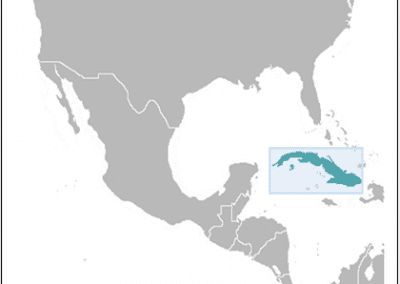
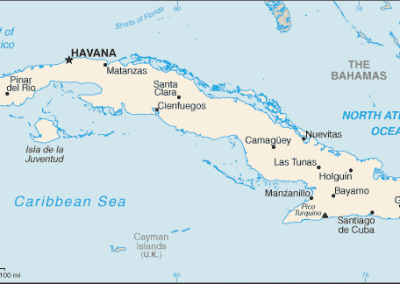
Cuba
(República de Cuba (Republic of Cuba))

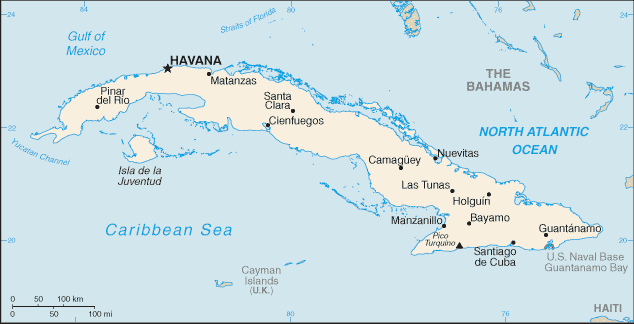



Capital: Havana
Population (Estimated July 2012): 11,075,244
Area: 109,886 km2 or 42,427 mi2
Currency: Cuban peso (CUP)
Official Language: Spanish
Political Information: Unitary Republic, Communist State
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 85% of the population are Roman Catholic and 15% have other religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Pico Turquino at 2,005m or 6,578ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2010): $57.49 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2010): $114.1 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2010): $9,900 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): -5:00
Wildlife:
Counties/Provinces/States: 15 provinces (provincias, singular – provincia) and 1 special municipality* (municipio especial); Artemisa, Camaguey, Ciego de Avila, Cienfuegos, Granma, Guantanamo, Holguin, Isla de la Juventud*, La Habana, Las Tunas, Matanzas, Mayabeque, Pinar del Rio, Sancti Spiritus, Santiago de Cuba, Villa Clara
Leaders: Raúl Castro is both the president and Premier with J.R.M. Ventura as 1st Vice President.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Cuba
Cuba, located in the Caribbean Sea, is the largest island in the Caribbean and is known for its vibrant culture, stunning beaches, and rich history. The country is situated just south of the United States and east of Mexico, making it a popular tourist destination for travelers from around the world.
Cuba has a diverse geography, with mountains, plains, and beautiful coastlines. The island is home to a variety of ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, mangroves, and coral reefs. The warm climate and fertile soil make it an ideal location for agriculture, particularly the cultivation of sugar cane, tobacco, and coffee.
The history of Cuba is deeply intertwined with colonization and independence. The island was first colonized by the Spanish in the 15th century and remained under Spanish rule until the late 19th century. During this time, Cuba became a major hub for trade and commerce, particularly in sugar production. However, the harsh conditions faced by enslaved Africans brought to work on the plantations led to numerous uprisings and rebellions.
Cuban Revolution: The overthrow of Batista’s regime and the rise of Fidel Castro
The Cuban Revolution, which took place from 1953 to 1959, was a pivotal moment in Cuban history. It was led by Fidel Castro and his revolutionary movement, which sought to overthrow the corrupt regime of Fulgencio Batista.
The revolution was fueled by a number of factors, including widespread poverty and inequality, political repression, and economic dependence on the United States. The revolutionaries carried out guerrilla warfare tactics in the mountains of Cuba, gaining support from peasants and workers who were disillusioned with Batista’s regime.
Key figures in the revolution included Fidel Castro, who became the leader of Cuba after Batista fled the country; Che Guevara, an Argentine revolutionary who played a crucial role in the revolution; and Camilo Cienfuegos, a Cuban revolutionary who was known for his military leadership.
The impact of the Cuban Revolution was significant, both for Cuba and the world. Internally, the revolution led to the establishment of a socialist state in Cuba, with Fidel Castro as the leader. The government implemented a series of reforms, including nationalizing industries and redistributing land. Externally, the revolution had a major impact on the Cold War dynamics between the United States and the Soviet Union. The United States imposed an economic embargo on Cuba, which lasted for decades and had a profound effect on the Cuban economy.
Cuban Economy: A socialist system and its challenges
Cuba operates under a socialist economic system, which means that the means of production are owned and controlled by the state. The government plays a central role in planning and directing economic activity, with the goal of achieving social equality and providing basic needs for all citizens.
The Cuban economy faces a number of challenges, including limited access to foreign investment and technology due to the US embargo, inefficiencies in state-run enterprises, and a lack of diversification in industries. The country heavily relies on tourism, remittances from abroad, and exports of goods such as sugar, tobacco, and pharmaceuticals.
In recent years, Cuba has implemented a series of economic reforms aimed at opening up the economy and attracting foreign investment. These reforms include allowing small-scale private businesses to operate, encouraging foreign investment in certain sectors, and relaxing restrictions on travel and remittances. These reforms have had mixed results, with some sectors experiencing growth while others continue to struggle.
Cuban Cuisine: A fusion of African, Spanish and Caribbean influences
Cuban cuisine is a delicious fusion of African, Spanish, and Caribbean influences. The cuisine is known for its bold flavors, use of fresh ingredients, and unique cooking techniques.
Some popular dishes in Cuban cuisine include ropa vieja, which is shredded beef cooked in a tomato-based sauce; arroz con pollo, a flavorful chicken and rice dish; and lechon asado, a roasted pork dish. These dishes often incorporate ingredients such as rice, beans, plantains, and yuca.
The cuisine of Cuba is heavily influenced by the African slaves who were brought to the island during the colonial period. African cooking techniques and ingredients such as plantains, yams, and okra have become integral parts of Cuban cuisine. Spanish influences can be seen in dishes such as paella and flan, while Caribbean influences are evident in the use of tropical fruits and spices.
Cuban culinary traditions and customs are also an important part of the culture. Meals are often enjoyed with family and friends, and there is a strong emphasis on hospitality and sharing food. Cuban coffee is also a beloved tradition, with strong espresso served in small cups.
Cuban Music: The birthplace of salsa, son and other popular rhythms
Cuba is often referred to as the birthplace of many popular music genres, including salsa, son, and rumba. The country has a rich musical heritage that is deeply rooted in African rhythms, Spanish melodies, and Caribbean influences.
Cuban music history dates back to the colonial period when African slaves brought their musical traditions to the island. These traditions blended with Spanish melodies and instruments to create unique styles of music. One of the most influential genres to emerge from this fusion was son, which combines African percussion with Spanish guitar and vocals.
In the 20th century, Cuban music gained international recognition with the rise of salsa. Salsa is a vibrant and energetic genre that incorporates elements of son, jazz, and other Latin American rhythms. Artists such as Celia Cruz and Tito Puente helped popularize salsa around the world.
Cuban music continues to have a significant influence on the global music scene. Artists such as Buena Vista Social Club and Ibrahim Ferrer have brought traditional Cuban music to a wider audience, while contemporary artists like Gente de Zona and Descemer Bueno have incorporated elements of reggaeton and hip-hop into their music.
Cuban Sports: Passion for baseball and boxing
Sports play a significant role in Cuban culture, with baseball and boxing being the most popular sports in the country. Cuba has a long history of success in both sports, with many Cuban athletes achieving international acclaim.
Baseball is often referred to as the national sport of Cuba and has a passionate following. The country has produced many talented baseball players who have gone on to play in Major League Baseball in the United States. The Cuban national baseball team has also been highly successful, winning multiple Olympic gold medals and World Baseball Classic titles.
Boxing is another sport that is deeply ingrained in Cuban culture. The country has a rich boxing tradition and has produced numerous world champions. Cuban boxers are known for their technical skills, agility, and speed. The Cuban national boxing team has consistently performed well in international competitions, winning multiple Olympic gold medals.
Sports in Cuba are heavily supported by the government, which provides funding and resources for training facilities and coaching programs. The success of Cuban athletes in international competitions has helped to boost national pride and promote a positive image of the country on the global stage.
Cuban Art: A vibrant scene of painters, sculptors and writers
Cuba has a vibrant art scene that encompasses a wide range of mediums, including painting, sculpture, literature, and performance art. The country’s art history is deeply influenced by its political and social context, with artists often using their work to express their views on issues such as revolution, identity, and social justice.
Cuban art history dates back to the colonial period, with early artists drawing inspiration from European styles such as Baroque and Neoclassicism. In the 20th century, Cuban art underwent a period of experimentation and innovation, with artists embracing modernist and avant-garde movements.
Famous Cuban artists include Wifredo Lam, who is known for his fusion of African and European artistic traditions; Amelia Peláez, who is known for her vibrant and colourful paintings; and José Bedia, who incorporates Afro-Cuban religious and cultural symbols into his work.
The political and social climate in Cuba has had a significant impact on the art scene. During the revolution, the government promoted a socialist realist style of art that depicted the ideals of the revolution. However, in recent years, there has been a greater degree of artistic freedom, with artists exploring a wide range of styles and themes.
Cuban Cigars: The world’s best tobacco and cigar production
Cuba is renowned for its production of high-quality cigars, which are considered some of the best in the world. The country’s unique climate and soil conditions make it an ideal location for growing tobacco, and the art of cigar making has been passed down through generations.
The history of Cuban cigar production dates back to the 16th century when tobacco was first introduced to the island by the Spanish. The industry flourished in the 19th century, with Cuba becoming one of the largest exporters of cigars in the world.
Cuban cigars are known for their rich flavour, complex aromas, and expert craftsmanship. They are made using traditional methods, with each cigar being carefully hand-rolled by skilled artisans. The tobacco used in Cuban cigars is grown in the Vuelta Abajo region, which is known for its fertile soil and ideal climate.
The US embargo on Cuba has had a significant impact on the Cuban cigar industry. While Cuban cigars are highly sought after by enthusiasts around the world, they are illegal to import into the United States. This has created a thriving black market for Cuban cigars in the US, with many people willing to pay a premium for the authentic product.
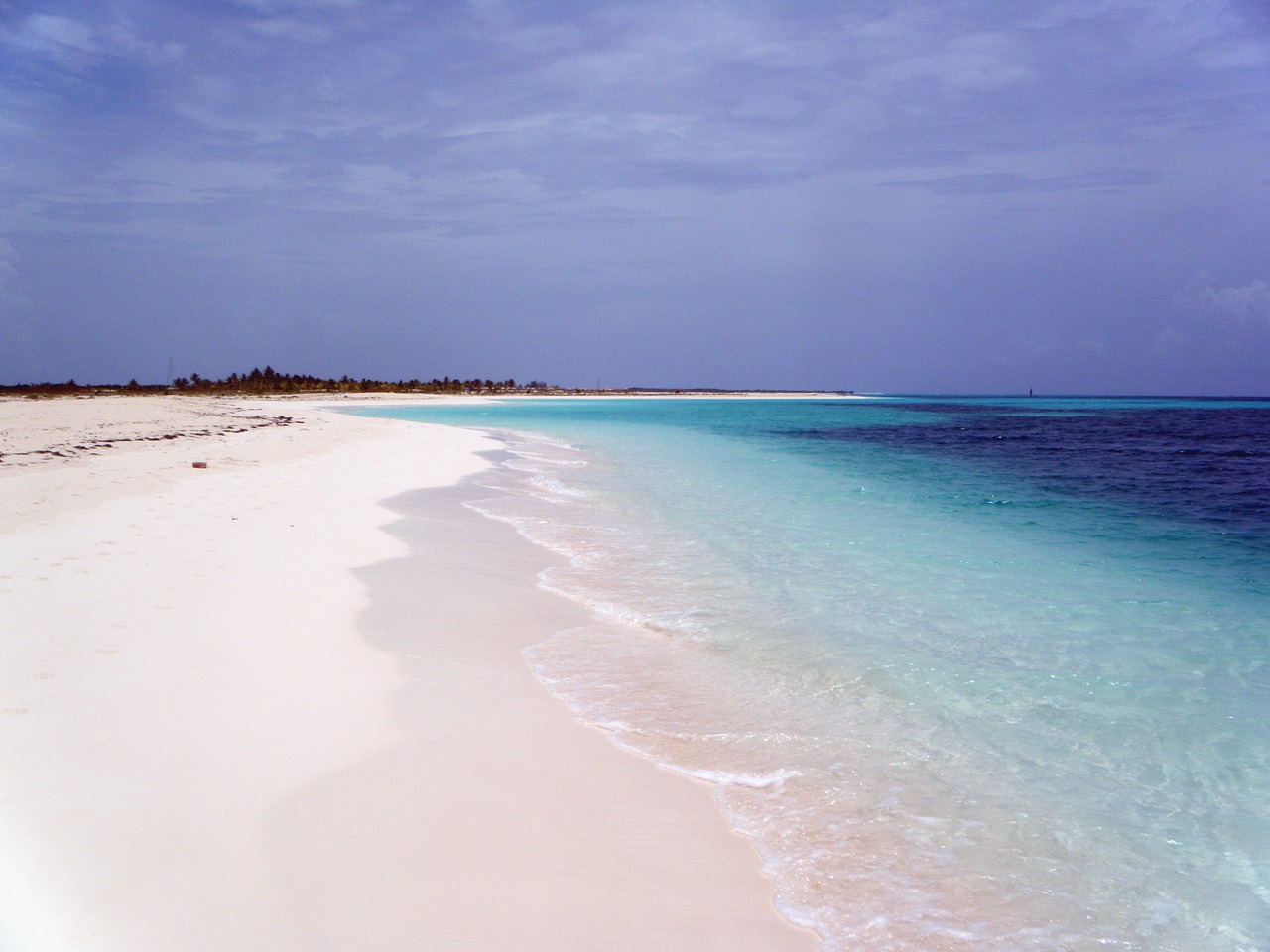
Cuban Tourism: A growing industry with stunning beaches and landmarks
Tourism is a growing industry in Cuba, with the country attracting millions of visitors each year. Cuba is known for its stunning beaches, vibrant culture, and historic landmarks, making it a popular destination for travellers from around the world.
Some of the most popular tourist destinations in Cuba include Havana, the capital city known for its colonial architecture and vibrant nightlife; Varadero, a beach resort town with pristine white sand beaches; and Trinidad, a UNESCO World Heritage site known for its well-preserved Spanish colonial architecture.
Cuba also offers a range of outdoor activities for visitors to enjoy, including snorkelling and diving in the crystal-clear waters of the Caribbean Sea, hiking in the lush mountains of the Sierra Maestra, and exploring the unique ecosystems of the Zapata Peninsula.
While tourism has brought economic benefits to Cuba, it also presents challenges. The country’s infrastructure is often unable to keep up with the demands of increasing numbers of tourists, leading to issues such as overcrowding and strain on resources. Additionally, there are concerns about the impact of tourism on Cuba’s cultural heritage and environment.
Despite these challenges, Cuba continues to attract visitors with its unique blend of history, culture, and natural beauty. The recent changes in diplomatic relations between Cuba and the United States have also opened up new opportunities for growth in the tourism industry.
Cuban-US Relations: A complex history of tension and recent diplomatic changes
The relationship between Cuba and the United States has been complex and fraught with tension for many years. The two countries have a long history of political and economic conflicts, which have had a profound impact on both nations.
The tensions between Cuba and the United States can be traced back to the Cuban Revolution and the subsequent establishment of a socialist state in Cuba. The United States viewed the revolution as a threat to its interests in the region and imposed an economic embargo on Cuba, which has lasted for over five decades.
The embargo has had a significant impact on the Cuban economy, limiting trade and investment opportunities and contributing to economic hardships for the Cuban people. It has also affected the daily lives of Cubans, with restrictions on travel and remittances from family members living in the United States.
In recent years, there have been significant changes in diplomatic relations between Cuba and the United States. In 2014, President Barack Obama announced a historic shift in US policy towards Cuba, including the restoration of diplomatic relations and the easing of travel and trade restrictions.
These changes have had a positive impact on Cuba, with an increase in tourism and foreign investment. However, there are still many challenges to overcome in order to fully normalize relations between the two countries, including the lifting of the US embargo and addressing human rights concerns.
Overall, Cuba is a fascinating country with a rich history, vibrant culture, and stunning natural beauty. From its colonial architecture to its world-renowned cigars and music, Cuba offers a unique experience for travelers. As the country continues to navigate its way through economic and political challenges, it remains an intriguing destination that captures the imagination of visitors from around the world.
FAQs
What is Cuba?
Cuba is an island country located in the Caribbean Sea. It is the largest island in the Caribbean and has a population of over 11 million people.
What is the capital of Cuba?
The capital of Cuba is Havana, which is also the largest city in the country.
What is the official language of Cuba?
The official language of Cuba is Spanish.
What is the currency of Cuba?
The currency of Cuba is the Cuban peso (CUP) and the Cuban convertible peso (CUC).
What is the climate like in Cuba?
The climate in Cuba is tropical, with warm temperatures throughout the year. The rainy season is from May to October, and the dry season is from November to April.
What is the political system of Cuba?
Cuba is a socialist state with a one-party system. The Communist Party of Cuba is the only legal political party in the country.
What is the literacy rate in Cuba?
The literacy rate in Cuba is over 99%, which is one of the highest in the world.
What are some popular tourist attractions in Cuba?
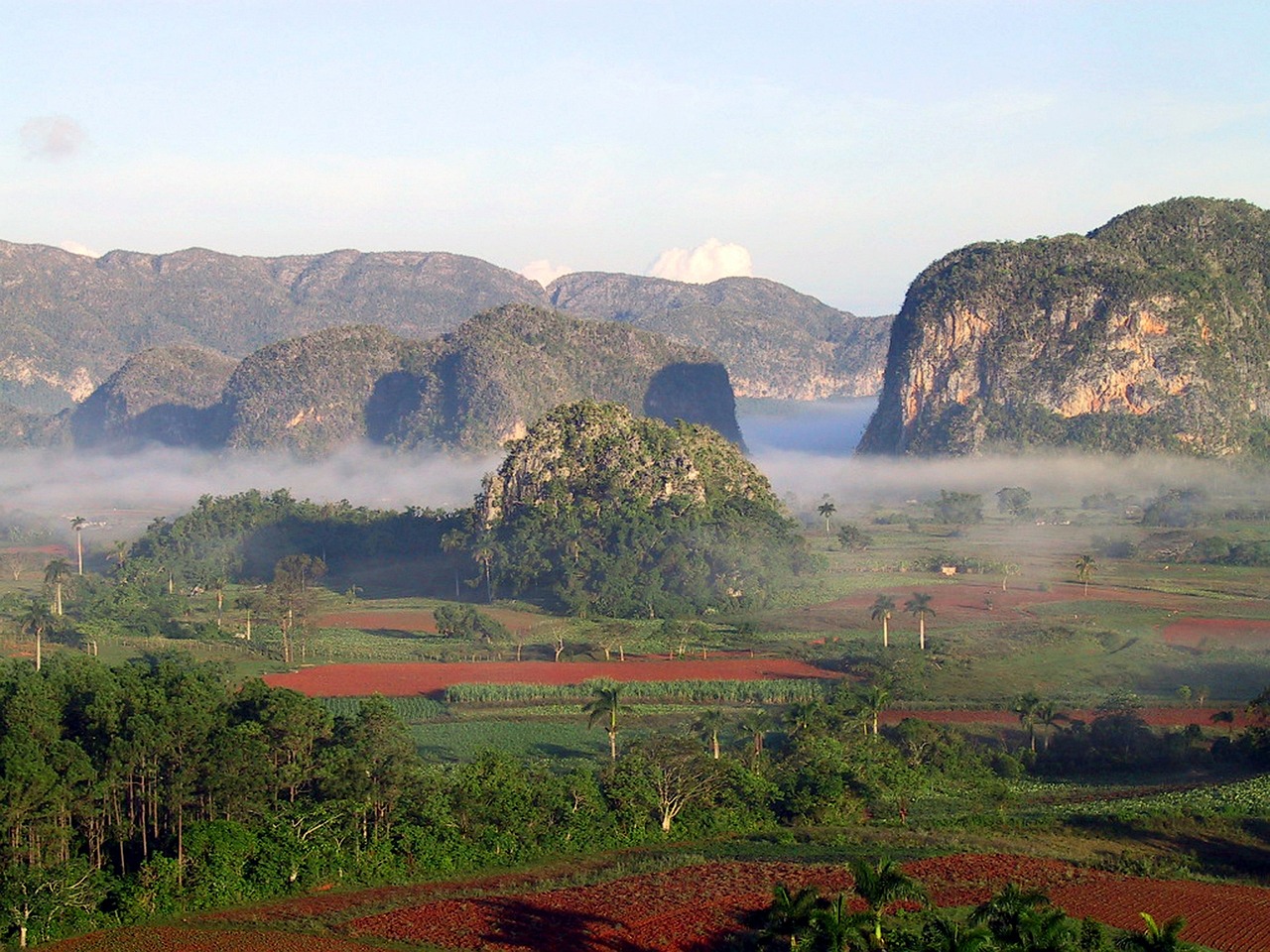
Some popular tourist attractions in Cuba include Havana, Varadero Beach, Trinidad, and the Viñales Valley.
What is the healthcare system like in Cuba?
Cuba has a universal healthcare system that is free for all citizens. The country has a high number of doctors per capita and is known for its medical research.
Climate Zones Of Cuba: Different climate regions Of Cuba
Cuba, the largest island in the Caribbean, is known for its diverse geography and climate. The country is located in the tropical region, which means it experiences warm temperatures throughout the year. However, due to its size and topography, Cuba is home to several distinct climate zones. Understanding these climate zones is crucial for various reasons, including agriculture and tourism. Summary Cuba has a diverse range of climate zones due to its location in the Caribbean. The tropical climate zone is the most prevalent in Cuba, with high temperatures and humidity year-round. The subtropical climate zone is characterized by mild winters and hot summers, with occasional hurricanes. The semi-arid climate zone experiences low rainfall and high temperatures, making it difficult for agriculture. The mountainous climate zone has cooler temperatures and higher rainfall, making it ideal for coffee and tobacco production. The coastal climate zone is influenced by sea breezes and has high humidity, while the rainforest climate zone is characterized by heavy rainfall. The seasonal climate zone experiences distinct wet and dry seasons, with hurricanes possible during the wet season. Cuba’s microclimates vary within each climate zone, affecting local agriculture and tourism. The impact of climate zones on Cuba’s agriculture and tourism is significant, with some areas more suitable for certain crops and activities than others. Tropical Climate Zone of Cuba The tropical climate zone is the most dominant in Cuba, covering a significant portion of the island. This zone is characterized by high temperatures and humidity throughout the year. The average temperature in this zone ranges from 24 to 27 degrees Celsius (75 to 81 degrees Fahrenheit). The...
Natural Resources of Cuba: Where Natural Resources are located In Cuba
Cuba is a country rich in natural resources, from its mineral deposits to its vast forests and agricultural lands. These resources play a crucial role in the country’s economy and provide opportunities for sustainable development. However, it is important to manage these resources in a sustainable manner to ensure their long-term availability and to minimize negative environmental impacts. This article will provide an overview of Cuba’s natural resources, their importance to the economy, and the need for sustainable resource management. Summary Cuba has a diverse range of natural resources, including minerals, forests, agriculture, marine life, renewable energy, water, and biodiversity. The country’s mineral deposits are concentrated in the eastern region, with nickel being the most significant resource. Cuba’s forests cover over 25% of the country and provide valuable timber resources, including mahogany and cedar. Agriculture is a vital sector in Cuba, with fertile lands producing crops such as sugar, tobacco, and coffee. Cuba’s coastal waters are rich in marine life, including fish, lobster, and shrimp, making it an important industry for the country. Overview of Cuba’s Natural Resources Cuba is located in the Caribbean Sea, with a tropical climate that supports a diverse range of natural resources. The country is blessed with an abundance of natural resources, including minerals, forests, agricultural lands, coastal waters, renewable energy sources, water resources, biodiversity, and wildlife. The geographical location and climate of Cuba contribute to its natural resource endowment. The country’s tropical climate provides favorable conditions for the growth of forests and agricultural crops. Additionally, Cuba’s location in the Caribbean Sea makes it rich in marine resources. These natural resources are of great...
Political Boundaries of Cuba: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Cuba is a country located in the Caribbean, known for its rich history, vibrant culture, and unique political system. Understanding Cuba’s political boundaries is crucial for anyone interested in studying or visiting the country. The political system in Cuba is a socialist republic, with the Communist Party of Cuba being the only legal political party. The President of Cuba is both the head of state and the head of government, and the National Assembly of People’s Power is the highest legislative body. Understanding political boundaries is important because it helps to provide context and insight into how a country is governed and organized. It allows us to understand the different levels of government and how they interact with each other. Additionally, understanding political boundaries can help us understand the cultural and social differences that exist within a country. Summary Cuba is divided into 15 provinces and one special municipality. Each province is further divided into municipalities and districts. The political boundaries of Cuba have evolved over time, reflecting changes in government and society. Provincial governments in Cuba play a significant role in local administration and economic development. Municipalities in Cuba have their own elected officials and are responsible for providing basic services to their communities. Provinces of Cuba: History and Overview Cuba is divided into 15 provinces and one special municipality, which is the Isle of Youth. The provinces have a long history that dates back to the colonial period when Cuba was under Spanish rule. The provinces were originally established as administrative divisions by the Spanish colonial government. Each province in Cuba has its own unique characteristics and...
Terrain and Topography of Cuba: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Cuba, the largest island in the Caribbean, is known for its stunning landscapes and diverse terrain. From its mountain ranges to its valleys, plains, coastlines, and unique karst formations, Cuba offers a wealth of natural beauty to explore. Understanding Cuba’s terrain is essential for appreciating its ecological significance, historical importance, and the impact it has on the country’s climate and ecosystems. Cuba’s geography is characterized by a mix of mountains, valleys, plains, and coastal regions. The island is located in the Caribbean Sea, south of the United States and east of Mexico. It stretches over 1,200 kilometers from east to west and covers an area of approximately 110,860 square kilometers. The diverse terrain of Cuba is a result of its geological history, which includes volcanic activity, tectonic movements, and erosion. Understanding Cuba’s terrain is important for several reasons. Firstly, it allows us to appreciate the country’s natural beauty and biodiversity. Cuba is home to a wide range of ecosystems, including forests, wetlands, mangroves, and coral reefs. Each of these ecosystems is influenced by the specific characteristics of the terrain in which they are found. Secondly, understanding Cuba’s terrain helps us understand its history and cultural significance. Many of Cuba’s mountains and valleys have played important roles in historical events and revolutions. By exploring these landscapes, we can gain a deeper understanding of Cuba’s past and its people. Summary Cuba’s terrain and topography is diverse and unique, featuring mountain ranges, valleys, plains, coastal regions, and karst landscapes. The Sierra Maestra and Sierra del Rosario mountain ranges offer stunning views and historical significance. The Viñales and Yumuri valleys are picturesque and...
History of Cuba
Cuba, a Caribbean island nation located just south of the United States, has a rich and complex history that spans centuries. From its indigenous peoples to its colonization by the Spanish, and from its involvement in the transatlantic slave trade to its struggle for independence, Cuba’s past is filled with significant events and influential figures. Understanding Cuba’s history is crucial for comprehending the country’s present challenges and the legacy of its revolutionary past. Summary Indigenous peoples inhabited Cuba before the arrival of Columbus. Spanish colonialism brought conquest and exploitation to Cuba. Cuba played a significant role in the transatlantic slave trade due to the sugar trade. The Ten Years’ War was Cuba’s first attempt at gaining independence from Spain. The Spanish-American War led to the United States’ intervention in Cuba and eventual control over the country. Pre-Columbian era: The indigenous peoples of Cuba Before the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1492, Cuba was inhabited by indigenous peoples known as the Taíno. The Taíno were part of the larger Arawak-speaking indigenous groups that populated the Caribbean islands. They lived in small villages and practiced agriculture, growing crops such as maize, yucca, and sweet potatoes. The Taíno also had a complex social structure, with chiefs ruling over different territories. The arrival of European colonizers had a devastating impact on the indigenous populations of Cuba. The Spanish brought diseases such as smallpox, measles, and influenza, to which the Taíno had no immunity. This led to a significant decline in their numbers, with many dying from these diseases or being killed by the Spanish in their quest for gold and other resources. By...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Cuba: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites in Cuba
Cuba is a country with a rich history and vibrant culture that has captivated the world for centuries. From its colonial past to its revolutionary present, Cuba offers a unique blend of influences that can be seen in its historic sites. Exploring these sites not only allows visitors to delve into the country’s fascinating past, but also provides a deeper understanding of its culture and identity. Summary Havana’s historic centre is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, showcasing the city’s rich history and architecture. The Monumental Cemetery of Havana reflects Cuban history and culture, with elaborate tombs and memorials. Trinidad is a colonial town preserved in time, with colourful buildings and cobblestone streets. The Mausoleum of Che Guevara pays tribute to the revolutionary hero and his legacy. The Museum of the Revolution takes visitors on a journey through Cuba’s revolutionary past, with exhibits and artefacts. The Historic Centre of Havana: A UNESCO World Heritage Site The historic center of Havana, also known as La Habana Vieja, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site that showcases the city’s colonial architecture and rich history. This area is home to numerous landmarks and buildings that date back to the 16th century, including the famous Plaza de la Catedral and Castillo de la Real Fuerza. The cobblestone streets and colorful buildings create a picturesque setting that transports visitors back in time. The UNESCO World Heritage Site designation of the historic center of Havana highlights its cultural and historical significance. It recognizes the importance of preserving and protecting this unique area for future generations to appreciate and enjoy. The designation also brings international attention to Havana’s...
Population Density of Cuba
Cuba, a Caribbean island nation located just south of the United States, is known for its vibrant culture, beautiful beaches, and rich history. However, one aspect of Cuba that often goes unnoticed is its population density. Population density refers to the number of people living in a given area, usually measured in square kilometers or square miles. Understanding Cuba’s population density is important as it can provide insights into the country’s social, economic, and political dynamics. Summary Cuba has a population density of 106 people per square kilometer. Cuba’s population density has been steadily increasing since the 1950s. Havana has the highest population density in Cuba, while the eastern provinces have the lowest. Factors affecting Cuba’s population density include government policies, economic opportunities, and natural disasters. Urbanization has led to higher population density in Cuba, while rural areas have experienced a decline in population. Overview of Cuba’s Population Density Cuba has a population density of approximately 106 people per square kilometer (275 people per square mile). This means that on average, there are 106 individuals living in every square kilometer of land in Cuba. Compared to other countries in the region, Cuba has a relatively high population density. For example, neighboring countries like the Dominican Republic and Haiti have population densities of 222 and 402 people per square kilometer respectively. Historical Trends in Cuba’s Population Density Cuba’s population density has fluctuated over time due to various factors. In the early 20th century, Cuba experienced a period of rapid population growth, fueled by immigration from Spain and other European countries. This led to an increase in population density as more...
Discovering the Vibrant Culture and Colourful History of Cuba: A Journey Through the Pearl of the Caribbean
Cuba, a vibrant and captivating country located in the Caribbean, is known for its rich culture and history. From its colonial past to the Cuban Revolution, the country has a fascinating story to tell. Cuba is also famous for its music, art, cuisine, and natural wonders. With its pristine beaches, lush rainforests, and stunning architecture, it is no wonder that Cuba has become a popular travel destination. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of Cuba’s culture and history that make it such a unique and enticing place to visit. Summary Cuba boasts a vibrant culture and colourful history, making it a must-visit destination. From colonial times to the revolution, Cuba’s rich history is fascinating and worth exploring. The people of Cuba are diverse and resilient, adding to the country’s unique character. Art, music, and cuisine in Cuba are a celebration of creativity, passion, and fusion of influences. Cuba’s natural wonders, stunning architecture, and love for life make it a truly unforgettable experience. Exploring Cuba’s Rich History Cuba’s history is deeply intertwined with its colonial past. The island was first colonized by the Spanish in the 15th century and remained under Spanish rule until the late 19th century. This colonial period left a lasting impact on Cuba’s architecture, language, and culture. Visitors to Cuba can explore the historic city of Havana, with its well-preserved colonial buildings and cobblestone streets. Other notable historical landmarks include the Castillo de la Real Fuerza, a fortress built in the 16th century to protect Havana from pirate attacks, and the Plaza de la Catedral, home to the stunning Havana Cathedral. The Cuban...