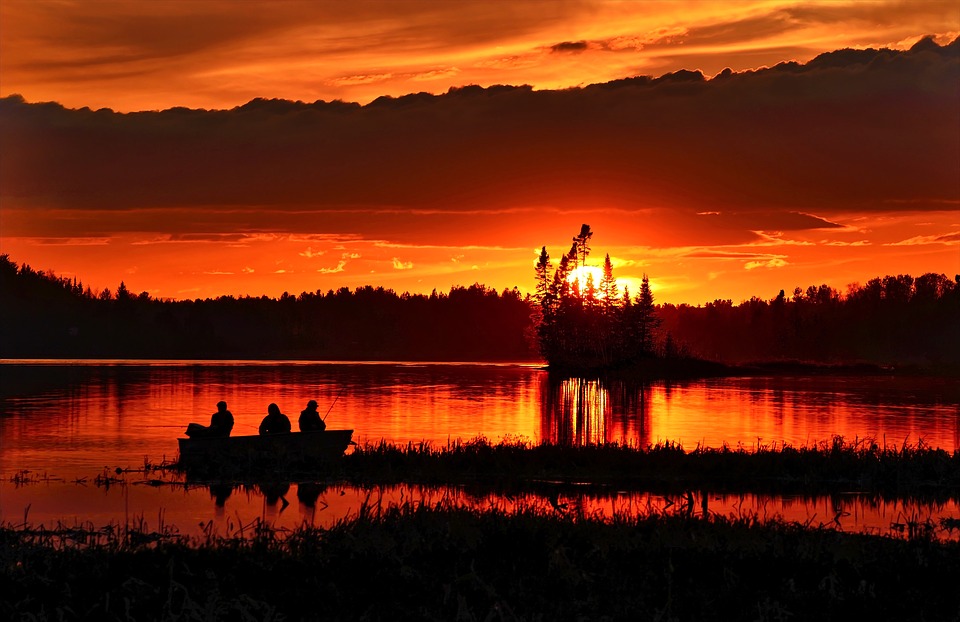
Canada

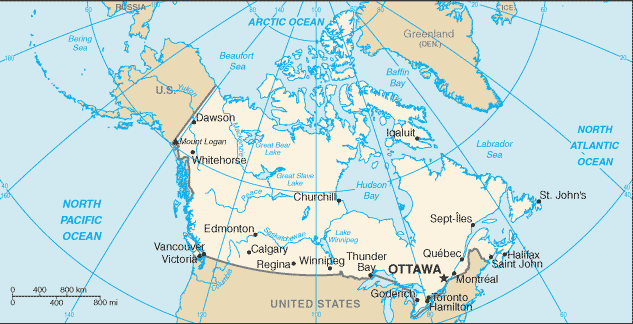






Capital: Ottawa
Population (Estimated July 2012): 34,300,083
Area: 9,984,670 km2 or 3,855,103 mi2
Currency: Canadian Dollar (Can$)
Official Language: English and French
Political Information: Federal Parliamentary Democracy and Constitutional Monarchy
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 42.6% of the population is Roman Catholic, 23.3% are Protestant, 4.4% have other Christian Beliefs, 1.9% are Muslim, 11.8% have other or unspecified religious beliefs and 16% have no religious beliefs)
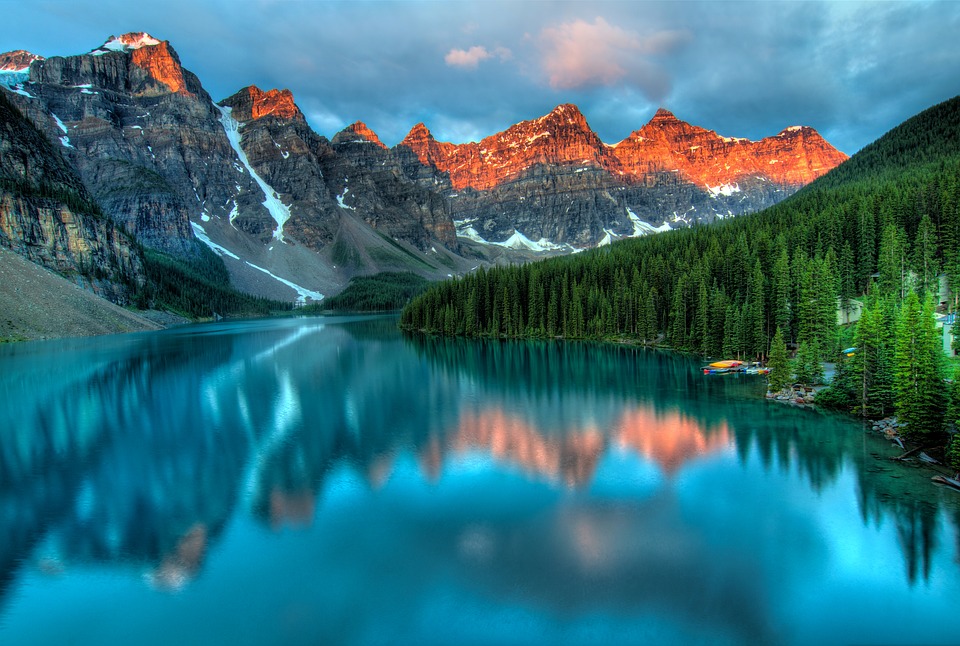
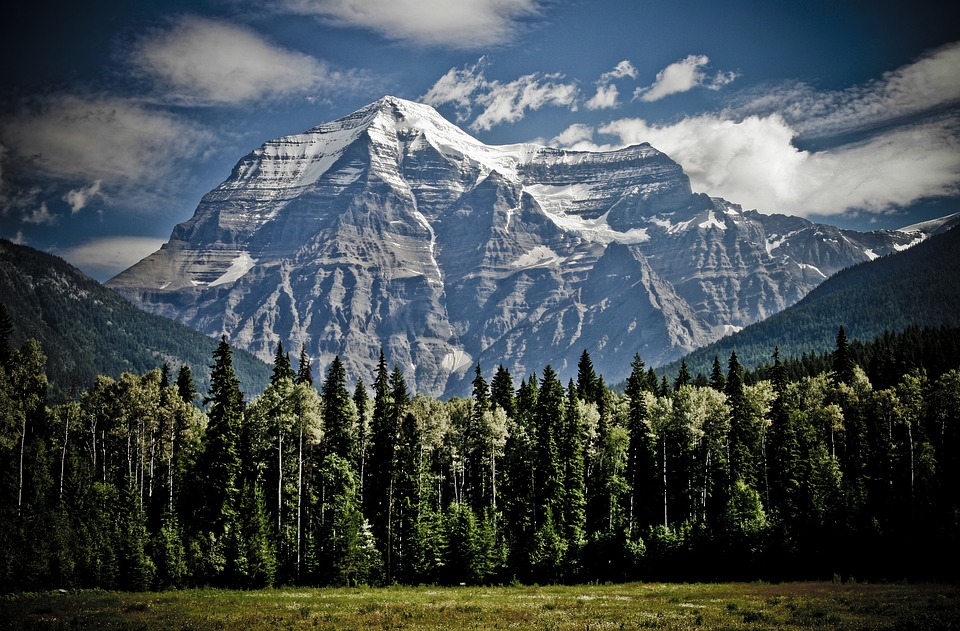
Highest Mountain: Mount Logan at 5,959m or 19,551ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $1.759 trillion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $1.389 trillion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $40,300 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): Between -3:30 to -8:00
Counties/Provinces/States: 10 provinces and 3 territories*; Alberta, British Columbia, Manitoba, New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Northwest Territories*, Nova Scotia, Nunavut*, Ontario, Prince Edward Island, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Yukon Territory*
Leaders: H.M. Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Governor General Julie PAYETTE (since 2 October 2017) with Prime Minister Justin Pierre James TRUDEAU (Liberal Party) (since 4 November 2015)
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Canada
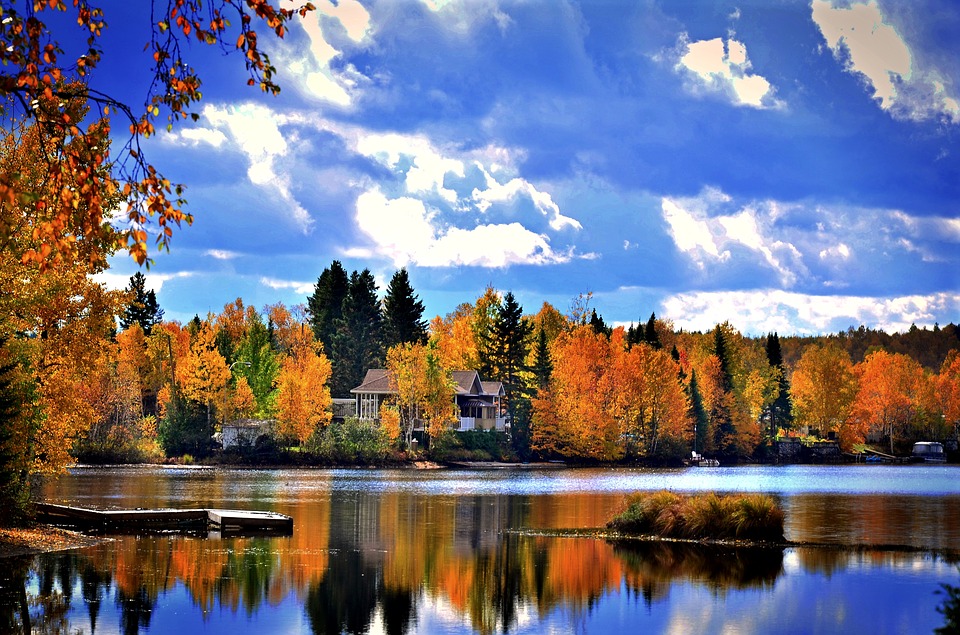
Canada is the second-largest country in the world, spanning over 9.9 million square kilometres. It is located in North America, sharing its southern border with the United States. Canada is known for its diverse geography, which includes vast forests, towering mountains, and beautiful coastlines. The country is divided into ten provinces and three territories, each with its own unique landscapes and attractions.
Canada has a population of approximately 38 million people, making it one of the least densely populated countries in the world. The population is incredibly diverse, with over 200 ethnic origins reported by Canadians. The largest ethnic groups include English, Scottish, Irish, Chinese, and Indian. This diversity is reflected in Canada’s multicultural society and contributes to its vibrant cultural scene.
Canada’s History: From Indigenous Peoples to Colonialism and Independence
Before European colonization, Canada was inhabited by various Indigenous peoples who had lived on the land for thousands of years. These Indigenous peoples had their own distinct cultures, languages, and ways of life. They relied on hunting, fishing, and gathering for their sustenance and had a deep spiritual connection to the land.
European colonization began in the 16th century when explorers from France and England arrived in Canada. This colonization had a significant impact on the Indigenous peoples, as they were forced off their lands and faced violence and disease brought by the Europeans. The fur trade became a major industry in Canada during this time, with European settlers establishing trading posts throughout the country.
In 1867, Canada achieved confederation and became a self-governing dominion within the British Empire. Over time, Canada gained more independence from Britain and eventually became fully independent in 1982 with the patriation of its constitution. Today, Canada is a parliamentary democracy with a constitutional monarchy, with Queen Elizabeth II as its head of state.
Canadian Culture: Art, Music, Literature, and Sports
Canada has a rich and diverse cultural scene, with contributions from artists, musicians, writers, and athletes. Canadian art encompasses a wide range of styles and mediums, from traditional Indigenous art to contemporary works. The Group of Seven, a group of Canadian landscape painters, is particularly renowned for their depictions of the country’s natural beauty.
In the music industry, Canada has produced many internationally acclaimed musicians across various genres. Artists such as Celine Dion, Justin Bieber, Drake, and The Weeknd have achieved global success. Canada is also known for its contributions to classical music, with the Toronto Symphony Orchestra and the Montreal Symphony Orchestra being highly regarded.
Canadian literature has produced many notable authors who have made significant contributions to the literary world. Margaret Atwood, Alice Munro, and Michael Ondaatje are just a few examples of Canadian authors who have received international recognition for their works. Canadian literature often explores themes of identity, multiculturalism, and the country’s unique landscapes.
Sports play a significant role in Canadian culture, with ice hockey being the most popular sport in the country. The National Hockey League (NHL) features several Canadian teams, and the sport is deeply ingrained in Canadian identity. Other popular sports include Canadian football, lacrosse, basketball, and soccer. Canada has produced many successful athletes who have excelled on the world stage.
Canadian Politics: The Federal System, Elections, and Political Parties
Canada operates under a federal system of government, which means power is divided between the federal government and the provinces/territories. The federal government is responsible for national issues such as defence, foreign policy, and trade, while the provinces/territories have jurisdiction over areas such as healthcare and education.
Elections in Canada are held at both the federal and provincial/territorial levels. The voting process is based on a first-past-the-post system, where the candidate with the most votes in each riding wins a seat in the legislative body. The leader of the political party with the most seats becomes the Prime Minister at the federal level or Premier at the provincial/territorial level.
There are several major political parties in Canada, including the Liberal Party, Conservative Party, New Democratic Party (NDP), and Green Party. The Liberal Party and Conservative Party have historically been the two dominant parties, with the NDP and Green Party gaining support in recent years. Each party has its own platform and policies, which they promote during election campaigns.
The Canadian Economy: Industries, Trade, and Employment
Canada has a diverse and robust economy, with various industries contributing to its GDP. Some of the major industries include natural resources (such as oil, gas, and minerals), manufacturing, technology, agriculture, and tourism. Canada is known for its abundance of natural resources and is one of the world’s largest exporters of energy products.
Trade is a vital component of Canada’s economy, with the United States being its largest trading partner. Canada is also a member of several trade agreements, including the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and the Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) with the European Union. These agreements have facilitated increased trade and investment opportunities for Canadian businesses.
The employment rate in Canada is relatively high, with various job opportunities available across different sectors. The country has a strong focus on education and skills training to ensure a skilled workforce. The government also implements policies to support job creation and economic growth.
Canadian Education: The Public School System and Higher Education
Education in Canada is primarily publicly funded and administered by each province/territory. The public school system provides free education from kindergarten to grade 12. The curriculum is standardized across the country but allows for some flexibility at the provincial/territorial level.
Higher education in Canada is highly regarded, with many universities and colleges offering a wide range of programs and degrees. Canadian universities are known for their research and innovation, attracting students from around the world. The country also has a strong focus on vocational and technical education, providing opportunities for practical skills training.
Education funding in Canada comes from a combination of federal, provincial/territorial, and local sources. Scholarships, grants, and loans are available to support students in their educational pursuits. The government also implements policies to ensure the accessibility and affordability of education for all Canadians.
Canadian Healthcare: Universal Coverage and Public Health Initiatives
Canada has a publicly funded healthcare system that provides universal coverage to all residents. The Canada Health Act ensures that essential medical services are accessible to everyone, regardless of their ability to pay. The healthcare system is primarily funded through taxes and administered by each province/territory.
In addition to universal coverage, Canada also has various public health initiatives and programs in place to promote the well-being of its population. These initiatives focus on areas such as disease prevention, health promotion, and emergency preparedness. The government works closely with healthcare professionals and organizations to implement these initiatives.
Healthcare funding in Canada is a topic of ongoing debate, as the system faces challenges such as long wait times for certain procedures and shortages of healthcare professionals in some areas. The government continues to invest in healthcare infrastructure and implement policies to address these issues.
Canadian Cuisine: Traditional and Modern Dishes
Canadian cuisine is influenced by its diverse cultural heritage and the availability of local ingredients. Traditional dishes often reflect the country’s history and include dishes such as poutine (French fries topped with cheese curds and gravy), tourtière (a meat pie), butter tarts, and Nanaimo bars.
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in traditional Canadian cuisine, with chefs putting modern twists on classic dishes. Farm-to-table dining and the use of locally sourced ingredients have also become popular trends in Canadian cuisine. The country’s multiculturalism is also reflected in its food scene, with a wide variety of international cuisines available.
Each region of Canada has its own unique culinary specialities. In the Maritimes, seafood dishes such as lobster rolls and clam chowder are popular. In Quebec, dishes such as poutine and maple syrup-infused desserts are iconic. In the prairie provinces, hearty meat dishes like bison burgers and Alberta beef are common. British Columbia is known for its fresh seafood and fusion cuisine.
Canadian Tourism: Natural Wonders, Cities, and Festivals
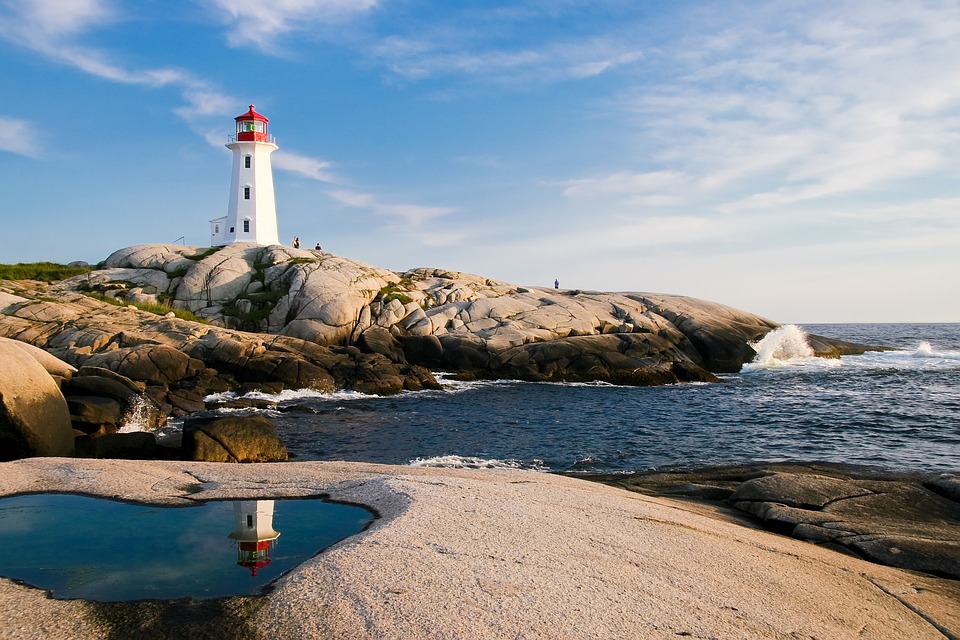
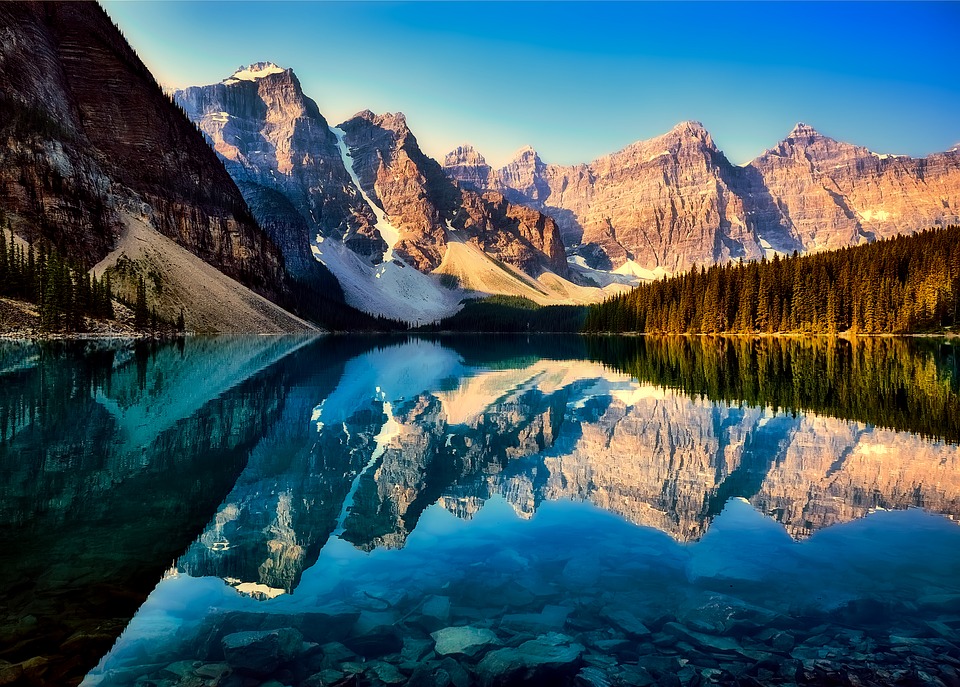
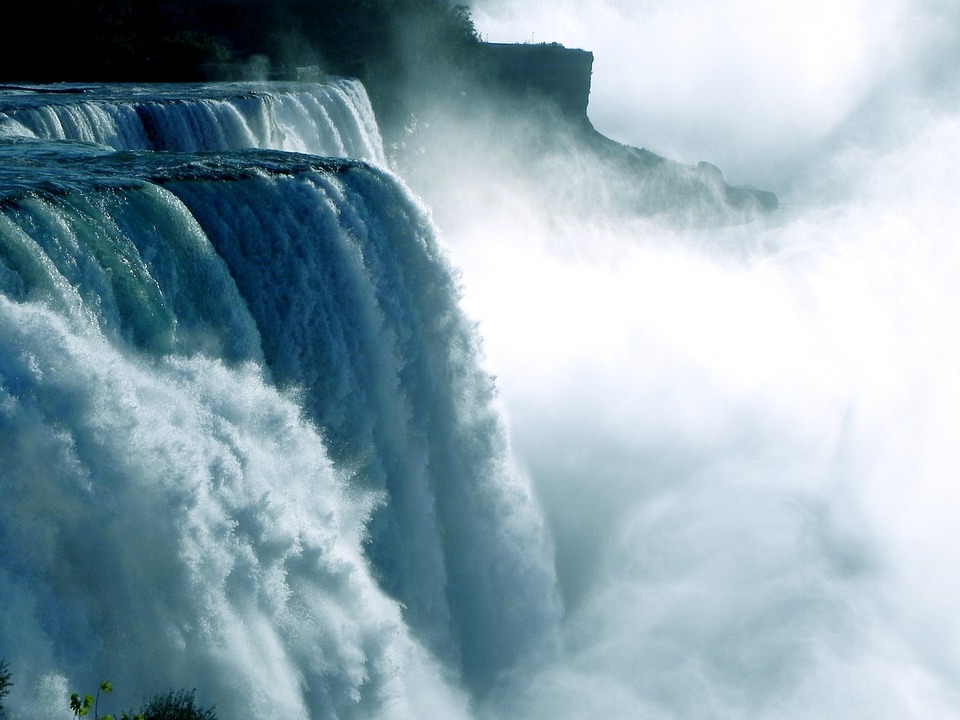
Canada is a popular tourist destination, known for its stunning natural landscapes and vibrant cities. The country is home to several natural wonders, including Niagara Falls, Banff National Park, Jasper National Park, and the Rocky Mountains. These attractions offer opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, skiing, and wildlife viewing.
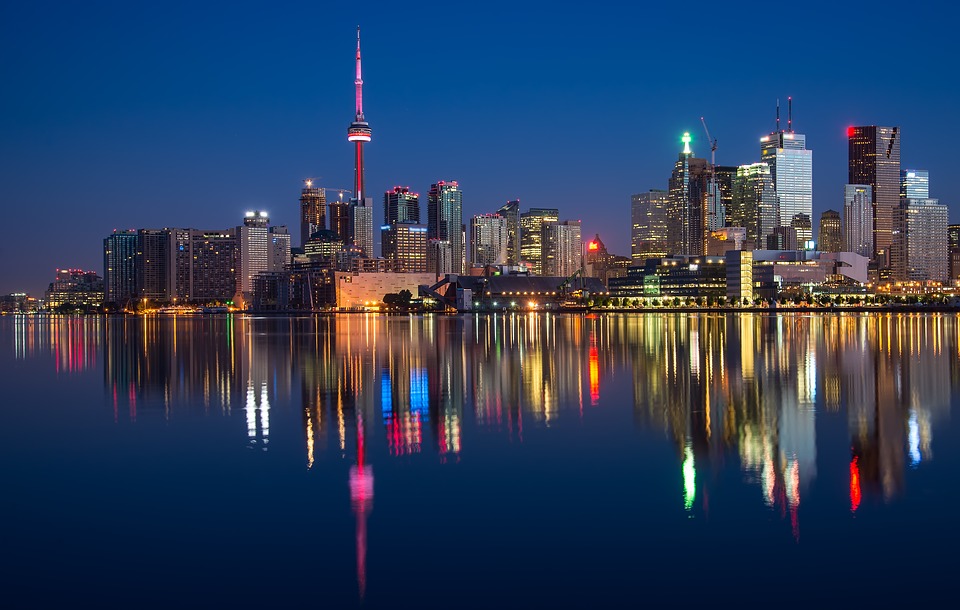
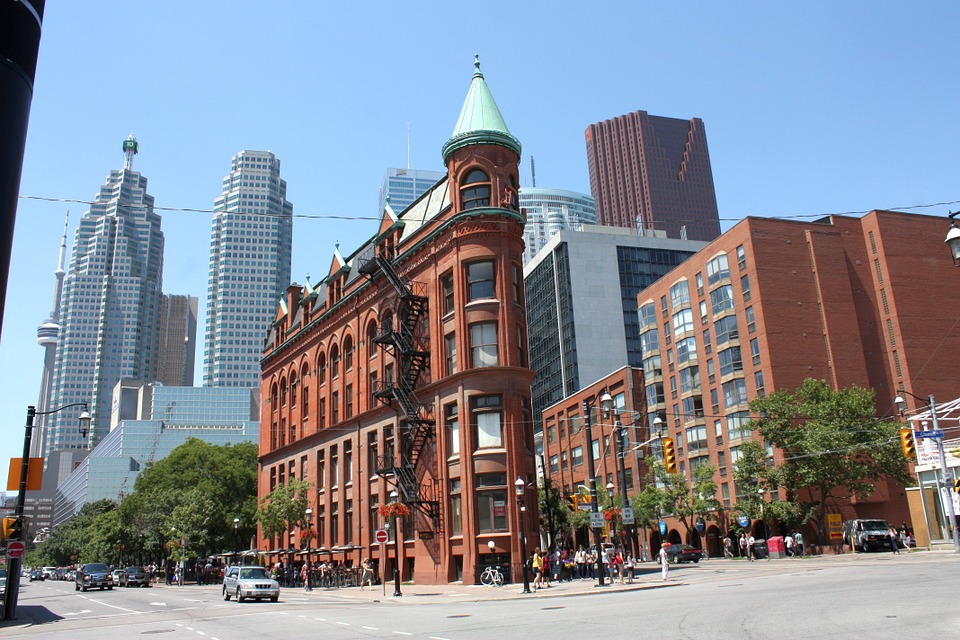
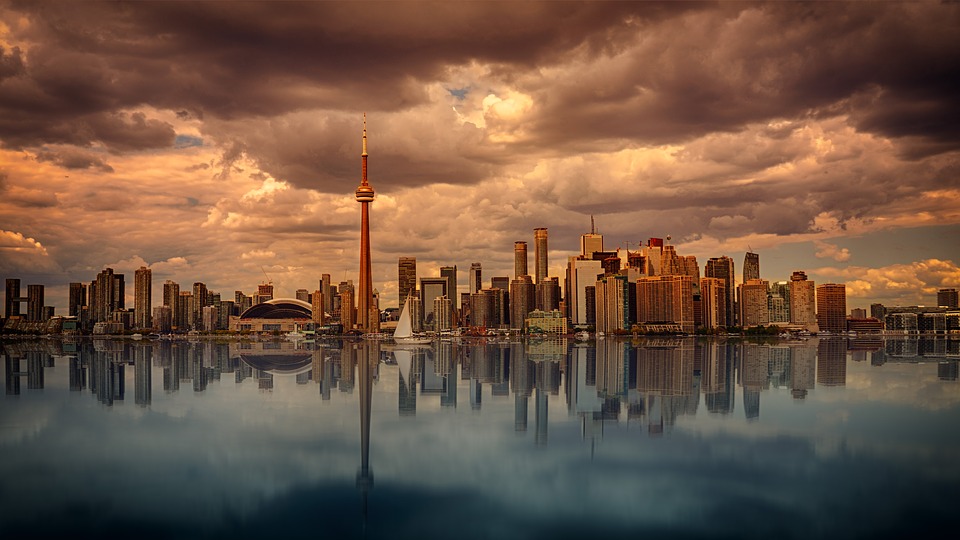
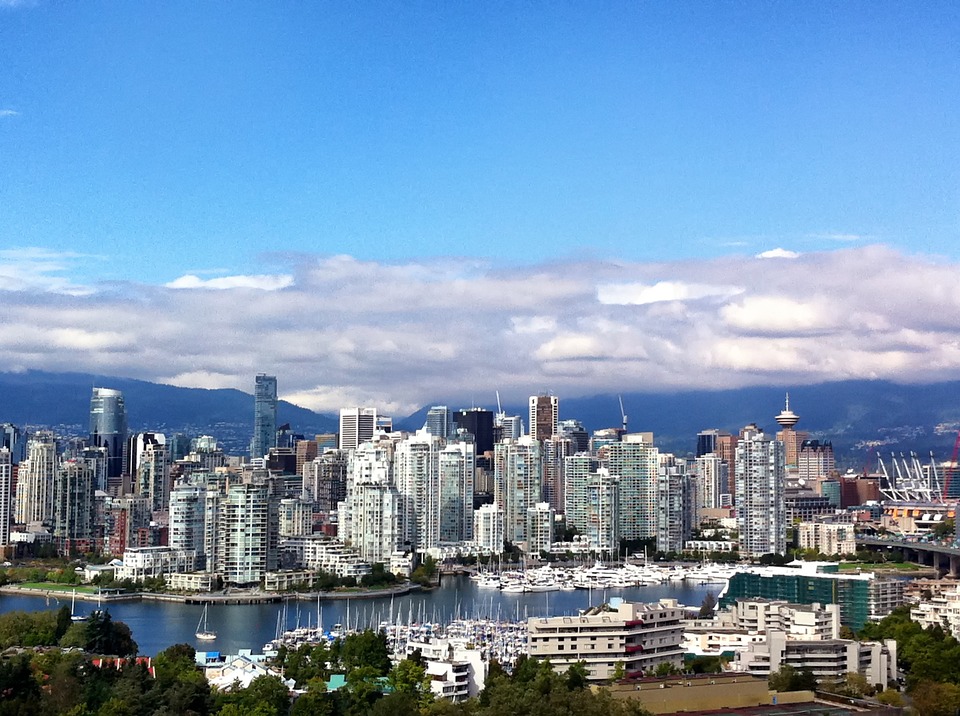
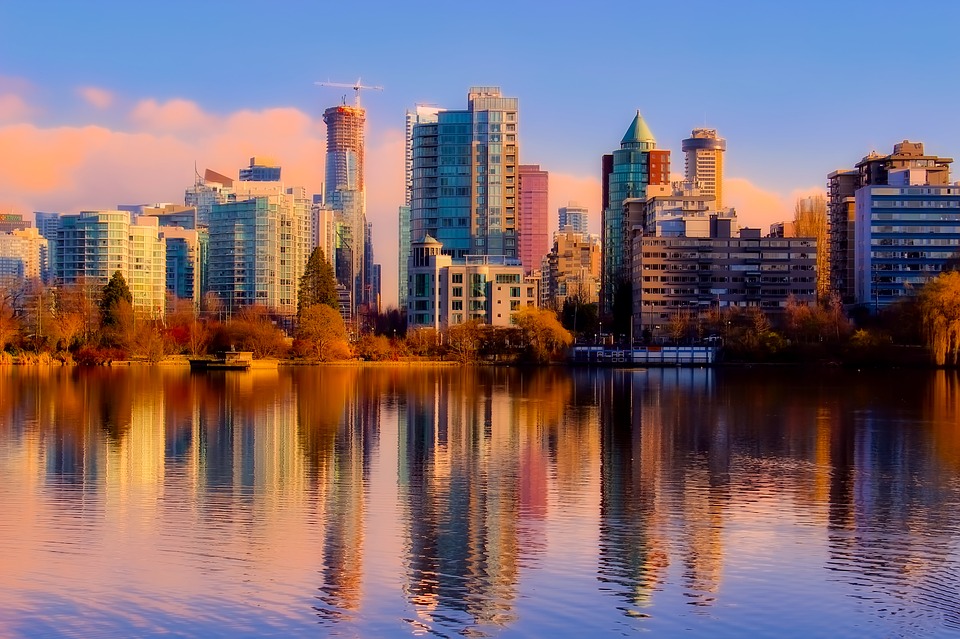
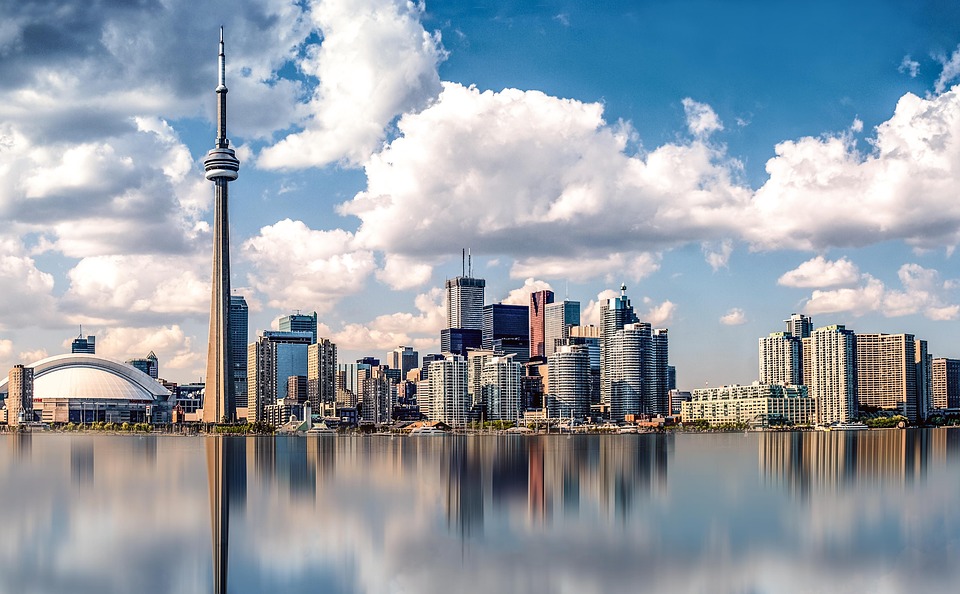
Canadian cities also attract tourists with their unique attractions and cultural offerings. Toronto, Canada’s largest city, is known for its diverse neighbourhoods, iconic CN Tower, and vibrant arts scene. Vancouver offers a mix of urban amenities and natural beauty, with Stanley Park and the nearby mountains being major draws. Montreal is renowned for its European charm, historic architecture, and lively festivals.
Throughout the year, Canada hosts numerous festivals and events that showcase its culture and traditions. The Calgary Stampede in Alberta is one of the largest rodeos in the world and celebrates Western heritage. The Montreal Jazz Festival is a renowned music festival that attracts artists from around the world. Winter festivals such as Winterlude in Ottawa and the Quebec Winter Carnival offer opportunities to embrace the Canadian winter.
Canadian Climate: Weather Patterns and Seasons Across the Country
Canada experiences a wide range of weather patterns and seasons due to its vast size and diverse geography. In general, the country has four distinct seasons: spring, summer, fall, and winter. However, the severity and duration of each season vary depending on the region.
In the northern parts of Canada, particularly in the territories, the winters are long and harsh, with temperatures dropping well below freezing. Summers are short but can be relatively warm. In the southern parts of Canada, the climate is more moderate, with milder winters and warmer summers.
Extreme weather events such as blizzards, hurricanes, and heat waves can occur in certain regions of Canada. These events can have a significant impact on communities and infrastructure. The government and local authorities have systems in place to monitor and respond to these events to ensure public safety.
Preparing for Canadian weather conditions involves dressing appropriately for the season and being aware of any weather warnings or advisories. It is also important to take precautions when participating in outdoor activities, such as hiking or skiing, to ensure personal safety.
Canada is a diverse and fascinating country with a rich history, vibrant culture, and strong economy. From its stunning natural landscapes to its bustling cities, there is something for everyone to explore and enjoy in Canada. The country’s multiculturalism is reflected in its art, music, literature, and cuisine. The political system ensures democratic representation at all levels of government, and the healthcare system provides universal coverage to all residents. With its thriving tourism industry and world-class educational institutions, Canada continues to attract visitors and students from around the world. Overall, Canada offers a high quality of life and opportunities for individuals to thrive in various aspects of their lives.
FAQs
What is Canada?
Canada is a country located in North America. It is the second-largest country in the world by land area and has a population of approximately 38 million people.
What is the capital city of Canada?
The capital city of Canada is Ottawa. It is located in the province of Ontario and has a population of approximately 1 million people.
What are the official languages of Canada?
The official languages of Canada are English and French. Both languages have equal status in the federal government and in the courts.
What is the currency of Canada?
The currency of Canada is the Canadian dollar. It is abbreviated as CAD and is divided into 100 cents.
What is the climate like in Canada?
Canada has a diverse climate due to its large size. The northern parts of the country have a polar climate, while the southern parts have a more temperate climate. The country experiences four distinct seasons: winter, spring, summer, and fall.
What are some famous landmarks in Canada?
Some famous landmarks in Canada include the CN Tower in Toronto, Niagara Falls, Banff National Park, and the Parliament Buildings in Ottawa.
What is the population of Canada?
As of 2021, the population of Canada is approximately 38 million people. The country has a relatively low population density, with most of the population concentrated in urban areas.
What is the economy of Canada like?
Canada has a mixed economy that is heavily reliant on natural resources such as oil, gas, and minerals. The country also has a strong manufacturing sector and a growing service sector. Canada is a member of the G7 and is considered to be one of the wealthiest countries in the world.
The Strategic Importance of Canada’s Military in Global Geopolitics
Canada has long been recognised as a leading nation in the realm of international peacekeeping, a commitment that dates back to the late 1940s. The country’s involvement in peacekeeping operations began in earnest with the establishment of the United Nations Emergency Force in 1956, which was created to address the Suez Crisis. This initiative not only marked Canada’s entry into peacekeeping but also showcased its willingness to engage in multilateral efforts to maintain global stability. Over the decades, Canada has contributed thousands of troops to various missions around the world, including significant deployments to places like Cyprus, Bosnia, and Rwanda. The Canadian Forces have been instrumental in providing humanitarian assistance, monitoring ceasefires, and facilitating the delivery of aid in conflict zones. The Canadian approach to peacekeeping is characterised by a commitment to multilateralism and a belief in the importance of diplomacy. Canadian peacekeepers are often seen as neutral parties, which allows them to operate effectively in complex environments. The country has also been a strong advocate for the protection of human rights and the promotion of democratic governance in post-conflict societies. This philosophy is evident in Canada’s participation in missions that not only focus on military presence but also on rebuilding efforts, such as those seen in Afghanistan and Haiti. The emphasis on training local security forces and supporting civil society initiatives reflects Canada’s understanding that sustainable peace requires more than just military intervention; it necessitates a comprehensive approach that addresses the root causes of conflict. Summary Canada has a long history of contributing to international peacekeeping efforts, demonstrating its commitment to global security and stability. Canada plays a...
How Canada’s Military Stacks Up Against Global Powers
Canada’s military strength is often overshadowed by the more prominent armed forces of larger nations, yet it possesses a unique and formidable presence on the global stage. The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF) is a well-structured institution that plays a crucial role in both national defence and international peacekeeping efforts. With a history steeped in participation in significant global conflicts, from the First and Second World Wars to contemporary missions in Afghanistan and beyond, Canada has established itself as a reliable ally and contributor to global security. The CAF is not merely a reflection of military might; it embodies the values of peace, security, and cooperation that Canada espouses on the world stage. The strength of Canada’s military is not solely defined by its size or budget but rather by its strategic capabilities, operational readiness, and commitment to international partnerships. The CAF comprises three main branches: the Canadian Army, the Royal Canadian Navy, and the Royal Canadian Air Force. Each branch is equipped to address various threats and challenges, ensuring that Canada can respond effectively to both domestic and international crises. This multifaceted approach allows Canada to maintain a balanced military posture, capable of engaging in diverse operations ranging from humanitarian assistance to combat missions. Summary Canada’s military strength is often overshadowed by global powers, but it plays a significant role in international military operations and alliances. Despite having a smaller military budget compared to global powers, Canada focuses on modernizing its military equipment and technology. Canada’s military personnel undergo rigorous training and are well-equipped to handle various national security challenges. Canada actively participates in international military operations and alliances,...
The Cost of Defence: How Much Does Canada Spend on Its Military?
Canada’s military spending has been a topic of considerable discussion and debate, particularly in the context of global security dynamics and national defence priorities. As a member of NATO and a participant in various international peacekeeping missions, Canada has a vested interest in maintaining a robust military capability. The evolution of Canada’s defence budget reflects not only the changing geopolitical landscape but also the nation’s commitment to its allies and its own sovereignty. In recent years, the government has faced increasing pressure to enhance military funding, particularly in light of rising tensions in Eastern Europe and the Asia-Pacific region. The historical context of Canada’s military expenditure reveals a complex interplay between fiscal responsibility and national security imperatives. Over the decades, Canada has oscillated between periods of significant investment in defence and times of austerity. The post-Cold War era saw a notable reduction in military spending, as the perceived threat level diminished. However, the resurgence of aggressive military posturing by nations such as Russia and China has prompted a reevaluation of defence strategies and budgets. This article delves into the intricacies of Canada’s defence budget, examining its components, comparisons with other nations, economic implications, and the ongoing debates surrounding military expenditure. Summary Canada’s military spending has been a topic of debate and discussion, with various perspectives on its importance and allocation. The breakdown of Canada’s defence budget reveals significant allocations to personnel, operations, and equipment. When compared to other countries, Canada’s military spending is relatively lower, but it still ranks among the top spenders in NATO. Military spending has a significant impact on Canada’s economy, creating jobs and driving innovation...
Inside Canada’s Army: Strengths, Challenges, and Future Plans
The Canadian Army, a vital component of the Canadian Armed Forces (CAF), has a rich history that dates back to the early 19th century. Established initially as a response to local conflicts and the need for defence against potential invasions, the army has evolved significantly over the years. Today, it stands as a modern, well-equipped force that plays a crucial role in both national defence and international peacekeeping efforts. The army’s structure is designed to be flexible and responsive, allowing it to adapt to various operational demands, whether they arise from domestic emergencies or international crises. Canada’s military identity is deeply intertwined with its commitment to peace and security, both at home and abroad. The army’s involvement in significant historical events, such as the two World Wars, the Korean War, and more recent missions in Afghanistan and Iraq, has shaped its reputation as a reliable ally on the global stage. The Canadian Army is not only tasked with defending the nation but also with contributing to international stability through various missions under the auspices of organisations like the United Nations and NATO. This dual role underscores the importance of a well-prepared and capable army in an increasingly complex global landscape. Summary Canada’s Army, also known as the Canadian Armed Forces, plays a crucial role in defending the country and contributing to international peacekeeping efforts. The strengths of Canada’s Army lie in its well-trained and professional personnel, modern equipment and technology, and strong international partnerships. Challenges faced by Canada’s Army include budget constraints, recruitment and retention issues, and the need to adapt to evolving security threats. Future plans for Canada’s...
Is Canada Ready for the Next Big Conflict? Analyzing Its Defense Readiness
Canada’s defence capabilities have evolved significantly over the years, shaped by a complex interplay of geopolitical realities, technological advancements, and domestic considerations. As a nation that spans vast geographical expanses, Canada faces unique challenges in ensuring its national security. The country’s defence posture is not solely about military might; it encompasses a comprehensive approach that includes diplomacy, intelligence, and international cooperation. In recent years, the global security landscape has become increasingly volatile, with rising tensions in various regions, prompting Canada to reassess its military readiness and strategic priorities. The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF) are tasked with safeguarding the nation’s interests both at home and abroad. This responsibility is underscored by Canada’s commitment to international peacekeeping and collective security through alliances such as NATO. However, the effectiveness of Canada’s defence capabilities is contingent upon a multitude of factors, including budgetary allocations, personnel readiness, and the ability to adapt to emerging threats. As the world grapples with challenges such as cyber warfare, terrorism, and geopolitical rivalries, understanding Canada’s current defence capabilities is crucial for evaluating its preparedness for potential conflicts. The allocation of funds for military spending is a critical determinant of a nation’s defence capabilities. In Canada, the defence budget has seen fluctuations over the years, influenced by political priorities and economic conditions. The 2022 federal budget allocated approximately CAD 24 billion to the Department of National Defence, marking a significant increase aimed at modernising the armed forces and addressing pressing security concerns. This funding is essential for maintaining operational readiness, investing in new technologies, and ensuring that personnel are adequately trained and equipped. However, despite these increases, critics argue...
Political Boundaries of Canada: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Canada is a vast country with diverse landscapes and a rich history. Understanding its political boundaries is crucial for both Canadians and non-Canadians alike. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of Canada’s political system, including its provinces and territories, the historical significance of its boundaries, the role of districts in Canadian politics, the evolution of its boundaries over time, the importance of boundaries in Canadian federalism, the impact on Indigenous communities, the challenges of maintaining boundaries, the role in international relations, and predictions for the future. Summary Canada is divided into provinces and territories, which are the main political divisions of the country. The historical significance of Canada’s political boundaries can be traced back to the country’s colonial past. Districts play an important role in Canadian politics, as they are used to elect members of parliament. Canada’s political boundaries have evolved over time, reflecting changes in the country’s demographics and political landscape. Boundaries are important in Canadian federalism, as they help to define the powers and responsibilities of different levels of government. Provinces and Territories: The Main Political Divisions of Canada Canada is divided into 10 provinces and 3 territories. The provinces are British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba, Ontario, Quebec, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, Nova Scotia, and Newfoundland and Labrador. The territories are Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut. Each province and territory has its own government and is responsible for various aspects of governance such as healthcare, education, and transportation. There are several key differences between provinces and territories. Provinces have more autonomy and power compared to territories. They have their own constitutions and can make decisions...
Climate Zones of Canada: Different climate regions Of Canada
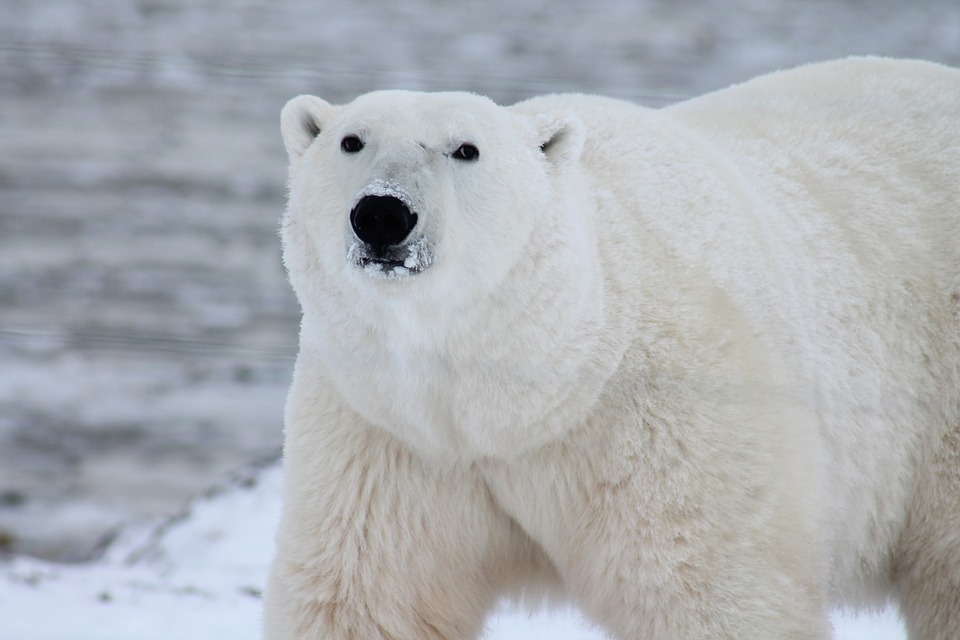
Canada is a vast country with diverse geography and climate. Understanding the different climate zones in Canada is crucial for various reasons, including agriculture, wildlife conservation, and human settlements. The country is divided into several climate zones, each with its own unique characteristics and impact on the environment. By studying and comprehending these climate zones, we can better adapt to the challenges they present and mitigate the impacts of climate change. Summary Canada has 10 distinct climate zones The Arctic Climate Zone is the coldest and driest in Canada The Subarctic Climate Zone has long, cold winters and short, cool summers The Maritime Climate Zone has mild winters and cool summers with high precipitation The Prairie Climate Zone has hot summers and cold winters with low precipitation Climate zones have significant impacts on Canadian life and economy, including agriculture, tourism, and transportation. The Arctic Climate Zone in Canada The Arctic climate zone in Canada is characterized by extremely cold temperatures, long winters, and short, cool summers. It covers a significant portion of the country’s northern regions, including parts of Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut, and Labrador. The Arctic climate zone has a profound impact on wildlife and human communities in these areas. The extreme cold temperatures in the Arctic climate zone make it challenging for many species to survive. However, some animals have adapted to this harsh environment, such as polar bears, Arctic foxes, and muskoxen. These animals have developed thick fur or blubber to insulate themselves from the cold and have specialized feeding habits to find food in the barren landscape. Human communities in the Arctic climate zone face...
Climate Zones of Canada: Different climate regions Of Canada
Canada is a vast country with a diverse range of climate zones, each with its own unique characteristics and weather patterns. Understanding these climate zones is crucial for various industries and activities, as it helps in planning and decision-making related to agriculture, tourism, infrastructure development, and environmental conservation. From the Arctic in the north to the Pacific in the west and the Atlantic in the east, Canada’s climate zones offer a wide range of opportunities and challenges. Summary Canada has 10 distinct climate regions, each with unique characteristics. The Arctic Climate Region is the coldest and driest region in Canada, with temperatures averaging below freezing. The Subarctic Climate Region experiences long, cold winters and short, cool summers. The Continental Climate Region has hot summers and cold winters, with a large temperature range throughout the year. The Maritime Climate Region has mild temperatures and high precipitation, with frequent fog and cloudy days. The Highland Climate Region is characterized by high elevation and cooler temperatures, with significant snowfall in the winter. The Boreal Climate Region has long, cold winters and short, cool summers, with a significant amount of precipitation. The Prairie Climate Region has hot summers and cold winters, with low precipitation and frequent droughts. The Pacific Climate Region has mild temperatures and high precipitation, with a significant amount of rainfall throughout the year. Climate change is impacting Canada’s climate zones, with changes in temperature, precipitation, and extreme weather events. The Arctic Climate Region of Canada The Arctic climate region covers the northernmost part of Canada, including the territories of Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut. This region experiences extremely cold temperatures...
Natural Resources of Canada: Where Natural Resources are located In Canada
Canada is known for its vast abundance of natural resources, which play a crucial role in the country’s economy and society. From forests and minerals to energy resources and water, Canada is rich in a wide variety of natural assets. These resources have been a driving force behind Canada’s economic growth and have contributed significantly to its status as one of the world’s wealthiest nations. Natural resources are essential to Canada’s economy, as they provide employment opportunities, generate revenue through exports, and attract foreign investment. The resource sector accounts for a significant portion of Canada’s GDP and is a major contributor to the country’s trade balance. Moreover, natural resources have shaped Canada’s history and culture, with industries such as forestry and mining playing a vital role in the development of many communities across the country. Summary Canada is rich in natural resources, including forests, minerals, energy, water, and wildlife. The country’s geography and climate play a significant role in shaping its natural resources and industries. Forests and wood products are a major contributor to Canada’s economy and provide numerous benefits, including carbon sequestration and recreation. Mining and mineral resources, such as gold, copper, and diamonds, are abundant in Canada and contribute to the country’s economic growth. Canada is a leading producer of oil, gas, and hydroelectricity, with a focus on sustainable energy development and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Overview of Canada’s Geography and Climate Canada is the second-largest country in the world by land area, spanning over 9.9 million square kilometers. Its geography is incredibly diverse, ranging from vast forests and mountains to arctic tundra and coastal regions. This...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Canada: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Canada
Canada is a country with a rich cultural history that spans thousands of years. From the Indigenous peoples who have inhabited the land for centuries, to the French and British settlers who arrived in the 17th and 18th centuries, to the diverse immigrant communities that have shaped the country in more recent years, Canada’s cultural heritage is diverse and fascinating. Exploring cultural destinations in Canada is not only a way to learn about the country’s history, but also a way to appreciate its vibrant and diverse culture. Summary Indigenous peoples have a rich history in Canada and their cultural significance can be explored through tours and experiences. The Canadian Museum of History is a must-visit destination for those interested in learning about Canada’s past and present. The Historic District of Old Quebec offers a journey through Canada’s French heritage, with its charming architecture and cultural landmarks. The Canadian War Museum pays tribute to the country’s military history and the sacrifices made by its soldiers. Banff National Park is a natural and cultural icon of Canada, offering breathtaking landscapes and opportunities for outdoor adventure. The History of Indigenous Peoples in Canada: A Tour of Cultural Significance The history of Indigenous peoples in Canada is an integral part of the country’s cultural heritage. Before European settlers arrived, Indigenous peoples had been living on the land for thousands of years, with distinct cultures, languages, and traditions. Today, there are over 600 recognized First Nations in Canada, each with their own unique history and cultural practices. Visiting Indigenous cultural destinations in Canada is a way to learn about and appreciate the rich heritage...
History of Canada
Canada, the second-largest country in the world, has a rich and diverse history that spans thousands of years. From the early Indigenous peoples who inhabited the land to the arrival of European explorers and colonizers, Canada’s history is a tapestry of cultures, conflicts, and triumphs. Understanding Canadian history is crucial for appreciating the country’s identity, values, and current challenges. By exploring the different periods and events that have shaped Canada, we can gain a deeper understanding of its people and their journey towards nationhood. Summary Early Indigenous Peoples of Canada were diverse and had complex societies. The Arrival of European Explorers and Colonizers brought disease and conflict to Indigenous communities. The French and British Struggle for Control led to the eventual formation of Canada as a nation. Canada played a significant role in World War I and World War II. The Quiet Revolution and the Rise of Quebec Nationalism challenged Canada’s unity. Early Indigenous Peoples of Canada Before European contact, Canada was home to a wide range of Indigenous peoples who had developed unique cultures and societies. These Indigenous groups, including the Inuit, First Nations, and Métis, had diverse languages, traditions, and ways of life. They had a deep connection to the land and relied on hunting, fishing, and gathering for their sustenance. European colonization had a profound impact on Indigenous peoples in Canada. The arrival of explorers and settlers led to conflicts over land and resources, as well as the introduction of diseases that devastated Indigenous populations. Many Indigenous communities were displaced from their traditional territories or forced into assimilation by European powers. The Arrival of European Explorers...
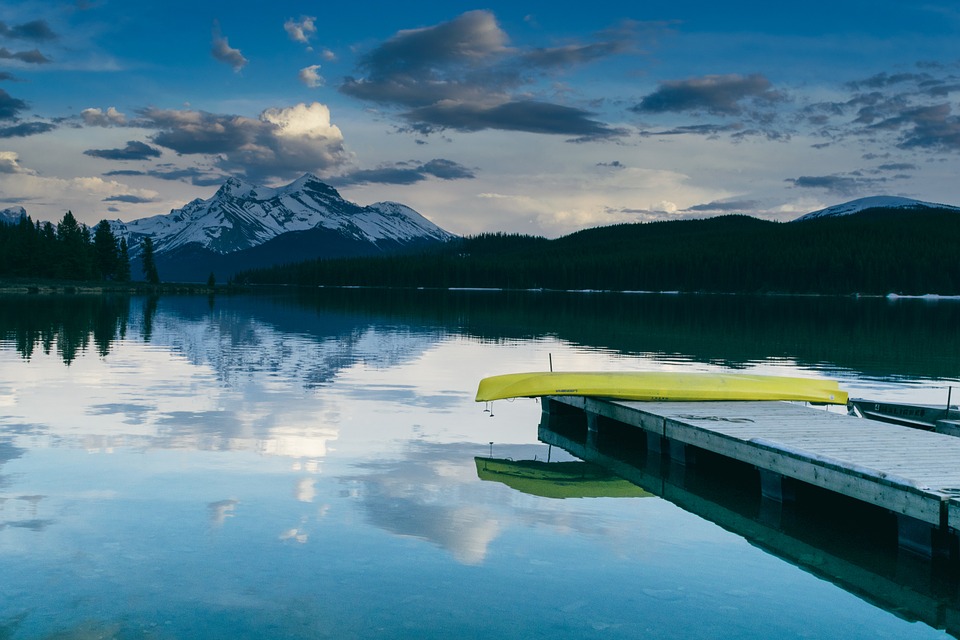
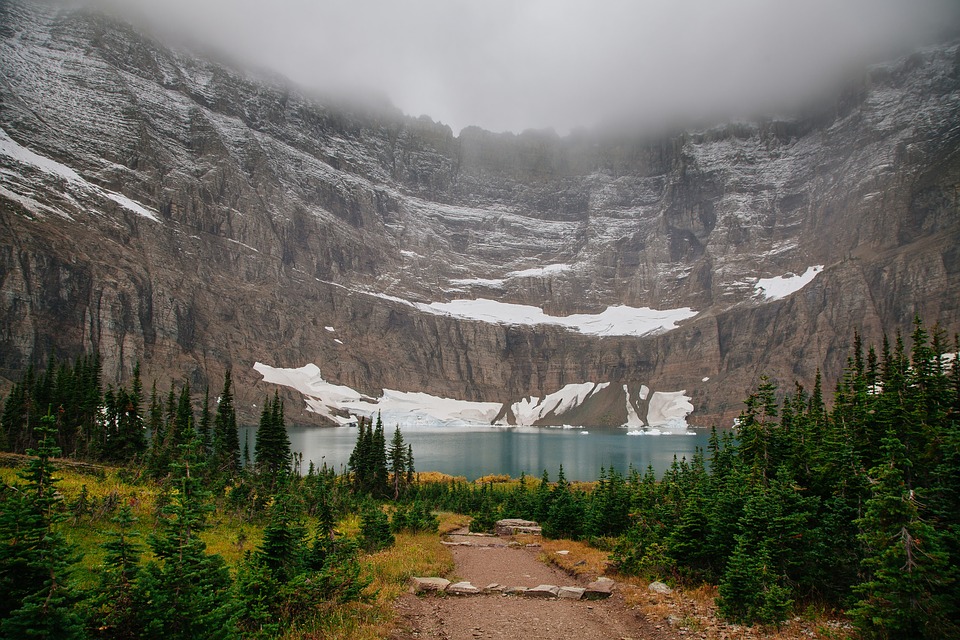
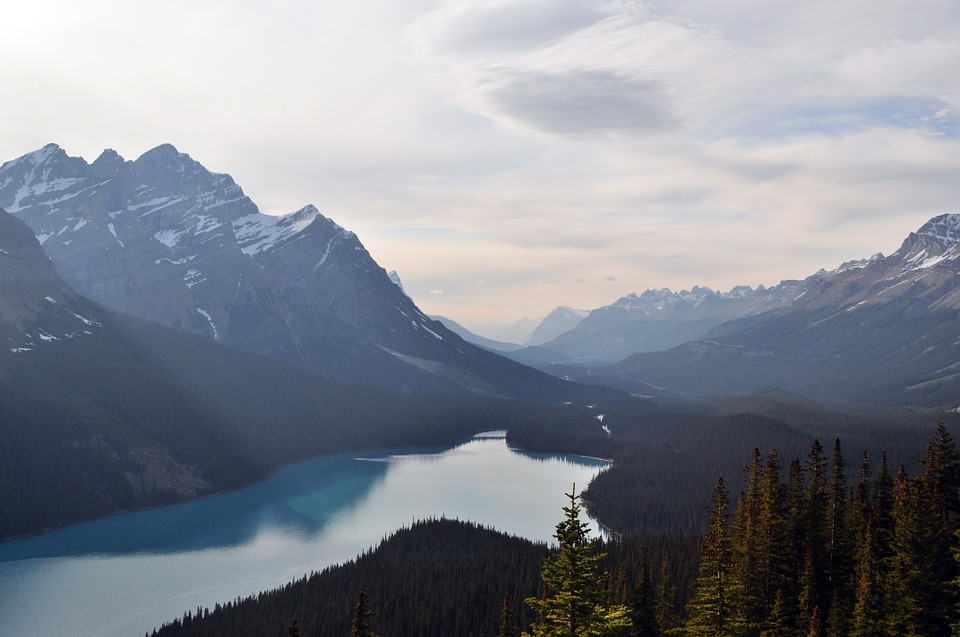
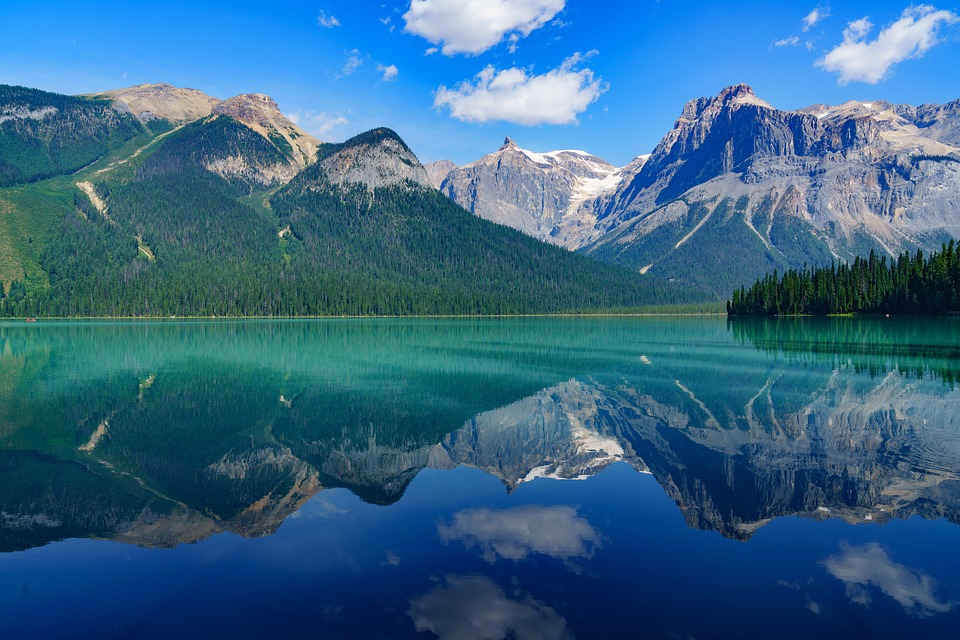
Terrain and Topography of Canada: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Canada is a country known for its vast and diverse terrain. From majestic mountain ranges to flat grasslands, Canada’s topography is as varied as it is beautiful. Understanding the geography of Canada is important for a number of reasons, including its impact on the climate, economy, and culture of the country. In this article, we will explore the different regions of Canada and delve into their unique features and significance. Summary Canada has a diverse terrain and topography, ranging from mountains to flatlands to frozen tundra. The Rocky Mountains are a majestic mountain range in western Canada, offering stunning views and outdoor activities. The Appalachian Mountains form the eastern edge of Canada, with a rich history and unique flora and fauna. The Canadian Shield is a vast plateau of ancient rocks, covering almost half of Canada’s land area. The Great Lakes Lowland is a flat and fertile region, home to many of Canada’s largest cities and agricultural areas. The Rocky Mountains: Canada’s Majestic Mountain Range The Rocky Mountains are one of Canada’s most iconic natural features. Stretching from British Columbia to Alberta, this mountain range is a sight to behold. The Rockies are known for their towering peaks, deep valleys, and stunning alpine scenery. They are also home to a variety of wildlife, including bears, elk, and mountain goats. Popular activities in the Rocky Mountains include hiking, skiing, and wildlife spotting. The region is dotted with national parks and protected areas, making it a haven for outdoor enthusiasts. Whether you’re scaling the heights of Mount Robson or exploring the turquoise waters of Lake Louise, the Rocky Mountains offer endless...














































































