Liquid Nitrogen is nitrogen gas (its normal state on earth) that has been cooled sufficiently enough for it to change into its liquid state.
Where Does Liquid Nitrogen Come From?
Use of Liquid Nitrogen in Science
Liquid Nitrogen use in Cuisine
Safety Concerns with Liquid Nitrogen
Liquid Nitrogen is nitrogen gas (its normal state on earth) that has been cooled sufficiently enough for it to change into its liquid state. Nitrogen becomes a liquid (at normal atmospheric pressure) between -210o C to -196o C (63 K to 77.2 K or -346°F to -320.44°F).
Where Does Liquid Nitrogen Come From?
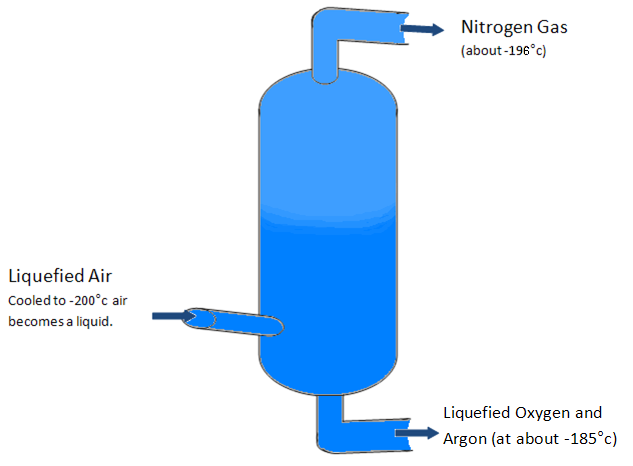
Nitrogen is obtained industrially from fractional distillation, a process that involves cooling air down to -200° C so it becomes a liquid. This is then allowed to heat in a chamber by several degrees until the air becomes -190 C and the nitrogen becomes a gas once more. At this point the collected nitrogen can then be cooled to -195 ˚C or more when it becomes liquid Nitrogen (nitrogen’s boiling point – when it becomes a gas – is -195.8 ˚C).
Air is made up of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and 1% of other substances. This means that air is a very good source of nitrogen and the most efficient way of extracting it is through fractional distillation. In many cases fractional distillation required heating the original substance to extract its required parts but fractional distillation of air requires cooling to low temperatures. As the nitrogen is already cooled to -196 ˚C for extraction only a small amount of extra energy is required to cool it into liquid nitrogen.
In liquid state nitrogen takes up 694 times less room than in its gas state, which is why it may be transported as a liquid in large quantities for logistical reasons. However nitrogen is sometimes transported pressurized in its gas state and then cooled to produce the liquid nitrogen for various applications.
Use of Liquid Nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen is used in cryogenics which is the study of the property of materials at very low temperature. Liquid nitrogen is the most common substance used to reduce temperatures as it is legal and easily accessible.
Liquid helium is also used as it has a lower boiling point allowing people to reach lower temperatures. Liquid helium is generally only used when extremely low temperatures are required, such as creating “low temperature or Type I superconductivity”, but as global quantities of helium are running low, Nitrogen is used when possible.
Use of Liquid Nitrogen in Science
Liquid Nitrogen is used to cool biological samples to preserve them for future study. This process is known as cryopreservation.
When studying the DNA of samples, chemicals known as re-agents are used and these re-agents need to be kept cool, in a freezer, to work. As repeatedly placing samples in these re-agents would increase their temperature liquid Nitrogen is sometimes used to cool the samples reducing the problem.
Liquid Nitrogen is used in the process of making materials superconductive. Superconductivity is a property found in around half the elements of the periodic table. When these materials, mainly metals and ceramics, are cooled below a certain temperature – known as the transition temperature (Tc) they provide no electrical or magnetic resistance. Type I superconductive materials require liquid helium to reduce their temperature enough to reach the transition temperature but type II has higher transition temperatures so liquid nitrogen is used.
Medical Applications
Liquid nitrogen is often used to quickly freeze materials such blood, tissues and stem cells, bone marrow etc for subsequent medical procedures or analysis.
Liquid Nitrogen is used to freeze sperm and egg cells used in fertility treatment and it is also used for cryotheropy or cryosurgery such as the removal of waltz, moles and to treat some skin cancers.
Use in Special effects
When liquid nitrogen comes into contact with other surfaces that are higher temperature the nitrogen gas begins to boil producing plumes of nitrogen gas. This is used as a visual effect in theatres and films to produce smoke or mimic boiling water etc.
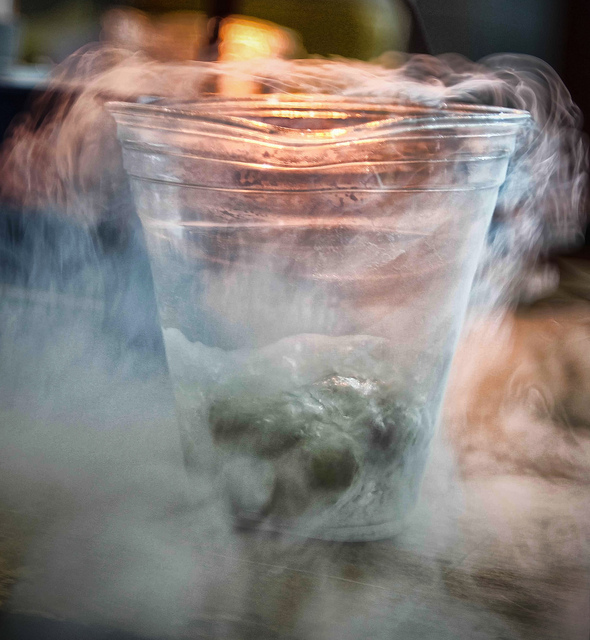
Liquid Nitrogen use in Cuisine
It has also found it’s way into the production of cocktails where a small amount is added to the drink making it smoke. The use of it in drinks has been scrutinised when a girl celebrating her 18th birthday consumed one of these cocktails where the liquid nitrogen had not fully evaporated. The extremely cold temperature caused her stomach to freeze resulting in its removal.
Safety Concerns with Liquid Nitrogen
When handling liquid nitrogen extreme care is required and protective clothing should be worn at all time. The liquid nitrogen will freeze any surface instantly including flesh which will be permanent damage to the skin. Any surface that comes into contact with the liquid nitrogen will also be extremely cold especially metals which if touched may stick skin to the surface possible resulting in the flesh being ripped off when trying to remove from the surface. Protective eyewear should also be worn as the nitrogen gas released may too be cold enough to damage sensitive body pars such as eyes. A well ventilated room should also be used when handling liquid nitrogen; the nitrogen gas released will expand to approximately 700 times the volume of the liquid and this gas will displace oxygen possible resulting in asphyxiation and this can happen before symptoms are visible. Also due to rapid expansion of nitrogen gas, explosion due to pressure may occur in closed systems.
Cryogenic materials such as liquid nitrogen are too cold for many substances including plumbing so liquid nitrogen should not be disposed of down drains etc.