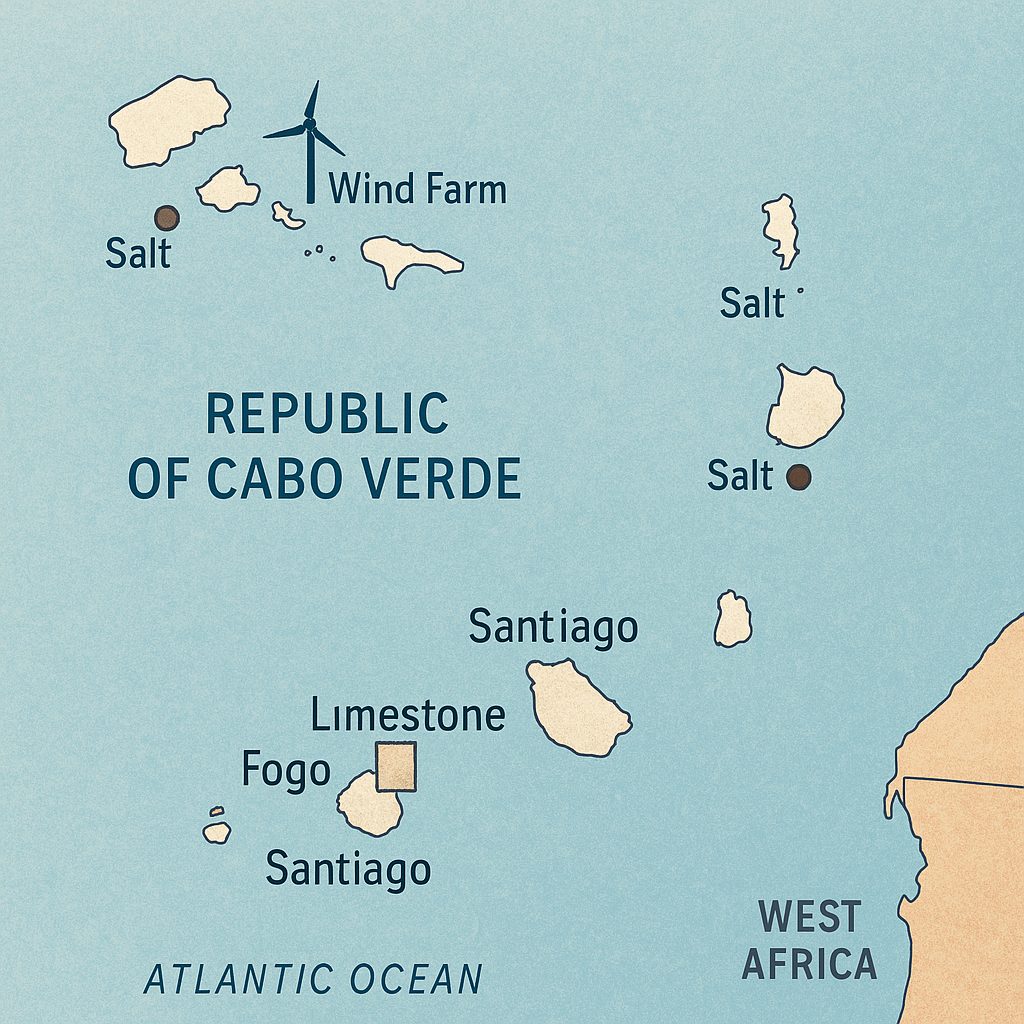
Natural Resources of Cape Verde: Where Natural Resources Are in Cabo Verde
Cape Verde, also known as Cabo Verde, is a stunning island nation in the Atlantic Ocean off the west coast of Africa. Although it’s famous for its beautiful beaches and thriving tourism sector, there’s more to explore beneath the surface. This article dives deep into Cape Verde’s natural resources, examining how this archipelago manages to thrive with limited natural wealth. From renewable energy efforts to unique geological formations, this post is a must-read for anyone interested in sustainable development, energy resources, and economic resilience in small island nations.
Article Outline
-
Where is Cape Verde and What Makes It Unique?
-
Does Cape Verde Have Abundant Natural Resources?
-
What Are the Mineral Resources in Cape Verde?
-
How Important Is Agriculture in Cabo Verde?
-
What Role Does Renewable Energy Play in Cape Verde’s Economy?
-
How Are Water Resources Managed in Cape Verde?
-
Why Is Tourism So Important for the Cape Verde Islands?
-
What Is the Government of Cape Verde Doing to Boost Resource Efficiency?
-
How Did Cape Verde’s Strategic Location Shape Its Resource Use?
-
What Can Other Nations Learn from Cabo Verde’s Development Model?
1. Where is Cape Verde and What Makes It Unique?
Cape Verde is an island nation located in the Atlantic Ocean, around 570 kilometers off the west coast of Africa. It comprises ten main islands and several smaller islets, forming the Cape Verde archipelago. The islands are split into two groups: Barlavento (windward) and Sotavento (leeward).
The cape verde islands are volcanic islands, which contributes to their rugged terrain and limited arable land. The island of Fogo, for instance, is home to an active volcano, Pico do Fogo, and its unique volcanic soil affects both habitation and agriculture. Despite being uninhabited until the 15th century, when the Portuguese arrived, Cape Verde became a strategic port, especially as mid-Atlantic shipping lanes made Cape Verde an ideal hub for trans-Atlantic navigation.
2. Does Cape Verde Have Abundant Natural Resources?
Contrary to many of its African neighbors, Cape Verde has few natural resources. In fact, verde has limited mineral or energy resources, and the limited natural resources challenge both industrial development and food security.
Some natural resources include salt, limestone, and basalt, often used in cement production. However, these resources in Cape Verde are not in quantities large enough to sustain major export industries. As a result, Cabo Verde’s economic model leans more on services, tourism, and renewable energy than traditional resource extraction.
3. What Are the Mineral Resources in Cape Verde?
Mineral resources in Cape Verde are sparse but not nonexistent. The islands contain small deposits of limestone, basalt, and pozzolana — a volcanic ash used in construction. These are primarily used in cement production and are not significant export commodities.
One key site is the island of Fogo, where volcanic activity has created a geology suitable for cement and stone materials. The islands of Sal and Boa Vista also contain salt pans, as resources include salt, traditionally used for both domestic consumption and limited export.
4. How Important Is Agriculture in Cabo Verde?
Agriculture plays a minor but symbolic role in Cape Verde’s economy. The arable land is extremely limited, and significant agricultural production is hampered by frequent droughts, scarce water, and volcanic terrain.
Most agricultural production occurs on the island of Santiago, the largest and most populous island. Here, Cape Verdeans grow corn, beans, sweet potatoes, and bananas primarily for local consumption. Yet, only a small percent of the population is engaged in full-time farming, and the sector struggles to meet domestic demand.
5. What Role Does Renewable Energy Play in Cape Verde’s Economy?
Given the scarcity of fossil fuels, renewable energy has become a cornerstone of development in Cape Verde. The government of Cape Verde has committed to an ambitious energy transition plan aiming for 100% renewable electricity generation in the future.
Wind and solar are the primary sources. The Sal and Boa Vista islands host wind farms, while solar panels dot many rural areas. These systems are vital to reducing dependency on imported fuel and promoting renewable energy and energy efficiency.
The emphasis on renewable energy aligns with global sustainability goals and showcases Cape Verde as a model for small island nation innovation in the face of limited natural resources.
6. How Are Water Resources Managed in Cape Verde?
Water resources are among the most challenging issues for Cape Verde. The country lacks rivers and large freshwater lakes, relying mainly on underground aquifers, desalination, and rainwater harvesting.
To improve water resources, Cape Verdean authorities have implemented desalination plants, especially on dry islands like Sal and Boa Vista. Despite these efforts, water scarcity remains a significant barrier to both agriculture and human development. Innovative conservation and recycling techniques are crucial for managing this scarce resource.
7. Why Is Tourism So Important for the Cape Verde Islands?
With Cape Verde has few natural exploitable resources, tourism has emerged as a vital economic pillar. Its sunny climate, beautiful beaches, and cultural richness draw visitors primarily to islands like Sal, Boa Vista, and Fogo.
The international airport on Sal supports much of the country’s tourism activity. This industry helps offset the economic limitations imposed by limited natural resources and generates income for thousands of cabo verdeans.
Tourism not only boosts the domestic economy through remittances and services but also encourages infrastructure development and international investment in the verde archipelago.
8. What Is the Government of Cape Verde Doing to Boost Resource Efficiency?
The government of Cape Verde has focused on sustainable development through infrastructure, education, and renewable technology investments. With help from international donors and development agencies, it has built solar parks, wind farms, and water desalination plants.
Public-private partnerships also play a role in boosting energy resources and expanding access to electricity, particularly on remote or less inhabited islands like Santo Antão. Efforts continue to improve waste management, energy efficiency, and conservation programs to stretch the country’s limited natural assets.
9. How Did Cape Verde’s Strategic Location Shape Its Resource Use?
Cape Verde’s strategic location along transatlantic maritime routes gave it historic importance for trade and refueling. In colonial times, Portugal changed Cape Verde’s status to a major port and slave trade hub.
Later, the independence of Cape Verde in 1975 led to political and economic restructuring. Despite cape verde and portuguese guinea initially forming a single liberation movement — the African Party for the Independence — the two eventually separated paths.
Today, the country’s geographic position is still advantageous. The shipping lanes made Cape Verde a stopover for airlines and sea vessels, facilitating cape verde’s economy and integration into global systems.
10. What Can Other Nations Learn from Cabo Verde’s Development Model?
Despite its limited natural resources, Cabo Verde is often praised for good governance, political stability, and sustainable development. The political conditions in Cape Verde have enabled long-term planning and significant strides in health, education, and infrastructure.
Other nations, particularly those with scarce mineral resources, can study Cape Verde’s strategic use of renewable energy, tourism, and international cooperation. The role of the cape verde government, especially in environmental stewardship, offers a blueprint for resilience and innovation under constraint.
Summary: Key Takeaways on Cape Verde’s Natural Resources
-
Cape Verde, also called Cabo Verde, is a volcanic archipelago with ten main islands in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of West Africa.
-
It has limited natural resources, including salt, limestone, and volcanic rock, mostly used in cement production.
-
Cape Verde has few natural exploitable resources, making sectors like tourism and renewable energy critical.
-
Agricultural production is minimal due to poor soil and water resources.
-
The government of Cape Verde promotes renewable energy and energy efficiency with wind farms and solar projects on Sal, Boa Vista, and other islands.
-
Water scarcity is a major issue managed through desalination and conservation.
-
Cape Verde’s strategic location along mid-Atlantic shipping lanes historically boosted its geopolitical importance.
-
The verde became independent in 1975, and cape verdeans elected a national government that emphasized development and sustainability.
-
Cape Verde remains an example of how innovation, governance, and geographic advantage can overcome limited natural wealth.
-
Key islands like Fogo, Sal, and Boa Vista are central to both the economic and environmental narrative of the country.
The Geographical Location of Cape Verde’s Natural Resources
Cape Verde is situated in the Atlantic Ocean, approximately 570 kilometers off the coast of Senegal. The archipelago consists of ten main islands and several smaller ones. Its location has a significant impact on the natural resources found in Cape Verde. The islands are volcanic in origin, resulting in a diverse terrain that includes mountains, valleys, and coastal plains.
The climate in Cape Verde is classified as tropical dry, with a rainy season from August to October. The islands receive limited rainfall, making water scarcity a significant challenge for the country. The combination of volcanic soil and limited rainfall has shaped the agricultural potential of Cape Verde. However, the islands’ location also provides opportunities for renewable energy generation, as they are exposed to strong winds and abundant sunlight.
Overview of Cape Verde’s Mineral Resources
Cape Verde has a variety of mineral resources, although they are not extensively exploited. Some of the minerals found in the country include limestone, pozzolana (a volcanic ash used in cement production), clay, and salt. Limestone is used for construction purposes, while pozzolana is an essential ingredient in cement manufacturing.
The mining industry in Cape Verde is relatively small but has the potential for growth. The government has taken steps to attract foreign investment and promote mining activities in the country. However, challenges such as limited infrastructure and a lack of skilled labor hinder the development of the sector. Additionally, the sustainable management of mineral resources is crucial to avoid environmental degradation and ensure long-term benefits for the country.
Cape Verde’s Agricultural Resources: Crops and Livestock
| Category | Metric | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Crops | Arable land | 10.53% |
| Crops | Permanent crops | 1.32% |
| Crops | Land under irrigation | 10 km² |
| Livestock | Cattle | 50,000 |
| Livestock | Goats | 200,000 |
| Livestock | Sheep | 50,000 |
Agriculture plays a vital role in Cape Verde’s economy, employing a significant portion of the population and contributing to food security. The main crops grown in the country include maize, beans, cassava, sweet potatoes, and bananas. Livestock farming is also prevalent, with cattle, goats, and poultry being the primary livestock raised.
However, Cape Verde faces several challenges in its agricultural sector. The limited availability of arable land and water resources restricts agricultural production. The country heavily relies on food imports to meet its needs, making it vulnerable to price fluctuations and supply disruptions. Climate change and desertification further exacerbate these challenges, as they lead to decreased rainfall and increased soil erosion.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for agricultural development in Cape Verde. The government has implemented initiatives to promote sustainable farming practices and improve irrigation systems. Additionally, there is potential for agro-tourism, where visitors can experience local agriculture and contribute to the local economy.
The Potential of Cape Verde’s Fishing Industry
Cape Verde’s location in the Atlantic Ocean provides abundant fish stocks and a thriving fishing industry. The country’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) covers approximately 800,000 square kilometers, offering vast opportunities for commercial fishing. Tuna, lobster, shrimp, and various species of fish are among the main catches in Cape Verde.
The fishing industry in Cape Verde faces challenges such as overfishing and illegal fishing by foreign vessels. These activities threaten the sustainability of fish stocks and the livelihoods of local fishermen. However, the government has implemented measures to combat illegal fishing and promote sustainable fishing practices.
There are also opportunities for value-added activities in the fishing sector, such as fish processing and aquaculture. These activities can create employment opportunities and increase the value of fish exports. Additionally, the development of eco-tourism centered around fishing can contribute to the local economy while promoting conservation efforts.
Cape Verde’s Renewable Energy Resources
Cape Verde has abundant renewable energy resources, particularly wind and solar energy. The islands’ exposure to strong winds and ample sunlight makes them ideal for harnessing these energy sources. The government has recognized the potential of renewable energy and has implemented initiatives to promote its development.
Wind farms have been established on several islands, providing a significant portion of the country’s electricity needs. Solar power plants and solar water heaters are also becoming increasingly common. These renewable energy sources not only reduce reliance on fossil fuels but also contribute to the country’s energy security and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
However, challenges such as limited funding and technical expertise hinder the widespread adoption of renewable energy in Cape Verde. The government is working to address these challenges by attracting investment and providing incentives for renewable energy projects. The development of a sustainable energy sector can create jobs, reduce energy costs, and improve access to electricity in remote areas.
The Role of Water Resources in Cape Verde’s Development
Water scarcity is a significant challenge in Cape Verde due to its limited rainfall and arid climate. The country relies heavily on desalination plants and imported water to meet its water needs. However, these solutions are costly and not sustainable in the long term.
To address water scarcity, the government has implemented measures to manage and conserve water resources effectively. These include the construction of reservoirs, rainwater harvesting systems, and the promotion of water-saving practices. Additionally, there is potential for wastewater treatment and reuse to meet non-potable water demands.
Investing in water infrastructure and management can have multiple benefits for Cape Verde. It can improve access to clean drinking water, support agricultural production, and promote tourism. Furthermore, sustainable water management is crucial for preserving the country’s fragile ecosystems and biodiversity.
Biodiversity in Cape Verde: Endemic Species and Conservation Efforts
Cape Verde is home to a unique biodiversity, with many species found nowhere else in the world. The islands’ isolation and diverse habitats have contributed to the evolution of endemic plants, birds, reptiles, and marine life. However, this biodiversity is under threat from human activities, climate change, and invasive species.
Conservation efforts in Cape Verde aim to protect and restore the country’s natural habitats and endemic species. National parks and protected areas have been established to preserve biodiversity and promote eco-tourism. Additionally, initiatives are in place to raise awareness about the importance of conservation and involve local communities in sustainable practices.
Challenges in biodiversity conservation include limited funding, inadequate enforcement of regulations, and a lack of capacity for research and monitoring. However, there are opportunities for sustainable development through eco-tourism, research collaborations, and partnerships with international organizations.
Challenges and Opportunities in Harnessing Cape Verde’s Natural Resources
Cape Verde faces several challenges in harnessing its natural resources for sustainable development. Limited infrastructure, including transportation networks and energy grids, hinders the exploitation of mineral resources and the distribution of agricultural products. Additionally, a lack of skilled labor and technical expertise poses challenges in various sectors.
Climate change is another significant challenge for Cape Verde’s natural resources. Rising temperatures, decreased rainfall, and increased frequency of extreme weather events threaten agricultural production, water availability, and biodiversity. Adapting to these changes requires investment in climate-resilient infrastructure and the promotion of sustainable practices.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for sustainable development and growth in Cape Verde. The country can leverage its renewable energy potential to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote clean energy solutions. Investing in agriculture can improve food security, create employment opportunities, and reduce dependence on food imports. Additionally, eco-tourism and conservation efforts can contribute to the local economy while preserving the country’s unique natural heritage.
The Future of Cape Verde’s Natural Resources
Cape Verde’s natural resources hold significant potential for sustainable development and growth. The country’s mineral resources, agricultural land, fish stocks, renewable energy sources, water, and biodiversity provide opportunities for economic diversification and job creation. However, harnessing these resources effectively requires addressing challenges such as limited infrastructure, climate change, and a lack of technical expertise.
The government of Cape Verde has recognized the importance of sustainable resource management and has implemented initiatives to promote renewable energy, conservation, and water management. These efforts, combined with investment from the private sector and international collaborations, can pave the way for a prosperous future for Cape Verde.
By harnessing its natural resources in a sustainable manner, Cape Verde can achieve economic growth, improve living standards, and preserve its unique natural heritage for future generations. With careful planning and effective management, the country can become a model for sustainable development in the region.
FAQs
What are the natural resources of Cape Verde?
Cape Verde’s natural resources include salt, basalt rock, limestone, kaolin, fish, and agricultural land.
Where is salt found in Cape Verde?
Salt is found in the salt flats of Sal Island, Boa Vista Island, and Maio Island.
Where is basalt rock found in Cape Verde?
Basalt rock is found in the islands of Santiago, Fogo, and Brava.
Where is limestone found in Cape Verde?
Limestone is found in the islands of Santo Antão, São Nicolau, and São Vicente.
Where is kaolin found in Cape Verde?
Kaolin is found in the island of São Nicolau.
What types of fish are found in Cape Verde?
Cape Verde’s waters are rich in fish, including tuna, marlin, swordfish, grouper, and snapper.
How much agricultural land does Cape Verde have?
Cape Verde has approximately 10% of its land dedicated to agriculture, with crops such as corn, beans, sweet potatoes, and bananas being grown.