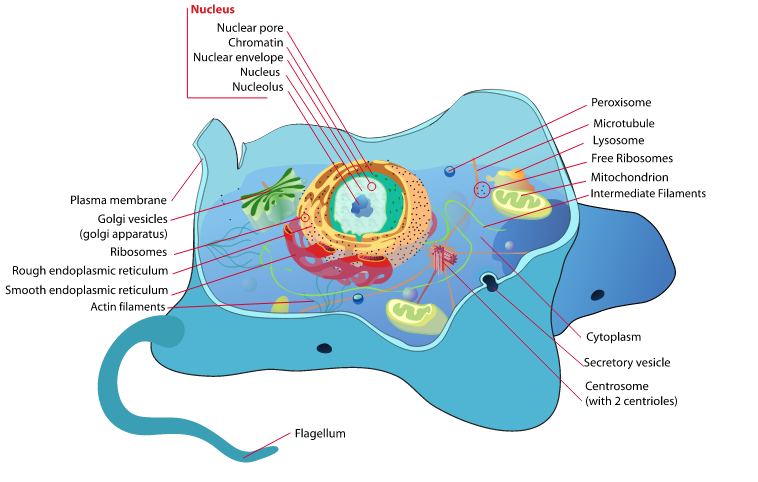
Cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the interior of cells. It is a vital component of all living cells and plays a crucial role in their functioning. The term “cytoplasm” comes from the Greek words “kytos,” meaning “container,” and “plasma,” meaning “formed substance.” It was first coined by Rudolf Virchow in 1855.
The cytoplasm is essential for various cellular processes, including metabolism, energy production, and transport of molecules. It provides a medium for chemical reactions to occur and supports the structure and shape of the cell. Without cytoplasm, cells would not be able to carry out their functions and would cease to exist.
Key Takeaways
- Cytoplasm is the living substance of cells that plays a crucial role in cell metabolism and energy production.
- The cytoplasm is composed of various organelles that work together to maintain cellular functions.
- Cytoplasmic streaming is an important process that helps in the movement of molecules within cells.
- Cytoplasmic changes can have a significant impact on cellular health and disease.
- Advancements in cytoplasmic research can lead to new innovations and discoveries in the field of cell biology.
Understanding the Composition and Structure of Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is composed of various components, including water, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, ions, and organelles. Water makes up the majority of the cytoplasm’s composition, accounting for about 70-80% of its volume. Proteins are also abundant in the cytoplasm and are involved in various cellular processes.
The structure of the cytoplasm is complex and dynamic. It consists of a network of filaments called the cytoskeleton, which provides structural support to the cell and helps maintain its shape. The cytoskeleton is made up of three types of filaments: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules.
The Role of Cytoplasm in Cell Metabolism and Energy Production
Cell metabolism refers to all the chemical reactions that occur within a cell to maintain life. These reactions include processes such as synthesis of molecules, breakdown of molecules for energy, and elimination of waste products. The cytoplasm plays a crucial role in cell metabolism by providing a medium for these reactions to occur.
One important aspect of cell metabolism is energy production. The cytoplasm is involved in the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the primary source of energy for cellular processes. ATP is generated through a process called cellular respiration, which takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria.
Exploring the Intricate Network of Organelles within the Cytoplasm
| Organelle | Function | Size (micrometers) |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Contains genetic material and controls cell activities | 5-10 |
| Mitochondria | Produces energy for the cell through cellular respiration | 1-10 |
| Ribosomes | Produces proteins for the cell | 0.02-0.05 |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Transports proteins and lipids throughout the cell | 30-100 |
| Golgi Apparatus | Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport | 1-3 |
| Lysosomes | Breaks down waste materials and cellular debris | 0.1-1 |
| Peroxisomes | Breaks down fatty acids and detoxifies harmful substances | 0.1-1 |
The cytoplasm contains various organelles, which are specialized structures that perform specific functions within the cell. These organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm and are involved in processes such as protein synthesis, energy production, and waste disposal.
Some of the organelles found in the cytoplasm include the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and ribosomes. The ER is involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism, while the Golgi apparatus is responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins for transport. Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, producing ATP through cellular respiration. Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis.
The Importance of Cytoplasmic Streaming in Cell Functioning
Cytoplasmic streaming, also known as cyclosis or protoplasmic streaming, refers to the movement of cytoplasm within a cell. It is a dynamic process that helps distribute nutrients, organelles, and other substances throughout the cell.
Cytoplasmic streaming is facilitated by the cytoskeleton and motor proteins. The cytoskeleton provides a framework for the movement of cytoplasmic components, while motor proteins use ATP to generate force and move along the cytoskeletal filaments.
This process is essential for cell functioning as it allows for efficient distribution of materials within the cell. It helps maintain homeostasis by ensuring that all parts of the cell receive necessary nutrients and molecules.
The Significance of Cytoplasmic Inclusions in Cellular Processes

Cytoplasmic inclusions are non-living substances that are present within the cytoplasm. They can be either temporary or permanent and serve various functions within the cell.
There are several types of cytoplasmic inclusions, including lipid droplets, glycogen granules, pigment granules, and crystalloids. Lipid droplets store energy in the form of lipids, while glycogen granules store glucose for energy production. Pigment granules, such as melanin, provide color to cells and tissues. Crystalloids are crystalline structures that can store waste products or excess ions.
These cytoplasmic inclusions play important roles in cellular processes. For example, lipid droplets provide a source of energy during times of nutrient scarcity, while glycogen granules release glucose when energy is needed. Pigment granules protect cells from harmful ultraviolet radiation, and crystalloids help maintain ion balance within the cell.
Cytoplasmic Transport: The Movement of Molecules within Cells
Cytoplasmic transport refers to the movement of molecules and organelles within the cytoplasm. It is essential for various cellular processes, including protein synthesis, signal transduction, and waste removal.
There are two main types of cytoplasmic transport: passive transport and active transport. Passive transport does not require energy and occurs through diffusion or facilitated diffusion. Active transport, on the other hand, requires energy and involves the use of carrier proteins or pumps to move molecules against their concentration gradient.
Cytoplasmic transport is facilitated by motor proteins, such as kinesin and dynein, which move along the cytoskeletal filaments. These motor proteins use ATP to generate force and transport molecules or organelles to their desired locations within the cell.
The Impact of Cytoplasmic Changes on Cellular Health and Disease
Changes in the cytoplasm can have significant effects on cellular health and contribute to the development of various diseases. For example, alterations in cytoplasmic pH can disrupt cellular processes and lead to cell death. Changes in cytoplasmic ion concentrations can also affect cell signaling and communication.
Certain diseases are caused by cytoplasmic changes. For example, Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by the accumulation of abnormal protein aggregates called amyloid plaques in the cytoplasm. These plaques disrupt cellular processes and lead to the death of brain cells.
The Future of Cytoplasmic Research: Advancements and Innovations
Cytoplasmic research is an active area of study, and advancements in technology are allowing scientists to explore the cytoplasm in greater detail. New imaging techniques, such as super-resolution microscopy, are providing high-resolution images of the cytoplasm and its components.
Researchers are also studying the role of the cytoplasm in various diseases and developing targeted therapies. For example, drugs that target specific organelles within the cytoplasm are being developed for the treatment of cancer.
The Vitality of Cytoplasm and its Crucial Role in Life Processes
In conclusion, cytoplasm is a vital component of all living cells and plays a crucial role in their functioning. It provides a medium for chemical reactions to occur, supports the structure of the cell, and facilitates various cellular processes.
The cytoplasm is composed of various components, including water, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, ions, and organelles. It has a complex structure that includes a network of filaments called the cytoskeleton.
The cytoplasm is involved in cell metabolism and energy production through processes such as cellular respiration. It also contains organelles that perform specific functions within the cell.
Cytoplasmic streaming helps distribute nutrients and organelles throughout the cell, while cytoplasmic inclusions serve various functions within the cell.
Cytoplasmic transport allows for the movement of molecules and organelles within the cell, and changes in the cytoplasm can impact cellular health and contribute to disease development.
Advancements in cytoplasmic research are allowing scientists to explore the cytoplasm in greater detail and develop targeted therapies for various diseases.
Overall, the cytoplasm is a vital and dynamic component of cells, playing a crucial role in life processes. Without it, cells would not be able to carry out their functions and life as we know it would not exist.
FAQs
What is cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the cell and surrounds the nucleus in eukaryotic cells.
What is the function of cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm serves as a medium for the organelles to carry out their functions, and it also helps in the movement of materials within the cell.
What is cytosol?
Cytosol is the liquid component of cytoplasm that surrounds the organelles and contains various molecules such as enzymes, ions, and nutrients.
What are the organelles found in cytoplasm?
The organelles found in cytoplasm include mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes.
What is the difference between cytoplasm and cytoskeleton?
Cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell, while cytoskeleton is a network of protein fibers that provides structural support and helps in cell movement.
What is the role of cytoplasm in cell division?
During cell division, cytoplasm divides along with the nucleus to form two daughter cells.
What happens to cytoplasm during apoptosis?
During apoptosis, cytoplasm undergoes changes such as condensation and fragmentation, leading to the death of the cell.