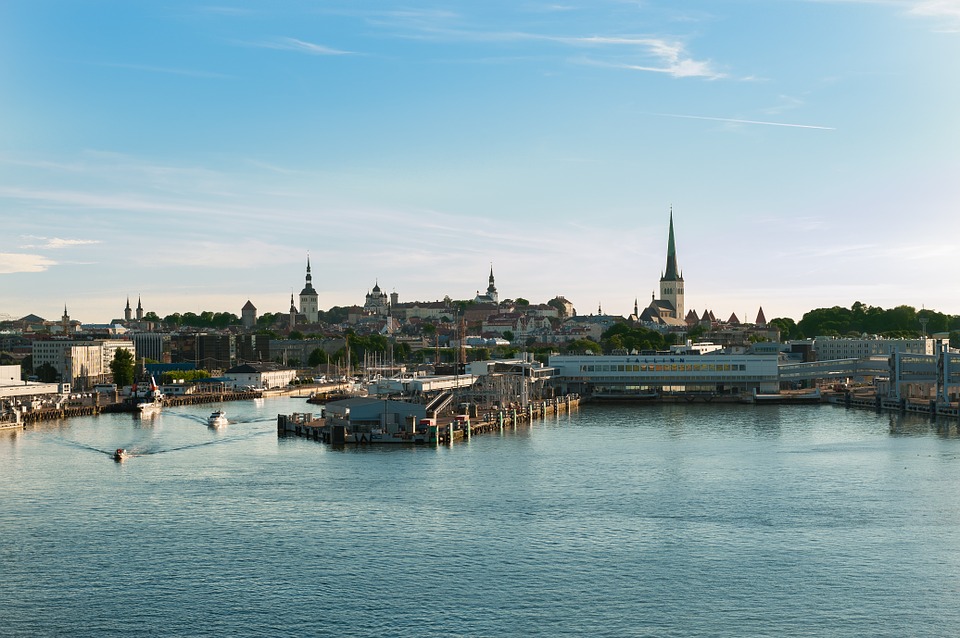
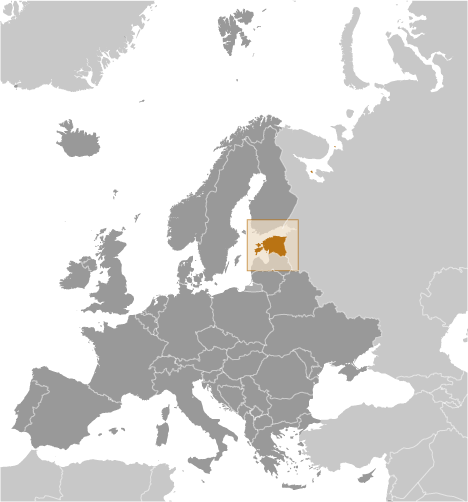
Estonia
(Eesti Vabariik (Republic of Estonia))
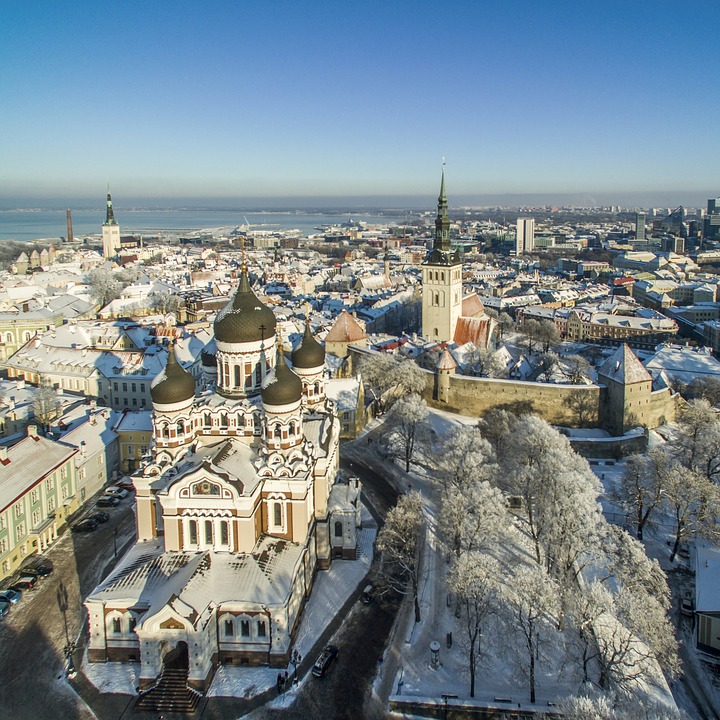
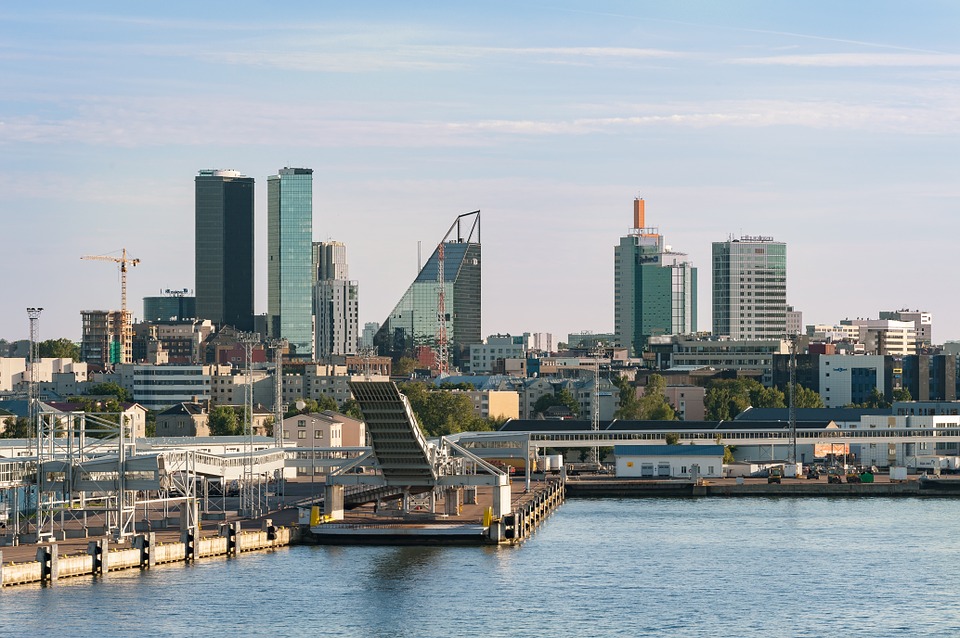
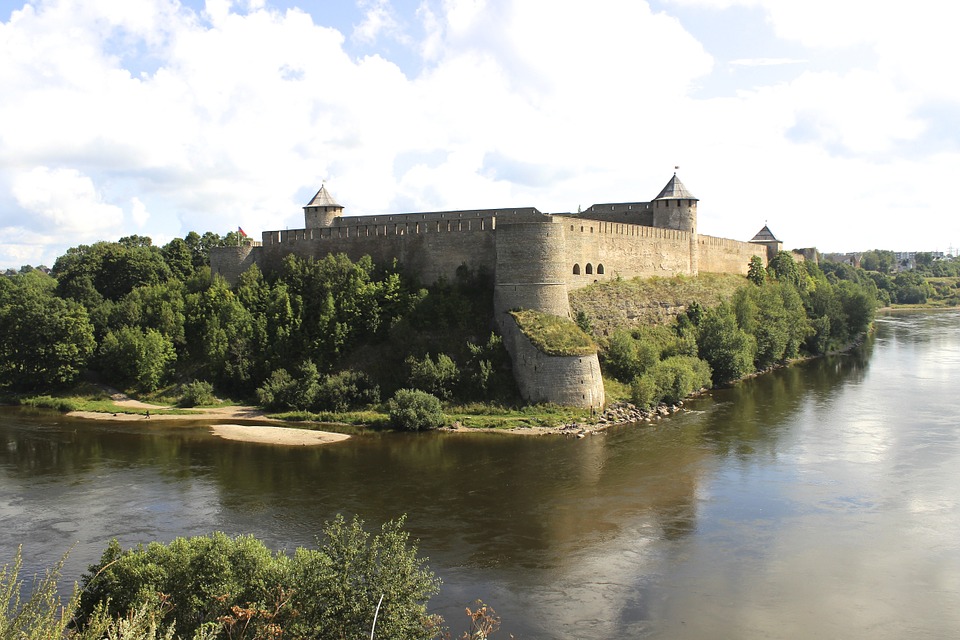

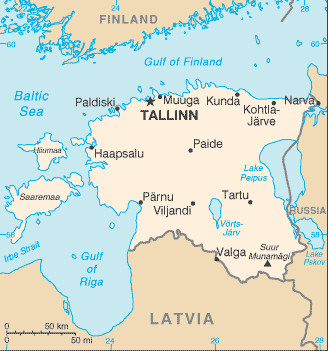

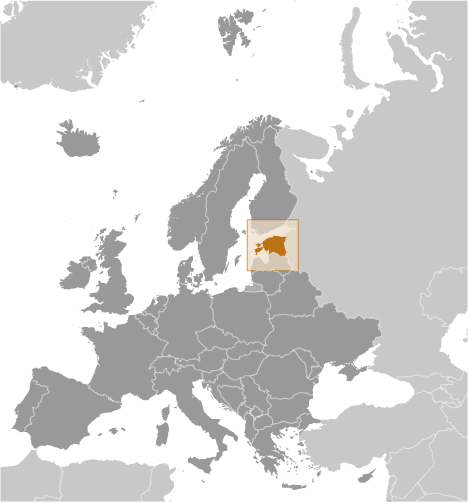




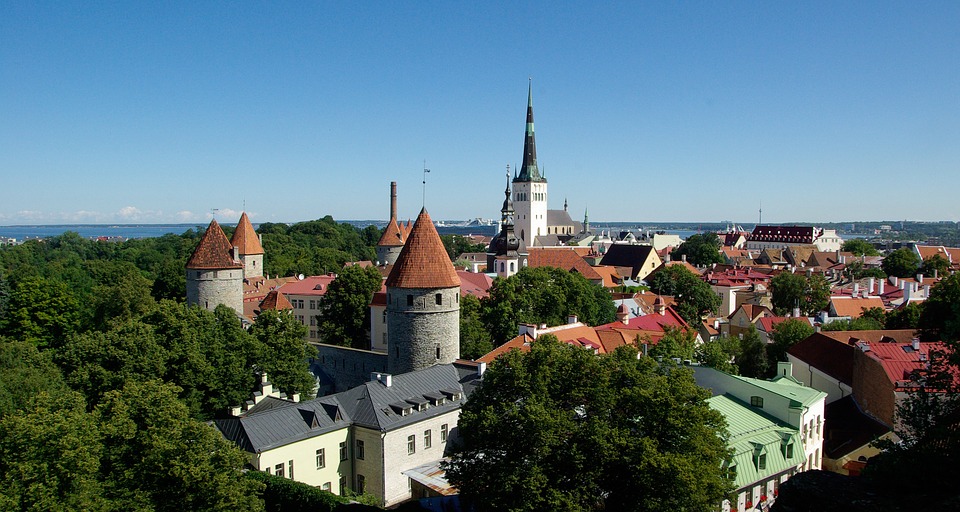
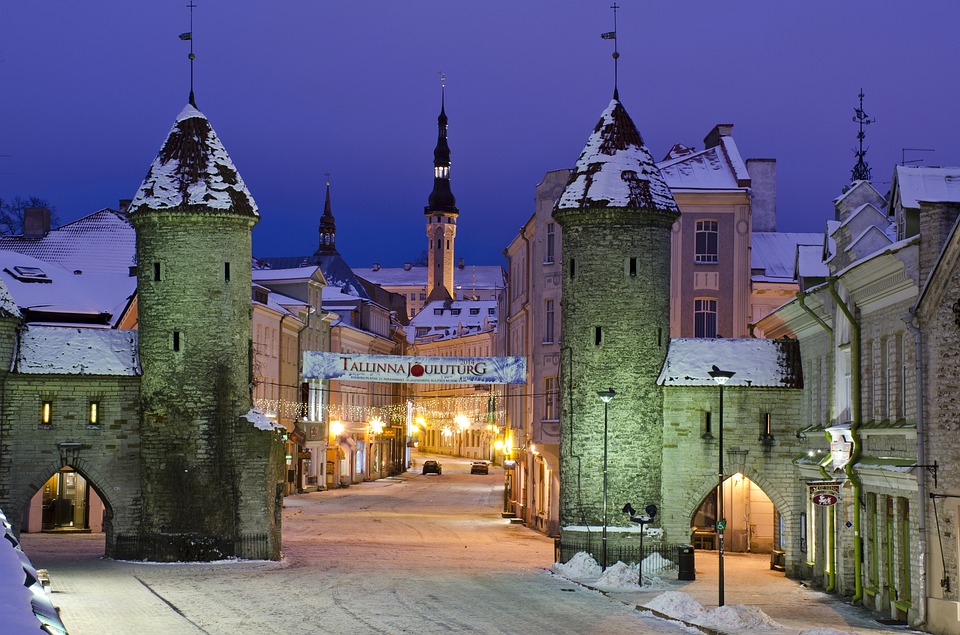
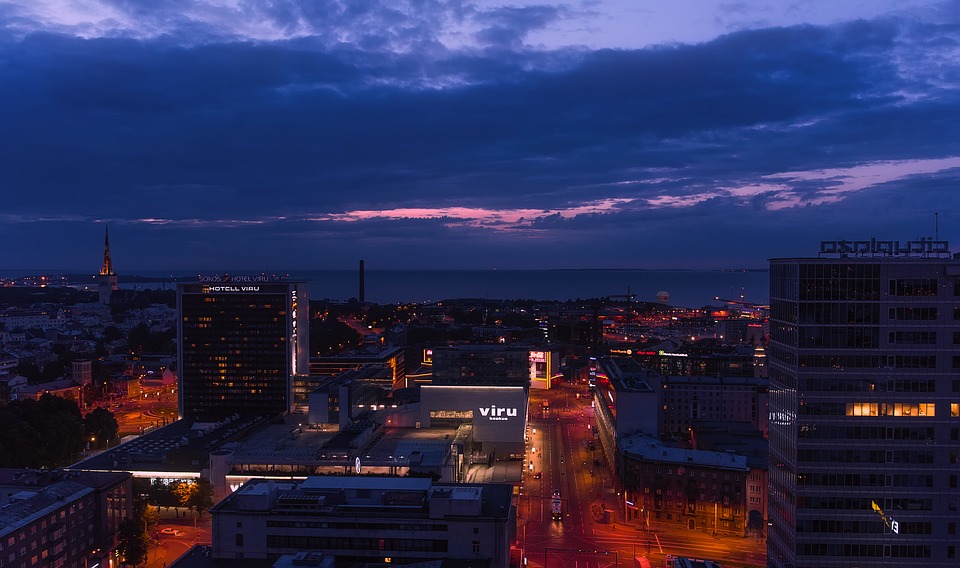
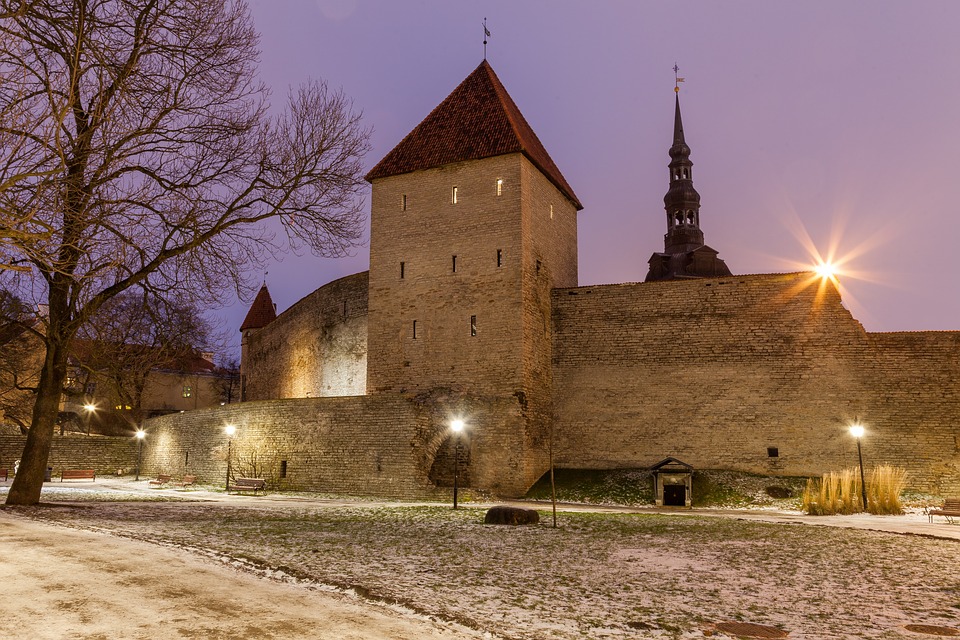
Capital of Estonia: Tallinn
Population (Estimated July 2012): 1,274,709
Area: 45,227 km2 or 17,462 mi2
Currency: Euro (€)
Official Language: Estonian
Political Information: Parliamentary Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 13.6% of the population are Evangelical Lutheran, 12.8% Orthodox, 34.1% are unaffiliated, 33.4% have other religious beliefs and 6.1% have no religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Suur Munamagi at 318m or 1,043ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $22.5 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $27.02 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $20,200 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +2:00
Counties/Provinces/States: 15 counties (maakonnad, singular – maakond); Harjumaa (Tallinn), Hiiumaa (Kardla), Ida-Virumaa (Johvi), Jarvamaa (Paide), Jogevamaa (Jogeva), Laanemaa (Haapsalu), Laane-Virumaa (Rakvere), Parnumaa (Parnu), Polvamaa (Polva), Raplamaa (Rapla), Saaremaa (Kuressaare), Tartumaa (Tartu), Valgamaa (Valga), Viljandimaa (Viljandi), Vorumaa (Voru)
note: counties have the administrative center name following in parentheses
Leaders: President Toomas Hendrik Ilves with Andrus Ansip as Prime Minister.
Additional: Independence from Russia was officially recognised on the 2nd of February 1920 however due to World War II Soviet forces re-occupied Estonia between 1940 and 1941, then by the Germans between 1941 and 1944. Estonia was then under Russian occupation again from 1944 until 20th August 1991 when their independence was restored.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Estonia
Estonia, a small country in Northern Europe, is known for its rich history, beautiful landscapes, and vibrant culture. With a population of just over 1.3 million people, Estonia is one of the smallest countries in the European Union. The capital city, Tallinn, is a popular tourist destination, known for its well-preserved medieval old town and stunning architecture. Estonia is also famous for its digital innovation, with a highly developed e-government system and a thriving tech industry. The country has a unique blend of Nordic, Baltic, and Russian influences, which is reflected in its language, cuisine, and traditions. Estonia’s natural beauty, from its pristine coastline to its dense forests and picturesque lakes, makes it a popular destination for nature lovers and outdoor enthusiasts.
Estonia has a fascinating history, having been ruled by various powers throughout the centuries, including the Danes, Swedes, Germans, and Russians. The country gained independence from the Soviet Union in 1991 and has since undergone rapid economic and social development. Estonia is a member of the European Union, NATO, and the Schengen Area, and it has embraced Western values while also preserving its unique cultural identity. The country has a high standard of living and is known for its progressive policies, including e-residency, which allows people from all over the world to start and run businesses in Estonia. With its rich history, diverse culture, and stunning natural landscapes, Estonia is a hidden gem waiting to be explored.
History and Culture of Estonia
Estonia has a rich and complex history that has shaped its unique culture and identity. The country’s history dates back thousands of years, with evidence of human settlement dating back to the Mesolithic period. Throughout its history, Estonia has been influenced by various powers, including the Vikings, Germans, Swedes, and Russians. In 1918, Estonia declared independence from Russia, only to be occupied by the Soviet Union in 1940 and then by Nazi Germany during World War
After the war, Estonia was once again incorporated into the Soviet Union until it regained independence in 1991. This tumultuous history has left its mark on Estonian culture, with a strong sense of national pride and resilience.
Estonia’s culture is a unique blend of Nordic, Baltic, and Russian influences, reflected in its language, music, art, and traditions. The country is known for its vibrant folk music and dance traditions, with colourful costumes and lively performances that celebrate the country’s heritage. Estonian cuisine is also influenced by its diverse history, with dishes featuring local ingredients such as fish, potatoes, and rye bread. The country’s rich cultural heritage is celebrated through various festivals and events throughout the year, showcasing traditional music, dance, and crafts. Estonia’s cultural scene is also thriving, with a growing number of artists, musicians, and designers gaining international recognition. From its ancient roots to its modern innovations, Estonia’s history and culture are an integral part of what makes the country so special.
Geography and Climate of Estonia
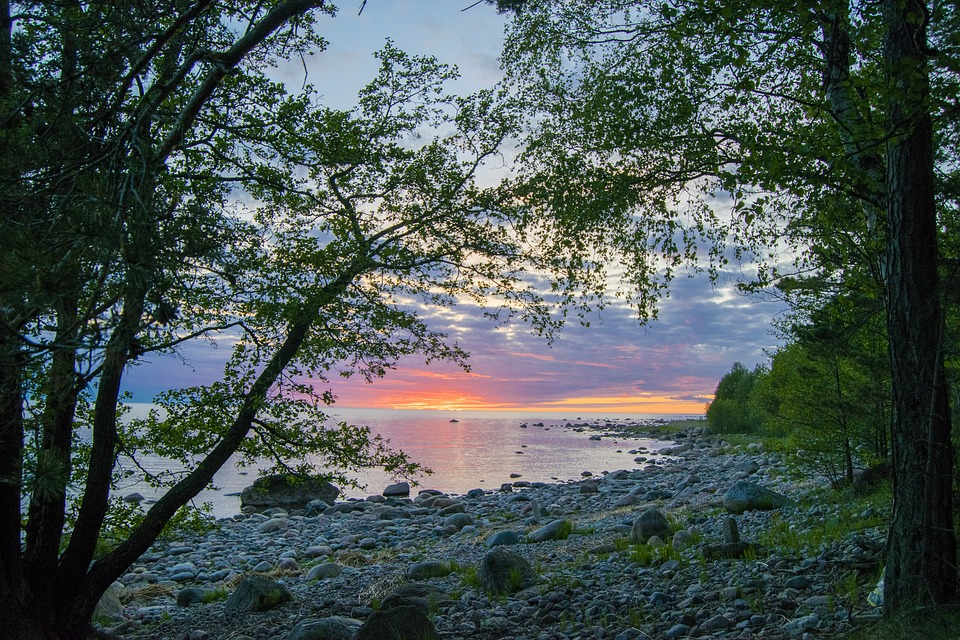
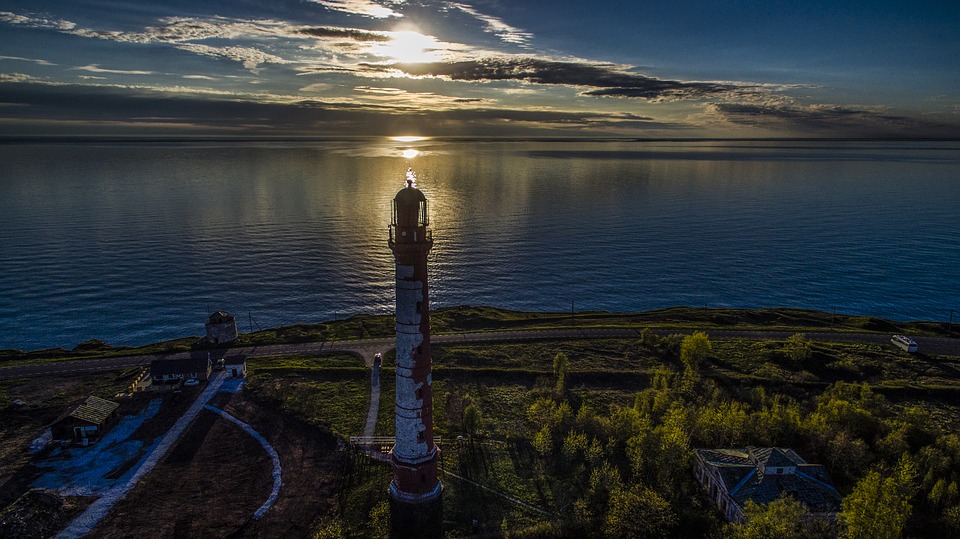
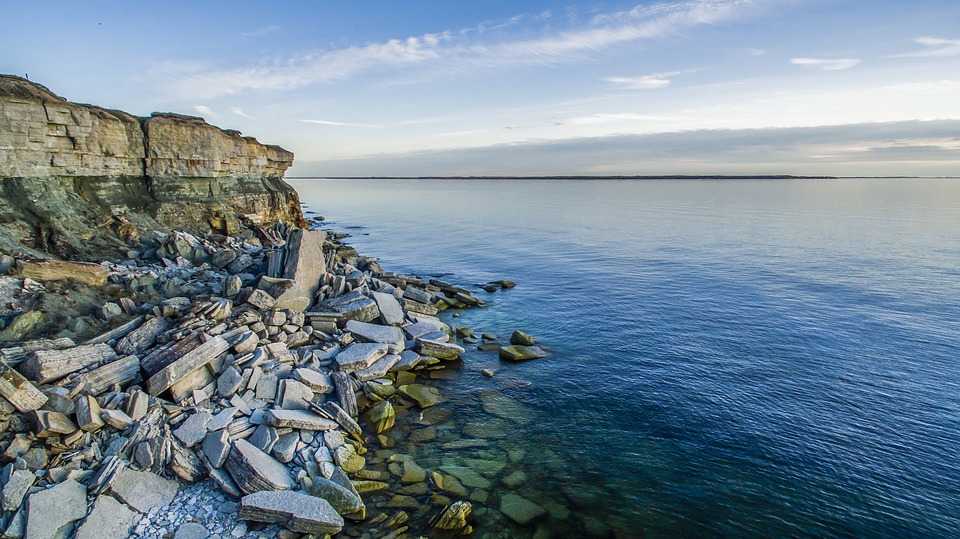
Estonia is a small country located in Northern Europe, bordered by the Baltic Sea to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the north. The country’s diverse landscape includes a pristine coastline, dense forests, picturesque lakes, and rolling hills. Estonia is known for its natural beauty, with over half of its land covered by forests and numerous protected areas that are home to a wide variety of flora and fauna. The country’s numerous islands, including Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, are popular destinations for nature lovers and offer opportunities for hiking, birdwatching, and relaxation by the sea.
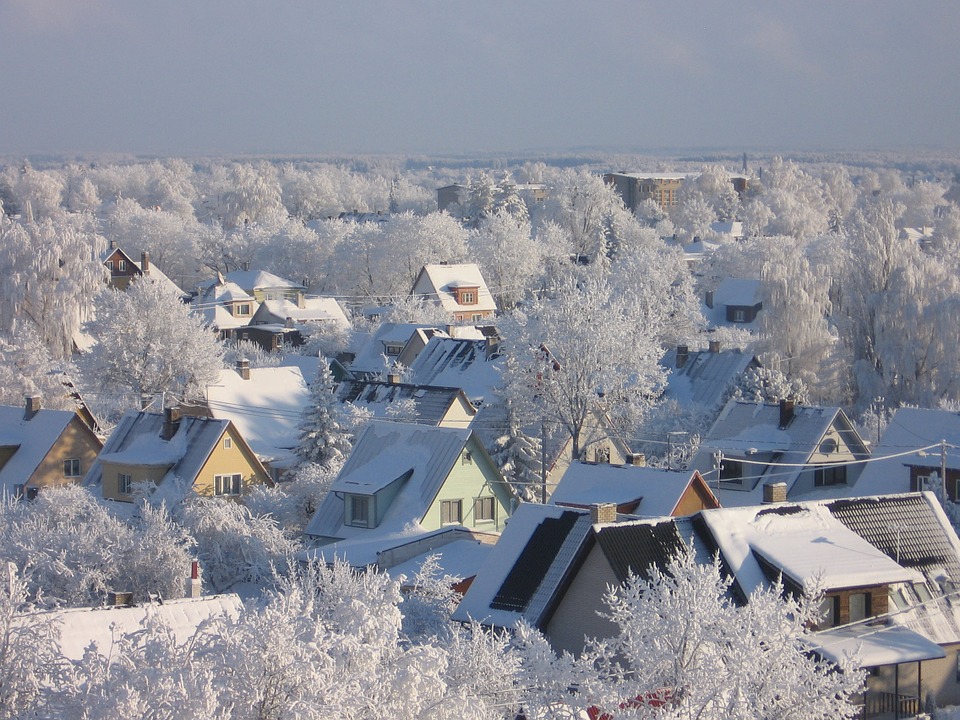
Estonia has a temperate climate with four distinct seasons. Summers are mild and pleasant, with long daylight hours that make it an ideal time for outdoor activities. Winters can be cold and snowy, especially in the eastern part of the country, where temperatures can drop well below freezing. Spring and autumn are transitional seasons with changing weather patterns and beautiful displays of nature as the landscape transforms. The country experiences a fair amount of rainfall throughout the year, which contributes to its lush greenery and abundant wildlife. With its diverse geography and ever-changing climate, Estonia offers something for everyone, whether you’re seeking outdoor adventure or simply want to immerse yourself in the beauty of nature.
Economy and Industry in Estonia
Estonia has undergone rapid economic development since gaining independence from the Soviet Union in 1991. The country has transitioned from a centrally planned economy to a market-based economy with a strong emphasis on innovation and technology. Estonia is known for its digital innovation and e-government system, which has streamlined processes and made it easier for businesses to operate in the country. The tech industry is a major driver of the economy, with a growing number of startups and tech companies gaining international recognition. Estonia has also attracted foreign investment in various sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, and finance.
The country’s strategic location on the Baltic Sea has made it an important hub for trade and transportation in Northern Europe. The port of Tallinn is one of the busiest in the region, handling a significant amount of cargo and passenger traffic. Estonia’s diverse economy also includes agriculture, forestry, and tourism, with the latter becoming an increasingly important sector due to the country’s natural beauty and cultural attractions. The government has implemented pro-business policies to attract investment and promote entrepreneurship, making Estonia an attractive destination for both local and foreign businesses. With its dynamic economy and focus on innovation, Estonia is well-positioned for continued growth and prosperity in the years to come.
Government and Politics in Estonia
Estonia is a parliamentary republic with a multi-party political system. The country’s government is divided into three branches: the executive branch led by the Prime Minister, the legislative branch consisting of the unicameral Parliament (Riigikogu), and the judicial branch headed by the Supreme Court. Estonia gained independence from the Soviet Union in 1991 and has since established a democratic system based on the rule of law and respect for human rights. The country is known for its progressive policies, including e-residency, which allows people from all over the world to start and run businesses in Estonia.
Estonia is a member of the European Union, NATO, and the Schengen Area, and it has embraced Western values while also preserving its unique cultural identity. The government has implemented various reforms to modernise the country’s institutions and promote transparency and accountability. Estonia’s political landscape is characterised by a diverse range of political parties representing different ideologies and interests. The country has made significant strides in promoting gender equality and LGBTQ+ rights, with several women holding key positions in government and society. With its commitment to democracy and human rights, Estonia continues to play an important role in shaping the future of Europe.
Education and Healthcare in Estonia
Estonia places a strong emphasis on education and healthcare as fundamental pillars of its social welfare system. The country has a well-developed education system that provides free education at all levels, from preschool to university. Estonian students consistently perform well in international assessments of academic achievement, reflecting the high quality of education in the country. The government has invested in modernising schools and promoting digital literacy to prepare students for success in the 21st century. Higher education institutions in Estonia offer a wide range of degree programmes in various fields, attracting students from around the world.
Estonia also provides universal healthcare coverage to its citizens through a national health insurance system. The country has made significant investments in healthcare infrastructure and technology to ensure access to high-quality medical services for all residents. The government has implemented various public health initiatives to promote healthy lifestyles and prevent diseases. Estonia’s healthcare system is characterised by a strong focus on preventive care and patient-centred services. The country has also been at the forefront of digital innovation in healthcare, with electronic health records and e-prescriptions that have improved efficiency and patient outcomes. With its commitment to providing accessible education and healthcare services, Estonia is dedicated to ensuring the well-being of its citizens.
Tourism and Attractions in Estonia
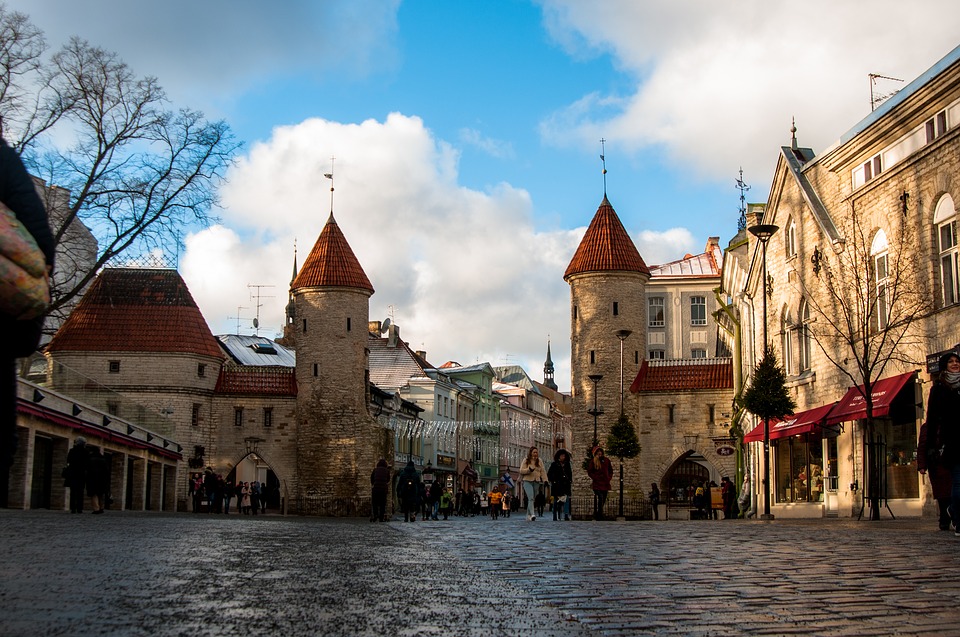
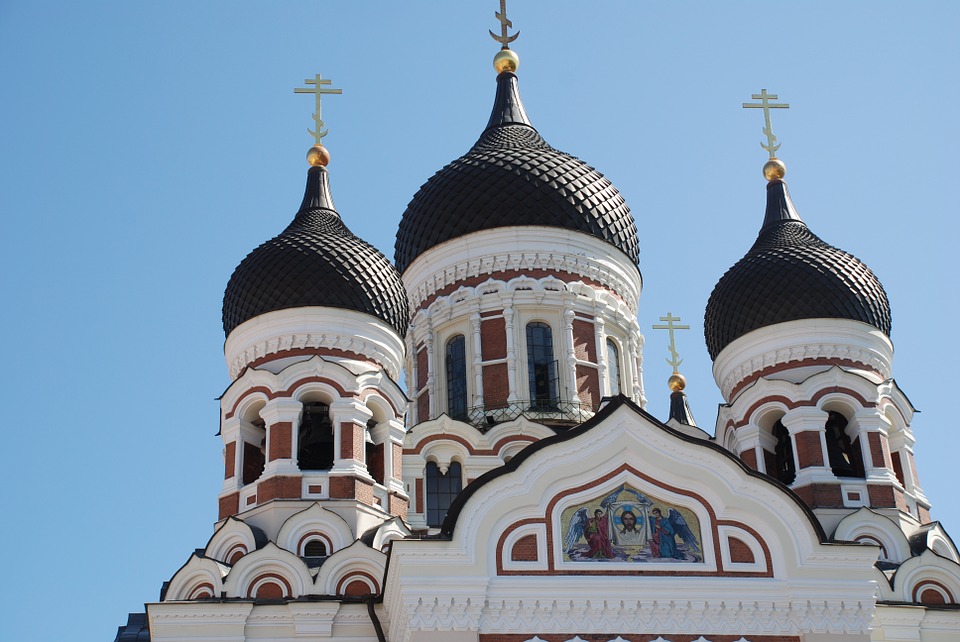
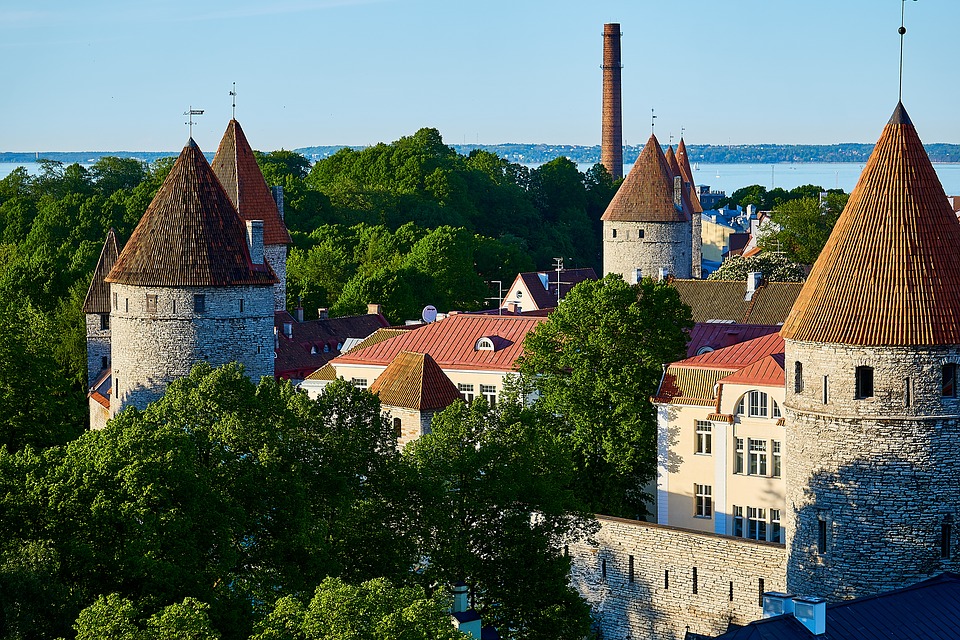
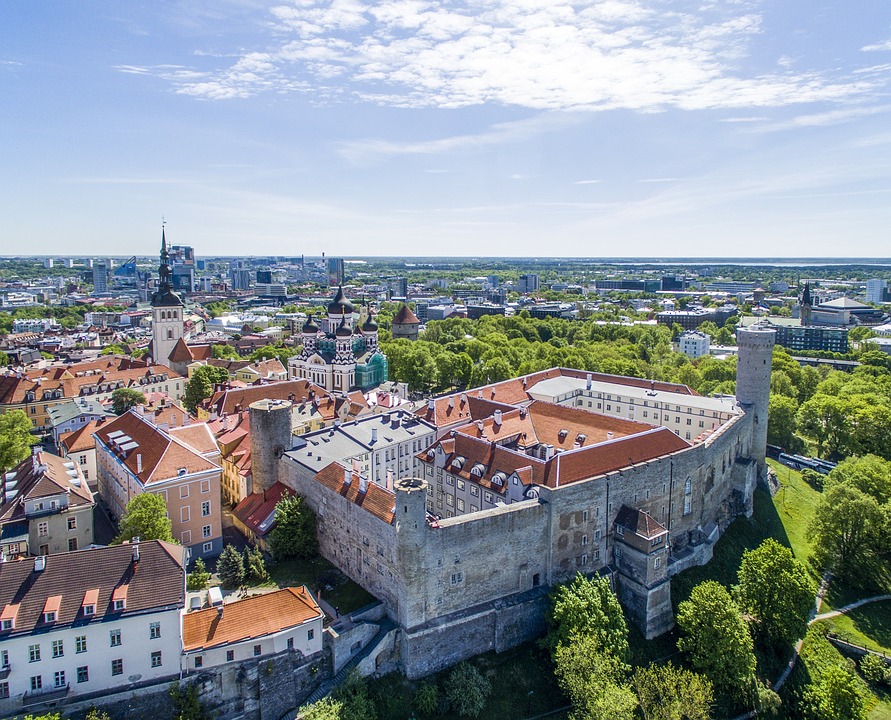
Estonia is a hidden gem waiting to be discovered by travellers seeking natural beauty, rich history, and vibrant culture. The capital city of Tallinn is a popular tourist destination known for its well-preserved medieval old town, stunning architecture, and charming cobblestone streets. Visitors can explore historic landmarks such as Toompea Castle, Alexander Nevsky Cathedral, and St. Olaf’s Church while immersing themselves in the city’s unique atmosphere. Tallinn also offers a thriving culinary scene with traditional Estonian dishes as well as international cuisine.
Beyond Tallinn, Estonia boasts numerous attractions that showcase its natural beauty and cultural heritage. Lahemaa National Park is a must-visit destination for nature lovers, offering diverse landscapes including forests, bogs, lakes, and coastal areas. The park is home to various species of wildlife and provides opportunities for hiking, birdwatching, and exploring ancient manors. Saaremaa Island is another popular destination known for its picturesque countryside, historic windmills, and unique culture. Visitors can relax on sandy beaches or visit local artisans producing traditional handicrafts.
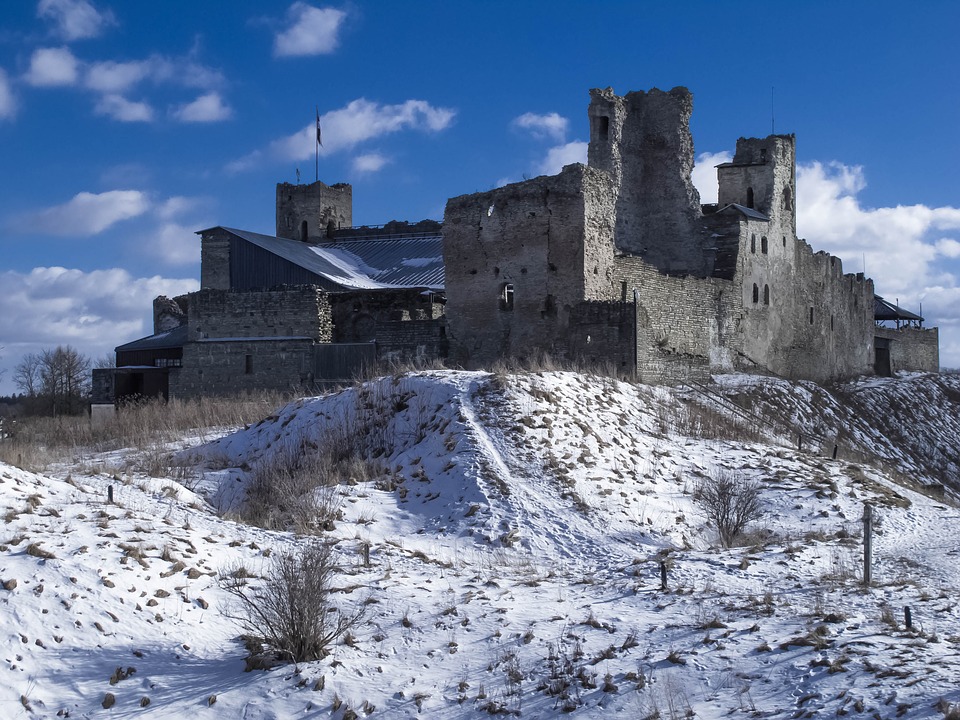
Estonia’s rich history is also reflected in its numerous castles and manor houses scattered throughout the countryside. These historic landmarks offer insight into the country’s past while providing stunning backdrops for photography enthusiasts. The country’s vibrant cultural scene includes numerous festivals celebrating music, dance, art, and traditional crafts throughout the year. From ancient ruins to modern innovations, Estonia offers something for every type of traveller looking to explore this enchanting corner of Northern Europe.
FAQs
What is the capital of Estonia?
The capital of Estonia is Tallinn.
What is the population of Estonia?
As of 2021, the population of Estonia is approximately 1.3 million people.
What is the official language of Estonia?
The official language of Estonia is Estonian.
What is the currency used in Estonia?
The currency used in Estonia is the Euro (EUR).
What are some popular tourist attractions in Estonia?
Some popular tourist attractions in Estonia include Tallinn Old Town, Lahemaa National Park, Kadriorg Palace, and the Estonian Open Air Museum.
What is the climate like in Estonia?
Estonia has a temperate climate, with warm summers and cold winters. The country experiences all four seasons.
What are some traditional dishes in Estonian cuisine?
Some traditional dishes in Estonian cuisine include black bread, herring, kama (a traditional Estonian finely milled flour mixture), and kohuke (a sweet curd snack).
What are some famous Estonians?
Some famous Estonians include composer Arvo Pärt, writer Jaan Kross, and former President Toomas Hendrik Ilves.
Climate Zones Of Estonia: Different climate regions Of Estonia
Estonia, a small country in Northern Europe, is known for its diverse climate zones. The country is divided into four main climate regions: coastal, continental, maritime, and subarctic. Each of these regions has its own unique characteristics and influences the weather patterns and environmental conditions in the country. Estonia’s climate is greatly influenced by its proximity to the Baltic Sea and the Gulf of Finland, as well as its northern latitude. The combination of these factors results in a wide range of temperatures, precipitation levels, and weather patterns throughout the year. Understanding the different climate zones in Estonia is essential for understanding the country’s environment, agriculture, and overall way of life. Summary Estonia has four main climate zones: coastal, continental, maritime, and subarctic. The coastal climate region experiences mild winters and cool summers due to the influence of the Baltic Sea. The continental climate region has cold winters and warm summers, with large temperature variations throughout the year. The maritime climate region has mild winters and cool summers, with high humidity and frequent precipitation. The subarctic climate region has short, cool summers and long, cold winters with heavy snowfall. Coastal Climate Region The coastal climate region in Estonia is characterized by mild winters and cool summers. This region is heavily influenced by the Baltic Sea, which helps to moderate temperatures throughout the year. The proximity to the sea also results in higher levels of precipitation, particularly during the autumn and winter months. The coastal region is home to a variety of plant and animal species that thrive in the moist and temperate climate. The mild temperatures and ample rainfall...
Political Boundaries of Estonia: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Estonia, a small country in Northern Europe, is known for its rich history and unique political boundaries. The country is bordered by the Gulf of Finland to the north, the Baltic Sea to the west, Latvia to the south, and Russia to the east. Estonia’s political boundaries have evolved over the centuries, influenced by various historical, cultural, and geopolitical factors. The country is divided into 15 counties, which are further divided into municipalities and parishes. These political boundaries play a crucial role in shaping the governance and administration of the country, as well as its cultural and social dynamics. Estonia’s political boundaries have been shaped by its complex history, which includes periods of foreign rule and occupation. The country has been influenced by various empires and kingdoms, including the Swedish, Danish, German, and Russian. These influences have left a lasting impact on Estonia’s political boundaries, as well as its cultural and linguistic diversity. The country’s unique position at the crossroads of Eastern and Western Europe has also played a significant role in shaping its political boundaries. Estonia’s strategic location has made it a coveted territory throughout history, leading to numerous border changes and territorial disputes. As a result, Estonia’s political boundaries have been subject to constant evolution and adaptation, reflecting the country’s dynamic and diverse heritage. Summary Estonia’s political boundaries are defined by its borders with Russia, Latvia, and the Baltic Sea. The country is divided into 15 counties, each with its own government and administrative structure. Within these counties, there are 79 municipalities, which are further divided into 213 administrative units. Estonia’s historical boundaries have shifted over time...
Terrain and Topography of Estonia: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Estonia, a small country in Northern Europe, is known for its diverse and unique terrain and topography. The country is characterized by its flat coastal lowlands, rolling plains, hilly landscapes, and numerous rivers and valleys. The terrain of Estonia has been shaped by various geological processes over millions of years, resulting in a landscape that is both beautiful and diverse. From the coastal areas to the inland regions, Estonia’s terrain offers a wide range of natural features that make it a fascinating destination for nature lovers and outdoor enthusiasts. Estonia’s terrain is largely influenced by its location on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea. The country is bordered by Latvia to the south and Russia to the east, and its coastline stretches for over 3,700 kilometers, making it the longest coastline of any Baltic state. The terrain of Estonia is also influenced by its glacial history, with much of the landscape being shaped by the movement of glaciers during the last Ice Age. As a result, Estonia’s terrain is characterized by a mix of flat coastal lowlands, rolling plains, and hilly landscapes, creating a diverse and varied topography that is unique to the region. With its rich geological history and diverse natural features, Estonia’s terrain offers a wealth of opportunities for exploration and discovery. Summary Estonia’s terrain is characterized by a diverse landscape of coastal lowlands, plains, hills, valleys, and river systems. The coastal lowland and plains of Estonia are located in the northern part of the country and are known for their sandy beaches and limestone cliffs. The hilly landscape of Estonia is found in the southern...
History of Estonia
Estonia’s history dates back to the early settlements of the indigenous Finno-Ugric tribes, such as the Estonians, Livonians, and Setos. These tribes lived in the region for thousands of years, developing their own unique culture and traditions. The Viking Age, which began in the late 8th century, had a significant impact on Estonia’s history. The Vikings, known for their seafaring and trading skills, established trade routes along the Baltic Sea and made contact with the indigenous tribes of Estonia. This contact led to cultural exchange and the introduction of new technologies and ideas to the region. During the Viking Age, Estonia became a target for Viking raids, leading to conflicts between the indigenous tribes and the Viking invaders. The Vikings established settlements along the coast of Estonia and engaged in trade with the local population. This period of contact with the Vikings had a lasting impact on Estonia’s culture and language, with many words of Scandinavian origin being incorporated into the Estonian language. The Viking Age also saw the establishment of the first towns and trading centers in Estonia, laying the foundation for the region’s future development as a hub for trade and commerce. Summary Early settlements in Estonia date back to around 8500 BC, and the Viking Age brought significant influence and trade to the region. The medieval period saw the Teutonic Order establish control over Estonia, leading to centuries of German influence and rule. Swedish and Russian rule followed, with Estonia becoming a part of the Russian Empire in the early 18th century. Estonia declared independence in 1918, leading to the Estonian War of Independence against Soviet...
Natural Resources of Estonia: Where Natural Resources are located In Estonia
Estonia, a small country in Northern Europe, is blessed with a diverse range of natural resources that have played a significant role in shaping its economy and culture. From lush forests and abundant water resources to valuable mineral deposits and fertile agricultural land, Estonia’s natural resources have been a source of wealth and sustenance for its people for centuries. The country’s strategic location on the Baltic Sea has also made it a hub for trade and commerce, further enhancing the importance of its natural resources. In this article, we will explore the various natural resources that Estonia is endowed with and their impact on the country’s development and prosperity. Summary Estonia is rich in natural resources, including forests, oil shale, peat, water resources, agricultural land, and biodiversity. Forests and timber are a significant natural resource in Estonia, covering over half of the country’s land area and providing economic and environmental benefits. Oil shale is a key energy resource in Estonia, used for electricity production and heating, but it also poses environmental challenges due to its high carbon emissions. Estonia has significant peat and mineral deposits, which are important for the country’s economy and provide opportunities for sustainable resource management. Water resources and wetlands are abundant in Estonia, supporting diverse ecosystems and providing important habitats for wildlife. Forests and Timber Estonia is home to extensive forests that cover over half of its land area, making it one of the most forested countries in Europe. The country’s forests are predominantly composed of pine, spruce, birch, and aspen trees, which not only provide a habitat for diverse wildlife but also serve as...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Estonia: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites in Estonia
Estonia, a small Baltic country in Northern Europe, is a land of rich cultural and historical heritage. From medieval old towns to pristine national parks, Estonia offers a diverse range of cultural and historical sites that showcase the country’s unique identity and traditions. The country’s tumultuous history, marked by periods of foreign rule and occupation, has shaped its cultural landscape, resulting in a fascinating blend of influences from various European powers. This article will explore some of Estonia’s most significant cultural and historical sites, shedding light on the country’s rich heritage and the stories behind these iconic landmarks. Summary Estonia is home to a wealth of cultural and historical sites that showcase its rich heritage. The Old Town of Tallinn is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, offering a glimpse into Estonia’s medieval past. Lahemaa National Park is a treasure trove of natural beauty and cultural heritage, preserving Estonia’s diverse landscapes and historical sites. The Song Festival Grounds are a testament to Estonia’s musical and cultural traditions, hosting the renowned Estonian Song Festival. The Kumu Art Museum is a must-visit for art enthusiasts, displaying Estonia’s artistic heritage and contemporary works. The Old Town of Tallinn: A UNESCO World Heritage Site The Old Town of Tallinn, Estonia’s capital city, is a well-preserved medieval gem that has earned its place as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. With its cobblestone streets, historic buildings, and imposing city walls, the Old Town is a living testament to Estonia’s medieval past. The town’s origins date back to the 13th century when it was established by the crusading knights of the Teutonic Order. Over the centuries, Tallinn...
Population Density of Estonia
Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured in square kilometres or square miles. It is an important demographic indicator that provides insights into the distribution of people within a given region. Population density can vary widely from one place to another, and it is influenced by a variety of factors such as geographical features, economic opportunities, and social and cultural factors. Understanding population density is crucial for urban planning, resource allocation, and the provision of public services. Summary Population density refers to the number of people living per square kilometre in a specific area. Factors affecting population density in Estonia include economic opportunities, natural resources, and infrastructure development. Urban areas in Estonia have higher population density compared to rural areas, where the population is more dispersed. Historical trends show fluctuations in population density in Estonia due to factors such as war, migration, and economic changes. Population density in Estonia has a significant impact on the demand for infrastructure and services, such as transportation, healthcare, and education. Factors Affecting Population Density in Estonia Estonia, a small Baltic country in Northern Europe, has a population density of around 30 people per square kilometre. This relatively low population density can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, Estonia has a significant amount of forested land, accounting for nearly half of its territory. This limits the amount of habitable land available for settlement, thereby affecting population distribution. Additionally, the country has a history of emigration, particularly during the Soviet era, which has contributed to a decrease in population density. Economic opportunities also play a role in...
Exploring the Charm and Innovation of Estonia: A Journey Through the Land of the Tallinn
Nestled in Northern Europe, Estonia is a small but vibrant country with a population of just over 1.3 million people. Despite its size, Estonia has made a name for itself on the global stage with its unique culture, rich history, and commitment to innovation. Located on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, Estonia shares borders with Russia to the east and Latvia to the south. Its capital city, Tallinn, is a medieval gem that attracts visitors from all over the world. Estonia has a fascinating history that dates back thousands of years. It has been influenced by various cultures and empires throughout the centuries, including the Vikings, Germans, Swedes, and Russians. Despite periods of occupation and struggle for independence, Estonia has managed to maintain its cultural identity and traditions. Today, Estonia is known for its forward-thinking approach to technology and sustainability, making it a unique and exciting destination for travellers. Summary Estonia is a small nation with a big heart, known for its rich cultural heritage and natural wonders. Tallinn is a medieval city with modern twists, offering a unique blend of old and new. Estonia’s cultural heritage ranges from folk traditions to contemporary art, showcasing the country’s diverse artistic scene. Estonia’s natural wonders include pristine forests and stunning coastline, making it a perfect destination for nature lovers. Estonia’s tech-savvy revolution has made it a leader in innovation, with a focus on sustainability, wellness, and community. Discovering the allure of Tallinn: A medieval city with modern twists Tallinn, the capital city of Estonia, is a true gem that seamlessly blends medieval charm with modern attractions. The heart...