Biology (from the Latin ‘bios’ meaning life and ‘logia’ meaning study of) is the study of all organisms and all aspects of their life-cycles.
Biology
Biology (from the Latin ‘bios’ meaning life and ‘logia’ meaning study of) is the study of all organisms and all aspects of their life-cycles. The subject of Biology, as we know it today, was born in the nineteenth century along with physics, chemistry and the scientific method. Before then ‘Natural Philosophy’ which was the study of nature and the physical universe, included biology, chemistry and physics.
Natural Philosophy The study of our natural world is known to date back to the time of Mesopotamia around 3,100 BC but as this was the beginning of written historic record the study probably existed long before this time. Modern Biology The first great development of modern biology came from Charles Darwin, who is often referred to as the father of modern biology. Although known for his work ‘On the Origin of Species’ (published in 1859), Darwin produced nineteen additional publications, wrote hundreds of scientific papers and fourteen thousand letters, all of which laid the foundations for Biology as a subject we recognise today. Although he did not invent the theory of evolution, he certainly made the idea more accessible to the world. His theory was evolution by natural selection; where by an organism with a mutation may be better adapted to certain environmental changes and therefore improve their chance of survival. This means the organism with the useful mutation is more likely to survive, reproduce and hopefully pass on the useful mutation. Overtime species are able to adapt to the world around them and this process gave the Galapagos Islands (and the world) the rich diversity of its inhabitants. Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA was first discovered in 1869 but its role was not known at the time. It was in 1943 that it was discovered that it is DNA that is responsible for programming the genetic makeup of organisms and passing on the mutations Darwin had discovered. This new understanding of how amino acids are programmed on a cellular level to make up various parts of the organism was a huge leap forward but new profound discoveries are being made everyday in the field of biology.
Sydney Funnel-web Spider: The Deadly Arachnid Lurking in Australia’s Backyard
The Sydney Funnel-web Spider (Atrax robustus) is widely regarded as Australia’s most dangerous arachnid. Found primarily in the Sydney region, this spider is known for its highly venomous bite, which can be fatal if left untreated. Understanding the dangers...
Arachnophobia Alert: The Deadly Bite of the Brazilian Wandering Spider (Phoneutria spp.)
The Brazilian Wandering Spider, also known as the banana spider or armed spider, is a highly venomous spider that is native to South and Central America. It belongs to the genus Phoneutria, which means “murderess” in Greek, and is considered one of the...
Cells Test – Cell Structure Test
Your Cells Test may take a minute to load. If you have to navigate away from this page for any reason, don’t worry, you will have the option to resume your test from the point you left upon your return. The test may have multiple choice,...
Animal Phylum – Phyla
Kingdom Animalia – Phylum (Phyla = plural): (within the animal kingdom there are some 36 phyla but of these phyla there are nine that are most commonly used. These nine are listed first) What are Phyla or Phylum? The Most Common Phyla Annelida Arthropoda or...
Taxonomy – The Classification of Organisms
Taxonomy is a branch of biology concerned with the classification of organisms into groups such as Kingdom, Phylum, Class etc. History of Taxonomy Modern Taxonomy History of Taxonomy Over the ages many people have set out to categorise the world around...
Mammals
The term Mammals is the name given to a group of animals that produce milk for their young (in mammary glands) which currently accounts for 5,000 species. What are Mammals? Rise of mammals Common characteristics Hair Three Middle Ear Bones Milk...
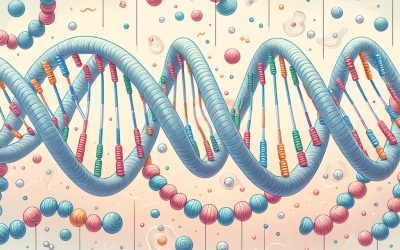
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is found in every cell of every living organism on the planet. It is the code which contains the genetic makeup of the organism. The Structure of DNA Polynucleotides Dideoxynucleic acid molecule consisting of...
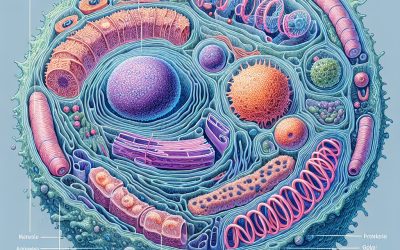
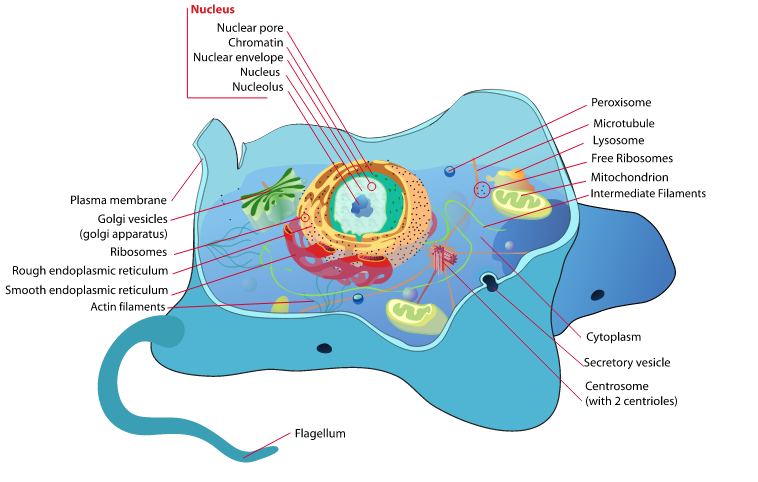
Cells and Cell Structure
The term organism means anything that is living and all organisms whether they are plant, animal, bacteria are made of microscopic cells, each type with unique cell structure. Common Characteristics of all cells Cytoplasm Plasma Membrane Ribosomes Types of...