Jordan
(Al-Mamlakah al-Urduniyyah al-Hāshimiyyah (Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan))


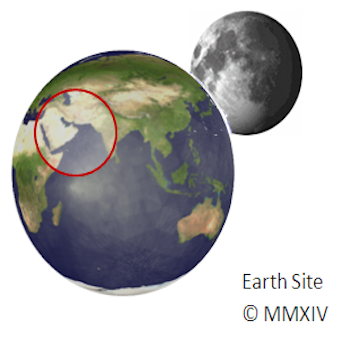



Capital: Amman
Population (Estimated July 2012): 6,508,887
Area: 88,778 km2 or 34,277 mi2
Currency: Jordanian Dinar (JD)
Official Language: Arabic
Political Information: Constitutional Monarchy
Official Religion: Islam
(approximately 92% of the population are Sunni Muslim, 6% are Christian of various denominations and 2% have other religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Jabal Umm ad Dami at 1,854m or 6,083ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a country’s economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $28.4 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and the use of resources but is not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $36.82 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $5,900 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +2:00
Wildlife:
Counties/Provinces/States: 12 governorates (muhafazat, singular – muhafazah); Ajlun, Al ‘Aqabah, Al Balqa’, Al Karak, Al Mafraq, ‘Amman, At Tafilah, Az Zarqa’, Irbid, Jarash, Ma’an, Madaba
Leaders: King Abdullah II with Prime Minister Awn Shawkat al-Khasawneh.
Additional: Gained Independence from British administration on the 25th of May 1946.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Jordan
Jordan, officially known as the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country located in the Middle East. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and east, Iraq to the north-east, Syria to the north, and Israel and Palestine to the west. The capital city of Jordan is Amman, which is also the largest city in the country. Jordan has a rich history dating back to ancient times, with evidence of human habitation dating back to the Paleolithic period. The country is known for its stunning landscapes, including the famous archaeological site of Petra, which is a UNESCO World Heritage site. Jordan is also home to the Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth, and the Wadi Rum desert, which has been featured in numerous films due to its otherworldly beauty.
Jordan is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary government. The current monarch, King Abdullah II, has been in power since 1999 and is known for his efforts to modernize the country and promote economic development. The official language of Jordan is Arabic, and Islam is the predominant religion, with the majority of the population being Sunni Muslims. The country has a diverse population, with a mix of Bedouin tribes, Palestinians, and other ethnic groups. Jordan is known for its hospitality and welcoming nature, and visitors to the country often remark on the warmth and friendliness of the people. With its rich history, stunning landscapes, and vibrant culture, Jordan is a fascinating destination for travellers seeking to explore the wonders of the Middle East.
History and Culture of Jordan
The history of Jordan dates back thousands of years, with evidence of human settlement in the region dating back to the Paleolithic period. The area that is now Jordan has been inhabited by various ancient civilizations, including the Nabateans, who built the famous city of Petra, and the Romans, who left behind impressive ruins such as the ancient city of Jerash. In more recent history, Jordan was part of the Ottoman Empire before becoming a British mandate following World War
In 1946, Jordan gained independence and became a sovereign state. The country has since played a key role in regional politics and has been a haven for refugees from neighbouring countries.
Jordanian culture is a rich tapestry of traditions that have been shaped by its diverse history and influences from neighbouring regions. The country’s cuisine, music, and art reflect this diversity, with influences from Arab, Bedouin, and Palestinian cultures. Traditional Jordanian music often features instruments such as the oud and the qanun, and traditional dances such as the dabke are popular at weddings and other celebrations. Jordanian cuisine is known for its use of fresh herbs and spices, with dishes such as mansaf (a traditional Bedouin dish of lamb cooked in fermented dried yogurt) and falafel being popular staples. The country also has a thriving arts scene, with contemporary artists drawing inspiration from both traditional and modern influences. With its rich history and vibrant culture, Jordan offers visitors a unique opportunity to immerse themselves in the traditions of the Middle East.
Geography and Landmarks of Jordan
Jordan is a country of diverse landscapes, ranging from the fertile Jordan Valley in the west to the arid desert regions in the east. The country is home to several natural wonders, including the Dead Sea, which is famous for its high salt content and buoyant waters. The Dead Sea is also one of the lowest points on Earth, sitting at around 430 meters below sea level. Another iconic landmark in Jordan is Petra, an ancient city carved into rose-red cliffs that dates back to around 300 BCE. This UNESCO World Heritage site is one of the most famous archaeological sites in the world and is a must-see for visitors to Jordan.
In addition to its natural wonders, Jordan is also home to several impressive historical landmarks. The ancient city of Jerash, also known as Gerasa, is one of the best-preserved Roman cities in the world and features impressive ruins such as the Oval Plaza and the Temple of Artemis. The desert landscape of Wadi Rum is another iconic landmark in Jordan, with its towering sandstone mountains and vast open spaces making it a popular destination for adventure seekers and nature lovers alike. With its diverse landscapes and rich history, Jordan offers visitors a wealth of landmarks to explore and discover.
Economy and Industry in Jordan
Jordan has a mixed economy that is based on agriculture, industry, and services. The country’s main agricultural products include fruits, vegetables, olives, and grains, with irrigation playing a key role in supporting agriculture in the arid climate. In recent years, Jordan has also made efforts to develop its industrial sector, with a focus on manufacturing and export-oriented industries such as textiles, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. The country has also made significant investments in renewable energy sources such as solar power, with several large-scale solar projects currently underway.
The services sector is also an important part of Jordan’s economy, with tourism playing a key role in driving economic growth. The country has made efforts to promote itself as a tourist destination, with initiatives such as the Jordan Pass offering visitors access to multiple attractions at a discounted price. In addition to tourism, other key sectors in the services industry include finance, telecommunications, and information technology. Despite these efforts, Jordan faces economic challenges such as high unemployment rates and a large public debt burden. However, with ongoing efforts to diversify its economy and attract foreign investment, Jordan has the potential to become a regional hub for trade and commerce.
Jordanian Cuisine and Culinary Traditions
Jordanian cuisine is a reflection of the country’s rich history and diverse cultural influences. The cuisine features a wide variety of dishes that are made using fresh herbs and spices, with an emphasis on simple yet flavourful ingredients. One of the most famous dishes in Jordanian cuisine is mansaf, which is considered the national dish of Jordan. Mansaf consists of lamb cooked in fermented dried yogurt and served with rice or bulgur wheat. Another popular dish is falafel, which consists of deep-fried balls made from ground chickpeas or fava beans and served with pita bread and tahini sauce.
In addition to these traditional dishes, Jordanian cuisine also features a wide variety of mezze (appetizers) such as hummus, baba ghanoush (smoky eggplant dip), and tabbouleh (a salad made from parsley, mint, bulgur wheat, tomatoes, and onions). These mezze are often served alongside freshly baked bread and are a staple at family gatherings and celebrations. Jordanian cuisine also features a wide variety of desserts such as knafeh (a sweet pastry made from shredded filo dough filled with cheese or nuts) and baklava (a sweet pastry made from layers of filo dough filled with nuts and sweetened with honey or syrup). With its emphasis on fresh ingredients and bold flavours, Jordanian cuisine offers visitors a unique culinary experience that reflects the country’s rich cultural heritage.
Tourism and Attractions in Jordan
Jordan is a popular tourist destination known for its stunning landscapes, rich history, and warm hospitality. One of the most famous attractions in Jordan is Petra, an ancient city carved into rose-red cliffs that dates back to around 300 BCE. This UNESCO World Heritage site is one of the most iconic archaeological sites in the world and is a must-see for visitors to Jordan. Another popular destination is the Dead Sea, which is famous for its high salt content and buoyant waters. Visitors can float effortlessly in the mineral-rich waters while enjoying stunning views of the surrounding desert landscape.
For nature lovers and adventure seekers, Wadi Rum is a must-visit destination. This vast desert landscape features towering sandstone mountains and offers opportunities for hiking, rock climbing, and camping under the stars. The ancient city of Jerash is another popular attraction in Jordan, known for its well-preserved Roman ruins such as the Oval Plaza and the Temple of Artemis. In addition to these iconic landmarks, Jordan also offers opportunities for cultural experiences such as visiting traditional Bedouin camps or exploring vibrant markets in cities such as Amman. With its diverse attractions and warm hospitality, Jordan offers visitors a unique opportunity to explore the wonders of the Middle East.
Current Events and Future Outlook for Jordan
In recent years, Jordan has faced economic challenges such as high unemployment rates and a large public debt burden. However, the country has made efforts to diversify its economy through initiatives such as promoting tourism and investing in renewable energy sources such as solar power. In addition to economic challenges, Jordan has also faced political instability due to conflicts in neighbouring countries such as Syria and Iraq. Despite these challenges, Jordan has remained relatively stable compared to other countries in the region.
Looking towards the future, Jordan has the potential to become a regional hub for trade and commerce due to its strategic location and efforts to attract foreign investment. The country’s rich history and diverse landscapes make it an attractive destination for tourists seeking to explore the wonders of the Middle East. With ongoing efforts to modernize its economy and promote sustainable development, Jordan has the potential to overcome its current challenges and emerge as a thriving nation in the years to come.
FAQs
What is Jordan?
Jordan is a country located in the Middle East, bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and east, Iraq to the north-east, Syria to the north and Israel and Palestine to the west.
What is the capital of Jordan?
The capital of Jordan is Amman, which is also the largest city in the country.
What is the official language of Jordan?
The official language of Jordan is Arabic.
What is the currency of Jordan?
The currency of Jordan is the Jordanian Dinar (JOD).
What are the popular tourist attractions in Jordan?
Some popular tourist attractions in Jordan include the ancient city of Petra, the Dead Sea, Wadi Rum desert, and the historic city of Jerash.
What is the climate like in Jordan?
Jordan has a mostly arid climate with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The climate can vary depending on the region, with the desert areas experiencing extreme temperatures.
What is the population of Jordan?
As of 2021, the population of Jordan is estimated to be around 10 million people.
What is the government system in Jordan?
Jordan is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary government. The King of Jordan is the head of state, and the Prime Minister is the head of government.
Political Boundaries of Jordan: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Jordan, officially known as the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country located in the Middle East, bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and east, Iraq to the north-east, Syria to the north, and Israel and Palestine to the west. The country has a rich history and is known for its diverse cultural heritage, ancient ruins, and stunning landscapes. Jordan’s political boundaries have evolved over time, influenced by historical, geographical, and geopolitical factors. The country’s borders have been shaped by various treaties, agreements, and conflicts, which have had a significant impact on its governance and administration. The political boundaries of Jordan play a crucial role in defining the country’s territorial integrity and sovereignty. They determine the extent of Jordan’s jurisdiction and authority over its territory, as well as its relationships with neighbouring countries. The delineation of these boundaries has been a complex and contentious issue, shaped by historical events, colonial legacies, and regional power dynamics. Understanding Jordan’s political boundaries is essential for comprehending the country’s governance structure, administrative divisions, and historical context. Summary Jordan’s political boundaries have evolved over time, shaping the country’s governance and administration. The administrative divisions of Jordan are divided into 12 provinces, each with its own governor appointed by the central government. Local governance in Jordan is further divided into districts, each with its own council responsible for local administration and development. The historical boundaries of Jordan have been influenced by ancient and modern geopolitical factors, impacting the country’s territorial integrity and sovereignty. The political boundaries of Jordan have significant implications for the country’s governance, including challenges and controversies surrounding border disputes and refugee...
Terrain and Topography of Jordan: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Jordan is a country located in the Middle East, with a diverse and varied terrain and topography that makes it a unique and fascinating destination for travellers and nature enthusiasts. The country is home to a wide range of landscapes, including majestic mountains, magnificent valleys, and vast plains, each with its own distinct characteristics and beauty. From the towering peaks of the Jordanian highlands to the sprawling deserts of the east, Jordan’s terrain and topography offer a rich tapestry of natural wonders that are waiting to be explored and appreciated. The terrain of Jordan is largely defined by its location at the crossroads of three continents – Africa, Asia, and Europe. This geographical position has resulted in a diverse and varied landscape that is characterised by dramatic contrasts and breathtaking scenery. From the rugged mountains of the north to the arid deserts of the south, Jordan’s terrain and topography are a testament to the country’s rich natural heritage and geological history. With its diverse range of ecosystems and habitats, Jordan is home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, making it a haven for biodiversity and a paradise for nature lovers. Summary Jordan’s terrain and topography are diverse, ranging from mountains to valleys and plains. The majestic mountains of Jordan, such as the Ajloun and Dana mountains, offer stunning natural beauty and opportunities for outdoor activities. The magnificent valleys of Jordan, including the Jordan Valley and Wadi Rum, are known for their unique landscapes and historical significance. The vast plains of Jordan, like the Jordanian Desert and the Eastern Desert, contribute to the country’s diverse terrain and...
Climate Zones of Jordan: Different climate regions Of Jordan
Jordan is a country located in the Middle East, with a diverse range of climate zones due to its varied topography and geographical location. The climate in Jordan can be classified into several distinct regions, each with its own unique characteristics and weather patterns. These climate zones include the Mediterranean, desert, highland, arid, semi-arid, and steppe regions. Each of these regions has a significant impact on the environment, agriculture, and daily life of the people living in these areas. The diverse climate zones in Jordan are a result of the country’s location between the Mediterranean Sea and the Arabian Desert. The varying elevations and geographical features also contribute to the different climate patterns experienced across the country. Understanding these climate zones is crucial for anyone looking to visit or live in Jordan, as it can greatly affect travel plans, outdoor activities, and overall comfort. In this article, we will explore each of these climate regions in detail, providing insight into the unique characteristics and weather patterns of each area. Summary Jordan has diverse climate zones, including the Mediterranean, Desert, Highland, Arid, Semi-arid, and Steppe regions. The Mediterranean climate region in Jordan is characterized by mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. The Desert climate region in Jordan experiences extremely hot and dry conditions, with very little rainfall. The Highland climate region in Jordan has cooler temperatures and more precipitation due to its higher elevation. The Arid climate region in Jordan is extremely dry and experiences very high temperatures, with little to no rainfall. The Mediterranean Climate Region The Mediterranean climate region in Jordan is located in the northwest part...
History of Jordan
Jordan has a rich and diverse history that dates back to ancient times. The region that is now Jordan was home to several ancient civilizations, including the Ammonites, Edomites, and Moabites. These ancient peoples left behind a wealth of archaeological treasures, including impressive ruins, temples, and tombs. The city of Jerash, for example, is home to some of the best-preserved Roman ruins in the world, while the ancient city of Petra is a UNESCO World Heritage site and one of the New Seven Wonders of the World. The ancient civilizations of Jordan were known for their advanced architecture, art, and engineering. The Nabateans, in particular, were skilled builders and craftsmen, as evidenced by the intricate carvings and structures at Petra. The region was also an important trade route, connecting the Mediterranean world with the Arabian Peninsula and beyond. This made it a melting pot of cultures and ideas, leading to a rich tapestry of traditions and beliefs. The ancient civilizations of Jordan laid the foundation for the region’s cultural and historical identity, and their legacy can still be seen and felt today. Jordan’s ancient civilizations also made significant contributions to art, literature, and philosophy. The Nabateans, for example, were known for their intricate rock-cut architecture and sophisticated water management systems. The city of Petra, their most famous achievement, is a testament to their engineering prowess and artistic sensibilities. The ancient city is home to impressive structures such as the Treasury and the Monastery, which showcase the Nabateans’ mastery of stone carving and design. Additionally, the region was a hub for trade and commerce, leading to the exchange of ideas...
Natural Resources of Jordan: Where Natural Resources are Located in Jordan
Jordan is a country rich in natural resources, despite its arid climate and limited land area. The country is strategically located in the Middle East, sharing borders with Israel, Syria, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia. Jordan‘s natural resources include water, minerals, agriculture, energy, and stunning landscapes that attract tourists from around the world. The sustainable management of these resources is crucial for the country’s economic development and environmental preservation. Summary Jordan is rich in natural resources, including water, minerals, agriculture, energy, and tourism attractions. Water scarcity is a major challenge in Jordan, with the country being one of the most water-poor in the world. Jordan has significant mineral resources, including phosphate, potash, and oil shale, which are important for the country’s economy. Agriculture is a vital sector in Jordan, with the country producing a variety of crops despite its arid climate. Jordan is working towards developing its renewable energy sector to reduce its reliance on imported energy resources. Water Resources in Jordan Water is a precious resource in Jordan, where the climate is predominantly arid. The country faces significant challenges in meeting the water needs of its growing population and agricultural sector. Jordan’s main sources of water include surface water from the Jordan River and underground water from aquifers. However, these sources are under pressure due to over-extraction, pollution, and climate change. The government has implemented various water management strategies, such as water conservation measures, wastewater treatment, and the development of desalination plants. Additionally, international cooperation with neighbouring countries on water sharing agreements is essential for ensuring sustainable access to water resources in the region. Jordan’s water resources are vital...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Jordan: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Jordan
The ancient city of Petra, nestled in the rugged mountains of southern Jordan, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the most iconic archaeological sites in the world. Known as the “Rose City” due to the pink hue of its rock-cut architecture, Petra was the capital of the Nabatean Kingdom and flourished as a major trading hub from the 4th century BC to the 2nd century AD. The city’s most famous structure is the Treasury, carved into the sandstone cliff and adorned with intricate carvings and columns. As visitors pass through the narrow Siq, a natural rock formation, they are greeted with the awe-inspiring sight of the Treasury, which has been featured in numerous films and is a symbol of Jordan‘s rich history and cultural heritage. Beyond the Treasury, Petra is home to a wealth of archaeological wonders, including the Royal Tombs, the Roman Theatre, and the Monastery, all of which showcase the advanced engineering and artistic skills of the Nabateans. The city’s complex water management system, which allowed it to thrive in the arid desert environment, is a testament to the ingenuity of its ancient inhabitants. Exploring Petra is a journey back in time, as visitors wander through the ancient streets, marvel at the intricate rock-cut facades, and imagine the bustling city that once stood at the crossroads of ancient trade routes. With its rich history and stunning natural beauty, Petra continues to captivate and inspire visitors from around the world. Summary Petra is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the most famous archaeological sites in the world. Jerash is a testament to Jordan’s...
Population Density of Jordan
Jordan is a small country located in the Middle East, with a population density of around 113 people per square kilometer. The population density in Jordan is unevenly distributed, with the majority of the population concentrated in urban areas such as the capital city of Amman. The country’s population density has been steadily increasing over the years, posing various challenges for the government in terms of managing resources, infrastructure, and social services. Understanding the factors influencing population density in Jordan is crucial for developing effective policies and initiatives to manage and sustain the country’s population growth. Jordan’s population density is influenced by a variety of factors, including geographical features, economic opportunities, and government policies. The country’s diverse landscape, which includes deserts, mountains, and fertile valleys, has a significant impact on population distribution. Urban areas such as Amman and Zarqa are attractive to migrants due to the availability of employment opportunities, educational institutions, and healthcare facilities. Additionally, the influx of refugees from neighbouring countries has also contributed to the increase in population density in certain regions. As a result, the government has been faced with the challenge of providing adequate infrastructure and resources to support the growing population. Summary Jordan has a population density of 113 people per square kilometre, making it one of the most densely populated countries in the Middle East. Factors influencing population density in Jordan include urbanisation, economic opportunities, and natural resources. The majority of Jordan’s population is concentrated in urban areas, with Amman being the most densely populated city. High population density in urban areas puts pressure on infrastructure, housing, and resources such as water...
Exploring the Wonders of Jordan: A Journey Through the Land of Ancient Civilizations
Jordan, located in the heart of the Middle East, is a country that is rich in history and culture. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south, Iraq to the east, Syria to the north, and Israel and Palestine to the west. With its strategic location, Jordan has been a crossroads of civilizations for thousands of years, resulting in a diverse and fascinating cultural heritage. The history of Jordan dates back to ancient times, with evidence of human habitation dating back to the Paleolithic period. Throughout its history, Jordan has been home to numerous civilizations, including the Nabataeans, Romans, Byzantines, and Ottomans. This rich history is evident in the country’s archaeological sites, such as Petra and Jerash, which attract visitors from around the world. In addition to its historical significance, Jordan is also known for its vibrant culture. The country is home to a diverse population, with Arab Bedouin tribes making up a significant portion of the population. The traditional Bedouin way of life can still be seen in many parts of Jordan, particularly in the desert regions. Jordan is also known for its warm hospitality and friendly people. Visitors to the country are often struck by the genuine kindness and generosity of the Jordanian people. This hospitality is deeply rooted in Jordanian culture and is a reflection of the country’s values and traditions. Summary Jordan is a country with a rich history and culture. Petra is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a must-visit destination in Jordan. Wadi Rum is a natural wonder with stunning desert landscapes. The Dead Sea is a unique natural phenomenon and a...
Remembering King Hussein Bin Talal of Jordan: A Legacy of Leadership and Humanity
Introduction King Hussein Bin Talal of Jordan, a revered statesman and a symbol of unity, passed away on February 7, 1999. His demise marked the end of an era and left a profound impact on both the people of Jordan and the international community. This article aims to honor his memory and highlight the incredible legacy he left behind. King Hussein Bin Talal of Jordan: A Remarkable Journey King Hussein Bin Talal’s remarkable journey began on November 14, 1935, when he was born in Amman, Jordan. Crowned as the king at the tender age of 17, he ruled the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan for an unprecedented 46 years until his passing. Passionate Leadership and Political Influence As a leader, King Hussein possessed an unparalleled passion for his country and its people. He dedicated his life to safeguarding Jordan’s sovereignty, promoting regional stability, and advocating for peace in the Middle East. Under his reign, Jordan experienced significant political stability and economic growth, becoming an influential voice in regional affairs. A Bridgebuilder and Peacemaker King Hussein played a pivotal role in mediating conflicts and fostering dialogue between nations. His commitment to peaceful coexistence led to the signing of the historic peace treaty with Israel in 1994, which transformed the region’s geopolitical landscape. His efforts in nurturing diplomatic ties have earned him immense respect and acclaim worldwide. A Beacon of Humanity Beyond his political achievements, King Hussein stood as a beacon of humanity. He championed numerous causes, including education, healthcare, and the empowerment of women. His charitable initiatives, such as the establishment of the King Hussein Cancer Foundation, continue to positively impact...


































