World Geography
Geography is the study of the Earth’s landscapes, environments, and the relationships between people and their surroundings. It encompasses both the physical aspects of the Earth, such as its landforms, bodies of water, and climate, as well as the human aspects, including population distribution, cultures, and economies. World geography is a broad field that seeks to understand the complexities of our planet and how humans interact with it. By studying world geography, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity of our planet and the interconnectedness of its various regions.
Geography is a multidisciplinary field that draws on elements of physical science, social science, and humanities. It involves the use of maps, spatial analysis, and geographic information systems (GIS) to understand the Earth’s surface and the processes that shape it. World geography also encompasses the study of human geography, which examines the ways in which people and their activities are distributed across the Earth. By understanding world geography, we can better appreciate the environmental, cultural, and economic challenges facing different regions of the world. This knowledge is crucial for addressing global issues such as climate change, resource management, and international development.
The Five Oceans and Seven Continents
The Earth’s surface is divided into five major oceans: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern (or Antarctic), and Arctic Oceans. These vast bodies of water play a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate and supporting diverse marine ecosystems. The oceans also serve as important transportation routes and a source of food and other natural resources for human societies around the world.
In addition to the oceans, the Earth’s landmasses are divided into seven continents: Africa, Antarctica, Asia, Europe, North America, Australia (or Oceania), and South America. Each continent has its own unique physical and cultural characteristics, shaped by millions of years of geological processes and human history. From the deserts of Africa to the rainforests of South America, the continents offer a rich tapestry of landscapes and environments for exploration and study.
Major Mountain Ranges and Deserts
The Earth’s surface is also marked by major mountain ranges and deserts that have shaped the planet’s physical and cultural landscapes. The Himalayas, for example, are the highest mountain range in the world and are home to diverse ecosystems and cultures in countries such as India, Nepal, and Bhutan. The Andes in South America, the Rockies in North America, and the Alps in Europe are other prominent mountain ranges that have influenced human settlement patterns and economic activities.
Deserts cover about one-third of the Earth’s land surface and are characterized by low precipitation and extreme temperatures. The Sahara Desert in Africa is the largest hot desert in the world, while the Gobi Desert in Asia is one of the largest cold deserts. Deserts are not only home to unique flora and fauna but have also been important trade routes and cultural crossroads throughout history.
Climate Zones and Biomes
The Earth’s climate is influenced by a variety of factors, including latitude, altitude, ocean currents, and prevailing winds. As a result, the planet is divided into different climate zones, each with its own characteristic weather patterns and ecosystems. The equator, for example, experiences a tropical climate with high temperatures and heavy rainfall, while the polar regions have a cold and dry climate.
These climate zones give rise to different biomes, or large ecological areas characterized by distinct plant and animal communities. The tropical rainforest biome, found near the equator, is home to a diverse array of species and is vital for regulating the Earth’s climate. The grasslands biome, found in regions such as the African savannah and North American prairies, supports grazing animals and has been important for human agriculture throughout history.
Human Geography and Population Distribution
Human geography examines the ways in which people and their activities are distributed across the Earth’s surface. It encompasses topics such as population growth, migration patterns, urbanization, and cultural diversity. Understanding human geography is crucial for addressing global challenges such as poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation.
Population distribution is uneven across the world, with some regions experiencing rapid population growth while others are declining. The majority of the world’s population lives in Asia, particularly in countries such as China and India. Urban areas are also growing rapidly, with more than half of the world’s population now living in cities. This trend has significant implications for infrastructure development, resource management, and social inequality.
Historical and Cultural Geography
Historical geography examines how human activities have shaped the Earth’s landscapes over time. It explores topics such as colonialism, trade routes, and the rise and fall of empires. Cultural geography focuses on how human cultures have developed in different regions of the world and how they interact with their environments.
The Silk Road, for example, was an ancient trade route that connected China with Europe and facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies across Eurasia. This historical trade route had a profound impact on the development of cultures and economies along its path. Similarly, cultural geographers study how different societies have adapted to their environments through practices such as agriculture, architecture, and religious beliefs.
The Importance of Geographic Knowledge
Geographic knowledge is crucial for addressing global challenges such as climate change, resource management, and international development. By understanding world geography, we can better appreciate the environmental, cultural, and economic challenges facing different regions of the world. This knowledge is crucial for addressing global issues such as climate change, resource management, and international development.
Geographic knowledge also helps us to understand our interconnectedness with other regions of the world. By studying world geography, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity of our planet and the interconnectedness of its various regions. This understanding can foster a sense of global citizenship and empathy for people from different cultures and backgrounds.
In conclusion, world geography is a complex and multifaceted field that encompasses both physical and human aspects of the Earth’s landscapes. By studying world geography, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity of our planet and the interconnectedness of its various regions. This knowledge is crucial for addressing global challenges such as climate change, resource management, and international development. It also helps us to understand our interconnectedness with other regions of the world and fosters a sense of global citizenship.
FAQs
What is world geography?
World geography is the study of the Earth’s landscapes, environments, and the relationships between people and their environments. It encompasses the physical features of the Earth, as well as the human activity that takes place on it.
Why is world geography important?
World geography is important because it helps us understand the world around us. It provides insights into the physical and human processes that shape our planet, and helps us make informed decisions about how to interact with our environment.
What are the main branches of world geography?
The main branches of world geography include physical geography, which focuses on the Earth’s natural features and processes, and human geography, which examines the relationships between people and their environments.
How does world geography impact our daily lives?
World geography impacts our daily lives in numerous ways, from influencing the weather and climate we experience, to shaping the availability of natural resources and influencing the distribution of populations and cultures around the world.
What are some key concepts in world geography?
Key concepts in world geography include location, place, human-environment interaction, movement, and region. These concepts help geographers understand and interpret the world around them.
Arkansas
Arkansas, also known as “The Natural State,” is a state located in the southern region of the United States. It is bordered by six states, including Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, Texas to the southwest, and Oklahoma to the west. With a population of over three million people, Arkansas is known for its natural beauty, diverse landscape, and rich history. The nickname “The Natural State” is fitting for Arkansas due to its abundance of natural resources and scenic beauty. The state is home to numerous national parks, forests, rivers, and lakes, making it a haven for outdoor enthusiasts. From the majestic Ozark Mountains in the northwestern part of the state to the fertile Delta region in the east, Arkansas offers a wide range of natural wonders to explore. Summary Arkansas is known as “The Natural State” due to its diverse landscape and abundant natural resources. The state has a rich history dating back to Native American settlements and eventual statehood in 1836. Arkansas boasts a varied geography and climate, from the Ozark Mountains to the Mississippi Delta. The economy of Arkansas is driven by agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism. Arkansas has a vibrant culture with a strong emphasis on music, food, and festivals. History of Arkansas: From Native American Settlements to Statehood Arkansas has a long and complex history that dates back thousands of years. The area that is now Arkansas was originally inhabited by various Native American tribes, including the Quapaw, Osage, Caddo, and Cherokee. These tribes lived off the land and developed their own unique cultures and traditions. European...
Arizona
Arizona, also known as the Grand Canyon State, is a land of natural wonders and rich cultural heritage. Located in the southwestern region of the United States, Arizona is known for its diverse landscape, ranging from deserts to mountains. The state has a fascinating history and is home to numerous Native American tribes. One of the most famous attractions in Arizona is the Grand Canyon, a breathtaking natural wonder that attracts millions of visitors each year. Summary Arizona is known as the Grand Canyon State, home to one of the world’s most famous natural wonders. The state’s geography ranges from desert landscapes to mountain ranges, offering diverse outdoor activities. Arizona has a rich history and culture of Native American tribes, with many reservations still present today. The Wild West era is also a significant part of Arizona’s history, with cowboys, outlaws, and gunfights shaping the state’s identity. Arizona’s national parks, including the Grand Canyon, offer breathtaking views and opportunities for hiking, camping, and exploring the great outdoors. Geography of Arizona: From Desert to Mountains Arizona’s geography is incredibly diverse, offering a wide range of outdoor activities for nature enthusiasts. The state is known for its vast deserts, including the Sonoran Desert, which is home to unique plant and animal species. The desert landscape provides opportunities for activities such as hiking, off-roading, and exploring ancient Native American ruins. In addition to deserts, Arizona is also home to stunning mountain ranges such as the San Francisco Peaks and the Santa Catalina Mountains. These mountains offer opportunities for hiking, camping, and even skiing during the winter months. The state’s diverse geography makes...
Alaska
Alaska, the largest state in the United States, is often referred to as the Last Frontier. It is located in the extreme northwest of North America, separated from the rest of the country by Canada. Alaska has a rich history that dates back thousands of years, with indigenous people inhabiting the land long before European explorers arrived. The state was purchased from Russia by the United States in 1867 and became a territory before eventually gaining statehood in 1959. The nickname “The Last Frontier” is fitting for Alaska due to its vast and untamed wilderness. With its rugged mountains, expansive forests, and icy glaciers, Alaska offers a sense of adventure and exploration that is unparalleled. The state is known for its remote and isolated communities, where residents must rely on their resourcefulness and resilience to survive in such a harsh and unforgiving environment. Alaska truly represents the last frontier of America, a place where nature still reigns supreme. Summary Alaska is the last frontier of America, known for its unique geography, climate, and rich cultural heritage. Alaska is home to a thriving wildlife, including polar bears, whales, and more. Alaska’s natural resources, such as oil, gas, and fisheries, play a significant role in the state’s economy. The Northern Lights and the Iditarod sled dog race are iconic attractions in Alaska. Despite its beauty, living in Alaska can be challenging due to harsh winters and isolation. Alaska’s Unique Geography and Climate Alaska’s geography is incredibly diverse and breathtakingly beautiful. The state is home to towering mountain ranges, including the famous Denali (formerly known as Mount McKinley), which is the highest...
Alabama
Alabama, located in the southeastern region of the United States, is a state with a rich history and vibrant culture. It is known for its southern hospitality, diverse landscapes, and significant contributions to American history. From the Civil Rights Movement to its musical heritage, Alabama has played a pivotal role in shaping the nation. Alabama became the 22nd state to join the United States in 1819. It was named after the Alabama River, which runs through the state. The state has a population of approximately 5 million people and is home to several notable figures and events in American history. Rosa Parks, a civil rights activist, famously refused to give up her seat on a bus in Montgomery, Alabama, sparking the Montgomery Bus Boycott and becoming a symbol of the Civil Rights Movement. The state is also known for its connection to the space program, as Huntsville is home to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center. Summary Alabama is a southern state with a rich history and culture. Alabama’s geography ranges from mountains to beaches, offering diverse landscapes. The people of Alabama are known for their unique traditions and diverse communities. Alabama’s economy is driven by agriculture, industry, and tourism. Alabama is home to famous landmarks and attractions, including civil rights monuments and natural wonders. Alabama’s Geography: From Mountains to Beaches and Everything in Between Alabama boasts a diverse landscape that includes mountains, forests, rivers, and beaches. The northern part of the state is characterized by the Appalachian Mountains, which offer stunning views and opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking and camping. The central region of Alabama is known...
Australian History: History of Australia
Australia, known for its stunning landscapes and unique wildlife, has a rich and complex history that spans thousands of years. From the arrival of the Aboriginal Australians, the first inhabitants of the continent, to the British colonisation and the establishment of the Commonwealth of Australia, the country’s past has shaped its present and future. Understanding Australia’s history is crucial for appreciating its diverse culture, political system, and social dynamics. In this article, we will delve into the key events and turning points in Australian history, exploring their impact on the nation’s identity and development. Summary Aboriginal Australians were the first inhabitants of Australia, with a rich and diverse culture that dates back tens of thousands of years. Captain Cook’s arrival in 1770 marked the beginning of British colonisation, which would have a profound impact on the continent and its people. The Gold Rush of the 1850s was a turning point in Australian history, bringing wealth and prosperity but also social and political upheaval. The Eureka Stockade of 1854 is remembered as a symbol of Australian democracy, as miners rebelled against unfair working conditions and demanded greater representation. Federation in 1901 saw the birth of the Commonwealth of Australia, a new nation with its own constitution and government. Aboriginal Australians: The First Inhabitants of Australia Before the arrival of European settlers, Australia was home to a diverse range of Aboriginal cultures and languages. It is estimated that Aboriginal Australians have inhabited the continent for at least 65,000 years. These indigenous peoples had a deep connection to the land and lived in harmony with nature. They had complex social structures, rich...
Water Bodies Of Australia: Lakes, Rivers and Seas of Australia
Australia is home to a diverse range of water bodies, including rivers, lakes, seas, and oceans. These water bodies play a crucial role in the country’s ecosystem, supporting a wide variety of plant and animal life. They also provide important resources for various industries, such as tourism, agriculture, and maritime activities. In this article, we will explore some of Australia‘s most iconic water bodies and discuss their significance to the country. Summary Australia is home to a diverse range of water bodies, including rivers, lakes, seas, and oceans. The Great Barrier Reef is one of Australia’s most iconic natural wonders, known for its stunning coral formations and diverse marine life. The Murray River is the longest river in Australia, spanning over 2,500 kilometers and supporting a range of ecosystems and communities. Lake Eyre is Australia’s largest salt lake, located in the arid outback and known for its unique wildlife and stunning landscapes. The Tasman Sea separates Australia and New Zealand, and is an important shipping route and fishing ground for both countries. The Great Barrier Reef: Australia’s Iconic Coral Sea The Great Barrier Reef is one of Australia’s most famous natural wonders. Stretching over 2,300 kilometers along the Queensland coast, it is the largest coral reef system in the world. The reef is home to a vast array of marine life, including over 1,500 species of fish and 600 types of coral. The Great Barrier Reef is not only a natural wonder but also a major tourist attraction. It attracts millions of visitors each year who come to explore its vibrant coral gardens and swim with its diverse marine...
Cultural or Historical Sites Of Australia: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Australia
Australia is a country known for its rich cultural and natural heritage. From iconic landmarks to ancient sites, Australia offers a diverse range of attractions that showcase its unique history and beauty. These sites are not only important for preserving the country’s past, but also for promoting tourism and contributing to the economy. In this article, we will explore some of Australia’s most significant cultural and natural sites, including the Sydney Opera House, Uluru-Kata Tjuta National Park, the Great Barrier Reef, the Royal Botanic Garden, the Port Arthur Historic Site, the National Gallery of Victoria, the Australian War Memorial, the Old Melbourne Gaol, the National Museum of Australia, and the Daintree Rainforest. Summary The Sydney Opera House is a world-renowned cultural icon of Australia. Uluru-Kata Tjuta National Park is a sacred site of Aboriginal culture and spirituality. The Great Barrier Reef is a natural wonder and historical site with a rich marine biodiversity. The Royal Botanic Garden is a historical landmark of Sydney with a diverse collection of plants. The Port Arthur Historic Site is a symbol of Australia’s convict past and a popular tourist destination. The Sydney Opera House: A Cultural Icon of Australia The Sydney Opera House is perhaps one of the most recognizable landmarks in Australia. Designed by Danish architect Jørn Utzon, it was officially opened in 1973 and has since become a symbol of Australian culture and creativity. The Opera House is not only renowned for its architectural design but also for the wide range of cultural events and performances it hosts. The design of the Sydney Opera House is characterized by its distinctive...
Australia’s Major Natural Resources: Exploring Mineral Resources, Mines, and Economic Power
Australia’s Major Natural Resources: Exploring Mineral Resources, Mines, and Economic Power Australia is a land rich in opportunity, quite literally. From the dusty plains of Western Australia to the rugged terrain of South Australia, the nation is blessed with a wealth of natural resources. It stands tall on the global stage as a leading exporter of mineral resources, boasting world-class mines, massive iron ore deposits, and abundant natural gas reserves. This blog post is a deep dive into Australia’s natural resource landscape—exploring its vast mineral wealth, the dynamics of its powerful mining industry, and how these resources shape the Australian economy. Whether you’re a student, researcher, investor, or simply curious about Australian mining, this article offers valuable insights into one of the world’s richest lands beneath the soil. Article Outline What Makes Australia Rich in Natural Resources? How Important is Iron Ore to the Australian Economy? Where Are the Major Uranium Deposits in Australia? What Role Does Natural Gas Play in Australia’s Energy Mix? Exploring Australia’s Copper and Zinc Reserves Why is Bauxite Crucial to Australia’s Mining Sector? How Valuable Are Australia’s Mineral Sands? The Role of Queensland and New South Wales in Mining What Is the Status of Nickel and Lithium Mining in Australia? What Are the Environmental and Economic Challenges Facing the Mining Industry? 1. What Makes Australia Rich in Natural Resources? Australia’s natural resources are the result of millions of years of geological processes that created rich mineral deposits across the continent. This includes a wide variety of metal ores, energy resources, and industrial minerals. From iron ore to natural gas, bauxite to uranium, the country...
Political Boundaries Of Australia: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Australia is a vast and diverse country, with a complex system of political boundaries that play a crucial role in its governance. Understanding these boundaries is essential for comprehending the political landscape of the country and how power is distributed among its various regions. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of political boundaries in Australia, including the provinces and districts that make up its governance structure. By delving into the historical evolution of these boundaries and examining their impact on modern-day Australia, we can gain a deeper understanding of the challenges and prospects for political boundaries in the country. Summary Australia is divided into six states and two territories, each with their own political boundaries. The provinces of Australia are further divided into districts, which play a significant role in local governance. The historical evolution of Australia’s political boundaries has been shaped by colonialism, federation, and Indigenous sovereignty. Political boundaries in Australia play a crucial role in the distribution of power and resources, and can impact social and economic outcomes. Maintaining political boundaries in Australia can be challenging due to factors such as population growth and changing community needs. Provinces of Australia: A Brief Overview Provinces, also known as states or territories, are the primary political divisions in Australia. There are six states – New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, and Western Australia – and two mainland territories – the Australian Capital Territory (ACT) and the Northern Territory. Each province has its own government and is responsible for various aspects of governance within its jurisdiction. New South Wales is the oldest and most populous state in...
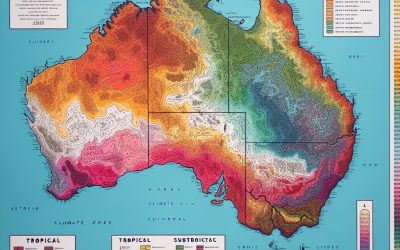
Climate Zones Of Australia: Different Climate Regions Of Australia
Australia is a vast and diverse country, known for its unique wildlife, stunning landscapes, and extreme weather conditions. The country is home to a wide range of climate zones, each with its own distinct characteristics and weather patterns. Understanding these climate zones is crucial for various reasons, including agriculture, tourism, and environmental conservation. Summary Australia has eight climate zones, each with unique features and characteristics. The tropical climate zone in Australia is characterized by high temperatures, high humidity, and heavy rainfall. The subtropical climate zone in Australia experiences mild winters and hot summers, with occasional droughts and bushfires. The Mediterranean climate zone in Australia is known for its mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers, and is home to unique vegetation such as eucalyptus forests. The desert climate zone in Australia covers a large portion of the country and is characterized by low rainfall, high temperatures, and unique flora and fauna adapted to the harsh conditions. Tropical Climate Zone in Australia: Features and Characteristics The tropical climate zone in Australia is located in the northern part of the country, covering areas such as Queensland and the Northern Territory. This region experiences high temperatures and humidity throughout the year, with distinct wet and dry seasons. The wet season, also known as the monsoon season, brings heavy rainfall and occasional cyclones. The vegetation in the tropical climate zone is lush and diverse, with rainforests being a prominent feature. The wildlife in this region is also unique, with species such as kangaroos, wallabies, and various bird species being commonly found. Subtropical Climate Zone in Australia: Climate and Weather Patterns The subtropical climate...
Terrain and Topography Of Australia: Mountains, Valleys, and Plains in Australia.
Australia is a vast and diverse country, known for its unique and varied terrain. From the rugged mountains of the Great Dividing Range to the barren wilderness of the Nullarbor Plain, Australia‘s geography plays a crucial role in shaping its climate, environment, and culture. Understanding the terrain and topography of Australia is essential for various purposes, including tourism, agriculture, and environmental management. Summary Australia’s terrain is diverse and dynamic, with a range of landscapes from mountains to deserts to coastal plains. The Great Dividing Range is the longest mountain range in Australia, stretching over 3,500 km. The Australian Alps are the highest mountains in Australia, with Mount Kosciuszko reaching 2,228 metres. The Western Plateau is a vast and arid landscape, covering over two-thirds of the country. The Murray-Darling Basin is Australia’s most important agricultural region, producing over one-third of the country’s food. The Great Dividing Range: Australia’s Longest Mountain Range The Great Dividing Range is a significant geographical feature that stretches over 3,500 kilometers along the eastern coast of Australia. It is the longest mountain range in the country and plays a crucial role in shaping Australia’s geography and climate. The range acts as a natural barrier, separating the coastal regions from the inland areas. It influences rainfall patterns, with the eastern side receiving more rainfall than the western side. The Great Dividing Range is home to several popular tourist destinations. The Blue Mountains, located just outside of Sydney, offer stunning views, deep valleys, and ancient rock formations. The Snowy Mountains, located in New South Wales and Victoria, are a popular destination for skiing and snowboarding during the winter...
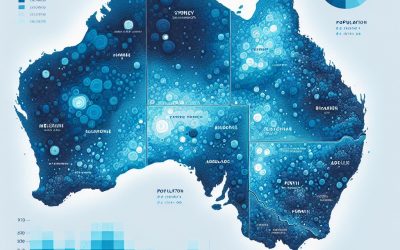
Population Density Of Australia
CC BY 4.0 License ABS Digital Atlas of Australia Australia, known for its vast landscapes and unique wildlife, is also home to a relatively small population compared to its land size. With a population of approximately 26 million people, Australia has a population density of around 3 people per square kilometre. This low population density is due to the country’s large land area, which spans over 7.6 million square kilometres. Despite this, studying population density in Australia is of great importance as it provides insights into various social, economic, and environmental issues that affect the country. Summary Australia has a relatively low population density compared to other developed countries. Population density is the number of people living in a given area, and it has significant social, economic, and environmental implications. Factors affecting population density in Australia include geography, climate, infrastructure, and economic opportunities. Population density varies greatly across different regions of Australia, with major cities having much higher densities than rural areas. Urbanisation and rural-urban migration are major drivers of population density shifts in Australia, with implications for housing, transportation, and social services. Understanding Population Density and Its Significance Population density refers to the number of individuals living in a specific area, usually measured in terms of people per square kilometre. It is an important metric for understanding the distribution of people within a country or region. By studying population density, researchers and policymakers can gain insights into various social, economic, and environmental issues. From a social perspective, population density can provide insights into the availability and accessibility of social services such as healthcare, education, and transportation. Higher...