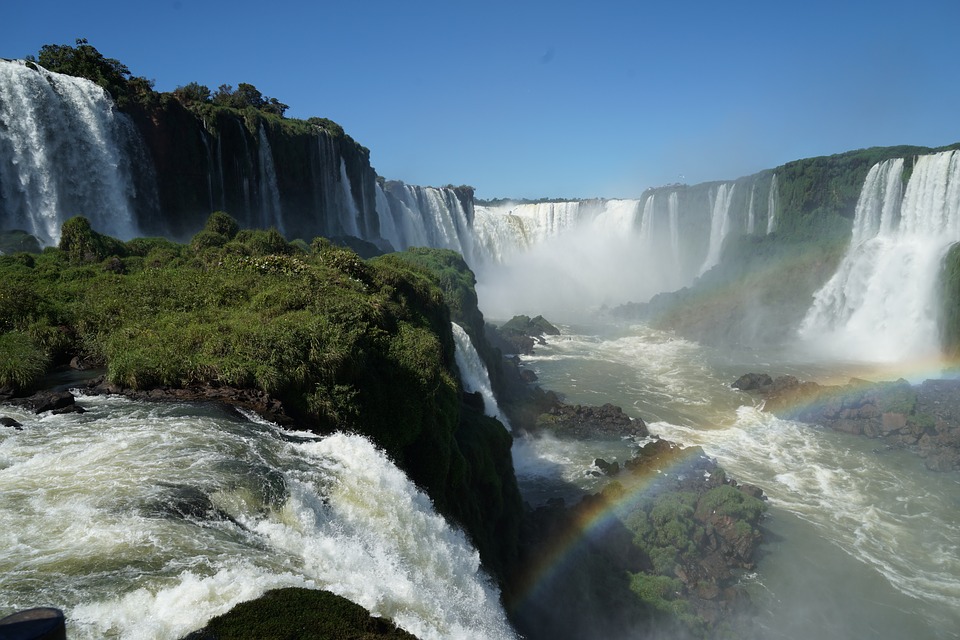
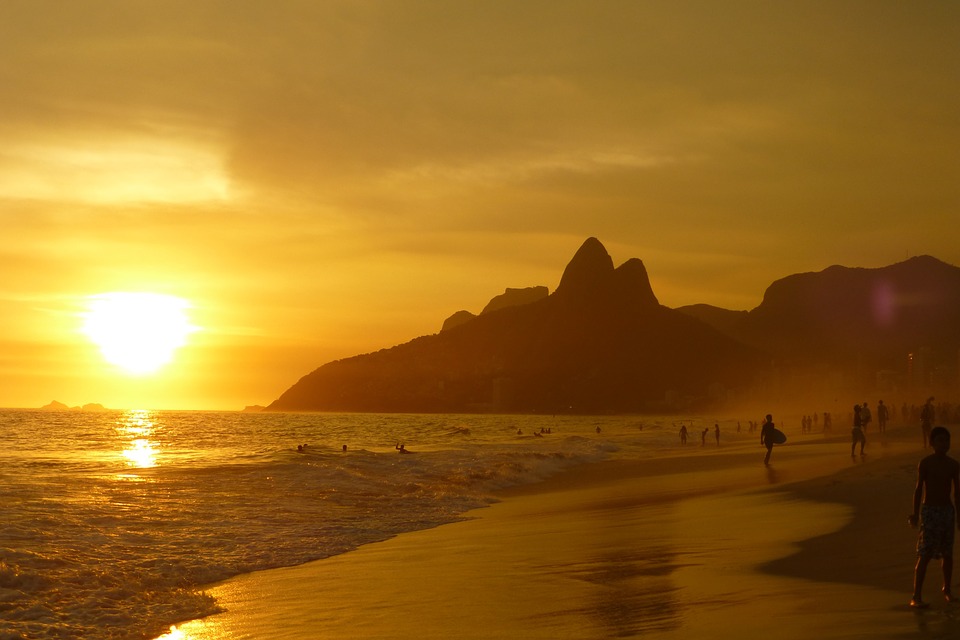
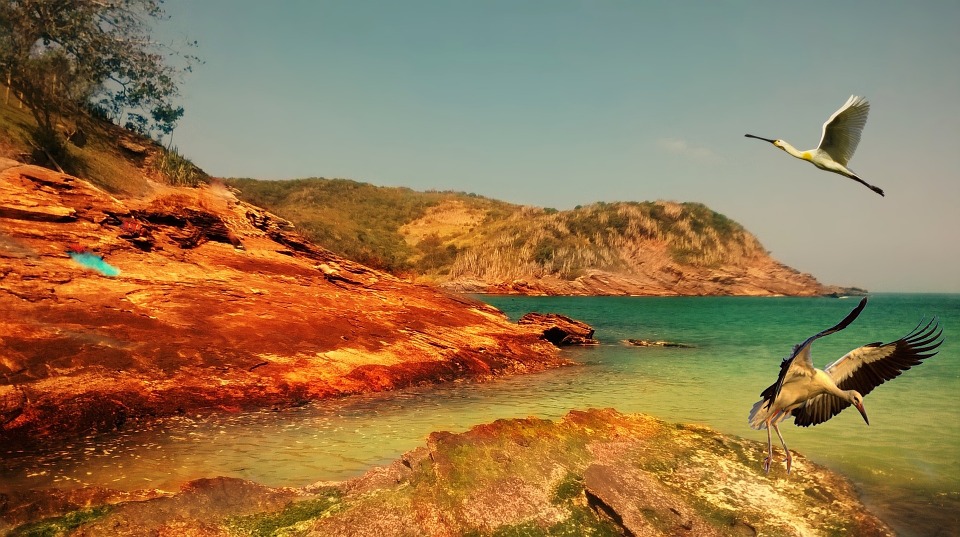
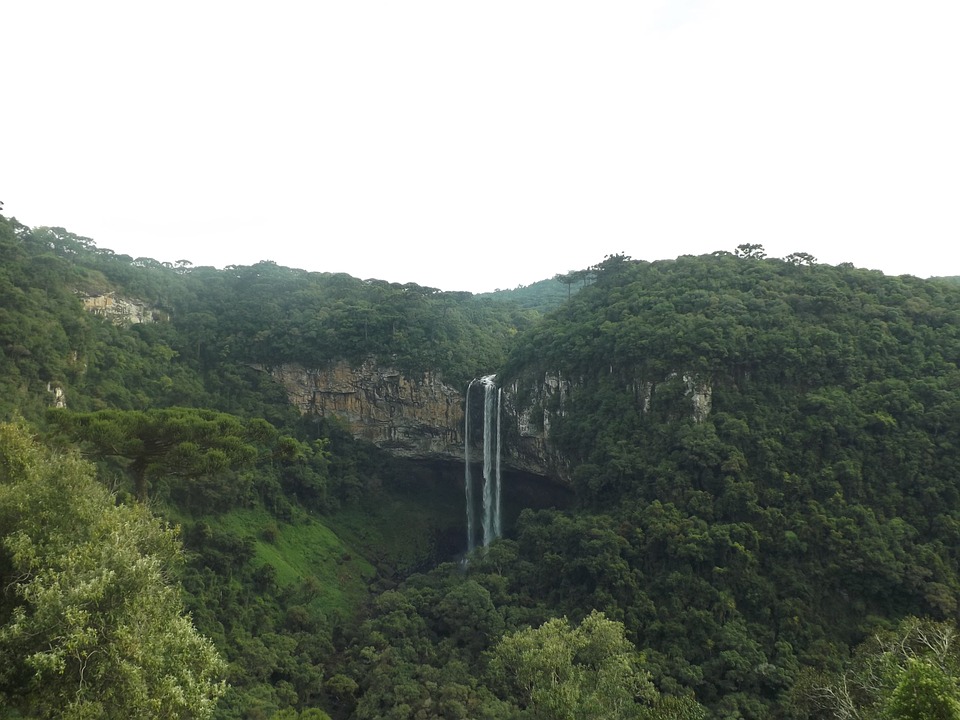
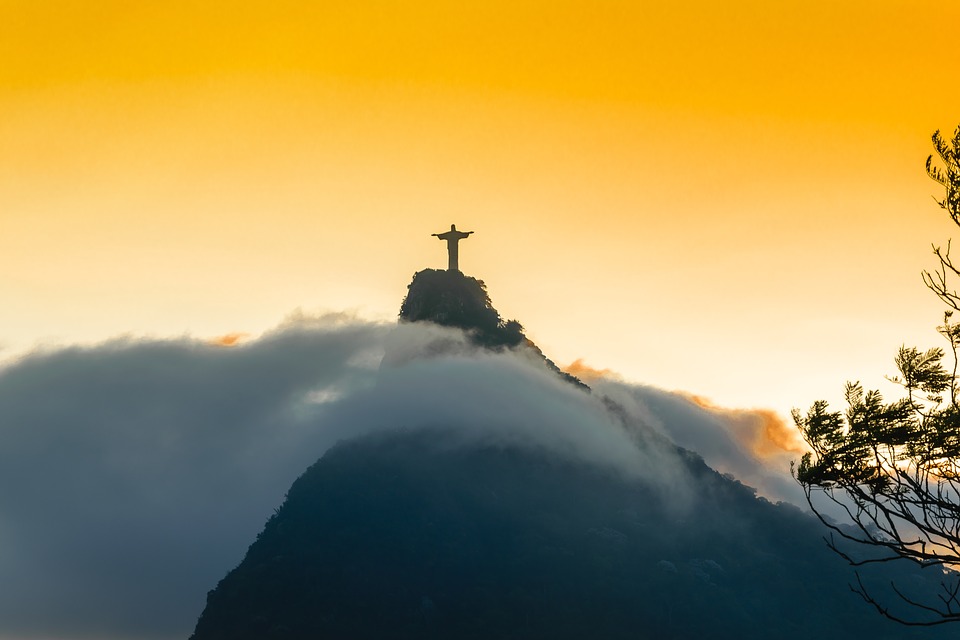
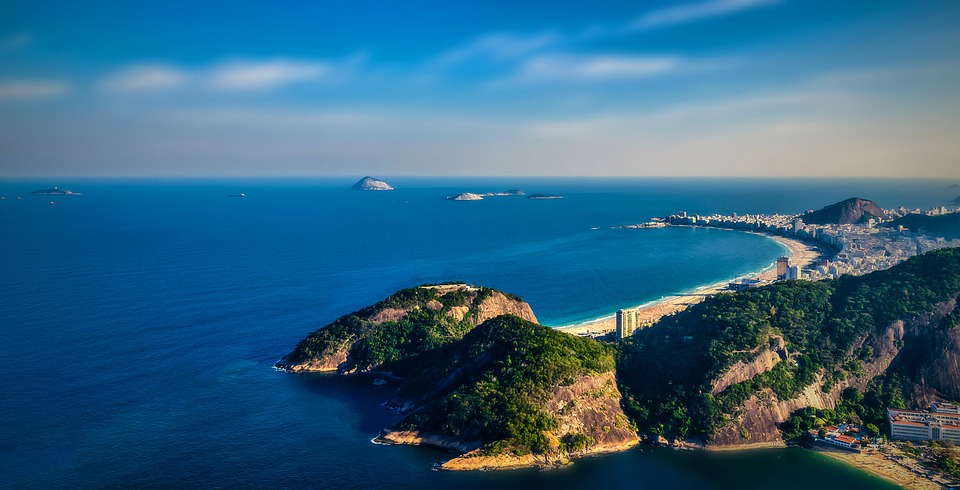
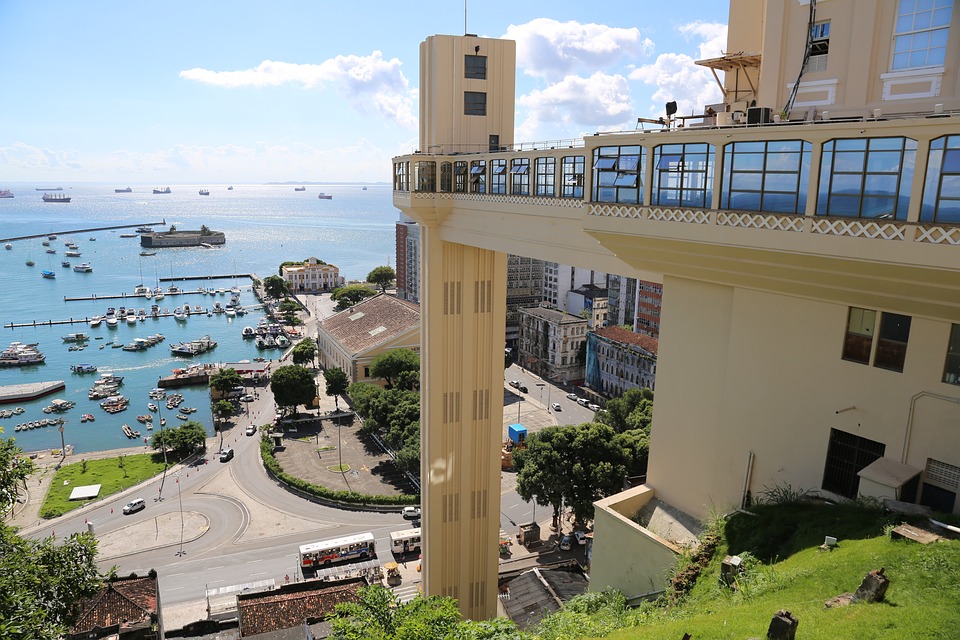
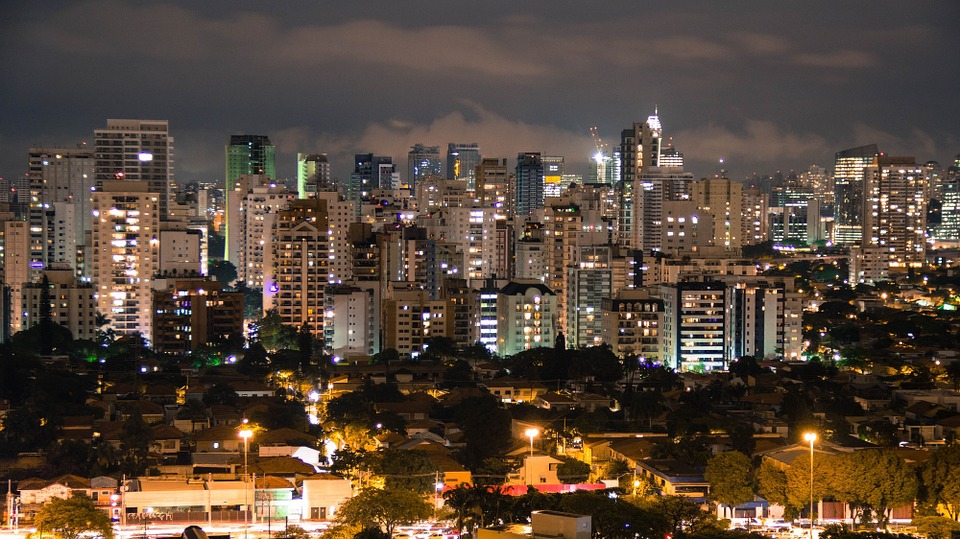
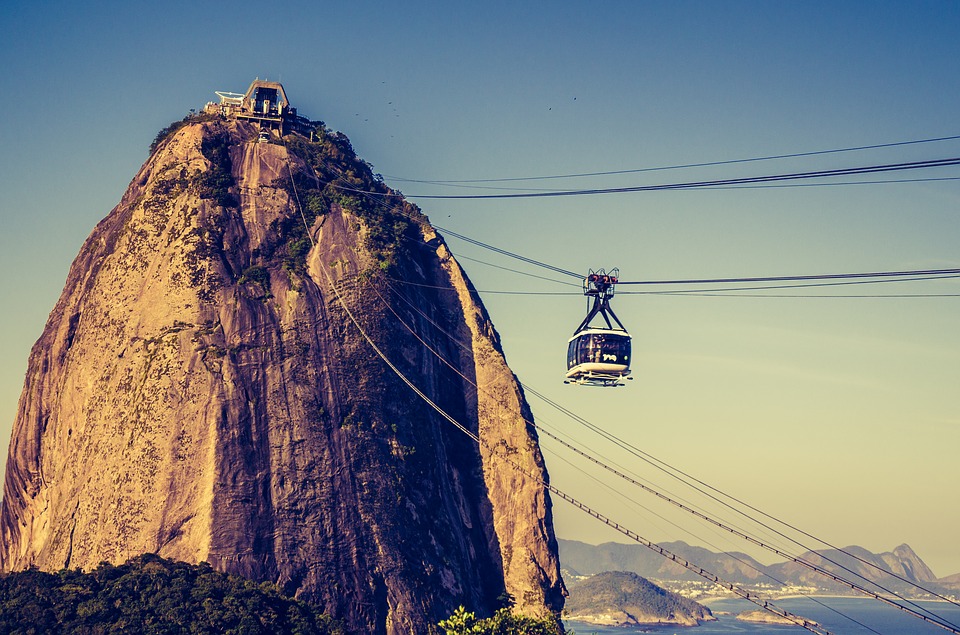
Brazil
(República Federativa do Brasil (Federative Republic of Brazil))
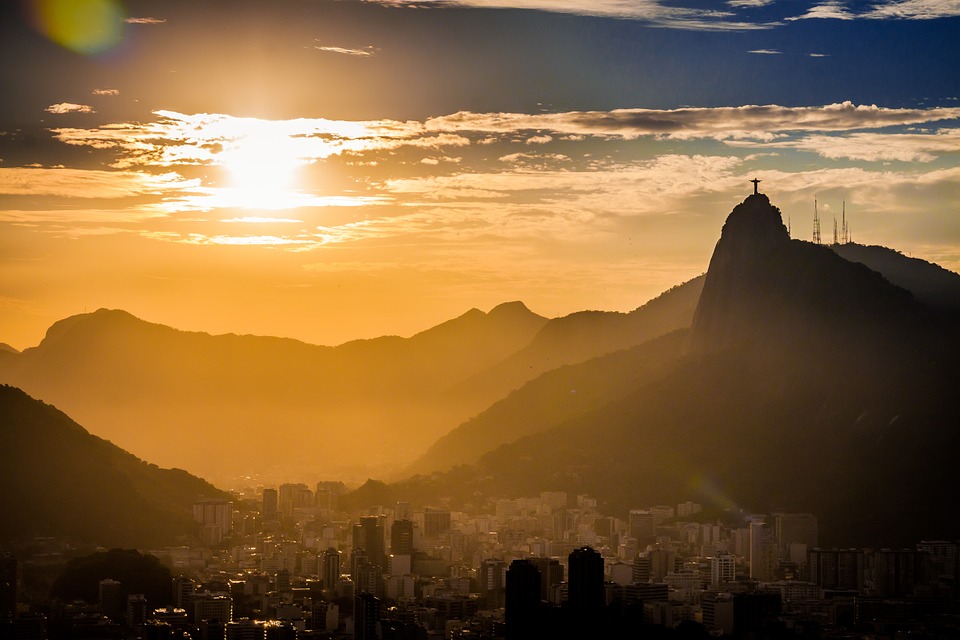

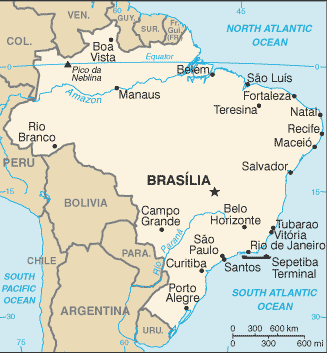
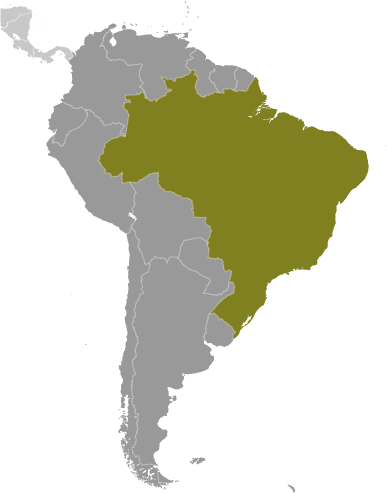




Capital of Brazil : Brasília
Population (Estimated July 2012): 205,716,890
Area: 8,514,877 km2 or 3,287,612 mi2
Currency: Real (R$; plural Reais)
Official Language: Portuguese
Political Information: Federal Presidential Constitutional Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 75%of the population are Roman Catholic)
Highest Mountain: Pico da Neblina (Fog Peak) at 2,994m or 9,823ft
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $2.518 trillion (US$) or £1.51 trillion (GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $2.309 trillion (US$) or £1.385 trillion (GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $11,600 (US$) or £6,960 (GBP)
Time Zone GMT (UTC): -3:00
Counties/Provinces/States: 26 states (estados, singular – estado) and 1 federal district* (distrito federal); Acre, Alagoas, Amapa, Amazonas, Bahia, Ceara, Distrito Federal*, Espirito Santo, Goias, Maranhao, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Para, Paraiba, Parana, Pernambuco, Piaui, Rio de Janeiro, Rio Grande do Norte, Rio Grande do Sul, Rondonia, Roraima, Santa Catarina, Sao Paulo, Sergipe, Tocantins
Leaders: President is Dilma Rousseff and Michel Temer as Vice President.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
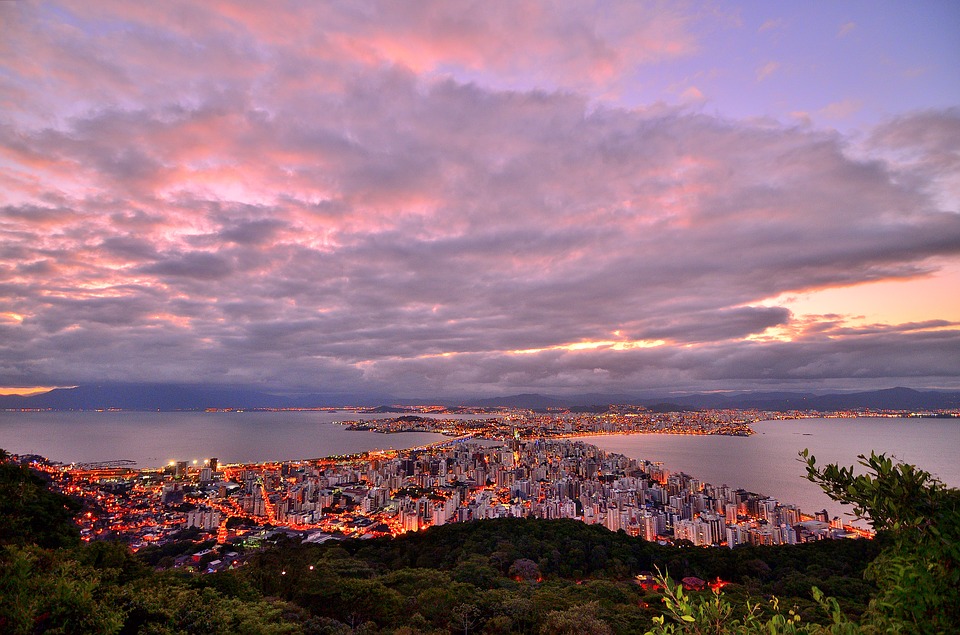
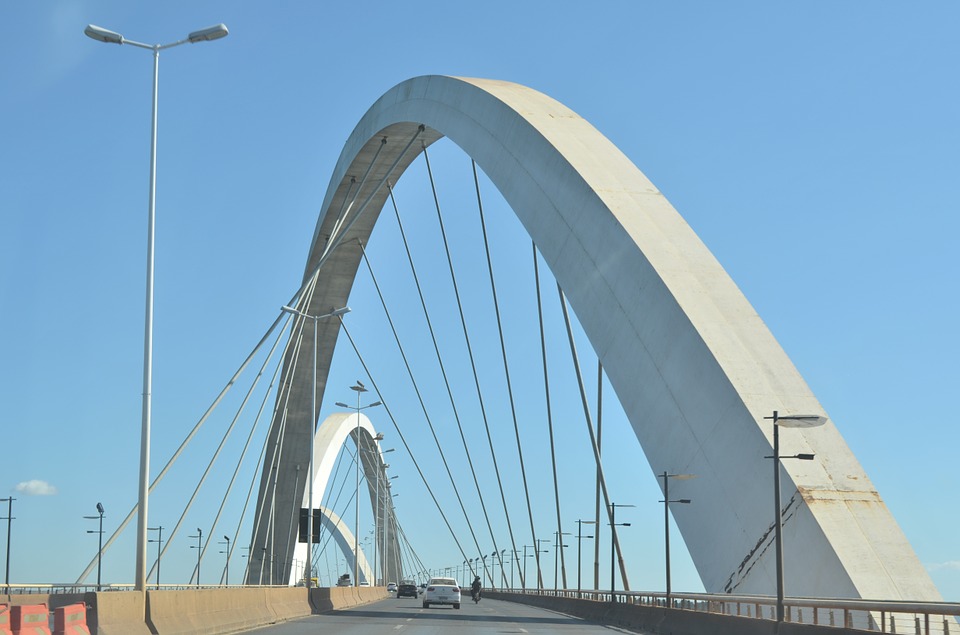
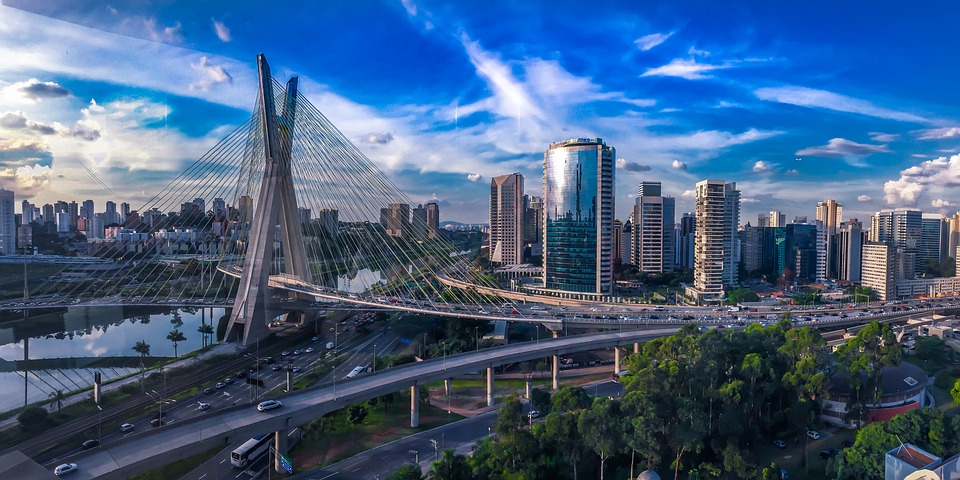
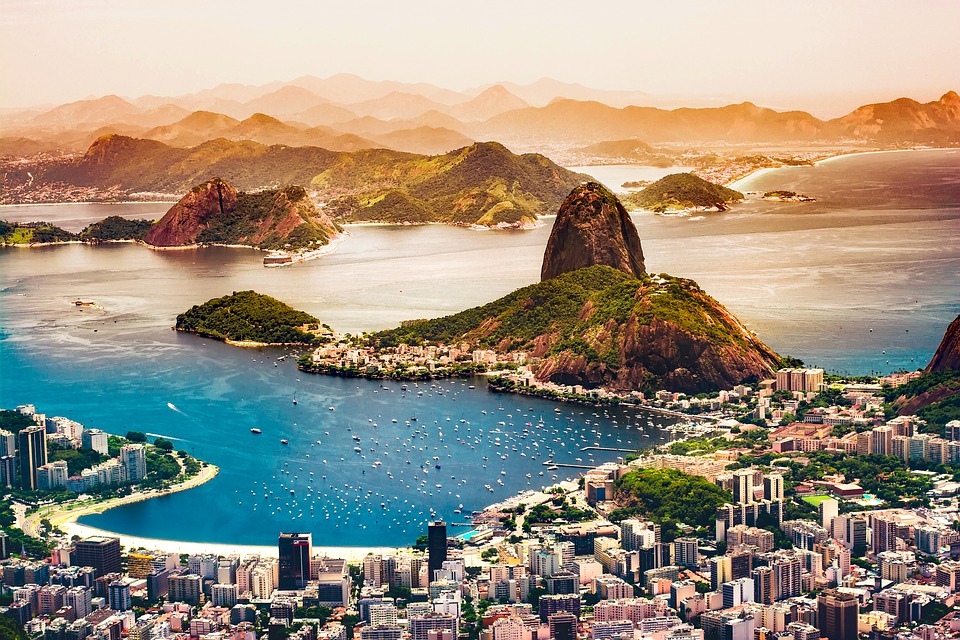
Brazil, located in South America, is the largest country on the continent and the fifth largest in the world. It spans over 8.5 million square kilometres and has a population of approximately 211 million people. Brazil is known for its vibrant culture, stunning natural landscapes, and emerging economy. It is a country of great importance in South America and the world.
Brazil’s Rich Cultural Heritage and Diversity
Brazil’s culture is a melting pot of influences from its indigenous people, Portuguese colonizers, African slaves, and immigrants from Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. This rich blend of cultures has shaped Brazilian traditions, art, music, and literature.
Brazilian art is diverse and reflects the country’s cultural heritage. From indigenous art to modernist movements like Tarsila do Amaral’s Anthropophagy, Brazilian art showcases a unique fusion of styles and themes. Brazilian music is also incredibly diverse, with genres such as samba, bossa nova, and forró gaining international recognition. Brazilian literature has produced renowned authors like Machado de Assis and Clarice Lispector, whose works explore themes of identity, race, and social inequality.
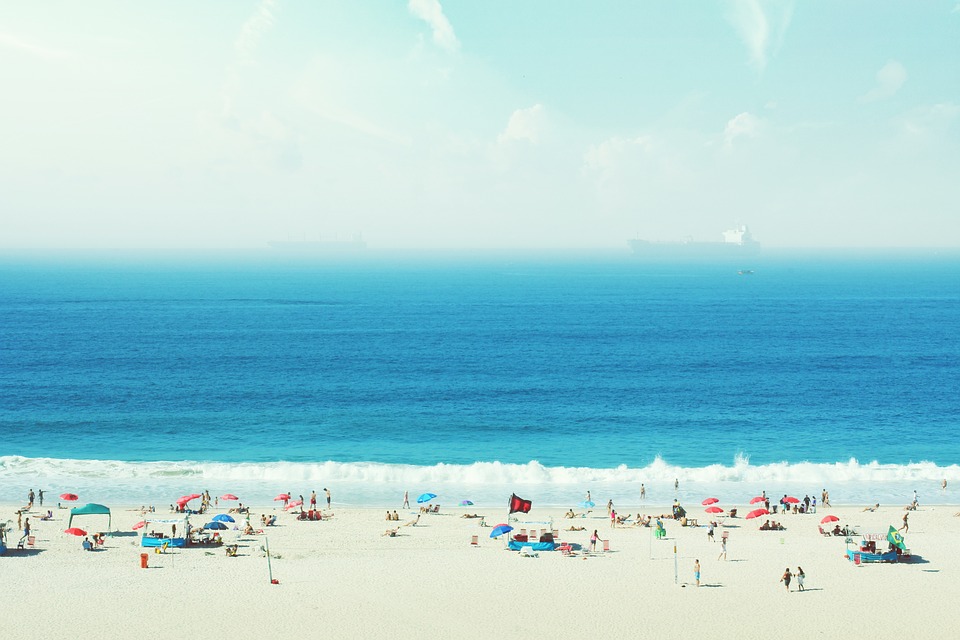
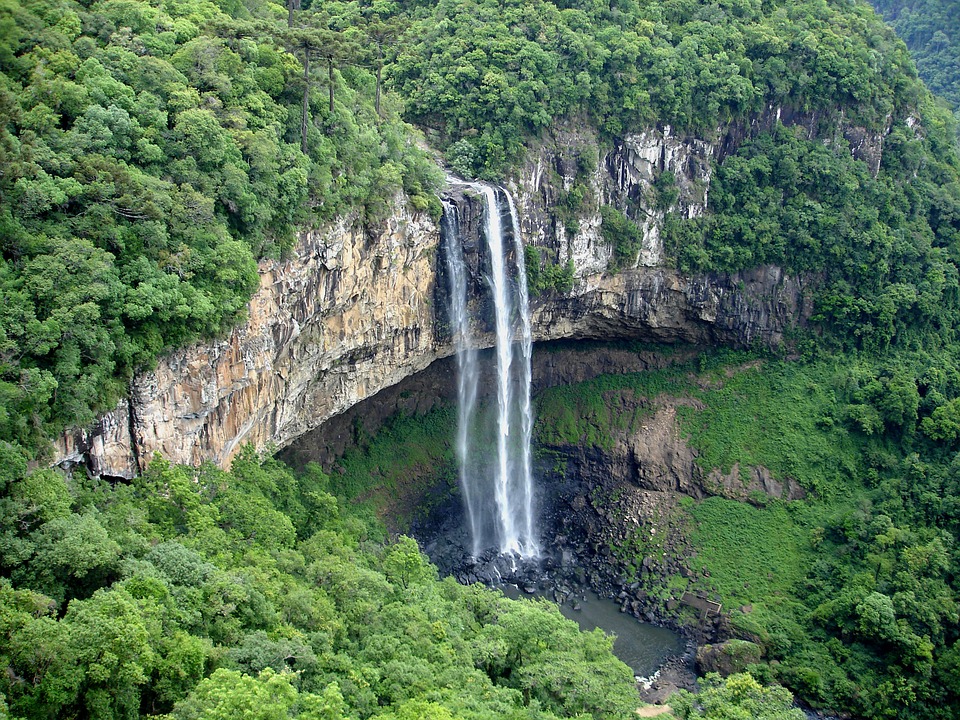
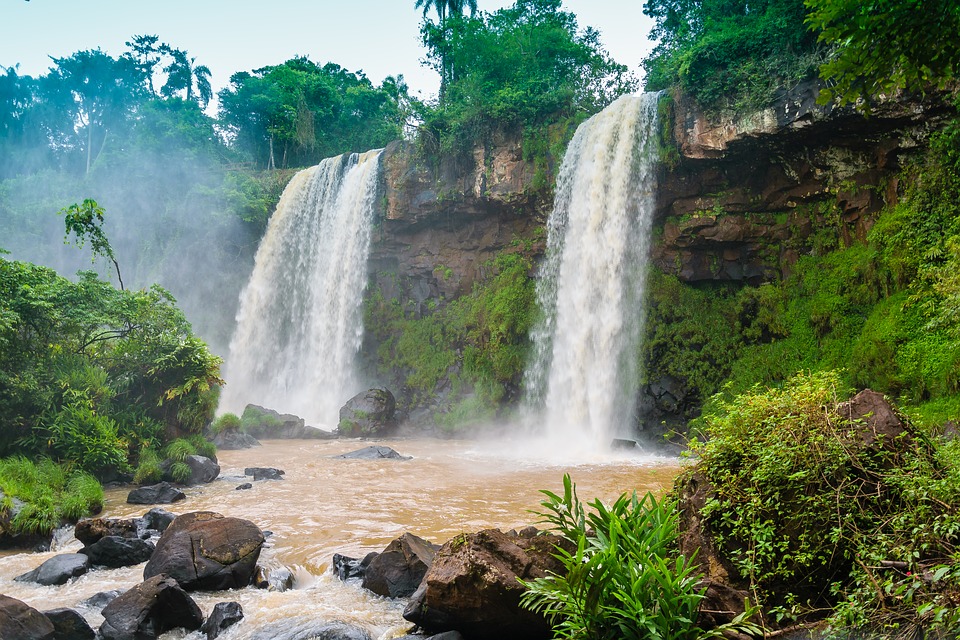
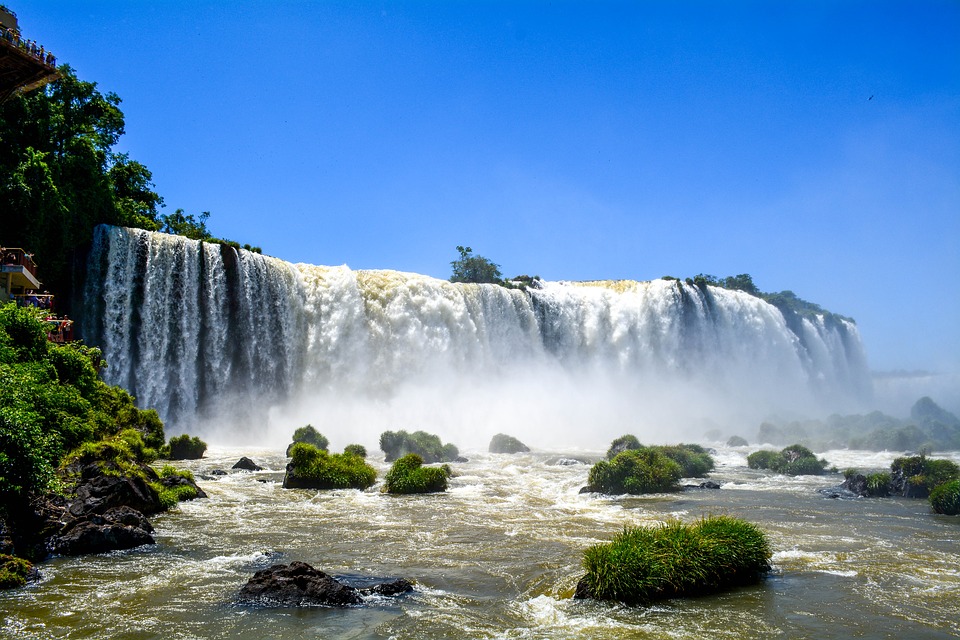
Brazil’s Natural Wonders: From the Amazon to the Beaches
Brazil is home to a wide range of ecosystems, making it one of the most biodiverse countries in the world. The Amazon rainforest is the largest tropical rainforest on Earth and plays a crucial role in regulating the planet’s climate. The Pantanal wetlands are another natural wonder, known for their incredible biodiversity and stunning landscapes.
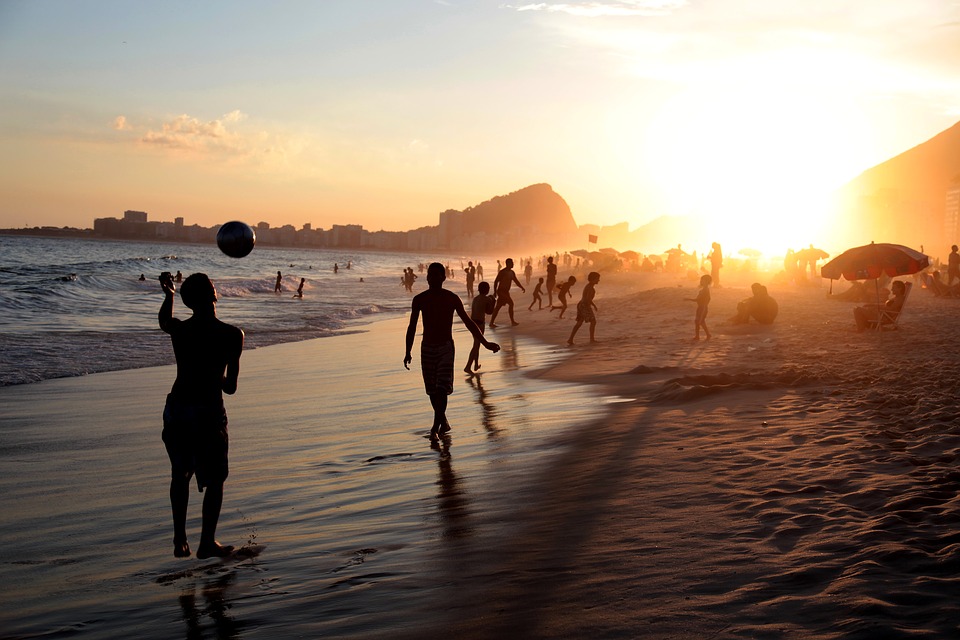
Brazil’s coastline stretches for over 7,000 kilometres and boasts some of the most beautiful beaches in the world. From Copacabana in Rio de Janeiro to Praia do Forte in Bahia, Brazil offers a variety of beach destinations for tourists to enjoy.
Preserving Brazil’s natural resources is of utmost importance. Deforestation in the Amazon and pollution in the oceans are major challenges that need to be addressed. Sustainable development and conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the preservation of Brazil’s natural wonders for future generations.
Brazil’s Economy: Emerging Markets and Growing Industries
Brazil has the largest economy in South America and is considered one of the world’s emerging markets. It has a diverse economy, with major industries including agriculture, manufacturing, mining, and services.
Brazil is a major player in the global economy, being one of the largest producers and exporters of agricultural products such as soybeans, coffee, and beef. It is also a leading producer of iron ore and has a growing manufacturing sector.
However, Brazil faces challenges such as income inequality, corruption, and an outdated infrastructure. To overcome these challenges, Brazil needs to invest in education, innovation, and infrastructure development. By doing so, Brazil can continue to grow and attract foreign investment.
Brazilian Cuisine: A Fusion of Flavours and Influences
Brazilian cuisine is a reflection of the country’s diverse cultural heritage. It combines indigenous ingredients with Portuguese, African, and immigrant influences.
Feijoada is one of Brazil’s most famous dishes, a hearty black bean stew with pork. Other popular dishes include acarajé (deep-fried balls of black-eyed pea dough filled with shrimp), pão de queijo (cheese bread), and brigadeiro (chocolate truffles).
Brazilian cuisine also includes a variety of tropical fruits such as açaí, guava, and passion fruit. These fruits are often used in juices, desserts, and cocktails.
Food plays an important role in Brazilian culture, with meals being a time for family and friends to come together. Barbecues, known as churrascos, are a popular social gathering where people enjoy grilled meats and traditional side dishes.
Brazil’s Festivals and Celebrations: Carnivals, Football and More
Brazil is famous for its vibrant festivals and celebrations. The most well-known is the Rio Carnival, a week-long extravaganza of music, dance, and elaborate costumes. The carnival attracts millions of tourists from around the world who come to experience the energy and excitement of the event.
Football is another major celebration in Brazil. The country has a deep passion for the sport, and football matches are a time for people to come together and support their favourite teams. The Maracanã Stadium in Rio de Janeiro is one of the most iconic football stadiums in the world.
Other festivals celebrated in Brazil include Festa Junina, a traditional celebration of rural life with music, dance, and food; and Bumba Meu Boi, a folk festival that tells the story of a resurrected ox.
These festivals and celebrations are not only a time for joy and entertainment but also hold cultural significance. They showcase Brazil’s rich traditions and bring people together to celebrate their shared heritage.
Brazil’s People: Warm and Welcoming with a Passion for Life
Brazilian people are known for their warmth, friendliness, and passion for life. They have a strong sense of community and value relationships with family and friends.
Hospitality is an important aspect of Brazilian culture. Visitors are often welcomed with open arms and treated like family. Brazilians are known for their generosity and willingness to help others.
Brazilian values include joy, resilience, and adaptability. Despite facing challenges such as poverty and inequality, Brazilians have a positive outlook on life and find ways to enjoy themselves through music, dance, and social gatherings.
Brazil’s History: From Colonialism to Modernity
Brazil was colonized by the Portuguese in the 16th century and remained under Portuguese rule until it gained independence in 1822. The country has a complex history marked by slavery, social inequality, and political changes.
Brazil’s modern history has seen periods of military dictatorship, economic instability, and social unrest. However, in recent years, Brazil has made significant progress in terms of democracy and social development.
Brazil’s history has shaped its culture and society. The legacy of slavery and colonialism is still evident in issues of race and inequality. However, Brazil is also a country that celebrates its diversity and strives for social justice.
Brazil’s Environmental Challenges: Conservation Efforts and Sustainable Development
Brazil faces significant environmental challenges, including deforestation in the Amazon rainforest, pollution in its rivers and oceans, and the impact of climate change.
Conservation efforts are crucial to protect Brazil’s natural resources. Initiatives such as protected areas, reforestation projects, and sustainable agriculture practices are being implemented to preserve the country’s biodiversity.
Sustainable development is also a priority for Brazil. The country is investing in renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power, as well as promoting eco-tourism and responsible farming practices.
Preserving Brazil’s natural resources is not only important for the environment but also for the livelihoods of local communities who depend on these resources for their survival.
Brazil’s Future: Opportunities and Challenges in a Rapidly Changing World
Brazil has great potential for growth and development. It has a young population, abundant natural resources, and a diverse economy. However, it also faces challenges such as income inequality, corruption, and environmental degradation.
To overcome these challenges, Brazil needs to invest in education, innovation, and infrastructure development. It also needs to address social inequalities and promote sustainable development practices.
By harnessing its strengths and addressing its weaknesses, Brazil can continue to thrive in the 21st century. With its rich cultural heritage, stunning natural landscapes, and vibrant people, Brazil is truly a South American gem.
Natural Resources of Brazil: Where Natural Resources are Located in Brazil
Natural Resources of Brazil: Where Natural Resources are Located in Brazil Brazil, the world’s fifth-largest country by area, is a land blessed with a variety of natural resources that not only shape its economy but also have far-reaching impacts on the global climate and trade. From its hydroelectric power infrastructure to the lush Amazon rainforest, Brazil’s abundant renewable and biological resources make it a powerhouse in Latin America. This article dives deep into the natural resources of Brazil, how they’re managed, and their significance on both local and international levels, especially through the lens of institutions like the World Bank. Whether you’re interested in hydropower, mining, agriculture, or renewable energy, this article is worth reading for a comprehensive understanding of how Brazil leverages its vast natural heritage to remain a major power in the modern world. Article Outline 1. What Makes Brazil So Rich in Natural Resources? 2. How Important Is Hydroelectric Power in Brazil? 3. What Role Does the Amazon Rainforest Play in Brazil’s Economy? 4. Why Are Brazil’s Mineral Reserves So Strategic? 5. How Does Brazil Balance Energy Production with Environmental Concerns? 6. What Are Brazil’s Major Agricultural Products and Their Global Impact? 7. How Does the Brazilian Government Manage Its Natural Resources? 8. What Are the Challenges Facing Brazil’s Renewable Energy Future? 9. How Do Water Bodies and Rivers Contribute to Brazil’s Energy Potential? 10. What Is the Role of the World Bank in Developing Brazil’s Resource Sectors? 1. What Makes Brazil So Rich in Natural Resources? Brazil’s vast land area includes a rich mosaic of ecosystems and climates that support an impressive variety of...
Political Boundaries of Brazil: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Brazil, the largest country in South America, is known for its vibrant culture, diverse landscapes, and rich history. One aspect of Brazil that often goes unnoticed but is of great importance is its political boundaries. These boundaries define the country’s territorial limits and play a crucial role in shaping its governance and development. In this article, we will explore Brazil’s political boundaries in detail, examining their historical significance, the evolution of the provincial system, the role of districts and municipalities, territorial disputes, and the impact on regional development. By understanding Brazil’s political boundaries, we can gain a deeper insight into the country’s complex political landscape. Summary Brazil’s political boundaries are divided into 26 states and one federal district. The provincial system in Brazil has evolved over time, with changes in the number and size of provinces. Understanding Brazil’s districts is important for navigating the country’s complex political system. Brazil’s political boundaries have historical significance, reflecting the country’s colonial past and territorial expansion. The formation and governance of Brazil’s provinces vary, with some having more autonomy than others. Brazil’s Political Boundaries: An Overview Brazil shares borders with ten neighboring countries, including Argentina, Bolivia, Colombia, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, Venezuela, and French Guiana. These borders are defined by natural features such as rivers and mountains and are crucial for maintaining peaceful relations with its neighbors. The country is also divided into 26 states and one federal district, which is home to the capital city of Brasília. Each state has its own government and is responsible for local governance within its borders. The federal government plays a significant role in defining...
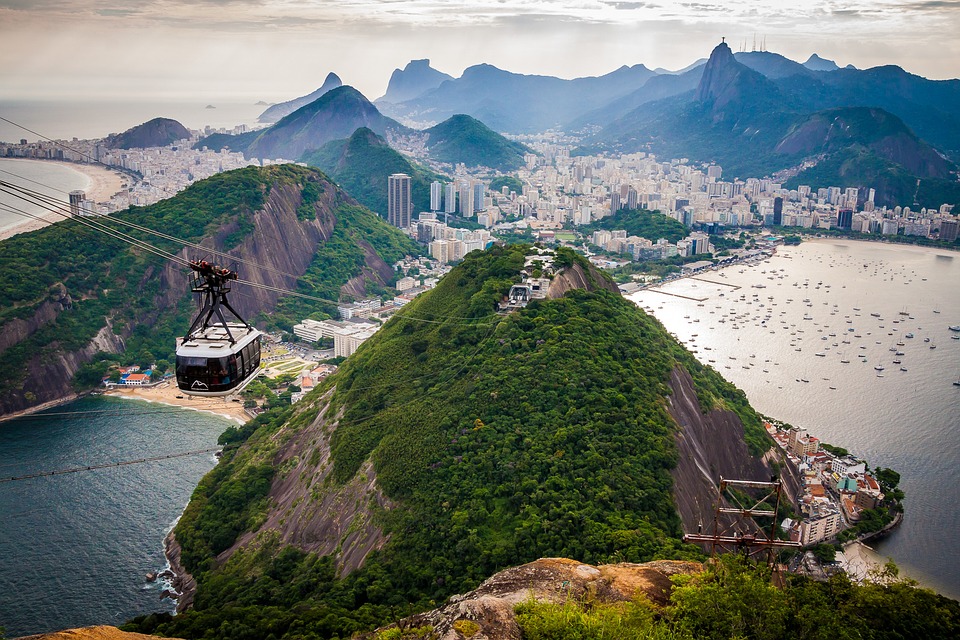
Cultural or Historical Sites of Brazil: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Brazil
Brazil is a country known for its rich cultural heritage and diverse history. From its indigenous roots to its colonial past, Brazil’s history has shaped its architecture, art, and traditions. This article will explore the various aspects of Brazil’s cultural heritage, including its colonial architecture, ancient ruins, historic churches, museums and art galleries, national parks, iconic landmarks, festivals, Afro-Brazilian culture, Portuguese influence, and historical sites of resistance. By delving into these different facets of Brazil’s heritage, we can gain a deeper understanding and appreciation for the country’s vibrant culture. Summary Brazil’s colonial architecture boasts a rich history that reflects the country’s diverse cultural influences. Ancient ruins of Brazil’s indigenous peoples offer a glimpse into the country’s pre-colonial past and cultural heritage. Brazil’s historic churches and cathedrals hold significant religious and cultural importance for the country’s people. Museums and art galleries in Brazil offer a fascinating insight into the country’s art, history, and culture. Brazil’s national parks and protected areas are crucial for preserving the country’s unique biodiversity and natural beauty. The Rich History of Brazil’s Colonial Architecture Brazil’s colonial period had a significant impact on its architecture. The Portuguese arrived in Brazil in the 16th century and established colonies along the coast. They brought with them their architectural styles, which were influenced by the Renaissance and Baroque movements in Europe. Examples of colonial architecture can be found in cities such as Salvador and Olinda. Salvador, the capital of the state of Bahia, is known for its well-preserved colonial architecture. The historic center of Salvador, known as Pelourinho, is a UNESCO World Heritage site and is home to numerous colonial...
Climate Zones of Brazil: Different climate regions Of Brazil
Brazil, the largest country in South America, is known for its diverse geography and rich natural resources. This diversity is also reflected in its climate zones, which vary from hot and humid in the north to mild and wet in the southeast. Understanding these climate zones is important for both travelers and residents alike, as it can help them prepare for the weather conditions they may encounter. Summary Brazil has a diverse range of climate zones, each with its own unique weather patterns and characteristics. The tropical climate zone in the north is hot and humid, while the subtropical climate zone in the south has milder temperatures. The semi-arid climate zone in the northeast is dry and hot, while the equatorial climate zone in the Amazon is rainy and humid. The highland climate zone has cool temperatures in the mountainous regions, while the coastal climate zone has warm and wet weather along the coastline. Climate change is having a significant impact on Brazil’s climate zones, presenting challenges for the country’s economy and environment. The Tropical Climate Zone: Hot and Humid Weather in the North The tropical climate zone covers most of the northern region of Brazil, including the states of Amazonas, Pará, and Roraima. This region experiences high temperatures and humidity year-round, with average temperatures ranging from 25 to 30 degrees Celsius (77 to 86 degrees Fahrenheit). The rainy season in this zone typically occurs from December to May, with heavy rainfall and occasional thunderstorms. The hot and humid weather in the north can be challenging for travelers who are not accustomed to such conditions. It is important to...
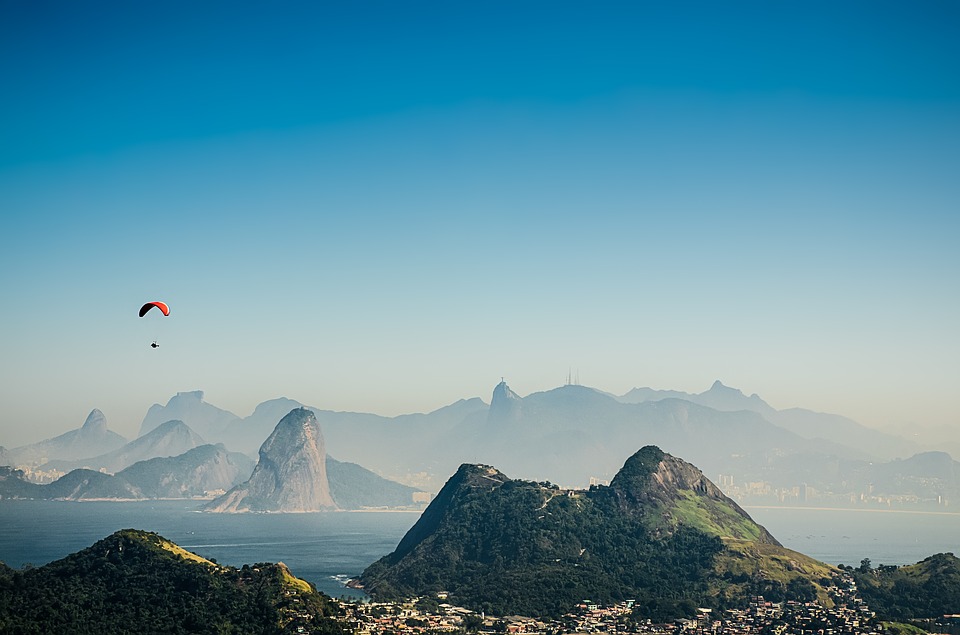
Terrain and Topography of Brazil: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Brazil is a country known for its diverse and stunning topography. From majestic mountains to vast plains, lush rainforests to beautiful beaches, Brazil offers a wide range of landscapes that attract tourists from all over the world. Understanding Brazil’s geography is important not only for those who wish to explore its natural wonders, but also for those who want to understand the country’s culture and history. In this article, we will take a closer look at Brazil’s diverse topography and explore the activities and attractions that each region has to offer. Summary Brazil’s topography is incredibly diverse, with a range of landscapes from mountains to plains to wetlands. The majestic mountains of Brazil offer stunning views and opportunities for hiking and adventure. The Amazon Basin is a unique landscape with unparalleled biodiversity and cultural significance. The Brazilian highlands feature rolling hills and plateaus, as well as important agricultural regions. The coastal regions of Brazil offer beautiful beaches and cliffs, while the Cerrado and Pantanal showcase unique ecosystems. The Majestic Mountains of Brazil Brazil is home to several mountain ranges, each with its own unique beauty and charm. One of the most famous mountain ranges in Brazil is the Serra da Mantiqueira, located in the southeastern part of the country. This mountain range is known for its stunning landscapes, with peaks reaching over 2,000 meters in height. The Serra da Mantiqueira offers a variety of activities for outdoor enthusiasts, including hiking, rock climbing, and horseback riding. Visitors can also enjoy the breathtaking views from the top of the mountains or relax in one of the many charming towns nestled in...
History of Brazil
Brazil, the largest country in South America, has a rich and complex history that has shaped its present-day society and culture. From its pre-colonial indigenous peoples to its colonial period under Portuguese rule, Brazil’s past is filled with significant events and influences. Understanding Brazil’s history is crucial for comprehending the challenges and opportunities that the country faces today. By examining the various periods and key moments in Brazil’s past, we can gain insights into the factors that have shaped its economy, society, and political landscape. Summary Indigenous peoples were the original inhabitants of Brazil before the arrival of the Portuguese. Brazil’s colonial period was marked by Portuguese rule and the exploitation of resources. Brazil played a significant role in the Atlantic slave trade, with millions of Africans brought over as slaves. Brazil gained independence from Portugal in the 19th century, establishing a monarchy under Pedro II. Brazil has experienced political turmoil and instability, including a military dictatorship and struggles for democracy. Pre-colonial Brazil: The Indigenous Peoples Before the arrival of the Portuguese in the 16th century, Brazil was home to a diverse array of indigenous peoples. These indigenous groups had their own unique cultures, languages, and ways of life. They lived off the land, engaging in hunting, fishing, and agriculture. The indigenous peoples of Brazil had a deep connection to nature and believed in the spiritual significance of their surroundings. However, the arrival of European colonizers had a devastating impact on Brazil’s indigenous populations. The Portuguese brought diseases such as smallpox, measles, and influenza, which decimated indigenous communities who had no immunity to these diseases. Additionally, the colonizers forcibly...
Population Density of Brazil
Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured per square kilometer. It is an important indicator of how crowded or sparsely populated an area is. Studying population density in Brazil is crucial as it provides insights into the distribution of people across the country and helps policymakers make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, infrastructure development, and urban planning. Brazil, the largest country in South America, has a diverse population with varying levels of density across its regions. Understanding the historical trends, regional variations, and factors affecting population density in Brazil is essential for addressing social, economic, and environmental challenges associated with high population density. Summary Brazil has a high population density, with over 211 million people living in the country. Historical trends show that Brazil’s population density has increased over time, with a significant shift towards urban areas. Brazil’s urban population density is much higher than its rural population density, with cities like Sao Paulo and Rio de Janeiro being some of the most densely populated in the world. Regional variations in Brazil’s population density exist, with the Southeast region being the most densely populated and the North region being the least densely populated. Factors affecting Brazil’s population density include migration, fertility rates, and government policies. Managing population density is crucial for sustainable economic development in Brazil. Historical Trends in Brazil’s Population Density Brazil’s population has experienced significant growth over the years. In the early 20th century, the country had a relatively low population density due to its vast land area and limited settlement. However, with advancements in healthcare, sanitation, and transportation...
Exploring the Vibrant Culture and Breathtaking Landscapes of Brazil
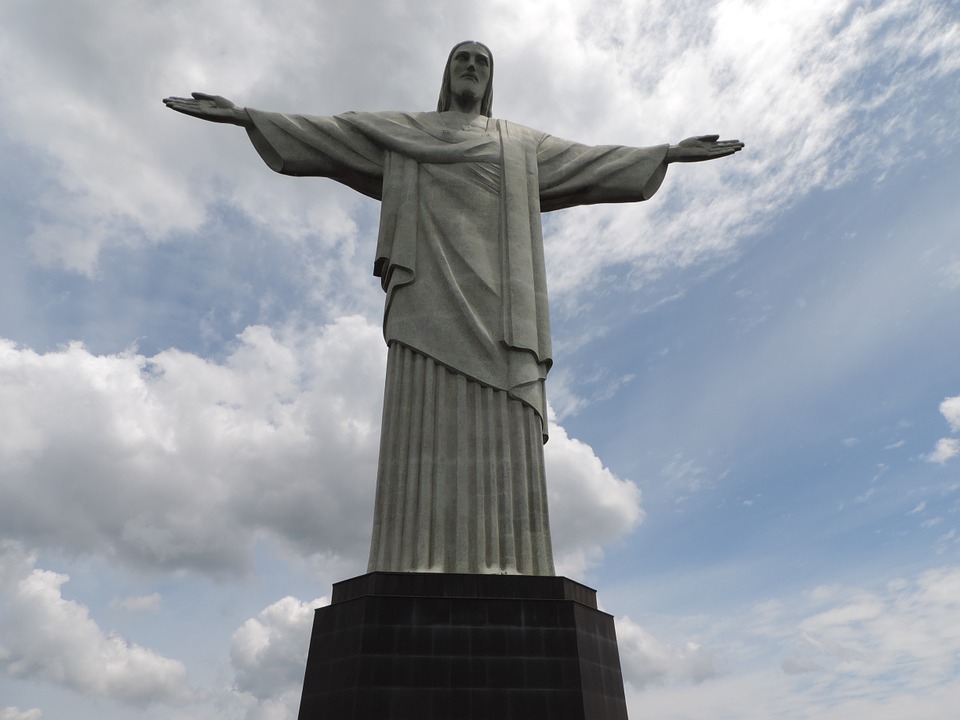
Brazil is a country known for its vibrant culture, rich history, and diverse landscapes. From the bustling streets of Rio de Janeiro to the vast Amazon Rainforest, Brazil offers a unique and unforgettable experience for travelers. In this blog post, we will take a journey through Brazil’s rich cultural heritage, exploring its history, architecture, festivals, art, cuisine, natural wonders, adventure sports, and warm hospitality. By the end of this article, you will have a deeper understanding of what makes Brazil such a fascinating and captivating destination. Key Takeaways Brazil has a rich cultural heritage that spans centuries and includes influences from indigenous tribes, European colonizers, and African slaves. Brazilian architecture is a marvel to behold, with styles ranging from colonial to modern and featuring iconic landmarks like the Christ the Redeemer statue in Rio de Janeiro. Brazilian festivals and celebrations are colorful and lively, with Carnival being the most famous and attracting millions of visitors each year. Brazil is home to a vibrant artistic scene, with music, dance, and visual arts that showcase the country’s diverse cultural influences. Brazilian cuisine is a gastronomic adventure, with dishes that range from traditional feijoada to modern fusion cuisine that incorporates local ingredients and flavors. Brazil’s Rich Cultural Heritage: A Journey Through Time Brazil’s cultural heritage is deeply rooted in its history. The country has been inhabited by indigenous tribes for thousands of years, and their influence can still be seen today. These tribes have left behind a legacy of art, music, dance, and spirituality that is an integral part of Brazilian culture. The arrival of the Portuguese in the 16th century marked...
Arachnophobia Alert: The Deadly Bite of the Brazilian Wandering Spider (Phoneutria spp.)
The Brazilian Wandering Spider, also known as the banana spider or armed spider, is a highly venomous spider that is native to South and Central America. It belongs to the genus Phoneutria, which means “murderess” in Greek, and is considered one of the most dangerous spiders in the world. The spider gets its name from its wandering behavior, as it does not build a web to catch its prey like other spiders. The Brazilian Wandering Spider is known for its large size, with a leg span that can reach up to 6 inches. It has a brown or tan body with distinctive markings on its abdomen. The spider is also known for its aggressive behavior and quick movements, making it a formidable predator. Key Takeaways The Brazilian Wandering Spider is one of the most venomous spiders in the world. They can be identified by their brown or black color, hairy legs, and distinctive red or pink marking on their abdomen. The venom of the Brazilian Wandering Spider can cause muscle spasms, paralysis, and even death in severe cases. Symptoms of a bite include pain, swelling, sweating, and difficulty breathing. Treatment for a bite includes seeking immediate medical attention, administering antivenom, and managing symptoms. How to identify a Brazilian Wandering Spider The Brazilian Wandering Spider can be identified by its physical characteristics. It has a large, robust body with long legs and a distinctive pattern on its abdomen. The spider’s body is usually brown or tan in color, with darker markings that resemble a violin shape on its abdomen. One way to differentiate between male and female Brazilian Wandering Spiders...














































