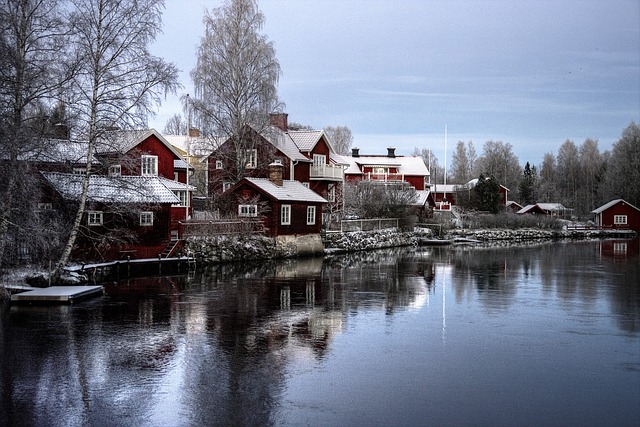
Sweden
(Konungariket Sverige (Kingdom of Sweden))

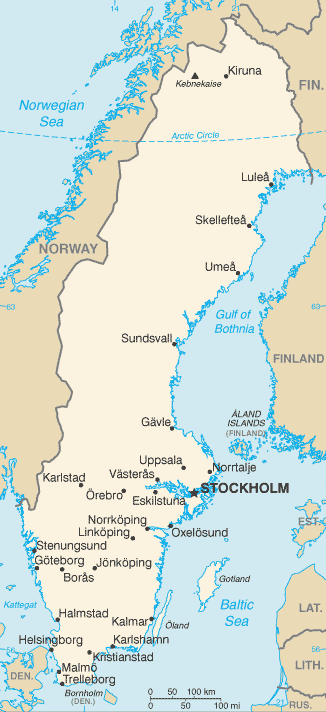

Capital: Stockholm
Population (Estimated July 2012): 9,103,788
Area: 450,295km2 or 173,860mi2
Currency: Swedish Krona (SEK)
Official Language: Swedish
Political Information: Constitutional Monarchy with Parliamentary Democracy
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 87% of the population is Lutheran and 13% have other religious beliefs)
Highest Mountain: Kebnekaise Sydtopp at 2,104m or 6,903ft
Largest River:
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +1:00
Wildlife:
Counties/Provinces/States: 21 counties (lan, singular and plural); Blekinge, Dalarna, Gavleborg, Gotland, Halland, Jamtland, Jonkoping, Kalmar, Kronoberg, Norrbotten, Orebro, Ostergotland, Skane, Sodermanland, Stockholm, Uppsala, Varmland, Vasterbotten, Vasternorrland, Vastmanland, Vastra Gotaland
Sweden
Sweden, the largest country in Northern Europe, is characterised by its diverse geography, which ranges from vast forests and numerous lakes to rugged mountains and a long coastline. The country spans approximately 450,000 square kilometres, making it the third-largest country in Europe by area. Sweden is bordered by Norway to the west and Finland to the east, while the southern tip is connected to Denmark via the Øresund Bridge.
The landscape is predominantly flat or gently rolling, with the Scandinavian Mountains running along the western border. This mountainous region is home to Sweden’s highest peak, Kebnekaise, which rises to 2,106 metres above sea level. The climate of Sweden varies significantly from north to south.
The northern regions experience a subarctic climate, characterised by long, cold winters and short, mild summers. In contrast, southern Sweden enjoys a temperate maritime climate, with milder winters and warmer summers. The coastal areas are influenced by the Gulf Stream, which helps moderate temperatures.
Precipitation is fairly evenly distributed throughout the year, although the northern parts receive more snow during winter months. The unique geographical features and climate contribute to Sweden’s stunning natural beauty, with its extensive archipelagos, dense forests, and pristine lakes.
Summary
- Sweden is located in Northern Europe and has a diverse geography, including mountains, forests, and thousands of coastal islands.
- The climate in Sweden varies from the mild and temperate south to the subarctic north, with long, cold winters and short, warm summers.
- Sweden has a rich history, from the Viking era to the modern day, and is known for its cultural contributions to literature, art, and design.
- The Swedish economy is highly developed, with a strong focus on exports, particularly in engineering, telecommunications, and pharmaceuticals.
- Sweden has a well-regarded education system and provides universal healthcare to its citizens, focusing on preventive care and patient autonomy.
History and Culture of Sweden
The Early Inhabitants and the Viking Age
The early inhabitants of the region were hunter-gatherers who settled around 12,000 years ago. By the Viking Age (circa 800-1050 AD), Sweden had emerged as a significant power in Northern Europe. Swedish Vikings were known for their seafaring skills and established trade routes that extended as far as Byzantium and North America.
The Middle Ages and the Emergence of a Unified State
The establishment of Christianity in the 11th century marked a significant turning point in Swedish history, leading to the gradual unification of various tribes under a central authority. The Middle Ages saw Sweden become part of the Kalmar Union with Denmark and Norway, which lasted from 1397 until 1523. This period was marked by political strife and power struggles.
Modern Sweden and its Cultural Heritage
The 17th century was a golden age for Sweden, as it expanded its territory through military conquests during the Thirty Years’ War. However, this expansion came to an end with the Great Northern War (1700-1721), leading to a decline in Swedish power. The 19th century was characterised by industrialisation and social reform, laying the groundwork for modern Swedish society. Swedish culture is deeply influenced by its history and geography. The country is known for its contributions to literature, music, and art. Renowned figures such as playwright August Strindberg and poet Karin Boye have left an indelible mark on Swedish literature. In music, Sweden has produced globally successful pop artists like ABBA and Roxette, while traditional folk music remains an integral part of cultural identity. The concept of “lagom,” which translates to “just the right amount,” encapsulates the Swedish ethos of moderation and balance in life.
Economy and Industry of Sweden
Sweden boasts a highly developed economy that is characterised by a combination of free-market capitalism and extensive welfare benefits. The country has consistently ranked among the top nations in terms of GDP per capita, reflecting its strong economic performance. Key sectors driving the economy include manufacturing, services, and technology.
Sweden is home to several multinational corporations such as Volvo, Ericsson, and H&M, which have made significant contributions to both domestic and global markets. The manufacturing sector remains vital to Sweden’s economy, with a focus on high-value products such as machinery, vehicles, and pharmaceuticals. The automotive industry is particularly noteworthy; Volvo and Scania are two prominent manufacturers that have established a reputation for quality and innovation.
Additionally, Sweden has made substantial investments in renewable energy technologies, positioning itself as a leader in sustainability. Wind power and bioenergy are increasingly important components of the energy mix, reflecting Sweden’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions. The service sector has also seen remarkable growth over recent decades, accounting for a significant portion of GDP.
Financial services, information technology, and telecommunications are among the most prominent industries within this sector. Stockholm has emerged as a major tech hub in Europe, often referred to as “the Silicon Valley of Europe,” due to its vibrant startup ecosystem and access to venture capital. This dynamic environment fosters innovation and entrepreneurship, contributing to Sweden’s reputation as a global leader in technology.
Education and Healthcare in Sweden
Sweden’s education system is renowned for its high standards and accessibility. Education is compulsory for children between the ages of 6 and 16, with a strong emphasis on equality and inclusivity. The system is divided into several stages: preschool (förskola), compulsory school (grundskola), upper secondary school (gymnasieskola), and higher education (universitet).
Public education is funded by taxes, ensuring that all children have access to quality education regardless of their socio-economic background. Higher education institutions in Sweden are known for their research-oriented approach and international collaboration. Universities such as Lund University and Uppsala University are recognised globally for their academic excellence.
Moreover, many programmes are offered in English, attracting students from around the world. The emphasis on critical thinking and creativity prepares students for a rapidly changing job market.
Healthcare is primarily publicly funded through taxation, ensuring that all residents have access to medical services without direct costs at the point of care. The system is decentralised; regional authorities manage healthcare services tailored to local needs. This structure allows for flexibility and responsiveness to community health challenges.
The quality of healthcare in Sweden is generally high, with a focus on preventive care and patient-centred approaches. The country has made significant strides in areas such as maternal health and chronic disease management. However, challenges remain, including waiting times for certain procedures and access to specialised care in rural areas.
Despite these issues, Sweden’s commitment to universal healthcare reflects its broader social values of equity and solidarity.
Swedish Cuisine and Traditions
Swedish cuisine is characterised by its simplicity and reliance on high-quality ingredients sourced from the surrounding environment. Traditional dishes often feature fish, meat, potatoes, and seasonal vegetables. One of the most iconic dishes is “köttbullar,” or Swedish meatballs typically served with lingonberry sauce and creamy gravy alongside mashed potatoes or boiled potatoes.
Another staple is “gravad lax,” which consists of cured salmon seasoned with dill and served with mustard sauce. The concept of “fika,” which refers to taking a break for coffee or tea accompanied by pastries or sandwiches, plays an essential role in Swedish culture. Fika is not merely about consuming food; it embodies social interaction and relaxation.
It is common for colleagues to gather for fika during work hours or for friends to meet at cafés to enjoy this cherished tradition. Seasonal celebrations also play a significant role in Swedish culture. Midsummer is one of the most important festivals, celebrated around the summer solstice with maypole dancing, flower crowns, and traditional foods like herring and new potatoes.
Christmas traditions include “julbord,” a festive buffet featuring various dishes such as ham, meatballs, pickled herring, and saffransbullar (saffron buns). These culinary traditions reflect Sweden’s agricultural heritage and connection to nature.
Wildlife and Nature in Sweden
Conservation Efforts
Reindeer herding remains an integral part of Sami culture in northern Sweden, where these animals are raised for their meat, hides, and antlers. The country’s commitment to conservation is evident through its numerous national parks and nature reserves that protect these habitats. For instance, Abisko National Park in Lapland offers stunning views of the Northern Lights during winter months while providing opportunities for hiking during summer months.
National Parks and Wilderness Areas
Similarly, Sarek National Park is known for its rugged terrain and untouched wilderness, attracting outdoor enthusiasts seeking adventure. Sweden’s extensive coastline features thousands of islands that contribute to its rich biodiversity.
Coastal Habitats and Activities
The archipelagoes around Stockholm and Gothenburg are popular destinations for both locals and tourists alike. These areas provide habitats for various bird species such as eagles and ospreys while offering opportunities for activities like kayaking and sailing.
Tourism and Attractions in Sweden
Tourism plays a significant role in Sweden’s economy, attracting millions of visitors each year who come to experience its natural beauty, cultural heritage, and vibrant cities. Stockholm, the capital city built on 14 islands connected by bridges, offers a unique blend of history and modernity. Visitors can explore Gamla Stan (the Old Town) with its cobblestone streets lined with colourful buildings dating back to the 13th century or visit world-class museums such as the Vasa Museum which houses a well-preserved 17th-century warship.
Gothenburg on the West Coast is another popular destination known for its picturesque canals and lively food scene.
Malmö offers a different experience with its modern architecture exemplified by the Turning Torso skyscraper and beautiful parks along the waterfront.
Beyond urban attractions lies Sweden’s breathtaking natural landscapes that entice outdoor enthusiasts year-round. The northern region offers opportunities for skiing in winter or hiking during summer months amidst stunning scenery like fjords or mountains. The Icehotel in Jukkasjärvi provides a unique experience where guests can stay overnight in rooms made entirely of ice while enjoying activities like dog sledding or snowmobiling.
Modern Society and Politics in Sweden
Modern Swedish society is characterised by its commitment to equality, sustainability, and social welfare. The country consistently ranks high on various indices measuring quality of life, happiness levels, gender equality, and environmental sustainability. This commitment stems from a long-standing tradition of social democracy that prioritises collective welfare over individual gain.
Sweden’s political landscape features multiple parties representing diverse ideologies; however, social democratic principles have historically dominated governance since the early 20th century. The Social Democratic Party has been instrumental in shaping policies related to healthcare, education, labour rights, gender equality, environmental protection among others. In recent years there has been growing discourse around immigration policies due to increased inflows from conflict zones such as Syria or Afghanistan leading up to debates about integration strategies within society while maintaining cultural identity amidst diversity challenges faced by many European nations today.
Sweden’s approach towards modern challenges reflects its historical values rooted deeply within democratic principles ensuring that all voices are heard while striving towards progress through collaboration rather than division fostering an inclusive environment where everyone can thrive regardless of background or beliefs.
One interesting article related to Sweden can be found in the Array, which discusses the country’s innovative approach to sustainability. Sweden has been at the forefront of implementing eco-friendly practices and policies, such as investing in renewable energy sources and promoting recycling. This article highlights how Sweden’s commitment to sustainability has made it a global leader in environmental conservation. To read more about Sweden’s sustainability efforts, you can visit the article here.
FAQs
What is the capital of Sweden?
The capital of Sweden is Stockholm.
What is the population of Sweden?
As of 2021, the population of Sweden is approximately 10.4 million people.
What is the official language of Sweden?
The official language of Sweden is Swedish.
What is the currency used in Sweden?
The currency used in Sweden is the Swedish Krona (SEK).
What are some popular tourist attractions in Sweden?
Some popular tourist attractions in Sweden include the Vasa Museum, Stockholm Old Town (Gamla Stan), the Icehotel in Jukkasjärvi, and the Northern Lights in Swedish Lapland.
What is the climate like in Sweden?
Sweden has a varied climate, with the south experiencing milder winters and warmer summers, while the north has colder winters and shorter summers. The coastal areas tend to have milder temperatures due to the influence of the Gulf Stream.
What are some traditional Swedish dishes?
Some traditional Swedish dishes include meatballs (köttbullar), herring, gravlax, and smörgåsbord (a buffet-style meal with a variety of dishes).
What are some famous Swedish companies?
Some famous Swedish companies include IKEA, Volvo, H&M, Ericsson, and Spotify.
Political Boundaries of Sweden: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Political boundaries serve as the framework within which a nation operates, delineating areas of governance, cultural identity, and historical significance. In Sweden, these boundaries are not merely lines on a map; they represent centuries of evolution, shaped by historical events, cultural shifts, and administrative needs. The political landscape of Sweden is characterised by a unique interplay between its provinces and districts, each contributing to the nation’s identity and governance structure. Understanding these boundaries is essential for grasping the complexities of Swedish society and its political system. Sweden’s political boundaries have been influenced by various factors, including geography, historical conflicts, and socio-economic developments. The country is divided into 21 counties, which serve as the primary administrative divisions. Each county is further subdivided into municipalities, creating a multi-layered governance structure that reflects both local needs and national policies. This intricate system of boundaries not only facilitates governance but also fosters a sense of belonging among the citizens, linking them to their historical and cultural roots. Summary Sweden is divided into 25 provinces, each with its own unique historical and cultural significance. The districts of Sweden serve as administrative and political divisions, playing a crucial role in governance and public administration. The historical boundaries of Sweden have evolved over time, impacting the country’s political landscape and cultural identity. A comparison of provinces and districts in Sweden reveals the diverse nature of the country’s political boundaries. Political boundaries play a significant role in Swedish governance, shaping policies and decision-making processes. Provinces of Sweden: Historical and Cultural Significance Historical Roots There are traditionally 25 provinces, each with its own distinct identity, traditions, and dialects....
Natural Resources of Sweden: Where Natural Resources are Located in Sweden
Sweden, a Nordic country renowned for its stunning landscapes and commitment to environmental sustainability, is endowed with a wealth of natural resources. The nation’s geography, characterised by vast forests, numerous lakes, and a rugged coastline, plays a pivotal role in shaping its resource base. Natural resources...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Sweden: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Sweden
Sweden, a nation steeped in rich history and vibrant culture, boasts an array of cultural and historical sites that reflect its storied past and artistic heritage. From the majestic palaces of its royal family to the remnants of ancient...
Climate Zones of Sweden: Different Climate Regions Of Sweden
Sweden, a country renowned for its stunning natural landscapes and rich biodiversity, is characterised by a variety of climate zones that significantly influence its ecology, agriculture, and human activities. The geographical expanse...
Terrain and Topography of Sweden: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Sweden, a Scandinavian nation renowned for its stunning natural beauty, boasts a diverse terrain that ranges from rugged mountains to serene lowlands. The country’s geographical features are shaped by a combination of glacial activity, tectonic movements, and the influence of the Baltic Sea. This unique topography not only defines the landscape but also plays a crucial role in the climate, biodiversity, and human activities within the region. Sweden‘s terrain is characterised by its vast forests, numerous lakes, and extensive coastline, which together create a rich tapestry of ecosystems and habitats. The northern part of Sweden is dominated by the Scandinavian Mountains, which stretch along the border with Norway. These mountains are not only significant for their height but also for their ecological importance, providing habitats for various species and influencing weather patterns. In contrast, the southern regions of Sweden feature rolling hills and fertile plains that support agriculture and urban development. This juxtaposition of highlands and lowlands contributes to the country’s varied climate, which ranges from subarctic in the north to temperate in the south, further enriching its environmental diversity. Summary Sweden’s terrain is characterized by a diverse landscape of mountains, valleys, lowlands, and plains. The mountain ranges in Sweden, such as the Scandinavian Mountains, offer stunning natural beauty and recreational opportunities. The valleys and lowlands of Sweden are home to fertile farmlands and important waterways, contributing to the country’s agricultural and economic activities. The plains of Sweden, including the coastal plains and the inland plains, play a significant role in the country’s infrastructure and human settlements. Sweden’s varied terrain has a significant impact on the environment, influencing biodiversity,...
Population Density of Sweden
Population density is a critical demographic metric that reflects the number of individuals living per unit area, typically expressed in persons per square kilometre. In Sweden, a country renowned for its stunning natural landscapes and high quality of life, population density presents a unique narrative. With a total land area of approximately 450,000 square kilometres and a population of around 10.5 million, Sweden exhibits a relatively low average population density of about 25 people per square kilometre. However, this figure belies the complexities of population distribution across the nation, where urban centres are densely populated while vast rural areas remain sparsely inhabited. The geographical layout of Sweden plays a significant role in shaping its population density. The country is characterised by extensive forests, lakes, and mountains, which limit habitable land. Furthermore, the historical development of cities and towns has led to concentrated populations in specific regions, particularly along the eastern coastline and in the southern parts of the country. This uneven distribution raises important questions about resource allocation, infrastructure development, and social services, making it essential to delve deeper into the factors influencing population density in Sweden. Summary Sweden has a relatively low population density compared to other European countries, with the majority of its population concentrated in urban areas. Factors contributing to population density in Sweden include urbanization, immigration, and economic opportunities in urban centres. The urban population in Sweden is significantly higher than the rural population, leading to challenges in infrastructure and resource management. High population density in urban areas puts pressure on transportation, housing, and healthcare systems in Sweden. Government policies and initiatives aim to manage...
History of Sweden
The history of Sweden can be traced back to its early settlements, which emerged during the Stone Age. Archaeological evidence suggests that the region was inhabited as far back as 12,000 years ago, with hunter-gatherer communities thriving in the fertile lands and along the coastlines. These early inhabitants relied on fishing, hunting, and foraging for sustenance, gradually developing tools and techniques that would enable them to adapt to their environment. By the time of the Bronze Age, around 1800 BC, the population had begun to establish more permanent settlements, leading to the construction of burial mounds and the development of trade networks with neighbouring regions. The Viking Age, spanning from approximately 800 to 1050 AD, marked a significant turning point in Sweden‘s history. The Swedish Vikings were known for their seafaring prowess, exploring and raiding territories across Europe, Asia, and even North America. They established trade routes that connected Sweden to distant lands, facilitating the exchange of goods such as furs, amber, and iron. Notably, the Vikings from Sweden ventured eastward into what is now Russia, founding settlements along the rivers and establishing trade links with the Byzantine Empire. This era not only contributed to the economic prosperity of Sweden but also laid the groundwork for cultural exchanges that would shape the nation’s identity. Summary Early settlements in Sweden date back to the Stone Age, with evidence of Viking Age settlements and trade routes. The Christianization of Sweden began in the 9th century and was completed by the 12th century, leading to the establishment of the Swedish Church. The Kalmar Union in the 14th century brought Sweden, Denmark, and...
Discovering Sweden: A Journey Through the Land of the Midnight Sun
Sweden, located in Northern Europe, is a land of contrasts. From its stunning natural landscapes to its vibrant cities, Sweden offers a unique blend of beauty and modernity. The country is known for its vast forests, crystal-clear lakes, and picturesque archipelagos. Its geography is diverse, with mountains in the north and rolling plains in the south. The climate varies from mild summers to cold winters, making it an ideal destination for both outdoor enthusiasts and city dwellers. The Swedish culture and lifestyle are deeply rooted in nature and sustainability. Swedes have a strong connection to the environment and prioritize eco-friendly practices. They value simplicity, equality, and work-life balance. The Swedish lifestyle is often described as “lagom,” which means finding the perfect balance in all aspects of life. This philosophy is reflected in their approach to work, relationships, and leisure activities. Summary Sweden is a land of contrasts, with a rich history and culture, natural wonders, delicious cuisine, and hidden gems. Exploring the natural wonders of Sweden is a must-do, from the Northern Lights to the Swedish archipelago and the midnight sun. The Swedish cuisine is a delicious journey, with traditional dishes like meatballs, herring, and cinnamon buns. Stockholm is the capital city and has many hidden gems to discover, from trendy neighborhoods to historic landmarks. The Sami people are the indigenous culture of Sweden, and learning about their traditions and way of life is a fascinating experience. The Rich History and Culture of Sweden Sweden has a rich history that has shaped its culture and identity. The country was once a powerful empire that controlled vast territories in Northern...