Plant cells are the basic structural and functional units of plants. They are eukaryotic cells, meaning they have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Plant cells are vital to the ecosystem as they are responsible for the growth, development, and reproduction of plants. Without plant cells, life on Earth as we know it would not be possible.
Key Takeaways
- Plant cells are the building blocks of plants and play a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth.
- The anatomy of plant cells includes various structures such as the cell wall, chloroplasts, and vacuoles, each with unique functions.
- Plant cells are essential for photosynthesis, which harnesses the power of the sun to produce energy for the plant.
- Plant cells are crucial for food production and play a significant role in feeding the world’s population.
- Plant cells are diverse, adaptable, and have the potential to unlock new possibilities for research and innovation.
The Anatomy of Plant Cells: Structure and Function
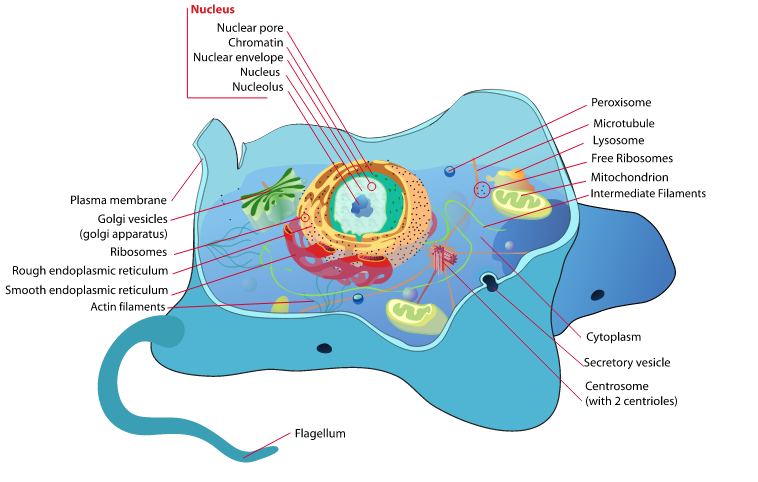
Plant cells have several distinct parts that work together to carry out various functions. The cell wall is a rigid outer layer that provides support and protection to the cell. It is made up of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate. Inside the cell wall is the cell membrane, which controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains the genetic material, DNA. It regulates all cellular activities and is responsible for cell division and reproduction. Surrounding the nucleus is the cytoplasm, a gel-like substance that contains various organelles.
The Unique Characteristics of Plant Cells: Cell Walls, Chloroplasts, and Vacuoles
One of the unique characteristics of plant cells is the presence of a cell wall. The cell wall provides structural support and protection to the cell. It also helps maintain the shape of the cell and prevents it from bursting under pressure.
Another unique feature of plant cells is the presence of chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. They contain chlorophyll, a pigment that captures sunlight and uses it to produce glucose, a form of sugar that serves as an energy source for plants.
Plant cells also have large central vacuoles that store water, nutrients, and waste products. The vacuole helps maintain turgor pressure, which gives plants their rigidity and allows them to stand upright. It also plays a role in the storage and breakdown of various substances.
The Role of Plant Cells in Photosynthesis: Harnessing the Power of the Sun
| Plant Cell Component | Function | Role in Photosynthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Chloroplasts | Site of photosynthesis | Contain chlorophyll pigments that absorb light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen |
| Thylakoid Membrane | Site of light-dependent reactions | Contains photosystems that capture light energy and transfer it to electron transport chains to produce ATP and NADPH |
| Stroma | Site of light-independent reactions | Contains enzymes that use ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide into glucose through the Calvin cycle |
| Cell Wall | Provides structural support and protection | Allows for gas exchange and regulates water uptake and loss for photosynthesis to occur efficiently |
| Vacuole | Stores water, nutrients, and waste products | Regulates turgor pressure to maintain cell shape and support photosynthesis |
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen. It takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells. During photosynthesis, chlorophyll absorbs sunlight and uses it to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Plant cells play a crucial role in photosynthesis as they contain the chloroplasts necessary for this process. Without plant cells, photosynthesis would not be possible, and plants would not be able to produce their own food.
The Importance of Plant Cells in Food Production: Feeding the World
Plant cells are essential for food production as they are responsible for the growth and development of crops. Many staple crops, such as rice, wheat, and corn, rely on plant cells for their growth and production.
Plant cells also contribute to food production through the production of fruits and vegetables. Fruits are the mature ovaries of flowering plants and contain seeds that can be used for reproduction. Vegetables are various parts of plants, such as leaves, stems, and roots, that are consumed for their nutritional value.
The Diversity of Plant Cells: From Simple to Complex

Plant cells come in a variety of forms, ranging from simple to complex. Simple plant cells, such as those found in algae and mosses, have a basic structure with minimal organelles. They are capable of carrying out basic functions such as photosynthesis and reproduction.
Complex plant cells, on the other hand, have a more advanced structure with specialized organelles. These cells are found in higher plants such as trees and flowering plants. They have a well-developed nucleus, numerous organelles, and a complex network of membranes.
The Life Cycle of Plant Cells: Growth, Division, and Differentiation
The life cycle of plant cells involves several stages, including growth, division, and differentiation. Plant cells undergo mitosis, a process of cell division that results in the formation of two identical daughter cells. This allows plants to grow and develop.
During differentiation, plant cells become specialized and take on specific functions. Some cells differentiate into root cells, while others become leaf cells or stem cells. This specialization allows plants to carry out different functions and adapt to their environment.
The Adaptability of Plant Cells: Surviving in Challenging Environments
Plant cells have the remarkable ability to adapt to different environments. They can survive in extreme conditions such as high temperatures, low water availability, and high salinity. This adaptability is due to various mechanisms such as the production of protective compounds, changes in cell structure, and the ability to regulate water loss.
Some plants have developed unique adaptations to survive in challenging environments. For example, cacti have thick stems that store water, allowing them to survive in arid regions. Mangroves have specialized roots that can tolerate high salt concentrations, enabling them to grow in coastal areas.
The Future of Plant Cell Research: Unlocking the Potential of Plants
Plant cell research is an active field with many exciting developments and potential applications. Scientists are studying plant cells to understand their structure and function better. This knowledge can be used to improve crop yields, develop new medicines, and find solutions to environmental challenges.
One area of research is genetic engineering, which involves modifying the DNA of plants to enhance their traits or introduce new ones. This technology has the potential to create crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases, require less water and fertilizer, and produce higher yields.
Another area of research is the study of plant cell metabolism. By understanding how plants produce and store energy, scientists can develop new ways to harness this energy for various applications, such as biofuels and renewable energy sources.
Celebrating the Wonders of Plant Cells and Their Contributions to Life on Earth
Plant cells are the building blocks of plants and play a vital role in the ecosystem. They are responsible for the growth, development, and reproduction of plants. Plant cells have unique characteristics such as cell walls, chloroplasts, and vacuoles that enable them to carry out essential functions such as photosynthesis.
Plant cells are crucial for food production as they are responsible for the growth of crops and the production of fruits and vegetables. They also have the remarkable ability to adapt to different environments, allowing them to survive in challenging conditions.
The future of plant cell research holds great promise for improving crop yields, developing new medicines, and finding solutions to environmental challenges. By unlocking the potential of plant cells, scientists can contribute to a more sustainable and prosperous future for all.
FAQs
What are plant cells?
Plant cells are the basic unit of life in plants. They are eukaryotic cells that have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole.
What is the cell wall in plant cells?
The cell wall is a rigid layer that surrounds the cell membrane of plant cells. It is made up of cellulose and provides structural support and protection to the cell.
What are chloroplasts in plant cells?
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that are responsible for photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy and converts it into chemical energy.
What is the central vacuole in plant cells?
The central vacuole is a large organelle found in plant cells that stores water, nutrients, and waste products. It also helps maintain turgor pressure, which is important for plant growth and development.
What are some unique characteristics of plant cells?
Some unique characteristics of plant cells include the presence of a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole. They also have plasmodesmata, which are channels that allow for communication between adjacent cells. Additionally, plant cells can undergo cell division throughout their lifespan, allowing for continuous growth and development.