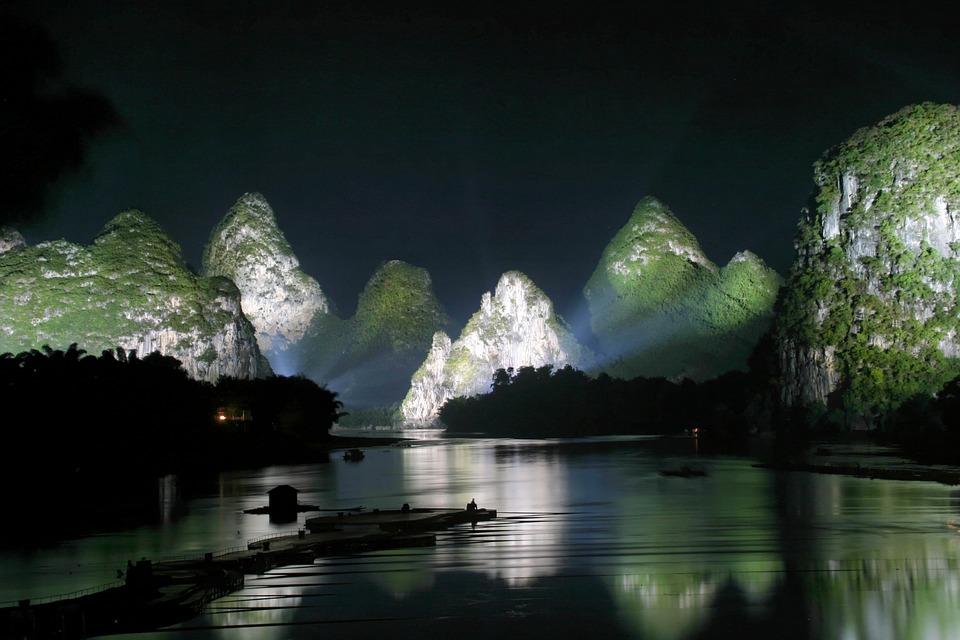
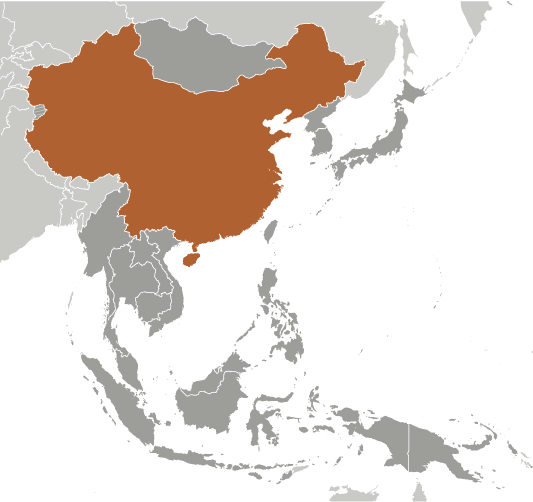
China
(Zhonghua Renmin Gongheguo (People’s Republic of China))
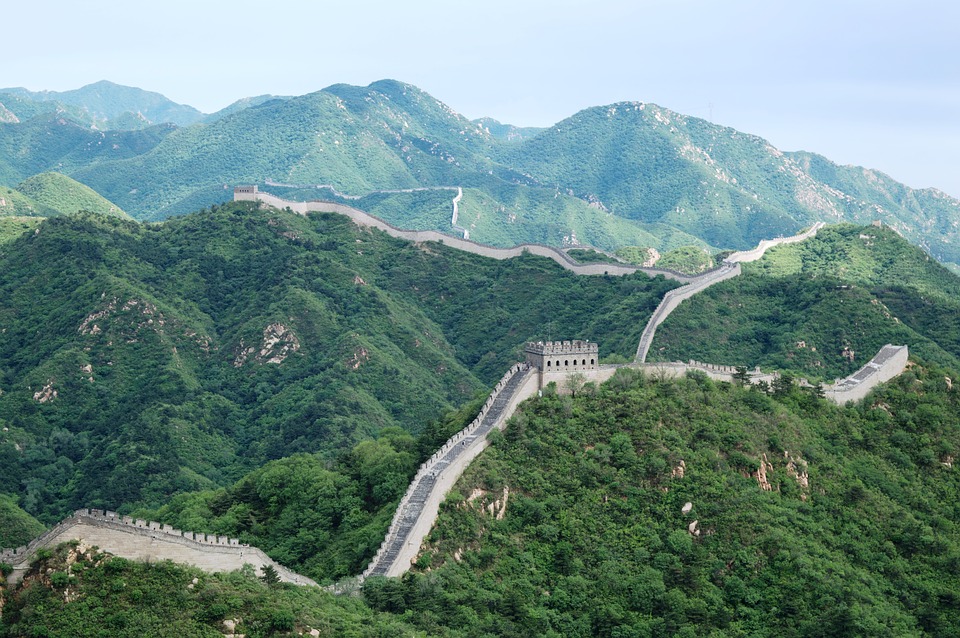

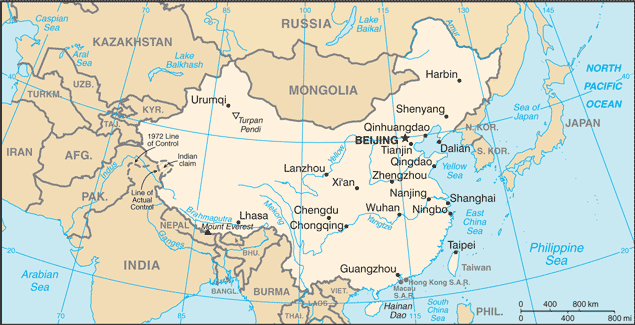







Capital of China: Beijing (Peking)
Population (Estimated July 2012): 1,343,239,923
Area: 9,572,900 km2 or 3,696,100 mi2
Currency: Renminbi (yuan) (Y)
Official Language: Mandarin Chinese
Political Information: Communist State
Official Religion: No Official Religion
Highest Mountain: Qowowuyag at 8,188m or 26,864 feet (Everest is partially in China but the peak is in Nepal)
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $6.989 trillion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $11.29 trillion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $8,400 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +8:00
Counties/Provinces/States: 23 provinces (sheng, singular and plural), 5 autonomous regions (zizhiqu, singular and plural), and 4 municipalities (shi, singular and plural)
provinces: Anhui, Fujian, Gansu, Guangdong, Guizhou, Hainan, Hebei, Heilongjiang, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangsu, Jiangxi, Jilin, Liaoning, Qinghai, Shaanxi, Shandong, Shanxi, Sichuan, Yunnan, Zhejiang; (see note on Taiwan)
autonomous regions: Guangxi, Nei Mongol (Inner Mongolia), Ningxia, Xinjiang Uygur, Xizang (Tibet)
municipalities: Beijing, Chongqing, Shanghai, Tianjin
note: China considers Taiwan its 23rd province; see separate entries for the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau
Leaders: Premier LI Keqiang (since 16 March 2013); Executive Vice Premiers HAN Zheng (since 19 March 2018), SUN Chunlan (since 19 March 2018), LIU He (since 19 March 2018), HU Chunhua (since 19 March 2018)
cabinet: State Council appointed by National People’s Congress
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
China
China, with its rich history, vibrant culture, and booming economy, holds a significant place in the world today. As the most populous country in the world and the second-largest economy, China’s influence is felt across various sectors, including politics, economics, and culture. In this blog post, we will explore the different aspects of China that make it such a fascinating and important country. From its ancient dynasties to its modern rise as a global superpower, we will delve into China’s history, culture, cuisine, natural wonders, and more.
The purpose of this blog post is to provide readers with a comprehensive overview of China’s significance in the world. By exploring various aspects of Chinese history, culture, and society, we hope to shed light on the country’s unique characteristics and its impact on the global stage. Whether you are planning a trip to China or simply interested in learning more about this fascinating country, this blog post will serve as a valuable resource.
China’s History: From Ancient Dynasties to Modern Times
China has a rich and storied history that dates back thousands of years. The country has been ruled by numerous dynasties throughout its history, each leaving its mark on Chinese culture and society. From the Xia Dynasty in 2070 BCE to the Qing Dynasty in 1912 CE, China has seen the rise and fall of many powerful empires.
In modern times, China has undergone significant changes that have shaped its current status as a global superpower. The establishment of the People’s Republic of China in 1949 marked the beginning of a new era for the country. Under the leadership of Chairman Mao Zedong, China underwent a series of political and social reforms that aimed to transform the country into a socialist state.
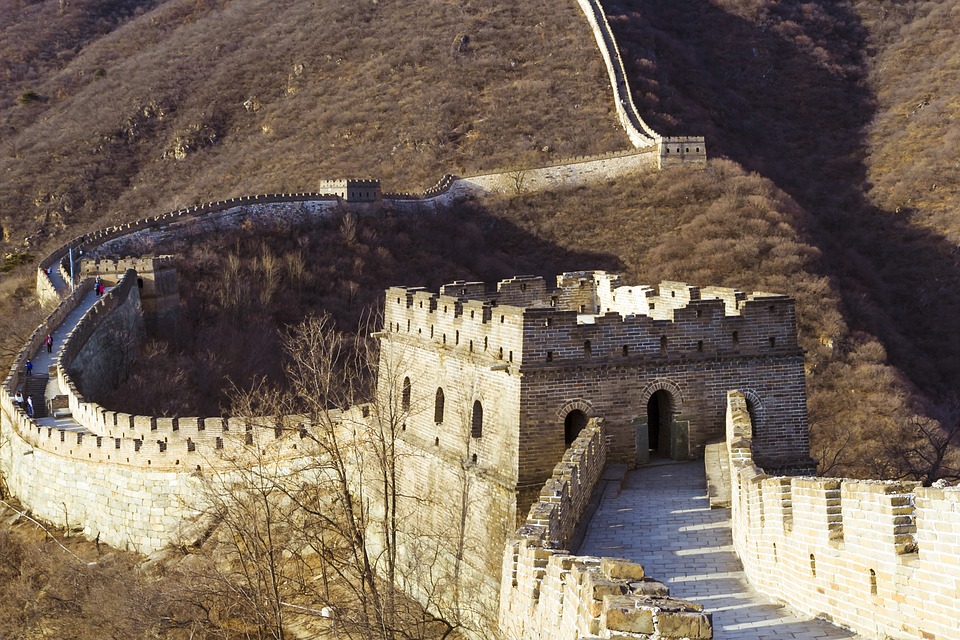
The Great Wall of China: A Wonder of the World
One of China’s most iconic landmarks is the Great Wall. Stretching over 13,000 miles, the Great Wall is a testament to China’s rich history and engineering prowess. Built over centuries to protect the country from invasions, the Great Wall is now a popular tourist attraction that attracts millions of visitors each year.
The Great Wall holds great significance in Chinese culture and is considered one of the Seven Wonders of the World. It is a symbol of China’s strength and resilience, as well as a reminder of its ancient history. Visitors to the Great Wall can explore various sections of the wall, each offering breathtaking views and a glimpse into China’s past.
Chinese Culture: Art, Music, and Literature
Chinese culture is renowned for its rich artistic traditions, beautiful music, and profound literature. Chinese art encompasses a wide range of mediums, including painting, calligraphy, ceramics, and sculpture. Traditional Chinese painting often features landscapes, flowers, and birds, while calligraphy is considered a highly respected art form.
Chinese music has a long history that dates back thousands of years. Traditional Chinese music is characterized by its use of unique instruments such as the guzheng (a plucked string instrument) and the erhu (a two-stringed fiddle). Chinese opera is also an important part of Chinese culture and combines music, dance, and drama.
Chinese literature has produced many famous writers and poets throughout history. From ancient classics such as “The Art of War” by Sun Tzu to modern works like “Red Sorghum” by Mo Yan, Chinese literature offers a wealth of stories and insights into Chinese society.
Chinese Cuisine: From Dumplings to Peking Duck
Chinese cuisine is known for its diverse flavours, fresh ingredients, and intricate cooking techniques. With its wide variety of regional cuisines, China offers a culinary experience like no other. From spicy Sichuan dishes to delicate Cantonese dim sum, there is something to satisfy every palate.
Some popular Chinese dishes include dumplings, Peking duck, Kung Pao chicken, and Mapo tofu. Chinese cuisine also places a strong emphasis on the balance of flavours, with dishes often combining sweet, sour, salty, and spicy elements. Whether you are a fan of spicy food or prefer milder flavours, Chinese cuisine has something for everyone.
China’s Natural Wonders: Mountains, Rivers, and Lakes
China is blessed with a diverse and breathtaking natural landscape. From towering mountains to winding rivers and serene lakes, China’s natural wonders attract millions of visitors each year. Mount Everest, the highest peak in the world, is located on the border between China and Nepal and is a popular destination for mountaineers.
The Yangtze River, the longest river in Asia, flows through China and offers stunning views of the surrounding countryside. The Li River in Guilin is known for its picturesque karst landscape and is a popular destination for river cruises. China is also home to many beautiful lakes, including the famous West Lake in Hangzhou and Lake Tai in Jiangsu.
China’s Economic Growth: The Rise of a Superpower
In recent decades, China has experienced rapid economic growth that has propelled it to become the world’s second-largest economy. This economic transformation has lifted millions of people out of poverty and has had a profound impact on the global economy.
China’s economic growth has been driven by various industries, including manufacturing, technology, and finance. The country is known as the “factory of the world” due to its large-scale manufacturing capabilities. Chinese companies such as Huawei, Alibaba, and Tencent have become global leaders in their respective industries.
Chinese Education System: A Focus on Academic Excellence
China’s education system is known for its emphasis on academic excellence and rigorous testing. The country places a strong emphasis on education as a means to social mobility and economic success. Chinese students consistently rank among the top performers in international assessments such as the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA).
The Chinese education system is highly competitive, with students facing intense pressure to succeed academically. The Gaokao, China’s national college entrance examination, is a high-stakes test that determines a student’s future prospects. Despite the challenges, China’s education system has produced many talented individuals who have gone on to make significant contributions in various fields.
China’s Population: The World’s Most Populous Country
China is home to the largest population in the world, with over 1.4 billion people. The country’s population presents both challenges and opportunities. On one hand, China’s large population puts pressure on resources and infrastructure. On the other hand, it provides a vast consumer market and a source of skilled labor.
China has implemented various policies to manage its population, including the famous one-child policy that was in place from 1979 to 2015. While the policy helped control population growth, it also led to a gender imbalance and an aging population. China is now facing the challenge of balancing economic growth with social welfare and sustainability.
Chinese Festivals: Celebrating Tradition and Culture
Chinese festivals are an important part of Chinese culture and are celebrated with great enthusiasm and joy. These festivals are deeply rooted in tradition and offer a glimpse into China’s rich cultural heritage. From the vibrant celebrations of Chinese New Year to the solemn rituals of the Qingming Festival, each festival has its own unique customs and significance.
Chinese New Year, also known as Spring Festival, is the most important festival in China. It marks the beginning of the lunar calendar and is celebrated with fireworks, dragon dances, and family gatherings. Other popular festivals include the Lantern Festival, Mid-Autumn Festival, and Dragon Boat Festival.
China’s Future: Challenges and Opportunities in the 21st Century
Looking ahead, China faces both challenges and opportunities in the 21st century. As the country continues to grow economically and assert its influence on the global stage, it must also address various issues such as environmental degradation, income inequality, and political reform.
China’s Belt and Road Initiative, a massive infrastructure project that aims to connect Asia, Europe, and Africa, presents both economic opportunities and geopolitical challenges. The country’s technological advancements in areas such as artificial intelligence and renewable energy offer great potential for innovation and development.
In conclusion, China’s significance in the world cannot be overstated. From its ancient history to its modern rise as a global superpower, China has left an indelible mark on the world. Its rich culture, breathtaking natural wonders, delicious cuisine, and booming economy make it a country worth exploring and understanding.
As China continues to shape the world in the 21st century, it is important for us to appreciate its unique characteristics and contributions. By learning about China’s history, culture, and society, we can gain a deeper understanding of this fascinating country and its place in the world. Whether you are planning a trip to China or simply interested in expanding your knowledge, exploring China’s diverse aspects will undoubtedly enrich your understanding of this remarkable nation.
FAQs
What is China?
China is a country located in East Asia. It is the world’s most populous country with a population of over 1.4 billion people.
What is the capital of China?
The capital of China is Beijing.
What is the official language of China?
The official language of China is Mandarin Chinese.
What is the currency of China?
The currency of China is the Chinese yuan (CNY).
What is the government system of China?
China is a one-party socialist state with the Communist Party of China as the ruling party.
What is the economy of China like?
China has the world’s second-largest economy after the United States. It is a mixed economy with both state-owned enterprises and private businesses.
What are some famous landmarks in China?
Some famous landmarks in China include the Great Wall of China, the Forbidden City, the Terracotta Army, and the Yangtze River.
What is the education system like in China?
Education in China is compulsory for nine years and is divided into primary, secondary, and tertiary education. The country has a high literacy rate of over 96%.
What are some traditional Chinese festivals?
Some traditional Chinese festivals include the Chinese New Year, the Mid-Autumn Festival, and the Dragon Boat Festival.
Political Boundaries of China: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
China, officially known as the People’s Republic of China, is the world’s most populous country and the third-largest by land area. It is a vast country with a complex political landscape that is crucial to understand in order to comprehend its governance...
Natural Resources of China: Where Natural Resources are located In China
China, with its vast land area and diverse geography, is home to a wide range of natural resources. From minerals and forests to water and agricultural resources, China’s natural wealth plays a crucial role in its economy and society. Understanding the abundance...
Climate Zones of China: Different climate regions Of China
China is a vast country with a diverse range of climate zones. From the tropical regions in the south to the subarctic regions in the north, China experiences a wide variety of climates due to its large size and complex topography. Understanding these climate zones is...
History of China
China, with its rich and ancient history, has been home to numerous dynasties that have shaped the country’s culture, politics, and society. Understanding the different dynasties is crucial in comprehending the complexities of China’s past and its...
Cultural or Historical Sites of China: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In China
China is a country with a rich cultural heritage and iconic landmarks that have captivated the world for centuries. From the majestic Great Wall to the intricate Forbidden City, these landmarks offer a glimpse into China’s fascinating history and culture. In...
Population Density of China
China is the most populous country in the world, with a population of over 1.4 billion people. With such a large population, it is important to understand the concept of population density and its implications for the country. Population density refers to the number...
Terrain and Topography of China: mountains, valleys, and plains.
China, the world’s most populous country, is known for its vast and diverse terrain. From towering mountain ranges to expansive plains, lush valleys to unique karst landscapes, China’s topography is as varied as its culture and history. Understanding...
The Last Emperor of China: Aisin-Gioro Puyi
In the tumultuous history of China, there was one individual whose life encapsulated the rise and fall of an empire. Aisin-Gioro Puyi, the last emperor of China, navigated a treacherous political landscape and experienced firsthand the dramatic changes that swept his...
Exploring China’s Rich Cultural Heritage: A Journey Through Time
China has a rich and diverse cultural history that spans thousands of years. From ancient dynasties to modern times, China has been home to a wide range of artistic, intellectual, and culinary traditions. Preserving this cultural heritage is of utmost importance, as...