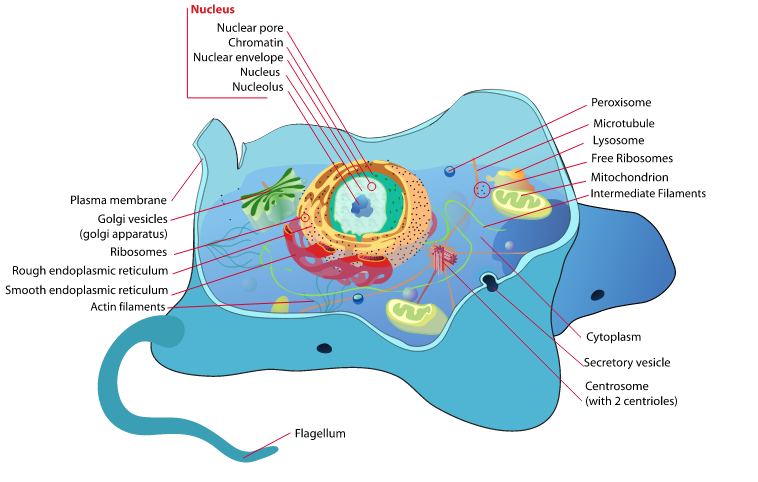
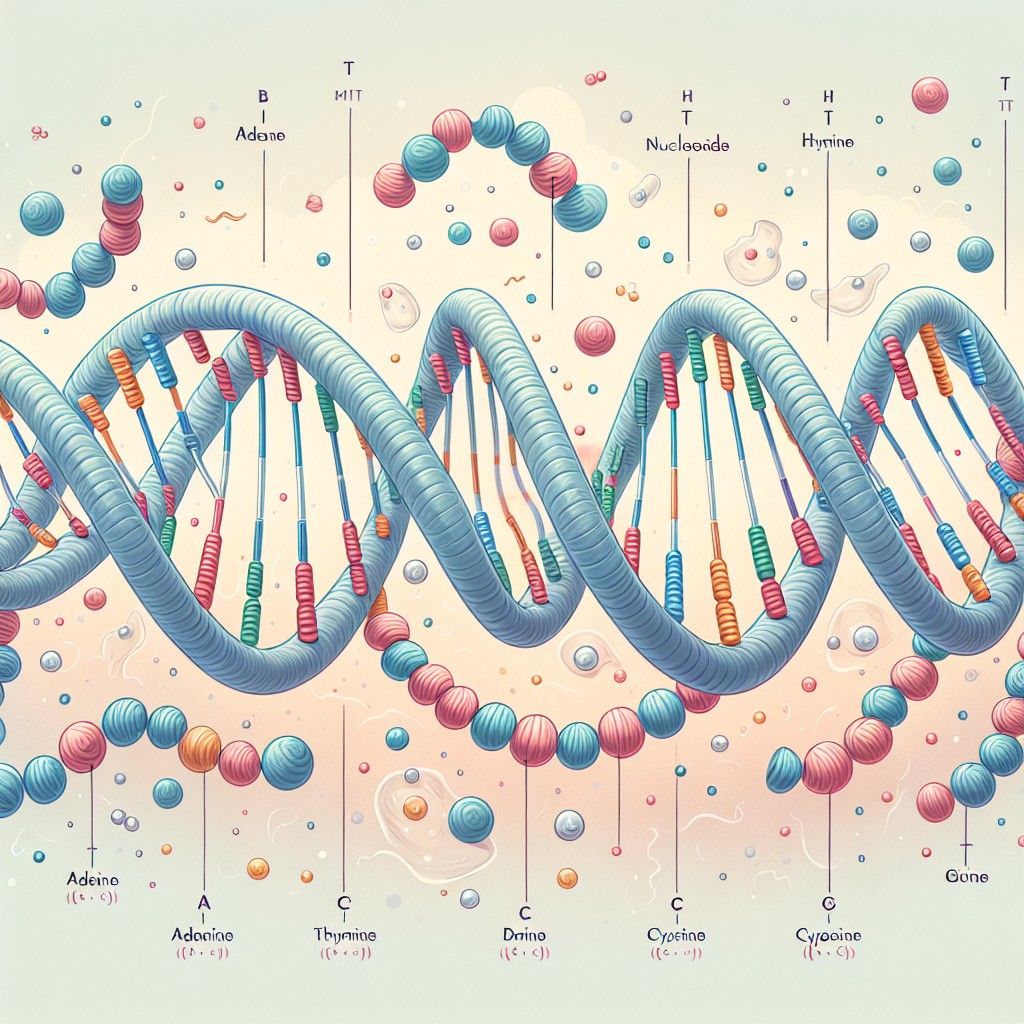
The nucleus is a vital component of eukaryotic cells, serving as the control center that regulates all cellular activities. It is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the genetic material of the cell, including DNA and RNA. The nucleus plays a crucial role in cell function, as it is responsible for regulating gene expression, controlling cell division, and maintaining genetic information.
Key Takeaways
- The nucleus is the control center of the cell, responsible for regulating cellular activities.
- The nucleus is composed of DNA, RNA, and proteins, and is surrounded by a nuclear envelope.
- The nucleus plays a crucial role in DNA replication, transcription, and translation.
- The nucleolus is responsible for ribosome synthesis, which is essential for protein production.
- The nucleus is involved in cell division and differentiation, and dysfunction can lead to various health issues.
The Structure and Composition of the Nucleus
The nucleus is surrounded by a double-layered membrane called the nuclear envelope. This envelope separates the contents of the nucleus from the rest of the cell and contains nuclear pores that allow for the exchange of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Within the nucleus, there are various components, including chromatin, nucleolus, and nucleoplasm.
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and proteins that make up the chromosomes. It is responsible for packaging and organizing the genetic material within the nucleus. The nucleolus is a distinct region within the nucleus where ribosomes are synthesized. It plays a crucial role in protein synthesis. The nucleoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the space between the nuclear envelope and chromatin.
The Functions of the Nucleus in the Cell
The nucleus performs several essential functions in the cell. One of its primary roles is to regulate gene expression. Gene expression refers to the process by which information encoded in DNA is used to synthesize proteins. The nucleus controls gene expression by selectively activating or deactivating specific genes.
The nucleus also plays a critical role in controlling cell division. It ensures that cells divide at the right time and in the right manner. This process is essential for growth, development, and tissue repair. The nucleus regulates cell division by coordinating DNA replication, chromosome segregation, and cytokinesis.
Furthermore, the nucleus is responsible for maintaining genetic information. It stores the DNA, which contains the instructions for building and maintaining an organism. The nucleus ensures the integrity of the genetic material by repairing DNA damage and preventing mutations.
The Importance of DNA and RNA in Nucleus Function
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| DNA | Contains genetic information that determines an organism’s traits and characteristics. |
| RNA | Transfers genetic information from DNA to ribosomes, where it is used to synthesize proteins. |
| Nucleus | Controls and regulates gene expression, cell division, and DNA replication. |
| Gene expression | The process by which genetic information is used to synthesize proteins and determine an organism’s traits. |
| Cell division | The process by which a single cell divides into two or more daughter cells, allowing for growth and repair of tissues. |
| DNA replication | The process by which DNA is copied before cell division, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic information. |
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are two types of nucleic acids that play crucial roles in nucleus function. DNA is the genetic material that carries the instructions for building and maintaining an organism. It is a long, double-stranded molecule that is tightly coiled into chromosomes within the nucleus.
RNA, on the other hand, is involved in gene expression. It acts as a messenger between DNA and the ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis. RNA molecules are transcribed from DNA and then translated into proteins.
The Role of the Nucleolus in Ribosome Synthesis
The nucleolus is a distinct region within the nucleus that plays a crucial role in ribosome synthesis. Ribosomes are cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis. They are composed of RNA and proteins.
The nucleolus contains the genes that encode for ribosomal RNA (rRNA). These genes are transcribed into rRNA molecules, which then combine with proteins to form ribosomes. The nucleolus also serves as a site for ribosome assembly.
Ribosomes are essential for protein synthesis, as they read the mRNA (messenger RNA) and translate it into proteins. Without functional ribosomes, cells would not be able to produce proteins, which are essential for all cellular processes.
The Connection between the Nucleus and Protein Synthesis

Protein synthesis is a complex process that occurs in multiple steps, with the nucleus playing a crucial role in this process. It begins with transcription, where DNA is transcribed into mRNA. This process occurs within the nucleus.
Once transcribed, mRNA molecules exit the nucleus through nuclear pores and enter the cytoplasm, where they are translated into proteins by ribosomes. The nucleus controls protein synthesis by regulating gene expression and determining which genes are transcribed into mRNA.
The Significance of Mitosis and Meiosis in Nucleus Replication
Mitosis and meiosis are two types of cell division that involve the replication of the nucleus. Mitosis is the process by which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It is essential for growth, development, and tissue repair.
Meiosis, on the other hand, is a specialized form of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells. It involves two rounds of division and results in the production of four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity.
Nucleus replication is essential in both mitosis and meiosis, as it ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic material. Without proper nucleus replication, errors can occur, leading to genetic abnormalities and diseases.
The Role of the Nucleus in Cell Division and Differentiation
Cell division and differentiation are two fundamental processes in multicellular organisms. Cell division allows for growth, development, and tissue repair, while cell differentiation leads to the formation of specialized cell types.
The nucleus plays a crucial role in both processes. During cell division, the nucleus coordinates DNA replication, chromosome segregation, and cytokinesis to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic material.
In cell differentiation, the nucleus controls gene expression to determine which genes are turned on or off in different cell types. This regulation allows cells to acquire specific functions and characteristics.
Stem cells are a unique type of cell that has the ability to differentiate into various cell types. The nucleus plays a critical role in stem cell research, as scientists study how the nucleus controls cell differentiation. Understanding this process can lead to advancements in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
The Impact of Nucleus Dysfunction on Human Health
Dysfunction of the nucleus can have severe consequences for human health. Many diseases are caused by mutations or abnormalities in the genes that control nucleus function.
For example, certain types of cancer are caused by mutations in genes that regulate cell division and DNA repair. These mutations can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and the formation of tumors.
Other diseases, such as genetic disorders, are caused by mutations in specific genes that affect nucleus function. These mutations can result in a wide range of symptoms and health problems.
Studying nucleus dysfunction is crucial for understanding the underlying causes of these diseases and developing effective treatments. Advances in nucleus research have led to the development of targeted therapies and gene editing techniques that show promise in treating genetic disorders and cancer.
Advances in Nucleus Research and Future Directions in Biology
In recent years, there have been significant advances in nucleus research, leading to a better understanding of its structure, function, and role in cellular processes. New technologies, such as high-resolution microscopy and genome sequencing, have allowed scientists to study the nucleus in more detail than ever before.
Future directions in nucleus research include further exploration of its role in gene expression, cell division, and differentiation. Scientists are also studying how changes in nucleus structure and function contribute to aging and age-related diseases.
Nucleus research is not only important for advancing our understanding of biology but also for developing new treatments for diseases. Targeted therapies that specifically target nucleus dysfunction are being developed, offering hope for improved treatments and outcomes for patients.
In conclusion, the nucleus is a vital organelle that serves as the control center of the cell. It regulates gene expression, controls cell division, and maintains genetic information. DNA and RNA play crucial roles in nucleus function, with DNA storing genetic information and RNA involved in gene expression. The nucleolus is responsible for ribosome synthesis, which is essential for protein synthesis. Dysfunction of the nucleus can have severe consequences for human health, leading to diseases such as cancer and genetic disorders. Advances in nucleus research have led to a better understanding of its structure and function, with future directions focusing on its role in cellular processes and disease treatment.
FAQs
What is a nucleus?
A nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells that contains the genetic material of the cell in the form of DNA.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The main function of the nucleus is to control gene expression and regulate cell growth and division. It also plays a role in the synthesis of RNA and the assembly of ribosomes.
What is the structure of the nucleus?
The nucleus is typically spherical or oval in shape and is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope has pores that allow for the exchange of materials between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The interior of the nucleus contains chromatin, which is composed of DNA and proteins, and a nucleolus, which is responsible for the synthesis of ribosomal RNA.
What types of cells have a nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. Eukaryotic cells include animal, plant, and fungal cells.
What happens if the nucleus is damaged or removed?
If the nucleus is damaged or removed, the cell may not be able to carry out its normal functions, including DNA replication and gene expression. This can lead to cell death or disease.