🌌 Introduction to Physics
The Science That Explains How the Universe Works
Physics is the science that seeks to understand the fundamental laws of nature—the forces, energies, and interactions that shape everything from the tiniest particles to the vastness of galaxies. It explores how objects move, why they move, and what rules govern their behavior.
At its heart, physics asks questions like:
-
Why do things fall?
-
How does light travel?
-
What causes electricity and magnetism?
-
What is time, space, energy, and matter?
Often called the “foundation of all sciences,” physics underpins everything from chemistry and biology to engineering and astronomy. Whether it’s explaining why the sky is blue, how bridges stay standing, or how smartphones work, physics provides the framework.
From Isaac Newton’s laws of motion to Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity, and from quantum mechanics to black holes, physics challenges us to think big—and small. It combines deep curiosity with mathematical precision to uncover the rules of reality.
Studying physics not only helps us understand the universe—it equips us with problem-solving skills that drive innovation and technological progress.
Physics by Topic
China’s Tianwen-1 Mars Mission: First Mars Sample Return Mission
China’s Tianwen-1 Mars Mission: First Mars Sample Return Mission Tianwen‑1 marked China’s grand debut on Mars, placing an orbiter, lander, and rover in one mission. Read on to discover how this daring launch reshaped space exploration, what lies ahead with the Tianwen‑3 sample return mission, and what it means in the global race to answer: Is there life on Mars? Outline What was Tianwen‑1, and why launch it? How did Tianwen‑1 reach and enter Mars orbit? What instruments did the Mars orbiter carry? How did the Zhurong rover perform its Mars mission? What scientific discoveries did Zhurong make? Why is Tianwen‑1 a milestone in planetary exploration? What is the plan for the Tianwen‑3 Mars sample‑return mission? How will Tianwen‑3 return samples from Mars to Earth? When and why will Tianwen‑3 launch? How does China’s mission compare to NASA/ESA? 1. What was Tianwen‑1, and why was it launched? China’s Tianwen‑1 Mars mission was the country’s first Mars mission to independently reach Mars with an orbiter, lander, and rover in one compact package—an approach never used previously by NASA or ESA. Launched from Wenchang on July 23, 2020, via Long March 5, it aimed to study Martian topography, geology, water‑ice presence, space environment, and the planet’s internal structure. China’s aim was clear: advance planetary exploration of China, close the technological gap with NASA, and position itself as a leader in deep space exploration. How did Tianwen‑1 reach and enter Mars orbit? After a nearly seven‑month journey through the inner solar system, Tianwen‑1 entered Mars orbit on February 10, 2021, at about 20:18 Beijing Time. Tianwen in Mandarin means “Questions to Heaven”—apt for a probe seeking answers about water, geology,...
Mars Colonisation: How Close Are We to Colonising Mars?
Mars Colonisation: How Close Are We to Colonising Mars? Mars, the fascinating red planet, has captured human imagination for decades. Today, Mars colonisation is evolving from science fiction into a genuine scientific and technological ambition propelled by organisations like SpaceX, NASA, and visionaries such as Elon Musk. This blog post dives into how close we are to sending humans on Mars, building cities on Mars, and making humans on Mars a reality. Whether you’re curious about the colonisation of Mars timeline, the mission to Mars, or the science and engineering that will get us there, this article is worth reading—it covers the latest developments, current challenges, future prospects, and why it matters for humanity. Article Outline What Is Driving Mars Colonisation? How Soon Will We See Humans on Mars? Who Is Leading the Mars Race — NASA, SpaceX, or Others? What Are the Biggest Challenges to Colonise Mars? How Will Astronauts Survive the Mars Journey? What Will a Mars Colony Need to Thrive? Can Robotics Prepare the Way to Colonise Mars? What Role Will Mars Settlement Play in Space Exploration? Can a City on Mars Support Lifelong Habitation? Why Mars Colonisation Matters for Earth and Beyond What Is Driving Mars Colonisation? Mars colonisation stems from a mix of technological ambition, existential exploration, and visionary leadership. Mars has long been our planet’s most Earth-like neighbour, earning its nickname as the red planet. It also represents the next logical step after the Moon to Mars transition. Visionaries like Elon Musk aim to build a multi-planetary civilisation, while NASA has rekindled its commitment under the Artemis program that includes Mars missions as a natural...
Flat Earth Debunked
Flat Earth Debunked and Why Some Still Believe the Earth Is Flat For centuries, people around the world have understood that the earth is a globe—a sphere floating in space. Yet today, a growing number of individuals still believe the earth is flat. This resurgence in flat earth beliefs is not just a quirky footnote in modern culture—it’s part of a broader trend of distrust, conspiracy theories, and rejection of scientific evidence. But why does this movement persist in the age of satellites and space travel? In this article, we’ll explore the origins of flat earth theory, examine the arguments made by flat-earthers, and provide the most compelling evidence for a spherical earth. Article Outline What Is the Flat Earth Theory and Where Did It Begin? Why Do Some People Believe the Earth Is Flat Today? What Role Does Conspiracy Play in the Flat Earth Belief? How Did Ancient Civilizations Understand the Shape of Earth? What Scientific Proof Refutes the Flat Earth Model? Can the Curvature of the Earth Be Seen with the Naked Eye? What Are Common Flat Earth Claims and How Are They Debunked? Is There a Psychological Reason People Believe in a Flat Earth? What Is the Flat Earth Society and Who Are Its Followers? How Can We Communicate Science in the Age of Misinformation? What Is the Flat Earth Theory and Where Did It Begin? The flat earth theory proposes that our planet is not a sphere but a plane or disk, sometimes depicted with the sun and moon hovering in circles above a flat world. This idea can be traced back to many ancient...
Can Humans Live on Mars – Colonising The Red Planet
Can Humans Live on Mars – Colonising The Red Planet Could humans really live on Mars? It’s a question that has fascinated scientists, storytellers, and space enthusiasts for generations. With NASA’s ambitious Moon to Mars program underway and an increasing global interest in interplanetary colonisation, the concept of building a human settlement on the Red Planet is becoming less science fiction and more science possibility. In this in-depth article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about what it would take to live on Mars—from the technical hurdles and the planetary conditions to the bold vision for Mars colonies. If you’ve ever imagined humans on Mars, this is your guide to the future of life beyond Earth. Article Outline: Questions About Living on Mars 1. What Makes Mars a Candidate for Human Settlement? 2. Could Humans Survive on Mars as It Is Today? 3. How Would We Get to Mars from Earth? 4. What Would a Day on Mars Be Like? 5. What Do We Know About the Martian Atmosphere? 6. Could We Find Water on Mars to Support Life? 7. How Would People Work on Mars and Stay Healthy? 8. What Kind of Food on Mars Could Sustain a Population? 9. Could Terraforming Mars Make It More Like Earth? 10. Is NASA Preparing a Real Mission to Mars? What Makes Mars a Candidate for Human Settlement? Mars, also called the Red Planet, is often viewed as the most promising destination for human settlement outside Earth. This is partly because it’s relatively close in our solar system and has a day length and seasonal cycle similar to...
The H-Bomb Chronicles: The Most Powerful Weapon in History
The hydrogen bomb, commonly referred to as the H-bomb, represents a significant milestone in the history of nuclear weaponry. Its development was catalysed by the geopolitical tensions of the early 20th century, particularly during and after World War The initial foray into nuclear fission, which culminated in the atomic bomb, laid the groundwork for the more powerful thermonuclear weapon. The first successful detonation of an atomic bomb by the United States in 1945 at the Trinity test site in New Mexico marked a pivotal moment in military history, but it also ignited a race for more destructive capabilities. Scientists and military strategists quickly recognised that fission-based weapons could be significantly enhanced through fusion processes, leading to the conceptualisation of the H-bomb. The Cold War Escalation The successful test by the Soviet Union marked a significant turning point in the Cold War, as it sparked a renewed sense of urgency amongst American scientists to develop a hydrogen bomb. The First Successful Test In 1952, the United States conducted its first successful test of an H-bomb, codenamed “Ivy Mike,” on the Enewetak Atoll in the Pacific Ocean. This test demonstrated the immense power of thermonuclear reactions, producing an explosion equivalent to 10.4 megatons of TNT, far surpassing the yield of any atomic bomb previously detonated. A New Era of Nuclear Capabilities Summary The H-Bomb was developed during the Cold War as a result of the arms race between the United States and the Soviet Union. The H-Bomb is a thermonuclear weapon that uses the energy from a primary fission reaction to ignite a secondary fusion reaction, resulting in a much more...
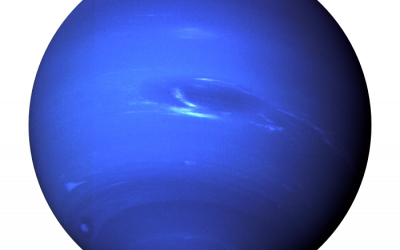
Exploring Neptune: The Planetary Guide to the Eighth Planet from the Sun
Exploring the Mysteries of Neptune: The Eighth Planet in Our Solar System Welcome to the outer reaches of our celestial neighborhood, where icy giants and distant moons dance in the darkness. In this article, we’re diving deep into the enigmatic world of Neptune, the eighth planet in the solar system and farthest planet from the sun. From its discovery to the latest missions, we’ll uncover the wonders of this captivating planet. Why Neptune? Unveiling the Secrets of the Distant Planet Neptune, named after the Roman god of the sea, holds a unique place in our solar system. This giant, icy world is 16 to 55 times the mass of Earth, making it one of the four gas giants along with Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus. Its striking blue hue, caused by the presence of methane in its atmosphere, sets it apart as one of the most visually stunning planets. Intriguingly, Neptune was the first planet to be discovered through mathematical predictions rather than through direct observation. French astronomer Urbain Le Verrier predicted its existence based on irregularities in the orbit of Uranus. Then, in 1846, Johann Gottfried Galle and Heinrich Louis d’Arrest observed Neptune for the first time, confirming its existence. But Neptune’s mysteries didn’t stop there. The planet boasts a turbulent atmosphere with winds that can reach up to 1,500 miles per hour (2,400 kilometers per hour), the fastest in the solar system. Its iconic feature, the Great Dark Spot, is a massive storm system comparable to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. However, unlike Jupiter’s storm, the Great Dark Spot on Neptune was short-lived and has since disappeared, leaving...
Venera 1: A Milestone in Venus Exploration
Introduction Venera 1, a Soviet spacecraft, holds a significant place in the history of space exploration. Launched on February 12, 1961, Venera 1 attempted the first ‘flyby’ of Venus, marking a groundbreaking milestone in our understanding of our neighboring planet. In this article, we will delve into the mission of Venera 1, the challenges it faced, and the valuable insights it provided about Venus. Venera 1’s Mission: To Explore Venus Venera 1’s primary mission was to gather data on Venus by performing a flyby. Equipped with scientific instruments, the spacecraft aimed to study the atmosphere, magnetic field, and cosmic radiation surrounding the planet. This ambitious undertaking raised hopes for a substantial leap forward in Venus exploration. The Journey of Venera 1 Venera 1 embarked on its journey towards Venus with great anticipation. However, the mission encountered multiple challenges along the way. Despite these obstacles, Venera 1 bravely headed towards its destination, demonstrating the courage and determination of the scientific community. The Challenges Faced by Venera 1 Communication Breakdowns: During the mission, the spacecraft faced difficulties in maintaining communication with Earth, hampering the flow of scientific data. These communication breakdowns posed a significant obstacle to the success of the mission. Navigational Issues: Venera 1 struggled to accurately navigate its path towards Venus due to limited knowledge of the planet’s gravitational field and atmospheric conditions. These navigational challenges further complicated the mission. Venera 1’s Encounter with Venus: What We Found Despite the difficulties encountered, Venera 1 successfully approached Venus on May 19, 1961. However, it did not achieve the intended flyby. Instead, the spacecraft passed within approximately 100,000 kilometers of Venus...
Captain Bruce McCandless: The Man Who Defied Gravity
Introduction Captain Bruce McCandless was a pioneer and a true legend in the field of aerospace engineering. His remarkable accomplishments and groundbreaking innovations have left an indelible mark on the history of space exploration. In this article, we will delve into the life and achievements of Captain Bruce McCandless, shedding light on his unparalleled expertise, authority, and trust in the aerospace industry. Early Life and Education Born on June 8, 1937, in Boston, Massachusetts, Bruce McCandless had always been fascinated with the boundless sky above him. Growing up, he nurtured a deep passion for aviation and astral science. This insatiable curiosity led him to pursue a degree in aerospace engineering at the United States Naval Academy, where he excelled both academically and as an accomplished pilot. The Journey to NASA After graduating from the Naval Academy, McCandless embarked on a journey that would lead him to the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). His exceptional skills as a pilot and his relentless dedication to his craft caught the attention of NASA officials, who recognized his potential to contribute significantly to the field of space exploration. Breaking Barriers: The Untethered Spacewalk Captain Bruce McCandless cemented his place in history when he made the iconic untethered spacewalk on February 7, 1984. Strapped to the Manned Maneuvering Unit (MMU), he ventured out into the vast expanse of space, becoming the first human to navigate without the use of a tether. This breathtaking feat showcased McCandless’ remarkable expertise and fearlessness, pushing the boundaries of what was deemed possible. The Legacy of Innovation McCandless’ groundbreaking achievement opened new doors for space exploration and laid...
The Sun Test
Your Sun Test may take a minute to load. If you have to navigate away from this page for any reason, don’t worry, you will have the option to resume your test from the point you left upon your return. The test may have multiple choice, multiple answer or true/false questions and is timed but has no time limit. It should be considered an aid to study for exams or merely a test of your knowledge base giving you indication of areas you may need further study in. Once you have completed your test you will be able to review your results. This will give you some indication of the area you need further study or which areas you are proficient. We recommend you take the Sun Test before reading the subject matter. If you score 80% or more than you have the option of skipping the section but if you score less than 80% we recommend you read the material associated. Then try the test again until you are able to gain a passing result of 80% correct. Error: Embedded data could not be displayed. Why Use the Sun Test? As previously stated tests give the user indication of their strengths and weaknesses. This allows them to spend less time studying things they are proficient in and spend more time improving their knowledge where they may have gaps. Tests are also a great tool for revision because they require the user to recall information they may have previously learnt, be it recently or some time ago....
Planet Earth Test
Your Planet Earth Test may take a minute to load. If you have to navigate away from this page for any reason, don’t worry, you will have the option to resume your test from the point you left upon your return. The test may have multiple choice, multiple answer or true/false questions and is timed but has no time limit. It should be considered an aid to study for exams or merely a test of your knowledge base giving you indication of areas you may need further study in. Error: Embedded data could not be displayed. Once you have completed your test you will be able to review your results. This will give you some indication of the area you need further study or which areas you are proficient. We recommend you take the Planet Earth Test before reading the subject matter. If you score 80% or more than you have the option of skipping the section but if you score less than 80% we recommend you read the material associated. Then try the test again until you are able to gain a passing result of 80% correct. Why Use the Planet Earth Test? As previously stated tests give the user indication of their strengths and weaknesses. This allows them to spend less time studying things they are proficient in and spend more time improving their knowledge where they may have gaps. Tests are also a great tool for revision because they require the user to recall information they may have previously learnt, be it recently or some time ago. This recall of information improves its retention in your...
The Solar System
THE SOLAR SYSTEM The Origin of The Solar System BasicAdvanced Around 5,000 million years ago the remnant of an exploded giant star (called a supernova) began to clump together under the force of gravity. These clumps were very small to start with but slowly as they continued to be attracted to one another they grew, eventually forming a huge disc with a large concentration of matter at its centre. Smaller clumps formed on the outskirts which over time became the planets and their moons while the much larger clump of hydrogen and helium started to heat under the increasing pressure of its own gravity. This ball of heated gas began to glow as the increasing pressure turned the gas into plasma and nuclear fission began producing more and more elements. About 5,000 years later our solar system had formed. The gas cloud left after the supernova would have contained many elements including elements much too heavy to be produced in a star the size of ours. The main four elements present in order of abundance would have been Hydrogen, Helium, Oxygen and silicon with hydrogen making up approximately 90% of the total matter. It would have only taken a small concentration of matter to form, which slowly began drawing the rest of the dust cloud into a rough central point through gravity over thousands of years. The cloud would begin to take the form of ball which is drawn into motion by the spin of the Milky Way, with the closest point to the centre of our galaxy moving faster collapsing the dust cloud. Newton’s Law of motion states that the conservation of angular momentum would cause...
Geography of Earth
The Geography of Earth is unique in our solar system in that it is predominantly covered by water with the oceans covering 70.1% of the surface and with only 29.1% dry land (this is without taking into account all the lakes and rivers etc). Land Mass Continents Six continent of the world Seven continents Islands Lines of Latitude Lines of Longitude Time Zones Interactive map of World Geography Earth’s Environment Temperature variations Topography Atmospheric Pressure The Geography of Earth is unique in our solar system in that it is predominantly covered by water with the oceans covering 70.1% of the surface and with only 29.1% dry land (this is without taking into account all the lakes and rivers etc). Land Masses Continents The land masses of the world are normally divided into seven continents. The term continent comes from the Latin “terra continens” meaning continuous land and this ambiguous term has led to many variations as to the number of continents. Six continent of the world There are a few variations in the six continent description of the world’s landmass. In the past it was considered that both North and South America as a single continent and this led to the Olympic symbol of five interlocking circles (Antarctica not included). This view has now changed but some now consider Europe and Asia to be a single continent known as Eurasia as they are a single landmass. However this logic would also revert thinking back to America as a single continent and Africa being combined with Asia and Europe to form a super continent. This would allow...