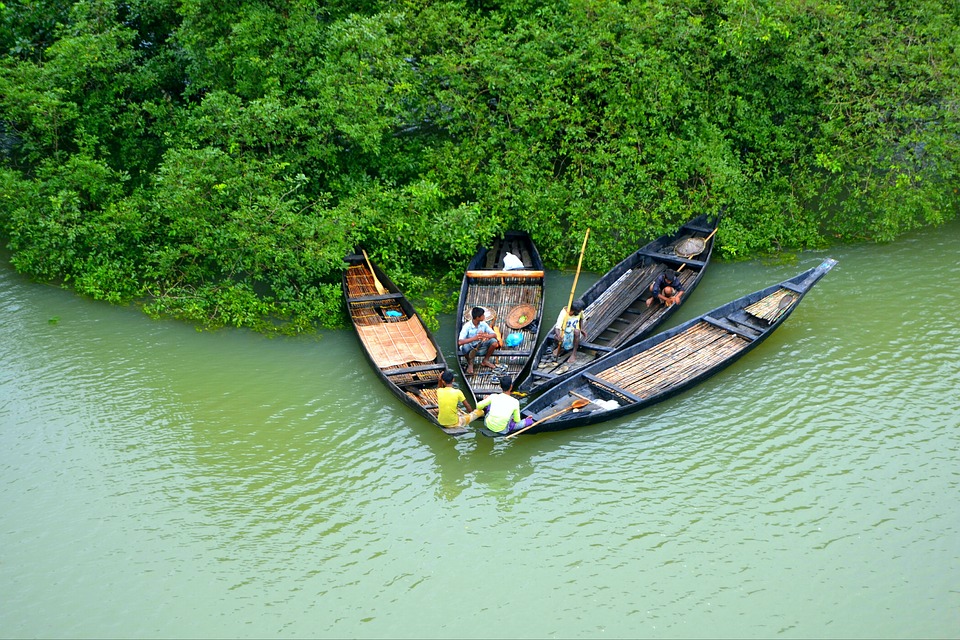
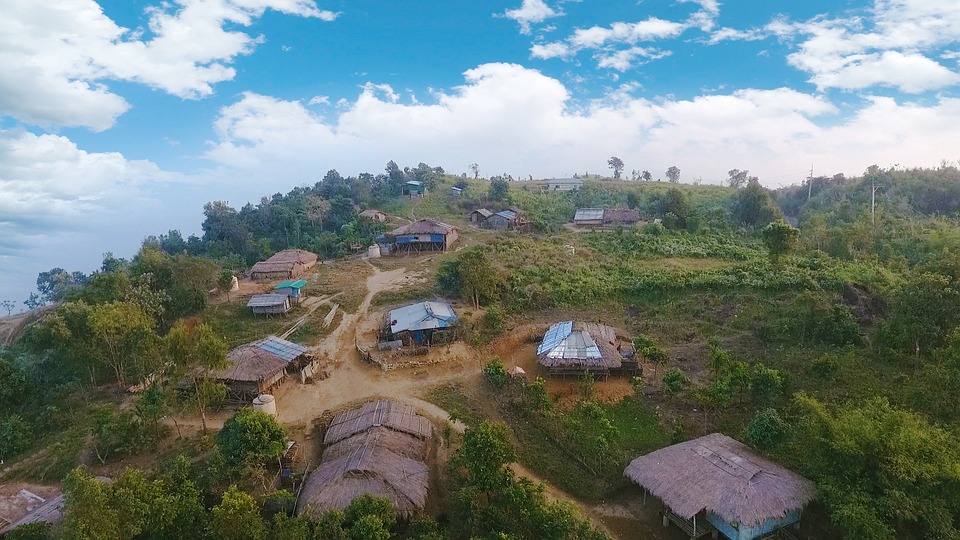
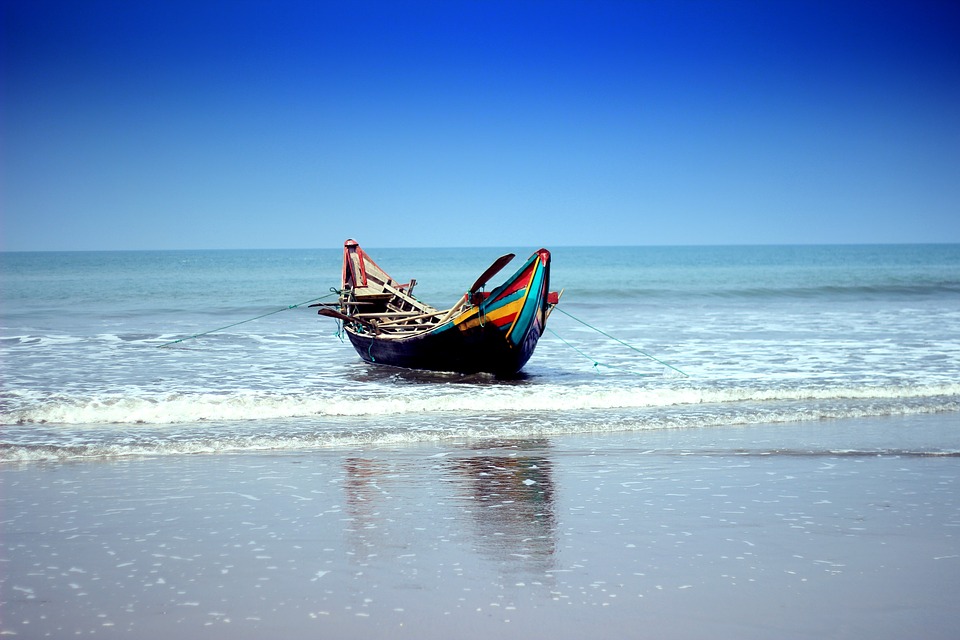
Bangladesh is a country with immense potential for tourism due to its natural beauty and cultural heritage. The country offers a diverse range of attractions for tourists, including pristine beaches, lush green forests, ancient archaeological sites, and vibrant cultural festivals.
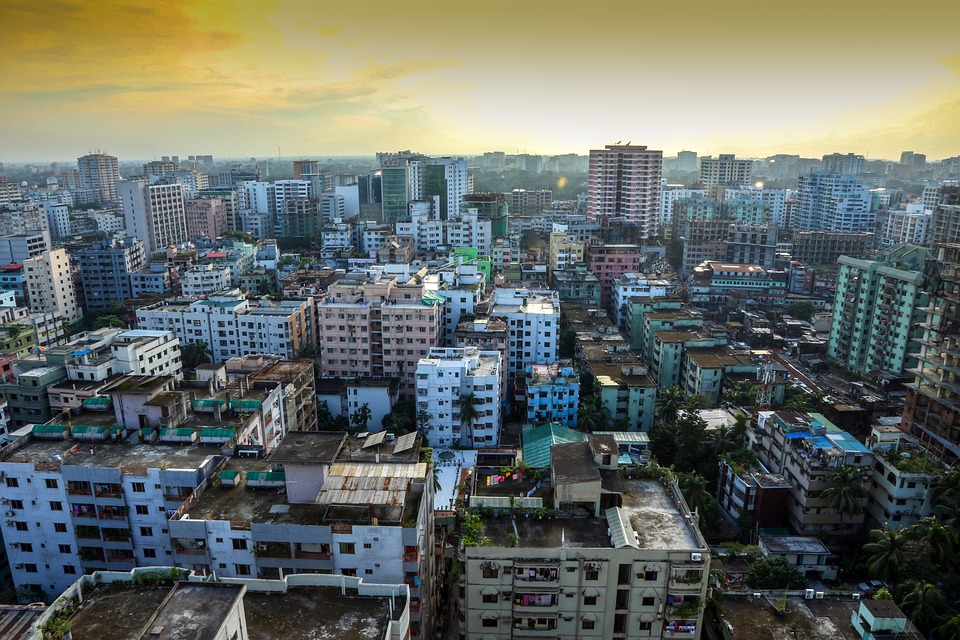
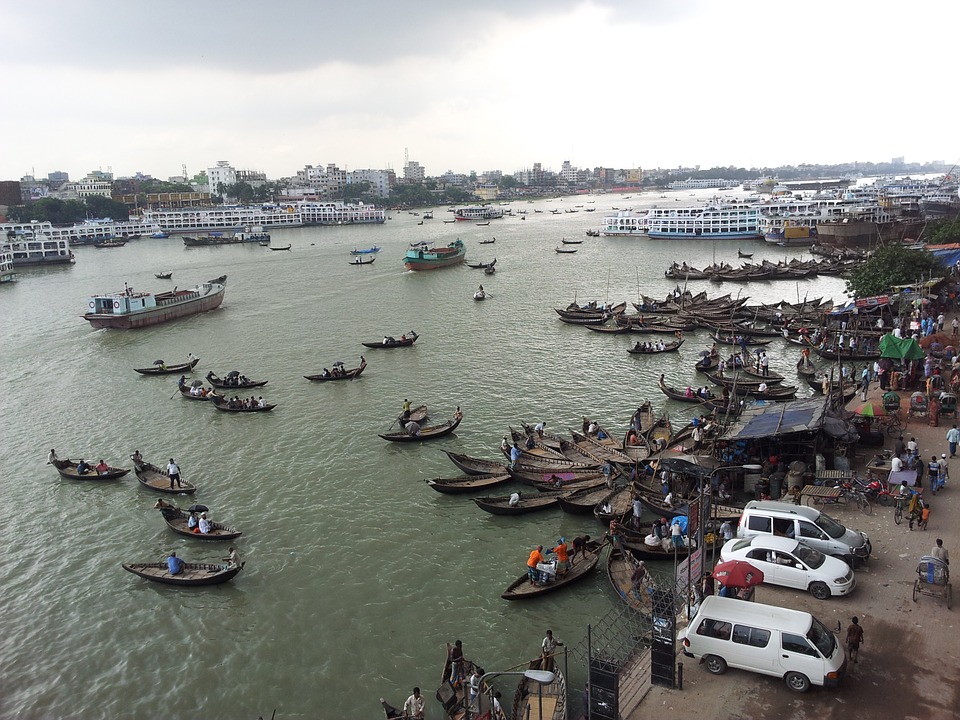
Some of the popular tourist destinations in Bangladesh include Cox’s Bazar, which is home to the world’s longest natural sandy beach, and the Sundarbans, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and the largest mangrove forest in the world. Other attractions include the historical city of Dhaka, the ancient ruins of Paharpur, and the tea gardens of Sylhet.
Bangladesh also has a rich cultural heritage, with a blend of Bengali, Mughal, and British influences. The country is known for its traditional music and dance forms, such as Baul music and Jatra performances. The vibrant festivals celebrated in Bangladesh, such as Pohela Boishakh (Bengali New Year) and Durga Puja, offer a glimpse into the country’s cultural traditions.
Despite its potential for tourism, Bangladesh has yet to fully capitalize on this sector. The government has taken steps to promote tourism and attract foreign investment, but there is a need for further infrastructure development and marketing efforts to attract more tourists to the country.
Environmental Issues in Bangladesh: Climate Change and Natural Disasters
Bangladesh is one of the most vulnerable countries in the world to climate change and natural disasters. The country is located in a low-lying delta region, making it prone to flooding and cyclones. Rising sea levels due to climate change pose a significant threat to coastal areas, where millions of people live.
In recent years, Bangladesh has experienced an increase in extreme weather events, including cyclones, floods, and droughts. These events have had devastating effects on the country’s infrastructure, agriculture, and livelihoods. The government has implemented various measures to mitigate the impact of climate change, including building cyclone shelters and embankments.
Efforts are also being made to promote sustainable development and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Bangladesh has set ambitious targets for renewable energy generation and has invested in solar power projects. The country is also working towards improving waste management and reducing pollution.
Future of Bangladesh: Opportunities and Challenges for Growth and Development
Bangladesh has great potential for economic growth and development in the coming years. The country’s strategic location, young and dynamic workforce, and emerging industries make it an attractive destination for foreign investment. The government has implemented various policies to promote investment and create a favourable business environment.
However, Bangladesh also faces several challenges that need to be addressed for sustained growth and development. These challenges include poverty, income inequality, corruption, inadequate infrastructure, and limited access to quality education and healthcare. The government needs to focus on addressing these issues and promoting inclusive growth.
In conclusion, Bangladesh is a land of diversity and culture with a rich history and vibrant society. The country has made significant progress in recent years in terms of economic growth, education, and healthcare. However, there are still challenges that need to be addressed for sustainable development. With the right policies and investments, Bangladesh has the potential to become a prosperous and developed nation in the future.
Population Density of Bangladesh
Bangladesh, a small country located in South Asia, is known for its high population density. With a land area of just 147,570 square kilometers, it is one of the most densely populated countries in the world. The population density of Bangladesh is estimated to be...
Terrain and Topography of Bangladesh: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Bangladesh, located in South Asia, is a country with a diverse and unique topography. From the mighty Himalayas in the north to the vast Ganges Delta in the south, Bangladesh’s terrain offers a wide range of landscapes and natural wonders. Understanding the...
Climate Zones of Bangladesh: Different Climate Regions Of Bangladesh
Bangladesh, located in South Asia, is a country known for its diverse geography and climate. It is bordered by India to the west, north, and east, and by Myanmar to the southeast. The country is home to a wide range of climate zones, each with its own unique...
Political Boundaries of Bangladesh: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Political boundaries refer to the demarcation lines that separate one political entity from another. These boundaries are crucial in defining the territorial limits of a country and determining its jurisdiction and governance. In the context of Bangladesh,...
Natural Resources of Bangladesh: Where Natural Resources are Located in Bangladesh
Natural resources refer to the materials or substances that occur naturally in the environment and are used by humans for various purposes. These resources can be classified into different categories such as forests, minerals, water, agricultural resources, fisheries...
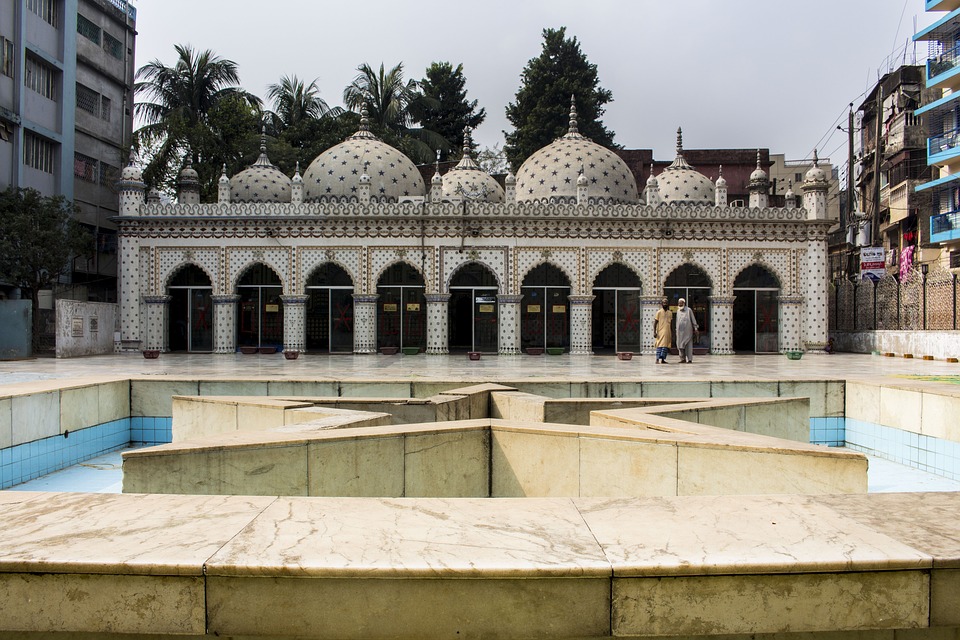
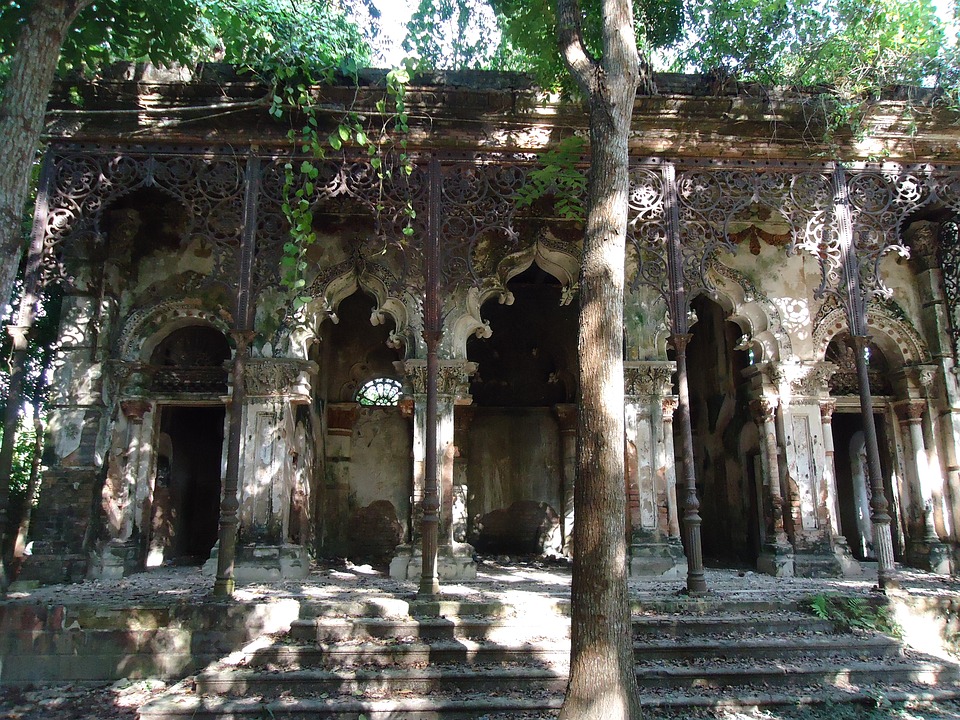
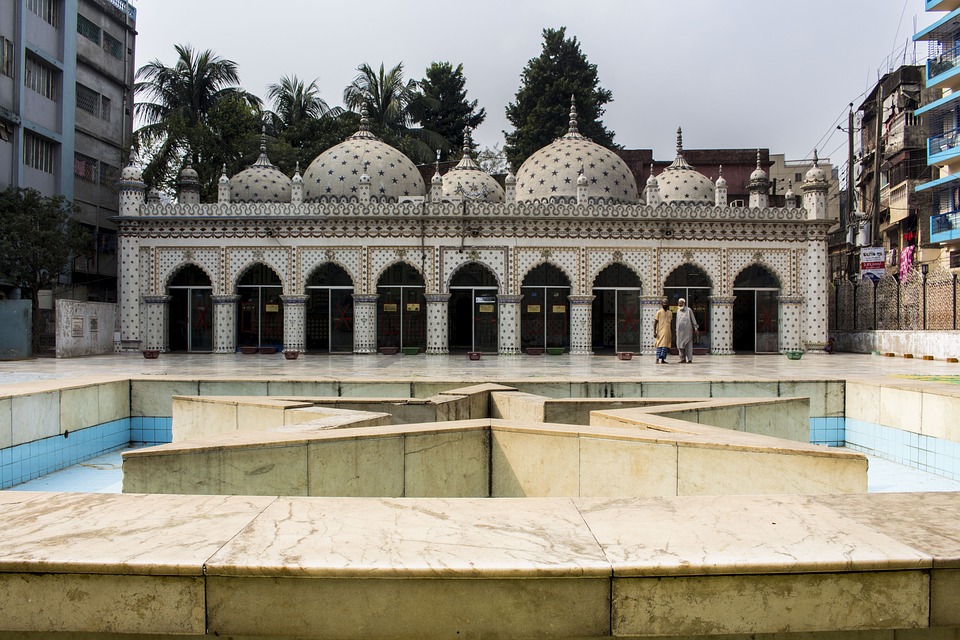
Cultural or Historical Sites of Bangladesh: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Bangladesh
Bangladesh, a country located in South Asia, is known for its rich cultural heritage. With a history that dates back thousands of years, Bangladesh has been influenced by various civilizations and empires, resulting in a diverse and vibrant culture. From ancient...
Unveiling the Hidden Beauty of Bangladesh: A Journey Through its Culture, Cuisine, and Scenic Landscapes
Nestled in South Asia, Bangladesh is a country that often goes unnoticed by travelers. However, those who venture to this enchanting land are rewarded with a wealth of cultural gems, natural wonders, and a rich history that dates back centuries. From its vibrant...