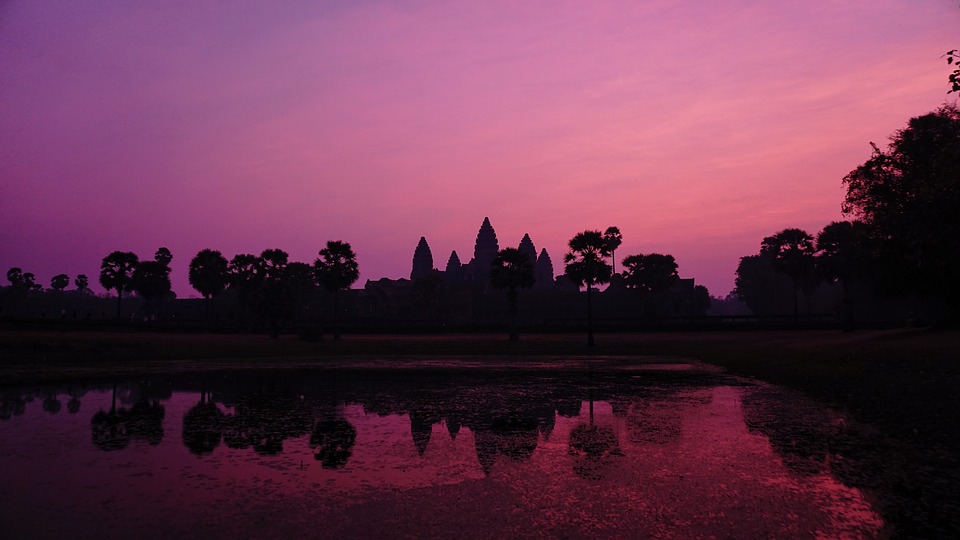
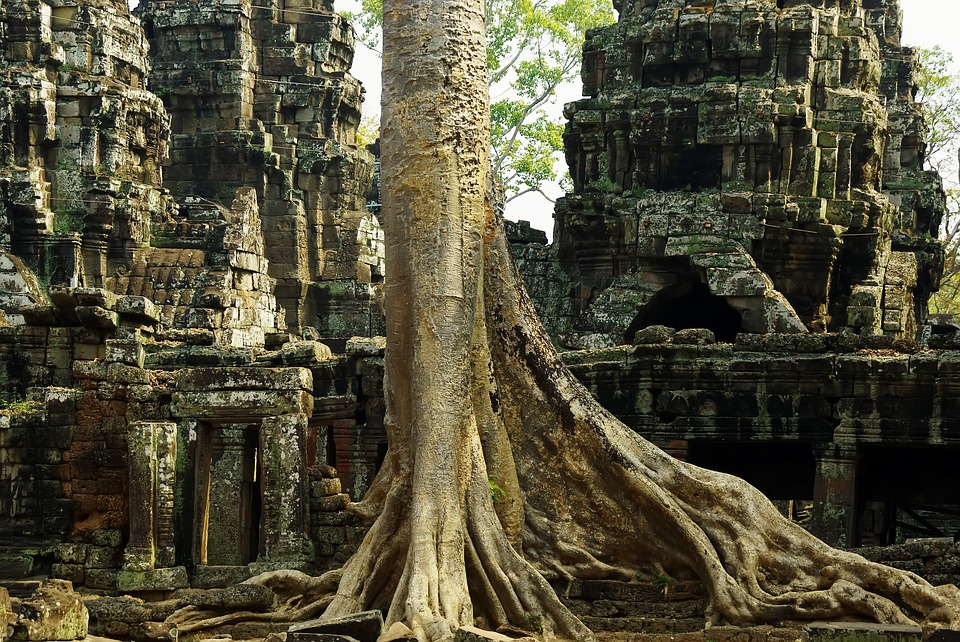
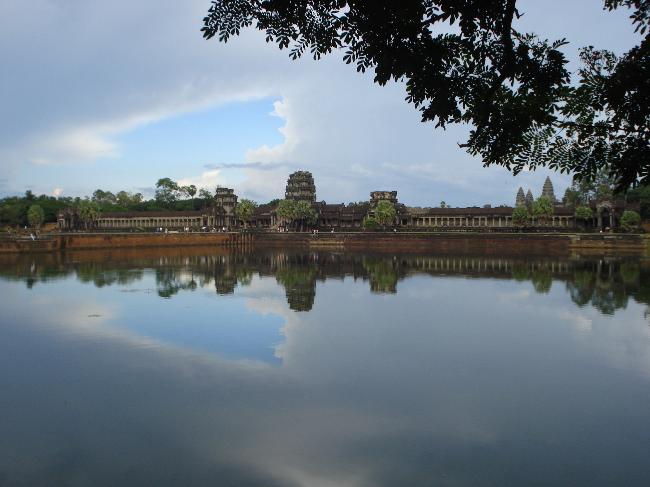
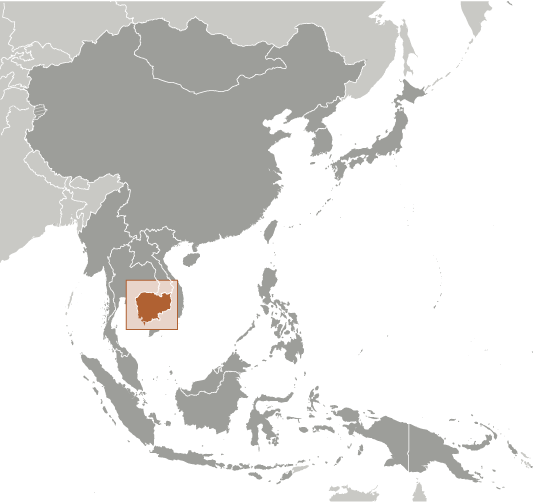
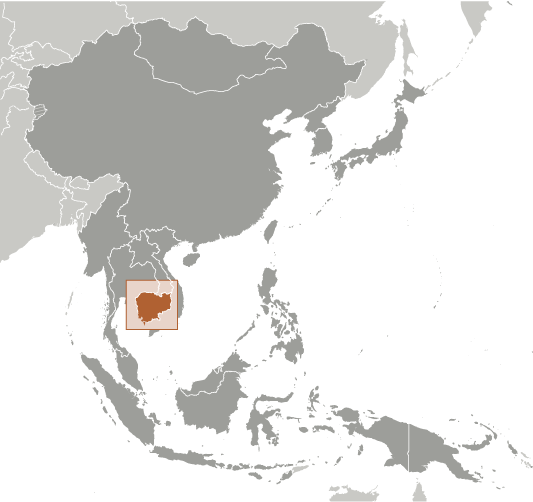
Cambodia
(Preahreacheanachakr Kampuchea (Kingdom of Cambodia))
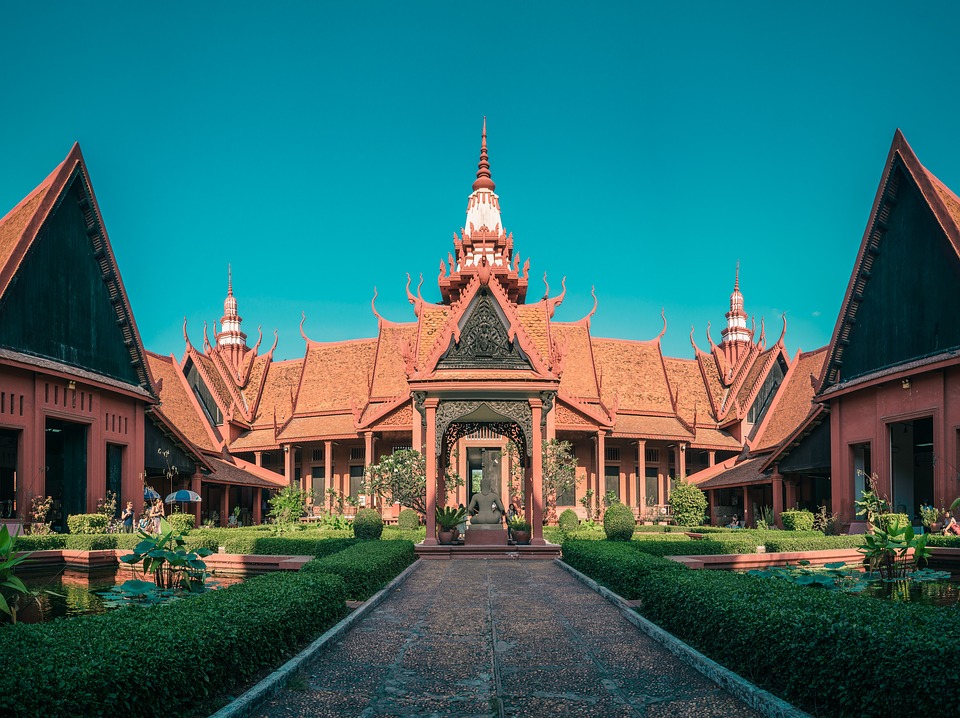
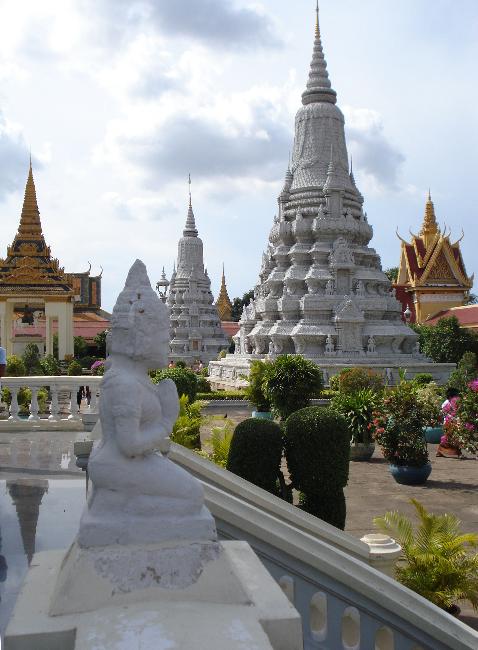

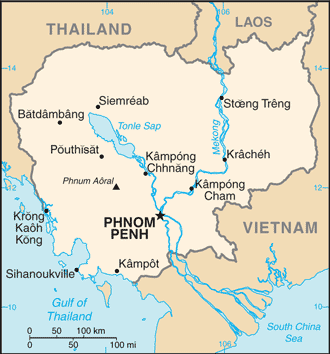






Capital: Phnom Penh
Population (Estimated July 2012): 14,952,665
Area: 181,035 km2 or 69,898 mi2
Currency: Riel (KHR)
Official Language: Khmer
Political Information: Parliamentary Democracy and Constitutional Monarchy
Official Religion: Buddhism
(approximately 96.4% of the population are Buddhist, 2.1% are Muslim, 1.3% have other religious beliefs and 0.2% have unspecified religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Phnum Aoral at 1,810m or 5,938ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $13.2 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $32.95 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $2,300 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +7:00
Counties/Provinces/States: 23 Provinces (khett, singular and plural) and 1 municipality (krong, singular and plural)
Provinces: Banteay Mean Choay, Batdambang, Kampong Cham, Kampong Chhnang, Kampong Spoe, Kampong Thum, Kampot, Kandal, Kaoh Kong, Keb, Krachen, Mondol Kiri, Otdar Mean Choay, Pailin, Pouthisat, Preah Seihanu (Sihanoukville), Preah Vihear, Prey Veng, Rotanokiri, Siem Reab, Stoeng Treng, Svay Rieng, Takev
Municipalities: Phnum Penh (Phnom Penh)
Leaders: King Norodom SIHAMONI (since 29 October 2004) and Prime Minister HUN SEN (since 14 January 1985); Permanent Deputy Prime Minister MEN SAM AN (since 25 September 2008); Deputy Prime Ministers SAR KHENG (since 3 February 1992), TEA BANH, Gen., HOR NAMHONG, NHEK BUNCHHAY (all since 16 July 2004), BIN CHHIN (since 5 September 2007), KEAT CHHON, YIM CHHAI LY (since 24 September 2008), KE KIMYAN (since 12 March 2009)
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Cambodia
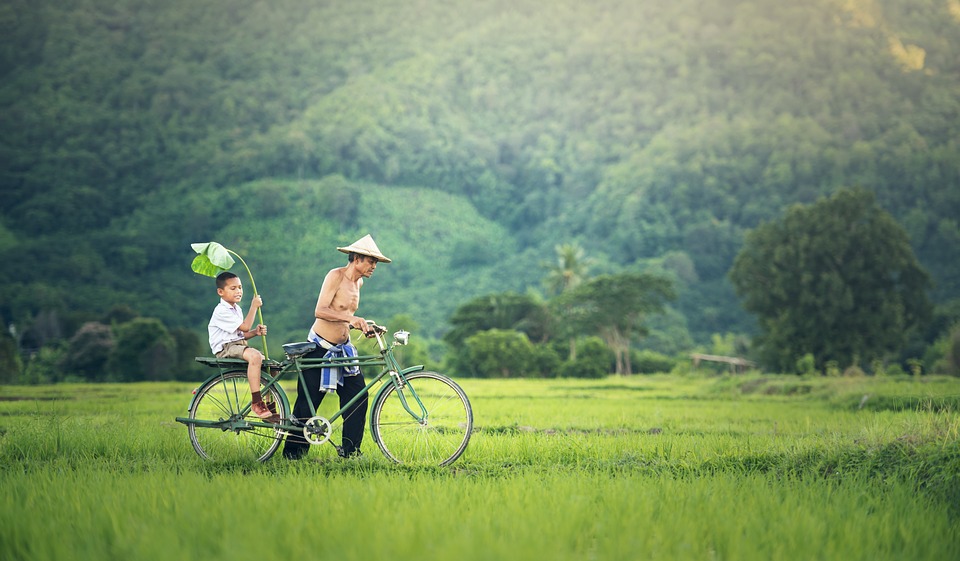
Located in Southeast Asia, Cambodia is a country with a rich cultural heritage and a fascinating history. It shares borders with Thailand, Laos, and Vietnam, and is known for its stunning landscapes, ancient temples, and vibrant traditions. Cambodia has a complex history, with influences from various empires and colonial powers shaping its culture and society. Despite facing challenges in the past, Cambodia has emerged as a resilient nation that takes pride in its cultural heritage.
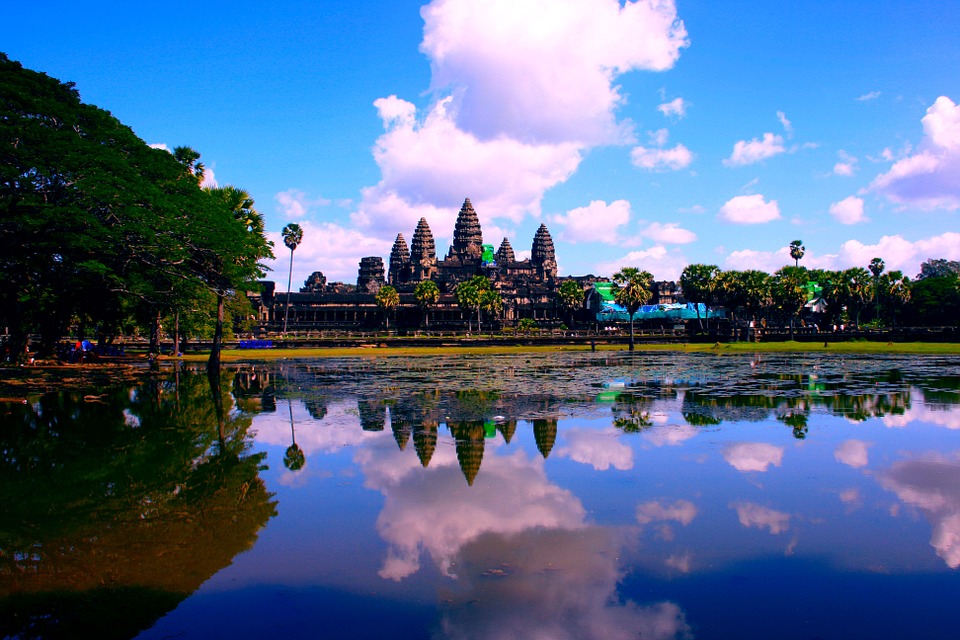
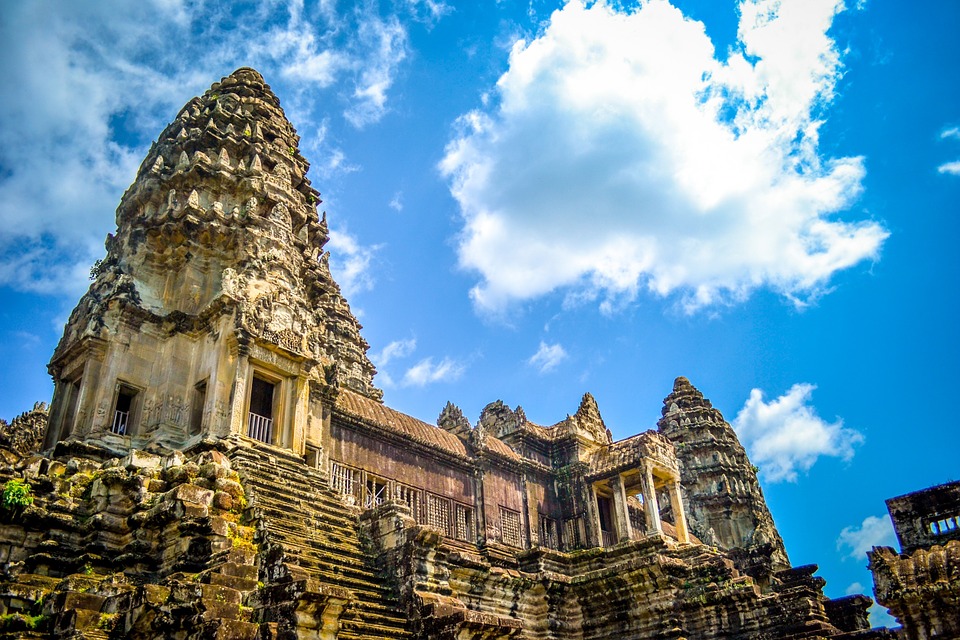
The cultural heritage of Cambodia is of great importance to the country and its people. It serves as a reminder of the nation’s history and identity, and plays a significant role in shaping the country’s tourism industry. The ancient temples of Angkor Wat, for example, attract millions of visitors each year who come to marvel at the architectural wonders and learn about the rich history of the Khmer Empire. Cambodia’s cultural heritage also includes traditional arts and crafts, such as dance, music, and handicrafts, which are passed down through generations and celebrated as an integral part of Cambodian identity.
Geography and Climate of Cambodia: From the Mekong River to the Cardamom Mountains
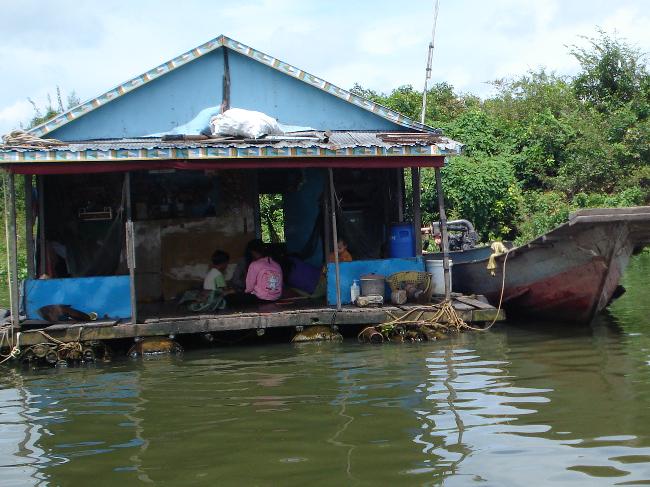
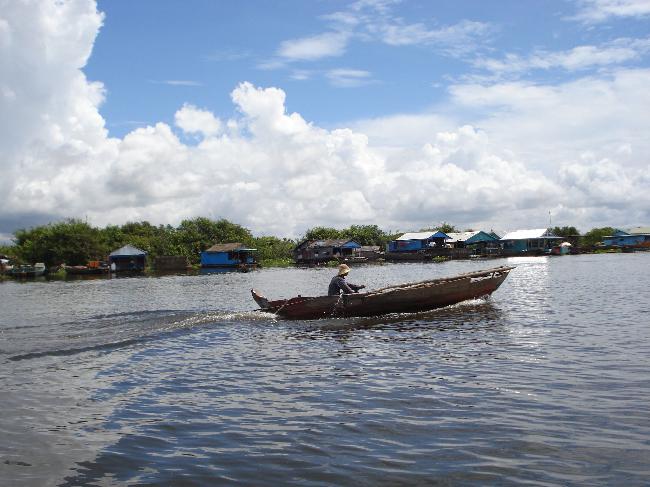
Cambodia is characterized by diverse geography and topography. The country is largely flat, with the Mekong River running through its heart. The river is not only an important waterway for transportation and trade but also provides fertile soil for agriculture. The Tonle Sap Lake, located near the capital city of Phnom Penh, is another significant geographical feature of Cambodia. It is the largest freshwater lake in Southeast Asia and supports a rich ecosystem.
In addition to its rivers and lakes, Cambodia is also home to mountain ranges such as the Cardamom Mountains in the southwest and the Dangrek Mountains in the north. These mountains provide a habitat for diverse flora and fauna, including endangered species such as tigers and elephants. The country’s geography and topography contribute to its unique climate, which is characterized by a tropical monsoon season from May to October and a dry season from November to April.
Cambodian People and Society: Diversity, Language, and Religion
Cambodia is a diverse country with a population of over 16 million people. The majority of the population is of Khmer ethnicity, but there are also significant minority groups such as the Cham, Chinese, and Vietnamese. This diversity is reflected in the country’s culture, traditions, and cuisine.
The official language of Cambodia is Khmer, which is spoken by the majority of the population. Khmer is a Mon-Khmer language and has its own unique script. While English is not widely spoken in Cambodia, it is becoming increasingly popular, especially among the younger generation.
Religion plays a significant role in Cambodian society, with Buddhism being the dominant religion. The majority of Cambodians are Theravada Buddhists, and temples can be found throughout the country. These temples serve as places of worship, as well as centers for community gatherings and cultural events.
Cambodian Cuisine: Exploring the Flavours of Khmer Food
Khmer cuisine is known for its bold flavors and use of fresh ingredients. It draws influences from neighboring countries such as Thailand and Vietnam but has its own unique twist. Rice is a staple in Cambodian cuisine and is often served with various meats, vegetables, and sauces.
One popular Khmer dish is amok, which is a steamed curry made with fish or chicken, coconut milk, and spices. Another famous dish is lok lak, which consists of stir-fried beef served with rice or noodles. Cambodian cuisine also includes a variety of soups, salads, and desserts.
In addition to its savory dishes, Cambodia is also known for its street food culture. Street vendors can be found throughout the country, selling snacks such as fried noodles, grilled meats, and fresh fruit shakes. Exploring the flavors of Khmer food is a must for any visitor to Cambodia.
Famous Landmarks and Tourist Attractions in Cambodia: Angkor Wat, Phnom Penh, and More
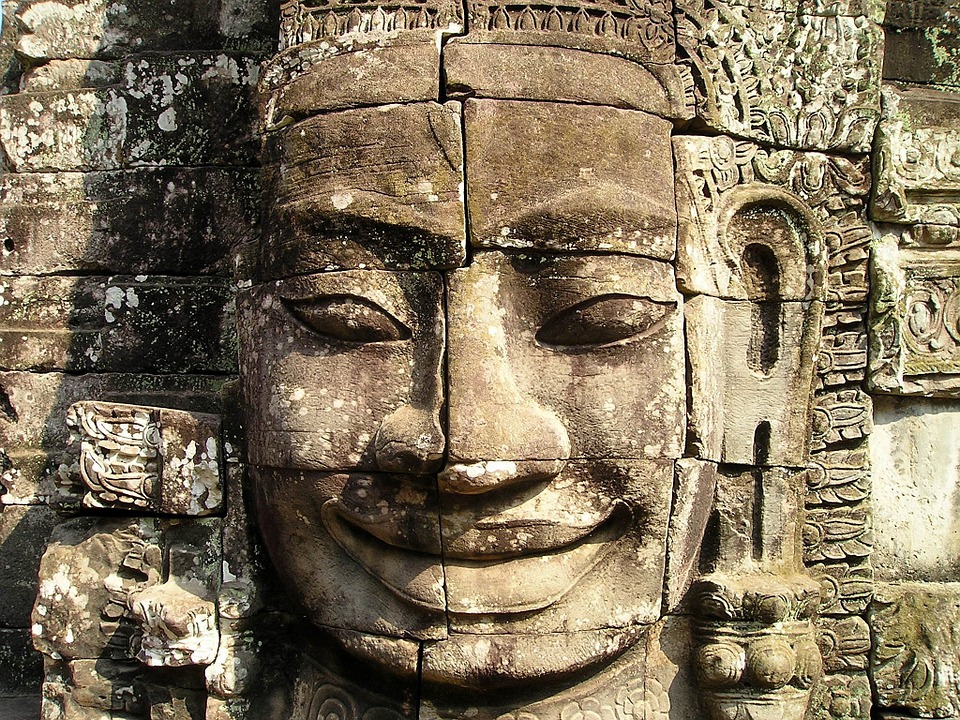
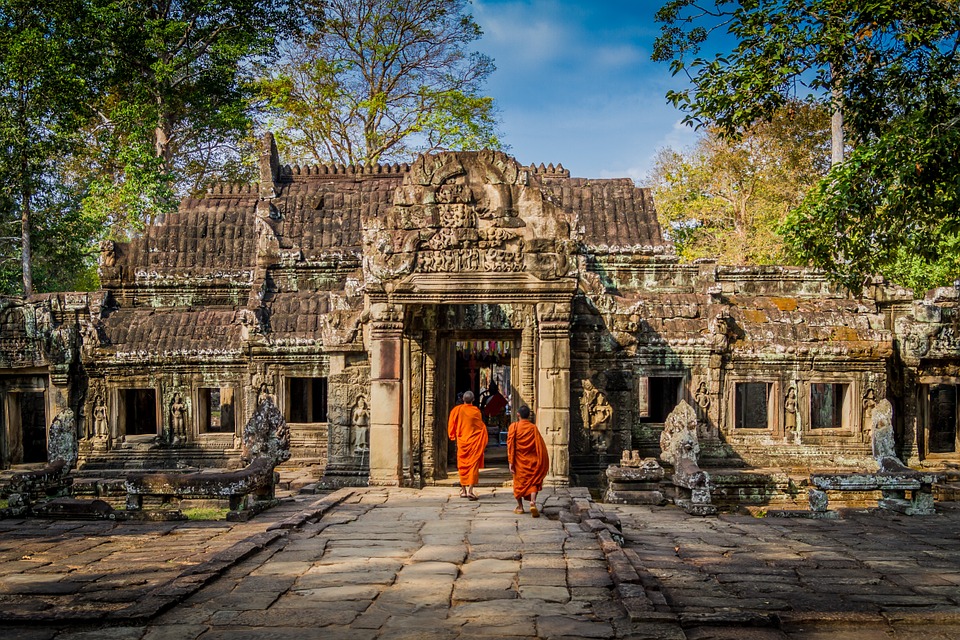
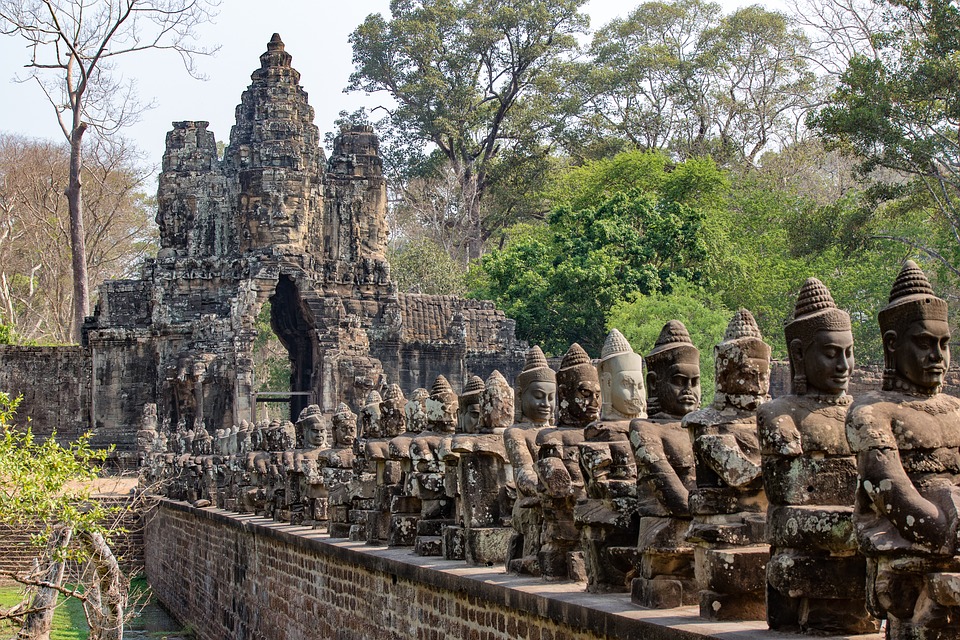
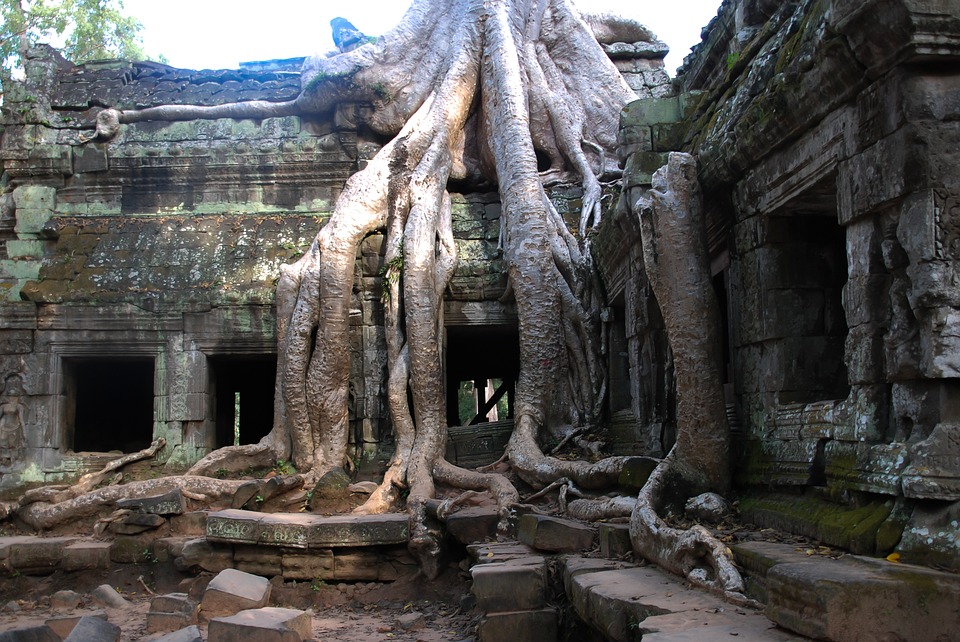
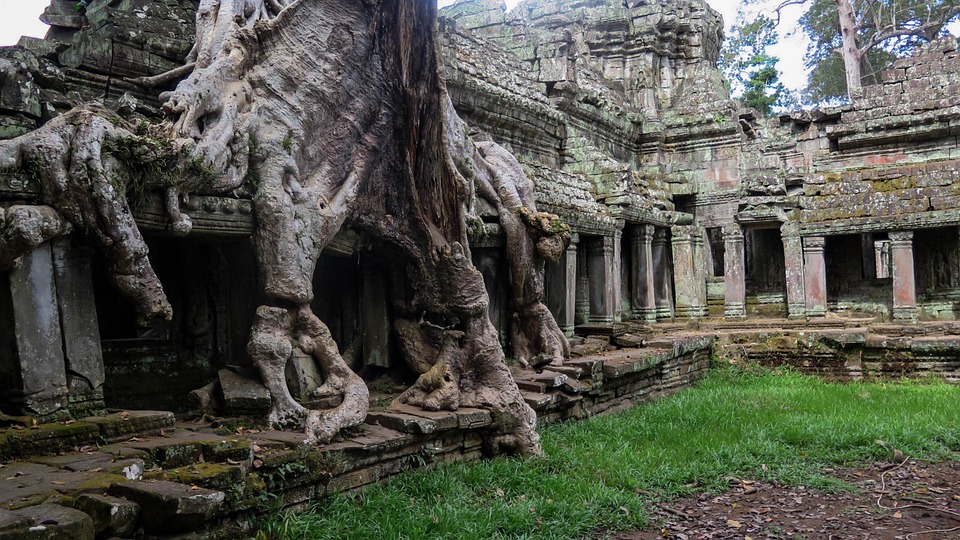
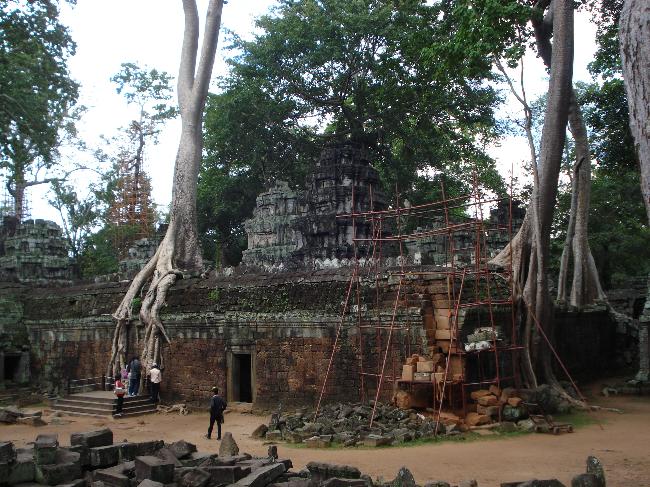
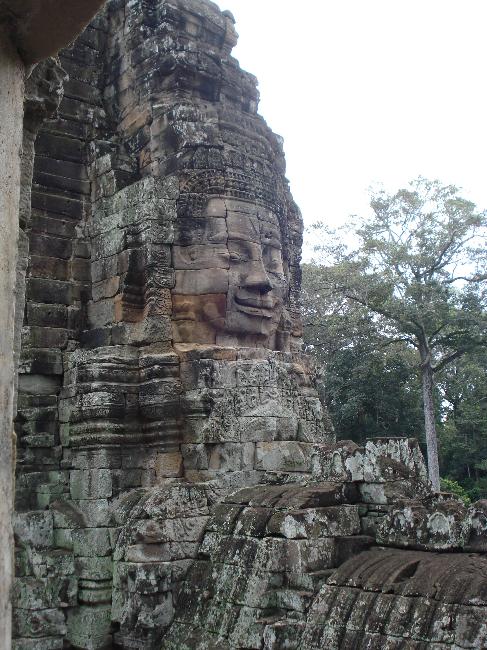
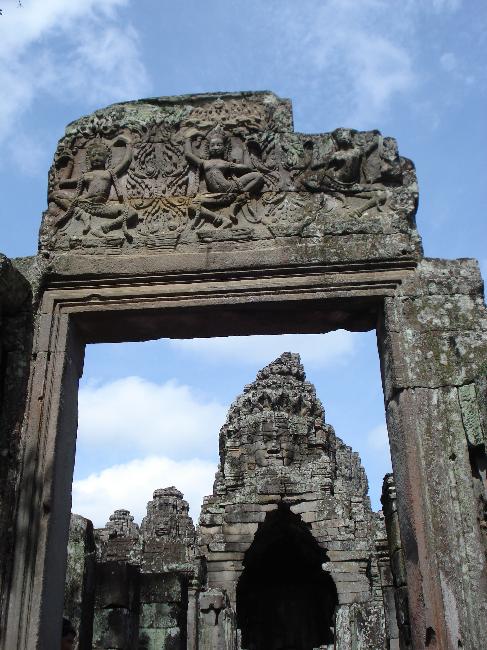
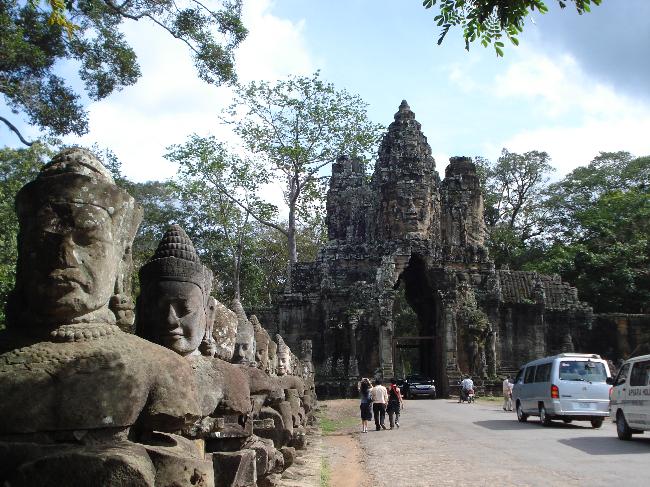
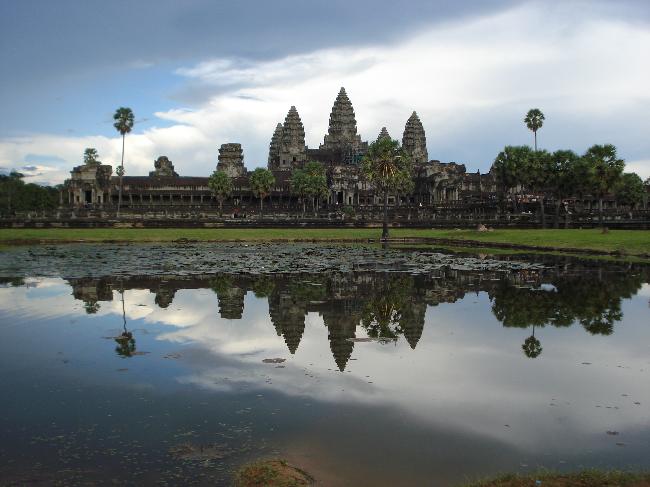
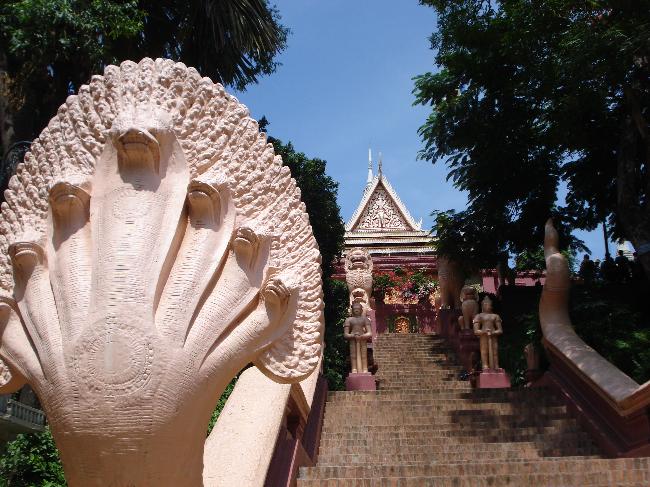
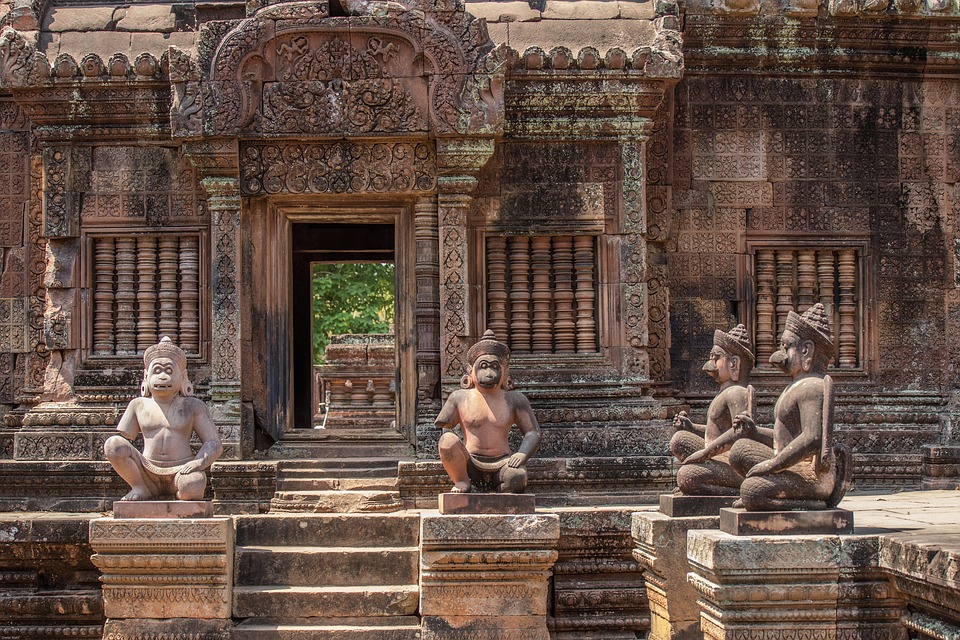
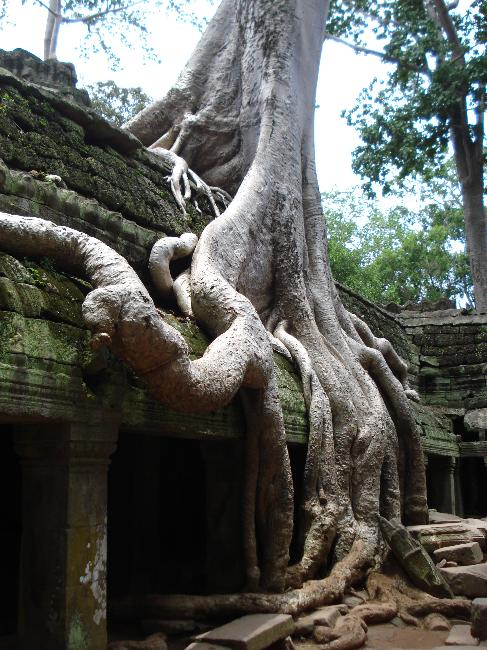
Cambodia is home to several famous landmarks and tourist attractions that draw visitors from around the world. The most iconic of these is Angkor Wat, a massive temple complex located in Siem Reap. Built in the 12th century, Angkor Wat is the largest religious monument in the world and is a UNESCO World Heritage site. Its intricate carvings and stunning architecture make it a must-visit destination for history and culture enthusiasts.
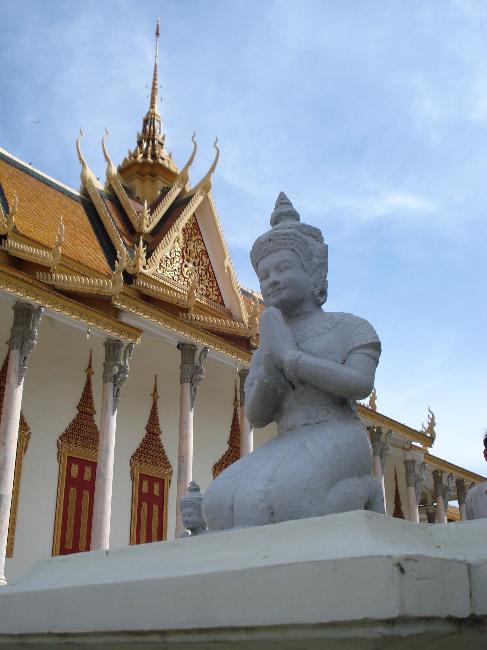
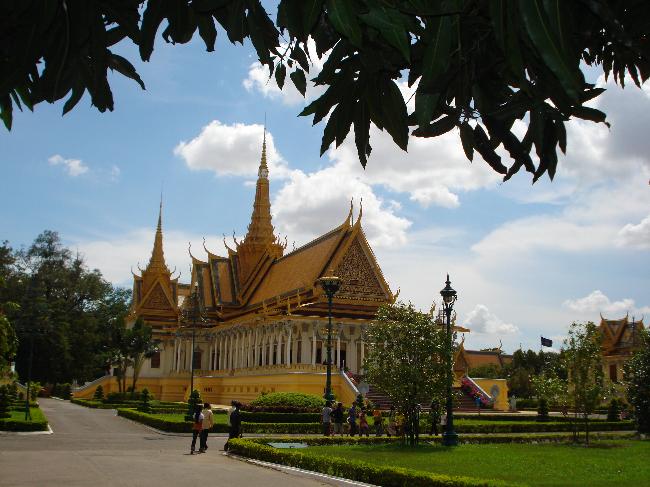
Another popular tourist destination in Cambodia is the capital city of Phnom Penh. Here, visitors can explore the Royal Palace, which serves as the residence of the King of Cambodia. The palace complex includes several buildings, including the Silver Pagoda, which houses many national treasures.
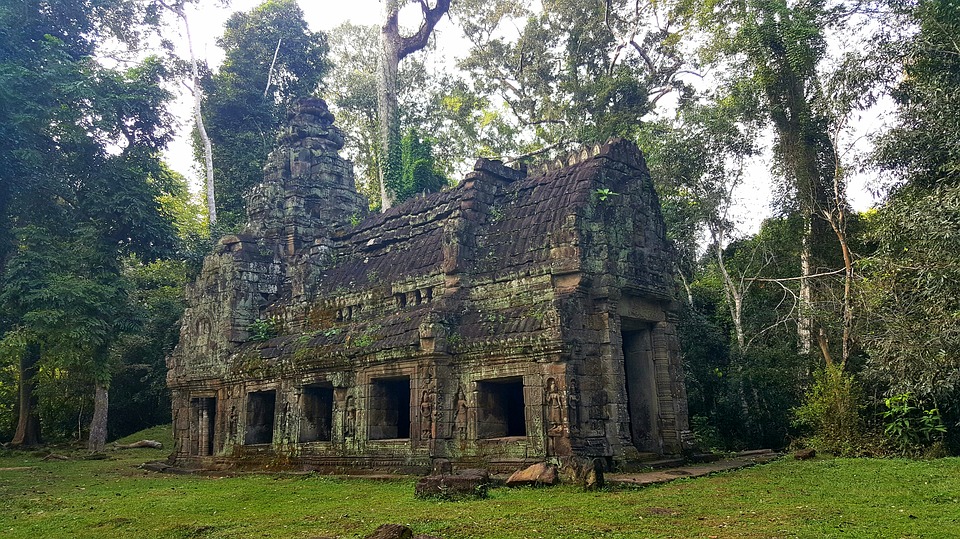
Other notable landmarks in Cambodia include the ancient city of Koh Ker, the beach town of Sihanoukville, and the floating villages on Tonle Sap Lake. Each of these destinations offers a unique glimpse into Cambodia’s history, culture, and natural beauty.
Cambodian Arts and Crafts: Traditional Dance, Music, and Handicrafts
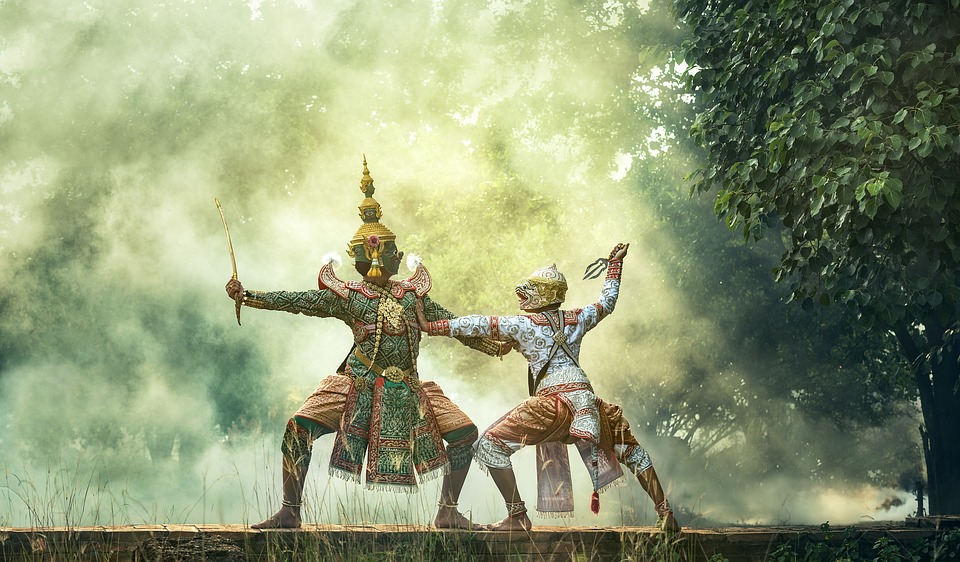
Cambodia has a rich tradition of arts and crafts that are deeply rooted in its cultural heritage. Traditional dance and music are an integral part of Cambodian culture and are often performed during religious ceremonies and festivals. The most famous form of traditional dance is the Apsara dance, which is characterized by graceful movements and intricate costumes.
In addition to dance, traditional music plays an important role in Cambodian culture. The pinpeat orchestra, for example, consists of traditional instruments such as xylophones, drums, and gongs. These instruments are used to accompany dance performances and other cultural events.
Cambodia is also known for its handicrafts, which include silk weaving, pottery, and wood carving. Silk weaving is a traditional craft that has been passed down through generations. The intricate patterns and vibrant colors of Cambodian silk are highly prized and can be found in clothing, scarves, and home decor items.
Cambodia’s Troubled Past: The Legacy of the Khmer Rouge Regime
Cambodia’s recent history is marked by the dark period of the Khmer Rouge regime, which lasted from 1975 to 1979. Under the leadership of Pol Pot, the Khmer Rouge implemented radical policies that resulted in the deaths of an estimated 1.7 million people, through execution, forced labor, and starvation.
The legacy of the Khmer Rouge regime continues to impact Cambodia today. Many Cambodians still bear the scars of this traumatic period, with survivors and their families seeking justice and healing. Efforts have been made to document the atrocities committed during this time, with the establishment of the Extraordinary Chambers in the Courts of Cambodia (ECCC) to prosecute those responsible for crimes against humanity.
Despite the challenges faced by Cambodia in its recent history, the country has shown remarkable resilience and determination to move forward. Efforts have been made to rebuild and develop the country, with a focus on education, infrastructure, and economic growth. Cambodia’s troubled past serves as a reminder of the importance of peace, justice, and human rights.
Current Political and Economic Situation in Cambodia: Challenges and Opportunities
Cambodia’s current political situation is characterized by a one-party system, with the ruling Cambodian People’s Party (CPP) holding a majority in parliament. While there have been concerns about political freedoms and human rights in recent years, Cambodia has made progress in terms of economic development.
The country has experienced steady economic growth over the past decade, with tourism, garment manufacturing, and agriculture being key sectors. However, Cambodia still faces challenges such as corruption, income inequality, and a lack of infrastructure. Efforts are being made to address these issues and promote sustainable and inclusive development.
Cambodia’s strategic location in Southeast Asia also presents opportunities for economic growth and regional cooperation. The country is part of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and has signed various free trade agreements with neighbouring countries. These agreements aim to promote trade and investment, as well as enhance regional integration.
Environmental Issues in Cambodia: Deforestation, Wildlife Conservation, and Climate Change
Cambodia faces several environmental issues that threaten its natural resources and biodiversity. Deforestation is a major concern, with illegal logging and land encroachment leading to the loss of forests and wildlife habitats. This has a significant impact on the country’s ecosystems and contributes to climate change.
Wildlife conservation is another important issue in Cambodia. The country is home to several endangered species, including tigers, elephants, and freshwater dolphins. Efforts are being made to protect these species through the establishment of protected areas and conservation projects.
Climate change is also a growing concern in Cambodia, with rising temperatures and changing weather patterns affecting agriculture and water resources. The government has recognized the importance of addressing climate change and has implemented initiatives to promote renewable energy, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and build climate resilience.
Future Prospects for Cambodia: Building a Sustainable and Inclusive Society
Despite the challenges it faces, Cambodia has a promising future ahead. The country has made significant progress in terms of economic development and poverty reduction, with improvements in education, healthcare, and infrastructure. Efforts are also being made to promote sustainable tourism and protect the environment.
Building a sustainable and inclusive society is a key priority for Cambodia’s future. This includes promoting social justice, human rights, and gender equality. It also involves investing in education and skills development to empower the younger generation and ensure they have the tools they need to succeed.
Cambodia’s rich cultural heritage and natural beauty provide a strong foundation for sustainable development. By preserving its cultural traditions, protecting its natural resources, and promoting responsible tourism, Cambodia can continue to thrive and build a brighter future for its people.
FAQs
What is Cambodia?
Cambodia is a country located in Southeast Asia. It shares borders with Thailand, Laos, and Vietnam.
What is the capital city of Cambodia?
The capital city of Cambodia is Phnom Penh.
What is the population of Cambodia?
As of 2021, the estimated population of Cambodia is around 16.7 million people.
What is the official language of Cambodia?
The official language of Cambodia is Khmer.
What is the currency of Cambodia?
The currency of Cambodia is the Cambodian riel, although the US dollar is also widely used.
What is the climate like in Cambodia?
Cambodia has a tropical climate with two distinct seasons: the rainy season from May to October and the dry season from November to April.
What are some popular tourist attractions in Cambodia?
Some popular tourist attractions in Cambodia include the Angkor Wat temple complex, the Royal Palace in Phnom Penh, and the beaches of Sihanoukville.
What is the main religion in Cambodia?
The main religion in Cambodia is Buddhism, with around 95% of the population practicing this religion.
What is the government system in Cambodia?
Cambodia is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system of government. The current king is Norodom Sihamoni.
Political Boundaries of Cambodia: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Cambodia, officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a Southeast Asian country located in the southern part of the Indochinese Peninsula. It shares its borders with Thailand to the west, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east and southeast. Understanding Cambodia’s political boundaries is crucial for various reasons, including governance, administration, and territorial disputes. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Cambodia’s political boundaries, including its provinces, districts, historical boundaries, border disputes, administrative divisions, provincial capitals, ethnic diversity, geographical features, and future political landscape. Summary Cambodia is divided into 25 provinces and 1 municipality. Each province is further divided into districts, which are responsible for local administration. Cambodia’s historical boundaries have been shaped by various empires and colonial powers. Border disputes with neighbouring countries have posed challenges for Cambodia’s political boundaries. Cambodia’s administrative divisions have undergone changes and developments over time. Provinces of Cambodia: History and Overview Cambodia is divided into 25 provinces and the capital city of Phnom Penh. Each province has its own unique history and cultural heritage. The provinces are further divided into districts and communes. Some of the provinces have a rich historical background, such as Siem Reap, which is home to the famous Angkor Wat temple complex. Other provinces, like Kampong Cham and Battambang, are known for their agricultural productivity. The population and economic statistics of each province vary significantly. Phnom Penh, being the capital city, has the highest population and is the economic hub of the country. It is followed by provinces like Kampong Cham and Battambang. The provinces located along the border regions often have a lower...
Climate Zones of Cambodia: Different climate regions Of Cambodia
Cambodia is a country located in Southeast Asia, bordered by Thailand, Laos, and Vietnam. It has a diverse geography, with mountains, plateaus, and coastal areas. The climate in Cambodia is influenced by the monsoon season, which brings heavy rainfall and distinct wet and dry seasons. Understanding Cambodia’s climate zones is important for various reasons, including agriculture, tourism, and conservation efforts. Summary Cambodia has a diverse range of climate zones due to its location in Southeast Asia. The Tropical Wet and Dry Climate Zone is characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons. The Tropical Monsoon Climate Zone experiences heavy rainfall during the monsoon season. The Temperate Highland Climate Zone has cooler temperatures due to its higher elevation. Climate change is impacting Cambodia’s climate zones, leading to more extreme weather events. Tropical Wet and Dry Climate Zone The tropical wet and dry climate zone is characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons. The wet season typically lasts from May to October, with heavy rainfall and high humidity. The dry season, on the other hand, occurs from November to April and is characterized by lower rainfall and cooler temperatures. Regions in Cambodia that fall under this climate zone include the central lowlands and the Mekong River Basin. These areas are known for their fertile soil and are important for agriculture, particularly rice cultivation. The wet season provides ample water for irrigation, while the dry season allows for harvesting. Vegetation found in this climate zone includes deciduous forests, grasslands, and shrubs. Wildlife commonly found in this region includes elephants, tigers, deer, and various bird species. Tropical Monsoon Climate Zone The tropical monsoon climate...
Terrain and Topography of Cambodia: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Cambodia, located in Southeast Asia, is a country known for its rich history, vibrant culture, and stunning landscapes. Understanding the terrain and topography of Cambodia is crucial for various reasons. It helps in understanding the country’s biodiversity, planning for agriculture and infrastructure development, and preparing for natural disasters. Cambodia’s terrain consists of mountainous regions, central plains, coastal lowlands, and river basins. Each of these regions plays a significant role in the country’s development and should be studied in detail. Summary Cambodia’s terrain is diverse, ranging from mountainous regions to coastal lowlands. The Cardamom Mountains and Dangrek Mountains are two prominent mountain ranges in Cambodia. The Tonle Sap Basin and Mekong River and Delta are important water systems in Cambodia. Topography plays a significant role in Cambodia’s climate, with the country experiencing both wet and dry seasons. Cambodia’s terrain has a significant impact on agriculture and infrastructure development. The Mountainous Regions of Cambodia Cambodia is home to several mountain ranges that run across the country. The most prominent ones include the Cardamom Mountains in the southwest and the Dangrek Mountains in the north. These mountainous regions are not only visually stunning but also serve as important habitats for a diverse range of flora and fauna. They are home to many endangered species, making them crucial for biodiversity conservation efforts. Moreover, these mountain ranges also attract tourists from around the world. The lush green forests, cascading waterfalls, and breathtaking views make them popular destinations for hiking, trekking, and wildlife spotting. The tourism industry plays a significant role in Cambodia’s economy, and these mountainous regions contribute to its growth. The Central Plains...
History of Cambodia
Introduction Cambodia is a country with a rich and vibrant history that dates back thousands of years. From the early civilizations of Funan and Chenla to the rise and fall of the Angkor Empire, Cambodia has played a significant role in shaping Southeast Asian culture and history. Understanding Cambodia’s history is crucial in order to appreciate the country’s cultural heritage and to learn from its past experiences. In this article, we will explore the different eras of Cambodia’s history, from the pre-Angkor era to modern times, and discuss the importance of preserving Cambodia’s cultural heritage. Pre-Angkor Era: The Early Civilizations of Cambodia The pre-Angkor era in Cambodia saw the rise of two powerful kingdoms: Funan and Chenla. Funan, which existed from the 1st to the 6th century AD, was one of the earliest Indianized states in Southeast Asia. It was a major center for trade and played a crucial role in spreading Indian culture and religion throughout the region. Funan’s influence can be seen in the art, architecture, and language of later Khmer civilizations. After the decline of Funan, the Chenla kingdom emerged as a dominant power in Cambodia. Chenla was divided into two periods: Chenla Proper and Water Chenla. During this time, Buddhism became the dominant religion in Cambodia, and many temples and religious structures were built. The Chenla period also saw advancements in agriculture, trade, and irrigation systems. The Rise of Angkor: The Golden Age of Cambodia The Angkor Empire, which existed from the 9th to the 15th century AD, is considered the golden age of Cambodia. The empire was known for its impressive architecture, including the...
Population Density of Cambodia
Cambodia, located in Southeast Asia, is a country with a population density that has been steadily increasing over the years. With an estimated population of over 16 million people, Cambodia has a population density of approximately 92 people per square kilometer. This makes it one of the most densely populated countries in the region. Understanding population density is crucial for policymakers and planners as it helps in making informed decisions regarding resource allocation, infrastructure development, and social services. Summary Cambodia has a population density of 92 people per square kilometer. Cambodia’s population growth has fluctuated throughout history due to various factors such as war and disease. There are significant regional differences in population density, with the highest densities found in the central lowlands and the lowest in the mountainous regions. Urbanisation has contributed to the increase in population density, with Phnom Penh being the most densely populated city in Cambodia. Factors such as high fertility rates, rural-urban migration, and lack of family planning contribute to Cambodia’s high population density. Historical Overview of Cambodia’s Population Growth Cambodia’s population growth has seen significant fluctuations over the years. In the 1960s, the population growth rate was relatively low due to political instability and conflicts. However, after the Khmer Rouge regime ended in 1979, the population began to recover and grow rapidly. The population growth rate peaked in the 1990s and has since slowed down but remains steady. Several factors have contributed to Cambodia’s population growth. Improved healthcare and access to medical facilities have led to a decline in infant mortality rates and an increase in life expectancy. Additionally, high fertility rates have...
Natural Resources of Cambodia: Where Natural Resources are located In Cambodia
Natural Resources of Cambodia: Where Natural Resources are located in Cambodia Cambodia is a nation endowed with abundant natural resources, yet its true economic potential remains partially untapped due to challenges in natural resource governance. From the fertile banks of the Mekong River to rich forestry zones and promising offshore oil reserves, Cambodia has much to offer. This article will explore the natural resources of Cambodia, their importance to the Cambodian economy, and the policies guiding their sustainable use. Whether you’re a researcher, investor, or geography enthusiast, this deep dive offers essential insights into Cambodia’s strategic natural wealth. Article Outline What Are the Most Valuable Natural Resources in Cambodia Today? How Do Cambodia’s Mineral Resources Contribute to Its Economy? What Role Does the Mekong River Play in Cambodia’s Natural Resource Landscape? Is Cambodia Rich in Oil and Natural Gas? How Important Is Forestry and Timber to Cambodia? Why Is Tonle Sap Lake Crucial to Cambodian Livelihoods and Water Resources? How Does Biodiversity Fit Into Cambodia’s Ecosystem and Natural Resource Strategy? What Are the Key Challenges in Cambodia’s Natural Resource Governance? How Are Cambodia’s Natural Resources Tied to the Agricultural and Fishery Sectors? What Is the Future of Energy in Rural Areas and Sustainable Development in Cambodia? What Are the Most Valuable Natural Resources in Cambodia Today? Cambodia’s landscape is rich with natural resources that span a wide spectrum—from forestry and water to mineral resources and natural gas. The country’s abundant natural resources are mainly hosted in provinces like Kampot, and areas around the Mekong basin, making them crucial for both domestic use and export potential. Key natural resources of...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Cambodia: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Cambodia
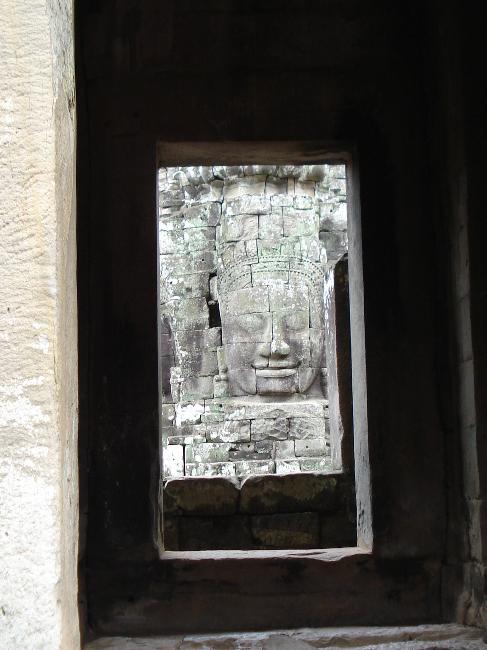
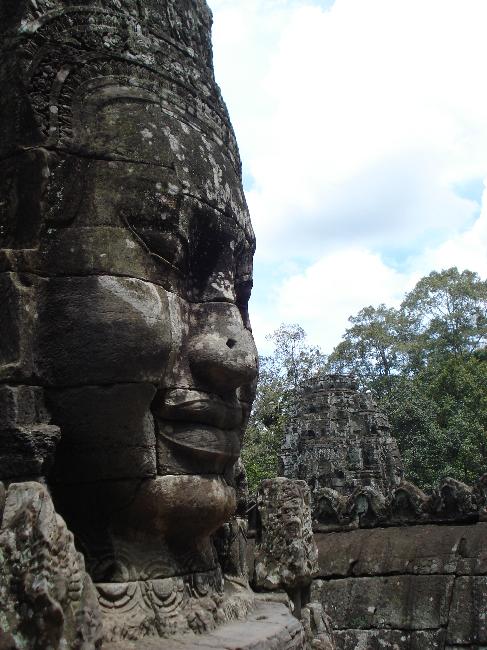
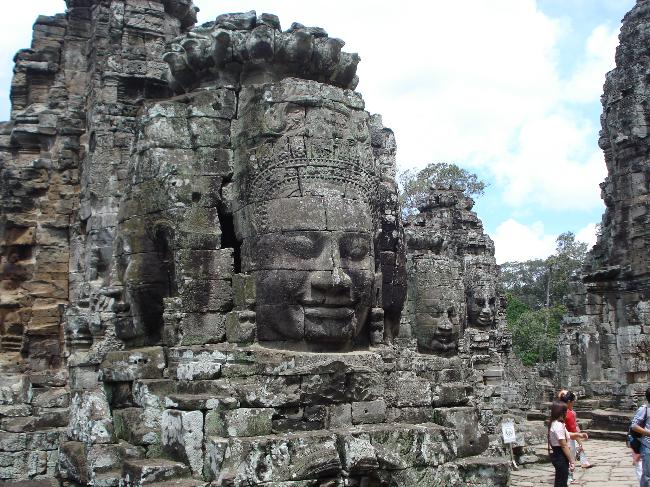
Cambodia is a country with a rich cultural and historical heritage that dates back thousands of years. From the magnificent temples of Angkor Wat to the tragic history of the Khmer Rouge regime, Cambodia’s past is both fascinating and heartbreaking. It is important to preserve and promote Cambodia’s cultural heritage in order to educate future generations and ensure that these important sites are protected for years to come. Summary Cambodia has a rich cultural and historical heritage worth exploring. Angkor Wat is a magnificent symbol of Cambodia’s glory and a must-visit site. The Royal Palace of Phnom Penh is a testament to Cambodia’s monarchy and its history. The Killing Fields of Choeung Ek serve as a reminder of Cambodia’s tragic past and the atrocities committed during the Khmer Rouge regime. The Bayon Temple is a breathtaking masterpiece of Khmer architecture and a must-see attraction. The Magnificent Angkor Wat Angkor Wat is perhaps the most famous and iconic temple in Cambodia. Built in the 12th century, it was originally a Hindu temple dedicated to the god Vishnu, but later became a Buddhist temple. The temple complex covers an area of over 400 acres and is surrounded by a moat. The main temple is made up of five towers, each representing a mountain in Hindu mythology. Visiting Angkor Wat is a truly awe-inspiring experience. The intricate carvings and stunning architecture are a testament to the skill and craftsmanship of the Khmer people. It is recommended to visit Angkor Wat early in the morning or late in the afternoon to avoid the crowds and witness the temple at its most beautiful. The...
Discovering the Hidden Gems of Cambodia: A British Traveller’s Insightful Journey
Cambodia, a country located in Southeast Asia, is a land of rich history, vibrant culture, and breathtaking landscapes. From its ancient temples to its bustling cities, Cambodia offers a unique and unforgettable travel experience. In recent years, Cambodia has become an increasingly popular tourist destination, attracting visitors from all over the world. This article will explore the different regions of Cambodia and the attractions they have to offer. Cambodia has a fascinating history that dates back thousands of years. The Khmer Empire, which ruled over much of Southeast Asia from the 9th to the 15th century, left behind a legacy of magnificent temples and architectural wonders. The most famous of these temples is Angkor Wat, a UNESCO World Heritage site and one of the largest religious monuments in the world. Cambodia’s culture is deeply rooted in its history, with influences from Hinduism and Buddhism evident in its art, architecture, and traditions. In recent years, Cambodia has seen a surge in tourism as more and more people discover its beauty and charm. The country offers a unique blend of ancient history and modern attractions, making it an appealing destination for all types of travelers. From exploring ancient temples to relaxing on pristine beaches, Cambodia has something to offer everyone. Summary Cambodia is a hidden gem with a unique allure that is worth exploring. Siem Reap is a charming destination that offers a chance to explore the ancient temples of Angkor. Battambang is a serene haven for art and culture enthusiasts. Phnom Penh is a city with a dark history that is shrouded in mystique and worth uncovering. Kep is a...