Biology (from the Latin ‘bios’ meaning life and ‘logia’ meaning study of) is the study of all organisms and all aspects of their life-cycles.
Biology
Biology (from the Latin ‘bios’ meaning life and ‘logia’ meaning study of) is the study of all organisms and all aspects of their life-cycles. The subject of Biology, as we know it today, was born in the nineteenth century along with physics, chemistry and the scientific method. Before then ‘Natural Philosophy’ which was the study of nature and the physical universe, included biology, chemistry and physics.
Natural Philosophy The study of our natural world is known to date back to the time of Mesopotamia around 3,100 BC but as this was the beginning of written historic record the study probably existed long before this time. Modern Biology The first great development of modern biology came from Charles Darwin, who is often referred to as the father of modern biology. Although known for his work ‘On the Origin of Species’ (published in 1859), Darwin produced nineteen additional publications, wrote hundreds of scientific papers and fourteen thousand letters, all of which laid the foundations for Biology as a subject we recognise today. Although he did not invent the theory of evolution, he certainly made the idea more accessible to the world. His theory was evolution by natural selection; where by an organism with a mutation may be better adapted to certain environmental changes and therefore improve their chance of survival. This means the organism with the useful mutation is more likely to survive, reproduce and hopefully pass on the useful mutation. Overtime species are able to adapt to the world around them and this process gave the Galapagos Islands (and the world) the rich diversity of its inhabitants. Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA was first discovered in 1869 but its role was not known at the time. It was in 1943 that it was discovered that it is DNA that is responsible for programming the genetic makeup of organisms and passing on the mutations Darwin had discovered. This new understanding of how amino acids are programmed on a cellular level to make up various parts of the organism was a huge leap forward but new profound discoveries are being made everyday in the field of biology.
Smooth Sailing: Exploring the Functions and Importance of the Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a complex network of membranous tubules and sacs that are found in eukaryotic cells. It is one of the most important organelles in the cell, playing a crucial role in various cellular processes. The ER is involved in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, calcium homeostasis, drug metabolism, and the immune response, among other functions. The structure of the endoplasmic reticulum is highly dynamic and can vary depending on the cell type and its specific functions. There are two main types of ER: rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The RER is characterized by the presence of ribosomes on its surface, giving it a rough appearance under a microscope. The SER, on the other hand, lacks ribosomes and appears smooth. Both types of ER are interconnected and work together to carry out their respective functions. The endoplasmic reticulum is essential for the survival and proper functioning of the cell. It serves as a site for the synthesis of proteins and lipids, as well as for the storage and release of calcium ions. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis by regulating various cellular processes. Without the endoplasmic reticulum, cells would not be able to function properly and would be unable to carry out essential processes necessary for their survival. Key Takeaways The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a complex network of membranes found in eukaryotic cells. There are two types of ER: rough ER, which is studded with ribosomes and involved in protein synthesis, and smooth ER, which is involved in lipid metabolism and calcium homeostasis. The ER plays a crucial...
Exploring the Intricacies of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: A Journey into Cellular Biology
The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is a vital organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including protein synthesis, folding, and transport. The RER is characterized by its rough appearance due to the presence of ribosomes on its surface. These ribosomes are responsible for the synthesis of proteins that are destined for secretion or insertion into the cell membrane. The RER is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and is involved in intercellular communication. Understanding the structure and function of the RER is crucial for advancing our knowledge of cellular processes and developing new treatments for diseases. Key Takeaways The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a complex network of membranes that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and folding. The ER is involved in cellular communication and the secretory pathway, which allows cells to secrete proteins and other molecules. The ER works closely with the Golgi apparatus to transport and modify proteins before they are released from the cell. The ER is involved in cellular stress responses and can contribute to the development of diseases if not functioning properly. Research on the ER is ongoing and has the potential to lead to new discoveries and applications in the future. The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: An Overview of Its Structure and Function The rough endoplasmic reticulum is a network of interconnected membranous tubules and sacs called cisternae. It is located near the nucleus and extends throughout the cytoplasm of the cell. The RER is characterized by its rough appearance due to the presence of ribosomes attached to its surface. These ribosomes are responsible for protein...
Exploring the Intricacies of the Endoplasmic Reticulum: A Journey into the Cellular World
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a complex and dynamic organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including protein synthesis and folding, lipid metabolism, calcium signaling, cellular stress responses, autophagy, and cell-to-cell communication. The ER is composed of a network of interconnected tubules and flattened sacs called cisternae. It is divided into two main types: the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The RER is characterized by the presence of ribosomes on its surface, giving it a rough appearance under the microscope. It is primarily involved in protein synthesis and folding. The ribosomes on the RER synthesize proteins that are destined for secretion or insertion into the cell membrane. As the proteins are synthesized, they enter the lumen of the RER where they undergo folding and post-translational modifications. The RER also plays a role in quality control, ensuring that only properly folded proteins are allowed to leave the ER. On the other hand, the SER lacks ribosomes on its surface and is involved in various metabolic processes, including lipid metabolism, detoxification of drugs and toxins, and calcium storage. The SER is responsible for synthesizing lipids, such as phospholipids and cholesterol, which are essential components of cell membranes. It also plays a role in detoxifying harmful substances by modifying them to make them more water-soluble and easier to excrete from the cell. Additionally, the SER acts as a calcium reservoir, storing calcium ions that are important for various cellular processes. Key Takeaways The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a complex organelle with multiple functions in the cell. The ER plays a...
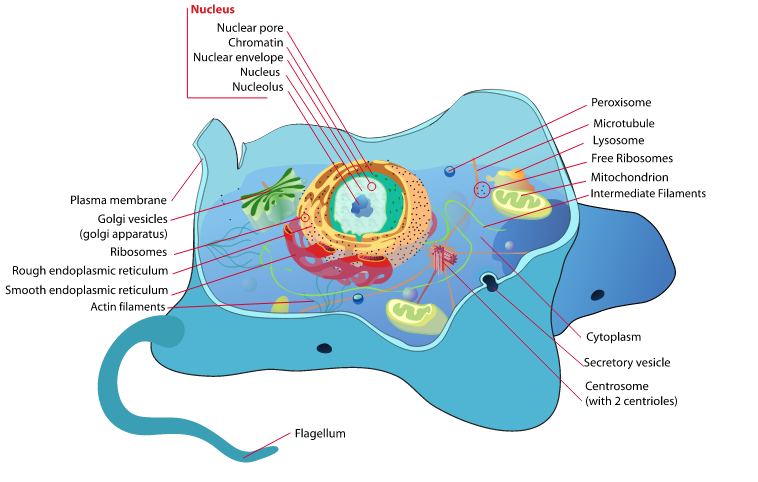
Nucleus: The Central Command of the Cell – Understanding its Importance in Biology
The nucleus is a vital component of eukaryotic cells, serving as the control center that regulates all cellular activities. It is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the genetic material of the cell, including DNA and RNA. The nucleus plays a crucial role in cell function, as it is responsible for regulating gene expression, controlling cell division, and maintaining genetic information. Key Takeaways The nucleus is the control center of the cell, responsible for regulating cellular activities. The nucleus is composed of DNA, RNA, and proteins, and is surrounded by a nuclear envelope. The nucleus plays a crucial role in DNA replication, transcription, and translation. The nucleolus is responsible for ribosome synthesis, which is essential for protein production. The nucleus is involved in cell division and differentiation, and dysfunction can lead to various health issues. The Structure and Composition of the Nucleus The nucleus is surrounded by a double-layered membrane called the nuclear envelope. This envelope separates the contents of the nucleus from the rest of the cell and contains nuclear pores that allow for the exchange of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Within the nucleus, there are various components, including chromatin, nucleolus, and nucleoplasm. Chromatin is a complex of DNA and proteins that make up the chromosomes. It is responsible for packaging and organizing the genetic material within the nucleus. The nucleolus is a distinct region within the nucleus where ribosomes are synthesized. It plays a crucial role in protein synthesis. The nucleoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the space between the nuclear envelope and chromatin. The Functions of the Nucleus in the Cell The nucleus performs...
Discovering the Commonalities: Unveiling the Similarities of Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells are a type of cell that make up the complex organisms we see around us, including plants, animals, fungi, and protists. These cells are characterized by having a distinct nucleus that houses their genetic material, as well as other membrane-bound organelles that perform specific functions within the cell. In contrast, prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are essential for the survival and functioning of living organisms. They are responsible for carrying out all the necessary processes for life, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and response to stimuli. Without eukaryotic cells, complex life as we know it would not exist. Key Takeaways Eukaryotic cells are complex cells that contain a nucleus and other organelles. The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains genetic material. Mitochondria are important organelles that produce energy for the cell. Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis in the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, cytoskeleton, lysosomes, and chloroplasts all play important roles in eukaryotic cell structure and function. The Structure of Eukaryotic Cells: A Closer Look Eukaryotic cells have a complex structure that allows them to carry out their various functions. At the most basic level, they are surrounded by a cell membrane that separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment. Inside the cell membrane is the cytoplasm, a gel-like substance that contains all the organelles and other cellular components. One of the most important organelles in eukaryotic cells is the nucleus. The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and is responsible for...
The Complex World of Eukaryotic Cells: A Closer Look at the Building Blocks of Life
Eukaryotic cells are the building blocks of complex organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi. They are characterized by having a distinct nucleus that houses their genetic material, as well as other membrane-bound organelles. In contrast, prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The complexity of eukaryotic cells arises from their ability to perform a wide range of specialized functions, which is essential for the survival and functioning of multicellular organisms. Eukaryotic cells are much larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells. They have a variety of organelles that perform specific functions within the cell. These organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and cytoskeleton. Each organelle has its own unique structure and function, contributing to the overall complexity of eukaryotic cells. The importance of eukaryotic cells in living organisms cannot be overstated. They are responsible for carrying out essential processes such as growth, development, reproduction, and metabolism. Eukaryotic cells also play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis within an organism by responding to changes in their environment and coordinating the activities of different cell types. Without eukaryotic cells, complex life as we know it would not be possible. Key Takeaways Eukaryotic cells are complex due to their membrane-bound organelles and specialized functions. The cell membrane regulates what enters and exits the cell, maintaining homeostasis. The nucleus contains genetic material and controls cellular processes through gene expression. Mitochondria produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus work together to synthesize, modify, and transport proteins and lipids. The Cell Membrane: The Gatekeeper of Eukaryotic Cells The cell...
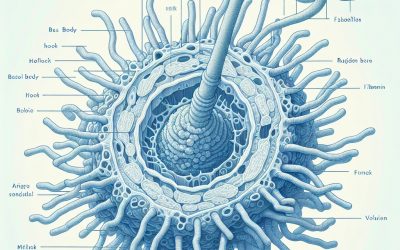
Uncovering the Wonders of Prokaryotic Flagellum: A Fascinating Look at Bacterial Movement
The prokaryotic flagellum is a whip-like appendage found on the surface of many bacteria. It is responsible for bacterial movement, allowing these microorganisms to navigate their environment and find optimal conditions for growth and survival. The flagellum is a complex structure that consists of several components, including a filament, a hook, and a basal body. This intricate machinery enables bacteria to move in response to various stimuli, such as light, temperature, and chemical gradients. The ability to move is crucial for bacteria as it allows them to search for nutrients, avoid harmful substances, and escape from predators. Bacterial movement is not only important for individual cells but also for the survival of bacterial populations as a whole. By being able to move towards favorable conditions and away from unfavorable ones, bacteria can increase their chances of survival and reproduction. Key Takeaways Prokaryotic flagellum is a whip-like structure that allows bacteria to move. The evolution of prokaryotic flagellum is still a topic of debate among scientists. The mechanics of prokaryotic flagellum involve a complex system of proteins and energy sources. Prokaryotic flagellum plays a crucial role in bacterial survival by aiding in nutrient acquisition and defense against predators. There are different types of prokaryotic flagellum, each with unique adaptations for specific environments. The basics of prokaryotic flagellum: Understanding the structure and function of bacterial movement. The prokaryotic flagellum is composed of three main parts: the filament, the hook, and the basal body. The filament is a long, helical structure made up of a protein called flagellin. It extends from the cell surface and acts as a propeller, generating the force...
Revolutionize Your Daily Routine with Capsule – The Ultimate Productivity Tool
In today’s fast-paced world, productivity has become a key factor in achieving success both personally and professionally. With so many tasks and responsibilities to juggle, it can be challenging to stay organized and focused. That’s where Capsule comes in. Capsule is a revolutionary productivity tool designed to help individuals streamline their daily lives and maximize their efficiency. In this article, we will explore what Capsule is, how it can help you, and the benefits of incorporating it into your routine. Key Takeaways Capsule is a productivity tool that helps you organize your tasks and goals. Using Capsule can increase productivity by helping you prioritize and focus on important tasks. Capsule can revolutionize your morning routine by providing a clear plan for the day ahead. Capsule is the ultimate tool for time management, allowing you to track and manage your time effectively. Capsule can help you stay focused and motivated by breaking down larger goals into smaller, achievable tasks. What is Capsule and How Can It Help You? Capsule is a digital tool that combines various features to help individuals manage their time, stay organized, and achieve their goals. It acts as a central hub for all your tasks, appointments, and reminders, allowing you to have a clear overview of your day and prioritize your activities effectively. With Capsule, you can create to-do lists, set reminders, track your progress, and even collaborate with others on shared projects. One of the key benefits of Capsule is its ability to integrate with other productivity tools and platforms, such as calendars, email clients, and project management software. This seamless integration allows you to...
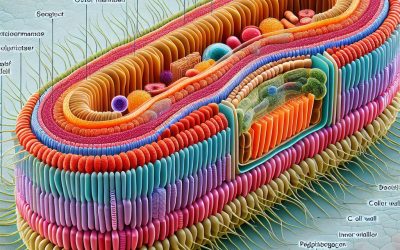
The Mighty Shield: Understanding the Importance of Bacteria Cell Wall in Microbial World
The bacteria cell wall is a crucial component of the microbial world. It provides structural support to the cell, protects against environmental stressors, plays a role in antibiotic resistance, impacts pathogenesis and disease, and has evolved over time to adapt to different environments. Understanding the structure and function of the bacteria cell wall is essential for studying microbiology and has significant implications in various fields such as biotechnology and industry. Key Takeaways Bacteria cell walls play a crucial role in maintaining cell shape and integrity. The cell wall also protects against environmental stressors and contributes to antibiotic resistance. The diversity of bacteria cell walls across different species has evolutionary significance. Bacteria cell walls have applications in biotechnology and industry. Overall, the bacteria cell wall is vital to the microbial world. The Structure and Composition of Bacteria Cell Wall The bacteria cell wall is composed of different layers and components that vary between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. In gram-positive bacteria, the cell wall consists of a thick layer of peptidoglycan, which is made up of repeating units of sugar molecules cross-linked by short peptide chains. This layer provides rigidity and strength to the cell. On the other hand, gram-negative bacteria have a thinner layer of peptidoglycan surrounded by an outer membrane composed of lipopolysaccharides (LPS). The LPS layer acts as a barrier against certain antibiotics and toxins. The Importance of Bacteria Cell Wall in Maintaining Cell Shape and Integrity The bacteria cell wall plays a crucial role in maintaining the shape and integrity of the cell. It provides structural support, preventing the cell from collapsing under its own weight. The...
Nucleoid: The Central Hub of Bacterial DNA Organization
The nucleoid is a distinct region within bacterial cells where the genetic material, DNA, is located. Unlike eukaryotic cells, bacteria do not have a membrane-bound nucleus. Instead, their DNA is organized and compacted within the nucleoid. The nucleoid plays a crucial role in bacterial physiology as it houses the genetic information necessary for cell growth, division, and survival. The nucleoid is essential for bacterial cells as it contains all the genetic instructions required for their survival and reproduction. It serves as the control center for gene expression, regulating the synthesis of proteins and other molecules necessary for cellular processes. The nucleoid also plays a role in DNA replication and repair, ensuring the accurate transmission of genetic information to daughter cells during cell division. Key Takeaways The nucleoid is the region in bacteria where the genetic material is located. The nucleoid is not enclosed by a membrane and is composed of DNA, RNA, and proteins. Nucleoid proteins play a crucial role in DNA compaction and regulation. The interactions between nucleoid proteins and DNA are essential for proper DNA replication and transcription. Environmental factors can affect nucleoid organization and function, making it a potential target for antibacterial drug development. Anatomy and Structure of the Nucleoid The size and shape of the nucleoid can vary depending on the bacterial species and growth conditions. In general, the nucleoid is compacted into a dense mass within the bacterial cell. It is typically located near the center of the cell, although its exact position can vary. The composition of the nucleoid primarily consists of DNA, which is tightly packed and organized within the cell. The...
Unleashing the Power of Plasmids: How Genetic Engineering is Revolutionizing Science
Genetic engineering is the process of manipulating an organism’s genetic material to alter its characteristics or create new traits. This field of science has revolutionized various industries, including medicine, agriculture, and environmental conservation. At the heart of genetic engineering are plasmids, which are small, circular DNA molecules that can replicate independently within a host cell. Plasmids play a crucial role in genetic engineering as they serve as the building blocks for introducing foreign DNA into an organism. These small DNA molecules can be easily manipulated in the laboratory and can carry specific genes or traits that scientists want to introduce into an organism. By using plasmids, scientists can transfer genes between different organisms, creating genetically modified organisms (GMOs) with desired traits. The importance of genetic engineering and plasmids in science cannot be overstated. They have opened up new possibilities for improving human health, increasing crop yields, and addressing environmental challenges. Through genetic engineering, scientists can develop new drugs, create disease-resistant crops, and even clean up polluted environments. The potential applications of genetic engineering and plasmids are vast and continue to expand as our understanding of genetics grows. Key Takeaways Plasmids are circular DNA molecules that can be used as tools in genetic engineering. Genetic engineering and plasmids have a long history, dating back to the 1970s. Applications of genetic engineering and plasmids include creating genetically modified organisms, producing recombinant proteins, and gene therapy. Advantages of genetic engineering and plasmids include the ability to create new medicines and crops, while limitations include ethical concerns and potential unintended consequences. Techniques used in genetic engineering and plasmids include PCR, CRISPR/Cas9, and gene...
Pili: The Superfood You Need to Add to Your Diet Now
Pili nuts, also known as Canarium ovatum, are a type of nut that is native to Southeast Asia, particularly the Philippines. They have been a staple in Filipino cuisine for centuries and are now gaining popularity worldwide as a nutritious superfood. Pili nuts are not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients that can benefit your overall health. Pili nuts have a rich history and origin. They have been cultivated in the Philippines for over 1,000 years and were traditionally used by indigenous communities for their medicinal properties. The trees that produce pili nuts are tall and majestic, reaching up to 30 meters in height. The nuts themselves are enclosed in a hard shell, which is cracked open to reveal the edible kernel inside. In terms of nutritional value, pili nuts are a powerhouse. They are rich in healthy fats, protein, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals. A 1-ounce (28-gram) serving of pili nuts contains approximately 200 calories, 22 grams of fat, 3 grams of protein, and 2 grams of fiber. They are also a good source of magnesium, phosphorus, and vitamin E. Key Takeaways Pili nuts are a nutritious superfood that are rich in healthy fats. Adding pili nuts to your diet can provide numerous health benefits, including protein and fiber. Pili nuts are a low-carb snack that can aid in weight loss. Pili nuts are an antioxidant-rich superfood that can boost your mood naturally. Incorporating pili nuts into your daily diet is easy and can be done in a variety of ways. Pili Nuts: A Rich Source of Healthy Fats One of the key nutritional benefits...