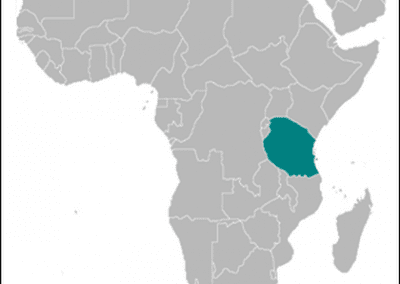
Tanzania
(Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania (Swahili); United Republic of Tanzania (English))
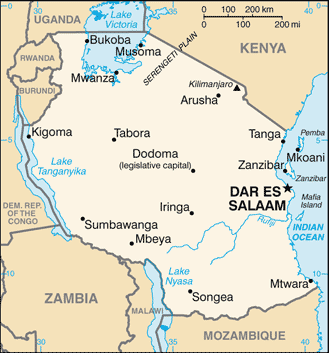



Capital: Dar es Salaam
Population (Estimated July 2012): 43,601,796
Area: 945,090km2 or 364,901mi2
Currency: Tanzanian Shilling (TZS)
Official Language: Swahili and English
Political Information: Presidential Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion
(approximately 35% of the mainland population are Muslim, 35% have indigenous beliefs and 30% are Christian. Approximately 100% of the population on the two islands (Zanzibar and Pemba) are Muslim)
Highest Mountain: Mount Kilimanjaro at 5,895m or 19,340ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a country’s economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $23.2 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and the use of resources but is not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $63.44 billion (US$) or (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $1,500 (US$) or (GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +3:00
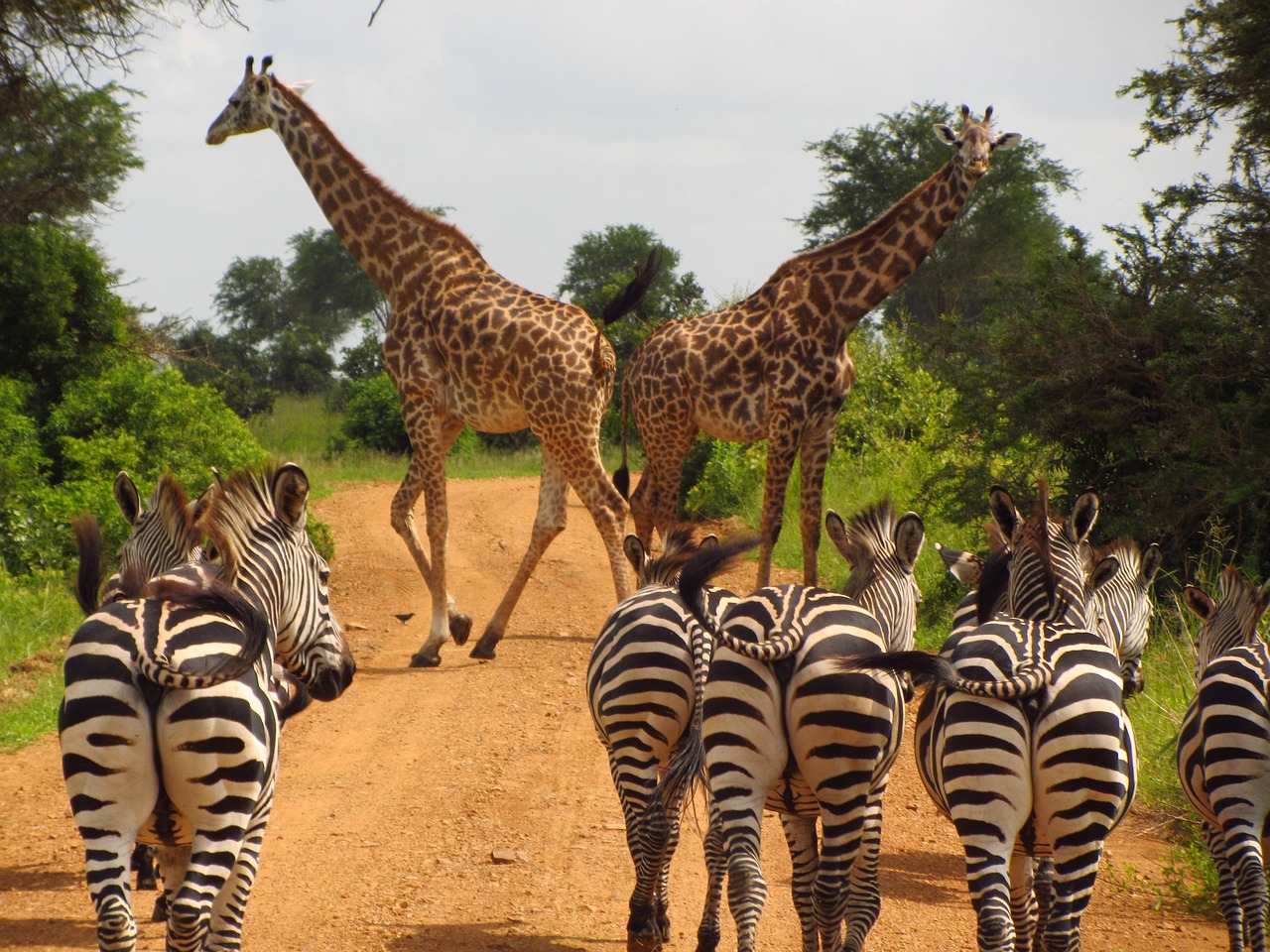
Wildlife:
Counties/Provinces/States: 26 regions; Arusha, Dar es Salaam, Dodoma, Iringa, Kagera, Kigoma, Kilimanjaro, Lindi, Manyara, Mara, Mbeya, Morogoro, Mtwara, Mwanza, Pemba North, Pemba South, Pwani, Rukwa, Ruvuma, Shinyanga, Singida, Tabora, Tanga, Zanzibar Central/South, Zanzibar North, Zanzibar Urban/West
Leaders: President Jakaya Kikwete and Vice President Mohammed Gharib Bilal (the president is both chief of state and head of government)
Additional: Zanzibar is part of the Republic of Tanzania but has a government led by President Ali Mohamed Shein (also Dr Ali Mohamed Shein). Tanzania’s highest mountain, Kilimanjaro, is also the highest Mountain on the continent of Africa.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Tanzania
Tanzania, a nation located in East Africa, is renowned for its rich tapestry of cultures, breathtaking landscapes, and diverse wildlife. It is bordered by eight countries, including Kenya and Uganda to the north, and Mozambique to the south, while the Indian Ocean lies to the east. The country is a melting pot of ethnicities, languages, and traditions, making it a fascinating study in cultural diversity.
Tanzania is home to Mount Kilimanjaro, the highest peak in Africa, and the Serengeti National Park, famous for its annual wildebeest migration. The capital city, Dodoma, serves as the political hub, while Dar es Salaam remains the largest city and a vital economic centre. The nation’s history is as varied as its geography.
From ancient trade routes that connected it to the Middle East and Asia to its colonial past under German and British rule, Tanzania has undergone significant transformations. The country gained independence in 1961, and since then, it has worked towards building a unified national identity while celebrating its diverse heritage. This blend of historical influences and contemporary developments shapes Tanzania’s unique character today.
Summary
- Tanzania is a diverse and culturally rich country located in East Africa, known for its stunning natural landscapes and wildlife.
- The geographical features of Tanzania include the iconic Mount Kilimanjaro, the Serengeti plains, and the beautiful coastline along the Indian Ocean.
- Tanzania is home to over 120 ethnic groups, each with its own unique traditions, languages, and customs, making it a melting pot of cultural diversity.
- The country boasts an abundance of wildlife and is famous for its national parks such as the Serengeti, Ngorongoro Crater, and Selous Game Reserve.
- Tanzania’s economy is largely based on agriculture, mining, and tourism, with a growing focus on industry and infrastructure development.
Geographical features of Tanzania
Tanzania’s geographical features are as diverse as its cultures. The country boasts a variety of landscapes, ranging from coastal plains along the Indian Ocean to highland plateaus and vast savannahs. Mount Kilimanjaro, standing at 5,895 metres, is not only the highest point in Africa but also a dormant volcano that attracts climbers from around the globe.
Its snow-capped summit is a striking contrast to the surrounding lush forests and arid plains. The Great Rift Valley runs through Tanzania, creating a series of lakes and valleys that are home to unique ecosystems. Lake Tanganyika, one of the deepest lakes in the world, is situated in the western part of the country and is known for its rich biodiversity.
The lake supports various fish species, some of which are endemic to its waters. Additionally, Lake Victoria, shared with Uganda and Kenya, is the largest lake in Africa and plays a crucial role in the livelihoods of millions who depend on its resources for fishing and agriculture.
Cultural diversity in Tanzania
Tanzania is a mosaic of cultures, with over 120 ethnic groups contributing to its rich cultural landscape. Each group has its own distinct language, traditions, and customs. The Sukuma people, for instance, are the largest ethnic group in Tanzania and are known for their agricultural practices and vibrant dance forms.
In contrast, the Maasai are renowned for their pastoral lifestyle and distinctive dress, which includes brightly coloured shuka cloths. Swahili culture also plays a significant role in Tanzania’s identity.
This is evident in the architecture of Zanzibar’s Stone Town, where narrow alleys are lined with intricately carved wooden doors and bustling markets filled with spices. The Swahili language serves as a unifying factor among Tanzanians, facilitating communication across diverse ethnic groups.
Wildlife and national parks in Tanzania
Tanzania is often referred to as one of the best wildlife destinations in the world, thanks to its extensive network of national parks and conservation areas. The Serengeti National Park is perhaps the most famous, known for its annual wildebeest migration that sees millions of animals traverse the plains in search of greener pastures. This natural spectacle attracts tourists and researchers alike, eager to witness one of nature’s most remarkable events.
Another significant area is Ngorongoro Crater, a UNESCO World Heritage Site that is home to an abundance of wildlife within its caldera. The crater provides a unique ecosystem where animals such as lions, elephants, and rhinos coexist in relative proximity due to the enclosed nature of the area. Tarangire National Park is also noteworthy for its large herds of elephants and iconic baobab trees that dot the landscape.
These parks not only serve as vital habitats for wildlife but also play an essential role in conservation efforts aimed at protecting endangered species.
Economy and industry in Tanzania
Tanzania’s economy is primarily based on agriculture, which employs a significant portion of the population. Key crops include coffee, tea, tobacco, and cashew nuts, which are vital for both domestic consumption and export. The agricultural sector faces challenges such as climate change and fluctuating market prices; however, it remains a cornerstone of the economy.
In addition to agriculture, Tanzania has been making strides in developing its mining sector. The country is rich in natural resources such as gold, diamonds, and tanzanite—a gemstone found only in Tanzania. Mining has become an increasingly important contributor to national revenue.
Furthermore, the government has been working to improve infrastructure to support industrial growth and attract foreign investment. This includes initiatives aimed at enhancing transportation networks and energy production capabilities.
Tourism in Tanzania
Tourism is a significant driver of Tanzania’s economy, attracting millions of visitors each year who come to experience its natural beauty and cultural richness. The country’s national parks are major attractions for wildlife enthusiasts and adventure seekers alike. In addition to safaris in the Serengeti or Ngorongoro Crater, tourists often visit Zanzibar for its stunning beaches and historical significance as a former trading hub.
Cultural tourism is also gaining traction as visitors seek authentic experiences with local communities.
This not only enriches the visitor experience but also provides economic benefits to communities that rely on tourism for their livelihoods.
Exploring Tanzania: A Safari Adventure
Embarking on a safari adventure in Tanzania is an exhilarating experience that requires careful planning to ensure a memorable journey. The first step in this process is to determine the type of safari that aligns with your interests and expectations. Tanzania offers a variety of safari experiences, from traditional game drives to walking safaris and even hot air balloon rides over the Serengeti.
Each option provides a unique perspective on the stunning landscapes and diverse wildlife, so it is essential to consider what you hope to gain from your adventure. Researching the different parks and reserves, as well as the specific wildlife you wish to see, can help narrow down your choices.
A typical safari can range from a few days to several weeks, depending on how many parks you wish to visit and the activities you want to engage in. It is advisable to create a rough itinerary that includes travel times between locations, as some parks are quite remote and may require long drives. Additionally, consider the time of year you plan to visit, as this can significantly impact wildlife visibility and overall experience.
Engaging with a reputable tour operator can also streamline the planning process, as they can provide valuable insights and assist with logistics, ensuring that your safari adventure unfolds seamlessly.
Summary
- When planning your safari adventure in Tanzania, consider the time of year, the national parks and game reserves you want to visit, and the type of accommodation you prefer.
- The best national parks and game reserves to visit in Tanzania include Serengeti National Park, Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Tarangire National Park, and Selous Game Reserve.
- On a safari in Tanzania, you can expect to see a wide variety of wildlife, including the Big Five (lion, elephant, buffalo, leopard, and rhinoceros), as well as diverse landscapes such as savannahs, forests, and lakes.
- The best time of year to visit Tanzania for a safari is during the dry season, from June to October, when wildlife viewing is at its peak.
- Safari accommodation options in Tanzania range from luxury lodges with all amenities to tented camps that provide a more immersive experience in nature.
- Cultural experiences to enjoy in Tanzania alongside your safari include visiting Maasai villages, exploring local markets, and learning about traditional tribal customs and rituals.
- To ensure a safe and enjoyable safari experience in Tanzania, follow the guidance of your experienced guide, respect wildlife and their habitats, and be prepared for the unpredictable nature of the wilderness.
- To minimise your impact on Tanzania’s wildlife and environment, practice responsible tourism by supporting conservation efforts, choosing eco-friendly accommodation, and respecting local customs and traditions.
The Best National Parks and Game Reserves to Visit in Tanzania
Tanzania is home to some of the most renowned national parks and game reserves in Africa, each offering distinct landscapes and wildlife experiences. The Serengeti National Park is perhaps the most famous, celebrated for its annual wildebeest migration, where millions of animals traverse the plains in search of greener pastures. This UNESCO World Heritage Site boasts an impressive array of wildlife, including lions, elephants, and cheetahs, making it a prime destination for photographers and nature enthusiasts alike.
The vastness of the Serengeti allows for both large herds and solitary animals to be observed in their natural habitat, providing an unparalleled safari experience. Another remarkable destination is Ngorongoro Crater, often referred to as one of the natural wonders of the world. This volcanic caldera is teeming with wildlife, including the endangered black rhino, and offers a unique opportunity to see a variety of species in a relatively small area.
The crater’s diverse ecosystems range from grasslands to forests, allowing for a rich tapestry of flora and fauna. Visitors can enjoy game drives along the crater floor, where they may encounter lions lounging in the sun or elephants foraging for food. The combination of stunning landscapes and abundant wildlife makes Ngorongoro a must-visit location for any safari itinerary.
What to Expect on a Safari in Tanzania: Wildlife and Landscape
A safari in Tanzania promises an immersive experience into the heart of Africa’s wilderness, where visitors can witness the intricate relationships between wildlife and their environments. The landscapes vary dramatically across the country, from the rolling savannahs of the Serengeti to the lush wetlands of Tarangire National Park. Each ecosystem supports a unique array of species, providing opportunities for diverse wildlife encounters.
For instance, Tarangire is renowned for its large elephant herds and iconic baobab trees, while Lake Manyara National Park is famous for its tree-climbing lions and vibrant birdlife. Wildlife sightings during a safari can be both exhilarating and humbling. The thrill of spotting a pride of lions resting under a tree or observing a herd of wildebeest grazing peacefully is an experience that stays with travellers long after they return home.
Moreover, Tanzania’s commitment to conservation means that many parks are well-managed, allowing for sustainable wildlife viewing without disturbing the animals. Visitors can expect knowledgeable guides who provide insights into animal behaviour and ecology, enhancing the overall experience.
The Best Time of Year to Visit Tanzania for a Safari
| Month | Weather | Wildlife | Crowds |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | Warm and dry | Great for seeing wildebeest calving | High |
| June | Mild temperatures | Good for seeing the Great Migration | High |
| September | Dry and cool | Excellent for wildlife viewing | Medium |
| November | Short rains | Good for birdwatching | Low |
Timing plays a pivotal role in planning a successful safari in Tanzania, as different seasons offer varying wildlife experiences. The dry season, which typically runs from June to October, is often considered the best time for game viewing. During these months, animals congregate around water sources, making them easier to spot.
The vegetation is less dense, providing clearer visibility for photographers and wildlife enthusiasts alike. This period coincides with the Great Migration in the Serengeti, where millions of wildebeest and zebras traverse the plains in search of food and water. Conversely, the wet season from November to May brings its own unique charm.
While some areas may become less accessible due to rain, this season is characterised by lush landscapes and vibrant flora. It is also an excellent time for birdwatching, as migratory species flock to Tanzania during this period. Additionally, many animals give birth during the wet season, providing opportunities to witness adorable young animals taking their first steps into the world.
Ultimately, the best time to visit depends on personal preferences and specific wildlife interests; each season offers distinct advantages that cater to different types of safari experiences.
Safari Accommodation Options in Tanzania: From Luxury Lodges to Tented Camps
When it comes to accommodation during your Tanzanian safari, there is an impressive range of options available to suit various budgets and preferences. Luxury lodges provide an opulent experience with stunning views, gourmet dining, and exceptional service. Many lodges are strategically located near national parks or game reserves, allowing guests easy access to wildlife viewing while enjoying all the comforts of high-end amenities.
For instance, lodges like Singita or Four Seasons offer lavish accommodations with private decks overlooking the savannah, creating an intimate connection with nature. On the other end of the spectrum are tented camps that offer a more rustic yet equally enchanting experience. These camps often provide a closer connection to nature, allowing guests to fall asleep to the sounds of wildlife just outside their tents.
Tented camps can range from basic setups with shared facilities to luxurious glamping experiences complete with en-suite bathrooms and fine dining under the stars. Camps like Olakira Camp or Serengeti Safari Camp offer mobile options that follow the migration route, ensuring guests are always in prime locations for wildlife viewing. Regardless of your choice of accommodation, each option provides a unique perspective on Tanzania’s breathtaking landscapes and rich biodiversity.
Cultural Experiences to Enjoy in Tanzania Alongside Your Safari
While Tanzania is renowned for its stunning wildlife and landscapes, it also boasts a rich cultural heritage that can enhance your safari experience. Engaging with local communities provides insight into traditional ways of life and fosters a deeper appreciation for the region’s diverse cultures. One such opportunity is visiting Maasai villages, where travellers can learn about their customs, rituals, and daily activities.
Participating in traditional dances or witnessing beadwork demonstrations allows visitors to connect with the Maasai people on a personal level while supporting their local economy. Additionally, exploring historical sites such as Stone Town in Zanzibar offers a glimpse into Tanzania’s complex history influenced by Arab, Persian, Indian, and European cultures. The winding streets are lined with intricately carved wooden doors and bustling markets filled with spices and textiles.
Guided tours can provide context about the island’s significance in trade routes and its role in shaping Tanzanian identity. By incorporating cultural experiences into your safari itinerary, you not only enrich your understanding of Tanzania but also contribute positively to local communities.
Tips for a Safe and Enjoyable Safari Experience in Tanzania
Ensuring a safe and enjoyable safari experience requires preparation and awareness of your surroundings. One essential tip is to adhere strictly to park regulations and guidelines provided by your guides. These rules are designed not only for your safety but also for the protection of wildlife and their habitats.
For instance, maintaining a safe distance from animals is crucial; approaching too closely can provoke stress or aggressive behaviour from wildlife. Additionally, always remain inside your vehicle during game drives unless instructed otherwise by your guide. Health considerations are also paramount when planning your safari adventure.
It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional regarding vaccinations and malaria prophylaxis before travelling to Tanzania. Carrying a basic first-aid kit can be beneficial for minor injuries or ailments during your trip. Furthermore, staying hydrated is essential in Tanzania’s warm climate; always carry sufficient water during excursions.
By taking these precautions and being mindful of your environment, you can ensure a safe and enjoyable safari experience that allows you to fully immerse yourself in Tanzania’s breathtaking wilderness.
Responsible Tourism: How to Minimise Your Impact on Tanzania’s Wildlife and Environment
As tourism continues to grow in Tanzania, it becomes increasingly important for visitors to engage in responsible practices that minimise their impact on wildlife and the environment. One effective way to do this is by choosing eco-friendly lodges or camps that prioritise sustainability in their operations. These establishments often implement measures such as solar energy use, water conservation practices, and waste management systems that reduce their ecological footprint while supporting local communities.
Additionally, participating in guided tours led by knowledgeable local guides can enhance your understanding of conservation efforts while ensuring that tourism benefits local economies directly. Supporting community-based tourism initiatives allows visitors to contribute positively while experiencing authentic cultural interactions. It is also vital to respect wildlife by observing them from a distance and refraining from feeding or disturbing them in any way.
By adopting these responsible tourism practices during your safari adventure in Tanzania, you play an essential role in preserving its natural beauty for future generations while enjoying an enriching travel experience.
Challenges and issues facing Tanzania
Despite its many strengths, Tanzania faces several challenges that hinder its development. One pressing issue is poverty; a significant portion of the population lives below the poverty line. Access to education and healthcare remains limited in rural areas, exacerbating inequalities between urban and rural populations.
Efforts to improve infrastructure have been made; however, many regions still lack basic services such as clean water and electricity. Environmental concerns also pose significant challenges for Tanzania. Deforestation due to agricultural expansion and logging threatens biodiversity and contributes to climate change.
Additionally, poaching remains a critical issue for wildlife conservation efforts; despite increased awareness and protective measures, illegal hunting continues to endanger species such as elephants and rhinos.
Future prospects for Tanzania
Looking ahead, Tanzania has considerable potential for growth and development if it can effectively address its challenges. The government has set ambitious goals for economic diversification beyond agriculture by investing in sectors such as manufacturing and tourism infrastructure. By enhancing connectivity through improved roads and airports, Tanzania aims to position itself as a regional hub for trade and tourism.
Furthermore, there is an increasing focus on sustainable development practices that balance economic growth with environmental conservation. Initiatives aimed at promoting eco-tourism can help protect natural resources while providing economic opportunities for local communities. By harnessing its rich cultural heritage alongside its natural beauty, Tanzania can create a more resilient economy that benefits all its citizens while preserving its unique identity for future generations.
One interesting article related to Tanzania can be found in the Array, which discusses the impact of tourism on the local economy in the country. The article highlights how the tourism industry in Tanzania has been growing steadily over the years, bringing in revenue and creating job opportunities for the local population. It also delves into the challenges faced by the industry, such as environmental concerns and the need for sustainable practices to ensure long-term success. Overall, this article provides valuable insights into the importance of tourism for Tanzania’s economy and the steps being taken to ensure its sustainability. Source
FAQs
What is the capital of Tanzania?
The capital of Tanzania is Dodoma, although the largest city and de facto capital is Dar es Salaam.
What is the population of Tanzania?
As of 2021, the estimated population of Tanzania is around 61 million people.
What is the official language of Tanzania?
The official languages of Tanzania are Swahili and English.
What is the currency of Tanzania?
The currency used in Tanzania is the Tanzanian shilling (TZS).
What are the major natural attractions in Tanzania?
Tanzania is home to several major natural attractions, including Mount Kilimanjaro, the Serengeti National Park, Ngorongoro Conservation Area, and the island of Zanzibar.
What is the climate like in Tanzania?
Tanzania has a varied climate, with coastal areas experiencing a tropical climate, while the central plateau has a temperate climate. The northern highlands and Mount Kilimanjaro have a cooler climate.
What are the major industries in Tanzania?
The major industries in Tanzania include agriculture, mining, tourism, and manufacturing.
What are the popular dishes in Tanzanian cuisine?
Popular dishes in Tanzanian cuisine include ugali (maize porridge), nyama choma (grilled meat), pilau (spiced rice), and samaki (fish) dishes.
Political Boundaries of Tanzania: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Tanzania, located in East Africa, is a nation characterised by its rich cultural diversity and complex political landscape. The country is bordered by eight nations, including Kenya and Uganda to the north, Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west, and Zambia, Malawi, and Mozambique to the south. Additionally, it has a coastline along the Indian Ocean to the east. These geographical features not only define Tanzania‘s physical space but also play a significant role in shaping its political boundaries. The delineation of these boundaries has been influenced by historical events, colonial legacies, and socio-political dynamics that continue to evolve. The political boundaries of Tanzania are not merely lines on a map; they represent the administrative divisions that govern the country. These divisions are crucial for the organisation of local governance, resource allocation, and the delivery of public services. Understanding Tanzania’s political boundaries requires an exploration of its provinces and districts, which serve as the fundamental units of administration. The interplay between these divisions and the historical context in which they were established provides insight into the current governance challenges faced by the nation. Summary Tanzania’s political boundaries are defined by its borders with neighbouring countries and its internal administrative divisions. The country is divided into 31 regions, which are further subdivided into districts, wards, and villages. Tanzania’s historical boundaries have been shaped by colonial rule and subsequent independence movements. The evolution of Tanzania’s political boundaries has been influenced by factors such as population growth, economic development, and political changes. Challenges and controversies surrounding Tanzania’s political boundaries include disputes over resource allocation and ethnic tensions....
Climate Zones of Tanzania: Different climate regions Of Tanzania
Tanzania, a country located in East Africa, is renowned for its diverse landscapes and rich biodiversity. This diversity is mirrored in its climate zones, which range from coastal areas to highland plateaus, and from semi-arid regions to tropical wet and dry climates. The geographical positioning of Tanzania, straddling the equator and bordered by the Indian Ocean, plays a significant role in shaping its climatic conditions. The interplay of altitude, latitude, and proximity to large bodies of water creates a mosaic of microclimates that influence not only the environment but also the livelihoods of millions of Tanzanians. Understanding Tanzania’s climate zones is crucial for various sectors, including agriculture, tourism, and conservation. Each zone presents unique characteristics that affect weather patterns, rainfall distribution, and temperature variations. For instance, the coastal regions experience a humid tropical climate, while the highlands enjoy cooler temperatures due to their elevation. This climatic diversity is not merely a geographical curiosity; it has profound implications for the flora and fauna that thrive in these environments, as well as for the human populations that depend on these ecosystems for their survival. Summary Tanzania’s climate zones are diverse and varied, ranging from coastal and lowland regions to highland and plateau areas. Coastal and lowland regions experience hot and humid climates, with high rainfall and tropical conditions. Highland and plateau regions have cooler temperatures and lower humidity, with distinct wet and dry seasons. Semi-arid and arid regions are characterised by low rainfall and high temperatures, leading to desert-like conditions in some areas. Tropical wet and dry regions have distinct wet and dry seasons, with high rainfall in the wet season...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Tanzania: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Tanzania
Tanzania, a nation rich in cultural heritage and historical significance, is a treasure trove of sites that reflect its diverse past and vibrant traditions. Nestled in East Africa, this country boasts a unique blend of indigenous cultures, Arab influences, and colonial legacies, all of which have shaped its identity over centuries. From ancient ruins to bustling markets, Tanzania‘s cultural and historical sites offer a glimpse into the lives of its people and the events that have shaped the region. The country’s landscape is dotted with remnants of its storied past, each telling a tale of resilience, adaptation, and the interplay of various civilisations. The significance of these sites extends beyond mere tourism; they are vital for understanding the socio-political dynamics that have influenced Tanzania’s development. Many of these locations are recognised as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, underscoring their global importance. Visitors to Tanzania are not merely observers; they become part of a narrative that spans millennia, engaging with the legacies of ancient peoples, colonial powers, and the ongoing evolution of contemporary Tanzanian society. This article delves into some of the most remarkable cultural and historical sites in Tanzania, each offering a unique perspective on the country’s rich tapestry. Summary Tanzania is home to a rich tapestry of cultural and historical sites that offer a glimpse into the country’s diverse heritage. The Great Mosque of Kilwa Kisiwani is a UNESCO World Heritage site and a testament to the region’s historical significance as a trading hub. The Stone Town of Zanzibar is a captivating blend of Swahili, Arab, Persian, Indian, and European influences, reflecting its role as a major trading port....
Natural Resources of Tanzania: Where Natural Resources are Located in Tanzania
Tanzania, located in East Africa, is endowed with a wealth of natural resources that play a pivotal role in its economy and the livelihoods of its people. The country boasts a diverse array of landscapes, from the majestic peaks of Mount Kilimanjaro to the expansive plains of the Serengeti, which are not only visually stunning but also rich in biodiversity. The natural resources of Tanzania can be broadly categorised into minerals, forests, agriculture, water, energy, and wildlife. Each of these categories contributes significantly to the nation’s economic framework and cultural heritage. The abundance of natural resources in Tanzania presents both opportunities and challenges. While these resources have the potential to drive economic growth and development, they also require careful management to ensure sustainability. The interplay between resource extraction, environmental conservation, and community needs is complex. As Tanzania continues to develop, the balance between utilising these resources for economic gain and preserving them for future generations remains a critical issue. Summary Tanzania is rich in natural resources, including minerals, forests, agriculture, water, energy, and wildlife. The country has significant mineral resources such as gold, diamonds, and gemstones, making it a key player in the global mining industry. Tanzania’s forest resources are under threat due to deforestation, illegal logging, and unsustainable land use practices. Agriculture is a major contributor to Tanzania’s economy, with a focus on crops such as maize, rice, and coffee, as well as livestock farming. Tanzania’s water resources are crucial for agriculture, energy production, and human consumption, but they are facing challenges such as pollution and over-extraction. Mineral Resources in Tanzania Tanzania is rich in mineral resources, which...
Terrain and Topography of Tanzania: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Tanzania, located in East Africa, is a nation renowned for its diverse and striking landscapes. The country boasts a rich tapestry of terrain that ranges from coastal beaches to towering mountains, expansive plateaus, and lush valleys. This geographical diversity is not merely a backdrop; it plays a crucial role in shaping the climate, ecosystems, and human activities within the region. The interplay of these various landforms creates a unique environment that supports an array of flora and fauna, making Tanzania one of the most biodiverse countries in the world. The topography of Tanzania is characterised by its dramatic contrasts. The Great Rift Valley slices through the country, creating a series of lakes and valleys that are home to unique wildlife and plant species. To the north, Mount Kilimanjaro rises majestically, its snow-capped peak visible for miles around, while the southern regions are dominated by the vast Selous Game Reserve and the rugged terrain of the Udzungwa Mountains. This article delves into the various aspects of Tanzania’s terrain and topography, exploring how these features influence both the natural world and human life. Summary Tanzania’s terrain and topography are incredibly diverse, ranging from high mountains to vast plains and stunning lakes and valleys. The Great Rift Valley is a remarkable geological feature that runs through Tanzania, offering breathtaking landscapes and unique ecosystems. The highlands and mountains of Tanzania, including Mount Kilimanjaro, provide habitat for a wide variety of wildlife and offer incredible trekking opportunities. The vast plains and plateaus of Tanzania are home to iconic African wildlife such as lions, elephants, and wildebeest, making them a popular destination for safari enthusiasts....
History of Tanzania
The early history of Tanzania is a tapestry woven from the threads of various cultures and peoples. Archaeological evidence suggests that the region has been inhabited for thousands of years, with the earliest human remains dating back to around 1. 9 million years ago, found in sites such as Olduvai Gorge. This area is often referred to as the “Cradle of Mankind” due to its rich fossil record, which includes the remains of early hominids like Homo habilis and Homo erectus. The Bantu migrations, which began around 1000 BCE, brought new agricultural practices and ironworking technology to the region, significantly transforming the social and economic landscape. By the first millennium CE, several distinct ethnic groups had established themselves in what is now Tanzania. The coastal areas saw the emergence of trade networks that connected the interior with the Indian Ocean, facilitating the exchange of goods such as ivory, gold, and slaves. The Swahili culture began to take shape during this period, blending African, Arab, and Persian influences. The establishment of city-states along the coast, such as Kilwa and Zanzibar, marked a significant development in trade and cultural exchange, laying the groundwork for future interactions with foreign powers. Summary Tanzania has a rich early history, with evidence of human habitation dating back over two million years. Arab and European influence in Tanzania began in the 8th century with the arrival of Arab traders, followed by Portuguese and Omani control in the 16th and 17th centuries. German colonial rule in Tanzania began in the late 19th century, leading to significant social and economic changes in the region. British colonial rule in...
Population Density of Tanzania
Tanzania, located in East Africa, is a nation characterised by its diverse landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and a population that has been steadily increasing over the years. As of the latest...