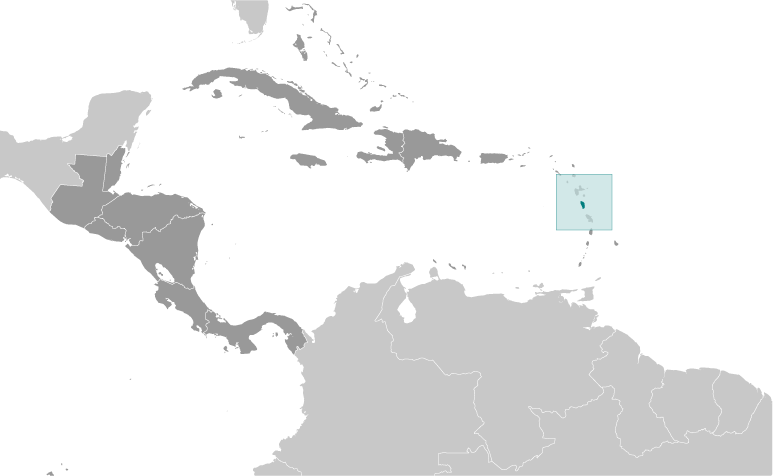
Dominica
(Commonwealth of Dominica)
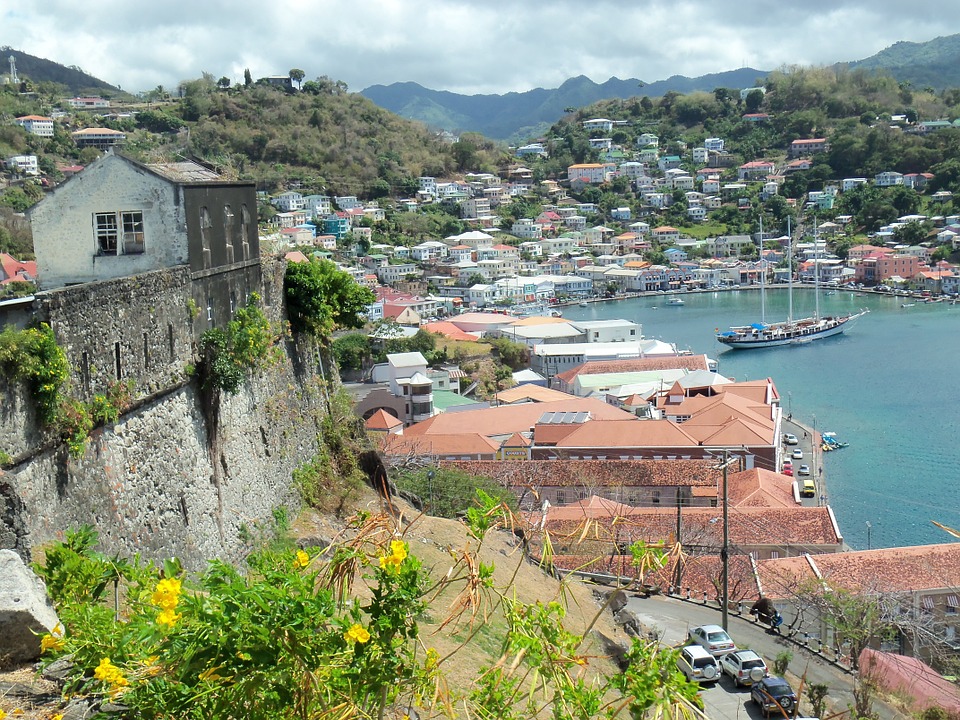
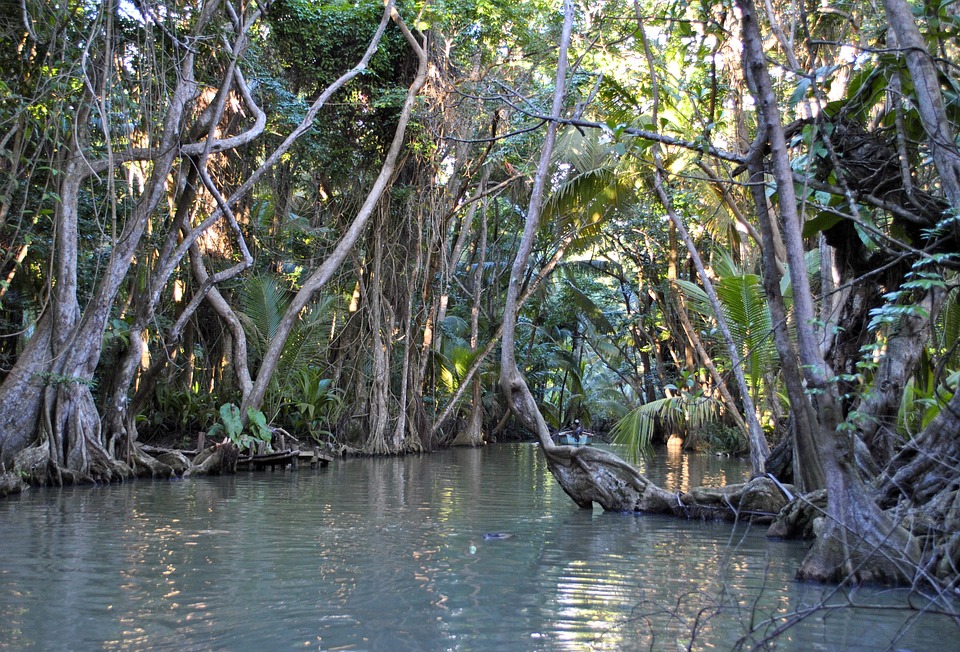
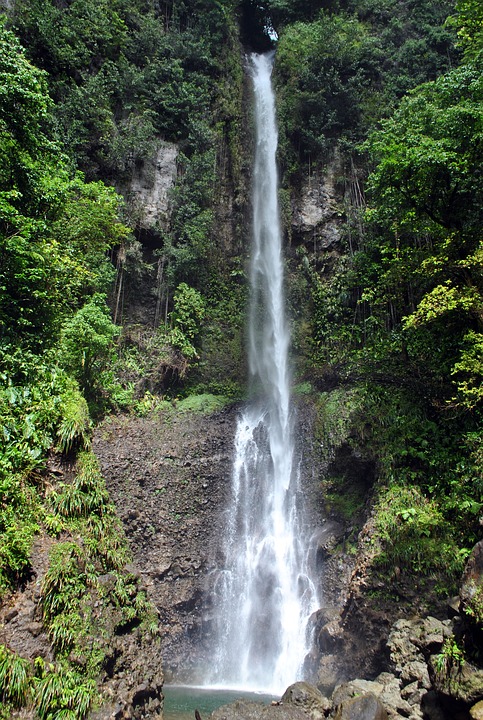
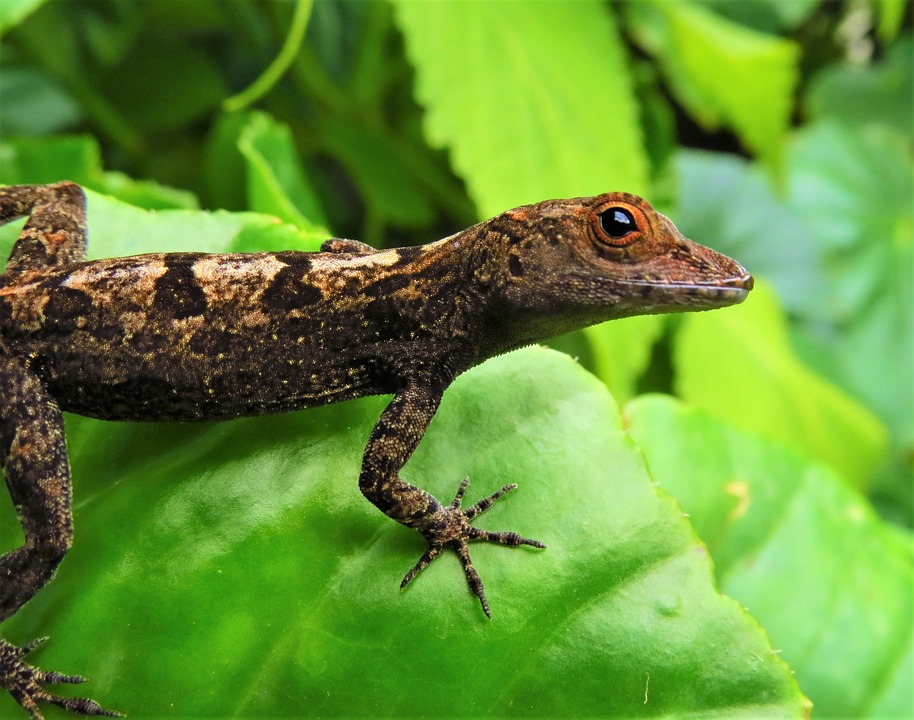

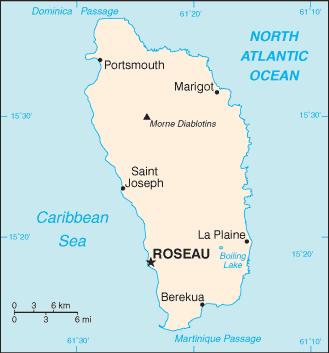




Capital: Roseau
Population (Estimated July 2012): 73,126
Area: 751 km2 or 290 mi2
Currency: Eastern Caribbean dollar (EC$)
Official Language: English
Political Information: Parliamentary Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 61.4% of the population are Roman Catholic, 20.6% are Protestant, 1.2% Jehovah’s witnesses, 7.7% are other Christian, 1.3% are Rastafarian, 1.6% have other religious beliefs and 6.1% have no religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Morne Diablotins at 1,447m or 4,747ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $500 million (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $1.02 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $13,600 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): -4:00
Counties/Provinces/States: 10 parishes; Saint Andrew, Saint David, Saint George, Saint John, Saint Joseph, Saint Luke, Saint Mark, Saint Patrick, Saint Paul, Saint Peter
Leaders: President Charles A. SAVARIN (since 2 October 2013) with Prime Minister Roosevelt SKERRIT (since 8 January 2004).
Additional: Gained Independence from the UK on the 3rd of November 1978.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Dominica
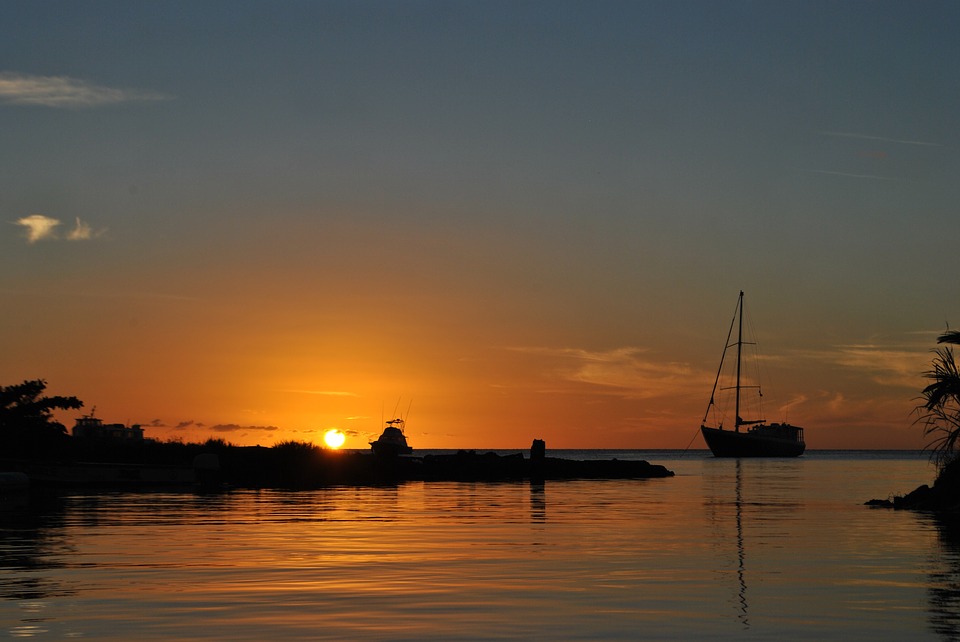
Dominica, also known as the Commonwealth of Dominica, is a small island nation located in the Caribbean Sea. It is part of the Lesser Antilles archipelago and is situated between the French overseas territories of Guadeloupe and Martinique. Dominica is often referred to as “The Nature Isle” due to its pristine natural beauty and abundant biodiversity.
The nickname “The Nature Isle” is fitting for Dominica because the island boasts an impressive array of natural wonders. From lush rainforests and cascading waterfalls to volcanic peaks and pristine beaches, Dominica offers a paradise for nature lovers and adventure seekers. The island is home to several national parks and protected areas, including Morne Trois Pitons National Park, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Dominica’s commitment to preserving its natural heritage has earned it a reputation as one of the most ecologically diverse countries in the world.
Geography and Climate of Dominica: A Tropical Paradise
Dominica covers an area of approximately 750 square kilometres (290 square miles) and has a population of around 70,000 people. The island is volcanic in origin and is characterized by rugged terrain, with steep mountains and deep valleys. The highest peak in Dominica is Morne Diablotins, which stands at 1,447 meters (4,747 feet) above sea level.
Dominica’s climate is tropical, with high temperatures and humidity throughout the year. The island experiences two distinct seasons: the dry season from December to May and the wet season from June to November. The wet season is also hurricane season in the Caribbean, and Dominica has been affected by several major hurricanes in recent years. Despite this, the island’s lush vegetation and fertile soil are a testament to its abundant rainfall.
History of Dominica: From Indigenous Peoples to Colonialism
Before the arrival of European colonizers, Dominica was inhabited by the Kalinago people, who called the island “Wai’tukubuli,” meaning “tall is her body.” The Kalinago were skilled seafarers and warriors, and they fiercely resisted European attempts to colonize the island.
In the late 15th century, Christopher Columbus became the first European to set foot on Dominica during his second voyage to the Americas. However, it was not until the 17th century that European colonization of Dominica began in earnest. The island changed hands several times between the French and the British, with each colonial power leaving its mark on Dominica’s culture and society.
Dominica gained independence from Britain on November 3, 1978, and became a republic within the Commonwealth in 2018. Since gaining independence, Dominica has faced various challenges, including economic instability and natural disasters. However, the island has also made significant progress in areas such as education, healthcare, and sustainable development.
Culture and Society of Dominica: A Fusion of African, European, and Indigenous Traditions
Dominica’s cultural heritage is a rich tapestry woven from the traditions of its African, European, and indigenous peoples. The island’s music, dance, and art reflect this diverse heritage and are an integral part of Dominican society.
Music plays a central role in Dominican culture, with genres such as calypso, reggae, soca, and bouyon being popular among both locals and visitors. Traditional dances such as the quadrille and bélé are also an important part of Dominican culture. These dances are often performed during festivals and celebrations, showcasing the island’s vibrant cultural traditions.
Dominica is also known for its vibrant arts scene, with many local artists gaining international recognition for their work. The island’s art reflects its natural beauty, with many artists drawing inspiration from Dominica’s landscapes and wildlife. Traditional crafts such as basket weaving and pottery are also an important part of Dominican culture, with artisans passing down their skills from generation to generation.
Language and Religion in Dominica: English and Christianity
English is the official language of Dominica, and it is widely spoken throughout the island. However, due to its colonial history and diverse population, other languages such as French Creole and Kalinago are also spoken by some communities.
Religion plays a significant role in Dominican society, with Christianity being the dominant faith. The majority of Dominicans are Roman Catholic, with the Catholic Church having a strong presence on the island. Other Christian denominations, such as Anglicanism and Pentecostalism, are also practised in Dominica. The island is known for its vibrant religious festivals and celebrations, which blend African, European, and indigenous traditions.
Economy of Dominica: Agriculture, Tourism, and Offshore Services
Dominica’s economy is primarily based on agriculture, tourism, and offshore financial services. The island has a strong agricultural sector, with bananas being the main export crop. Other agricultural products include citrus fruits, coconuts, and spices such as nutmeg and cinnamon.
Tourism is a growing industry in Dominica, with the island attracting visitors from around the world who come to experience its natural beauty and adventure sports. Dominica’s eco-tourism offerings, such as hiking trails, diving sites, and hot springs, make it a popular destination for nature lovers. The government has been actively promoting sustainable tourism practices to protect the island’s fragile ecosystems.
In recent years, Dominica has also developed an offshore financial services sector. The island offers a range of financial services, including offshore banking, insurance, and company registration. This sector has contributed to the diversification of Dominica’s economy and has helped attract foreign investment to the island.
Politics and Government of Dominica: A Parliamentary Democracy
Dominica is a parliamentary democracy with a political system based on the British model. The President of Dominica is the head of state, while the Prime Minister is the head of government. The country has a unicameral legislature, known as the House of Assembly, which is responsible for making laws.
The two major political parties in Dominica are the Dominica Labour Party (DLP) and the United Workers Party (UWP). Elections are held every five years, and the party that wins the majority of seats in the House of Assembly forms the government. The political landscape in Dominica is often characterized by a strong two-party system, with both parties having a significant following.
Dominica maintains diplomatic relations with several countries and is a member of various international organizations, including the United Nations and the Caribbean Community (CARICOM). The island has also been actively involved in regional initiatives aimed at promoting economic integration and cooperation among Caribbean nations.
Education and Healthcare in Dominica: Accessible and Affordable
Education in Dominica is accessible and affordable, with primary and secondary education being compulsory for all children. The island has a well-developed education system, with both public and private schools offering quality education to students. Dominica also has a tertiary education sector, with several universities and colleges providing higher education opportunities.
Healthcare in Dominica is provided through a combination of public and private healthcare facilities. The island has a network of health centres and hospitals that offer a range of medical services to residents. The government has made efforts to improve healthcare access and affordability, particularly in rural areas.
Tourism in Dominica: Eco-Tourism and Adventure Sports
Tourism is an important industry in Dominica, with the island attracting visitors from around the world who come to experience its natural beauty and adventure sports. Dominica’s eco-tourism offerings make it a popular destination for nature lovers, with opportunities for hiking, bird-watching, and exploring the island’s national parks.
The island is also known for its adventure sports, such as diving, snorkelling, and kayaking. Dominica’s underwater world is teeming with marine life, including colourful coral reefs and rare species of fish. The island’s volcanic landscape provides unique opportunities for adventure, with activities such as canyoning and zip-lining attracting thrill-seekers.
Dominica has been actively promoting sustainable tourism practices to protect its natural resources and preserve its unique ecosystems. The government has implemented initiatives to promote responsible tourism and has designated several marine protected areas to conserve the island’s marine biodiversity.
Future of Dominica: Sustainable Development and Resilience in the Face of Climate Change
Dominica faces several challenges in the future, including the need for sustainable development and resilience in the face of climate change. The island is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including rising sea levels, increased frequency and intensity of hurricanes, and changes in rainfall patterns.
In response to these challenges, Dominica has developed a Climate Resilience Execution Agency for Dominica (CREAD) to coordinate efforts to build resilience and adapt to climate change. The government has also launched initiatives to promote renewable energy and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Dominica has ambitious plans for the future, including infrastructure development projects and environmental protection initiatives. The government aims to improve access to basic services such as water, electricity, and healthcare, particularly in rural areas. The island also plans to invest in sustainable tourism infrastructure and promote eco-friendly practices.
In conclusion, Dominica is a Caribbean island nation known as “The Nature Isle” due to its pristine natural beauty and abundant biodiversity. The island’s geography and climate make it a tropical paradise, with lush rainforests, volcanic peaks, and pristine beaches. Dominica’s history is shaped by its indigenous peoples and European colonization, and its culture is a fusion of African, European, and indigenous traditions. The island’s economy is based on agriculture, tourism, and offshore financial services, and its political system is a parliamentary democracy. Dominica’s education and healthcare systems are accessible and affordable, and the island is known for its eco-tourism and adventure sports. The future of Dominica lies in sustainable development and resilience in the face of climate change, with the government implementing initiatives to protect the environment and promote renewable energy.
FAQs
What is Dominica?
Dominica is an island country located in the Caribbean Sea. It is part of the Lesser Antilles and is situated between the French islands of Guadeloupe and Martinique.
What is the capital city of Dominica?
The capital city of Dominica is Roseau. It is located on the western coast of the island and is the largest city in the country.
What is the population of Dominica?
As of 2021, the estimated population of Dominica is around 72,000 people.
What is the official language of Dominica?
The official language of Dominica is English. However, a French-based Creole language called Antillean Creole is also widely spoken.
What is the currency of Dominica?
The currency of Dominica is the Eastern Caribbean dollar (XCD). It is also used by several other countries in the Eastern Caribbean region.
What is the climate like in Dominica?
Dominica has a tropical climate with high humidity and temperatures that range from 20°C to 30°C throughout the year. The island is also prone to hurricanes and tropical storms during the hurricane season, which runs from June to November.
What are the main industries in Dominica?
The main industries in Dominica are agriculture, tourism, and offshore financial services. Bananas, citrus fruits, and coconuts are the main agricultural products, while tourism is a growing industry due to the island’s natural beauty and eco-tourism opportunities.
What are some popular tourist attractions in Dominica?
Some popular tourist attractions in Dominica include Boiling Lake, Trafalgar Falls, Morne Trois Pitons National Park, and Champagne Reef. The island is also known for its hiking trails, hot springs, and whale-watching opportunities.
Terrain and Topography of Dominica: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Dominica, also known as the “Nature Isle of the Caribbean,” is a stunning island located in the Eastern Caribbean. It is known for its lush rainforests, pristine rivers, and breathtaking landscapes. Understanding the terrain and topography of Dominica is crucial for appreciating the island’s beauty and diversity. From majestic mountains to deep valleys and fertile plains, Dominica’s terrain plays a vital role in shaping its ecosystem, climate, agriculture, tourism, and infrastructure development. Summary Dominica’s terrain is characterized by rugged mountains, deep valleys, and lush plains. The island’s majestic mountains, including Morne Trois Pitons and Morne Diablotin, offer breathtaking views and challenging hikes. Exploring the valleys of Dominica, such as Roseau Valley and Layou Valley, reveals hidden waterfalls and hot springs. The island’s fertile plains, such as the Roseau Valley and Portsmouth Valley, are ideal for agriculture and support a variety of crops. Dominica’s terrain has a significant impact on its climate, with the mountains creating a rain shadow effect and the valleys experiencing higher temperatures and humidity. Understanding Dominica’s geology, including its volcanic origins and tectonic activity, helps explain the island’s unique terrain. The island’s topography is crucial for agriculture, providing fertile land for crops and water sources for irrigation. Dominica’s unique terrain also attracts tourists, who come to hike, explore waterfalls, and experience the island’s natural beauty. Building infrastructure on Dominica’s terrain can be challenging, with steep slopes and unstable soil requiring careful planning and construction. Despite the challenges, Dominica’s diverse and beautiful landscape is worth appreciating and protecting. The Majestic Mountains of Dominica Dominica is home to a range of majestic mountains that dominate its landscape. The...
Climate Zones Of Dominica: Different climate regions Of Dominica
Dominica, also known as the “Nature Isle of the Caribbean,” is a small island nation located in the Eastern Caribbean. It is known for its lush rainforests, pristine beaches, and vibrant marine life. Dominica’s geography and climate play a crucial role in shaping its unique ecosystems and attracting tourists from around the world. Understanding Dominica’s climate zones is essential for travel and tourism as it helps visitors plan their trips accordingly. Each climate zone has its own distinct characteristics, which can greatly impact the activities and experiences available to tourists. By understanding the climate zones, visitors can make informed decisions about when to visit and what to expect during their stay. Summary Dominica has a diverse range of climate zones, including tropical rainforest, monsoon, savanna, humid subtropical, Mediterranean, arid and semi-arid, alpine, and polar. The tropical rainforest climate is characterized by high rainfall and temperatures, with lush vegetation and diverse wildlife. The tropical monsoon climate has distinct wet and dry seasons, with heavy rainfall during the wet season and cooler temperatures during the dry season. The tropical savanna climate is characterized by a long dry season and a shorter wet season, with grasslands and scattered trees. The humid subtropical climate has hot summers and mild winters, with moderate rainfall and a mix of deciduous and evergreen forests. Climate change is having a significant impact on Dominica’s climate zones, with rising temperatures, sea level rise, and more frequent extreme weather events. The Tropical Rainforest Climate of Dominica Dominica is home to one of the few remaining tropical rainforests in the Caribbean. The rainforest climate is characterized by high temperatures, abundant...
Political Boundaries of Dominica: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Dominica, also known as the “Nature Isle of the Caribbean,” is a small island nation located in the Eastern Caribbean Sea. It is known for its lush rainforests, volcanic peaks, and pristine beaches. Like any other country, Dominica has political boundaries that define its territories and administrative divisions. Understanding these political boundaries is crucial for various reasons, including governance, historical significance, and cultural identity. Summary Dominica’s political boundaries consist of 10 parishes and 3 electoral districts. The provinces of Dominica have evolved over time, with changes in boundaries and names. Understanding the districts of Dominica is important for effective governance and representation. Dominica’s political boundaries have historical significance, dating back to colonial times. Political boundaries play a crucial role in the governance and administration of Dominica. The Evolution of Dominica’s Provinces Dominica was originally inhabited by the Kalinago people before European colonization. During the colonial era, the island changed hands between the French and the British several times. As a result, the political boundaries of Dominica’s provinces evolved over time. The island was divided into two provinces, the French-controlled north and the British-controlled south. In 1763, after the Treaty of Paris, Dominica became a British colony. The island was then divided into six parishes: St. Andrew, St. David, St. George, St. John, St. Joseph, and St. Patrick. These parishes served as administrative divisions and were named after Christian saints. Understanding Dominica’s Districts In addition to provinces, Dominica is further divided into ten districts. These districts are smaller administrative divisions within the provinces and play a crucial role in local governance. The districts are Carib Territory, Castle Bruce, Saint David,...
History of Dominica
Dominica, also known as the “Nature Isle of the Caribbean,” is a small island nation located in the Eastern Caribbean Sea. It is known for its lush rainforests, pristine beaches, and vibrant culture. The history of Dominica is rich and diverse, shaped by the indigenous Kalinago people, European colonization, struggles for independence, and the island’s contributions to the abolition of slavery and fight against colonialism. Today, Dominica faces challenges such as climate change and economic growth, but remains resilient and hopeful for a bright future. Summary The Kalinago people are the indigenous population of Dominica, with a rich cultural heritage. European colonization brought the French and British to Dominica, leading to a complex history of power struggles and political change. The Windward Islands Federation played a key role in Dominica’s fight for independence. The Dominica Labour Party and the United Workers’ Party are the two major political parties in Dominica. Hurricane David had a devastating impact on Dominica’s development, highlighting the need for sustainable growth and climate resilience. Dominica’s Indigenous Peoples: The Kalinago The Kalinago people, also known as Caribs, are the indigenous inhabitants of Dominica. They have a long and storied history on the island, dating back thousands of years. The Kalinago were skilled seafarers and traders, known for their craftsmanship and knowledge of medicinal plants. They lived in harmony with nature and had a deep spiritual connection to the land. Today, the Kalinago people continue to preserve their culture and traditions. The Kalinago Territory, located on the eastern coast of Dominica, is home to the majority of the Kalinago population. Efforts have been made to promote sustainable...
Population Density of Dominica
Dominica, officially known as the Commonwealth of Dominica, is a small island nation located in the Caribbean Sea. It is part of the Lesser Antilles archipelago and is situated between the French overseas territories of Guadeloupe and Martinique. With a total land area of just 750 square kilometers, Dominica is one of the smallest countries in the world. Despite its small size, Dominica has a population of approximately 72,000 people. Population density is a measure of the number of people living in a given area, usually expressed as the number of individuals per square kilometer. It is an important demographic indicator that provides insights into how people are distributed across a country’s territory. Understanding population density can help policymakers and researchers analyze patterns of settlement, plan infrastructure development, and assess the availability of resources and services in different areas. Summary Dominica has a relatively low population density compared to other Caribbean countries. Historical trends show a gradual increase in population density, with a peak in the 1980s. Factors influencing population density include geography, climate, and economic opportunities. Regional variations in population density exist, with higher densities in urban areas and coastal regions. Urbanization has led to increased population density and pressure on natural resources in Dominica. Historical trends in Dominica’s population density Over the past century, Dominica has experienced fluctuations in its population density. In the early 1900s, the population density was relatively low, with only around 20 people per square kilometer. However, during the mid-20th century, there was a significant increase in population density due to factors such as improved healthcare and increased agricultural productivity. In recent decades,...
Population Density of Dominica
Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured per square kilometer or square mile. It is an important indicator of the level of development and resource distribution within a country. Understanding population density is crucial for policymakers and planners as it helps them make informed decisions regarding infrastructure development, resource allocation, and social services provision. In the case of Dominica, a small island nation in the Caribbean, understanding population density is particularly important due to its unique geographical and environmental characteristics. Dominica is known for its lush rainforests, volcanic peaks, and pristine rivers. The country’s population density plays a significant role in determining how these natural resources are managed and protected. Summary Dominica has a relatively low population density compared to other Caribbean countries. Dominica’s mountainous terrain and lack of flat land contribute to its low population density. Dominica’s population density has fluctuated over time due to factors such as natural disasters and economic opportunities. The majority of Dominica’s population is concentrated in urban areas, leading to higher population density in these regions. The environmental impact of population density in Dominica is a concern for sustainable development. Geographical Overview of Dominica Dominica is located in the Eastern Caribbean Sea, between the French overseas territories of Guadeloupe and Martinique. It covers an area of approximately 750 square kilometers (290 square miles), making it one of the smallest countries in the region. Despite its small size, Dominica boasts a diverse topography, with rugged mountains, deep valleys, and fertile coastal plains. The climate in Dominica is tropical, characterized by high humidity and rainfall throughout the...
Natural Resources of Dominica: Where Natural Resources are located In Dominica
Dominica, also known as the “Nature Isle of the Caribbean,” is a small island nation located in the Eastern Caribbean Sea. It is known for its lush rainforests, pristine rivers, and stunning natural beauty. Dominica is blessed with a wide range of natural resources, including forests, minerals, water, agriculture, marine resources, and energy sources. These resources play a crucial role in the country’s economy and provide livelihoods for its people. Summary Dominica is a small island nation in the Caribbean with abundant natural resources. Its location in the hurricane belt and volcanic terrain have shaped its natural resources. Dominica’s forests cover over 60% of the island and are home to a variety of tree species. Mineral resources in Dominica are limited, with only small-scale extraction of volcanic materials. Dominica’s water resources include numerous rivers, lakes, and waterfalls, which are important for tourism and agriculture. Dominica’s Geographical Location and its Impact on Natural Resources Dominica is situated between the French overseas territories of Guadeloupe to the north and Martinique to the south. Its location in the Caribbean makes it vulnerable to hurricanes and tropical storms, but it also provides a unique environment for diverse natural resources. The warm tropical climate and fertile soil contribute to the growth of lush forests and abundant agricultural crops. The island’s volcanic origin has also shaped its natural resources. Dominica is home to several active volcanoes, which have contributed to the formation of mineral deposits such as sulfur, clay, and pumice. The volcanic activity has also created hot springs and geothermal energy potential. Forest Resources in Dominica: Types and Distribution Dominica is renowned for its...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Dominica: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites in Dominica
Dominica, known as the “Nature Island of the Caribbean,” is not only blessed with stunning natural beauty but also a rich cultural heritage. This small island nation is home to a diverse population with a vibrant history that dates back centuries. Exploring Dominica’s historical sites is not only a way to learn about its past but also a means of preserving its cultural heritage for future generations. Summary Dominica is home to a rich cultural heritage, with numerous historical sites to explore. Visitors can trace the island’s history from pre-colonial times to the present day through its many sites. Indigenous sites offer a glimpse into the lives of Dominica’s ancestors and their way of life. Colonial legacy is also evident on the island, with must-visit sites from this period of history. Dominica’s religious heritage is also worth exploring, with churches, cathedrals, and temples to visit. Discovering Dominica’s Rich Cultural Heritage: A Guide to the Island’s Top Historical Sites Dominica is dotted with numerous historical sites that offer a glimpse into its fascinating past. From ancient indigenous settlements to colonial forts and churches, each site tells a unique story. These sites are not only important for understanding Dominica’s history but also for preserving its cultural heritage. One of the top historical sites on the island is Fort Shirley in Cabrits National Park. This 18th-century British fort played a significant role in the island’s colonial history and offers panoramic views of the surrounding area. Another must-visit site is the Kalinago Barana Autê, an indigenous village that showcases the traditional way of life of the Kalinago people, Dominica’s indigenous population. A Journey...