Biology (from the Latin ‘bios’ meaning life and ‘logia’ meaning study of) is the study of all organisms and all aspects of their life-cycles.
Biology
Biology (from the Latin ‘bios’ meaning life and ‘logia’ meaning study of) is the study of all organisms and all aspects of their life-cycles. The subject of Biology, as we know it today, was born in the nineteenth century along with physics, chemistry and the scientific method. Before then ‘Natural Philosophy’ which was the study of nature and the physical universe, included biology, chemistry and physics.
Natural Philosophy The study of our natural world is known to date back to the time of Mesopotamia around 3,100 BC but as this was the beginning of written historic record the study probably existed long before this time. Modern Biology The first great development of modern biology came from Charles Darwin, who is often referred to as the father of modern biology. Although known for his work ‘On the Origin of Species’ (published in 1859), Darwin produced nineteen additional publications, wrote hundreds of scientific papers and fourteen thousand letters, all of which laid the foundations for Biology as a subject we recognise today. Although he did not invent the theory of evolution, he certainly made the idea more accessible to the world. His theory was evolution by natural selection; where by an organism with a mutation may be better adapted to certain environmental changes and therefore improve their chance of survival. This means the organism with the useful mutation is more likely to survive, reproduce and hopefully pass on the useful mutation. Overtime species are able to adapt to the world around them and this process gave the Galapagos Islands (and the world) the rich diversity of its inhabitants. Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA was first discovered in 1869 but its role was not known at the time. It was in 1943 that it was discovered that it is DNA that is responsible for programming the genetic makeup of organisms and passing on the mutations Darwin had discovered. This new understanding of how amino acids are programmed on a cellular level to make up various parts of the organism was a huge leap forward but new profound discoveries are being made everyday in the field of biology.
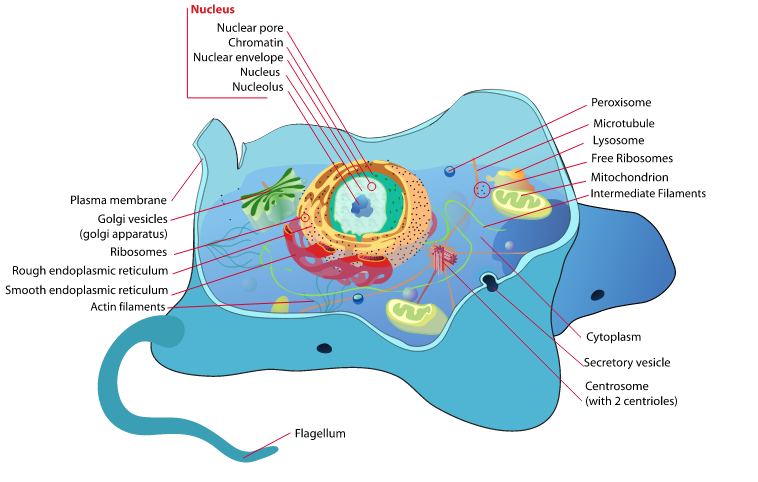
Exploring the Intricacies of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: A Journey into Cellular Biology
The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is a vital organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including protein synthesis, folding, and transport. The RER is characterized by its rough appearance due to the presence of...
Exploring the Intricacies of the Endoplasmic Reticulum: A Journey into the Cellular World
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a complex and dynamic organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including protein synthesis and folding, lipid metabolism, calcium signaling, cellular stress responses, autophagy, and...
Nucleus: The Central Command of the Cell – Understanding its Importance in Biology
The nucleus is a vital component of eukaryotic cells, serving as the control center that regulates all cellular activities. It is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the genetic material of the cell, including DNA and RNA. The nucleus plays a crucial role in cell...
Discovering the Commonalities: Unveiling the Similarities of Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells are a type of cell that make up the complex organisms we see around us, including plants, animals, fungi, and protists. These cells are characterized by having a distinct nucleus that houses their genetic material, as well as other membrane-bound...
The Complex World of Eukaryotic Cells: A Closer Look at the Building Blocks of Life
Eukaryotic cells are the building blocks of complex organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi. They are characterized by having a distinct nucleus that houses their genetic material, as well as other membrane-bound organelles. In contrast, prokaryotic cells,...
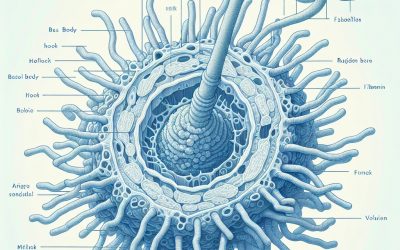
Uncovering the Wonders of Prokaryotic Flagellum: A Fascinating Look at Bacterial Movement
The prokaryotic flagellum is a whip-like appendage found on the surface of many bacteria. It is responsible for bacterial movement, allowing these microorganisms to navigate their environment and find optimal conditions for growth and survival. The flagellum is a...
Revolutionize Your Daily Routine with Capsule – The Ultimate Productivity Tool
In today’s fast-paced world, productivity has become a key factor in achieving success both personally and professionally. With so many tasks and responsibilities to juggle, it can be challenging to stay organized and focused. That’s where Capsule comes...
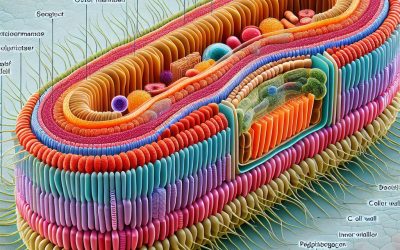
The Mighty Shield: Understanding the Importance of Bacteria Cell Wall in Microbial World
The bacteria cell wall is a crucial component of the microbial world. It provides structural support to the cell, protects against environmental stressors, plays a role in antibiotic resistance, impacts pathogenesis and disease, and has evolved over time to adapt to...
Nucleoid: The Central Hub of Bacterial DNA Organization
The nucleoid is a distinct region within bacterial cells where the genetic material, DNA, is located. Unlike eukaryotic cells, bacteria do not have a membrane-bound nucleus. Instead, their DNA is organized and compacted within the nucleoid. The nucleoid plays a...
Unleashing the Power of Plasmids: How Genetic Engineering is Revolutionizing Science
Genetic engineering is the process of manipulating an organism’s genetic material to alter its characteristics or create new traits. This field of science has revolutionized various industries, including medicine, agriculture, and environmental conservation. At...
Pili: The Superfood You Need to Add to Your Diet Now
Pili nuts, also known as Canarium ovatum, are a type of nut that is native to Southeast Asia, particularly the Philippines. They have been a staple in Filipino cuisine for centuries and are now gaining popularity worldwide as a nutritious superfood. Pili nuts are not...
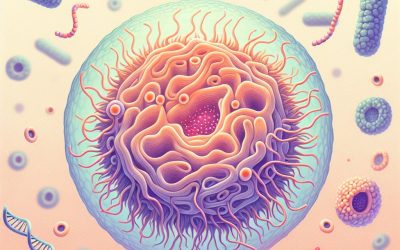
The Fascinating World of Bacteria Cells: Exploring the Microscopic Organisms that Rule our Planet
Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that are found in every corner of the Earth. They are among the oldest forms of life on our planet and have played a crucial role in shaping the world as we know it today. Bacteria are incredibly diverse and can be found in a...