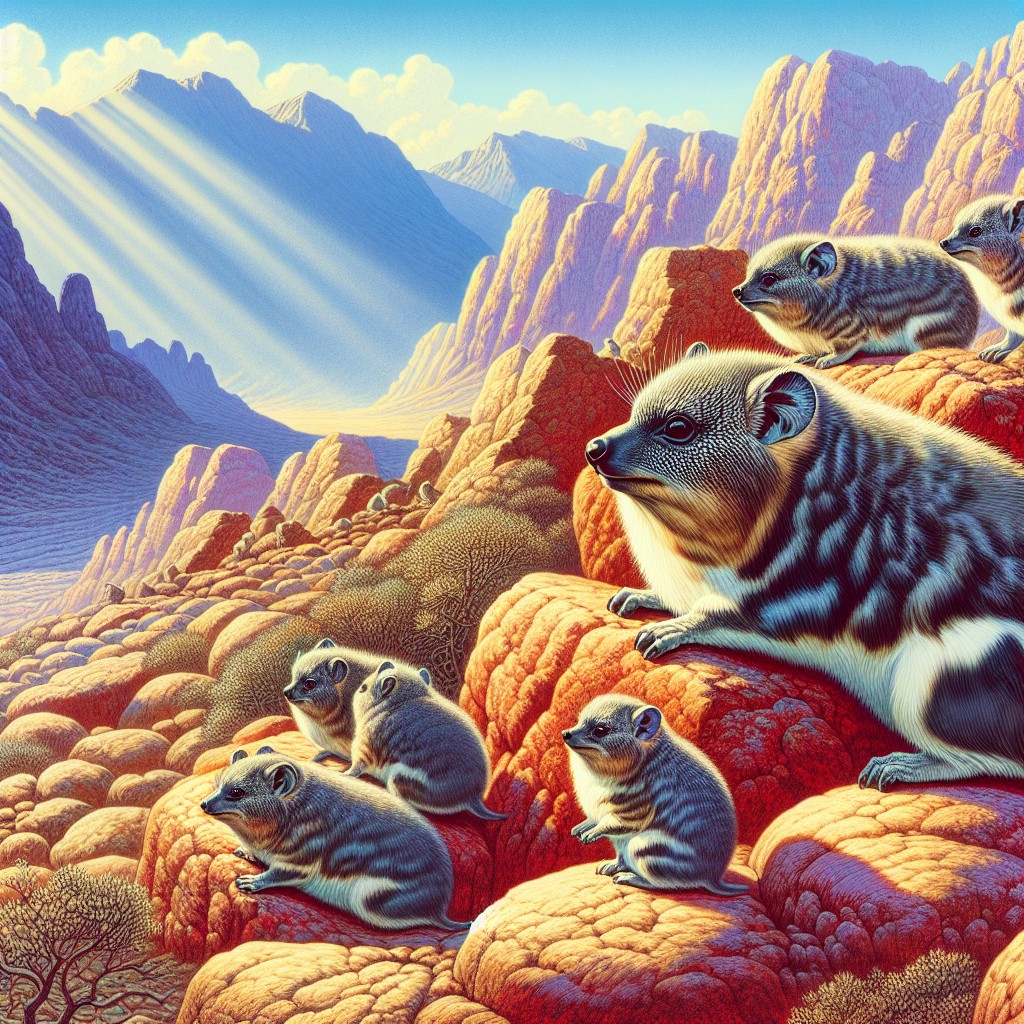
Hyracoidea, commonly known as hyraxes, are a group of small, herbivorous mammals that belong to the order Hyracoidea. They are native to Africa and the Middle East and are known for their unique physical characteristics and social behavior. Hyraxes have a long evolutionary history, dating back millions of years, and studying them provides valuable insights into the natural world.
The history of hyraxes can be traced back to the Eocene epoch, around 50 million years ago. Fossil evidence suggests that they were once widespread across Europe, Asia, and Africa. Over time, their range has become restricted to Africa and the Middle East. Despite their small size and seemingly insignificant presence, hyraxes play an important role in their ecosystems. They are considered a keystone species, as they help maintain the balance of plant communities through their feeding habits.
Studying hyraxes is important for several reasons. Firstly, they provide valuable information about the evolutionary history of mammals. Their unique characteristics and adaptations offer insights into how different species have evolved over time. Additionally, hyraxes are an important part of the food chain in their ecosystems. Understanding their behavior and interactions with other species can help researchers better understand the dynamics of these ecosystems.
Summary
- Hyracoidea are fascinating creatures with unique physical characteristics, social behaviours, and adaptations to their natural environment.
- Hyraxes have distinctive features such as small size, hoof-like toes, and teeth that never stop growing.
- Hyraxes are herbivores with a preference for leaves, fruits, and bark, and they have a unique digestive system that allows them to extract nutrients from tough plant material.
- Hyraxes are social animals that live in groups and have complex communication through vocalisations and body language.
- Hyraxes inhabit a variety of environments, from rocky outcrops to forests, and have adaptations such as thick fur and long claws to survive in their habitats.
The Physical Characteristics of Hyraxes: Understanding Their Unique Features
Hyraxes are small mammals, typically measuring between 40 to 60 centimeters in length and weighing between 2 to 5 kilograms. They have a stocky body structure with short legs and a short tail. Their body shape is similar to that of a guinea pig or a rabbit, with a rounded head and a compact body.
One of the most distinctive features of hyraxes is their fur and coloration. They have dense fur that helps them regulate their body temperature in their natural habitats. The color of their fur varies depending on the species and can range from gray to brown to reddish-brown. Some species also have markings or patterns on their fur, which can help with camouflage.
Hyraxes have specialized teeth and claws that are adapted for their herbivorous diet. They have large incisors that are used for gnawing on vegetation, as well as sharp premolars and molars for grinding plant material. Their claws are strong and curved, allowing them to grip onto rocks and climb trees if necessary.
The Diet of Hyraxes: Exploring Their Eating Habits and Preferences
Hyraxes are herbivores, meaning they primarily eat plant material. They have a specialized digestive system that allows them to efficiently extract nutrients from the tough plant fibers they consume. Their diet consists mainly of leaves, shoots, fruits, and bark.
The specific types of plants that hyraxes eat can vary depending on their habitat and availability. In some areas, they may feed on grasses and shrubs, while in others, they may consume a variety of tree leaves and fruits. They are known to be selective feeders, choosing the most nutritious parts of plants and avoiding toxic or unpalatable ones.
Hyraxes have a unique feeding behavior known as “hindgut fermentation.” This means that they have a large cecum in their digestive system where bacteria break down the cellulose in plant material. This process allows them to extract more nutrients from their food and is an adaptation to their herbivorous diet.
The Social Behaviour of Hyraxes: Uncovering Their Group Dynamics and Interactions
| Behaviour | Frequency | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Social grooming | 5 times per hour | 2-5 minutes |
| Agonistic interactions | 2-3 times per day | 10-15 seconds |
| Allogrooming | 2-3 times per day | 5-10 minutes |
| Foraging | 6-8 hours per day | N/A |
| Resting | 10-12 hours per day | N/A |
Hyraxes are highly social animals and live in groups called colonies or herds. The size and composition of these groups can vary depending on the species and habitat. Some species form small family groups consisting of a dominant male, several females, and their offspring, while others form larger groups with multiple males and females.
Communication within hyrax groups is essential for maintaining social cohesion and coordinating activities. They use a combination of vocalizations and body language to communicate with each other. Vocalizations include a variety of calls, such as alarm calls, contact calls, and territorial calls. These calls can vary in pitch, duration, and intensity, conveying different messages to other group members.
Reproductive behavior in hyraxes is also influenced by their social structure. Dominant males will mate with multiple females within their group, while subordinate males may have limited mating opportunities. Females have a gestation period of around seven months and give birth to a single offspring. The young hyrax, known as a pup, is precocial and can walk and feed shortly after birth.
Within hyrax groups, there is a dominance hierarchy that determines access to resources and mating opportunities. Dominant individuals have priority access to food and mates, while subordinate individuals must wait their turn. This hierarchy is established through aggressive interactions, such as vocal displays and physical confrontations.
The Habitat of Hyraxes: Examining Their Natural Environment and Adaptations
Hyraxes are native to Africa and the Middle East and can be found in a variety of habitats within these regions. They are adaptable animals and can be found in rocky areas, savannas, forests, and even urban environments. However, they are most commonly associated with rocky outcrops and cliffs.
Hyraxes have several adaptations that allow them to thrive in their natural habitats. Their stocky body shape and strong limbs make them excellent climbers, allowing them to navigate rocky terrain with ease. Their specialized teeth and digestive system enable them to efficiently extract nutrients from tough plant material. Additionally, their dense fur helps them regulate their body temperature in hot or cold environments.
In rocky habitats, hyraxes take advantage of the crevices and caves within the rocks for shelter and protection. They are agile climbers and can scale vertical surfaces using their strong claws. This ability to navigate rocky terrain provides them with protection from predators and allows them to access food sources that may be inaccessible to other herbivores.
The Reproduction of Hyraxes: Understanding Their Mating and Parenting Practices

Mating behavior in hyraxes is influenced by their social structure and dominance hierarchy. Dominant males will actively court females within their group, engaging in displays of aggression and vocalizations to assert their dominance. Once a female has been successfully courted, mating occurs.
Female hyraxes have a gestation period of around seven months, one of the longest among mammals of their size. This extended gestation period is thought to be an adaptation to their herbivorous diet, as it allows the fetus to develop fully before birth. After the gestation period, the female gives birth to a single pup.
Parental care in hyraxes is primarily provided by the female. The mother will nurse and protect her offspring, teaching them essential survival skills such as foraging and social interactions. The young hyrax will stay with its mother for several months before becoming independent.
The Communication of Hyraxes: Deciphering Their Vocalisations and Body Language
Hyraxes communicate with each other using a combination of vocalizations and body language. They have a wide range of vocalizations that serve different purposes. Alarm calls are used to alert other group members of potential threats, while contact calls are used to maintain social cohesion within the group. Territorial calls are used to establish boundaries and deter intruders.
In addition to vocalizations, hyraxes also use body language and gestures to communicate with each other. They may use postures, such as standing upright or crouching, to convey dominance or submission. Tail movements, ear positions, and facial expressions can also convey different messages to other group members.
Communication within hyrax groups is essential for coordinating activities and maintaining social cohesion. It allows individuals to stay connected, share information about food sources and potential threats, and establish social hierarchies. The ability to communicate effectively is crucial for the survival and success of the group.
The Predators of Hyraxes: Identifying Their Natural Enemies and Defences
Hyraxes have several natural predators that pose a threat to their survival. These predators include large carnivores such as lions, leopards, and hyenas. Birds of prey, such as eagles and owls, may also prey on young or vulnerable hyraxes.
To defend themselves against predators, hyraxes have developed several adaptations. Their ability to climb rocks and navigate vertical surfaces provides them with protection from ground-dwelling predators. They can seek refuge in crevices and caves that are inaccessible to larger predators.
Hyraxes also have a keen sense of hearing and can detect potential threats from a distance. They will emit alarm calls to alert other group members of approaching predators, allowing them to take evasive action. Additionally, their dense fur provides some protection against bites or scratches from predators.
The Cultural Significance of Hyraxes: Exploring Their Role in Folklore and Mythology
Hyraxes have played a significant role in the folklore and mythology of various cultures throughout history. In ancient Egypt, hyraxes were associated with the god Thoth, who was often depicted with the head of a hyrax. They were considered sacred animals and were believed to bring good fortune and protection.
In other African cultures, hyraxes were often associated with rainmaking rituals. Their ability to climb rocks and navigate difficult terrain was seen as a symbol of resilience and adaptability. They were believed to have the power to bring rain and fertility to the land.
In modern times, hyraxes continue to hold cultural significance in some African communities. They are sometimes used in traditional medicine or believed to have supernatural powers. Additionally, their unique characteristics and behavior make them a popular subject in wildlife documentaries and nature photography.
The Conservation of Hyraxes: Discussing the Threats to Their Survival and Protection Efforts
Hyraxes face several threats to their survival, primarily due to habitat loss and fragmentation. As human populations expand and encroach upon their natural habitats, hyraxes are losing access to food sources and suitable shelter. Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural activities all contribute to the destruction of their habitats.
Additionally, hyraxes are sometimes hunted for their meat or fur, although this is not a widespread threat. Climate change is also a concern, as it can disrupt the availability of food and water sources for hyraxes.
Conservation efforts for hyraxes focus on protecting their natural habitats and raising awareness about their importance in ecosystems. This includes establishing protected areas, implementing sustainable land-use practices, and promoting education and research about hyraxes.
Protecting hyraxes is not only important for their survival but also for the overall health of ecosystems. As herbivores, they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of plant communities. By preserving their habitats and ensuring their continued existence, we can help protect biodiversity and promote the sustainability of our natural world.
FAQs
What is Hyracoidea?
Hyracoidea is an order of mammals that includes hyraxes, also known as dassies or rock rabbits. They are small, herbivorous animals that are native to Africa and the Middle East.
What do hyraxes look like?
Hyraxes are small, furry animals that resemble rodents. They have short legs, rounded ears, and a short tail. They range in size from 30 to 70 centimeters in length and can weigh up to 5 kilograms.
What do hyraxes eat?
Hyraxes are herbivores and primarily eat leaves, fruits, and bark. They have a unique digestive system that allows them to extract nutrients from tough plant material.
Where do hyraxes live?
Hyraxes are native to Africa and the Middle East. They can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, savannas, and rocky areas.
Are hyraxes social animals?
Yes, hyraxes are social animals and live in groups called colonies. These colonies can range in size from a few individuals to over 50.
Do hyraxes have any predators?
Yes, hyraxes have several predators, including leopards, eagles, and snakes. They use their keen senses and agility to avoid these predators.
Are hyraxes endangered?
No, hyraxes are not currently considered endangered. However, some species are threatened by habitat loss and hunting. Conservation efforts are in place to protect these animals and their habitats.