Pakistan
(Islamic Republic of Pakistan)
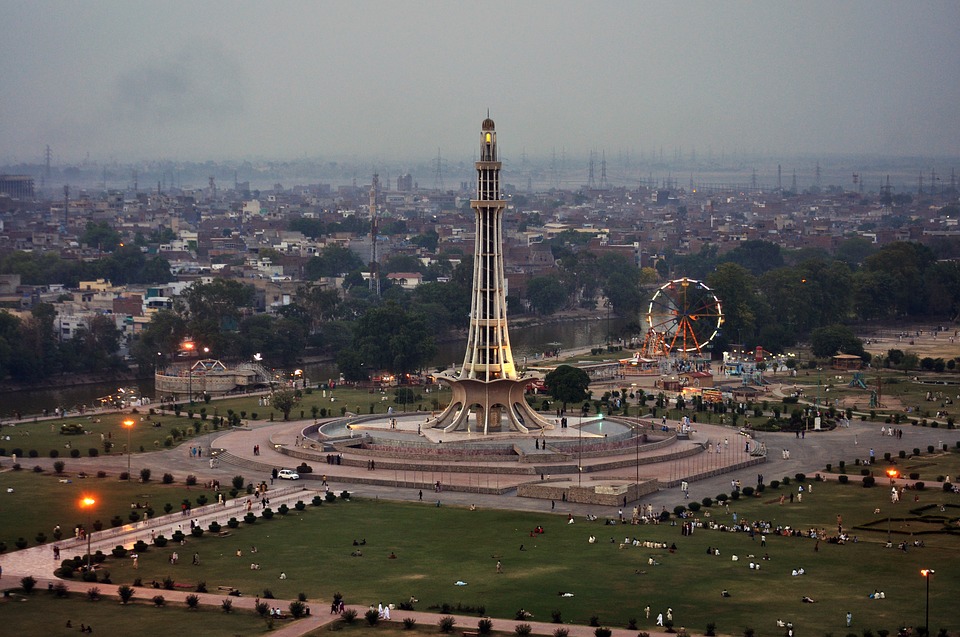

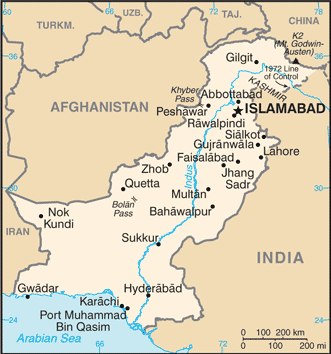
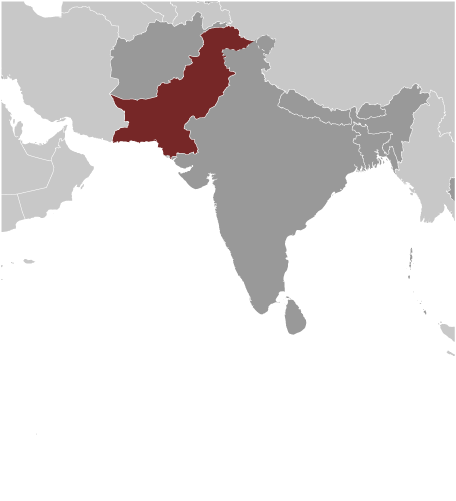





Capital of Pakistan: Islamabad
Population (Estimated July 2012): 190,291,129
Area: 796,096km2 or 307,374mi2
Currency: Pakistani Rupee (PKR)
Official Language: Urdu and English (but 48% of the population speak Punjabi the most spoken language in Pakistan)
Political Information: Federal Presidential, Parliamentary Republic
Official Religion: Islam
(approximately 95% of the population are Muslim and 5% are Christian or Hindu).
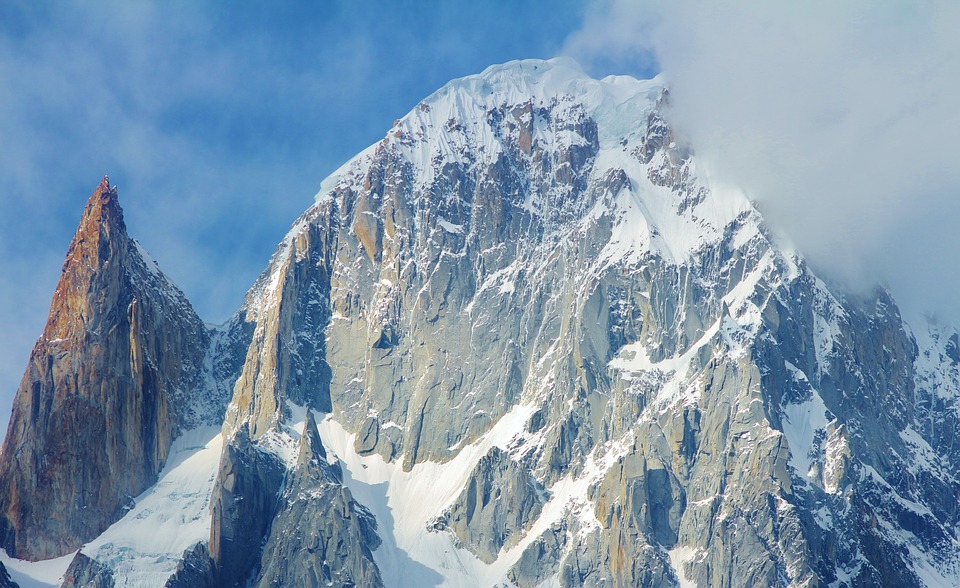
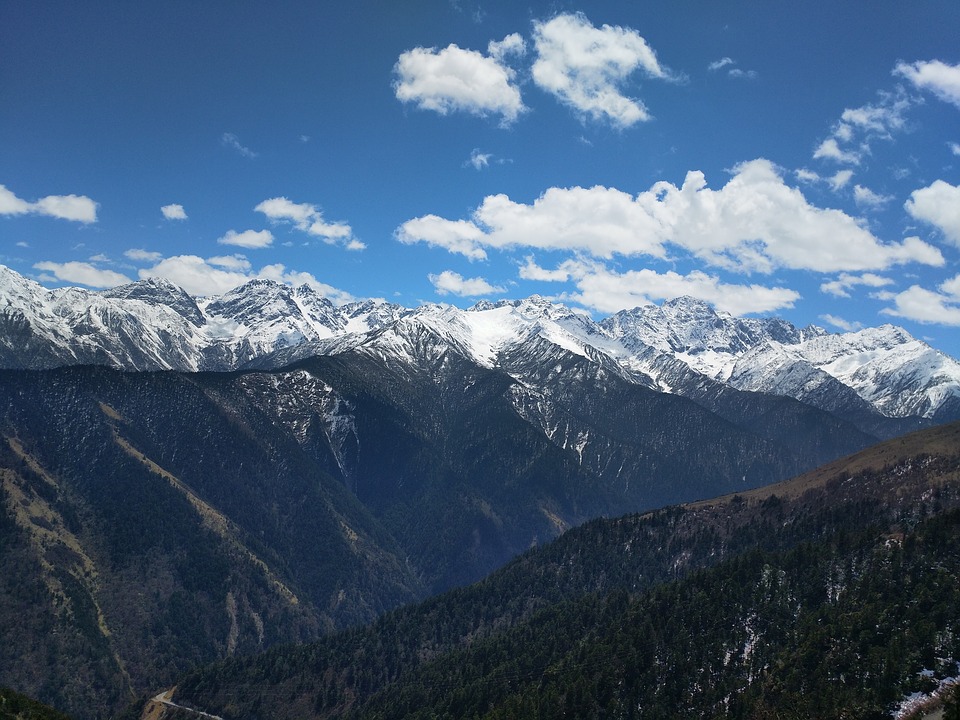
Highest Mountain: K2 at 8,611m or 28,251ft (worlds 2nd highest)
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $204.1 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $488 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $2,800 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +5:00
Counties/Provinces/States: 4 provinces, 1 territory*, and 1 capital territory**; Balochistan, Federally Administered Tribal Areas*, Islamabad Capital Territory**, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (formerly North-West Frontier Province), Punjab, Sindh
Leaders: President Mamnoon HUSSAIN (since 9 September 2013) with Interim Prime Minister Nasir-UL-MULK (since 1 June 2018); Imran KHAN to be sworn in as prime minister on 11 August 2018 following his party’s majority win in the 25 July 2018 National Asembly election
Additional: Gained independence from British India on the 14th of August 1947.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Pakistan
Pakistan, officially known as the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country situated in South Asia. It shares borders with India to the east, Afghanistan and Iran to the west, and China to the north. The Arabian Sea lies to the south of Pakistan.
With a population exceeding 220 million people, Pakistan is the fifth most populous country globally. The capital city is Islamabad, whilst Karachi is the largest city and economic centre of the country. The official languages are Urdu and English, and the currency is the Pakistani Rupee.
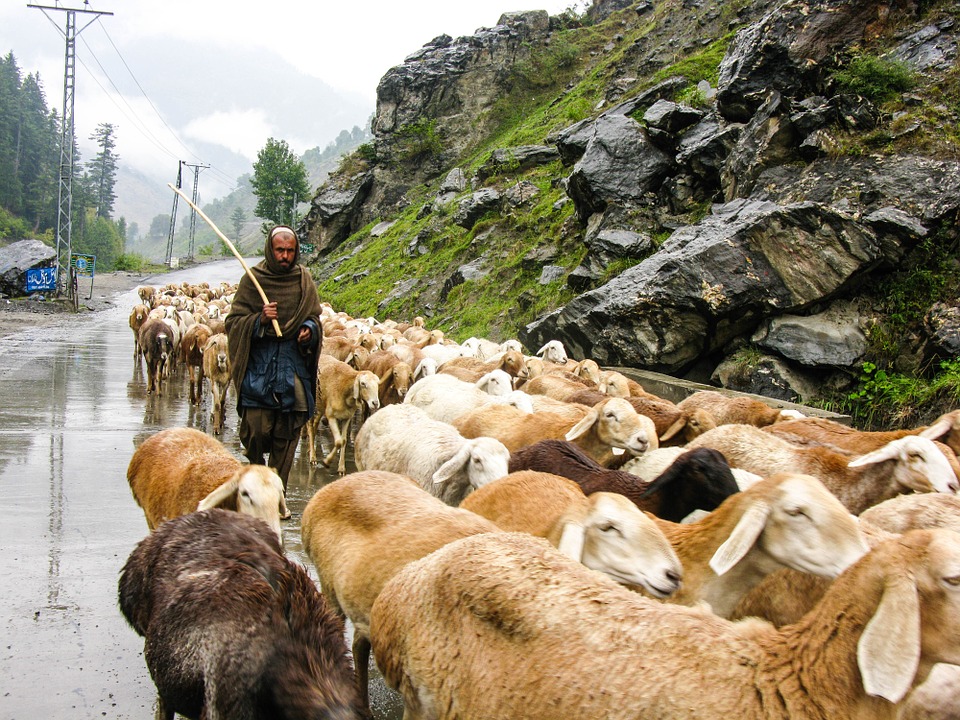
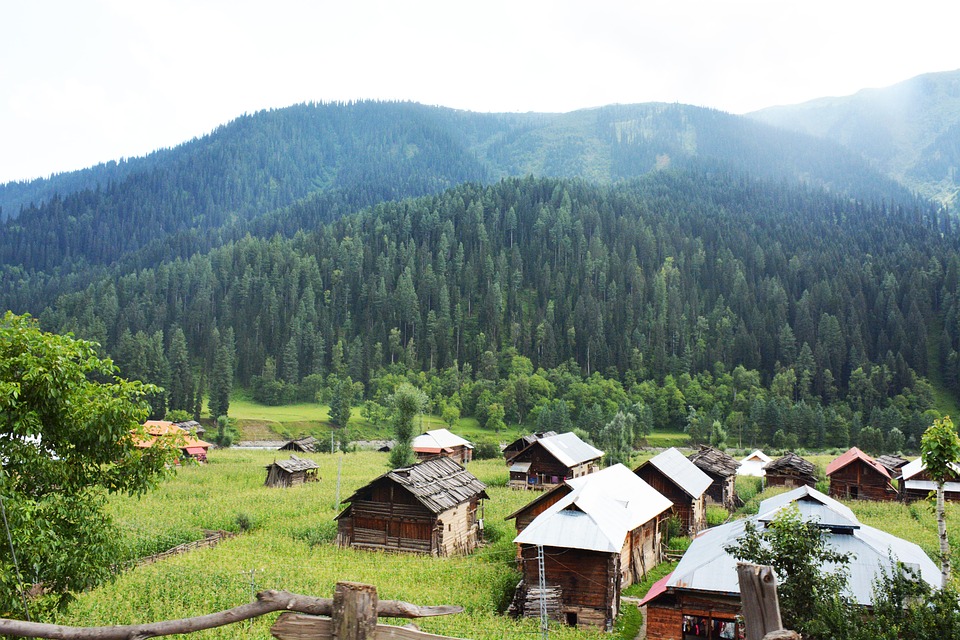
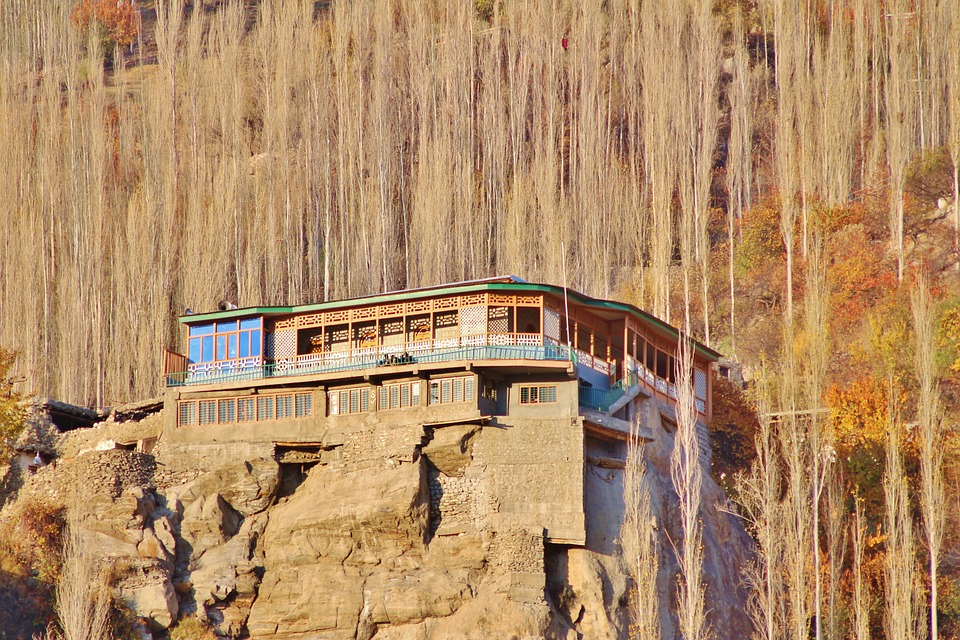
Pakistan boasts a rich and diverse cultural heritage, with influences from various civilisations including the Indus Valley Civilisation, Persian Empire, Islamic Caliphates, and British colonial rule. The country is renowned for its picturesque landscapes, historical sites, and vibrant traditions. From the snow-capped peaks of the Himalayas in the north to the sandy beaches of the Arabian Sea in the south, Pakistan offers a wide range of natural beauty and cultural experiences for visitors.
With a history spanning thousands of years, Pakistan possesses a unique blend of ancient traditions and modern influences, rendering it a captivating destination for travellers from across the globe.
Summary
- Pakistan is a diverse and vibrant country located in South Asia, with a rich history and culture.
- The geography of Pakistan ranges from mountains in the north to deserts in the south, with a variety of climates including arid, tropical, and temperate.
- Pakistan has a long and complex history, with influences from various empires and religions, leading to a diverse and unique culture.
- The economy of Pakistan is largely based on agriculture, textiles, and manufacturing, with a growing focus on technology and services.
- Pakistan is a federal parliamentary republic, with a multi-party system and a president as the head of state, and a prime minister as the head of government.
Geography and Climate of Pakistan
Mountainous Regions
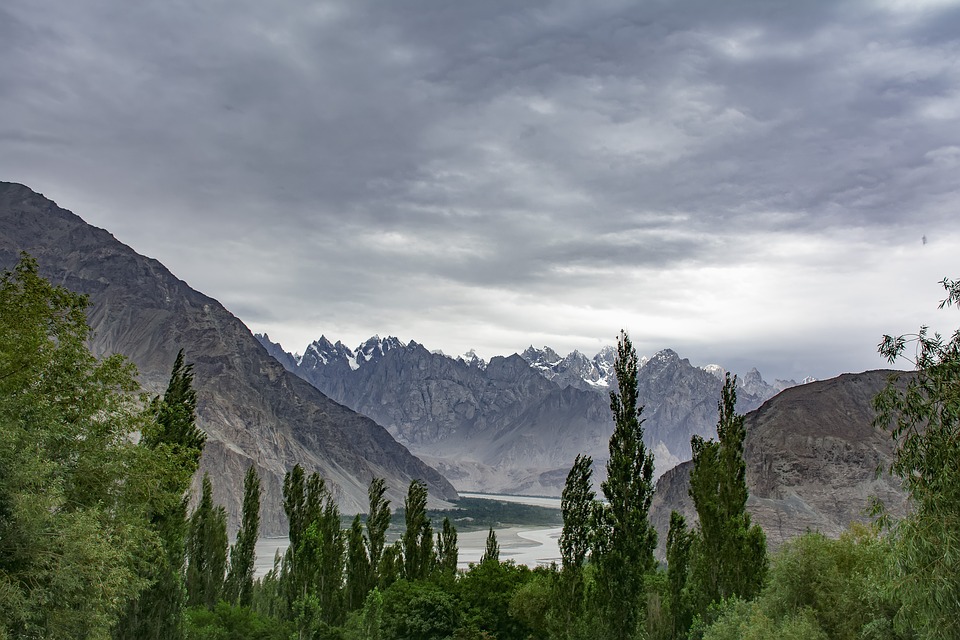
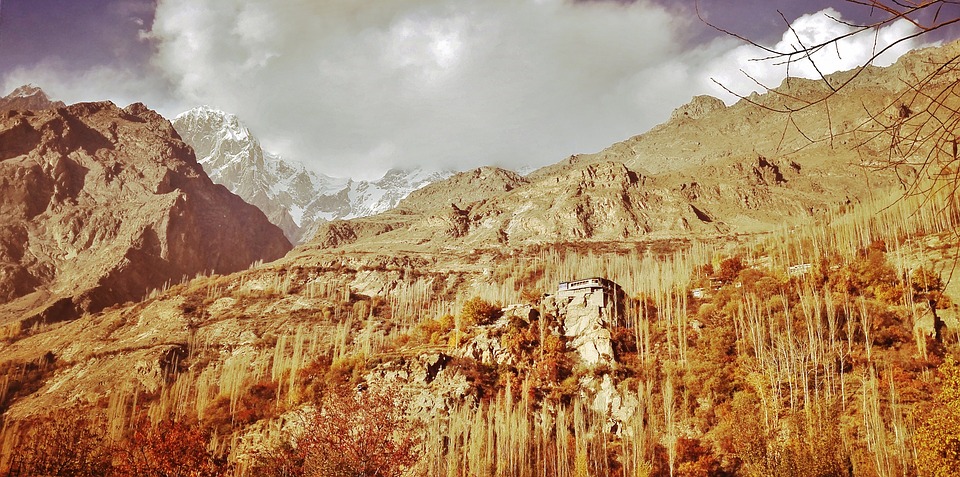
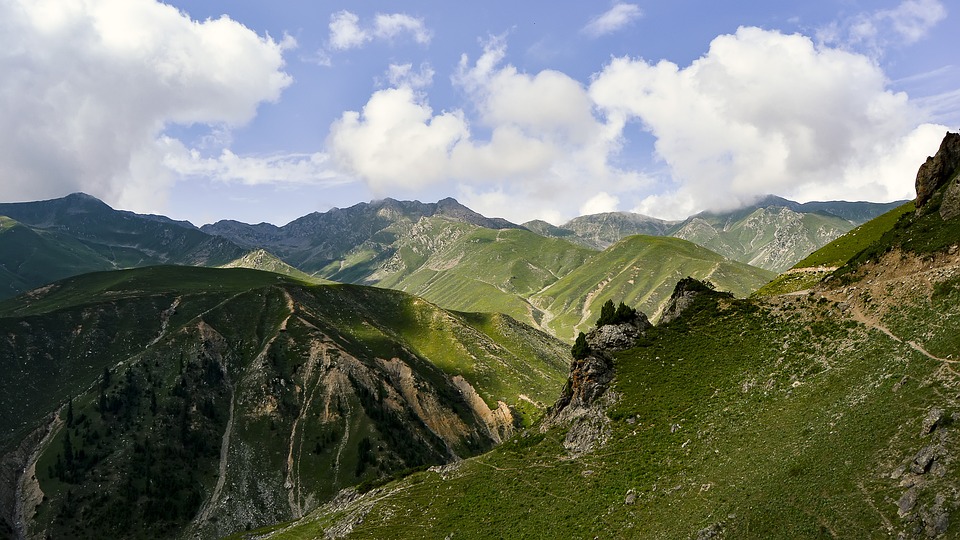
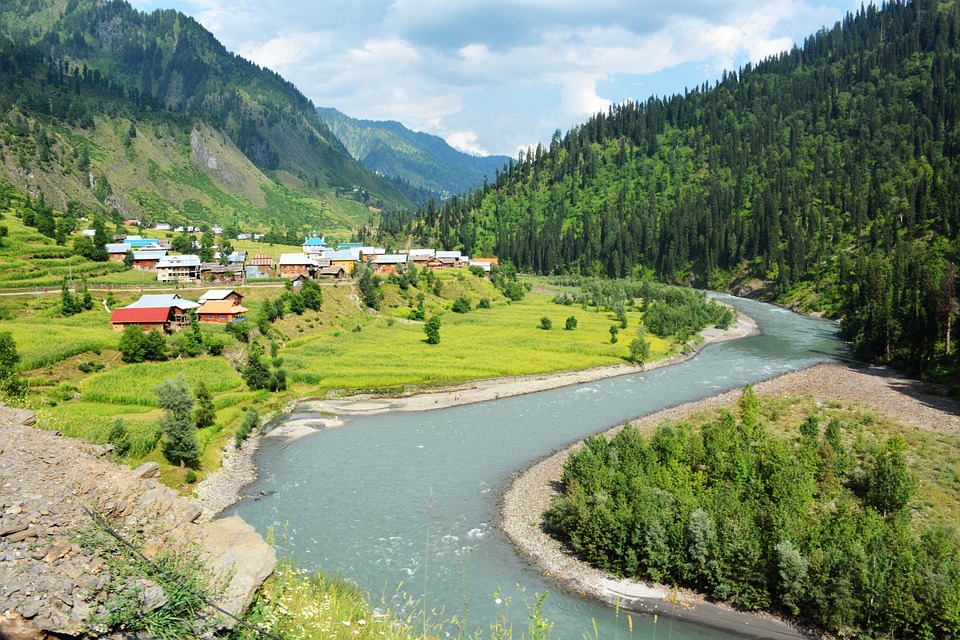
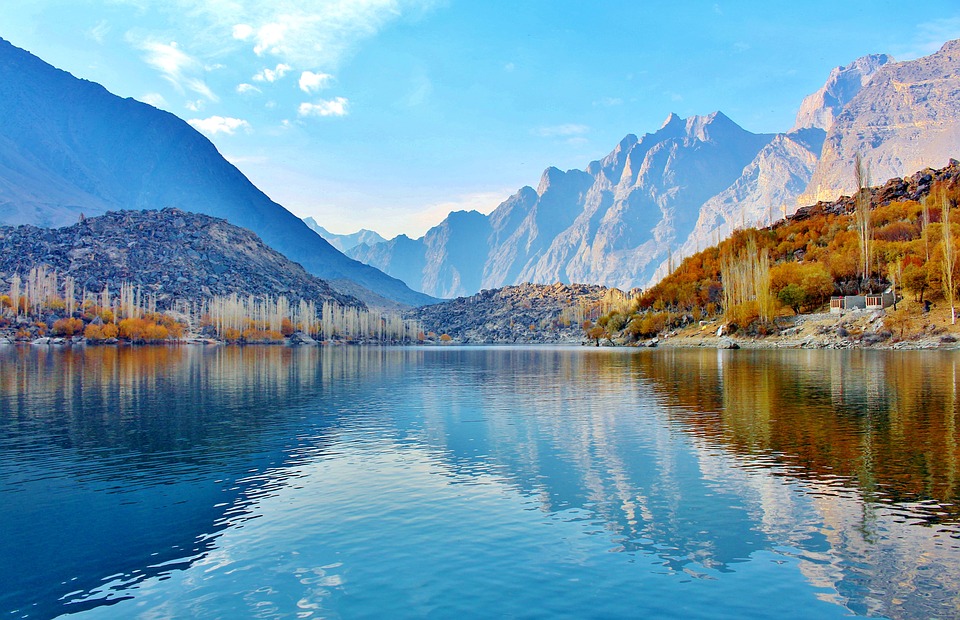
The northern region of Pakistan is dominated by the towering peaks of the Himalayas, including K2, the second highest mountain in the world.
Rivers and Deserts
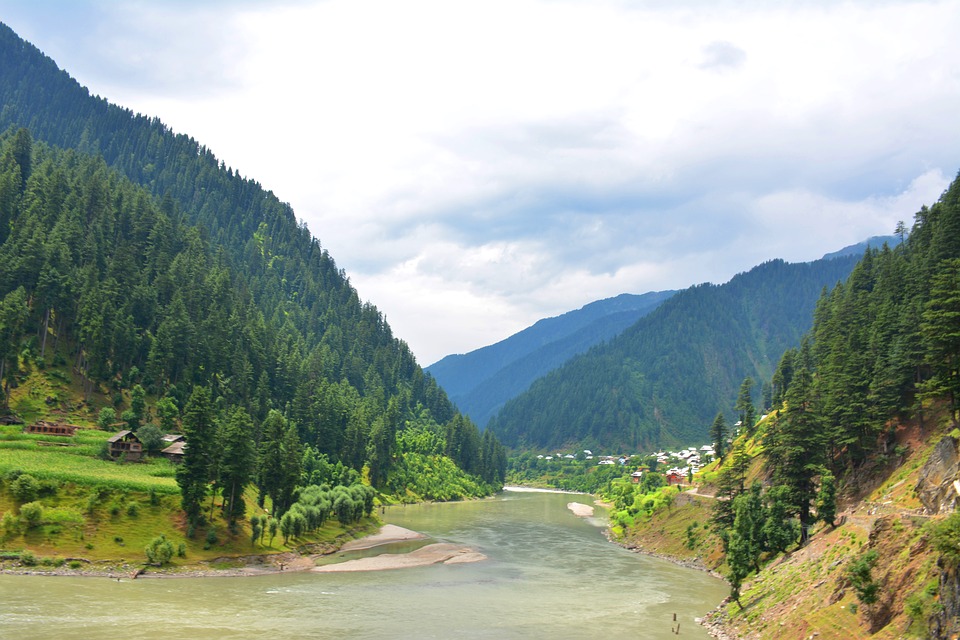
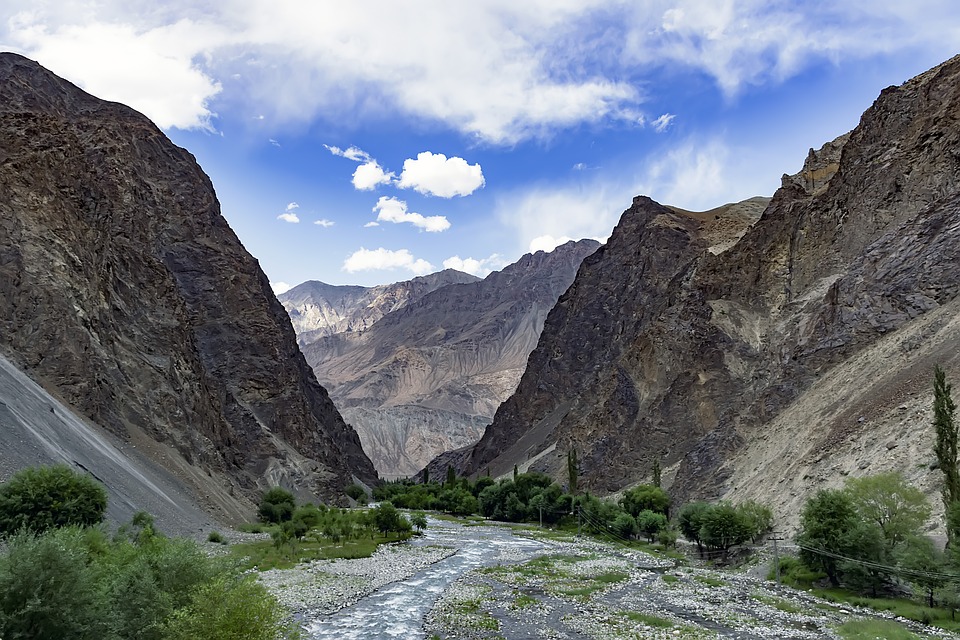
The Indus River, one of the longest rivers in Asia, flows through the country, providing water for agriculture and hydroelectric power. The Thar Desert in the southeast and the coastal areas along the Arabian Sea add to the variety of terrain found in Pakistan.
Climate and Biodiversity
The climate in Pakistan varies from region to region. In the northern areas, the climate is cold and mountainous, with heavy snowfall in the winter months. The central and southern regions experience hot summers and mild winters, while the coastal areas have a warm and humid climate. Monsoon rains from July to September bring much-needed water to the agricultural lands of Pakistan. The diverse geography and climate of Pakistan contribute to its rich biodiversity and make it an attractive destination for nature lovers and adventure seekers.
History and Culture of Pakistan
Pakistan has a rich history that dates back thousands of years. The region was home to one of the world’s earliest urban civilizations, the Indus Valley Civilization, which flourished around 2500 BCE. Over the centuries, Pakistan has been influenced by various empires and dynasties, including the Persian Empire, Maurya Empire, Mughal Empire, and British colonial rule.
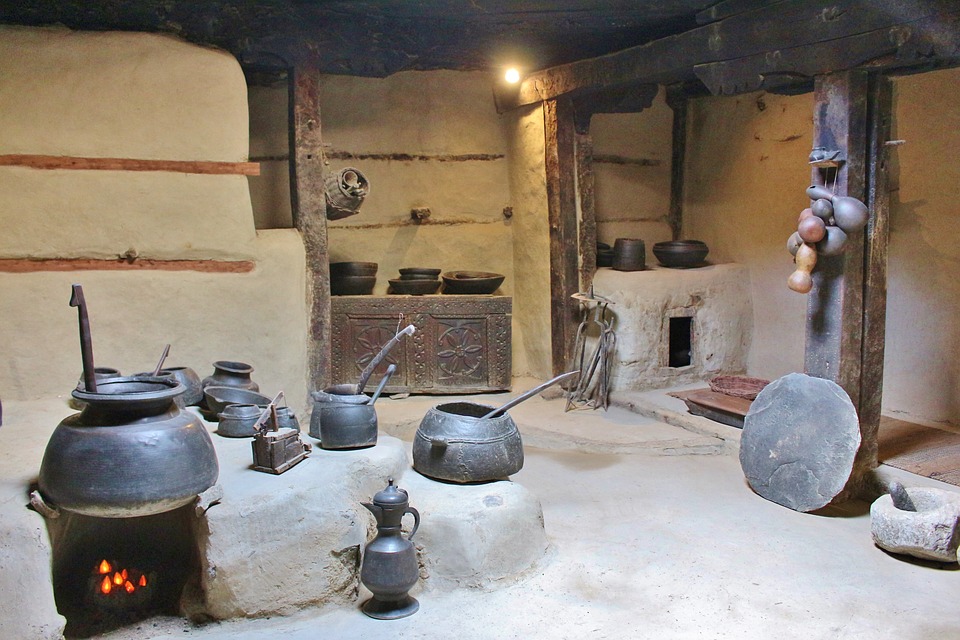
In 1947, Pakistan gained independence from British India, leading to the creation of two separate nations: India and Pakistan. The culture of Pakistan is a blend of various influences, including indigenous traditions, Islamic customs, and modern trends. The people of Pakistan are known for their hospitality, colourful festivals, traditional music and dance, and exquisite handicrafts.
The national dress for men is the shalwar kameez, while women often wear vibrant and intricately embroidered clothing such as the shalwar kameez or saree. The cuisine of Pakistan is diverse and flavourful, with dishes such as biryani, kebabs, and various types of bread being popular staples.
Economy and Industry in Pakistan
Pakistan has a mixed economy with agriculture, industry, and services sectors contributing to its GDP. The country is known for its agricultural products such as wheat, rice, cotton, and sugarcane. The textile industry is one of the largest contributors to Pakistan’s economy, with garments and textiles being major exports.
Other industries include manufacturing, construction, pharmaceuticals, and information technology. Despite its potential for growth, Pakistan faces challenges such as poverty, unemployment, and inflation. The government has been working on economic reforms to attract foreign investment and improve infrastructure.
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is a major development project that aims to improve transportation networks, energy infrastructure, and industrial cooperation between China and Pakistan. With its strategic location and young population, Pakistan has the potential to become a key player in regional trade and investment.
Politics and Government in Pakistan
Pakistan is a federal parliamentary republic with a multi-party system. The President is the head of state, while the Prime Minister is the head of government. The Parliament consists of two houses: the National Assembly and the Senate.
The judiciary is independent and plays a crucial role in upholding the rule of law. The political landscape in Pakistan has been marked by periods of military rule and civilian governments. The country has faced challenges such as corruption, terrorism, and political instability.
However, there have been efforts to strengthen democratic institutions and promote good governance. The 2018 general elections saw a peaceful transfer of power from one civilian government to another for the second time in Pakistan’s history, signalling progress towards a more stable political environment.
Tourism and Attractions in Pakistan
Exploring the Ancient Past
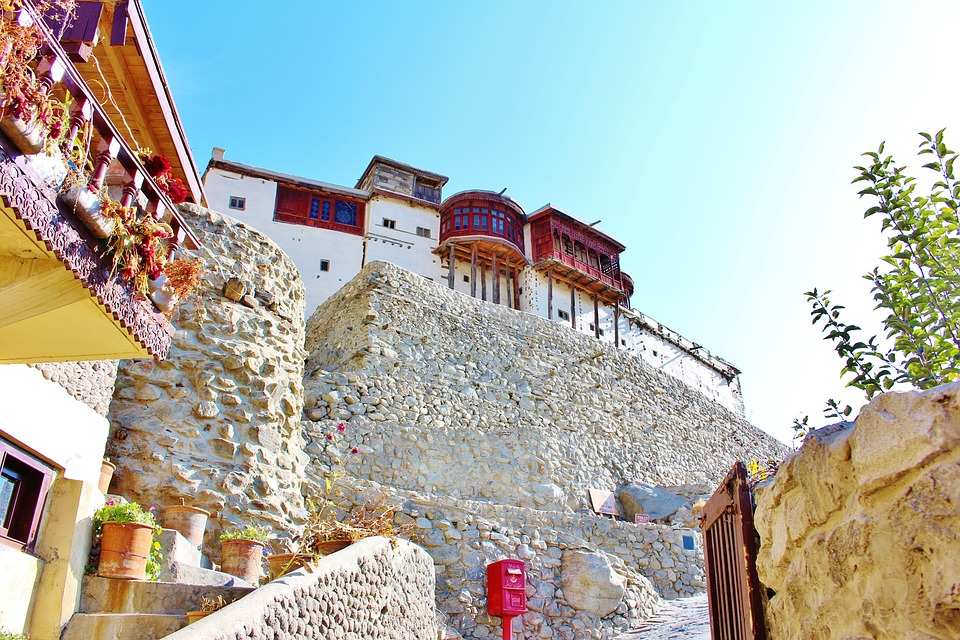
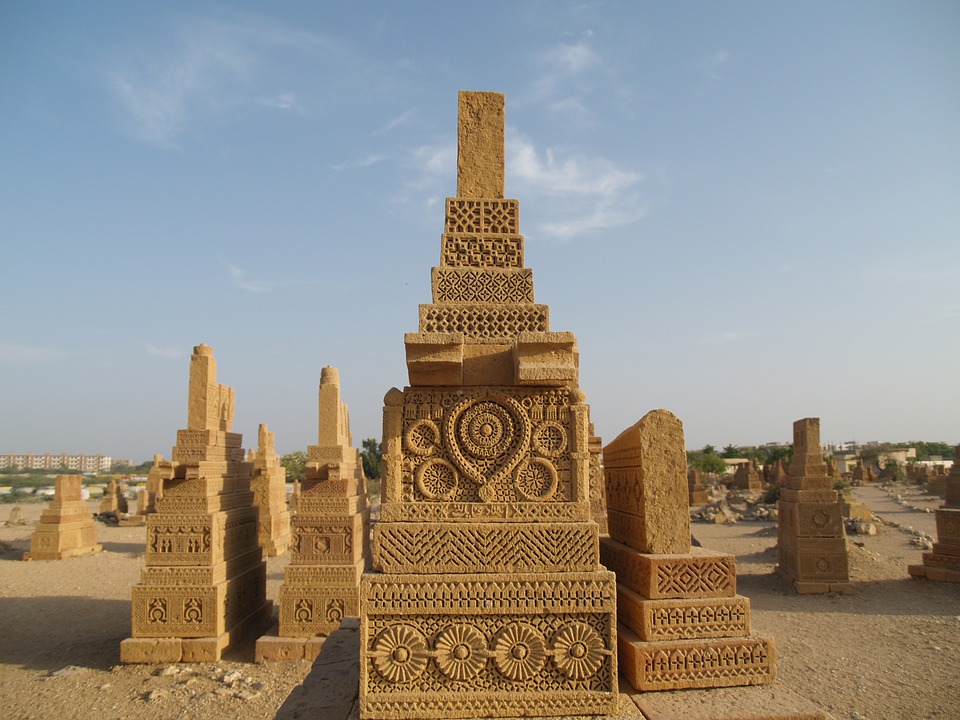
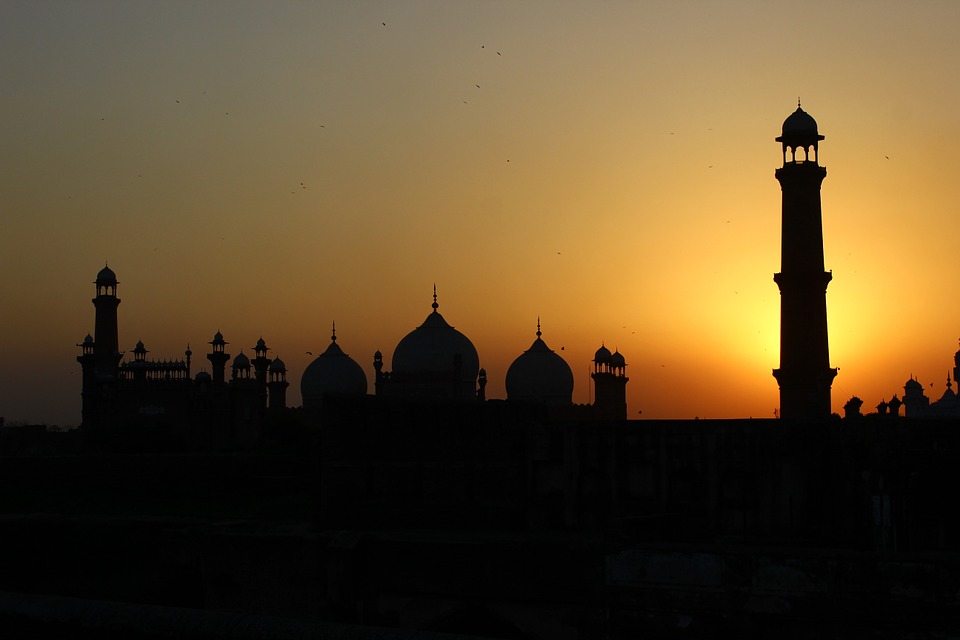
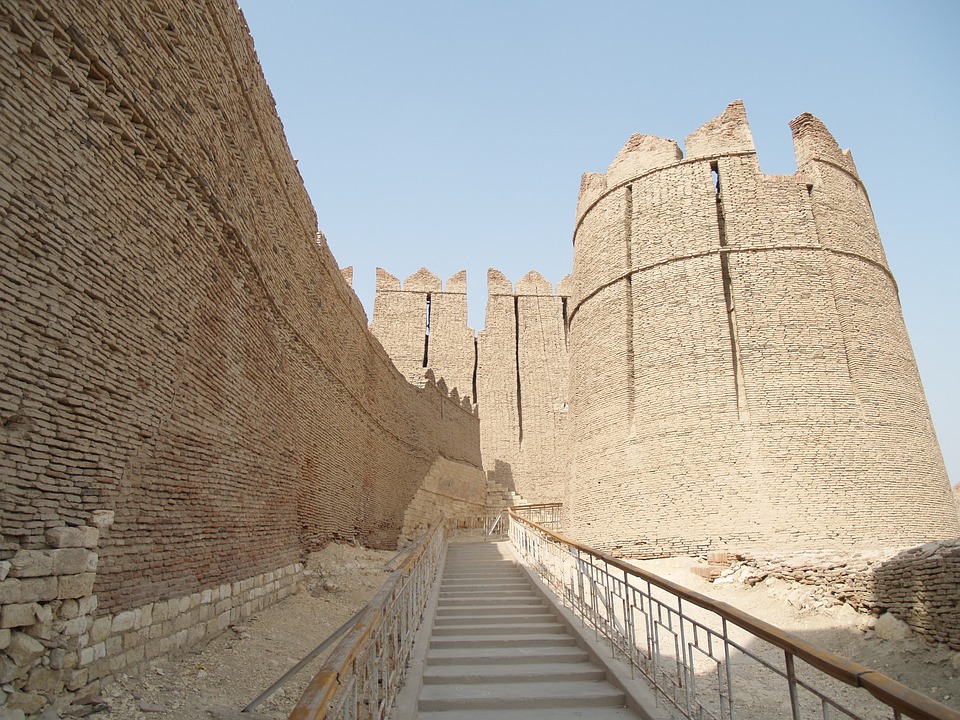
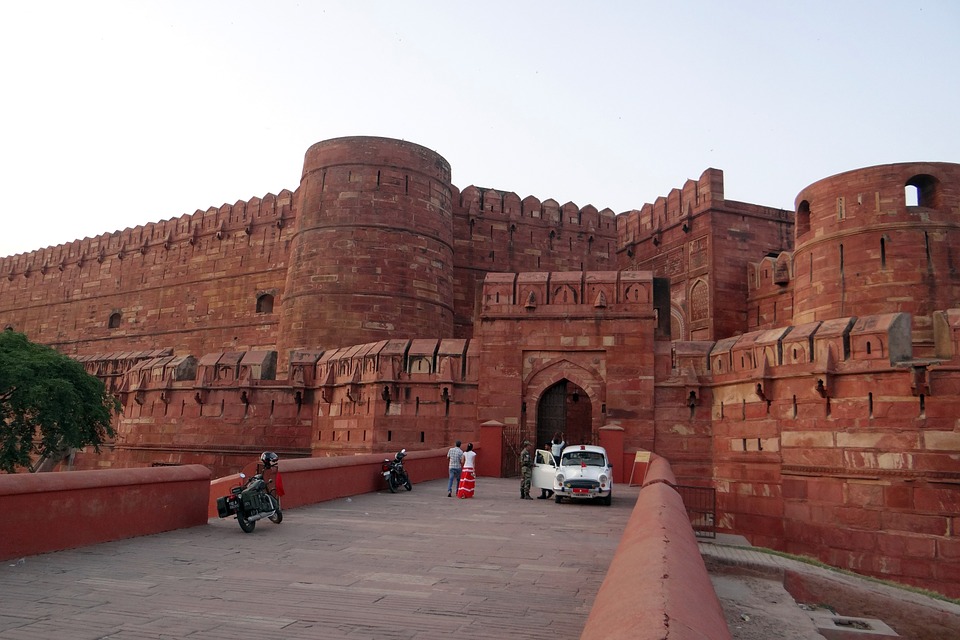
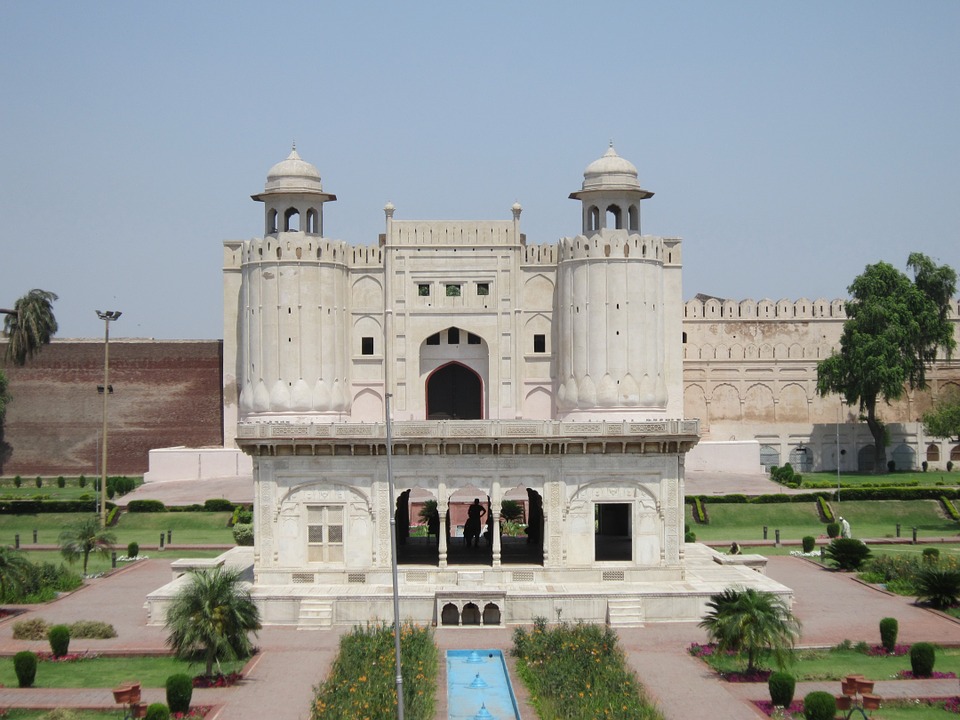
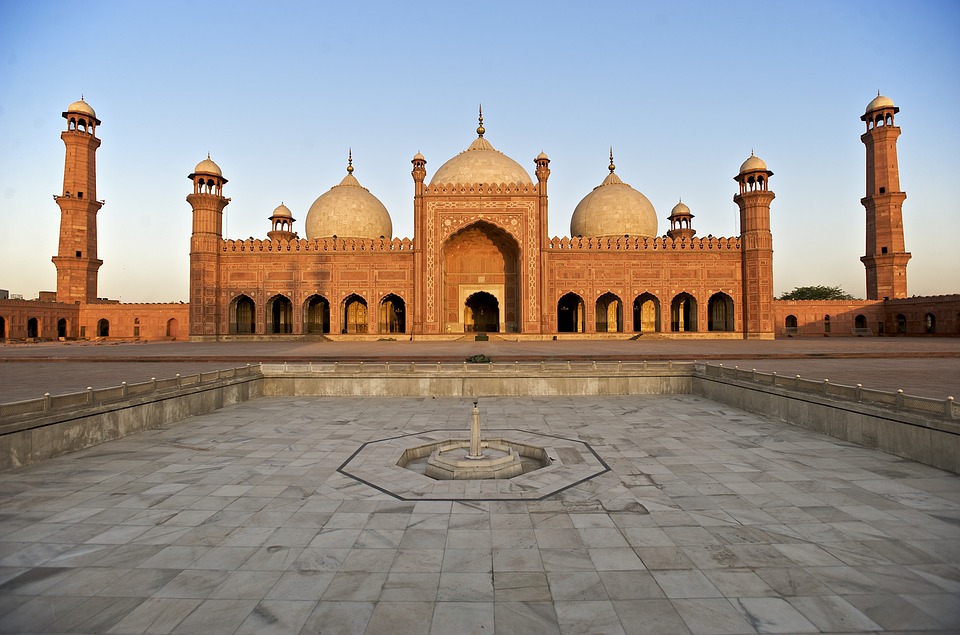
The ancient city of Mohenjo-daro, a UNESCO World Heritage site, provides a glimpse into the Indus Valley Civilisation with its well-planned streets and advanced drainage system. Lahore, the cultural capital of Pakistan, is known for its Mughal-era architecture including the Badshahi Mosque and Lahore Fort.
Natural Beauty and Adventure
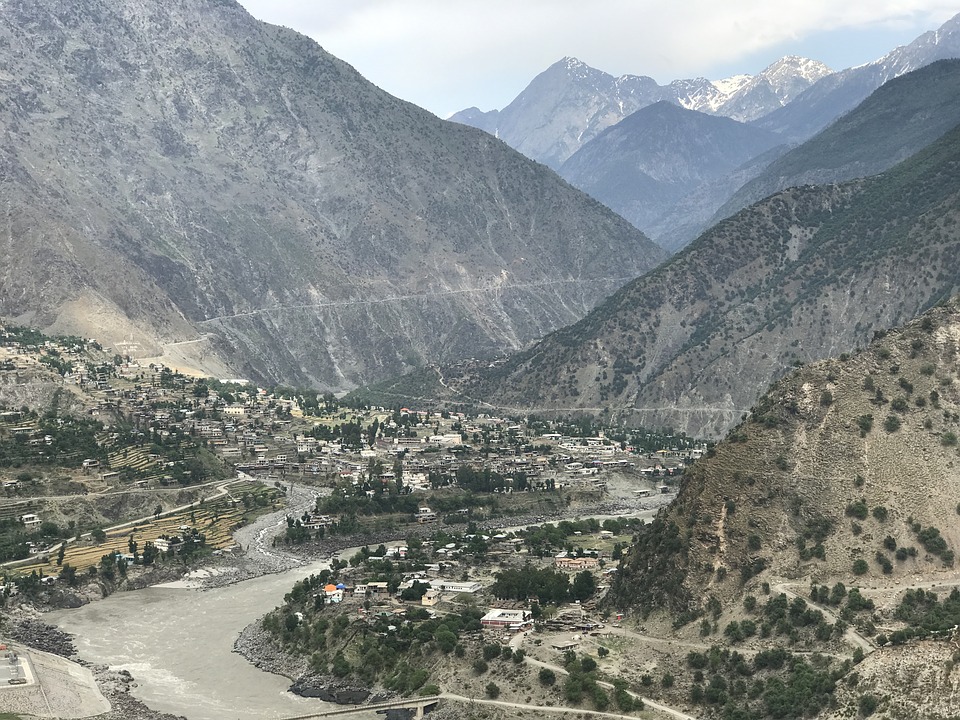
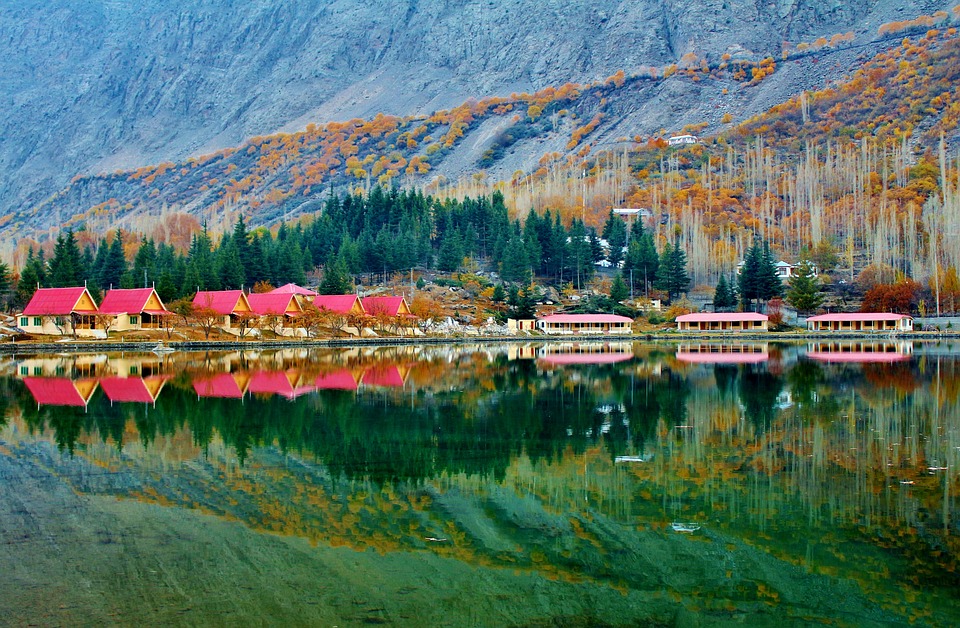
The northern areas of Pakistan are popular for their stunning landscapes, including lush valleys, crystal-clear lakes, and snow-capped peaks. Adventure enthusiasts can explore trekking routes in the Karakoram and Himalayan mountain ranges or go white-water rafting in the rivers of northern Pakistan. The coastal areas offer opportunities for water sports such as snorkelling and scuba diving.
Immersing in Local Culture
The diverse culture of Pakistan can be experienced through traditional festivals such as Basant (kite-flying festival) and Urs (Sufi shrine festivals). With its warm hospitality and breathtaking scenery, Pakistan has great potential to become a top tourist destination in South Asia.
Challenges and Opportunities in Pakistan
Pakistan faces various challenges that hinder its development and progress. These include poverty, illiteracy, healthcare issues, water scarcity, energy shortages, and security concerns. However, there are also opportunities for growth and improvement in key areas such as education, healthcare, infrastructure development, renewable energy sources, and regional cooperation.
The government has been working on initiatives to address these challenges through policies aimed at poverty alleviation, education reform, healthcare access, water management projects, energy sector reforms, and counter-terrorism efforts. International partnerships with countries such as China, Saudi Arabia, and Turkey have also provided opportunities for investment and development projects in Pakistan. In conclusion, Pakistan is a country with a rich history, diverse culture, stunning landscapes, and potential for growth.
Despite facing challenges in various sectors, there are opportunities for progress through economic reforms, political stability, tourism development, and international cooperation. With its strategic location at the crossroads of South Asia, Central Asia, and the Middle East, Pakistan has the potential to become a key player in regional trade and investment. As the country continues to work towards addressing its challenges and seizing opportunities for growth, it can emerge as a dynamic and thriving nation on the global stage.
One interesting article related to Pakistan is about the country’s efforts to combat climate change. According to a recent study, Pakistan is among the top ten countries most affected by climate change. The article discusses the impact of rising temperatures and extreme weather events on the country’s agriculture and economy, as well as the steps being taken to address these challenges. To learn more about Pakistan’s climate change efforts, you can read the full article here.
FAQs
What is the population of Pakistan?
The population of Pakistan is approximately 220 million, making it the 5th most populous country in the world.
What is the capital city of Pakistan?
The capital city of Pakistan is Islamabad.
What is the official language of Pakistan?
The official language of Pakistan is Urdu, while English is also widely used for official and business purposes.
What is the currency of Pakistan?
The currency of Pakistan is the Pakistani Rupee (PKR).
What are the major religions in Pakistan?
The major religion in Pakistan is Islam, with the majority of the population being Muslim. There are also small minorities of Hindus, Christians, and Sikhs.
What are the major industries in Pakistan?
The major industries in Pakistan include textiles, agriculture, manufacturing, and services. Agriculture is a significant sector, with the country being a major producer of cotton, wheat, and rice.
What is the climate like in Pakistan?
Pakistan has a varied climate, with hot summers and cold winters in most parts of the country. The northern areas experience snowfall in winter, while the southern areas have a hot and dry climate.
What are the major tourist attractions in Pakistan?
Pakistan is home to several tourist attractions, including the ancient city of Mohenjo-daro, the Badshahi Mosque in Lahore, the Karakoram Highway, and the beautiful Hunza Valley. The country also offers opportunities for trekking and mountaineering in the northern areas.
Political Boundaries of Pakistan: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Pakistan, a South Asian nation, shares borders with India to the east, Afghanistan and Iran to the west, and China to the north. The Arabian Sea lies to the south of Pakistan. The political boundaries of Pakistan have evolved over time, influenced by historical events, colonial legacies and geopolitical factors. The country’s borders have been a source of dispute and conflict, with contentious territories such as Kashmir and the Durand Line. The demarcation of political boundaries has significant implications for governance, administration and national identity in Pakistan. The political boundaries of Pakistan are defined by the internationally recognised borders with its neighbouring countries. These boundaries are vital for maintaining territorial integrity and sovereignty. The delineation of these borders has been a source of both stability and conflict, as evidenced by the Line of Control in Kashmir. The political boundaries also encompass the internal administrative divisions within Pakistan, including provinces, territories and tribal areas. These internal boundaries play a crucial role in the distribution of resources, representation and governance within the country. Understanding the complexities and significance of Pakistan’s political boundaries is essential for comprehending the country’s historical, political and social dynamics. Summary Pakistan’s political boundaries are defined by its borders with India, Afghanistan, Iran, and China, as well as the Arabian Sea to the south. The country is divided into four provinces – Punjab, Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and Balochistan – and two autonomous territories, Azad Jammu and Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan. The historical boundaries of Pakistan have evolved over time, including the partition of British India in 1947 and the secession of East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) in 1971. Challenges and...
Climate Zones of Pakistan: Different Climate Regions Of Pakistan
Pakistan is a diverse country with a wide range of climate zones, each possessing distinct characteristics and environmental challenges. The nation’s climate can be broadly categorised into tropical, arid and semi-arid, temperate, alpine and sub-alpine, and coastal regions. These climate zones are influenced by various factors, including the country’s geographical location, topography, and proximity to the Arabian Sea and the Himalayas. Understanding the different climate zones of Pakistan is crucial for addressing environmental issues, managing natural resources, and developing sustainable policies for the future. The diverse climate zones of Pakistan have a significant impact on the country’s agriculture, water resources, and overall environmental sustainability. From the hot and humid coastal regions to the cold and snowy alpine areas, each climate zone presents its own set of challenges and opportunities. As the effects of climate change become more pronounced, it is essential to understand how these changes will impact Pakistan’s climate zones and what measures can be taken to mitigate their effects. By examining each climate zone in detail, one can gain a better understanding of the unique environmental conditions and challenges facing Pakistan. Summary Pakistan has a diverse range of climate zones, influenced by its geography and topography. The tropical climate regions in Pakistan are characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall, particularly in the monsoon season. The arid and semi-arid climate regions in Pakistan experience low rainfall and high temperatures, leading to desertification in some areas. The temperate climate regions in Pakistan have moderate temperatures and distinct seasons, making them suitable for agriculture. The alpine and sub-alpine climate regions in Pakistan are characterized by cold temperatures and snowfall,...
Terrain and Topography of Pakistan: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Pakistan, situated in South Asia, shares borders with India to the east, Afghanistan and Iran to the west, and China to the north. The nation’s varied terrain and topography render it a region of remarkable natural splendour and geological importance. Spanning from the lofty summits of the Himalayas in the north to the expansive plains of the Indus River Valley in the south, Pakistan‘s landscape serves as a testament to the natural forces that have moulded it over millions of years. The country’s terrain and topography have been instrumental in shaping its climate, economy, and culture, making it a compelling subject of study for geographers, geologists, and nature enthusiasts alike. Summary Pakistan’s terrain and topography are incredibly diverse, ranging from majestic mountains to vast plains. The mountains of Pakistan, including the famous Karakoram and Himalayas, offer breathtaking landscapes and challenging trekking opportunities. The valleys of Pakistan, such as Swat Valley and Hunza Valley, are known for their natural beauty and unique cultural heritage. The vast plains of Pakistan, including the fertile Punjab region, are crucial for agriculture and contribute significantly to the country’s economy. The diverse terrain and topography of Pakistan have a significant impact on the country’s climate, influencing temperature, precipitation, and weather patterns. The Majestic Mountains of Pakistan The Himalayas: A Sight to Behold These mountains are not only a breathtaking sight but also play a crucial role in shaping Pakistan’s climate and providing a habitat for a diverse range of flora and fauna. The Karakoram Range: A Treasure Trove of Peaks The Karakoram Range, which is home to some of the world’s highest peaks, including K2...
History of Pakistan
The region of Pakistan boasts a rich and diverse history, with evidence of human habitation dating back to the Palaeolithic era. The ancient civilisations that flourished in this region include the Indus Valley Civilisation, one of the world’s oldest urban societies. The Indus Valley Civilisation, also known as the Harappan Civilisation, existed from approximately 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE and was located in what is now modern-day Pakistan and northwest India. The civilisation was renowned for its advanced urban planning, sophisticated drainage systems, and intricate pottery and jewellery. The cities of Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa are two of the most well-known sites from this ancient civilisation, and they provide valuable insights into the social, economic, and cultural aspects of the time. Moreover, the region of Pakistan has also been influenced by other ancient civilisations, such as the Persian Empire, the Maurya Empire, and the Gupta Empire. These empires left their mark on the region through trade, cultural exchange, and the spread of religious beliefs. The region was also a significant part of the Silk Road, an ancient network of trade routes that connected the East and West, further contributing to its cultural and economic significance. The ancient history of Pakistan is a testament to the region’s importance in shaping the development of human civilisation and its enduring legacy in the modern world. Summary Ancient civilizations in the region of Pakistan include the Indus Valley Civilization, which was one of the world’s earliest urban societies. The Islamic conquest and the Mughal Empire played a significant role in shaping the culture and history of the region, leaving behind architectural marvels and a...
Population Density of Pakistan
Population density refers to the number of people living per unit of area, typically per square kilometre or square mile. It is a crucial demographic indicator that aids in understanding the distribution of people within a given area. In Pakistan, population density varies significantly across different regions, with some areas being densely populated whilst others are sparsely populated. Understanding population density is vital for policymakers, urban planners, and researchers as it provides insights into the social, economic, and environmental dynamics of a region. Pakistan is the sixth most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 220 million people. The country’s population is growing at a rapid rate, and this growth has significant implications for its population density. As the population continues to increase, it places pressure on resources, infrastructure, and the environment. Therefore, understanding the factors affecting population density in Pakistan, as well as its impact on urban and rural areas, is essential for sustainable development and effective policymaking. Summary Population density refers to the number of people living per square kilometre and is a key indicator of the distribution of population in a specific area. Factors affecting population density in Pakistan include geographical features, economic opportunities, and government policies. Urban areas in Pakistan have higher population density compared to rural areas due to better job opportunities and access to amenities. High population density puts pressure on infrastructure and resources, leading to challenges such as inadequate housing and water scarcity, but also presents opportunities for economic growth and innovation. Government policies and initiatives to manage population density in Pakistan should focus on urban planning, improving access to...
Natural Resources of Pakistan: Where Natural Resources are Located in Pakistan
Pakistan possesses a diverse array of natural resources that are integral to the nation’s economy and development. These resources encompass minerals, agriculture, energy, water and forests. The country’s strategic geographical position has bestowed upon it a variety of mineral deposits, fertile arable land, plentiful water resources and a rich diversity of flora and fauna. The exploitation and conservation of these natural resources are paramount for sustainable development and the welfare of Pakistan‘s populace. The natural resources of Pakistan have the potential to make a substantial contribution to the country’s economy. However, the sustainable management and preservation of these resources are crucial to ensure their availability for future generations. The Pakistani government has implemented various initiatives to promote the sustainable utilisation of natural resources and address the challenges associated with their exploitation. This article shall examine the mineral, agricultural, energy, water and forest resources of Pakistan, as well as the challenges and conservation efforts related to these resources. Summary Pakistan is rich in natural resources, including minerals, agriculture, energy, water, and forests. The mineral resources in Pakistan include coal, salt, gypsum, limestone, and iron ore, among others. Pakistan’s agricultural resources are diverse, with the country being a major producer of wheat, rice, cotton, and sugarcane. Energy resources in Pakistan include natural gas, coal, and hydropower, with a growing focus on renewable energy sources. Water resources in Pakistan are crucial for agriculture and energy production, but the country faces challenges such as water scarcity and pollution. Mineral Resources in Pakistan Significance of Mineral Resources The mining and quarrying sector in Pakistan contributes significantly to the country’s economy and provides employment opportunities...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Pakistan: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Pakistan
Pakistan boasts a rich cultural and historical heritage, with numerous sites showcasing its diverse and vibrant past. From ancient ruins to grand mosques, imposing forts and splendid gardens, Pakistan‘s cultural and historical landmarks offer insight into the country’s extensive history and the influences that have shaped its identity. These sites stand as a testament to Pakistan’s historical significance, serving as a source of national pride and attracting tourists from across the globe. The cultural and historical sites in Pakistan reflect the nation’s multifaceted heritage, bearing influences from various civilisations and cultures that have left their imprint on the land. From the ancient Indus Valley civilisation to the Mughal Empire and beyond, Pakistan’s historical sites provide a captivating journey through time, illustrating the country’s evolution and its people’s contributions to world history. The ancient ruins of Mohenjo-daro, the magnificent Badshahi Mosque in Lahore, and the grand forts and gardens scattered throughout the landscape each recount a unique narrative, contributing to the rich tapestry of Pakistan’s cultural and historical legacy. Summary Pakistan is home to a rich tapestry of cultural and historical sites that date back thousands of years. The ancient ruins of Mohenjo-Daro offer a fascinating glimpse into one of the world’s earliest urban settlements. The Badshahi Mosque in Lahore is a stunning example of Mughal architecture and a symbol of the city’s rich cultural heritage. Lahore Fort and Rohtas Fort are grand structures that showcase the military prowess and architectural splendour of their respective eras. The Shalimar Gardens in Lahore are a testament to the Mughal love for nature and beauty, with their intricate design and serene atmosphere. The...
Exploring the Vibrant Culture and Heritage of Pakistan: A Journey Through the Land of the Pure
Pakistan, officially known as the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country located in South Asia. It shares borders with India to the east, Afghanistan and Iran to the west, and China to the north. With a population of over 220 million people, Pakistan is the fifth-most populous country in the world. The country is known for its diverse geography, ranging from the snow-capped peaks of the Himalayas in the north to the fertile plains of Punjab and Sindh in the south. Pakistan is often referred to as the “Land of the Pure,” a nickname that reflects its strong Islamic identity. The name “Pakistan” itself is derived from the Persian words “Pak” meaning pure and “Stan” meaning land. The country was created in 1947 as a homeland for Muslims in British India, following the partition of India. The idea behind Pakistan was to establish a separate state where Muslims could practice their religion freely and live according to their own cultural values. Summary Pakistan is known as the Land of the Pure. The country has a rich cultural diversity, with influences from various regions and religions. Pakistan has a long and ancient history, with evidence of human settlements dating back to prehistoric times. The Mughal era was a golden age of art and architecture in Pakistan, with iconic landmarks such as the Badshahi Mosque and Lahore Fort. Pakistan has a rich literary and poetic tradition, with famous writers such as Allama Iqbal and Faiz Ahmed Faiz. The Rich Cultural Diversity of Pakistan Pakistan is home to a rich tapestry of ethnic and linguistic groups, each with its own distinct...


































