Guadeloupe
(Département d’Outre-Mer de la Guadeloupe (Overseas Department of Guadeloupe))

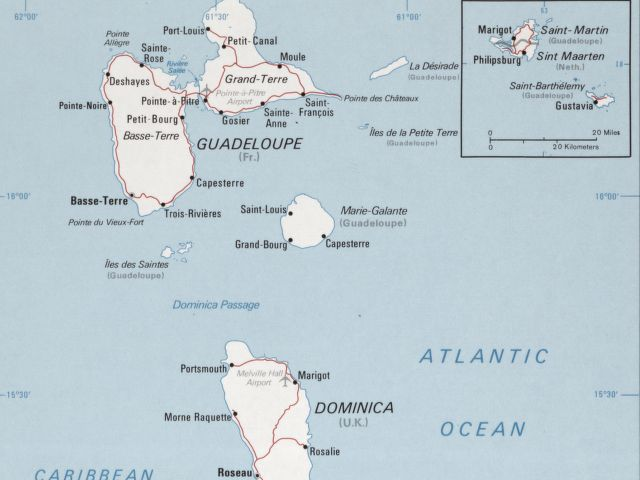

Capital of Guadeloupe: Basse-Terre
Population (Estimated July 2012): 454,000
Area: 1,630 km2 or 629 mi2
Currency: Euro (€)
Official Language: French
Political Information: Overseas Region of France
Official Religion: No Official Religion
Time Zone (GMT/UTC):
Leaders: President François Hollande with President of the General Council Jacques Gillot and President of the Regional Council Victorin Lurel.
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is a stunning archipelago located in the Caribbean, known for its beautiful beaches, lush rainforests, and vibrant culture. It is an overseas region of France and is composed of several islands, with the two main ones being Basse-Terre and Grande-Terre. The islands are surrounded by crystal-clear waters and offer a perfect blend of French and Caribbean influences. Guadeloupe is a popular destination for tourists seeking a tropical paradise with a touch of European charm.
The islands of Guadeloupe are rich in history and culture, with a diverse population that includes people of African, European, and East Indian descent. The official language is French, but Creole is widely spoken and is an integral part of the local culture. The music, dance, and cuisine of Guadeloupe are a reflection of this cultural diversity, making it a fascinating destination for those interested in experiencing the unique blend of Caribbean and European influences. With its stunning natural beauty and rich cultural heritage, Guadeloupe offers a truly unforgettable experience for visitors.
History and Culture of Guadeloupe
The history of Guadeloupe is a complex tapestry of colonialism, slavery, and resistance. The islands were originally inhabited by the Arawak and Carib people before being colonized by the French in the 17th century. The sugar industry brought an influx of African slaves to the islands, and the legacy of slavery continues to shape the culture and identity of Guadeloupe today. The islands have a long history of resistance and rebellion, with several uprisings against colonial rule, including the famous slave revolt led by Louis Delgrès in 1802.
The culture of Guadeloupe is a vibrant mix of African, European, and Caribbean influences. Music and dance are integral parts of the local culture, with traditional styles such as Gwo Ka and Zouk coexisting alongside modern genres like reggae and hip-hop. The cuisine of Guadeloupe is also a reflection of this cultural fusion, with dishes that blend French culinary techniques with local ingredients such as seafood, tropical fruits, and spices. The islands are also known for their vibrant festivals and celebrations, including Carnival and the Fête des Cuisinières, which showcase the rich cultural heritage of Guadeloupe.
Geography and Climate of Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is an archipelago located in the Leeward Islands of the Caribbean, with Basse-Terre and Grande-Terre being the two main islands. The landscape is diverse, with lush rainforests, volcanic peaks, and stunning beaches. Basse-Terre is home to La Soufrière, an active volcano that is the highest point in the Lesser Antilles. Grande-Terre, on the other hand, is known for its beautiful beaches and rolling hills. The islands are surrounded by coral reefs, making them a popular destination for snorkelling and diving.
The climate of Guadeloupe is tropical, with warm temperatures year-round and a wet season from June to November. The islands are prone to hurricanes during the wet season, so visitors should be mindful of weather forecasts when planning their trip. The trade winds help to keep the islands relatively cool, making it a pleasant destination for outdoor activities such as hiking and beach-going. With its diverse landscape and favourable climate, Guadeloupe offers something for every type of traveller, whether they are seeking adventure in the rainforest or relaxation on the beach.
Cuisine and Local Delicacies of Guadeloupe
The cuisine of Guadeloupe is a delicious blend of French culinary techniques and local ingredients, resulting in a unique and flavourful dining experience. Seafood plays a prominent role in Guadeloupean cuisine, with dishes such as court-bouillon (fish stew) and accras de morue (cod fritters) being popular choices. Local fruits such as guava, passion fruit, and mango are also used to create refreshing juices and desserts. One of the most iconic dishes of Guadeloupe is bokit, a fried bread filled with various ingredients such as chicken, fish, or vegetables.
Rhum agricole is a popular local spirit made from sugarcane juice, and it is used to create a variety of cocktails such as ti’punch and planteur. Visitors to Guadeloupe can also sample local delicacies such as boudin (blood sausage), colombo (a spicy curry dish), and dombrés (dumplings). The islands are also known for their vibrant markets where visitors can sample fresh produce, spices, and local specialities. With its diverse range of flavours and ingredients, the cuisine of Guadeloupe is a true reflection of the islands’ rich cultural heritage.
Popular Tourist Attractions in Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe offers a wide range of attractions for visitors to explore, from stunning natural landmarks to historical sites and cultural experiences. One of the most iconic landmarks in Guadeloupe is La Soufrière, an active volcano located on the island of Basse-Terre. Hiking to the summit of La Soufrière offers breathtaking views of the surrounding landscape and is a popular activity for adventurous travellers. Another must-see natural attraction is the Cascade aux Ecrevisses, a beautiful waterfall nestled in the heart of Basse-Terre’s rainforest.
For those interested in history and culture, Guadeloupe offers several fascinating sites to explore. The Memorial ACTe in Pointe-à-Pitre is a museum dedicated to the history of slavery and its impact on the Caribbean region. The museum provides a thought-provoking look at this dark chapter in history and its lasting effects on the people of Guadeloupe. The islands are also home to several charming towns and villages with colourful colonial architecture, such as Sainte-Anne and Deshaies. With its diverse range of attractions, Guadeloupe has something to offer for every type of traveller.
Activities and Outdoor Adventures in Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is a paradise for outdoor enthusiasts, offering a wide range of activities to enjoy amidst its stunning natural beauty. The islands are home to several national parks and nature reserves, providing ample opportunities for hiking, birdwatching, and wildlife spotting. The Parc National de la Guadeloupe encompasses much of Basse-Terre’s rainforest and is home to diverse flora and fauna, including the elusive raccoon-like animal known as the agouti.
The waters surrounding Guadeloupe are perfect for snorkelling, diving, and water sports such as kayaking and paddleboarding. The coral reefs are teeming with marine life, including colourful fish, sea turtles, and even dolphins. Visitors can also take boat tours to explore the nearby islands of Les Saintes and Marie-Galante, each offering their own unique charm and attractions. For those seeking adrenaline-pumping adventures, activities such as canyoning, zip-lining, and off-road excursions are also available. With its abundance of outdoor activities, Guadeloupe is an ideal destination for nature lovers and adventure seekers alike.
Practical Travel Tips for Visiting Guadeloupe
When planning a trip to Guadeloupe, there are several practical tips to keep in mind to ensure a smooth and enjoyable experience. Firstly, it’s important to note that Guadeloupe uses the euro as its currency, so visitors should be prepared to exchange their money accordingly. French is the official language spoken in Guadeloupe, so having some basic knowledge of French phrases can be helpful when communicating with locals.
The best time to visit Guadeloupe is during the dry season from December to May when the weather is pleasant and there is less risk of hurricanes. It’s also recommended to rent a car when exploring the islands as public transportation can be limited outside of major towns. Lastly, travellers should be mindful of their belongings and personal safety when visiting tourist areas or crowded places. With these practical tips in mind, visitors can make the most of their trip to Guadeloupe and enjoy all that this beautiful archipelago has to offer.
FAQs
What is Guadeloupe?
Guadeloupe is an overseas region of France located in the Caribbean. It is an archipelago consisting of several islands, with the main ones being Basse-Terre and Grande-Terre.
What is the capital of Guadeloupe?
The capital of Guadeloupe is Basse-Terre, which is located on the island of the same name.
What is the population of Guadeloupe?
As of 2021, the population of Guadeloupe is estimated to be around 395,700 people.
What is the official language of Guadeloupe?
The official language of Guadeloupe is French, as it is an overseas region of France.
What is the currency used in Guadeloupe?
The official currency of Guadeloupe is the Euro (EUR), as it is part of France.
What is the climate like in Guadeloupe?
Guadeloupe has a tropical climate, with warm temperatures throughout the year. It experiences a rainy season from June to November, and a dry season from December to May.
What are the main industries in Guadeloupe?
The main industries in Guadeloupe include agriculture (especially bananas and sugarcane), tourism, and light industry.
What are some popular tourist attractions in Guadeloupe?
Some popular tourist attractions in Guadeloupe include the La Soufrière volcano, the Jardin Botanique de Deshaies (botanical garden), and the beautiful beaches such as Grande Anse and Plage de la Datcha.
Terrain and Topography of Guadeloupe: mountains, valleys, and plains.
Guadeloupe, an overseas region of France located in the Caribbean, is a stunning archipelago consisting of five main islands. The terrain and topography of Guadeloupe are incredibly diverse, offering a wide range of landscapes that attract visitors from all over the world. From majestic mountains to lush valleys and serene plains, Guadeloupe’s terrain is a testament to the island’s natural beauty and ecological significance. The unique geological features of the islands have also played a crucial role in shaping the culture and history of the region, making it a fascinating destination for those interested in both natural and cultural exploration. Summary Guadeloupe’s terrain and topography are diverse, featuring mountains, valleys, and plains. The majestic mountains of Guadeloupe offer stunning views and challenging hiking opportunities. Exploring the lush valleys of Guadeloupe provides a chance to experience the island’s rich biodiversity. The serene plains of Guadeloupe offer a peaceful and picturesque landscape for visitors to enjoy. Guadeloupe’s terrain and topography are of ecological importance, supporting a wide range of plant and animal species. The Majestic Mountains of Guadeloupe One of the most striking features of Guadeloupe’s terrain is its majestic mountains, which dominate the landscape and offer breathtaking views of the surrounding islands and the Caribbean Sea. The highest peak in Guadeloupe is La Grande Soufrière, an active volcano located on the island of Basse-Terre. This imposing mountain stands at an impressive 1,467 meters (4,813 feet) above sea level and is a popular destination for hikers and nature enthusiasts. The rugged terrain of the mountains is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including rare species that are unique...
Climate Zones Of Guadeloupe: Different climate regions Of Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe, an archipelago located in the Caribbean, is known for its diverse climate zones that greatly influence the flora, fauna, and overall environment of the region. The climate of Guadeloupe is generally tropical, with high temperatures and humidity throughout the year. However, the archipelago’s unique geography and topography have resulted in the presence of different climate zones, each with its own distinct characteristics. Understanding these climate zones is crucial for anyone visiting Guadeloupe, as it can greatly impact their experience and activities on the islands. Summary Guadeloupe has a diverse climate with tropical maritime climate in coastal areas and subtropical climate in mountainous regions. The coastal areas experience warm temperatures and high humidity, with frequent rainfall and the potential for hurricanes. The mountainous regions have cooler temperatures and lower humidity, with more variation in rainfall and the potential for fog and mist. Trade winds play a significant role in Guadeloupe’s climate, bringing cooling breezes and influencing rainfall patterns. The diverse climate of Guadeloupe creates microclimates within the island, impacting the flora and fauna in different areas. Tropical Maritime Climate of the Coastal Areas The coastal areas of Guadeloupe are characterized by a tropical maritime climate, with warm temperatures and high humidity. The average temperature in these areas ranges from 25°C to 30°C throughout the year, with little variation between seasons. The proximity to the sea also results in frequent rainfall, especially during the wet season from June to November. The combination of warm temperatures and ample rainfall creates lush, tropical vegetation along the coast, including palm trees, mangroves, and vibrant flowers. The coastal climate also supports a diverse range...
Political Boundaries of Guadeloupe: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Guadeloupe is an overseas region of France located in the Caribbean. It is made up of several islands, with the main ones being Basse-Terre and Grande-Terre. The political boundaries of Guadeloupe are unique due to its status as an overseas region of France. As such, it is governed by the French Republic and is subject to French laws and regulations. The political boundaries of Guadeloupe are defined by its administrative divisions, which include provinces and districts. These boundaries play a crucial role in the governance and administration of the region, as they determine the allocation of resources, representation, and decision-making processes. The political boundaries of Guadeloupe are a reflection of its colonial history and its current status as an overseas region of France. Understanding these boundaries is essential for comprehending the political, social, and economic dynamics of the region. The provinces and districts of Guadeloupe are integral to its governance and play a significant role in shaping the lives of its inhabitants. In this article, we will explore the provinces and districts of Guadeloupe, examine its historical boundaries, compare its political boundaries with other regions, and assess the impact of these boundaries on governance. Additionally, we will discuss the future of Guadeloupe’s political boundaries and the potential changes that may occur in the coming years. Summary Guadeloupe is an overseas region of France with its own political boundaries and governance structure. The region is divided into two provinces, Basse-Terre and Grande-Terre, each with its own distinct characteristics and local government. Within the provinces, there are several districts that play a key role in local administration and decision-making. Guadeloupe’s historical...
History of Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe, an island located in the Caribbean, has a rich history that dates back to the early settlement by the Arawak and Carib peoples. These indigenous groups were the first to inhabit the island, and they lived off the land, fishing, hunting, and cultivating crops such as cassava, sweet potatoes, and yams. The Arawak and Carib peoples lived in harmony with nature and developed a unique culture that included art, music, and spiritual beliefs. They also built villages and engaged in trade with other indigenous groups in the region. The Arawak and Carib peoples’ presence on the island was disrupted with the arrival of European explorers in the late 15th century. The impact of European colonization on the indigenous population was devastating, as they were subjected to violence, disease, and forced labor. Many of the Arawak and Carib people were either killed or enslaved by the European colonizers, leading to a significant decline in their population. Despite this tragic history, the legacy of the Arawak and Carib peoples lives on in Guadeloupe through archaeological sites, cultural traditions, and the influence of their language on the Creole spoken in the region. Summary Arawak and Carib peoples were the early settlers of Guadeloupe Christopher Columbus and European colonization marked the arrival of the Europeans in Guadeloupe The establishment of the plantation economy and the slave trade had a significant impact on Guadeloupe’s history French and British struggles for control of the island shaped its political landscape The abolition of slavery and the rise of Guadeloupe as a French overseas department marked a significant shift in its status Arrival of Christopher Columbus...
Population Density of Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe is a beautiful archipelago located in the Caribbean, and it is an overseas region of France. The island is known for its stunning beaches, lush rainforests, and vibrant culture. Guadeloupe is made up of several islands, with the two main ones being Basse-Terre and Grande-Terre. The population of Guadeloupe is around 400,000 people, and it is a diverse mix of African, European, and Indian descent. The official language is French, and the majority of the population is Roman Catholic. The economy of Guadeloupe is heavily reliant on tourism, agriculture, and trade with mainland France. The island has a rich history, with influences from both the indigenous Carib people and European colonizers. Guadeloupe is a unique blend of Caribbean and French culture, making it a fascinating place to study population density and its impact on the environment and infrastructure. Summary Guadeloupe is an overseas region of France located in the Caribbean, known for its beautiful beaches and rich cultural heritage. Factors influencing population density in Guadeloupe include limited land availability, economic opportunities, and historical settlement patterns. The population in Guadeloupe is predominantly concentrated in urban areas, with rural areas experiencing lower population density. High population density in urban areas of Guadeloupe puts pressure on infrastructure, leading to issues such as traffic congestion and housing shortages. The high population density in Guadeloupe has environmental implications, including increased pollution and strain on natural resources. Guadeloupe’s population density is lower than some other Caribbean islands, such as Barbados and Trinidad and Tobago. Future trends in population density in Guadeloupe may be influenced by factors such as migration, economic development, and government policies....
Natural Resources of Guadeloupe: Where Natural Resources are located In Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe, an overseas region of France located in the Caribbean, is blessed with a rich abundance of natural resources. From its fertile soil for agriculture to its mineral deposits, marine life, and renewable energy sources, Guadeloupe has a diverse range of natural assets that contribute to its economic development and sustainability. The archipelago is made up of several islands, each with its own unique natural resources, making it a treasure trove for biodiversity and natural beauty. The natural resources of Guadeloupe play a crucial role in the livelihoods of its people and the overall economy of the region. The natural resources of Guadeloupe are not only essential for the local economy but also for the preservation of its unique ecosystems and biodiversity. The region’s lush vegetation, diverse wildlife, and marine life make it a haven for ecotourism and sustainable development. However, the responsible management and conservation of these natural resources are vital to ensure their long-term viability and the well-being of future generations. In this article, we will explore the various natural resources of Guadeloupe, their economic importance, and the conservation efforts being made to protect them for the future. Summary Guadeloupe is rich in natural resources, including agriculture, minerals, fishing, renewable energy sources, and biodiversity. Agriculture and farming play a significant role in Guadeloupe’s economy, with a focus on sugarcane, bananas, and tropical fruits. Guadeloupe has limited mineral resources, with deposits of volcanic rock, limestone, and clay used for construction and pottery. Fishing and aquatic resources are vital to Guadeloupe’s economy, with a variety of fish, shellfish, and crustaceans being harvested. Guadeloupe is making efforts to harness renewable...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Guadeloupe: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites in Guadeloupe
The Slave Memorial at Anse Cafard is a powerful and poignant reminder of the dark history of slavery in Guadeloupe. The memorial consists of 15 larger-than-life statues, arranged in a striking formation overlooking the sea. Each statue represents a slave, standing with their heads bowed and their arms crossed, in a solemn and dignified manner. The memorial was erected in 1998 to commemorate the 150th anniversary of the abolition of slavery in Guadeloupe, and it serves as a solemn tribute to the countless individuals who suffered and died as a result of the transatlantic slave trade. The location of the memorial is significant, as it overlooks the very spot where a tragic shipwreck occurred in 1830. The ship, called the “Marie-Céleste,” was carrying 160 enslaved Africans from West Africa to Guadeloupe when it ran aground on the rocky coast of Anse Cafard. The memorial serves as a reminder of the inhumanity and brutality of the slave trade, and it stands as a symbol of remembrance and reflection for visitors from around the world. The Slave Memorial at Anse Cafard is a sombre and moving testament to the resilience and strength of the human spirit in the face of unimaginable suffering and oppression. Summary The Slave Memorial at Anse Cafard is a powerful and moving tribute to the victims of the transatlantic slave trade. The Fort Delgrès in Basse-Terre offers a fascinating glimpse into the island’s history and the struggle for freedom. The Edgar Clerc Archaeological Museum showcases a rich collection of artefacts and exhibits that shed light on Guadeloupe’s pre-Columbian history. The Memorial ACTe in Pointe-à-Pitre is a thought-provoking...




















