Boron is a relatively rare metalloid both on earth and in the rest Universe. It is produced from cosmic rays and extracted from Borate minerals.
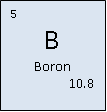
Classification: Metalloid
Atomic Mass: 10.811 (7) g/mol
Density: 2.34g/cm3
Colour: black
Boiling Point: 4200K (3927°C)
Melting Point: 2349K (2076°C)
Discovery of Boron
Boron (5B) compounds were used by ancient civilizations for thousands of years but the element itself wasn’t isolated until 1828. English Chemist Sir Humphrey Davy (whose assistant was Michael Faraday) originally used electrolysis to create 5B from a borates solution and named the substance boracium. Later he used boric acid combined with potassium to produce a purer form of 5B. This method was used by French chemists Joseph-Louis Gay-Lussac and Louis-Jaques Thénard
Sources
Commercially 5B is obtained by heating borax (Na2B4O7 10H2O) with carbon.
Uses
Boron can be taken as a dietary supplement and found naturally in various foods. Some evidence has shown that boron in your diet can help reduce bone loss, reduce the symptoms of osteoarthritis, improve cognative ability and cordination in older people and increase testosterone levels. There is not yet enough evidence to prove conclusively that this is the case. 5B is found naturally in fruits (such as raisins, avacado, prunes, apricots) beans and nuts (particularly brazil, hazil and cashew) or taken in supplements though anymore than 20mg a day is considered dangerous and believed to reduce an adult males ability to father a child. 5B was also used as a preservative during World War I and II.
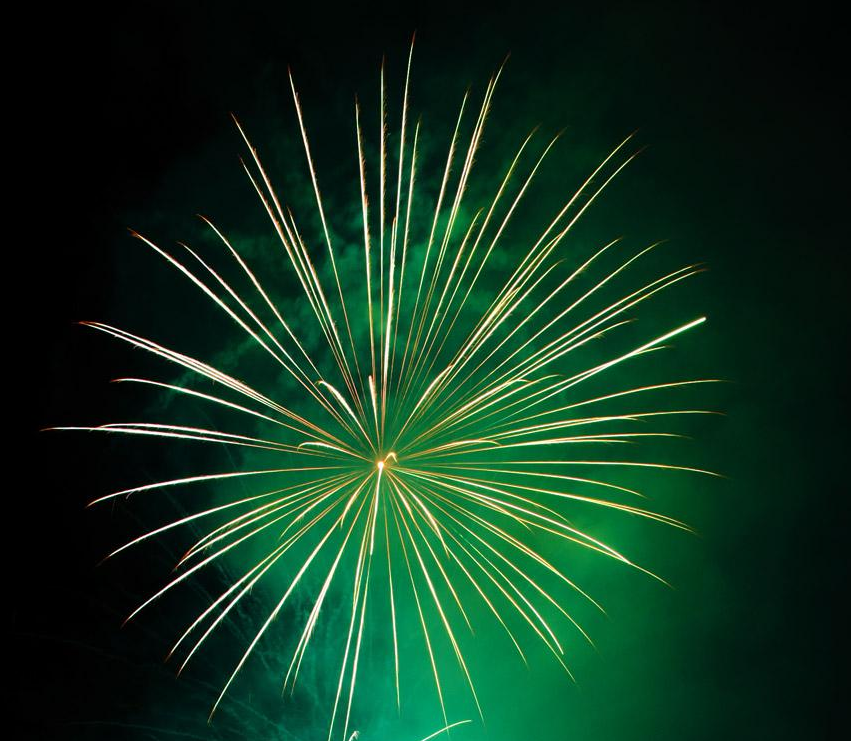
When ignited boron produces a green flame which is used in flares and pyrotechnics like fireworks.
An isotope of 5B (boron-10) is good at absorbing neutrons making it ideal for applications in the nuclear industry. It is used in control rods of nuclear reactors and in neutron detectors.
Boric acid is the most common form of Borate and used in capsule form to treat yeast infections. It can also be applied to skin as an astringent or to prevent infection and sometimes used as an ingredient in eye wash.
Fiberglass insulation is made from a compound of 5B called sodium tetraborate decahydrate and some glasses are also made from a boron compound.
5B is also used in Sodium perborate a mixture of hydrogen peroxide and sodium borate that is soluble in water and releases hydrogen peroxide. Sodium perborate is used as a bleaching agent in industrial detergents.
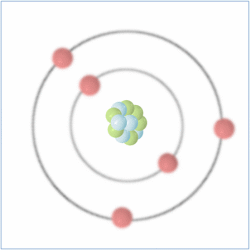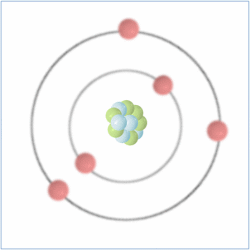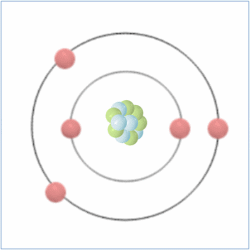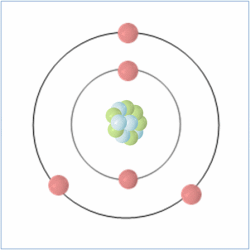
Shell Structure
<p”>
Protons = 5
Neutrons = 6
Electrons= 5
|
|
s |
p |
d |
f |
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
1 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
Absorption Lines
Emission Lines