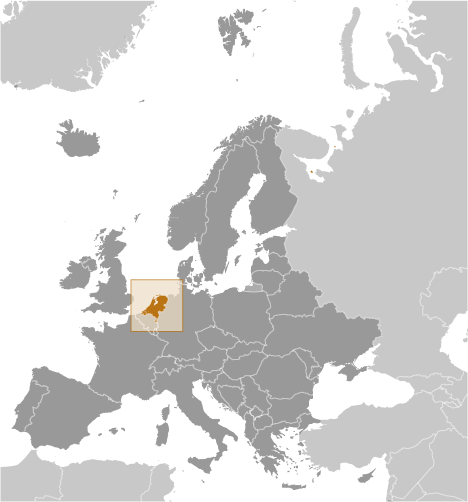
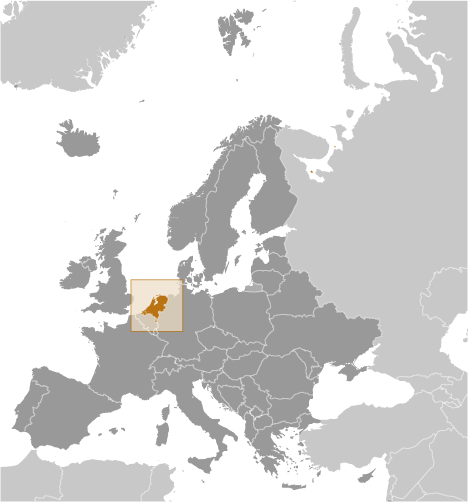
Netherlands
(Koninkrijk der Nederlanden (Kingdom of the Netherlands))
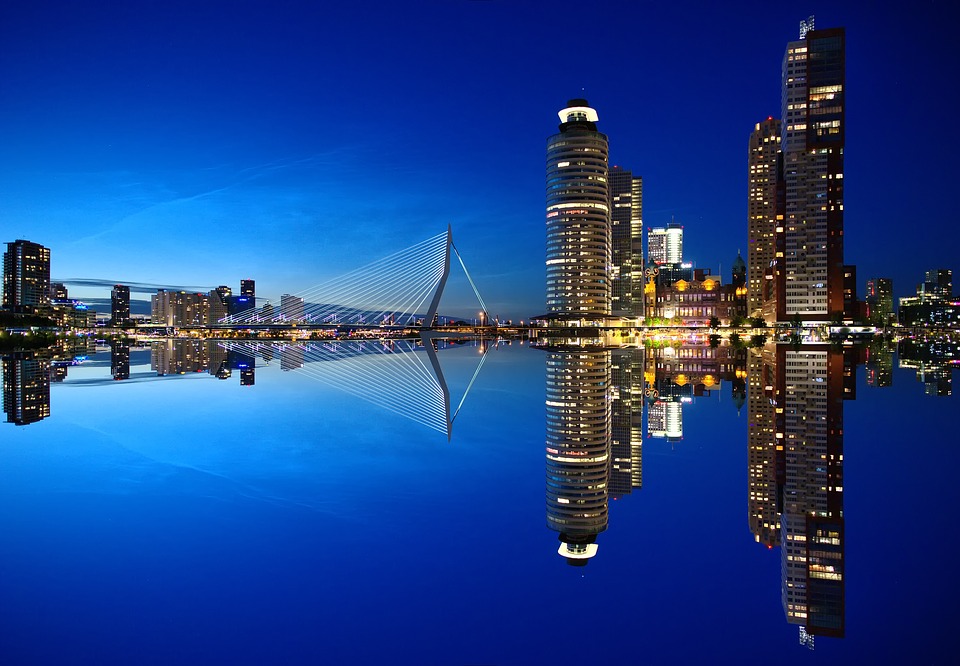
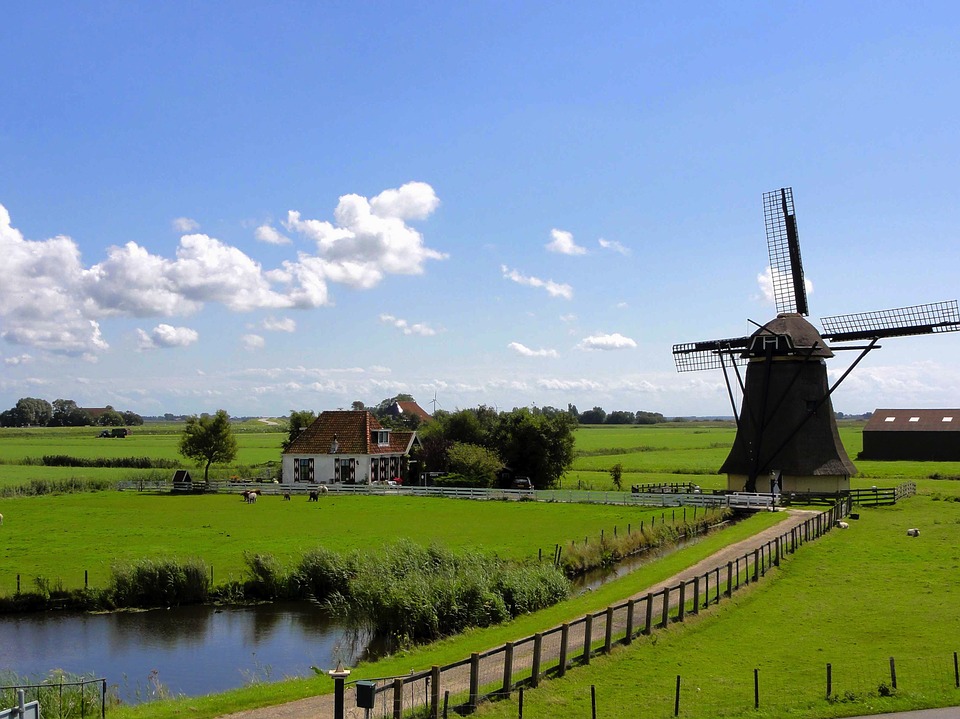

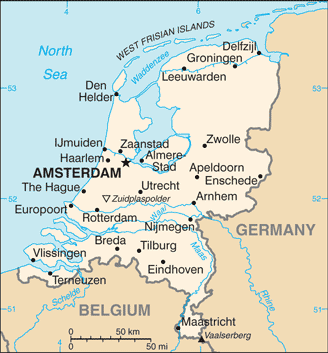





Capital of the Netherlands: Amsterdam
Population (Estimated July 2012): 16,730,632
Area: 41,543km2 or 16,040mi2
Currency: Euro (€)
Official Language: Dutch
Political Information: Constitutional Monarchy and Parliamentary Democracy
Official Religion: No Official Religion
(approximately 42% of the population have no religion, 30% are Roman Catholic, 20% are Protestant, 5.8% are Muslim and 2.2% have other religious beliefs).
Highest Point: Vaalserberg hill at 322m or 1,059ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011) $858.3 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $705.7 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011)
$42,300 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +1:00
Counties/Provinces/States: 12 provinces (provincies, singular – provincie); Drenthe, Flevoland, Fryslan (Friesland), Gelderland, Groningen, Limburg, Noord-Brabant (North Brabant), Noord-Holland (North Holland), Overijssel, Utrecht, Zeeland (Zealand), Zuid-Holland (South Holland)
Leaders: King WILLEM-ALEXANDER (since 30 April 2013); Heir Apparent Princess Catharina-Amalia (since 30 April 2013) with Prime Minister Mark RUTTE (since 14 October 2010; Deputy Prime Ministers (since 26 October 2017) .
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Netherlands
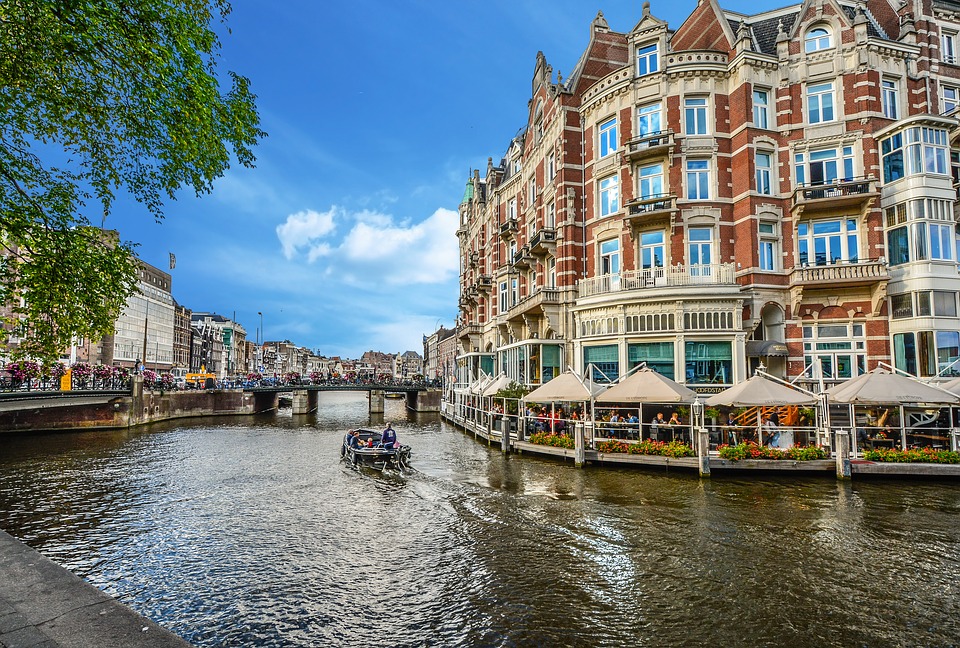
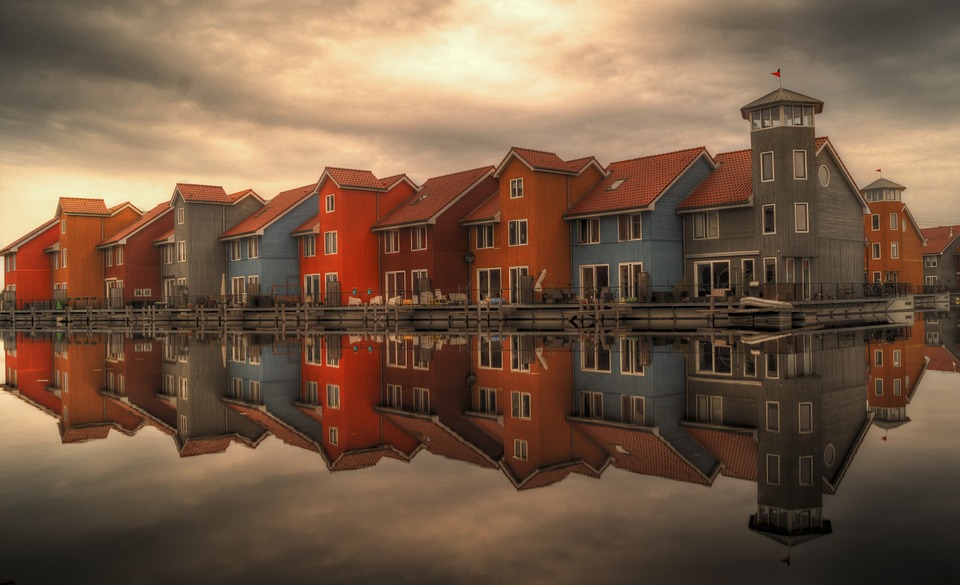
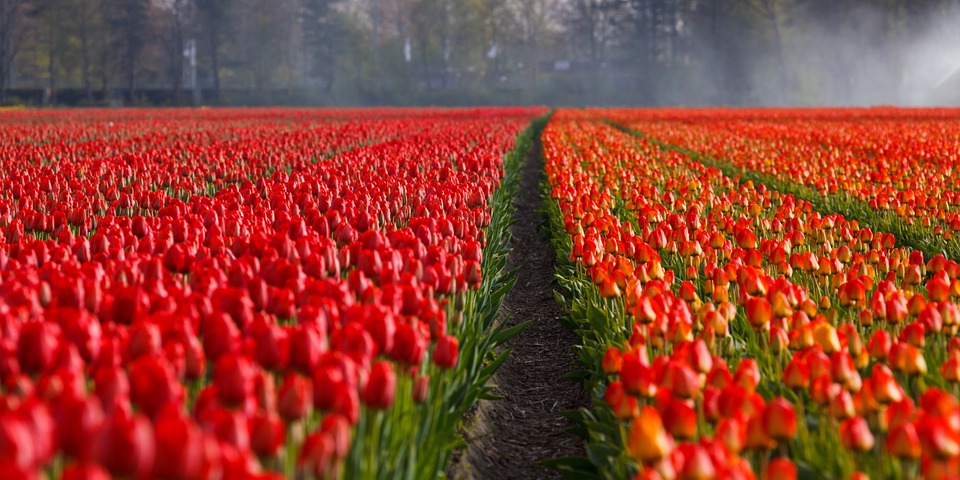
The Netherlands, officially known as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, is a densely populated country situated in Western Europe. It is renowned for its predominantly flat terrain, intricate canal networks, traditional windmills, and expansive tulip fields. The nation shares borders with Germany to the east and Belgium to the south, whilst the North Sea lies to the northwest.
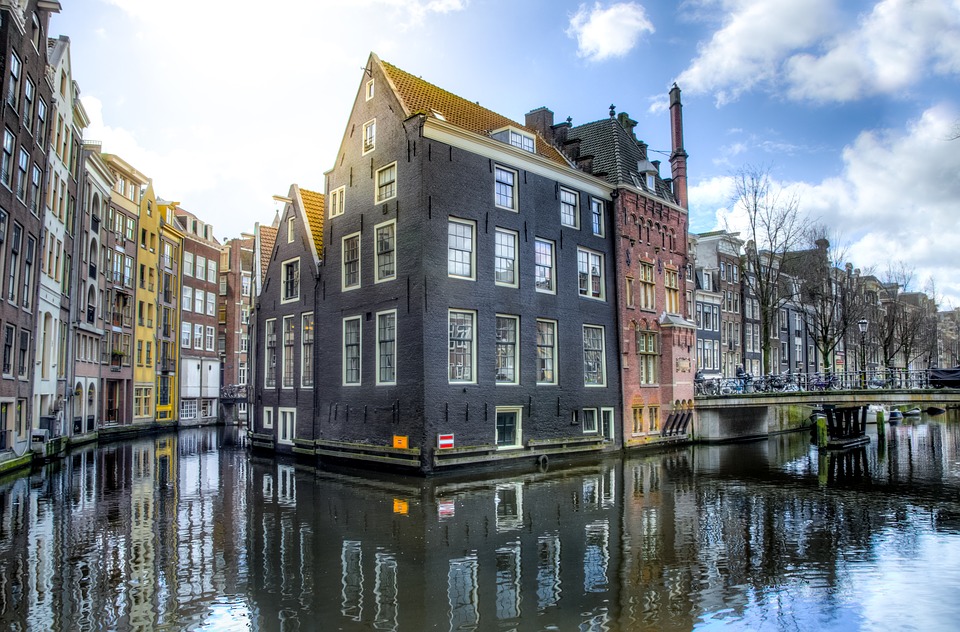
Amsterdam serves as the capital city and is notable for its rich artistic heritage, extensive canal system, and distinctive narrow houses featuring gabled façades. Dutch is the official language, and the Euro is the national currency. The country boasts a substantial historical legacy and a dynamic cultural landscape, rendering it a favoured destination for tourists.
The Netherlands is widely recognised for its progressive policies and liberal stance on social matters. It was amongst the earliest nations globally to enact legislation permitting same-sex marriage and has cultivated a reputation for open-mindedness and tolerance. Dutch society is characterised by directness and pragmatism, with a strong emphasis on individualism and personal liberties.
The country has a long-standing tradition of commerce and trade, hosting numerous multinational corporations and globally recognised brands. Additionally, the Netherlands has made significant contributions to the arts, with celebrated painters such as Rembrandt and Van Gogh originating from the country. The unique combination of historical significance, cultural diversity, and natural beauty offers visitors to the Netherlands a multifaceted and enriching experience.
Summary
- The Netherlands is a small, densely populated country in Western Europe known for its flat landscape, canals, tulip fields, windmills, and cycling routes.
- The history and culture of the Netherlands is rich and diverse, with influences from the Roman Empire, the Vikings, and the Dutch Golden Age.
- The geography of the Netherlands is characterized by its low-lying land and extensive network of canals, while landmarks such as the Keukenhof Gardens and the Rijksmuseum are popular tourist attractions.
- The Netherlands has a highly developed and open economy, with a focus on international trade, agriculture, and innovative industries such as technology and engineering.
- The education and healthcare systems in the Netherlands are known for their high quality and accessibility, with a strong emphasis on lifelong learning and preventive care.
- The Netherlands is home to many famous figures and events, including artists like Vincent van Gogh, scientists like Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, and the annual King’s Day celebration.
- Travel and tourism in the Netherlands are popular due to the country’s picturesque cities, historic sites, and natural beauty, as well as its well-developed transportation infrastructure.
History and Culture of the Netherlands
A Golden Age of Maritime and Economic Power
In the 17th century, the Netherlands experienced a Golden Age, during which it became a major maritime and economic power. This period saw the rise of Dutch trading companies such as the Dutch East India Company and the Dutch West India Company, which played a significant role in global trade and exploration.
A Flourishing of Arts and Culture
The Dutch Golden Age also saw a flourishing of arts and culture, with the country producing some of the world’s most renowned painters, including Rembrandt and Vermeer. The culture of the Netherlands is influenced by its history as a trading nation and its position as a melting pot of different cultures and influences.
A Rich Tradition of Folk Music, Dance, and Storytelling
The Dutch are known for their love of cycling, with bicycles being a popular mode of transportation in cities and towns across the country. The Netherlands is also famous for its cheese, with varieties such as Gouda and Edam being exported around the world. The country has a rich tradition of folk music and dance, with events such as the annual Tulip Festival showcasing traditional Dutch music and dance performances. The Dutch also have a strong tradition of storytelling and folklore, with tales of mythical creatures such as trolls and elves being passed down through generations. Overall, the history and culture of the Netherlands are diverse and vibrant, reflecting the country’s rich heritage and global influence.
Geography and Landmarks of the Netherlands
The Netherlands is known for its distinctive geography, with much of the country being situated below sea level. The landscape is characterized by flat plains, polders (land reclaimed from the sea), and dykes (embankments built to prevent flooding). The country is crisscrossed by an extensive network of canals, which are used for transportation, irrigation, and flood control.
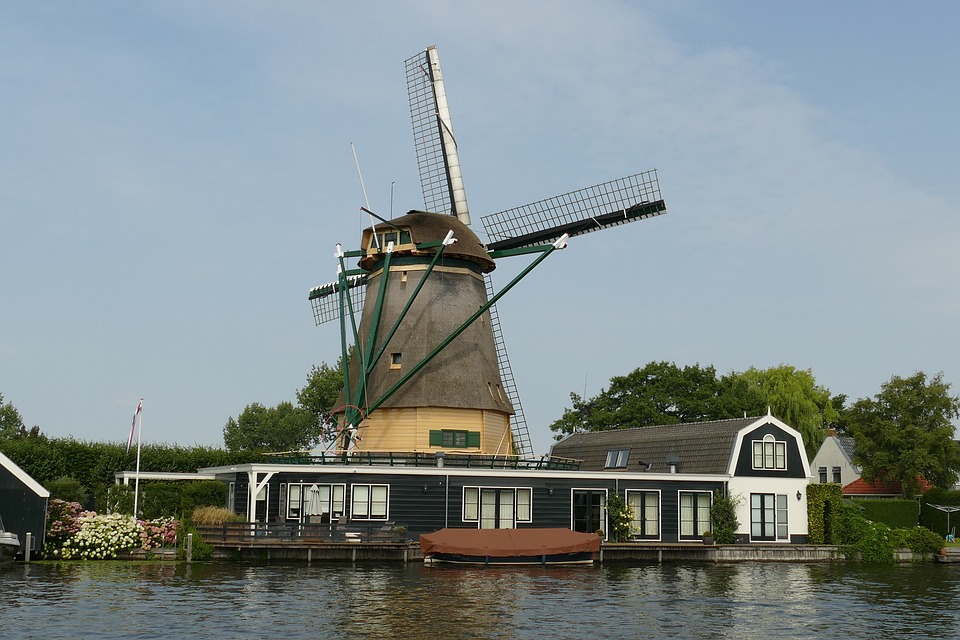
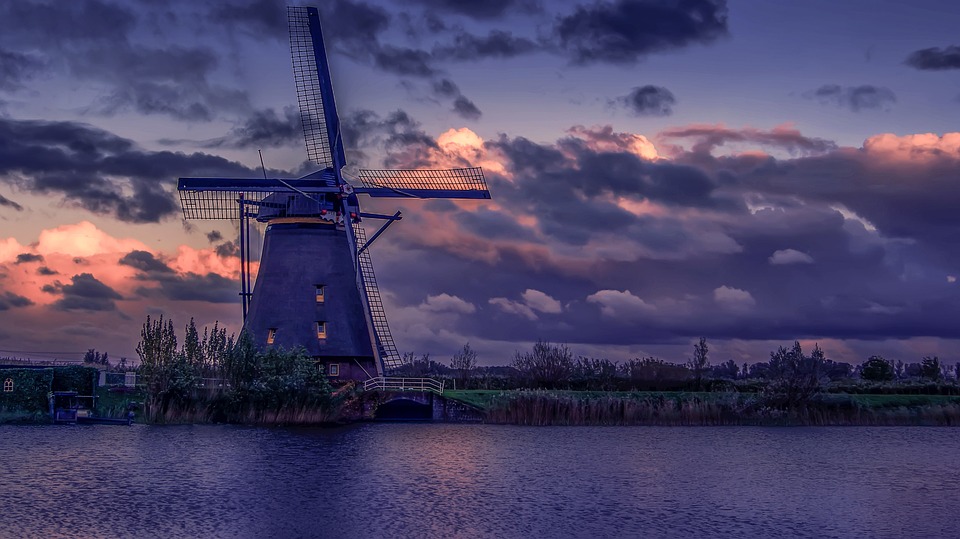
The Dutch countryside is dotted with picturesque windmills, which have been used for centuries to pump water out of low-lying areas and grind grain. The Netherlands is also famous for its tulip fields, which burst into vibrant bloom during the spring months, attracting visitors from around the world. The Netherlands is home to several iconic landmarks that showcase its rich history and cultural heritage.
One of the most famous landmarks in the country is the Anne Frank House in Amsterdam, where Jewish diarist Anne Frank hid from Nazi persecution during World War
The house has been preserved as a museum, offering visitors a poignant insight into the life of Anne Frank and the horrors of the Holocaust. Another notable landmark in the Netherlands is the Rijksmuseum, also located in Amsterdam, which houses an extensive collection of Dutch Golden Age paintings, including works by Rembrandt and Vermeer. The country is also home to several UNESCO World Heritage Sites, such as the historic canals of Amsterdam and the Wadden Sea, a unique coastal wetland area that is home to diverse wildlife.
Overall, the geography and landmarks of the Netherlands offer a fascinating glimpse into the country’s natural beauty and cultural significance.
Economy and Industry in the Netherlands
The Netherlands has a highly developed and diversified economy, with a strong focus on international trade and commerce. The country is known for its open economy and favourable business climate, making it an attractive destination for foreign investment. The port of Rotterdam is one of the largest and busiest in Europe, serving as a major hub for shipping and logistics.
The Netherlands is also a leading producer of agricultural products, particularly flowers, vegetables, and dairy products. The country is famous for its tulip industry, with millions of bulbs being exported around the world each year. In addition to agriculture and trade, the Netherlands has a thriving manufacturing sector, with a focus on high-tech industries such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.
The country is home to several multinational corporations, including Philips, Shell, Unilever, and ING Group. The Netherlands is also a global leader in sustainable energy technologies, with a strong emphasis on renewable energy sources such as wind power and solar energy. The Dutch government has implemented policies to promote innovation and entrepreneurship, leading to a dynamic start-up ecosystem in cities such as Amsterdam and Eindhoven.
Overall, the economy and industry in the Netherlands are characterised by innovation, sustainability, and global competitiveness.
Education and Healthcare in the Netherlands
Higher Education
Higher education in the Netherlands is also highly regarded, with several universities ranking among the top in the world. The country is known for its research-intensive universities and institutions that offer a wide range of degree programmes in fields such as engineering, science, business, arts, and humanities. Many courses are taught in English, making it an attractive destination for international students.
Healthcare System
The healthcare system in the Netherlands is based on a model of universal coverage and comprehensive care. All residents are required to have health insurance, which covers a wide range of medical services including hospital care, prescription drugs, mental health services, and maternity care. The Dutch healthcare system is known for its high quality of care and patient satisfaction rates.
Focus on Preventive Care
The country has a strong focus on preventive care and public health initiatives, with an emphasis on promoting healthy lifestyles and disease prevention. Overall, education and healthcare in the Netherlands are characterised by accessibility, quality, and innovation.
Famous People and Events in the Netherlands
The Netherlands has been home to many famous individuals who have made significant contributions to various fields. One of the most renowned figures in Dutch history is Vincent van Gogh, a post-impressionist painter whose works are celebrated for their emotional intensity and bold use of colour. Another iconic figure from Dutch history is Anne Frank, whose diary chronicling her experiences hiding from Nazi persecution during World War II has become one of the most widely read books in the world.
In addition to famous individuals, the Netherlands has been the site of several significant events that have shaped world history. One such event is the signing of the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713, which marked the end of the War of Spanish Succession and had far-reaching implications for European politics and diplomacy. Another notable event is the founding of the International Court of Justice in The Hague in 1945, which serves as the principal judicial organ of the United Nations.
Overall, famous people and events in the Netherlands have had a profound impact on global culture, politics, and society.
Travel and Tourism in the Netherlands
The Netherlands is a popular tourist destination known for its vibrant cities, picturesque countryside, rich cultural heritage, and friendly locals. One of the most popular tourist attractions in the country is Amsterdam, which offers a wealth of cultural experiences including world-class museums such as the Van Gogh Museum and Rijksmuseum, as well as charming neighbourhoods like Jordaan and De Pijp. Visitors can also explore Amsterdam’s iconic canal system by boat or bicycle or take a leisurely stroll through its historic streets lined with traditional Dutch architecture.
Beyond Amsterdam, visitors to the Netherlands can explore other charming cities such as Utrecht, Rotterdam, The Hague (Den Haag), Maastricht or Groningen each offering its own unique blend of history, culture, and modern amenities. The countryside offers opportunities for outdoor activities such as cycling through tulip fields or exploring national parks like Hoge Veluwe or De Biesbosch. The Netherlands also hosts several annual events that attract visitors from around the world such as King’s Day (Koningsdag) celebrations on April 27th or Carnival festivities in southern regions.
In conclusion, the Netherlands offers a diverse range of experiences for travellers seeking history, culture or natural beauty making it an ideal destination for those seeking an enriching travel experience.
FAQs
What is the Netherlands known for?
The Netherlands is known for its picturesque canals, tulip fields, windmills, and cycling culture. It is also famous for its cheese, particularly Gouda and Edam, as well as its rich art history, including the works of artists such as Rembrandt and Van Gogh.
What is the capital of the Netherlands?
The capital of the Netherlands is Amsterdam, which is also the largest city in the country.
What language is spoken in the Netherlands?
The official language of the Netherlands is Dutch. English is widely spoken and understood, particularly in urban areas and among the younger population.
What is the currency of the Netherlands?
The currency of the Netherlands is the Euro (€).
What are some popular tourist attractions in the Netherlands?
Popular tourist attractions in the Netherlands include the Rijksmuseum and Van Gogh Museum in Amsterdam, the Keukenhof Gardens, the Anne Frank House, the windmills at Kinderdijk, and the historic city of Utrecht.
What is the climate like in the Netherlands?
The Netherlands has a temperate maritime climate, with mild summers and cool winters. Rainfall is evenly distributed throughout the year.
What are some traditional Dutch foods?
Traditional Dutch foods include stroopwafels (syrup waffles), bitterballen (deep-fried meatballs), herring, pea soup (erwtensoep), and Dutch pancakes (pannenkoeken). The Netherlands is also famous for its cheese, including Gouda and Edam.
Political Boundaries of Netherlands: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
The political boundaries of the Netherlands are a crucial aspect of the country’s governance and administration. The Netherlands is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system, divided into 12 provinces, each with its own government and legislative powers. These provinces are further subdivided into municipalities, which serve as the basic administrative units responsible for local governance. The political boundaries of the Netherlands play a significant role in the distribution of power and resources, as well as in the implementation of policies and regulations at both the regional and local levels. Understanding the structure and function of these boundaries is essential for comprehending the political landscape of the Netherlands and the dynamics of its governance. The Netherlands has a long history of decentralisation, with a strong emphasis on regional autonomy and self-governance. This has led to the establishment of distinct political boundaries that delineate the jurisdiction and authority of each administrative unit. The provinces, municipalities, and districts all have specific roles and responsibilities in areas such as spatial planning, infrastructure development, social welfare, and cultural preservation. The political boundaries of the Netherlands reflect the country’s commitment to local democracy and participatory governance, as well as its efforts to ensure that decision-making processes are inclusive and responsive to the needs of different communities. As such, these boundaries are not merely administrative divisions, but also symbols of the Netherlands’ commitment to decentralisation and regional diversity. Summary The political boundaries of the Netherlands are defined by its 12 provinces, which play a crucial role in the country’s governance and administration. Provinces in the Netherlands have their own governments and are responsible for areas...
Climate Zones Of Netherlands: Different Climate Regions Of Netherlands
The Netherlands, a country situated in North-western Europe, experiences a diverse array of climate zones owing to its geographical position and topography. The nation is renowned for its predominantly flat terrain, with a considerable portion of its land area lying below sea level. This distinctive geographical characteristic, coupled with its proximity to the North Sea, plays a pivotal role in shaping the climate of the Netherlands. The country can be categorised into several distinct climate zones, each exhibiting its own set of features and weather patterns. These climate zones encompass the maritime climate, continental climate, Mediterranean climate, and mountain climate. Moreover, the urban heat island effect has emerged as a significant factor influencing the climate of urban areas in the Netherlands. Additionally, the impact of climate change has brought about perceptible alterations in the country’s weather patterns and has raised concerns regarding its long-term effects on the environment and society. Summary The Netherlands has a diverse range of climate zones, influenced by its proximity to the North Sea and its low-lying topography. The maritime climate of the Netherlands is characterized by mild winters, cool summers, and high levels of precipitation throughout the year. The continental climate of the Netherlands is marked by colder winters, warmer summers, and lower levels of precipitation compared to the maritime climate. The Mediterranean climate in the Netherlands is limited to small pockets in the southern region, with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The mountain climate in the Netherlands is found in the southern province of Limburg, with slightly cooler temperatures and higher precipitation compared to other parts of the country. The urban...
Terrain and Topography of Netherlands: mountains, valleys, and plains.
The Netherlands, also known as Holland, is a country situated in Northwestern Europe. It is renowned for its flat and low-lying terrain, with a substantial portion of the nation lying below sea level. The topography of the Netherlands is characterised by its extensive plains, river valleys, and delta regions. The country’s distinctive landscape has been moulded by centuries of human intervention and innovative water management systems. Despite its lack of natural elevation, the Netherlands has managed to flourish and develop a highly productive agricultural sector, as well as a sophisticated system of water management and flood protection. The topography of the Netherlands is largely defined by its low-lying plains, which cover a significant portion of the country’s land area. These plains are the result of centuries of sediment deposition from the numerous rivers that flow through the region. The flat terrain of the Netherlands has made it an ideal location for agriculture, with fertile soils and a mild maritime climate. However, it has also presented significant challenges in terms of managing water and preventing flooding, due to the country’s vulnerability to sea level rise and storm surges. Despite these challenges, the Dutch have developed innovative solutions to manage water and protect their land, making the Netherlands a global leader in water management and flood protection. Summary Netherlands is known for its low-lying plains and flat terrain, making it vulnerable to flooding. The absence of mountains in Netherlands contributes to its lack of natural barriers against water. The river valleys and delta regions play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of Netherlands. The topography of Netherlands has a significant...
History of Netherlands
The history of the Netherlands traces back to the early settlement of the region by various Germanic tribes, including the Frisians, Saxons and Batavians. The Romans also exerted considerable influence on the area, having conquered and established a presence in the region during the first century BC. Roman influence remains evident today in the form of archaeological sites, such as the remnants of Roman forts and roads. The Roman period had a lasting impact on the culture and language of the Netherlands. Latin, the language of the Romans, significantly influenced the development of Dutch, a Germanic language. Moreover, Roman law and governance systems left an enduring legacy in the region. The Roman period also witnessed the introduction of Christianity to the area, which would become a predominant religion in the centuries that followed. In essence, the early settlement and Roman influence laid the groundwork for the development of the Netherlands as a distinct cultural and political entity. The Dutch Golden Age Summary Early settlement in the Netherlands dates back to prehistoric times, with evidence of Roman influence in the region. The Dutch Golden Age saw a flourishing of art, trade, and science, making the Netherlands a major European power. The Dutch Republic fought for independence from Spanish rule in the Eighty Years’ War, leading to the establishment of an independent Dutch state. Dutch colonialism expanded with the establishment of the Dutch East India Company, leading to the Netherlands becoming a major colonial power in Asia. The Napoleonic Era saw the Netherlands being incorporated into the French Empire, followed by the establishment of the Kingdom of the Netherlands after Napoleon’s...
Population Density of Netherlands
The Netherlands is a small country situated in Western Europe, renowned for its flat terrain, extensive canal networks, and windmills. Despite its modest size, the Netherlands boasts one of the highest population densities globally, with over 17 million inhabitants occupying an area of merely 41,543 square kilometres. This places it as the 30th most densely populated nation worldwide. The high population density in the Netherlands is predominantly concentrated in the western region, particularly in the Randstad area, which encompasses the cities of Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, and Utrecht. The population density in this region is exceptionally high, exceeding 1,000 people per square kilometre. The substantial population density in the Netherlands is attributable to various factors, including historical urbanisation, economic prospects, and immigration. The country has a long-standing history of urbanisation, with cities such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam dating back to the medieval period. The Netherlands also possesses a robust economy, with a high standard of living and well-developed infrastructure, which attracts individuals from across the globe. Furthermore, the country maintains a relatively liberal immigration policy, which has resulted in an influx of migrants from other European nations as well as from former Dutch colonies. These factors have collectively contributed to the high population density in the Netherlands, which has both positive and negative implications for the nation. Summary The Netherlands has one of the highest population densities in the world, with over 17 million people living in a relatively small area. Factors contributing to the high population density include urbanization, immigration, and limited available land for expansion. High population density puts pressure on infrastructure and the environment, leading to...
Natural Resources of Netherlands: Where Natural Resources are Located in the Netherlands
The Netherlands, also known as Holland, is a country situated in Northwestern Europe. Despite its modest size, the Netherlands boasts a wealth of diverse natural resources. The nation is renowned for its predominantly flat terrain, with approximately one-quarter of its land area lying below sea level. This distinctive geographical feature has necessitated the development of an intricate network of dykes, canals, and polders to regulate water levels and prevent inundation. The Netherlands is celebrated for its agricultural prowess, with a substantial portion of its land devoted to farming and horticulture. In addition to its agricultural resources, the country possesses a well-developed energy sector, with a particular emphasis on renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. The Netherlands also benefits from significant water resources, including rivers, lakes, and coastal areas. Furthermore, the country has a history of mining and extraction of mineral resources, as well as a rich forest ecosystem. The sustainable management of these natural resources is crucial for the continued prosperity and well-being of the nation. Historically, the Netherlands has relied on its natural resources for sustenance and economic development. From its fertile agricultural lands to its abundant waterways and energy sources, the country has successfully harnessed these resources to build a robust and resilient economy. However, the management of these resources presents numerous challenges. The Netherlands’ low-lying geography renders it particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, such as rising sea levels and increased flooding. Additionally, the country’s high population density exerts pressure on its natural resources, leading to issues such as pollution and overexploitation. Consequently, sustainable management of natural resources has become a...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Netherlands: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites in Netherlands
The Anne Frank House in Amsterdam serves as a poignant memorial and educational centre, preserving the memory of Anne Frank and the Holocaust. Situated in the actual building where Anne Frank, her family, and four others concealed themselves from Nazi persecution during the Second World War, the museum offers visitors a sobering glimpse into the realities of life in hiding. The secret annex, accessed through a movable bookcase, has been meticulously preserved to reflect the conditions in which the occupants lived from 1942 to 1944. The museum also houses a comprehensive exhibition on the life of Anne Frank, the historical context of her diary, and the broader implications of the Holocaust. Since its opening to the public in 1960, the Anne Frank House has become one of Amsterdam’s most visited sites, attracting over a million visitors annually and serving as a crucial educational resource for understanding the consequences of discrimination and the importance of human rights. Summary The Anne Frank House stands as a powerful symbol of resilience and remembrance, preserving the memory of the Holocaust and inspiring visitors to reflect on the importance of tolerance and understanding. The Rijksmuseum offers a captivating journey through the rich artistic heritage of the Netherlands, showcasing masterpieces from the Dutch Golden Age and beyond. The Van Gogh Museum provides a fascinating insight into the life and art of Vincent van Gogh, allowing visitors to immerse themselves in the world of this iconic Dutch artist. The Keukenhof Gardens present a breathtaking display of Dutch floral culture, with millions of tulips and other flowers creating a vibrant and enchanting spectacle. The Kinderdijk Windmills are...